Formation Mechanism of Pores and Throats in the Permian Continental Shales of the Junggar Basin in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
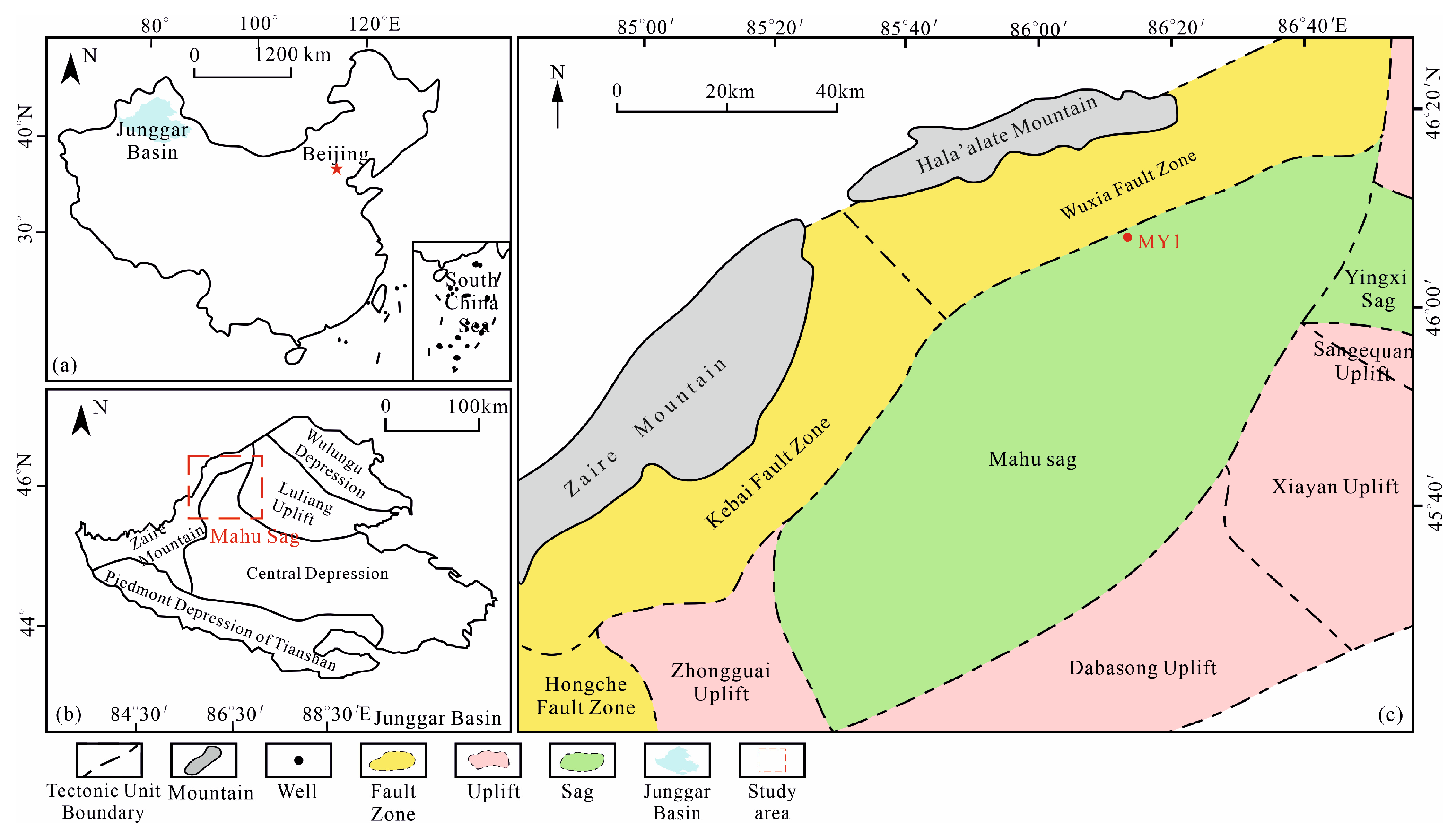
2. Regional Geological Setting
3. Sample Selection and Experimental Methods
3.1. Sample Selection
3.2. Mineral Composition Analysis
3.3. Porosity Analysis
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.5. Mercury Porosimeter
4. Results
