Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal Seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
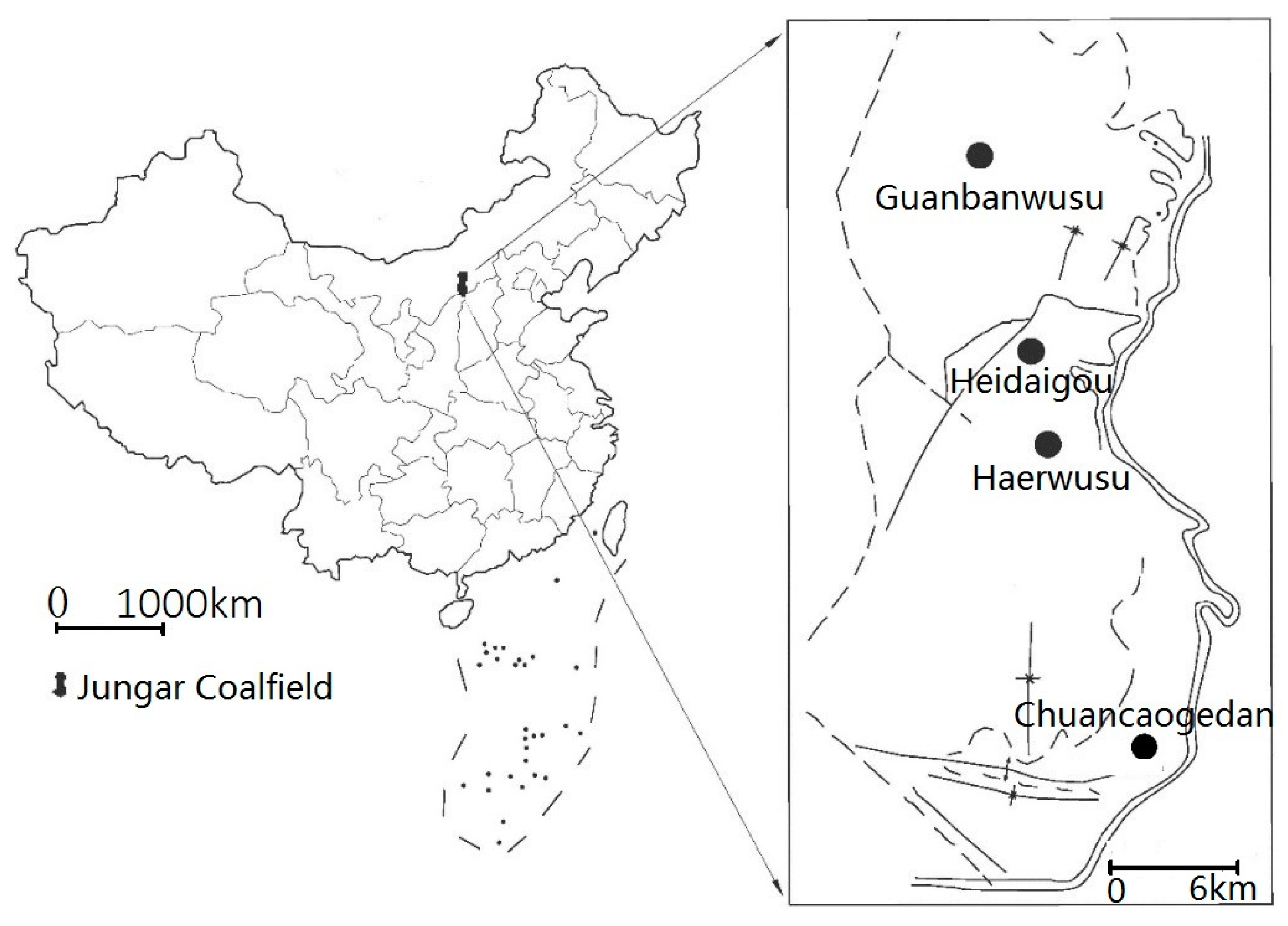
2. Geological Setting
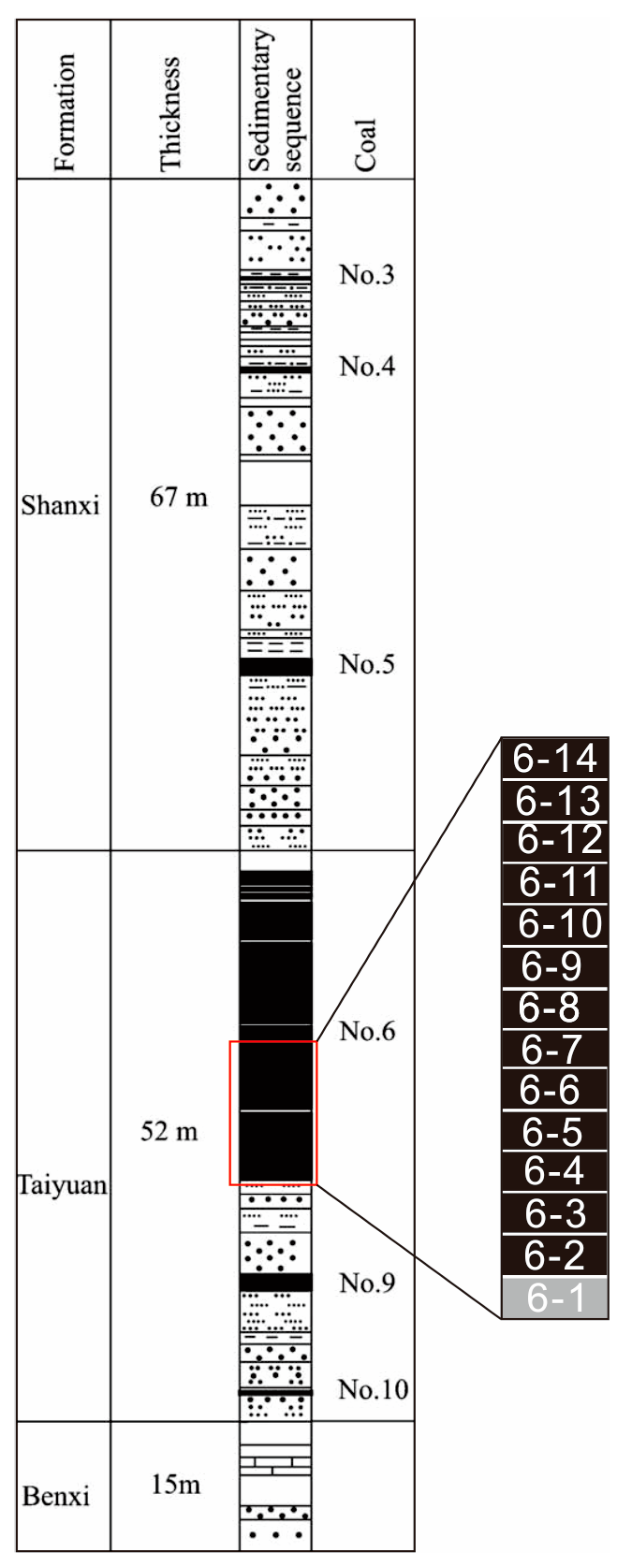
3. Samples and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
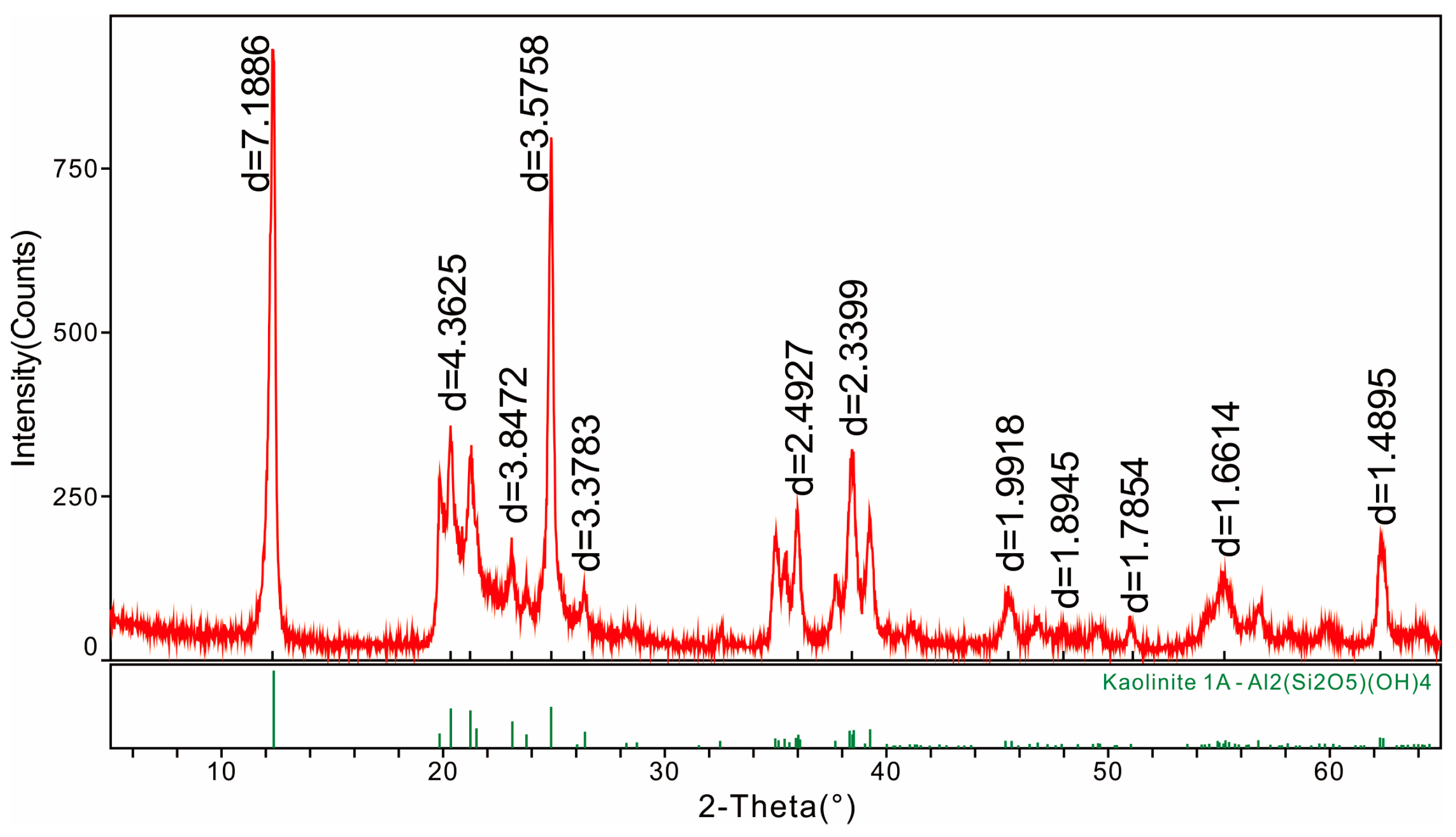
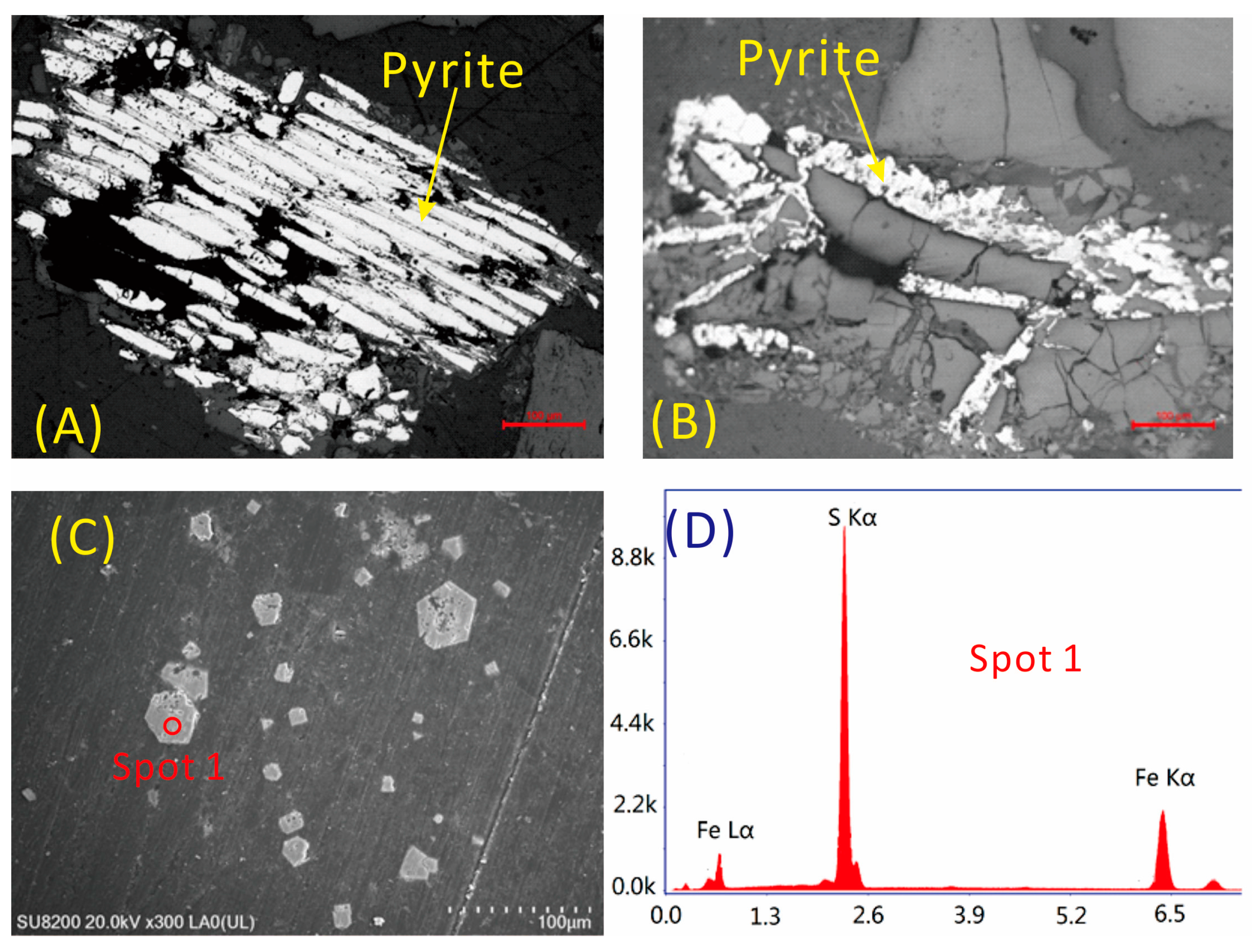
