Major Ion Characteristics Reveal How Basin Hydrogeology and Groundwater Evolution Control the Formation of Saline Water Types in Nie’er Co Terminal Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
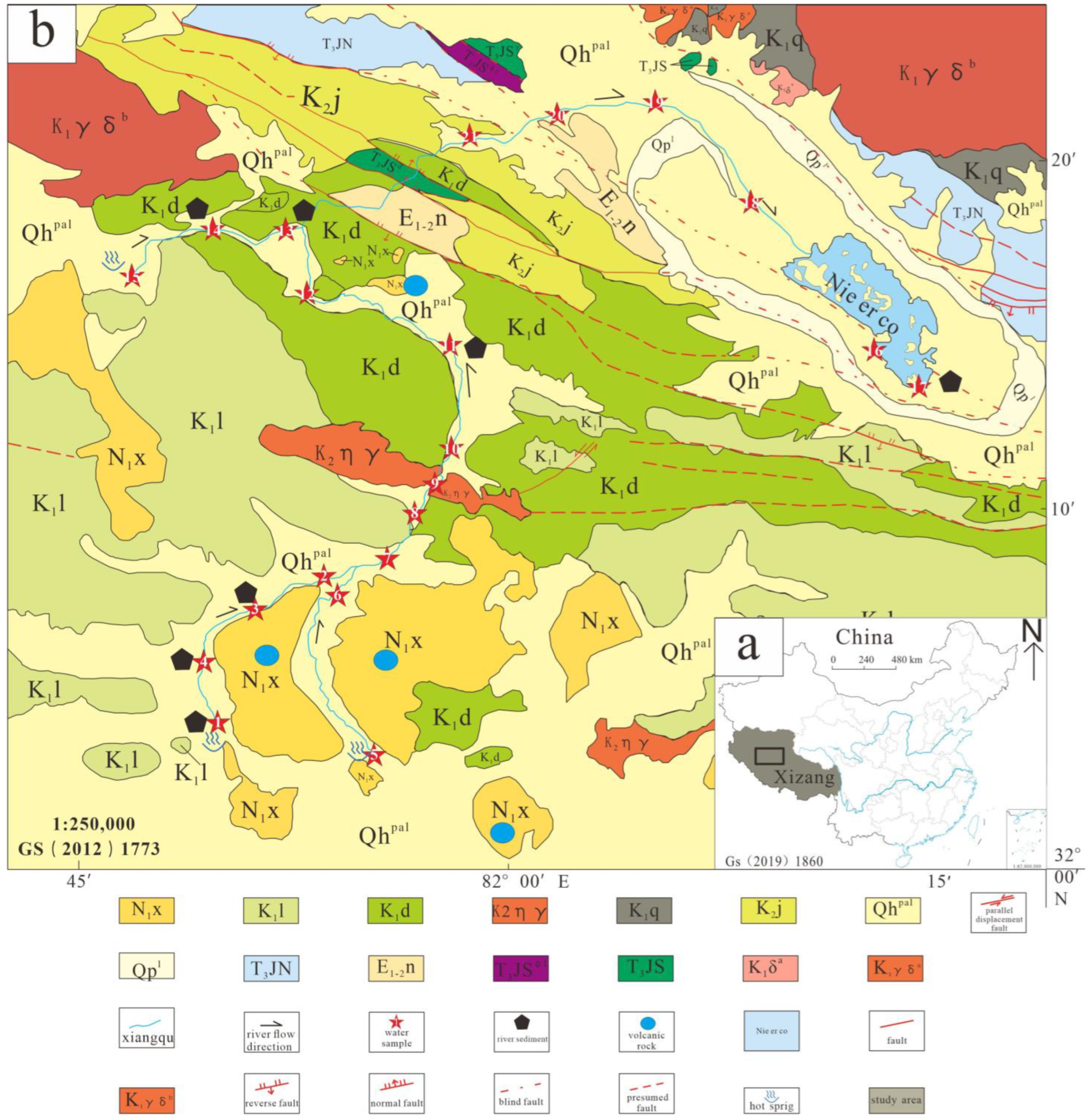
2.1. Study Area Geological and Hydrogeological Settings
2.1.1. Geological Settings
2.1.2. Hydrogeological Settings
2.2. Testing Methods
2.3. Analysis Methods
3. Results
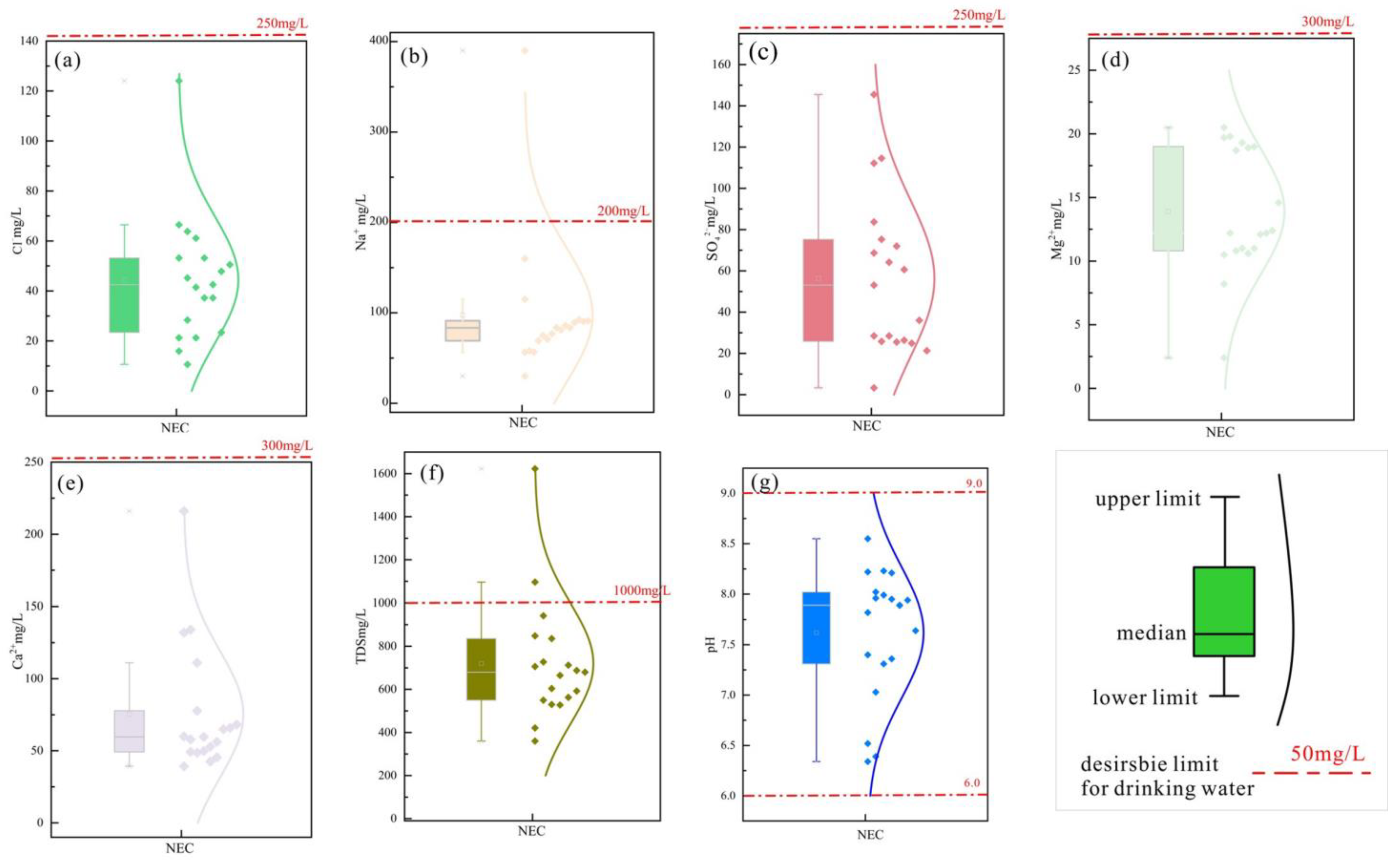
3.1. Water Sample Data Results
3.2. Solid Data Results
4. Discussion
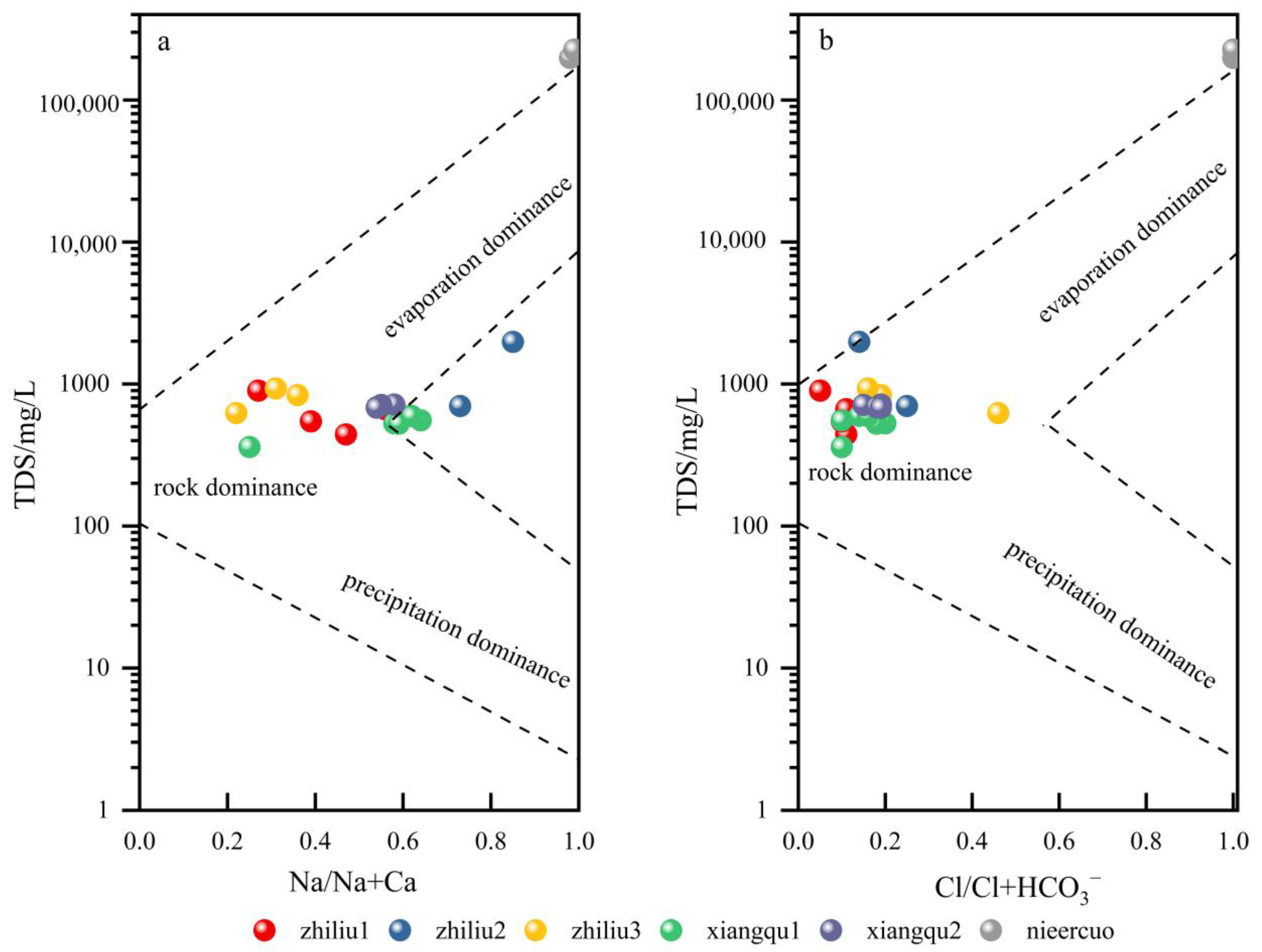
4.1. Hydrological Characteristics
4.1.1. Water Quality Assessment Based on the WQI
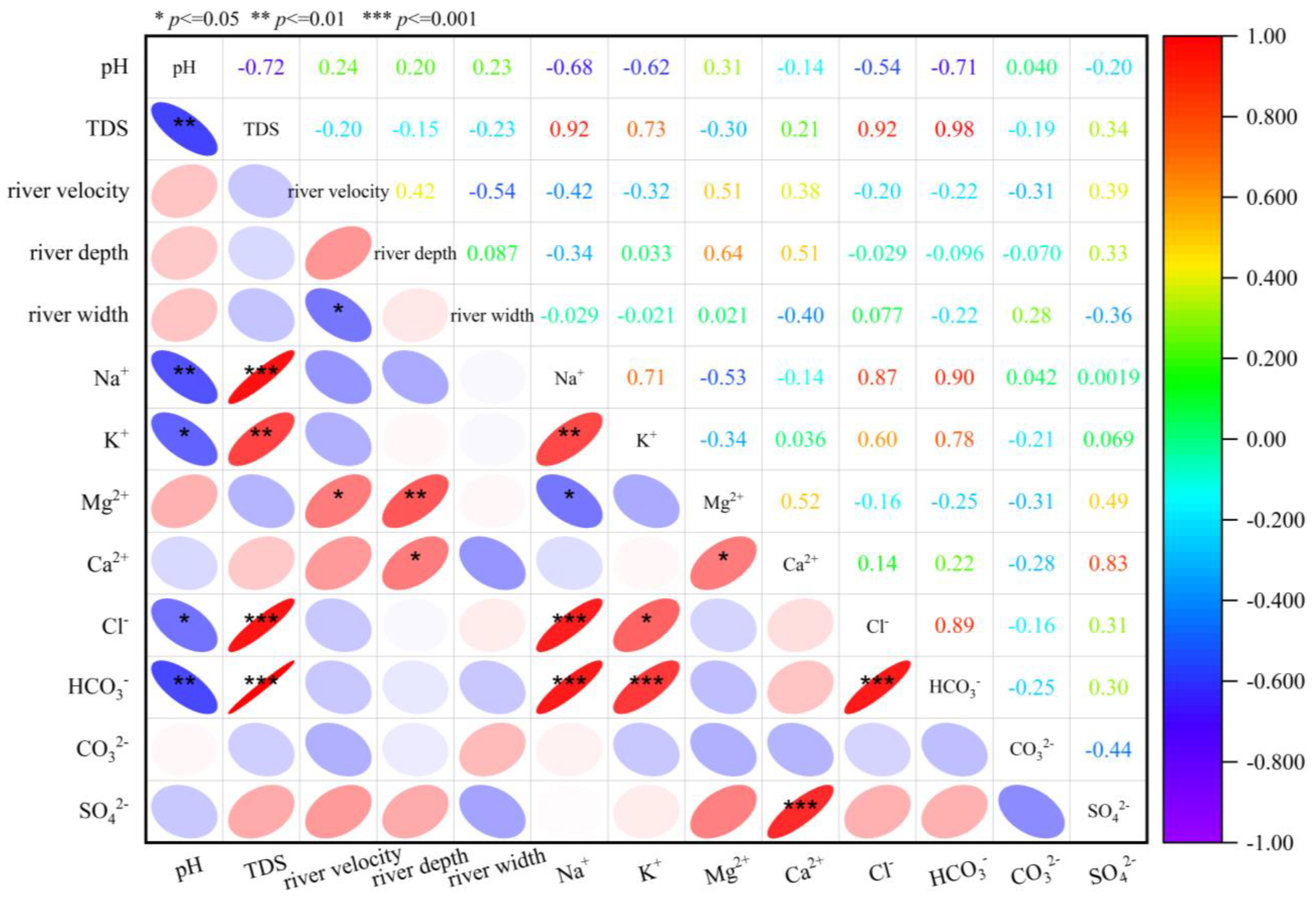
4.1.2. Correlation Between Rivers and Physicochemical Parameters of Water Samples
4.1.3. Distribution Characteristics of Hydrochemical Types
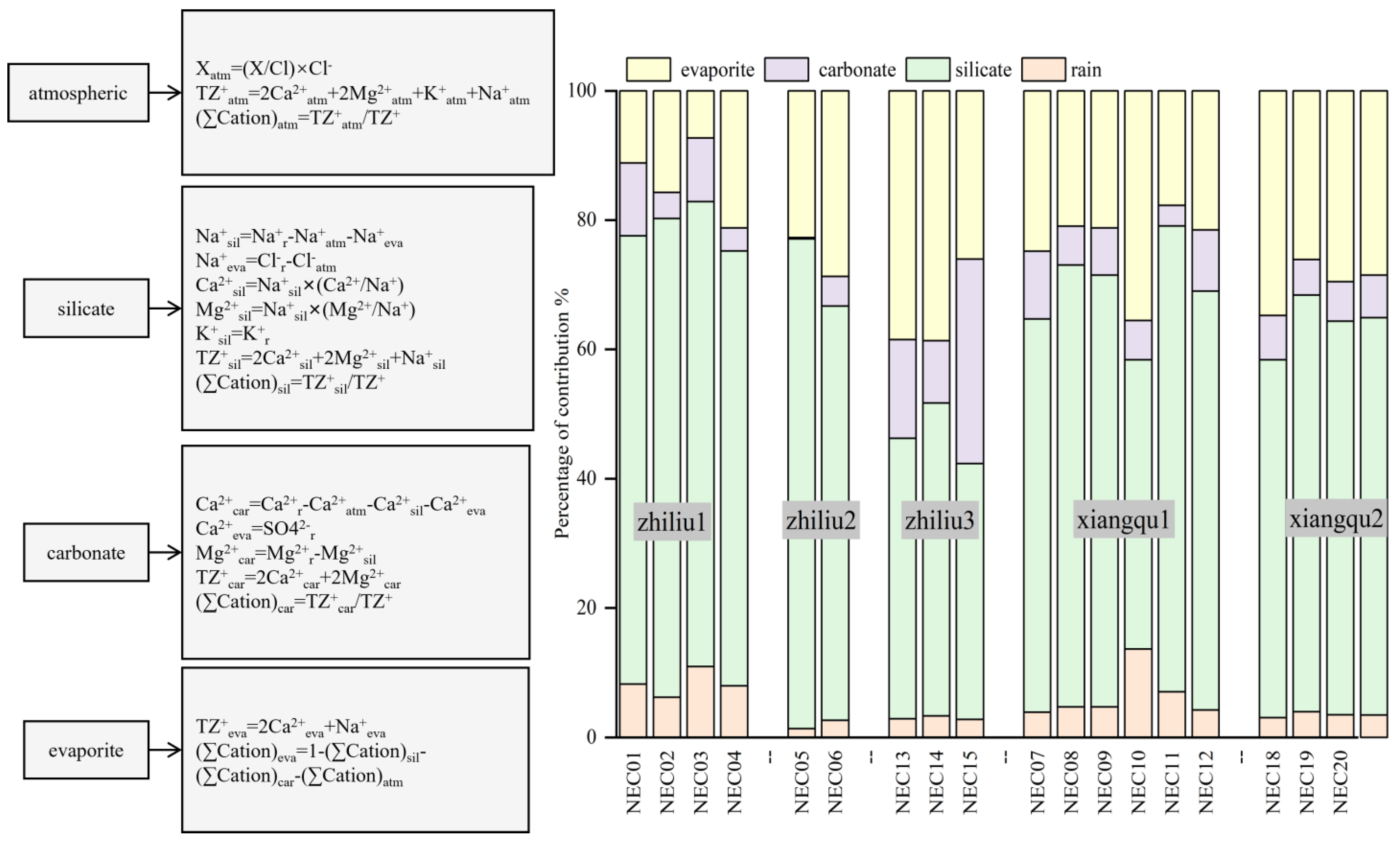
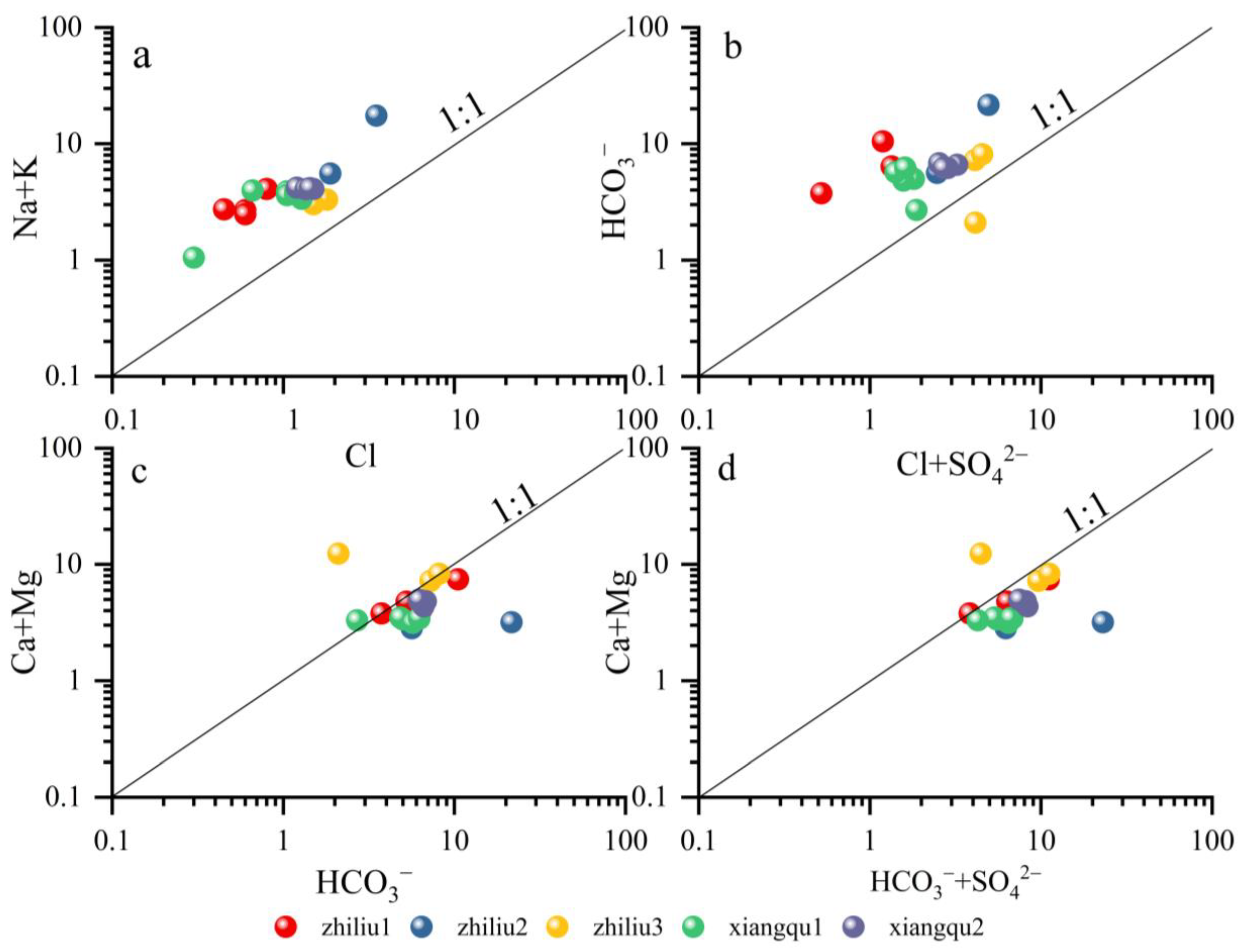
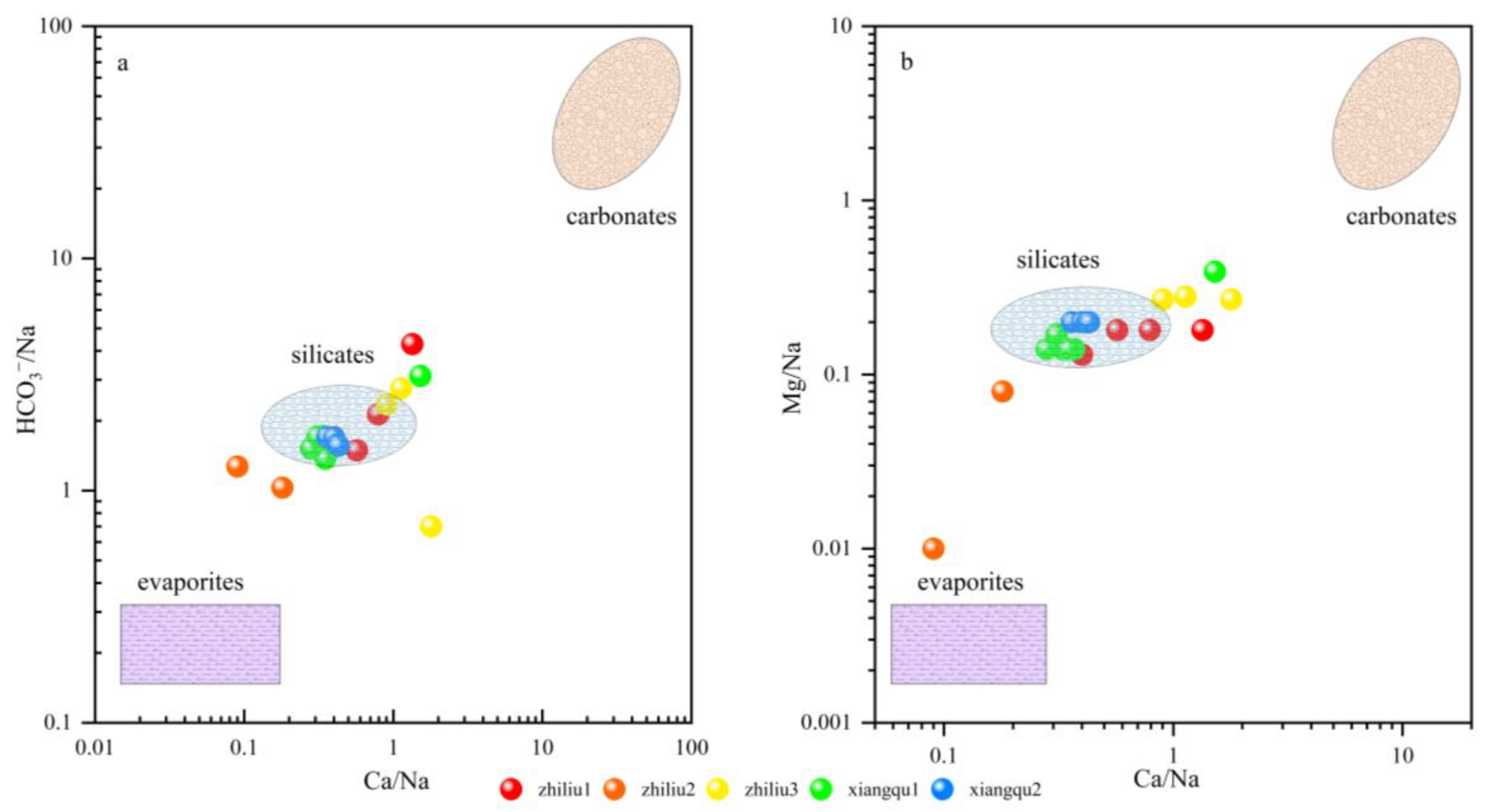
4.2. Source of Materials and Quantitative Contribution Rate
4.2.1. Qualitative Analysis of Principal Elements
4.2.2. Deep-Water Flow, Tributary Contribution Rate
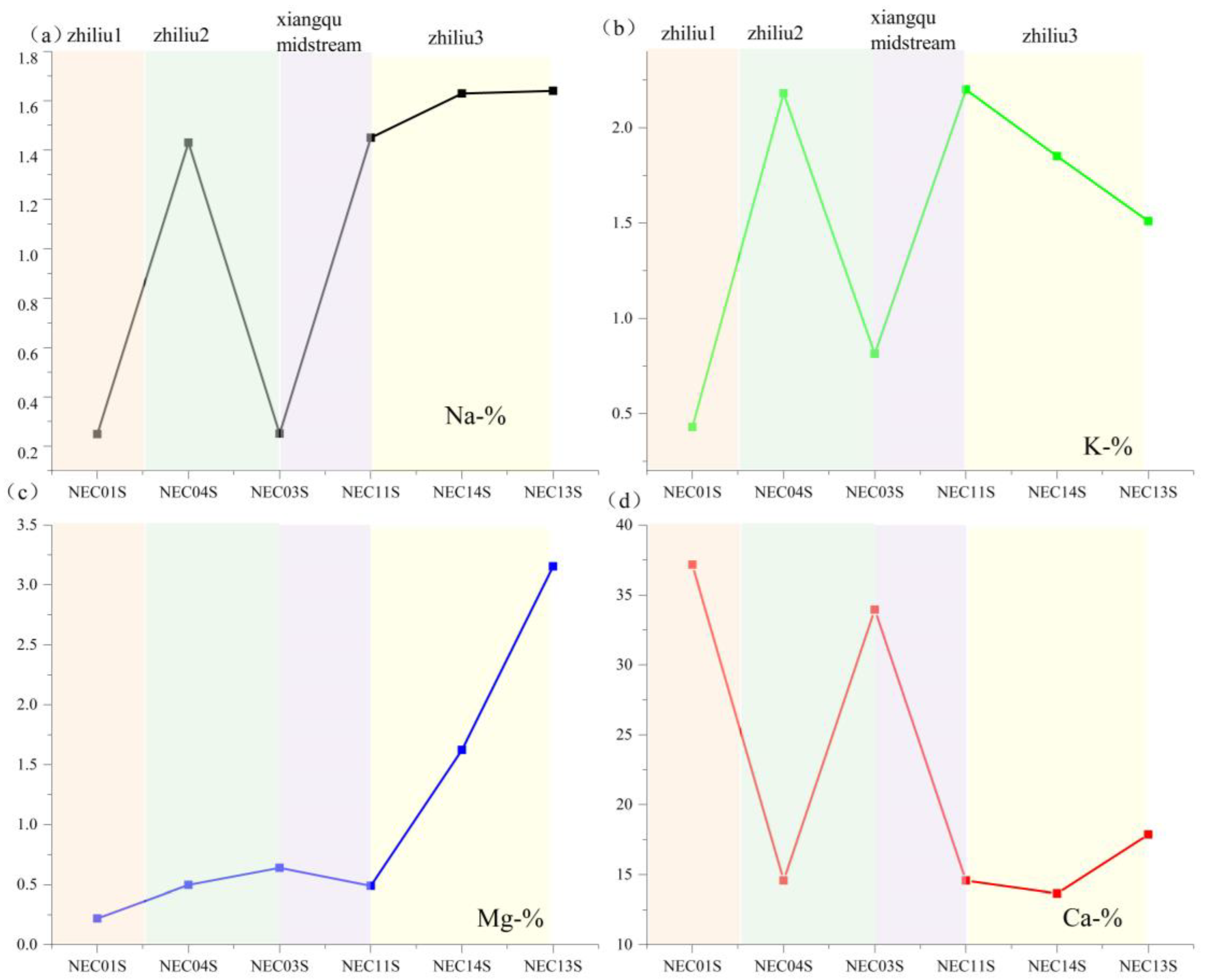
4.2.3. Minor Element Analysis
4.2.4. Contribution Rate of Surrounding Rock Weathering
4.3. Water–Rock Interaction
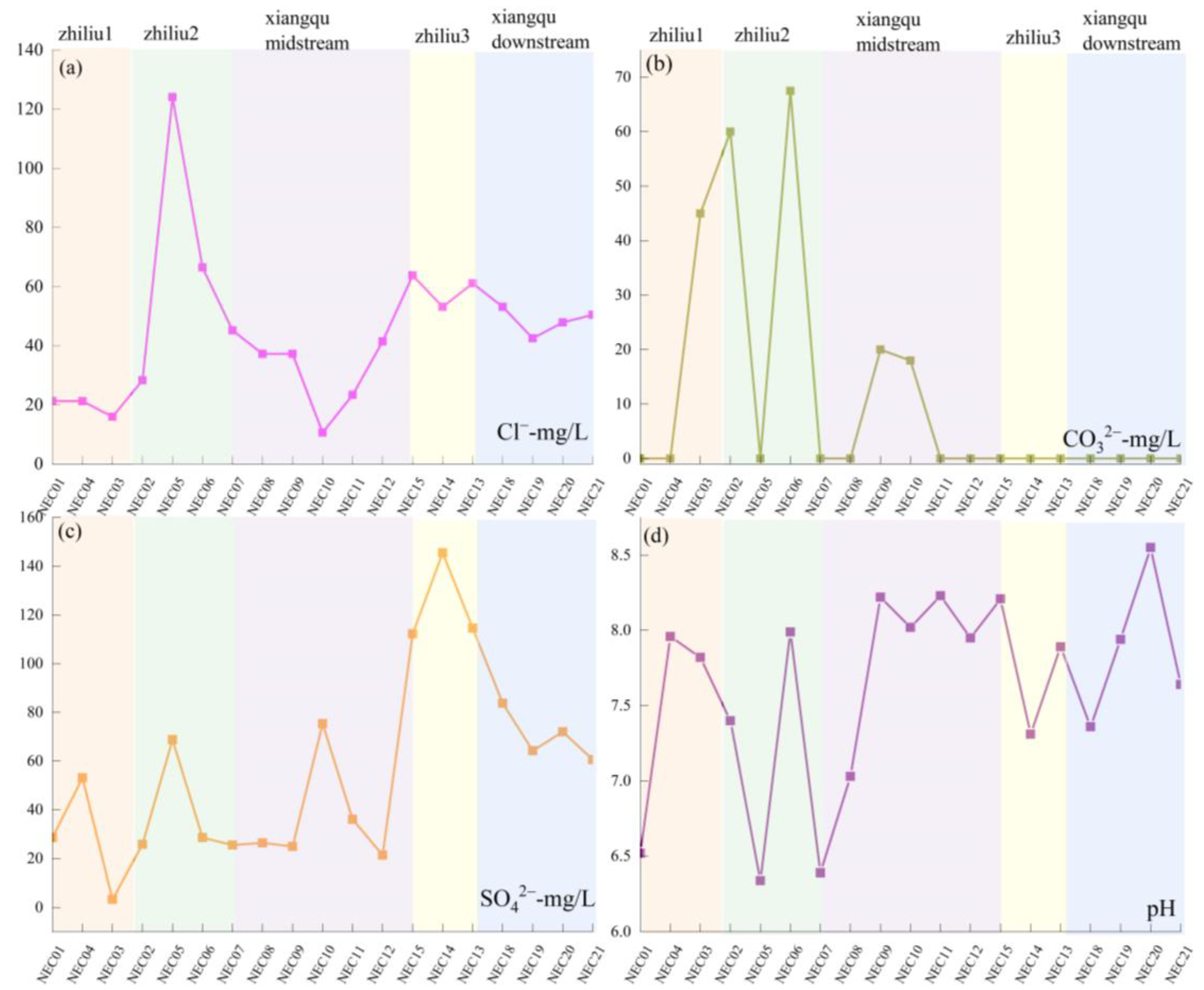
4.3.1. Spatial Variation of Main Ion Components
4.3.2. SI Saturation Index of Water Minerals
4.4. Comparative Analysis of the Evolutionary Mechanisms of Lake Nie’er Co and Global Terminal Lake Evolution
4.4.1. Formation Mechanism of Nie’er Co Lake
4.4.2. Comparative Analysis of Formation Mechanisms Between Nie’er Co Lake and Typical Terminal Salt Lakes Worldwide
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on WQI findings, it is confirmed that the water quality of the Xiangqu River basin flowing into Nie’er Co Lake is excellent and naturally formed, free from anthropogenic contamination. High-quality water carries salt ions generated by the weathering of the surrounding rock into the enclosed lake. Through prolonged evaporation and accumulation, salinity increases and ion concentrations become enriched, ultimately forming a terminal lake with extremely poor water quality;
- (2)
- Mechanism of hydrochemical evolution:
- (3)
- Elemental material sources:
- (4)
- Formation mechanism of Nie’er Co Salt Lake:
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols, G. Sedimentary processes, environments and basins. In Fluvial Systems in Desiccating Endorheic Basins; Nichols, G., Williams, E., Paola, C., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G. Tectonics of sedimentary basins. In Endorheic Basins; Busby, C., Azor, A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, L.; Liesa, C.L.; Simón, J.; Luzón, A. Sequence stratigraphy in continental endorheic basins: New contributions from the case of the northern extensional teruel basin. Sediment. Geol. 2025, 481, 106868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.; Dąbek-Głowacka, J.; Nowak, G.J.; Górecka-Nowak, A.; Wyrwalska, U.; Furca, M.; Wójcik-Tabol, P. Evolution of a late carboniferous fluvio-lacustrine system in an endorheic basin: Multiproxy insights from the Ludwikowice formation, intra-sudetic basin (SW Poland, NE Bohemian Massif). Minerals 2025, 15, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koycegiz, C. Seasonality effect on trend and long-term persistence in precipitation and temperature time series of a semi-arid, endorheic basin in central Anatolia, Turkey. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 2402–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvan, F.J.; Heredia, J.; Ruiz, J.M.; Pardo-Iguzquiza, E.; Garcia de Domingo, A.; Elorza, F.J. Hydrochemical and isotopes studies in a hypersaline wetland to define the hydrogeological conceptual model: Fuente de piedra lake (Malaga, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Naftz, D.; Spencer, R.; Oviatt, C. Geochemical evolution of great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Aquat. Geochem. 