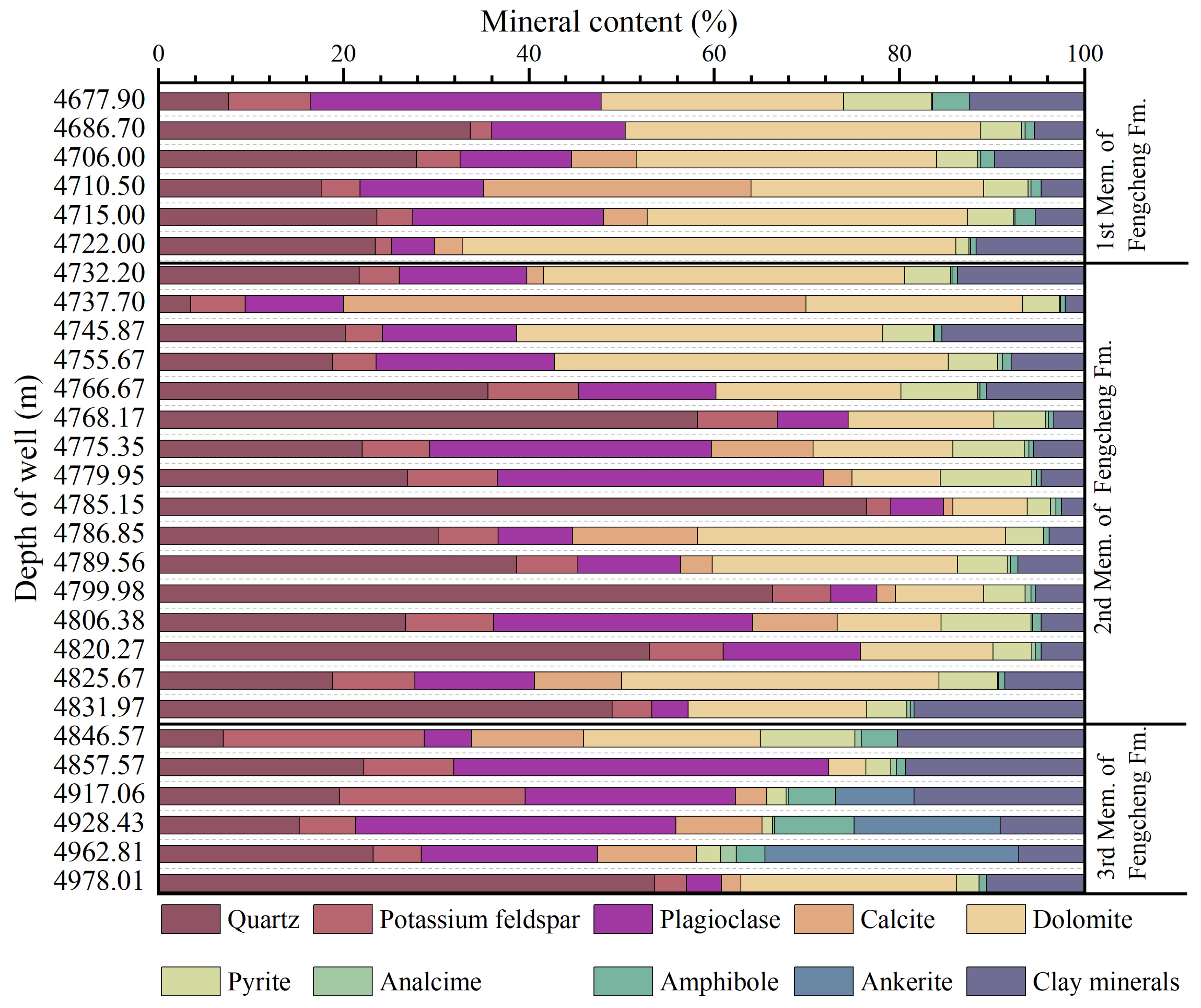
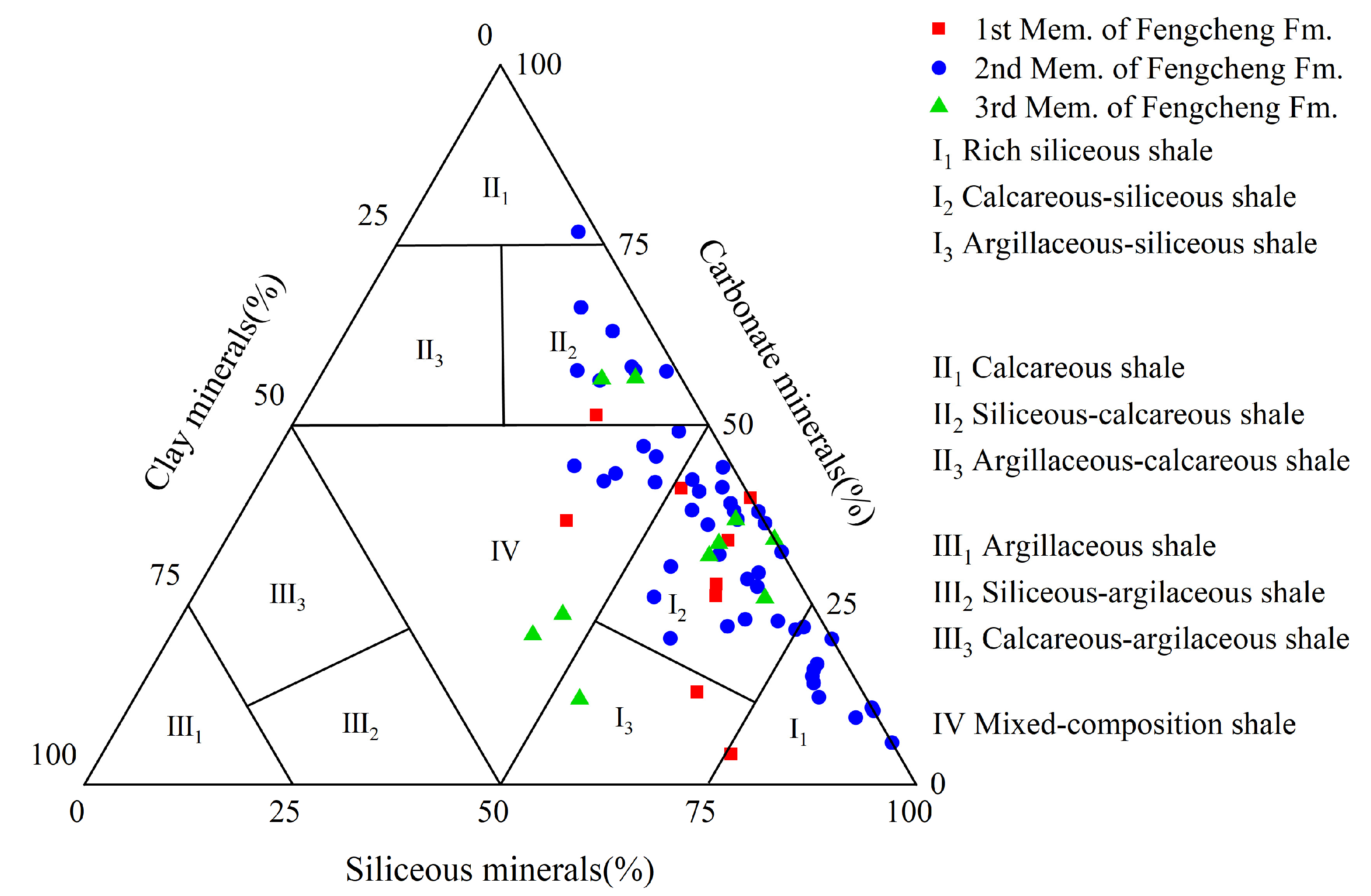
4.1. Characteristics of Mineral Composition and Type of Lithofacies
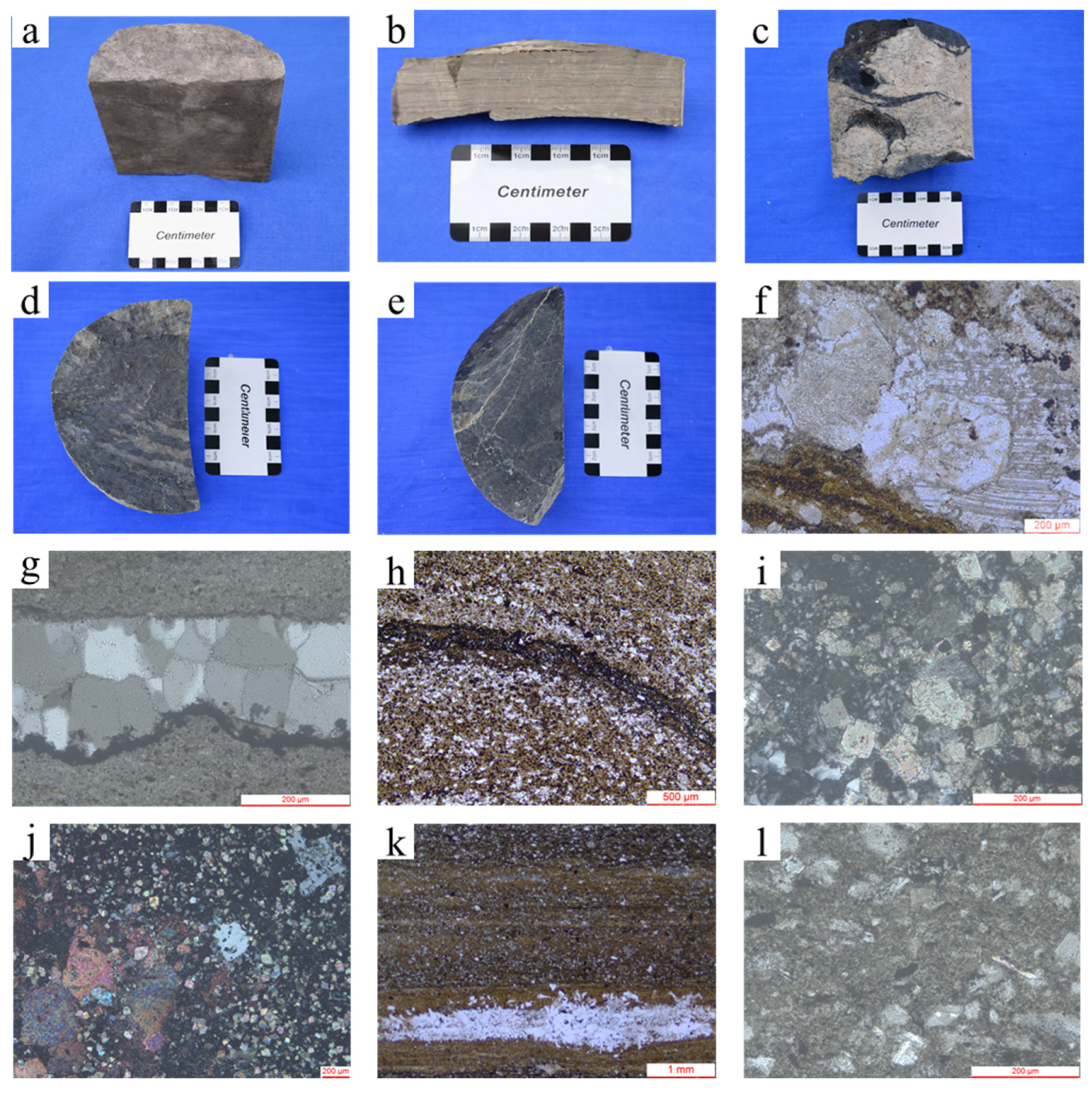
4.2. Characteristics of Core and Thin Sections
4.3. Types and Characteristics of Shale Pores and Throats
5. Discussion
5.1. Combination of Pores and Throats
5.2. Formation Mechanisms of Pores and Throats in Permian Continental Shales
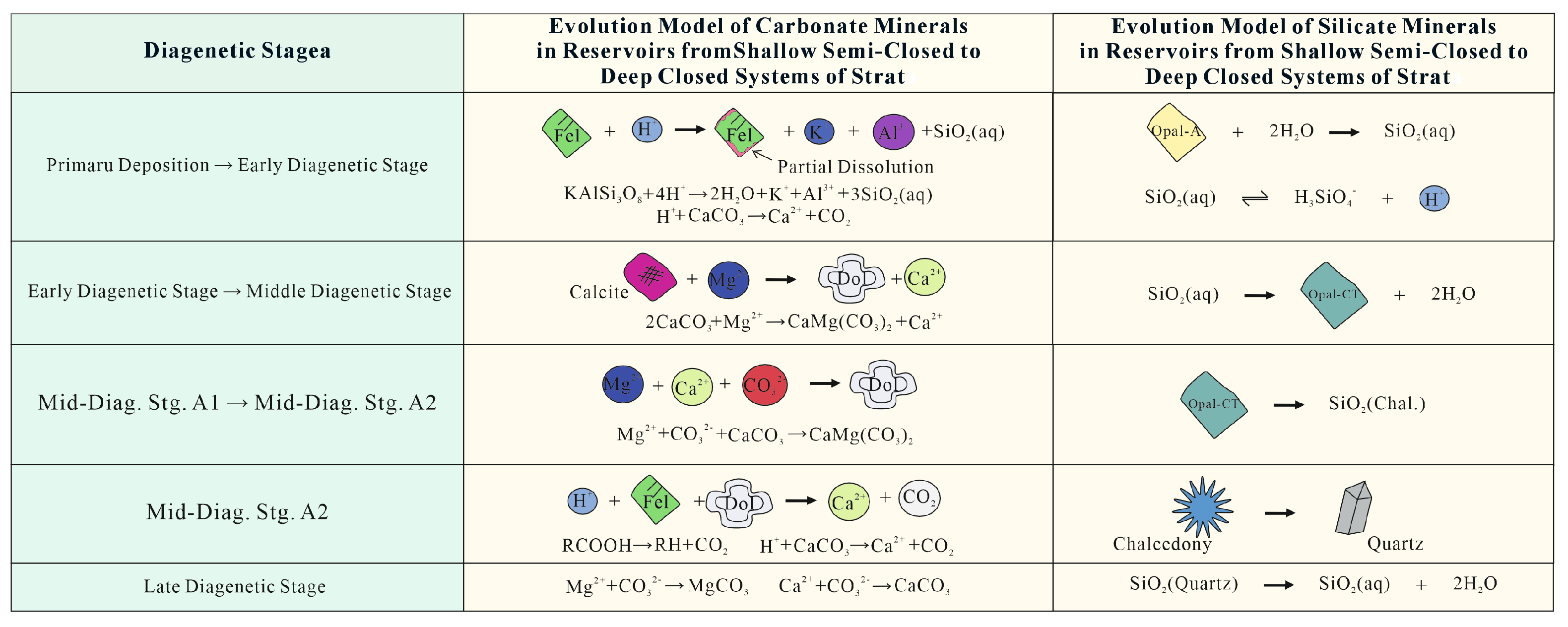
