Review of Enargite Flotation—Part I: Surface Characterization and Advances in Selective Flotation
Abstract
1. Introduction
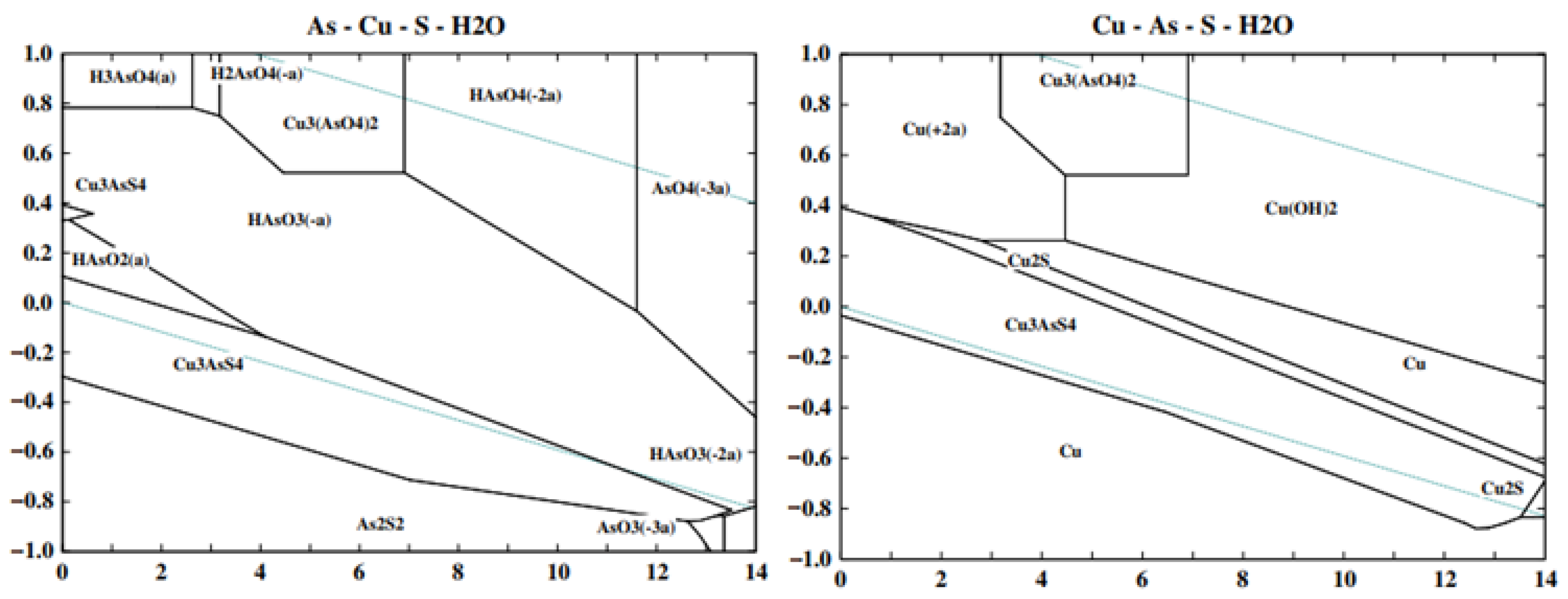
2. Surface and Electrochemical Properties of Enargite
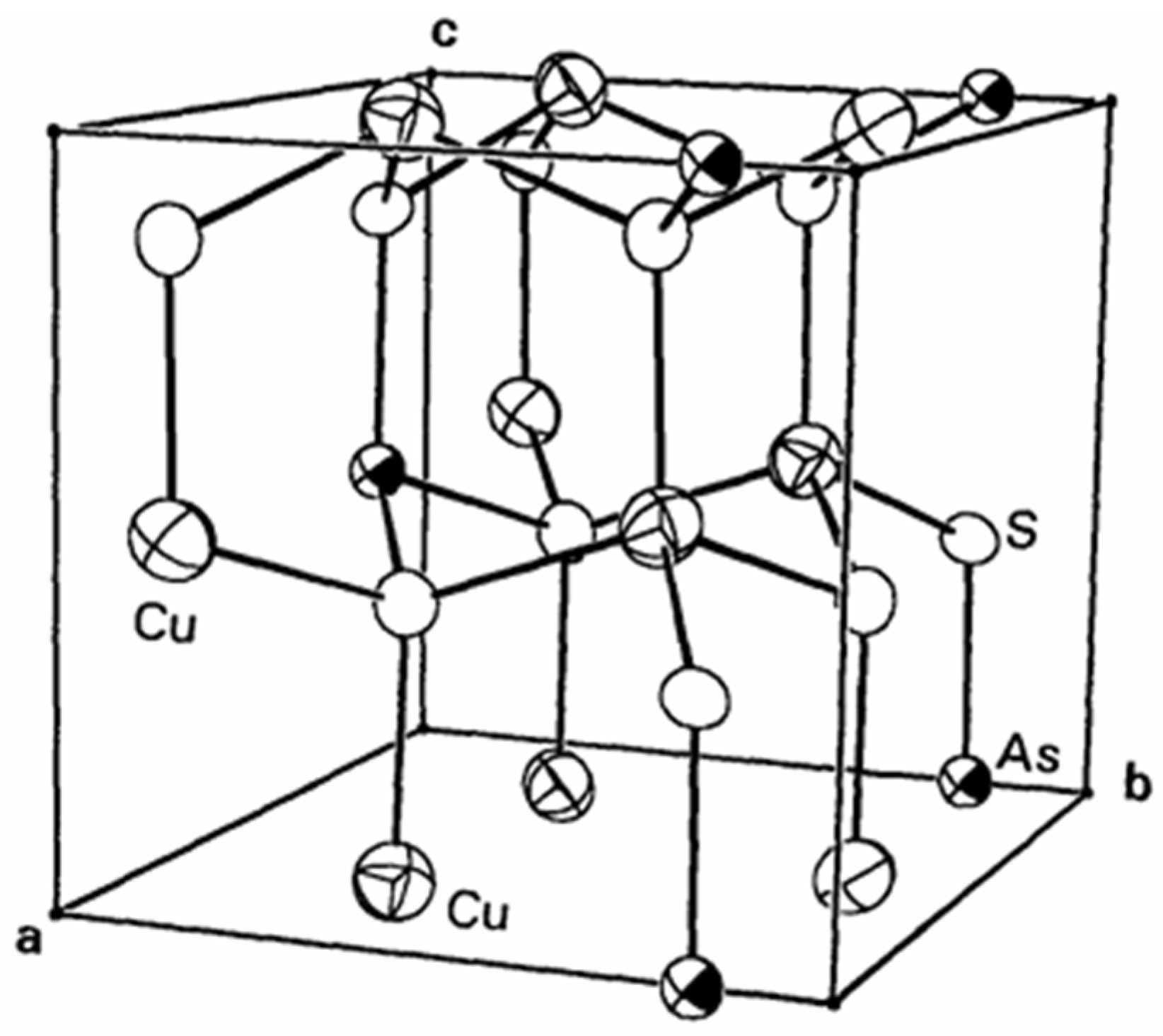
2.1. Chemical Surface Properties
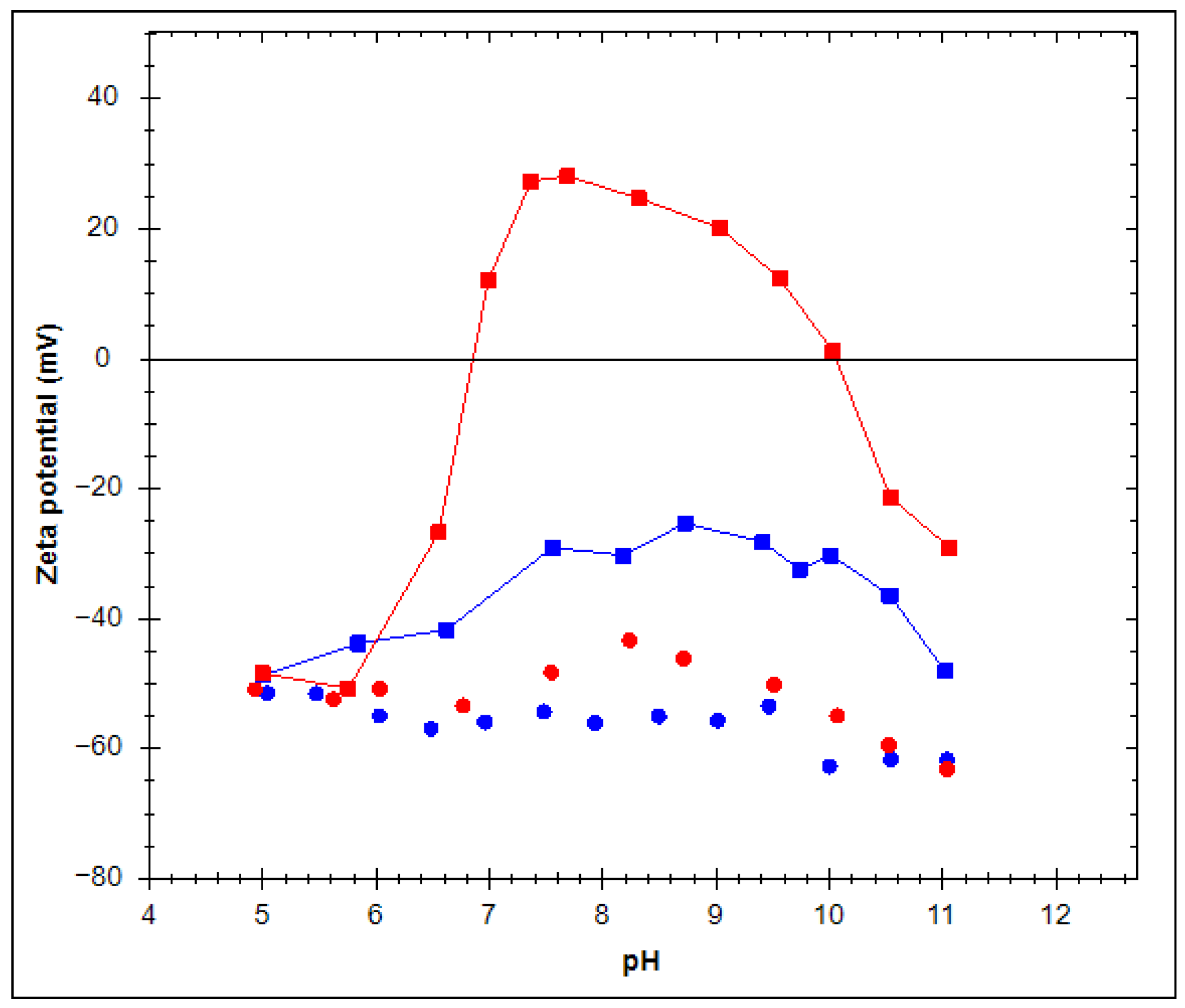
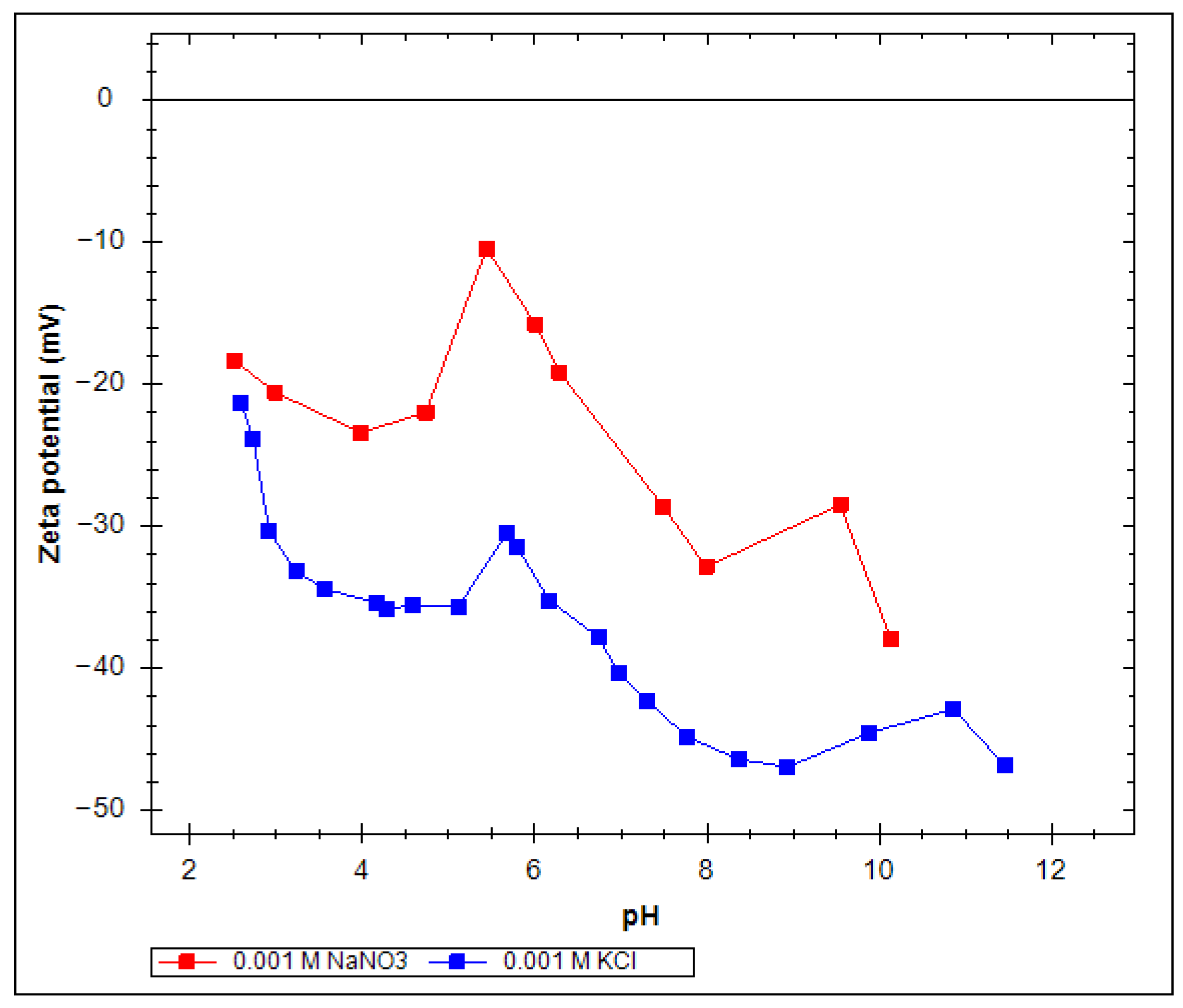
2.2. Zeta Potential
2.3. Effect of Electrochemical Potential on the Enargite Surface Properties
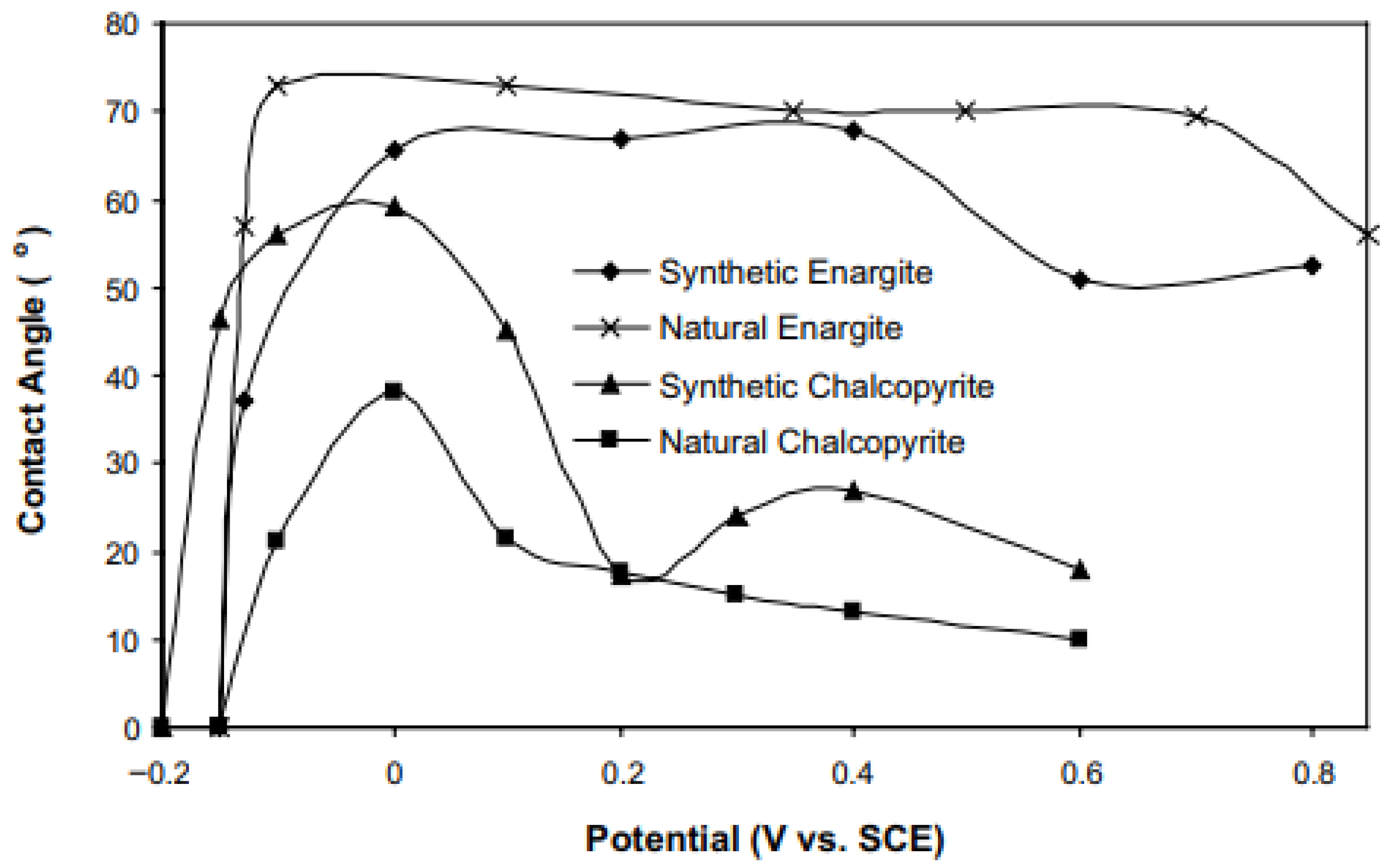
2.4. Contact Angle
3. Flotation of Enargite
3.1. Selective Flotation Reagents
3.2. Pulp Potential and pH Control
3.3. Reagents for Selective Oxidation of Enargite
3.4. Flotation of Enargite in Seawater
4. Research Opportunities
4.1. Electrochemical Effect of Pyrite
4.2. Surface Modification by Oxidation
4.3. Optimization of Selective Reagents
4.4. Ultrafine Particles
4.5. Seawater
4.6. Collector Stability in Saline Environments
4.7. Modeling
4.8. Industrial-Scale Applicability and Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, G.; Peng, Y.; Bradshaw, D. Flotation separation of copper sulphides from arsenic minerals at Rosebery copper concentrator. Miner. Eng. 2014, 66–68, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackowski, C.; Nguyen, A.V.; Bruckard, W.J. A critical review of surface properties and selective flotation of enargite in sulphide systems. Miner. Eng. 2012, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi-Khorami, M.; Manlapig, E.; Forbes, E. Relating the mineralogical characteristics of Tampakan ore to enargite separation. Minerals 2017, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Davenport, W.G. Extractive Metallurgy of Copper; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1994; p. 500. [Google Scholar]
- Córdova, R.; Gómez, H.; Real, S.G.; Schrebler, R.; Vilche, J.R. Characterization of natural enargite/aqueous solution systems by electrochemical techniques. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 2628–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, D.; Plackowski, C.; Nguyen, A.V. Surface properties of enargite in MAA depressant solutions. Miner. Eng. 2015, 71, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasiero, D.; Fullston, D.; Li, C.; Ralston, J. Separation of enargite and tennantite from non-arsenic copper sulfide minerals by selective oxidation or dissolution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2001, 61, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yen, W.-T. Selective flotation of enargite from chalcopyrite by electrochemical control. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi-Khorami, M.; Manlapig, E.; Forbes, E.; Bradshaw, D.; Edraki, M. Selective flotation of enargite from copper sulphides in Tampakan deposit. Miner. Eng. 2017, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepsen, R.; Gutierrez, L. Effect of Eh and pH on the flotation of enargite using seawater. Miner. Eng. 2020, 159, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, J.; de Delgado, G.D.; Delgado, J.; Castrillo, F.; Odreman, O. Single-crystal structure refinement of enargite [Cu3AsS4]. Mater. Res. Bull. 1994, 29, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.; Becker, U.; Wright, K. Sulphide mineral surfaces: Theory and experiment. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, K.M.; Vaughan, D.J. Sulfide mineral surfaces. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2006, 61, 505–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, K.M.; Vaughan, D.J. Reactivity of sulfide mineral surfaces. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2006, 61, 557–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Atzei, D.; Da Pelo, S.; Frau, F.; Lattanzi, P.; England, K.E.R.; Vaughan, D.J. Quantitative X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of enargite (Cu3AsS4) surface. Surf. Interface Anal. 2001, 31, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; PHI Division, Perkin Elmer Corporation: Springfield, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Stec, W.J.; Morgan, W.E.; Albridge, R.G.; Van Wazer, J.R. Measured binding energy shifts of the “3p” and “3d” electrons in arsenic compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1972, 11, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, P.; Leinen, D.; Pascual, J.; Ramos-Barrado, J.; Cordova, R.; Gómez, H.; Schrebler, R. SEM, EDX and EIS study of an electrochemically modified electrode surface of natural enargite (Cu3AsS4). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 494, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, P.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Cordova, R.; Leinen, D. XPS analysis of an electrochemically modified electrode surface of natural enargite. Surf. Interface Anal. 2000, 30, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A. Photoelectron core levels for enargite, Cu3AsS4. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, I.; Gutierrez, L.; Hernandez, V.; Diaz, E.; Ramirez, A. Hemicelluloses monosaccharides and their effect on molybdenite flotation. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, A.; Acuña, S.M.; Gutiérrez, L.; Toledo, P.G. Zeta Potential of Pyrite Particles in Concentrated Solutions of Monovalent Seawater Electrolytes and Amyl Xanthate. Minerals 2019, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullston, D.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Oxidation of synthetic and natural samples of enargite and tennantite: 1. Dissolution and zeta potential study. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.; Woods, R. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of the oxidation of chalcopyrite. Aust. J. Chem. 1984, 37, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S. Electrochemistry of sulfide flotation: Growth characteristics of surface coatings and their properties, with special reference to chalcopyrite and pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 33, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairthorne, G.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Effect of oxidation on the collectorless flotation of chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 49, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasiero, D.; Li, F.; Ralston, J. Oxidation of galena. II. Electrokinetic study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 164, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasiero, D.; Li, F.; Ralston, J.; Smart, R.S. Oxidation of galena surface I: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and dissolution kinetics studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 164, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.N.; Riley, K.W. Self-induced floatability of sulphide minerals: Examination of recent evidence for elemental sulphur as the hydrophobic entity. Surf. Interface Anal. 1991, 17, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullston, D.