2008, 15, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagniecki, E.; Vanden Berg, M.; Boyd, E.; Johnston, D.; Baxter, B. Sulfate-rich spring seeps and seasonal formation of terraced, crystalline mirabilite mounds along the shores of Great Salt Lake, Utah: Hydrologic and chemical expression during declining lake elevation. Chem. Geol. 2023, 636, 121650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorko, K.; Jewell, P.; Nicoll, K. Fluvial response to an historic lowstand of the great Salt Lake, Utah. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 37, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.; Arnold, L.; Gázquez, F.; May, J.; Marx, S.; Jankowski, N.; Chivas, A.; Garćia, A.; Cadd, H.; Parker, A.; et al. Late quaternary climate change in Australia’s arid interior: Evidence from Kati Thanda—Lake Eyre. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 292, 107635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel, M.; Karlstrom, K.; Crossey, L.; Love, A.; Priestley, S. Evidence for intra-plate seismicity from spring-carbonate mound springs in the Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre region, south australia: Implications for groundwater discharge from the great artesian basin. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 28, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiero, K.; Wakjira, M.; Gownaris, N.; Malala, J.; Keyombe, J.; Ajode, M.; Smith, S.; Lawrence, T.; Ogello, E.; Getahun, A.; et al. Lake Turkana: Status, challenges, and opportunities for collaborative research. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutz, A.; Schuster, M.; Boës, X.; Rubino, J. Orbitally-driven evolution of Lake Turkana (Turkana Depression, Kenya, Ears) between 1.95 and 1.72 ma: A sequence stratigraphy perspective. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 125, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloszies, C.; Forman, S.L.; Wright, D.K. Water level history for Lake Turkana, Kenya in the past 15,000 years and a variable transition from the African humid period to holocene aridity. Glob. Planet. Change 2015, 132, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.L.; Fan, Q.S.; Li, Q.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Yang, H.T.; Han, C.M. Recharge processes limit the resource elements of Qarhan Salt Lake in western China and analogues in the evaporite basins. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, G. Diversity of prokaryotic microorganisms in alkaline saline soil of the Qarhan Salt Lake area in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W. Uniconfined brine hydrochemistry characteristic and brine cause analysis of east section of Qarhan Salt Lake. J. Salt Lake Res. 2009, 17, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.P. Salt lake resources and eco-environment in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zheng, M.P. Geological features and metallogenic mechanism of the Nie’er co magnesium borate deposit,Tibet. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, Z.Y.; Yan, W.B.; Hao, Y.J.; Lin, Z.X. Zircon u-pb ages and geochemical characteristics of diabase in Nie’erco area, Central Tibet: Implication for Neo-Tethyan slab breakoff. Geol. China 2023, 50, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.Y.; Zheng, M.P.; Nie, Z.; Lv, Y.Y.; Wu, Q. Mg-borate deposit formation: Recharge and lake water hydrogeochemistry of Nie’ er co Lake, northwestern Tibet. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14506.28-2010; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Silicate Rocks—Part 28: Determination of 16 Major and Minor Elements Content. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=8C96145A08BB7CE3C1B2E6947DBBB4AA&refer=outter (accessed on 10 December 2025).