5.2.1. Role of Mineral Composition in Pore and Throat Development
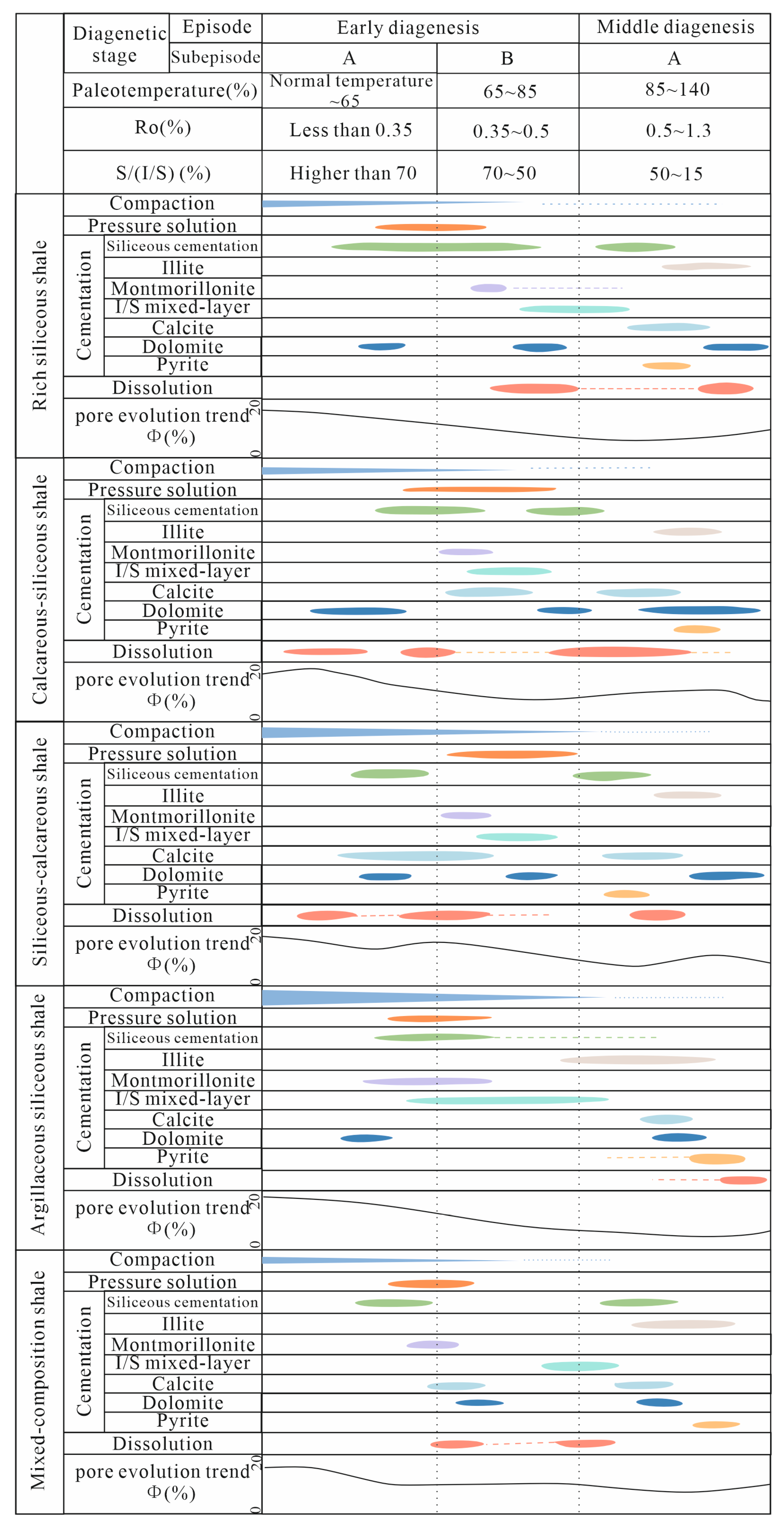
5.2.2. Impact of Diagenesis on Pore and Throat Development
5.3. Contribution to Industrial Hydrocarbon Production
6. Conclusions
- The pores of the Fengcheng Formation shales in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, are primarily intragranular, with pore sizes ranging from micrometer to nanometer scales. Rich siliceous shale (RSS) has larger pores, mainly with knot-like throats. Calcareous–siliceous shale (CSS) mainly features dissolved pores with relatively fine throat size. Siliceous–calcareous shale (SCS) primarily contains intragranular pores with diverse throat types. Argillaceous–siliceous shale (ASS) has low porosity, mainly with small pores and few throats. Mixed-composition shale (MCS) exhibits complex pore types and diverse throat types.