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Zeta potential study of the oxidation of copper sulfide minerals. Colloids Surf. A 1999, 146, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, T.W.; Moignard, M.S. A review of electrokinetic studies of metal sulfides. In Flotation—A.M. Gaudin Memorial Volume; Fuerstenau, M.C., Ed.; American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 1, pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.C.; Huang, C.P. Electrokinetic characteristics of some metal sulfide-water interfaces. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullston, D.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Oxidation of synthetic and natural samples of enargite and tennantite: 2. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4530–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, R.; Gomez, H.; Schrebler, R.; Real, S.G.; Vilche, J.R. An electrochemical study of enargite in aqueous solutions by transient techniques. In Proceedings—Electrochemical Society: 96–6 (Electrochemistry in Mineral and Metal Processing); The Electrochemical Society: Pennington, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 356–367. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, S.H.; Honores, S. Surface properties and floatability of enargite. In Proceedings of the XXI International Mineral Processing Conference, Rome, Italy, 23–27 July 2000; Massacci, P., Ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Rome, Italy, 2000; pp. B8b-47–B8b-53. [Google Scholar]
- Schwedt, G.; Rieckhoff, M. Separation of thio- and oxothioarsenates by capillary zone electrophoresis and ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 736, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackowski, C.; Hampton, M.A.; Bruckard, W.J.; Nguyen, A.V. An XPS investigation of surface species formed by electrochemically induced surface oxidation of enargite in the oxidative potential range. Miner. Eng. 2014, 55, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Baltierra, L. Study of the surface properties of enargite as a function of pH. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 77, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackowski, C.; Bruckard, W.J.; Nguyen, A.V. Surface characterisation, collector adsorption and flotation response of enargite in a redox potential controlled environment. Miner. Eng. 2014, 65, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauporté, T.; Schuhmann, D. An electrochemical study of natural enargite under conditions relating to those used in flotation of sulphide minerals. Colloids Surf. A 1996, 111, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Skinner, W.; Chen, M. Electrochemical and spectroscopic analysis of enargite (Cu3AsS4) dissolution mechanism in sulfuric acid solution. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ásbjörnsson, J.; Kelsall, G.H.