- GB/T 14506.30-2010; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Silicate Rocks—Part 30: Determination of 44 Elements. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=C7B39BCCDC84BC81FD9EFD9F6CDD7A16&refer=outter (accessed on 10 December 2025).
- HDB/T 3022-2018; Standard for Primary Trace Element Testing of Rocks. Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology: Beijing, China, 2018; (Internal Institutional Documents, Not Made Public, the Standard Number was Provided by the Testing Party).
- Zhang, X.R.; Fan, Q.S.; Li, Q.K.; Du, Y.S.; Qin, Z.J.; Wei, H.C.; Shan, F.S. The source, distribution, and sedimentary pattern of k-rich brines in the Qaidam Basin, western china. Minerals 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Duan, L.M.; Mao, H.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Luo, A.K.; Huang, L.; Yu, R.H.; Miao, P.; Zhao, Y.Z. Hydrochemical and isotopic fingerprints of groundwater origin and evolution in the Urangulan River Basin, China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.X.; Gao, Y.Y.; Qian, H.; Chen, J.; Li, W.Q.; Li, S.Q.; Liu, Y.X. Elucidating the hydrochemistry and REE evolution of surface water and groundwater affected by acid mine drainage. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Xu, J.X.; Han, W.H.; Han, J.B. Hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors of lakes in Hoh Xil. Earth Environ. 2024, 53, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N. Distribution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals and safe utilization in surface soils from high-selenium regions in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk. Assess. 2024, 38, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Luo, X.; Xu, J.F.; Dong, S.Q.; Liang, S.S.; Xu, L.F.; Liu, L.Z.; Li, Y.H. Effects of PH and hydrochemical types on archaealcommunity structures in salt lakes of Badain Jaran Desert, Inner Mongolia. Microbiol. China 2025, 52, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Y. Variation patterns of boron and lithium isotopes in salt lakes on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau and their application in evaluating resourcesin the Damxung Co salt lake. J. Geomech. 2024, 30, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.W.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hao, Q.C.; Chen, H.Z.; Qi, Z.X.; Yan, H.J.; Han, J.B.; et al. Hydrogeochemical signatures, genetic mechanisms, and sustainable utilization potential of Li-B-Sr enriched groundwater in a typical arid endorheic watershed on Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 61, 102731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Ahmed, T.; Uddin, M.; Al-Sulttani, A.; Shafiquzzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Ahmed, M.; Alamin; Mohadesh, M.; Haque, M.; et al. Evaluation of Water Quality Index (WQI) in and around Dhaka city using groundwater quality parameters. Water 2023, 15, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Li, L.M.; Zhu, H.X.; Chen, L.; Li, S.P.; Meng, F.W.; Zhang, X.Y. Multiple evaluations, risk assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in surface water and sediment of the Golmud River, northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1095731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.S.; Pandya, D.M.; Shah, M. A systematic and comparative study of Water Quality Index (WQI) for groundwater quality analysis and assessment. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 54303–54323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.U.; Khan, M.A.; Siddiqui, F.; Mahmood, N.; Salman, N.; Alamgir, A.; Shaukat, S.S. Geospatial assessment of water quality using Principal Components Analysis (PCA) and Water Quality Index (WQI) in Basho Valley, Gilgit Baltistan (northern areas of Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.Q.; He, Z.Q.; Diao, Y.S.; Huang, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, F.; Luo, A.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.B. Tracing the origins of strontium in strontium-rich mineral water usingstrontium, hydrogen and oxygen isotope analysis. Earth Environ. 2025, 53, 504–515. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.1139.p.20241231.1500.001.html (accessed on 31 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.T.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.K.; Wang, J.P.; Yu, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Huo, S.L. Sources and enrichment processes of rubidium and cesium in the Nalengele river and its terminal lakes, Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2024, 32, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Z.; Yang, X.P. Hydrochemical compositions of natural waters in ordos deserts and their influencing factors. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2224–2239. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=X7jC3qydZ5-s2HzJj08EMS1dKjwAYUdMcH6JTCWRim8w5Zf0-MwmUvurVpCtQxg2z9kmD8t3gtjqG1P65IVVsh9wqMQ_zL5wahcDgauXd9dPOcz2VhwQ2OTXBT2DNjP56KgkpvcNnpYSr84oBEjMPOHMynPWIRXIX_xvyfLJ0dPBULh3x8FSmg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Fan, Z.J.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.L.; Chen, M.E.; Shen, J.W.; Li, J.W. Analysis of nitrate sources and transformation processes in shallowgroundwater in typical mountainous agricultural area. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.J.; Chen, C. The classification method of water chemical types based on the principle of kurllov’s formula and shoka lev classification. Ground Water 2018, 40, 6–11. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=1UNTTfPTmO-rASOQuf1e3tOGNBBFXQRBv7XYr10Y4cwq37WMFYNxD9V2R3EqxARjrxmJLzeANvNWb5hUZouZ1ue4DrWTKcXWdnghmcly9lNDofL0uG0oXUl7mImDqRJkNrjcZHPELMXJo2fVVrtslD85Sc45G54OPqcct7_LchjSLH71HtK0Qw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Mercedes-Martin, R.; Ayora, C.; Tritlla, J.; Sanchez-Roman, M. The hydrochemical evolution of alkaline volcanic lakes: A model to understand the South Atlantic pre-salt mineral assemblages. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 198, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.L.; Shen, H.Y.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Xie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.P. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in gudui spring catchment. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4874–4883. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=1UNTTfPTmO_baOeHEuc421SPpsjJ5NjR9ydBeB2OoBJEL6atxBNOslNhSU1cW3J52xZTUhhpH2zg6zZ2U6RPSlHI3ufqAbbaLA9ZIkZ2yXXX4_WGWoyPyfpIjscCAOmqGmB_PNkGGKiDA5yOJ-jcDAybW81ibPpX-6Ae0rqXE0c7smHVkT6Dsw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Yang, N.; Guo, L.; Wang, G.C.; Xiong, L.Y.; Song, X.M.; Li, H. Application of major ions and SR isotopes to indicate the evolution of river water and shallow groundwater chemistry in a typical endorheic watershed, northwestern China. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 175, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liang, Y.P. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of ground karst water systems in the longzici spring catchment. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2087–2095. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=X7jC3qydZ5_mxdxbcWGo6AUSz4SLFixXp0ZDy2AsEz19AKNJA8UJSLCrPiyoyFauk03w2RPF7a-Ilpo8ZFXycNiTSsCHjjkQ8gVUgs3Uwh48J6tyXrj6ZnYNDaVq5vSQRd8sdOhXDHK2wBc1ZtrMB42nO4E7HEvrlyn1KIiasetOhAALwQioXA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Ren, X.