- Siliceous minerals contribute to the preservation of macropores and inhibit the formation of mesopores, with porosity positively correlated with the content of the siliceous minerals. Carbonate minerals promote the development of mesopores while inhibiting macropores. Clay minerals hinder pore development, leading to a negative correlation between porosity and clay content. The lithofacies with higher siliceous mineral content tend to have more macropores, the lithofacies containing carbonate minerals have more mesopores, and the lithofacies with higher clay content exhibit lower porosity.
- Diagenesis controls pore development through a “pore reduction to pore enhancement” mechanism. The initial compaction reduces porosity, while subsequent dissolution processes promote macropore formation. The cementation in different lithofacies affects porosity. In RSS, cementation inhibits pore damage. In CSS, cementation alternates with dissolution. In SCS, cementation by calcite reduces porosity. The pore evolution during diagenesis displays a difference with lithofacies.
- The pore–throat structure exerts a fundamental control on the effectiveness and producibility of Permian continental shale reservoirs. Lithofacies-dependent variations in pore scale, throat type, and connectivity systematically regulate effective porosity and hydrocarbon mobility, thereby governing reservoir quality. Consequently, lithofacies-based evaluation of pore–throat characteristics provides a basis for improving reservoir assessment and enhancing the accuracy of shale oil and gas resource estimation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fu, H.; Wang, Z. Research on Digital Core Characterization and Pore Structure Control Factors of Tight Sandstone Reservoirs in the Fuyu Oil Layer of the Upper Cretaceous in the Bayan Chagan Area of the Northern Songliao Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.; Hakhoo, N.; Bhat, G.M.; Hafiz, M.; Khan, M.R.; Misra, R.; Pandita, S.K.; Raina, B.K.; Thurow, J.; Thusu, B.; et al. Petroleum Systems and Hydrocarbon Potential of the North-West Himalaya of India and Pakistan. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 187, 109–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wang, H.; Ma, F.; Wu, Y. Distribution and Potential of Global Oil and Gas Resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, D.; Vishal, V.; Bahadur, J.; Agrawal, A.K.; Das, A.; Hazra, B.; Sen, D. Nano-Scale Physicochemical Attributes and Their Impact on Pore Heterogeneity in Shale. Fuel 2022, 314, 123070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, E.G.; Large, D.J.; Fletcher, R.S.; Rigby, S.P. Multi-Scale Pore Structural Change across a Paleodepositional Transition in Utica Shale Probed by Gas Sorption Overcondensation and Scanning. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 134, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M. Quantification of the Microstructures of Bakken Shale Reservoirs Using Multi-Fractal and Lacunarity Analysis. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, K.; Han, S.-J.; Sang, S.-X.; He, J.-J.; Baral, U.; Bhandari, S.; Mondal, D.; Zhou, X.-Z.; Liu, S.-Q. Impacts of Himalayan Tectonism on Eocene Gas Shale and Its Pore Structure within the Lesser Himalayas, Nepal: Insights for Shale Gas Accumulation and Preservation. Pet. Sci. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Tang, X.; He, W.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, L.; Lin, C. Characteristics and Genesis of Pore-Fracture System in Alkaline Lake Shale, Junggar Basin, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labani, M.M.; Rezaee, R.; Saeedi, A.; Hinai, A.A. Evaluation of Pore Size Spectrum of Gas Shale Reservoirs Using Low Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption, Gas Expansion and Mercury Porosimetry: A Case Study from the Perth and Canning Basins, Western Australia. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 112, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Cai, W.; Li, Z.; Lu, H. Microscopic Characterization and Fractal Analysis of Pore Systems for Unconventional Reservoirs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, D.; Xing, F. Effects of Organic Matter and Mineral Compositions on Pore Structures of Shales: A Comparative Study of Lacustrine Shale in Ordos Basin and Marine Shale in Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2018, 36, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ougier-Simonin, A.; Renard, F.; Boehm, C.; Vidal-Gilbert, S. Microfracturing and Microporosity in Shales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 198–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jia, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, B.; Jia, P.; Lan, Y.; Dong, D.; Qu, F. Characterization of Flow Parameters in Shale Nano-Porous Media Using Pore Network Model: A Field Example from Shale Oil Reservoir in Songliao Basin, China. Energies 2023, 16, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Xun, Y.; Liu, H.; Qi, B.