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Vaughan, D.J.; Wincott, P.L.; Hope, G.A. Electrochemical and surface analytical studies of enargite in acid solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, E250–E256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yen, W.T. Electrochemical study of synthetic and natural enargites. In Proceedings of the 24th International Mineral Processing Congress, Beijing, China, 24–28 September 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1138–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzi, P.; Da Pelo, S.; Musu, E.; Atzei, D.; Elsener, B.; Fantauzzi, M.; Rossi, A. Enargite oxidation: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 86, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Takatsugi, K.; Ishikura, K.; Hirajima, T. Spectroscopic study on oxidative dissolution of chalcopyrite, enargite and tennantite at different pH values. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 100, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welham, N. Mechanochemical processing of enargite (Cu3AsS4). Hydrometallurgy 2001, 62, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plackowski, C.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Bruckard, W.J. Fundamental studies of electrochemically controlled surface oxidation and hydrophobicity of natural enargite. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2371–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Garnica, R.; Castillo-Magallanes, N.; Rodríguez, I.; Cruz, R.; Lázaro, I. Electrochemical study of enargite within the mixed potential zone attained with different oxidizing reagents in an alkaline medium. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 425, 140719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, R.N.; Young, C.; Huang, H.; Hope, G. Spectroelectrochemistry of enargite III: Alkaline sulfide leaching. Min. Met. Explor. 2015, 32, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yen, W.-T. Surface potential and wettability of enargite in potassium amyl xanthate solution. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.H.; Yen, W.-T. Electrochemical investigation on wettability of enargite. In Proceedings of the Interactions in Mineral Processing the Fourth UBC-McGill International Symposium on Fundamentals of Mineral Processing as held at the 40th Annual Conference of Metallurgists of CIM(COM 2001), Toronto, ON, Canada, 26–29 August 2001; pp. 325–336. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Deng, R.; Liu, Q. Flotation separation of covellite and enargite via oxidation treatment. Minerals 2022, 12, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.T.; Bruckard, W.J.; Koh, P.T.L.; Nguyen, A.V. A review of factors that affect contact angle and implications for flotation practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 150, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Koch, K. Micro-, nano- and hierarchical structures for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and low adhesion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 1631–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Bruckard, W. Rejection of arsenic minerals in sulfide flotation—A literature review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajadod, J.; Yen, W.T. Arsenic content reduction in copper concentrates. In Proceedings of the 2nd UBC-McGill Bi-Annual International Symposium on Fundamental Mineral Processing: Processing of Complex Ores, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 17–19 August 1997; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, T.; Itoh, C.T.; Tozawa, K. Stabilities and solubilities of metal arsenites and arsenates in water and effect of sulfate and carbonate ions on their solubilities. In Arsenic Metallurgy Fundamentals and Application; Reddy, R.G., Hendrix, J.L., Queneau, P.B., Eds.