4.1. Minerals in the Coal
4.2. Major Element Contents in the No. 6 Coal
4.3. Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal
4.4. Paragenetic Association of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal
4.4.1. Affinity of the Elements
4.4.2. Cluster Analysis
4.5. Elevated Trace Elements in the Coal
4.5.1. Strontium
4.5.2. Lithium
4.5.3. Gallium
4.5.4. Zirconium
4.5.5. Cadmium
4.5.6. Lead
4.5.7. Thorium
5. Conclusions
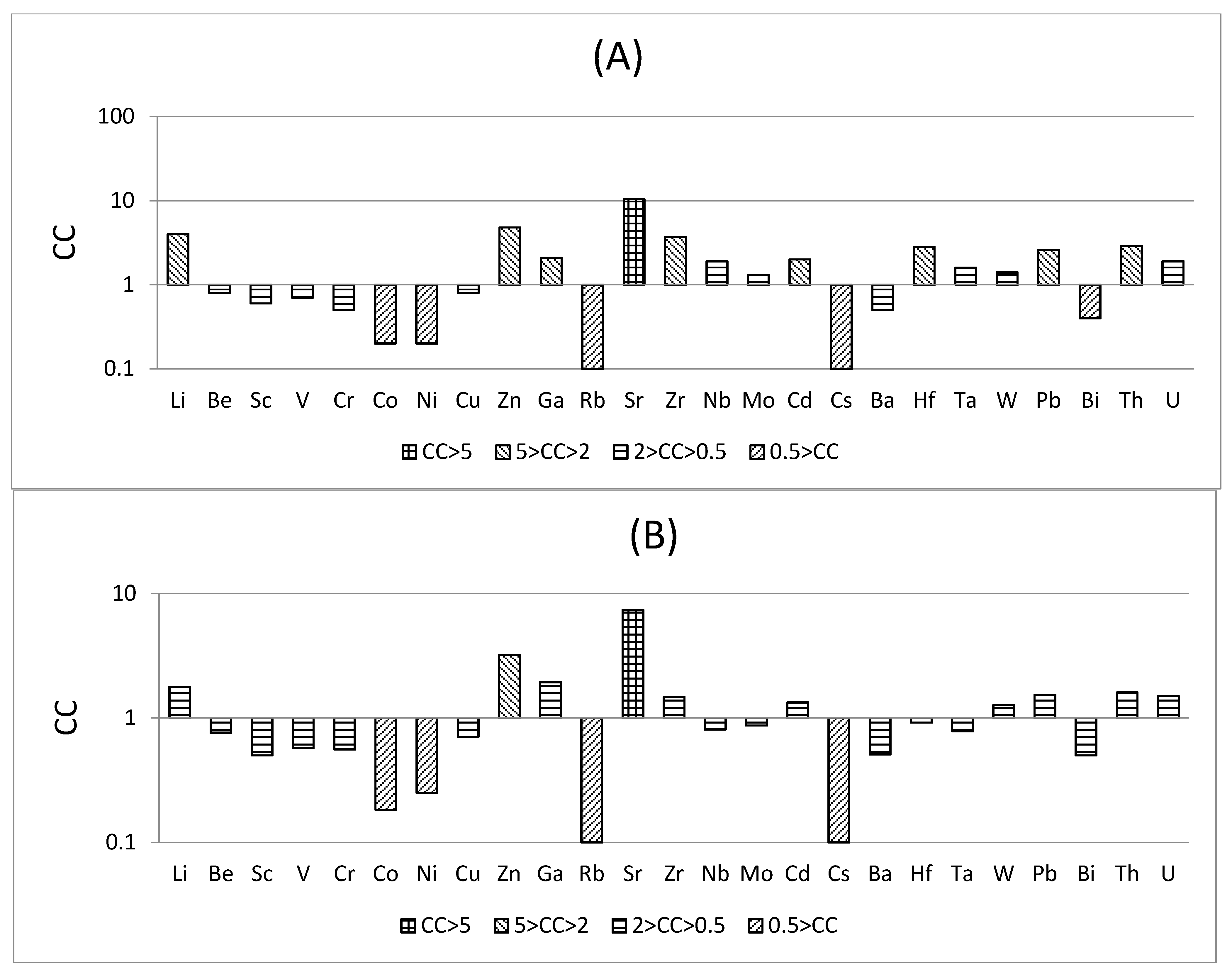
- The No. 6 coal from Chuancaogedan Mine is significantly enriched in Zn and Sr and is slightly enriched in Li, Ga, Zr, Gd, Hf, Pb, Th, and U compared with world hard coals. The major elements exhibit enrichment in Al2O3 (6.76%) and P2O5 (0.169%), but with a lower SiO2/Al2O3 ratio (1.20), compared to Chinese hard coals. The contents of Zn, Sr, Li, Ga, Zr, Gd, Hf, Pb, Th, and U are higher than those of world hard coals. Aluminum, Li, and Ga could be recovered as the byproducts from coal ash, and P, Pb, and U may be harmful to the environment during coal processing.