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yu, R.H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.Z. Hydrochemical variations and driving mechanisms in a large linked river-irrigation-lake system. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.G.; Zheng, M.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Xing, E.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ren, J.H.; Ling, Y. O, H, and Sr isotope evidence for origin and mixing processes of the gudui geothermal system, himalayas, China. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.L.; Miao, W.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, W.W.; Yuan, X.L. Trace element geochemistry and its constrains on lithium provenance of river sediments in the naringgele river catchment of qaidam basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2023, 31, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.Y.; Zheng, M.P.; Wang, Z.M.; Hao, W.L.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, X.B.; Han, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of brines in the Gasikule salt lake, northwest qaidam basin, China. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodbane, M.; Boudoukha, A.; Benaabidate, L. Hydrochemical and statistical characterization of groundwater in the chemora area, northeastern algeria. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 14858–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.H.; Pan, T.; He, M.Y.; Hou, D.B.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhou, J.D. Progress in the study of potassium, lithium, and boron salt resourcesin salt lakes of the qaidam basin on the qinghai-tibet plateau. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2025, 46, 376–396. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=X7jC3qydZ5-6TojRWhP7utZWMA8kZk-vTyAl9flAjNesXcLlup5Z4XDmJCPQ4IYjKdbssT3NPPEOQamQ4H1E0LddfHMUo3hH8OUb-hrHIvNOR8uZzf5pYUSd9VRFEFse_PaJ4IvKCjHRfoMiLVKiSKfKOXj0FUuxHkw9s1y796c_LtxFPodt3A==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Amroune, A.; Boudoukha, A.; Boumazbeur, A.; Benaabidate, L.; Guastaldi, E. Groundwater geochemistry and environmental isotopes of the hodna area, southeastern algeria. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 73, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | mg/L | pH | River | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | HCO3− | CO32− | SO42− | TDS | |||
| NEC01 | 56.40 | 8.70 | 10.50 | 132.00 | 21.27 | 590.00 | 0.00 | 28.50 | 848.49 | 6.52 | zhiliu1 |
| NEC02 | 115.00 | 13.60 | 12.20 | 60.00 | 28.36 | 389.00 | 60.02 | 25.80 | 706.30 | 7.4 | zhiliu1 |
| NEC03 | 58.00 | 0.40 | 10.80 | 57.90 | 15.95 | 228.83 | 45.02 | 3.30 | 421.33 | 7.82 | zhiliu1 |
| NEC04 | 56.70 | 8.20 | 11.00 | 77.80 | 21.27 | 320.36 | 0.00 | 53.10 | 549.67 | 7.96 | zhiliu1 |
| NEC05 | 390.00 | 20.70 | 2.40 | 59.70 | 124.08 | 950.00 | 0.00 | 68.70 | 1622.73 | 6.34 | zhiliu2 |
| NEC06 | 160.00 | 4.20 | 10.60 | 39.30 | 66.47 | 343.24 | 67.52 | 28.50 | 727.27 | 7.99 | zhiliu2 |
| NEC15 | 69.10 | 7.40 | 19.70 | 216.00 | 63.81 | 600.00 | 0.00 | 112.20 | 1096.73 | 6.39 | zhiliu3 |
| NEC14 | 75.00 | 8.80 | 19.80 | 134.00 | 53.18 | 497.31 | 0.00 | 145.50 | 941.92 | 7.03 | zhiliu3 |
| NEC13 | 70.80 | 6.50 | 20.50 | 111.00 | 61.15 | 442.40 | 0.00 | 114.60 | 835.77 | 8.22 | zhiliu3 |