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1988; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, W.T.; Tajadod, J. Selective flotation of enargite and chalcopyrite. In Proceedings of the XXI International Mineral Processing Conference, Rome, Italy, 23–27 July 2000; Volume B, pp. B8a-49–B8a-55. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, S.H.; Baltierra, L.; Muñoz, P. Depression of enargite by magnesium-ammonium mixtures. In Proceedings of the Copper 2003–Cobre 2003, the 5th International Conference, Santiago, Chile, 30 November–3 December 2003; Volume III, pp. 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Garritsen, J.; Wells, P.F.; Xu, M. Arsenic rejection in the flotation of Garson Ni–Cu ore. In Proceedings of the Centenary of Flotation Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 5–9 June 2005; pp. 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Tapley, B.; Yan, D. The selective flotation of arsenopyrite from pyrite. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajadod, J.; Yen, W.T. A comparison of surface properties and flotation characteristics of enargite and chalcopyrite. In Proceedings of the XX International Mineral Processing Congress, Aachen, Germany, 21–26 September 1997; Volume 3, pp. 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Tajadod, J. A laboratory study of removing arsenic from a synthetic copper concentrate. Int. J. Eng. 2000, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Suyantara, G.P.W.; Hirajima, T.; Miki, H.; Sasaki, K.; Kuroiwa, S.; Aoki, Y. Effect of Na2SO3 on the floatability of chalcopyrite and enargite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 173, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyantara, G.P.W.; Hirajima, T.; Miki, H.; Sasaki, K.; Kuroiwa, S.; Aoki, Y. Effect of H2O2 and potassium amyl xanthate on separation of enargite and tennantite from chalcopyrite and bornite using flotation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 152, 106371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Liu, Q.; Deng, R. Calcium lignosulfonate as a depressant for enhancing flotation separation of covellite and enargite. Min. Met. Explor. 2024, 41, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Qiu, G.H.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, D.Z. Recent development in researches of electrochemistry of sulfide flotation at Central South University of Technology. Trans. Met. Soc. China 2000, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kantar, C. Solution and flotation chemistry of enargite. Colloids Surf. A 2002, 210, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, G.H.; Yoon, R.-H. The collectorless flotation of chalcopyrite ores using sodium sulfide. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1984, 13, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Chander, S. Oxidation and wetting behavior of chalcopyrite in the absence and presence of xanthates. Min. Met. Explor. 