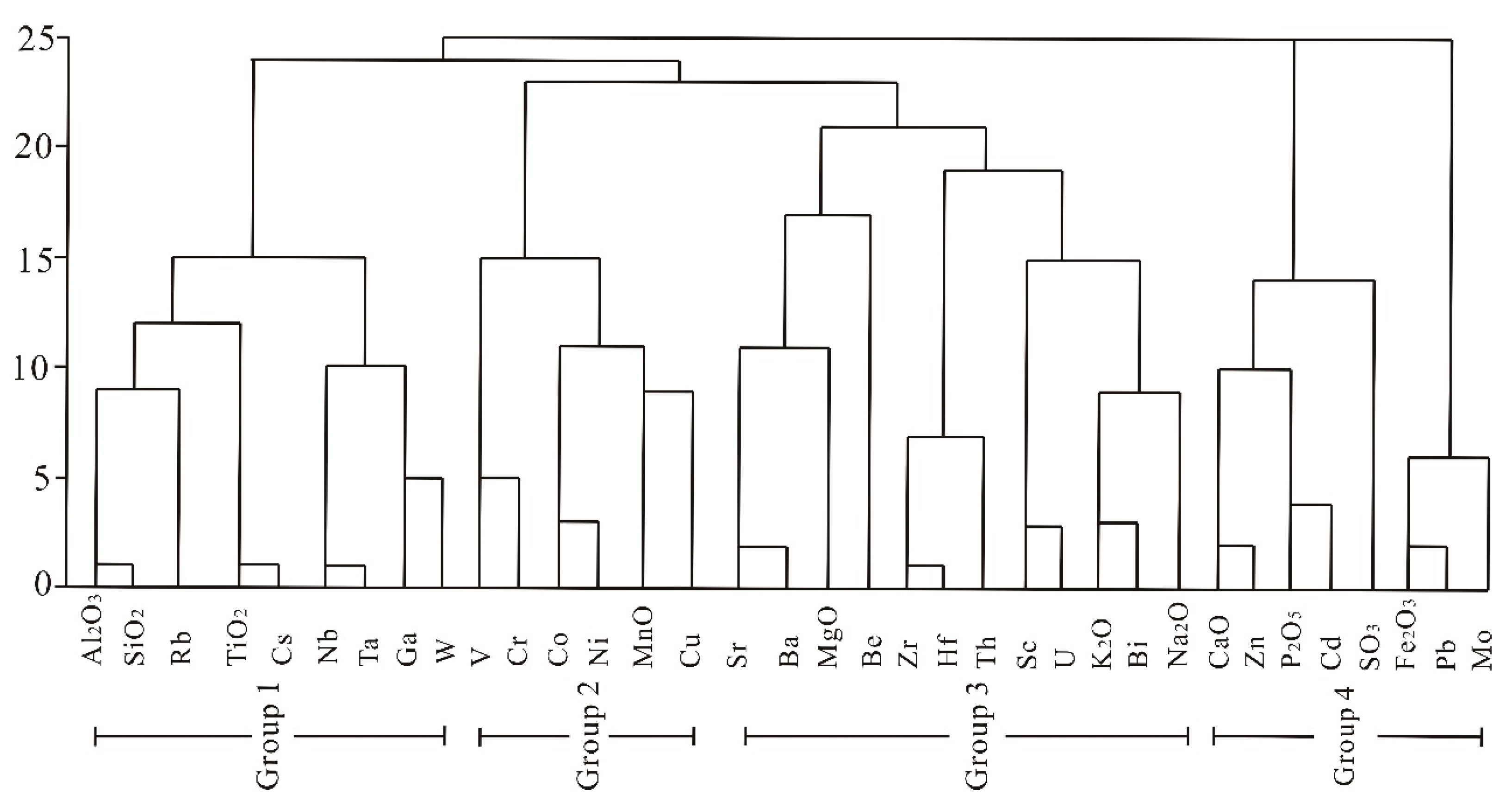
- The elements in the No. 6 coal may be classified into four groups of association according to their modes of occurrence. Group 1 includes Al2O3, SiO2, Li, Rb, TiO2, Cs, Nb, and Ta. Group 2 includes the elements V, Cr, Co, Ni, MnO, and Cu. Group 3 consists of Sr, Ba, MgO, Be, Zr, Hf, Th, Sc, U, K2O, Bi, and Na2O. Group 4 includes CaO, Zn, P2O5, Cd, SO3, Fe2O3, Pb, and Mo. Most of the elements in Group 1 and Group 2 are strongly correlated with the ash yield, but the elements of the remaining two associations have negative or weak correlation coefficients with the ash yield.
- The most probable carriers of Sr in the coal are barite and gorceixite. Lithium is mainly associated with kaolinite and possibly with illite. Gallium mainly occurs in inorganic association, including the clay minerals and diaspore, but is not related to sulfide. Zirconium occurs in association with sulfide minerals. Cadmium mainly occurs in sphalerite. Lead in the No. 6 coal may be associated with pyrite. Thorium may occur in accessory minerals in the coal and probably in the organic matter as well.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.Z.; Duan, P.P.; Li, X.W.; Wang, J.X.; Deng, X.L. Advance of mining technology for coals under buildings in China. World J. Eng. 2012, 9, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, G.; Donahoe, R. Leachability of elements in alkaline and acidic coal fly ash samples during batch and column leaching tests. Fuel 2013, 104, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Groves, S. Mobility of trace elements from selected Australian fly ashes and its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems. Fuel 2006, 85, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Duan, D.J. Concentrations of valuable elements of the coals from the Pingshuo Minging District, Ningwu Coalfield, Northern China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2013, 31, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Xiao, L.; Qin, S.J.; Wang, J.X.; Duan, D.J. The occurrence of barium in Jurassic coal in the Huangling 2 mine, Ordos Basin, northern China. Fuel 2014, 128, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jin, Z.; Lin, M.Y.; Kalkreuth, W. Further information of the associated Li deposits in the No. 6 coal seam at Junger Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 2013, 87, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.F.; Qin, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, J.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, G.D.; Liu, J.T. Distribution, occurrence and enrichment causes of gallium in coals from the Ningdong Coalfield, Inner Mongolia. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 181–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Li, S. Discovery of the superlarge gallium ore deposit in Jungar, Inner Mongolia, North China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 5, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Xiao, L.; Jin, Z.; Lin, M.; Blokhin, M. The relationship between trace element concentrations and coal-forming environments in the No. 6 Coal Seam, Haerwusu Mine, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2015, 33, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, D.; Chou, C.L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 74, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhao, L.; Peng, S.; Chou, C.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, Y. Abundances and distribution of minerals and elements in high-alumina coal fly ash from the Jungar Power Plant, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 81, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Song, H.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Hailiushu Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Implications of sediment-source region and acid hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 137, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y. Modes of occurrence of fluorine in the late paleozoic No. 6 coal from the Haerwusu surface mine, Inner Mongolia, China. Fuel 2011, 90, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Ren, D.Y. Analysis of annmalous high concentration of lead and selenium and their origin in the main minable coal seam in the Ningdong Coalfield. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2006, 35, 612–615. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.M.; Yang, Q.; Tang, D.Z. A study of abundances and distribution of ash yield, sulfur, phosphorus and chlorine content of the coals from Ordos Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 1996, 6, 53–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Sun, Y.Z.; Kalkreuth, W. Characteristics of trace elements of the No. 6 Coal in the Guanbanwusu Mine, Junger Coalfield, Inner Mongolia. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2011, 29, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zou, J.H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.L.; Wang, X.B.; Li, T.; Xue, W.F.; Liu, S.D.; Tian, H.M.; Sun, X.H.