| NEC07 | 77.00 | 11.80 | 11.00 | 49.20 | 45.20 | 305.10 | 0.00 | 25.50 | 530.10 | 8.02 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC08 | 83.70 | 10.20 | 12.10 | 48.60 | 37.22 | 381.38 | 0.00 | 26.40 | 604.12 | 8.23 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC09 | 81.10 | 3.00 | 12.20 | 49.80 | 37.22 | 294.93 | 20.01 | 24.90 | 527.38 | 7.95 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC10 | 30.00 | 0.30 | 8.20 | 52.80 | 10.64 | 164.75 | 18.01 | 75.30 | 360.03 | 8.21 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC11 | 86.00 | 10.70 | 12.40 | 42.50 | 23.40 | 347.81 | 0.00 | 36.00 | 563.14 | 7.31 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC12 | 83.40 | 3.50 | 14.60 | 45.50 | 41.48 | 378.32 | 0.00 | 21.30 | 592.32 | 7.89 | xiangqu1 |
| NEC18 | 89.40 | 7.00 | 18.70 | 56.30 | 53.18 | 350.00 | 0.00 | 83.70 | 664.88 | 7.36 | xiangqu2 |
| NEC19 | 92.50 | 6.60 | 19.30 | 65.00 | 42.54 | 414.94 | 0.00 | 64.20 | 712.20 | 7.94 | xiangqu2 |
| NEC20 | 90.50 | 7.60 | 18.90 | 65.90 | 47.86 | 378.32 | 0.00 | 72.00 | 687.90 | 8.55 | xiangqu2 |
| NEC21 | 91.20 | 5.40 | 19.00 | 68.20 | 50.52 | 378.32 | 0.00 | 60.60 | 680.06 | 7.64 | xiangqu2 |
| NEC16 | 46,200.00 | 8560.00 | 8990.00 | 777.00 | 63,810.00 | 0.00 | 3601.20 | 66,600.00 | 199,772.20 | 8.65 | Nie’erCo |
| NEC17 | 46,200.00 | 8710.00 | 9310.00 | 583.00 | 63,810.00 | 0.00 | 4200.00 | 68,500.00 | 202,572.00 | 9.21 | Nie’erCo |
| μg/g | Ba | Rb | Th | U | K | Nb | Ta | La | Ce | Sr | P | Nd | Hf | Zr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| volcanic rock | hs13-2 | 3274 | 241 | 151 | 41.3 | 41,700 | 29.5 | 1.82 | 142 | 325 | 1553 | 6530 | 210 | 19.5 | 601 |
| hs18-11 | 924 | 222 | 29.6 | 5.13 | 39,900 | 14.5 | 1.08 | 43 | 91.2 | 423 | 2550 | 45 | 5.97 | 170 | |
| hs11-3 | 2802 | 270 | 131 | 30.5 | 43,100 | 28.4 | 1.69 | 147 | 350 | 1599 | 8290 | 214 | 17 | 517 | |
| hs18-13 | 1278 | 286 | 39.9 | 7.27 | 43,800 | 18.6 | 1.33 | 48 | 109 | 549 | 3840 | 60.7 | 7.6 | 240 | |
| hs15 | 1243 | 257 | 44.9 | 9.35 | 43,100 | 18.3 | 1.33 | 49.3 | 112 | 495 | 7350 | 64.6 | 8.88 | 264 | |
| hs13-4 | 2849 | 290 | 140 | 33.6 | 44,100 | 29.2 | 1.8 | 118 | 271 | 1330 | 6360 | 190 | 18.7 | 548 | |
| hs18-9 | 1054 | 215 | 38.1 | 6.84 | 39,200 | 15.6 | 1.17 | 53.3 | 112 | 507 | 2660 | 57.3 | 6.65 | 199 | |
| hs06 | 784 | 308 | 41 | 8.15 | 47,300 | 14.7 | 1.29 | 75.4 | 157 | 259 | 1780 | 73.6 | 8.37 | 237 | |
| hs24 | 1409 | 272 | 64 | 7.36 | 44,400 | 18.2 | 1.24 | 56.1 | 129 | 501 | 3140 | 75.4 | 8.3 | 246 | |
| hs18-3 | 887 | 212 | 26.8 | 4.22 | 38,600 | 13.7 | 1.05 | 40.3 | 86.7 | 378 | 1970 | 41 | 4.97 | 160 | |
| hs01 | 1947 | 291 | 81.7 | 19.7 | 44,800 | 21.7 | 1.46 | 101 | 217 | 926 | 4410 | 122 | 12.7 | 387 | |
| hs02 | 1328 | 329 | 71.3 | 9.41 | 46,000 | 18 | 1.26 | 76.7 | 165 | 462 | 2950 | 93.9 | 11 | 320 | |
| hs22 | 1782 | 309 | 90.3 | 13.2 | 47,000 | 20.3 | 1.28 | 80.3 | 177 | 753 | 4110 | 108 | 11.5 | 337 | |
| hs12-2 | 1904 | 307 | 93.2 | 15.4 | 45,400 | 20.2 | 1.31 | 83.6 | 185 | 761 | 4360 | 117 | 12 | 357 | |
| hs03 | 1190 | 279 | 52.7 | 6.56 | 45,200 | 15.4 | 1.11 | 61.6 | 132 | 449 | 2710 | 71.6 | 7.61 | 228 | |
| hs14-4 | 1514 | 220 | 69 | 16.2 | 38,700 | 19.3 | 1.4 | 88.1 | 190 | 849 | 4120 | 110 | 9.49 | 294 | |
| hs20 | 2011 | 386 | 101 | 12 | 54,400 | 21.5 | 1.32 | 75.9 | 175 | 608 | 4540 | 115 | 10.2 | 322 | |
| hs27-03 | 1573 | 224 | 69.9 | 15.6 | 38,500 | 19.5 | 1.25 | 86.1 | 189 | 862 | 4120 | 111 | 9.91 | 325 | |
| hs02fh | 650 | 137 | 16.4 | 4.15 | 18,000 | 7.66 | 0.755 | 43.4 | 73.6 | 1046 | 1090 | 28.8 | 2.24 | 58.7 | |
| hs14-2 | 1795 | 202 | 76.9 | 19.1 | 36,600 | 18.6 | 1.27 | 79 | 185 | 926 | 4430 | 124 | 11.2 | 325 | |
| hs18-7 | 796 | 190 | 27.8 | 5.32 | 34,700 | 14 | 1.08 | 38.9 | 83.2 | 562 | 2390 | 41.5 | 5.15 | 142 | |
| hs01fh | 1614 | 232 | 73.3 | 15.7 | 38,400 | 19.2 | 1.29 | 92 | 205 | 924 | 4140 | 118 | 10.1 | 323 | |
| hs08 | 4545 | 242 | 110 | 27.4 | 41,500 | 12.8 | 0.942 | 290 | 433 | 2258 | 19,800 | 154 | 9.01 | 259 | |
| hs19 | 4064 | 650 | 201 | 23.9 | 73,400 | 31.4 | 1.49 | 126 | 300 | 1129 | 9030 | 204 | 17.7 | 586 | |