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C. An Investigation of Hydraulic Fracturing Initiation and Location of Hydraulic Fracture in Preforated Oil Shale Formations. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Yan, X.; Bai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, K. Effect of Pore Throats on the Reservoir Quality of Tight Sandstone: A Case Study of the Yanchang Formation in the Zhidan Area, Ordos Basin. Open Geosci. 2025, 17, 20220759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, Q.; Zhuo, X.; Zhuo, P. The Impact of Reservoir Parameters and Fluid Properties on Seepage Characteristics and Fracture Morphology Using Water-Based Fracturing Fluid. Processes 2025, 13, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, I.V.; Dejam, M.; Quillinan, S.A. A Critical Review of Experimental and Theoretical Studies on Shale Geomechanical and Deformation Properties, Fluid Flow Behavior, and Coupled Flow and Geomechanics Effects during Production. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2025, 306, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Jiang, Z.; Gong, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Wu, Q. The Shale Gas Migration Capacity of the Qiongzhusi Formation: Implications for Its Enrichment Model. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 056603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Liu, Z.; He, W.; Zhou, C.; Qin, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C. Multiple Enrichment Mechanisms of Organic Matter in the Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Tang, X.; Xu, L.; Wu, W.; Shi, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Quantitative Identification Method for Pores in Shale Inorganic Components Based on Pixel Information. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2025, 12, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Zhai, G.; Bao, S.; Xu, C.; et al. Porosity-Preserving Mechanisms of Marine Shale in Lower Cambrian of Sichuan Basin, South China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Tang, Y.; He, W.; Guo, X.; Zheng, M.; Huang, L. Orderly Coexistence and Accumulation Models of Conventional and Unconventional Hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wen, H.; Gibert, L.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Lei, H. Deposition and Diagenesis of the Early Permian Volcanic-Related Alkaline Playa-Lake Dolomitic Shales, NW Junggar Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 123, 104780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, Z.; He, W.; Huang, L.; Chang, Q.; Tang, X.; Ye, H. Geneses of Multi-Stage Carbonate Minerals and Their Control on Reservoir Physical Properties of Dolomitic Shales. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 153, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Meng, X.; Pu, R. Impacts of Mineralogy and Pore Throat Structure on the Movable Fluid of Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs in Coal Measure Strata: A Case Study of the Shanxi Formation along the Southeastern Margin of the Ordos Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Zhang, T.; Dodd, T.J.H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Ji, D.; Liu, Y. Sedimentary Characteristics of Deep-Marine Gravity Flows Influenced by Island–Arc Volcanism: A Case Study of Carboniferous Sedimentary Successions in the Junggar Basin, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 272, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Pore Structure of the Mixed Sedimentary Reservoir of Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Hashan Area, Junggar Basin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, T.; Cao, T.; Pang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Lin, X.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Jiang, L.; et al. Pore Structure and Geochemical Characteristics of Alkaline Lacustrine Shale: The Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin. Minerals 2023, 13, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Mou, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; An, H.; Mo, Q.; Long, H.; Dang, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of the Marine Shale of the Longmaxi Formation in the Changning Area, Southern Sichuan Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1018274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, S.; Yi, J.; Hu, Q. Nano-Scale Pore Structure and Fractal Dimension of Organic-Rich Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale from Jiaoshiba Area, Sichuan Basin: Investigations Using FE-SEM, Gas Adsorption and Helium Pycnometry. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 70, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardestani, R.; Patience, G.S.; Kaliaguine, S. Experimental Methods in Chemical Engineering: Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution Measurements-BET, BJH, and DFT. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, A.M.S.; El-Sayed, N.A.A. Controls of Pore Throat Radius Distribution on Permeability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 157, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Liu, C.; Shi, D.