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Adaohai Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Modes of occurrence and origin of diaspore, gorceixite, and ammonian illite. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Gu, L.D.; Seredin, V.V.; Liu, H.D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zou, J.H.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the coal in the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, China: Further evidence for the existence of an Al (Ga and REE) ore deposit in the Jungar Coalfield. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 98, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.L.; Li, S.S.; Jiang, Y.F. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the No. 6 Coal (Pennsylvanian) in the Jungar Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Kröner, A.; Windley, B. Geodynamic evolution of Central Asia in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 98, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.N.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, K.J. The Altai-Mongolia terrane in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB): A peri-Gondwana one? Evidence from zircon U–Pb, Hf isotopes and REE abundance. Precambrian Res. 2011, 187, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, P.; Kröner, A.; Windley, B.F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Episodic mantle melting-crustal reworking in the late Neoarchean of the northwestern North China Craton: Zircon ages of magmatic and metamorphic rocks from the Yinshan Block. Precambrian Res. 2012, 222, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Coal Research Institute (CCRI) Coal Analysis Laboratory. GB/T 482-2008 Sampling of Coal in Seam; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Zhao, C.L.; Duan, D.J.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Rare earth elements in No. 2 coal of Huangling mine, Huanglong Coalfield, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2012, 30, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Qin, S.J.; Xiao, L.; Li, Z.S.; Lin, M.Y. Occurrence of some vluable elements in the unique “high-aluminium coals” from the Jungar Coalfield, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.-L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y.P. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketris, M.P.; Yudovich, Y.E. Estimations of clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: World average for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Oxford: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.J.; Yang, P.Y.; Wang, G.L. Geochemistry of elements from the No. 3 coal seam of Shanxi Formation in the Yanzhou mining district. Geochimica 2003, 32, 255–262. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, S.M. Li distribution and mode of occurrences in Li-bearing coal seam #6 from the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2012, 30, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yamada, O.; Nakazato, T.; Zhang, Z.G.; Suzuki, Y.; Sakanishi, K. Statistical analysis of the concentrations of trace elements in a wide diversity of coals and its implications for understanding elemental modes of occurrence. Fuel 2008, 87, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.X. Minimum mining grade of the selected trace elements in Chinese coal. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 744–748. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.J.; Zhao, C.L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y. Review of coal as a promising source of lithium. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2015, 9, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of occurrence of environmentally sensitive trace elements of coal. In Environmental Aspects of Trace Elements of Coal; Swaine, D.J., Goodarzi, F., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.J.; Sun, Y.Z.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, C.L.; Gao, K. Coal deposits as promising alternative sources for gallium. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S. Coal deposits as a potential alternative source for lanthanides and yttrium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Finkelman, R.B. Metalliferous coals: A review of the main genetic and geochemical types. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Ruppert, L.F.; Eble, C.F. Lanthanide, yttrium, and zirconiumanomalies in the fire clay coal bed, Eastern Kentucky. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 39, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, Y.; Sang, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, Y. Sulfur variability and element eochemistry of the No. 11 coal seam from the Antaibao mining district, China. Fuel 2007, 86, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Chekryzhov, I.Y.; Seredin, V.V.; Nechaev, V.P.; Graham, I.T.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; Ren, D.; Wang, X. Metalliferous coal deposits in East Asia (Primorye of Russia and South China): A review of geodynamic controls and styles of mineralization. Gondwana Res. 2016, 29, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | LOI | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SiO2/Al2O3 | P2O5 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 | St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-1 (roof) | 20.24 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 34.98 | 43.30 | 1.24 | 0.025 | 0.072 | 0.06 | 0.85 | 0.0000 | 0.18 | 0.07 |