| hs06fh | 989 | 344 | 39.8 | 10.5 | 53,300 | 18 | 1.75 | 83.5 | 167 | 425 | 2300 | 76.6 | 12.2 | 356 | |
| hs27 | 965 | 322 | 46.3 | 8.8 | 58,200 | 15.5 | 1.23 | 90.2 | 168 | 385 | 3460 | 89.7 | 9.87 | 297 | |
| river sediments | nec01 | 274 | 38.7 | 11.9 | 2.52 | 4300 | 1.73 | 0.132 | 7.55 | 18.3 | 199 | 1000 | 10.8 | 1.04 | 33.9 |
| nec03gh | 354 | 72.6 | 24.9 | 4.8 | 8130 | 3.81 | 0.267 | 15.6 | 41.5 | 444 | 2490 | 23.1 | 2.6 | 87.3 | |
| nec04c | 449 | 102 | 13.2 | 2.55 | 21,800 | 7.15 | 0.63 | 24.9 | 45.5 | 351 | 860 | 19.9 | 3.32 | 105 | |
| nec11S | 429 | 103 | 12.5 | 2.34 | 22,000 | 7.26 | 0.613 | 25 | 45 | 381 | 870 | 21.3 | 3.06 | 102 | |
| nec13S | 282 | 72.8 | 7.9 | 2.95 | 15,100 | 4.1 | 0.366 | 20.9 | 41.7 | 1068 | 580 | 15.8 | 1.56 | 49.8 | |
| nec14S | 680 | 140 | 16.5 | 4.49 | 18,500 | 8.29 | 0.847 | 38.2 | 75.3 | 1091 | 1110 | 33.1 | 2.25 | 62.5 | |
| nec17S | 265 | 78.7 | 6.97 | 3.04 | 15,100 | 4.3 | 0.417 | 16.7 | 37.5 | 1051 | 560 | 14.2 | 1.57 | 48.2 | |
| μg/g | Sm | Eu | Ti | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Er | Yb | Lu | Pr | Ho | Tm | ||
| volcanic rock | hs13-2 | 43 | 6.72 | 13,200 | 25.5 | 3.14 | 11.6 | 45.1 | 4.41 | 3.31 | 0.354 | 48.3 | 1.36 | 0.386 | |
| hs18-11 | 8.76 | 1.45 | 6140 | 6.13 | 0.915 | 4.17 | 21.1 | 2.32 | 2.18 | 0.321 | 11.5 | 0.738 | 0.33 | ||
| hs11-3 | 39.2 | 5.84 | 11,600 | 24.2 | 2.92 | 10.7 | 36.6 | 4.26 | 2.71 | 0.384 | 50.5 | 1.28 | 0.422 | ||
| hs18-13 | 11.9 | 1.99 | 7480 | 7.89 | 1.17 | 5.39 | 25.5 | 2.68 | 2.34 | 0.335 | 14.9 | 0.933 | 0.36 | ||
| hs15 | 13.3 | 2.1 | 7770 | 8.74 | 1.25 | 5.67 | 28.6 | 3.02 | 2.7 | 0.427 | 15.5 | 0.976 | 0.419 | ||
| hs13-4 | 38.8 | 6.07 | 12,200 | 21.9 | 2.83 | 10.7 | 43 | 4.29 | 2.74 | 0.373 | 40.7 | 1.36 | 0.406 | ||
| hs18-9 | 10.4 | 1.79 | 6260 | 7.2 | 1 | 4.57 | 20.5 | 2.37 | 2.1 | 0.284 | 15.1 | 0.747 | 0.305 | ||
| hs06 | 11.8 | 1.42 | 6210 | 8.51 | 1.11 | 4.84 | 19.5 | 2.39 | 1.78 | 0.255 | 20.7 | 0.735 | 0.279 | ||
| hs24 | 14.1 | 2.25 | 7130 | 9.02 | 1.27 | 5.76 | 24 | 2.88 | 2.37 | 0.358 | 18.4 | 0.894 | 0.374 | ||
| hs18-3 | 7.69 | 1.3 | 5670 | 5.66 | 0.831 | 3.98 | 20 | 2.14 | 1.92 | 0.295 | 10.6 | 0.702 | 0.304 | ||
| hs01 | 20 | 3 | 8860 | 13.2 | 1.62 | 6.84 | 26.1 | 3.08 | 2.27 | 0.323 | 32.3 | 0.953 | 0.352 | ||
| hs02 | 16.5 | 2.32 | 7290 | 10.9 | 1.42 | 6.05 | 24.1 | 2.9 | 2.21 | 0.319 | 23.7 | 0.917 | 0.357 | ||
| hs22 | 19.3 | 2.98 | 7770 | 12 | 1.51 | 6.23 | 22.5 | 2.8 | 2.12 | 0.314 | 26.7 | 0.855 | 0.326 | ||
| hs12-2 | 20.8 | 3.25 | 8480 | 12.9 | 1.62 | 6.54 | 25.3 | 3.05 | 2.19 | 0.322 | 28.3 | 0.914 | 0.331 | ||
| hs03 | 13.2 | 1.94 | 6290 | 8.56 | 1.1 | 5.07 | 21 | 2.4 | 1.99 | 0.285 | 18.3 | 0.776 | 0.314 | ||
| hs14-4 | 17.5 | 2.77 | 7730 | 11.8 | 1.44 | 6.31 | 24.3 | 2.91 | 2.22 | 0.318 | 28.8 | 0.892 | 0.333 | ||
| hs20 | 21.3 | 3.27 | 7700 | 12.1 | 1.56 | 6.68 | 24.1 | 2.83 | 2.05 | 0.292 | 27.3 | 0.914 | 0.317 | ||
| hs27-03 | 18.2 | 2.76 | 7820 | 11.4 | 1.43 | 6.11 | 22.8 | 2.67 | 1.84 | 0.301 | 28.6 | 0.818 | 0.303 | ||
| hs02fh | 4.72 | 0.871 | 3190 | 3.7 | 0.482 | 2.3 | 9.37 | 1.16 | 0.963 | 0.153 | 7.84 | 0.375 | 0.157 | ||
| hs14-2 | 20.1 | 3.29 | 7610 | 12.4 | 1.52 | 6.42 | 23 | 2.89 | 1.99 | 0.261 | 29.4 | 0.839 | 0.305 | ||
| hs18-7 | 8 | 1.52 | 6370 | 5.81 | 0.86 | 4.28 | 19.5 | 2.29 | 2.07 | 0.312 | 10.7 | 0.774 | 0.329 | ||
| hs01fh | 18.5 | 2.93 | 7740 | 12.8 | 1.54 | 6.59 | 24 | 2.87 | 2.11 | 0.287 | 31.8 | 0.869 | 0.32 | ||
| hs08 | 23.9 | 3.56 | 7390 | 18.2 | 1.64 | 6.19 | 11.8 | 2.21 | 1.03 | 0.141 | 40.6 | 0.577 | 0.144 | ||
| hs19 | 41.9 | 6.44 | 10,600 | 23.6 | 2.65 | 10.1 | 28.2 | 3.67 | 2.03 | 0.263 | 44.7 | 1.06 | 0.287 | ||
| hs06fh | 11.5 | 1.66 | 6460 | 8.79 | 1.03 | 4.49 | 16.1 | 2.08 | 1.43 | 0.213 | 22.2 | 0.626 | 0.236 | ||
| hs27 | 14.7 | 1.95 | 9390 | 10.4 | 1.3 | 5.72 | 22.4 | 2.6 | 1.91 | 0.257 | 24.8 | 0.836 | 0.308 | ||