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. Characterization and Control of Pore Structural Heterogeneity for Low-Thermal-Maturity Shale: A Case Study of the Shanxi Formation in the Northeast Zhoukou Depression, Southern North China Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 943935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, N.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, P.; Lu, S. Organic-Rich Shale Lithofacies Classification Scheme: Application and Discussion. Nat. Resour. Res. 2025; Epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; He, W.-J.; Guo, X.-G.; Zhao, K.-B.; Li, W.-W. Discovery of Shale Oil in Alkaline Lacustrine Basins: The Late Paleozoic Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Kou, G.; Zhou, H.; Liu, W.; Duan, X.; Zhan, S.; Li, H.; Li, Q. Microscopic Pore-Throat Classification and Reservoir Grading Evaluation of the Fengcheng Formation in Shale Oil Reservoir. Unconv. Resour. 2024, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Classification of Microscopic Pore-Throats and the Grading Evaluation on Shale Oil Reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Jin, X.; Zhu, R.; Gong, G.; Sun, L.; Dai, J.; Meng, D.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; et al. Do Shale Pore Throats Have a Threshold Diameter for Oil Storage? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Mirzaei-Paiaman, A.; Liu, B.; Ostadhassan, M. A New Model to Estimate Permeability Using Mercury Injection Capillary Pressure Data: Application to Carbonate and Shale Samples. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Dang, W.; Luo, T.; Sun, W.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ji, W.; Shao, S.; et al. Discussion on the Rising Segment of the Mercury Extrusion Curve in the High Pressure Mercury Intrusion Experiment on Shales. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelly, E.N.; Yang, F.; Ngata, M.R.; Mwakipunda, G.C.; Shanghvi, E.R. A Field Study of Pore-Network Systems on the Tight Shale Gas Formation through Adsorption-Desorption Technique and Mercury Intrusion Capillary Porosimeter: Percolation Theory and Simulations. Energy 2024, 302, 131771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.; Huffman, K.; Thornton, D.; Elsworth, D. The Effects of Mineral Distribution, Pore Geometry, and Pore Density on Permeability Evolution in Gas Shales. Fuel 2019, 257, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Rezaee, R.; Smith, G.; Ekundayo, J.M. Shale Lithofacies Controls on Porosity and Pore Structure: An Example from Ordovician Goldwyer Formation, Canning Basin, Western Australia. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 89, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathia, E.J.; Bowen, L.; Thomas, K.M.; Aplin, A.C. Evolution of Porosity and Pore Types in Organic-Rich, Calcareous, Lower Toarcian Posidonia Shale. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 75, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Perez, D.; Fisher, Q.; Lorinczi, P.; Velásquez Arauna, A.; Valderrama Puerto, J. A Review on Greensand Reservoirs’ Petrophysical Controls. Minerals 2025, 15, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Lithofacies-Controlled Pore Characteristics and Mechanisms in Continental Shales: A Case Study from the Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, C.; Qiu, X.; Wen, R.; Hu, Q. Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamov, T.; White, V.; Idrisova, E.; Kozlova, E.; Burukhin, A.; Morkovkin, A.; Spasennykh, M. Alterations of Carbonate Mineral Matrix and Kerogen Micro-Structure in Domanik Organic-Rich Shale during Anhydrous Pyrolysis. Minerals 2022, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmings, J.F.; Dowey, P.J.; Taylor, K.G.; Davies, S.J.; Vane, C.H.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Rushton, J.C. Origin and Implications of Early Diagenetic Quartz in the Mississippian Bowland Shale Formation, Craven Basin, UK. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 120, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-M.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Yin, Z.-Y.; Zhu, R.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Bai, Y. Further Study on the Genesis of Lamellar Calcite Veins in Lacustrine Black Shale—A Case Study of Paleogene in Dongying Depression, China. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 1508–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L. Clay Mineral Characteristics and Smectite-to-Illite Transformation in the Chang-7 Shale, Ordos Basin: Processes and Controlling Factors. Minerals 2025, 15, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.S.; Schieber, J.; Kalinec, J. Clay Diagenesis and Overpressure Development in Upper Cretaceous and Tertiary Shales of South Texas. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 147, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørlykke, K.; Jahren, J. Open or Closed Geochemical Systems during Diagenesis in Sedimentary Basins: Constraints on Mass Transfer during Diagenesis and the Prediction of Porosity in Sandstone and Carbonate Reservoirs. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 2193–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, M.; Keene, J.B.; Gieskes, J.M. Diagenesis of Siliceous Oozes—I. Chemical Controls on the Rate of Opal-A to Opal-CT Transformation—An Experimental Study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 1041–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Memory, S.L.; Joseph, J.; Meshram, R.R. Mineralogical and Geochemical Studies of Shales from Kopili Formation, Dima Hasao District Assam, North East India: Insights into Diagenesis, Deposition and Provenance. Evol. Earth 2024, 2, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Pan, J.-F.; Li, Y.-W.; Sheng, J.J.; Ge, D.; Jia, R.; Guo, W. Evolution of the 3D Pore Structure of Organic-Rich Shale with Temperature Based on Micro-Nano CT. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tang, L.; Ma, K.; Yang, Y.; Jin, C.; Wu, L.; Li, X. The Control Effect of Burial Evolution Time Limit on the Organic Matter Pore Structure of Shale: A Case Study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation Shale from the Periphery of the Sichuan Basin in Southern China. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 9, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Lai, F.; Gao, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Luo, X.; et al. Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Pore Throat Structure of Shale Oil Reservoir in Saline Lake—A Case Study of Shale Oil of the Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Energies 2021, 14, 8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; An, C.; Dong, Z.; Xiao, D.; Yan, J.; Ding, G.; Yan, P.; Zhang, J. Reservoir Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Oil Content in Hybrid Sedimentary Rocks of the Lucaogou Formation, Western Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 736598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



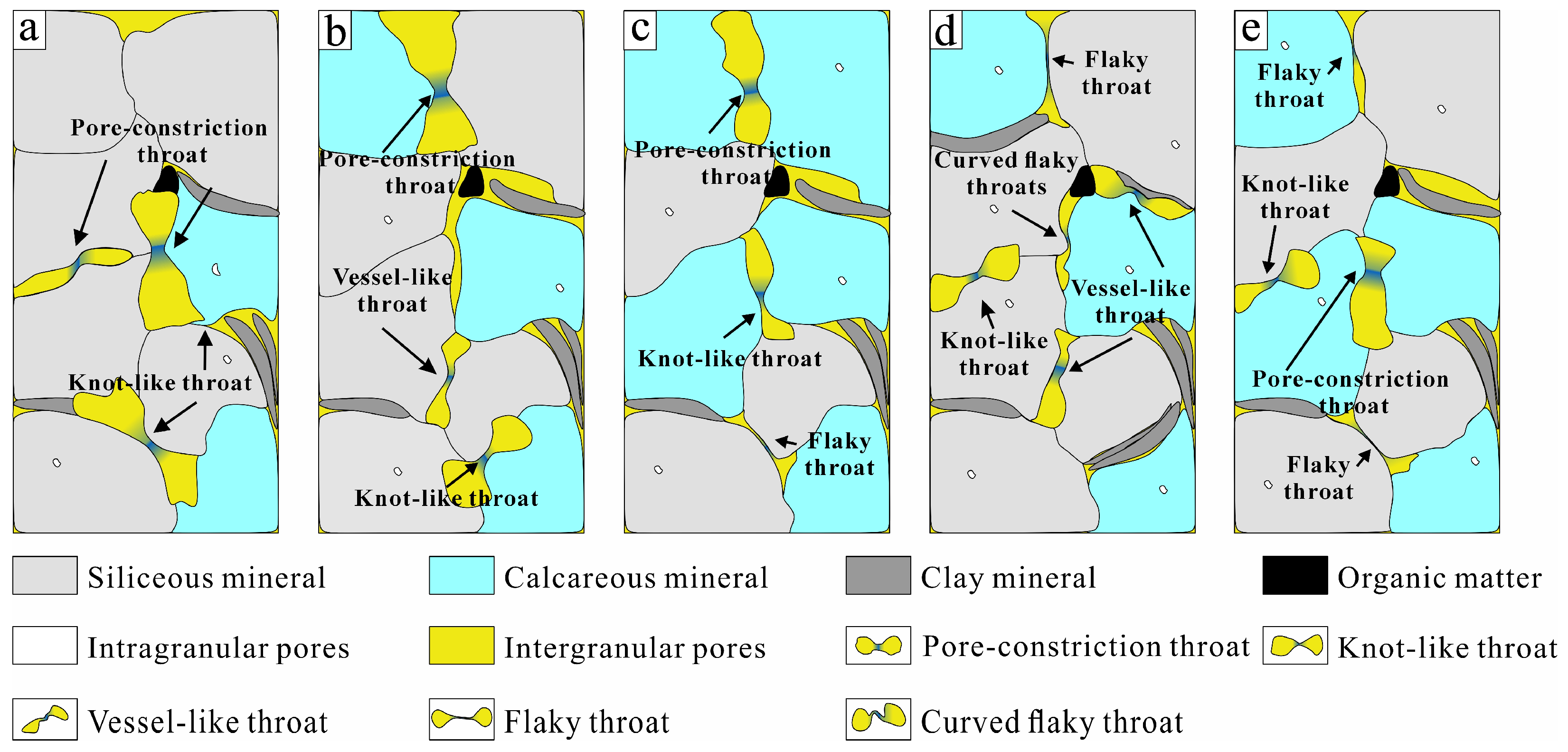


| Pore Characteristics | RSS | CSS | ASS | SCS | MCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative content of intergranular pores (%) | 55 | 68 | 20 | 59 | 23 |
| Relative content of intragranular pores (%) | 30 | 22 | 68 | 32 | 65 |
| Relative content of organic matter pores (%) | 15 | 10 | 12 | 9 | 12 |
| Pore size | Micron (2.1–17.2 μm) | Micron to sub-micron (0.21–8.9 μm) | Nanometer to micrometer (35 nm–6.5 μm) | Nanometer to micrometer (15 nm–7.3 μm) | Micron to sub-micron (0.19–5.8 μm) |
| Pore shape | Mainly irregular, few fissure-like pores. | Dissolution pores and intergranular pores, relatively regular. | Irregular and fissure-like pores, with a large number of tiny pores. | Mainly small, with circular or oval. | Mainly fissure-like and dissolution pores. |
| Characteristic Parameter | RSS | CSS | ASS | SCS | MCS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throat proportion (%) | Pore-constriction throats | 43 | 35 | 13 | 17 | 22 |
| Knot-like throats | 31 | 20 | 19 | 23 | 20 | |
| Vessel-like throats | 14 | 19 | 34 | 16 | 13 | |
| Flaky throats | 7 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 30 | |
| Curved flaky throats | 5 | 12 | 17 | 14 | 15 | |
| Throat size (nm) | Average diameter | 55 | 50 | 20 | 30 | 25 |
| Range | 3~70 | 3~60 | 2~25 | 2~40 | 3~35 | |
| Lithofacies | Porosity (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | Mercury Removal Efficiency (%) | Displacement Pressure (MPa) | Maximum Mercury Saturation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | 6.443 | −0.463 | 3.598 | 36.181 | 34.371 | 56.500 |
| CSS | 9.448 | −0.419 | 3.014 | 27.333 | 20.656 | 55.717 |
| SCS | 1.204 | −0.392 | 2.739 | 36.282 | 27.545 | 41.015 |
| ASS | 1.898 | −0.481 | 4.099 | 40.046 | 34.367 | 41.014 |
| MCS | 1.694 | −0.558 | 3.748 | 39.262 | 41.245 | 43.779 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Tang, X.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, W. Formation Mechanism of Pores and Throats in the Permian Continental Shales of the Junggar Basin in China. Minerals 2026, 16, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010038
Li Z, Tang X, Chen L, Jiang Z, Yuan Z, Yang L, Jiao Y, Shi W. Formation Mechanism of Pores and Throats in the Permian Continental Shales of the Junggar Basin in China. Minerals. 2026; 16(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ze, Xianglu Tang, Lei Chen, Zhenxue Jiang, Zhenglian Yuan, Leilei Yang, Yifan Jiao, and Wanxin Shi. 2026. "Formation Mechanism of Pores and Throats in the Permian Continental Shales of the Junggar Basin in China" Minerals 16, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010038
APA StyleLi, Z., Tang, X., Chen, L., Jiang, Z., Yuan, Z., Yang, L., Jiao, Y., & Shi, W. (2026). Formation Mechanism of Pores and Throats in the Permian Continental Shales of the Junggar Basin in China. Minerals, 16(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010038