| 6-2 | 95.21 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 1.96 | 2.29 | 1.17 | 0.004 | 0.019 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.0001 | 0.29 | 0.60 |
| 6-3 | 89.53 | 0.004 | 0.029 | 2.45 | 2.24 | 0.91 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.0005 | 5.48 | 4.37 |
| 6-4 | 96.00 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 1.64 | 1.87 | 1.14 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.0003 | 0.25 | 0.64 |
| 6-5 | 93.09 | 0.003 | 0.024 | 2.84 | 2.89 | 1.02 | 0.253 | 0.012 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.0003 | 0.23 | 0.75 |
| 6-6 | 91.29 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 3.69 | 4.23 | 1.15 | 0.125 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.0003 | 0.31 | 0.34 |
| 6-7 | 94.56 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 2.22 | 2.54 | 1.14 | 0.043 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.0005 | 0.41 | 0.74 |
| 6-8 | 76.45 | 0.010 | 0.069 | 9.10 | 13.91 | 1.53 | 0.006 | 0.077 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.0005 | 0.16 | 1.16 |
| 6-9 | 84.03 | 0.006 | 0.033 | 6.78 | 7.93 | 1.17 | 0.037 | 0.019 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.0004 | 0.62 | 0.73 |
| 6-10 | 85.25 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 6.24 | 6.96 | 1.12 | 0.389 | 0.007 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.0004 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
| 6-11 | 84.12 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 6.68 | 7.59 | 1.14 | 0.265 | 0.021 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.0010 | 0.66 | 0.87 |
| 6-12 | 87.32 | 0.002 | 0.019 | 4.69 | 4.79 | 1.02 | 0.796 | 0.005 | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.0006 | 1.06 | 1.43 |
| 6-13 | 88.58 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 4.77 | 5.16 | 1.08 | 0.368 | 0.010 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.0003 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| 6-14 | 82.97 | 0.006 | 0.024 | 6.57 | 7.57 | 1.15 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.0010 | 2.26 | 2.30 |
| Av. | 81.47 | 0.004 | 0.021 | 6.76 | 8.09 | 1.20 | 0.169 | 0.021 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.0004 | 0.93 | 1.13 |
| Guanbanwusu [17] | nd | 0.020 | 0.110 | 9.34 | 6.97 | 0.74 | 0.126 | 0.120 | 0.83 | 0.43 | 0.0140 | 0.73 | nd |
| Haerwusu [17] | nd | 0.070 | <0.110 | 8.89 | 6.19 | 0.70 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 1.33 | 0.47 | 0.0100 | 0.56 | nd |
| Heidaigou [17] | nd | 0.010 | 3.660 | 10.56 | 8.04 | 0.76 | 0.016 | 0.210 | 0.44 | 0.74 | 0.0060 | 0.93 | nd |
| China [26] | nd | 0.160 | 0.220 | 5.98 | 8.47 | 1.42 | 0.090 | 0.190 | 1.23 | 0.33 | 0.0200 | 4.85 | nd |
| Sample | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | Cd | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | W | Pb | Bi | Th | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-1 | 253 | 0.7 | 3.2 | 24.5 | 6.5 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 16.3 | 13.5 | 30.4 | 4.7 | 80.3 | 209 | 34.4 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 0.60 | 19.3 | 7.4 | 2.45 | 5.8 | 19.2 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 6.1 |
| 6-2 | 28.9 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 19.4 | 6.8 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 5.1 | 24.3 | 8.8 | 0.4 | 31.3 | 192 | 3.0 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 27.2 | 4.4 | 0.19 | 0.4 | 5.40 | 0.2 | 15.3 | 3.6 |
| 6-3 | 16.8 | 1.5 | <0.5 | 9.12 | 5.2 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 16.9 | 83.1 | 4.5 | 0.2 | 48.4 | 48.7 | 1.6 | 7.7 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 32.0 | 1.2 | 0.08 | 1.4 | 122 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 0.9 |
| 6-4 | 23.1 | 1.5 | <0.5 | 9.00 | 6.0 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 4.1 | 26.2 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 47.7 | 39.7 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 5.08 | 0.9 | 0.10 | 0.6 | 3.51 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 0.4 |
| 6-5 | 34.2 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 30.0 | 10.5 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 10.8 | 125 | 15.2 | 0.7 | 1623 | 407 | 11.3 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 0.04 | 112 | 9.9 | 0.27 | 0.9 | 15.2 | 0.3 | 23.8 | 5.2 |
| 6-6 | 33.2 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 11.7 | 6.4 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 7.5 | 160.5 | 8.7 | 0.4 | 759.7 | 7.6 | 56.7 | 3.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 60.1 | 30.3 | 54.1 | 5.5 | 17.8 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| 6-7 | 23.1 | 1.3 | <0.5 | 12.6 | 6.2 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 4.6 | 159 | 8.9 | 0.5 | 309 | 21.5 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.01 | 25.0 | 0.6 | 0.07 | 1.2 | 7.16 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| 6-8 | 88.6 | 2.0 | 5.2 | 33.8 | 8.9 | 2.0 | 5.3 | 19.2 | 83.6 | 13.1 | 1.6 | 5737 | 186 | 17.8 | 2.7 | 0.2 | 0.13 | 377 | 4.9 | 1.13 | 2.1 | 36.1 | 0.8 | 17.2 | 7.9 |