| river sediments | nec01 | 2.3 | 0.353 | 660 | 1.34 | 0.161 | 0.641 | 2.14 | 0.263 | 0.164 | 0.022 | 2.53 | 0.077 | 0.022 | |
| nec03gh | 4.29 | 0.676 | 1660 | 2.71 | 0.343 | 1.48 | 6.14 | 0.741 | 0.544 | 0.084 | 5.35 | 0.206 | 0.087 | ||
| nec04c | 3.85 | 0.737 | 2740 | 3.01 | 0.461 | 2.57 | 12.5 | 1.51 | 1.44 | 0.221 | 5.33 | 0.471 | 0.224 | ||
| nec11S | 4.05 | 0.691 | 2860 | 3.13 | 0.475 | 2.59 | 13.2 | 1.54 | 1.47 | 0.216 | 5.64 | 0.494 | 0.23 | ||
| nec13S | 2.76 | 0.392 | 1680 | 2.27 | 0.302 | 1.48 | 6.91 | 0.824 | 0.739 | 0.108 | 4.52 | 0.265 | 0.116 | ||
| nec14S | 5.31 | 0.981 | 3220 | 4.35 | 0.555 | 2.63 | 10.6 | 1.31 | 1.06 | 0.16 | 9.06 | 0.421 | 0.168 | ||
| nec17S | 2.65 | 0.456 | 1780 | 2.08 | 0.293 | 1.46 | 7.26 | 0.84 | 0.776 | 0.114 | 3.82 | 0.285 | 0.119 |
| Sample | WQI | Status | Sample | WQI | Status | Sample | WQI | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEC01 | 84.5 | good | NEC08 | 90.2 | good | NEC15 | 75.5 | fair |
| NEC02 | 86.5 | good | NEC09 | 91.1 | good | NEC18 | 88.8 | good |
| NEC03 | 91.8 | good | NEC10 | 92.4 | good | NEC19 | 89.5 | good |
| NEC04 | 90.5 | good | NEC11 | 91.5 | good | NEC20 | 89 | good |
| NEC05 | 61.3 | fair | NEC12 | 90.9 | good | NEC21 | 89.2 | good |
| NEC06 | 85.8 | good | NEC13 | 82.8 | good | NEC16 | 1.8 | very poor |
| NEC07 | 90.8 | good | NEC14 | 80.2 | good | NEC17 | 1.5 | very poor |
| Kn1 | Kn2 | Kn3 | Kn4 | Types | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEC01 | 4.50 | 4.70 | 0.22 | 4.85 | carbonate type |
| NEC02 | 6.22 | 6.58 | 0.43 | 7.48 | carbonate type |
| NEC03 | 3.99 | 4.03 | 0.06 | 4.73 | carbonate type |
| NEC04 | 3.61 | 4.21 | 0.68 | 4.12 | carbonate type |
| NEC05 | 21.21 | 22.31 | 1.15 | 22.06 | carbonate type |
| NEC06 | 8.23 | 8.80 | 0.73 | 10.45 | carbonate type |
| NEC07 | 5.07 | 5.49 | 0.52 | 6.20 | carbonate type |
| NEC08 | 6.28 | 6.72 | 0.54 | 7.85 | carbonate type |
| NEC09 | 5.08 | 5.48 | 0.50 | 6.32 | carbonate type |
| NEC10 | 3.00 | 4.23 | 1.43 | 3.46 | carbonate type |
| NEC11 | 6.34 | 6.99 | 0.85 | 8.18 | carbonate type |
| NEC12 | 6.29 | 6.65 | 0.47 | 8.31 | carbonate type |
| NEC13 | 3.36 | 4.24 | 1.03 | 3.99 | carbonate type |
| NEC14 | 3.23 | 4.18 | 1.09 | 3.71 | carbonate type |
| NEC15 | 0.54 | 1.02 | 0.52 | 0.59 | carbonate type |
| NEC16 | 0.37 | 7.19 | 85.71 | 4.63 | magnesium sulfate type |
| NEC17 | 1.82 | 9.83 | 135.85 | 30.89 | magnesium sulfate type |
| NEC18 | 5.37 | 6.49 | 1.49 | 7.15 | carbonate type |
| NEC19 | 4.92 | 5.68 | 0.99 | 6.38 | carbonate type |
| NEC20 | 4.46 | 5.31 | 1.09 | 5.74 | carbonate type |
| NEC21 | 4.34 | 5.03 | 0.89 | 5.55 | carbonate type |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Zheng, M.; Nie, Z.; Wang, K. Major Ion Characteristics Reveal How Basin Hydrogeology and Groundwater Evolution Control the Formation of Saline Water Types in Nie’er Co Terminal Lake. Minerals 2026, 16, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010034
Han J, Zheng M, Nie Z, Wang K. Major Ion Characteristics Reveal How Basin Hydrogeology and Groundwater Evolution Control the Formation of Saline Water Types in Nie’er Co Terminal Lake. Minerals. 2026; 16(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jiahuan, Mianping Zheng, Zhen Nie, and Kai Wang. 2026. "Major Ion Characteristics Reveal How Basin Hydrogeology and Groundwater Evolution Control the Formation of Saline Water Types in Nie’er Co Terminal Lake" Minerals 16, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010034
APA StyleHan, J., Zheng, M., Nie, Z., & Wang, K. (2026). Major Ion Characteristics Reveal How Basin Hydrogeology and Groundwater Evolution Control the Formation of Saline Water Types in Nie’er Co Terminal Lake. Minerals, 16(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010034