| 6-9 | 57.9 | 1.1 | 3.1 | 20.1 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 8.3 | 180 | 18.0 | 1.0 | 375 | 161 | 8.2 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.10 | 46.2 | 3.4 | 0.44 | 2.1 | 14.2 | 0.3 | 8.6 | 7.6 |
| 6-10 | 72.9 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 18.2 | 7.5 | 1.5 | 3.3 | 15.2 | 217 | 13.1 | 0.3 | 920 | 123 | 4.1 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 34.8 | 2.9 | 0.27 | 0.6 | 18.8 | 0.4 | 7.0 | 4.5 |
| 6-11 | 49.1 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 17.0 | 8.8 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 11.3 | 102 | 12.9 | 1.2 | 1075 | 104 | 7.7 | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.19 | 212 | 3.0 | 0.68 | 1.4 | 14.4 | 0.6 | 15.2 | 3.6 |
| 6-12 | 33.9 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 26.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 6.4 | 19.7 | 561 | 19.4 | 0.4 | 1759 | 122 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 2.7 | 0.03 | 90.9 | 3.0 | 0.21 | 0.8 | 27.4 | 0.6 | 8.4 | 5.6 |
| 6-13 | 40.4 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 21.1 | 12.8 | 1.3 | 4.8 | 9.7 | 81.1 | 13.8 | 0.5 | 1915 | 88.7 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 0.04 | 73.9 | 2.3 | 0.25 | 0.6 | 14.1 | 0.3 | 8.8 | 2.8 |
| 6-14 | 60.6 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 39.0 | 22.6 | 2.7 | 11.2 | 28.6 | 37.2 | 13.9 | 1.8 | 108 | 160 | 7.7 | 4.2 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 39.8 | 3.8 | 0.48 | 1.0 | 25.3 | 0.6 | 8.9 | 2.5 |
| Av. | 56.6 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 20.2 | 8.6 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 12.3 | 134.2 | 12.8 | 1.0 | 1037 | 132 | 7.6 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 0.10 | 81.0 | 3.4 | 0.47 | 1.4 | 23.1 | 0.4 | 9.3 | 3.6 |
| Guanbanwusu [17] | 175 | 1.64 | 6.87 | 38.3 | 16.2 | 1.28 | 2.76 | 13.3 | 29.1 | 12.9 | 2.99 | 703 | 143 | 11.1 | 1.83 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 62 | 3.96 | 0.85 | 1.1 | 26.5 | 0.49 | 12.9 | 3.74 |
| Haerwusu [17] | 116 | 2.8 | 7 | 27 | 10 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 13 | 40 | 18 | 1.3 | 350 | 268 | 13 | 1.6 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 41 | 7.2 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 30 | 0.5 | 17 | 3.7 |
| Heidaigou [17] | 38 | 2.3 | 8.4 | 32 | 15 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 16 | 17 | 45 | 2 | 423 | 234 | 13 | 3.1 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 56 | 8 | 1 | 1.8 | 36 | 0.8 | 18 | 3.9 |
| Clarke value [28] | 20 | 2.8 | 22 | 135 | 100 | 25 | 75 | 55 | 70 | 15 | 90 | 375 | 165 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 3 | 425 | 3 | 2 | 1.5 | 12.5 | 0.17 | 9.6 | 2.7 |
| China [26] | 31.8 | 2.1 | 4.2 | 35.1 | 15.4 | 7.1 | 13.7 | 17.5 | 41.4 | 6.6 | 9.3 | 140 | 89.5 | 9.4 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 159 | 3.7 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 15.1 | 0.8 | 5.8 | 2.4 |
| World [27] | 14 | 2 | 3.7 | 28 | 17 | 6 | 17 | 16 | 28 | 6 | 18 | 100 | 36 | 4 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 150 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.99 | 9 | 1.10.8 | 3.2 | 1.9 |
| Correlation With Ash Yield |
|
|
|
|
| Aluminosilicate Affinity |
| rAl–Si > 0.8 TiO2, Li, Ga, Rb, Nb, Cs, Ta, W |
| rAl–Si = 0.5–0.8 K2O, Bi, Na2O |
| rAl–Si = 0.3–0.5 Sc, Cu, Hf, U |
| Correlation Coefficients Between Selected Elements |
| V-Cr 0.7, V-Co 0.5, V-Ni 0.7, V-MnO 0.27, V-Cu 0.7 |
| Cr-Co 0.6, Cr-Ni 0.8, Cr-MnO 0.54, Cr-Cu 0.6 |
| Co-Ni 0.88, Co-MnO 0.5, Co-Cu 0.70 |
| Ni-MnO 0.71, Ni-Cu 0.73, MnO-Cu 0.5, Sr-Ba 0.90 |
| Li-K2O 0.77, Li-Bi 0.77, Li-W 0.93, Li-Ta 0.97, Li-Nb 0.94, Li-Rb 0.95, Li-Ga 0.81 |
| Th-Sc 0.68, Th-V 0.64, Th-Zr 0.89, Th-Hf 0.87, Cd-SO3 0.5 |
| Ga-S −0.25, Cd-Zn 0.90 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, L.; Zhao, B.; Duan, P.; Shi, Z.; Ma, J.; Lin, M. Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal Seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals 2016, 6, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020028
Xiao L, Zhao B, Duan P, Shi Z, Ma J, Lin M. Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal Seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals. 2016; 6(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Lin, Bin Zhao, Piaopiao Duan, Zhixiang Shi, Jialiang Ma, and Mingyue Lin. 2016. "Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal Seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China" Minerals 6, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020028
APA StyleXiao, L., Zhao, B., Duan, P., Shi, Z., Ma, J., & Lin, M. (2016). Geochemical Characteristics of Trace Elements in the No. 6 Coal Seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals, 6(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020028