1990, 7, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.Q.; Qiu, G.Z.; Xu, J. Electrodeposition of dixanthogen on surface of pyrrhotite electrode. Trans. Met. Soc. China 2000, 10, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.R.; Finch, J.A. Galvanic interactions studies on sulfide minerals. Can. Met. Q. 1988, 27, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trahar, W.; Senior, G.; Shannon, L. Interactions between sulfide minerals—The collectorless flotation of pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1994, 40, 287–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yen, W.T. Electrochemical floatability of enargite and effects of depressants. In Proceedings of the XXIII International Mineral Processing Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–8 September 2006; pp. 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, G.; Guy, P.; Bruckard, W. The selective flotation of enargite from other copper minerals—A single mineral study in relation to beneficiation of the Tampakan deposit in the Philippines. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckard, W.; Kyriakidis, I.; Woodcock, J. The flotation of metallic arsenic as a function of pH and pulp potential—A single mineral study. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckard, W.; Davey, K.; Jorgensen, F.; Wright, S.; Brew, D.; Haque, N.; Vance, E. Development and evaluation of an early removal process for the beneficiation of arsenic-bearing copper ores. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.K.; Heyes, G.W. The effect of water quality on the collectorless flotation of chalcopyrite and bornite. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Water Management in the Mining Industry, Santiago, Chile, 6–8 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.; Bruckard, W. The separation of arsenic from copper in a Northparkes copper–gold ore using controlled-potential flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, R.; Gathje, J. The metallurgical development of an enargite-bearing deposit. In Proceedings of the XXV International Mineral Processing Congress (IMPC), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 6–10 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, K. Laboratory flotation testing—An essential tool for ore characterisation. In Flotation Plant Optimisation: A Metallurgical Guide to Identifying and Solving Problems in Flotation Plants; Greet, C.J., Ed.; Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, VIC, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tayebi-Khorami, M.; Manlapig, E.; Forbes, E.; Edraki, M.; Bradshaw, D. Effect of surface oxidation on the flotation response of enargite in a complex ore system. Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Noaparast, M.; Karamoozian, M.; Ibric, S. Galvanic interaction between chalcopyrite and pyrite with low alloy and high carbon chromium steel ball. J. Chem. 2013, 817218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekçi, Z.; Demirel, H. Effects of galvanic interaction on collectorless flotation behaviour of chalcopyrite and pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 52, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Grano, S. Galvanic interaction of grinding media with pyrite and its effect on flotation. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Rao, S.; Finch, J.; Leroux, M. Complex sulphide ore processing with pyrite flotation by nitrogen. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1989, 26, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Grano, S.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Control of grinding conditions in the flotation of chalcopyrite and its separation from pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2003, 69, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabieh, A.; Albijanic, B.; Eksteen, J. A review of the effects of grinding media and chemical conditions on the flotation of pyrite in refractory gold operations. Miner. Eng. 2016, 94, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, D.; Buswell, A.; Harris, P.; Ekmekci, Z. Interactive effects of the type of milling media and copper sulphate addition on the flotation performance of sulphide minerals from Merensky ore Part I: Pulp chemistry. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 78, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, S.; Greet, C.; Bastin, D. Oxidative weathering of a copper sulphide ore and its influence on pulp chemistry and flotation. Miner. Eng. 2016, 99, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Bradshaw, D. The separation of chalcopyrite and chalcocite from pyrite in cleaner flotation after regrinding. Miner. Eng. 2014, 58, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Iwasaki, I. Pulp potential and its implications to sulphide flotation. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 1992, 11, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, D. Electrochemistry of Flotation of Sulphide Minerals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.R.; Labonte, G.; Finch, I.A. Electrochemistry in the plant. In Innovations in Flotation Technology; Marvos, P., Matis, K.A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Grano, S.; Lauder, D.; Johnson, N.; Ralston, J. An investigation of galena recovery problems in the Hilton concentrator of Mount Isa Mines Limited, Australia. Miner. Eng. 1997, 10, 1139–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greet, C.J. The significance of grinding environment on the flotation of UG2 ores. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2009, 109, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Grano, S.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Control of grinding conditions in the flotation of galena and its separation from pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2003, 70, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumball, J.; Richmond, G. Measurement of oxidation in a base metal flotation circuit by selective leaching with EDTA. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, G.; Trahar, W. The influence of metal hydroxides and collector on the flotation of chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 33, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R. Surface layers in base metal sulphide flotation. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, R.O.; Cyprus Mineral Company. Method for Achieving Enhanced Copper-Containing Mineral Concentrate Grade by Oxidation and Flotation. US Patent 5,295,585, 22 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Marasinghe, B.; Koleini, S.M. Separation of arsenic from mining and metallurgical wastes. In Proceedings of the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy Student Conference, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 28–29 April 1994; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W. Flotation separation of enargite from complex copper concentrates by selective surface oxidation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, H.T.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K.; Okamoto, H. Effects of sodium thiosulphate on chalcopyrite and tennantite: An insight for alternative separation technique. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2012, 102–103, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
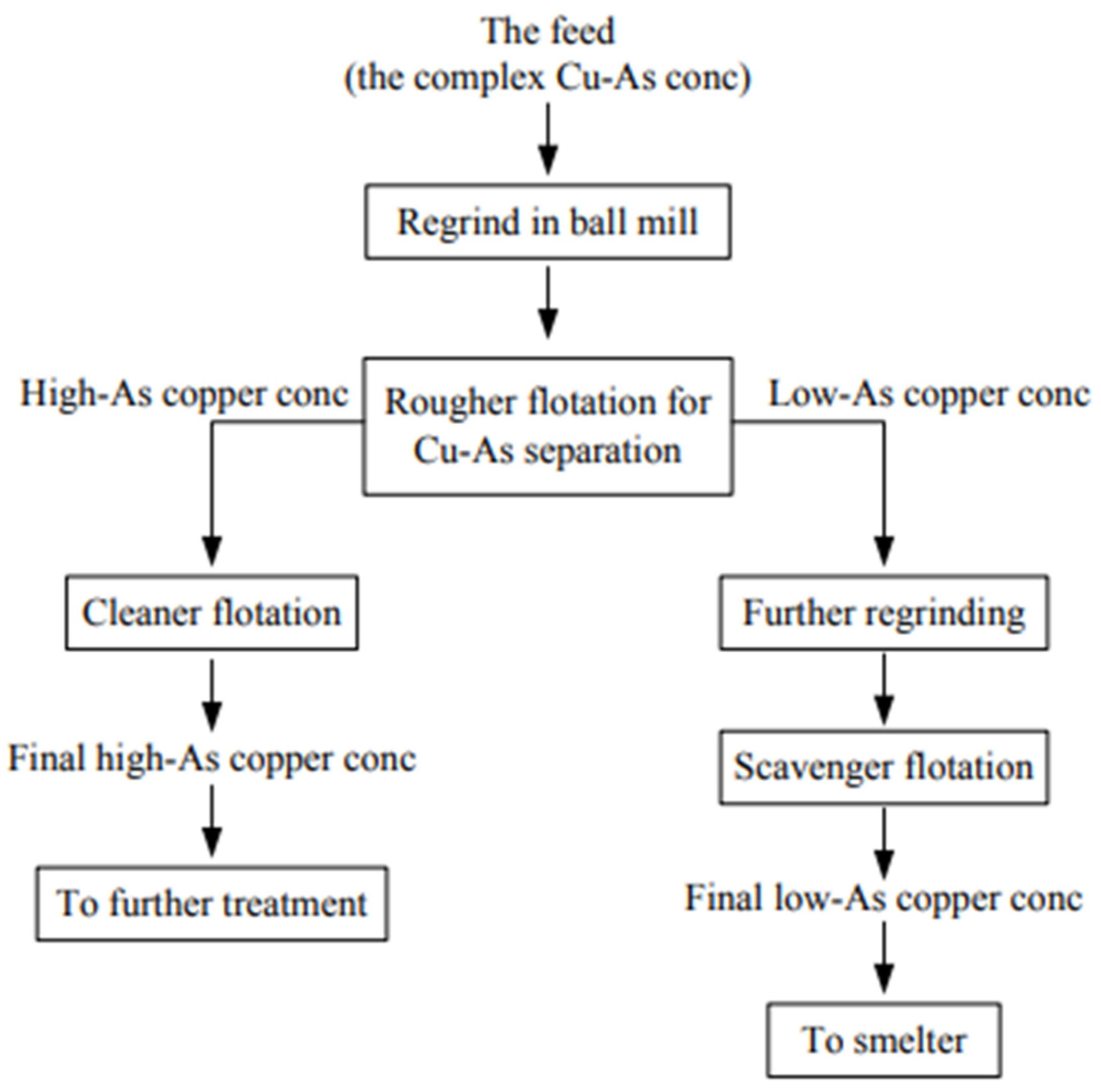
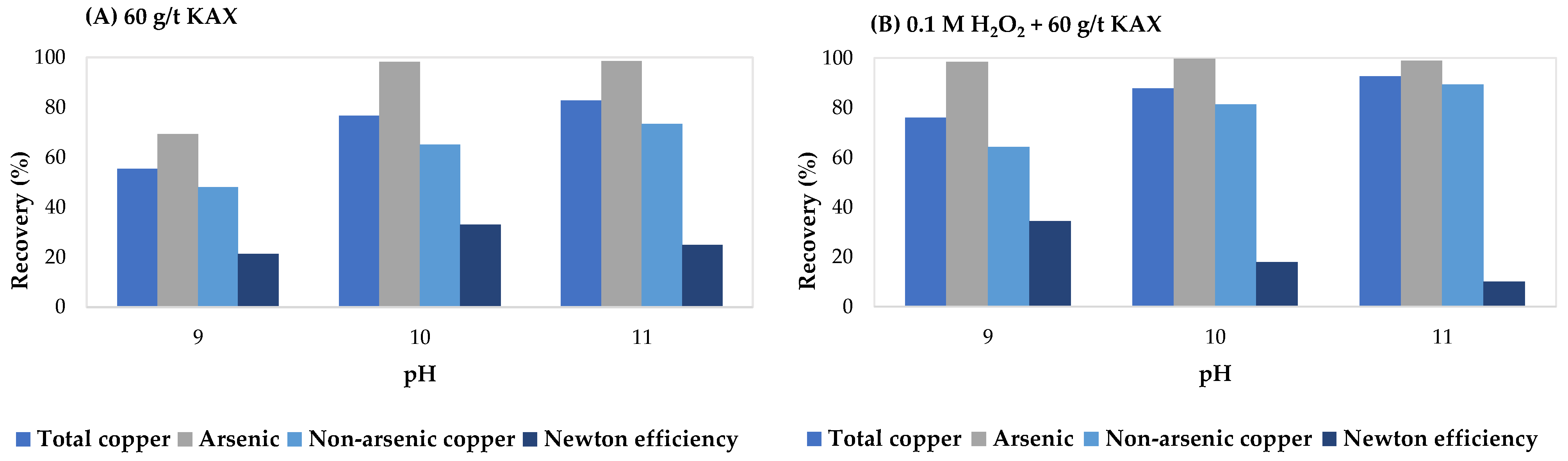
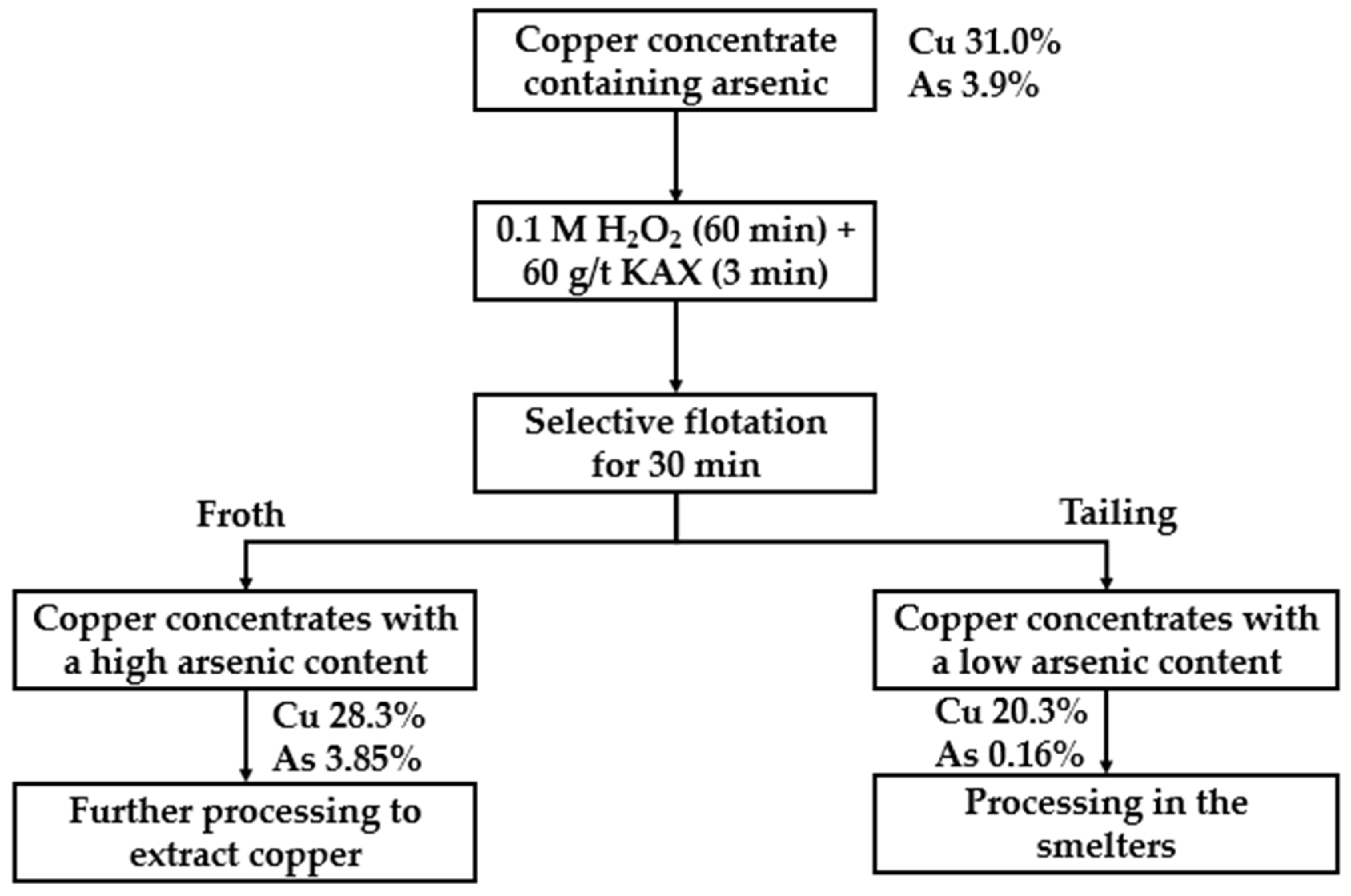
- Suyantara, G.P.W.; Miki, H.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ochi, D.; Aoki, Y. Selective flotation of copper concentrates containing arsenic minerals using potassium amyl xanthate and oxidation treatment. Mater. Trans. 2024, 65, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyantara, G.P.W.; Berdakh, D.; Miki, H.; Hirajima, T.; Sasaki, K.; Ochi, D.; Aoki, Y. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on selective flotation of chalcocite and enargite. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Laskowski, J.S. Froth flotation in saline water. KONA Powder Part. J. 2011, 29, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Uribe, L.; Laskowski, J.S. Depression of inherently hydrophobic minerals by hydrolysable metal cations: Molybdenite depression in seawater. In Proceedings of the 27th International Mineral Processing Congress (IMPC), Santiago, Chile, 20–24 October 2014; pp. 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Rebolledo, E.; Laskowski, J.S.; Gutierrez, L.; Castro, S. Use of dispersants in flotation of molybdenite in seawater. Miner. Eng. 2017, 100, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepsen, R.; Gutierrez, L.; Laskowski, J. Flotation behavior of enargite in the process of flotation using seawater. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
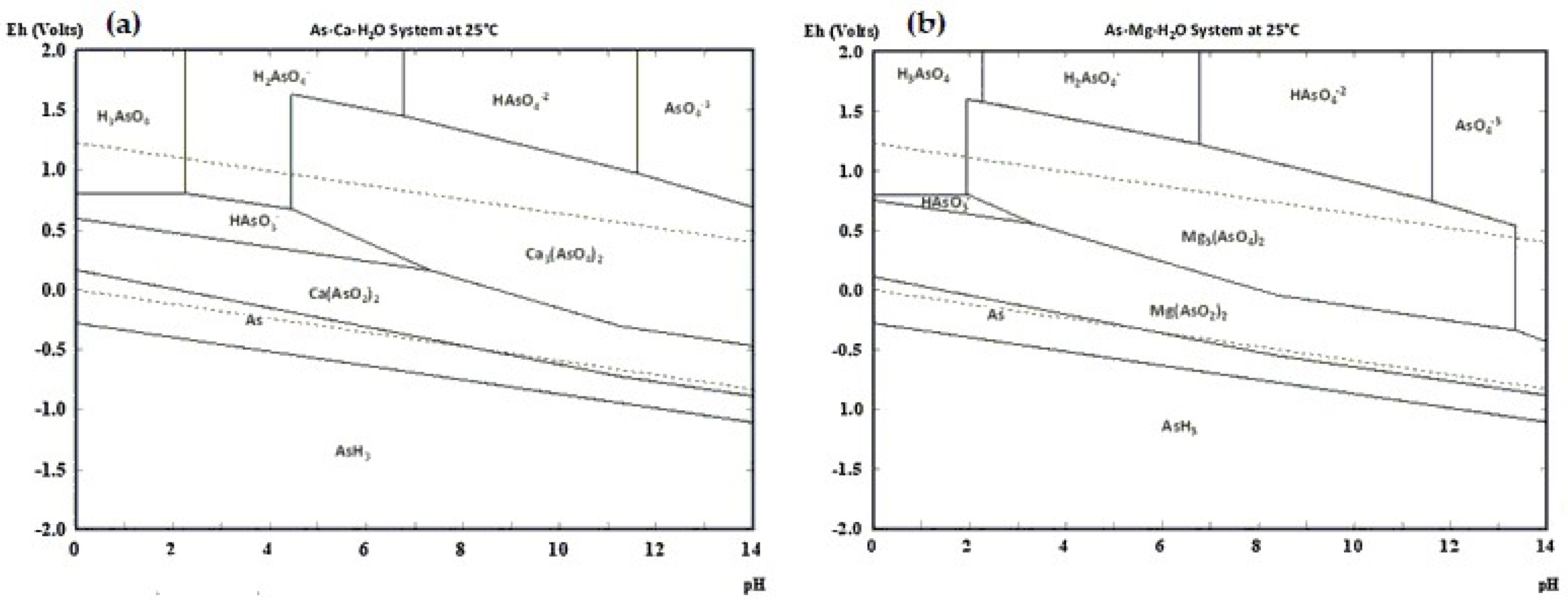
- Raposo, J.C.; Zuloaga, O.; Olazabal, M.A.; Madariaga, J.M. Study of the precipitation equilibria of arsenate anion with calcium and magnesium in sodium perchlorate at 25 °C. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Somasundaran, P. Reversal of bubble charge in multivalent inorganic salt solutions—Effect of magnesium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 146, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila-Pulido, G.; Uribe-Salas, A.; Álvarez-Silva, M.; López-Saucedo, F. The role of calcium in xanthate adsorption onto sphalerite. Miner. Eng. 2015, 71, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigauke, T.; Johnson, O.T.; Ndeshimona, V.L.; Mashingaidze, M.M. Advancements in nanotechnology for the enhanced flotation of fine mineral particles: A review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Q. Hydrodynamics of froth flotation and its effects on fine and ultrafine mineral particle flotation: A literature review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 173, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

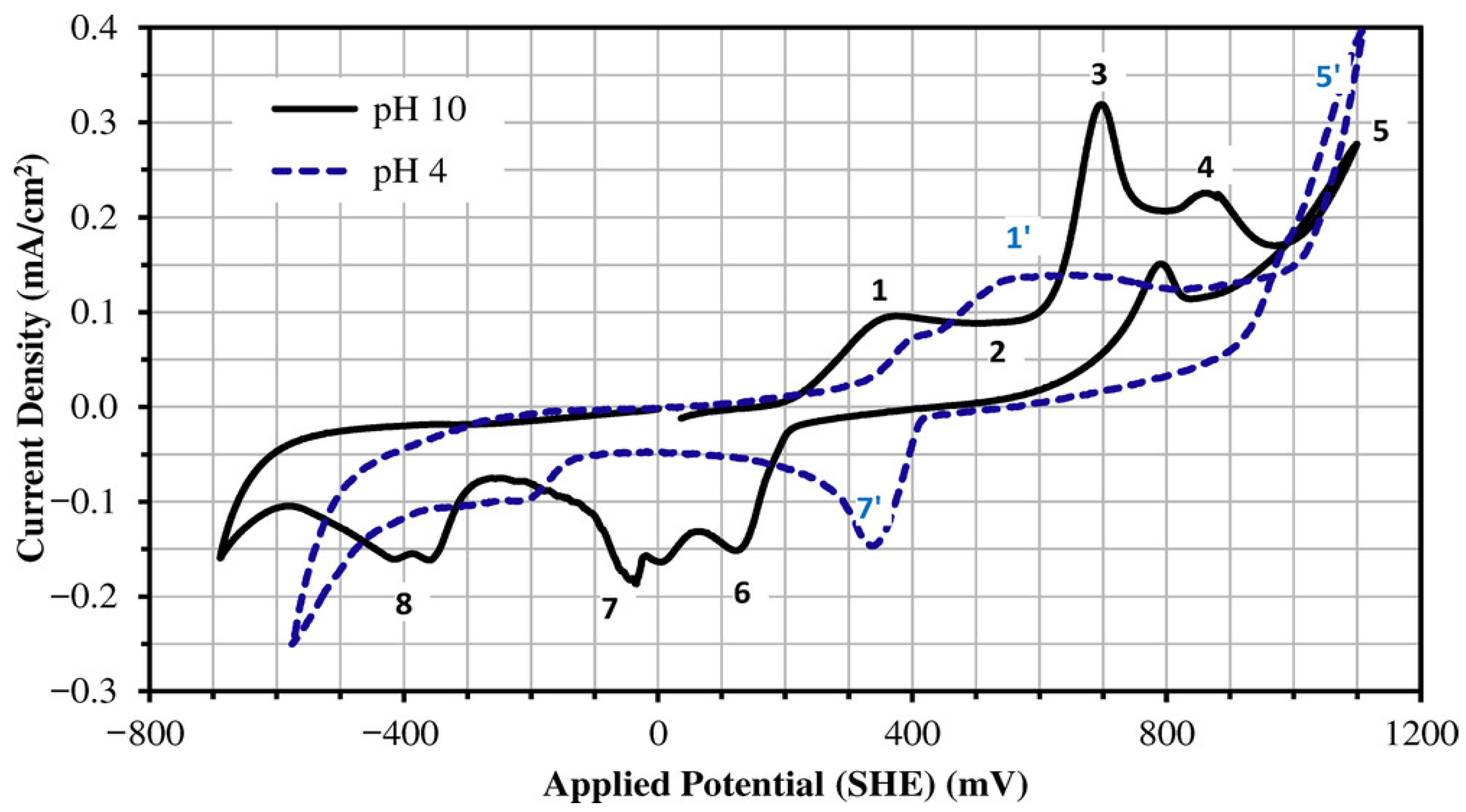
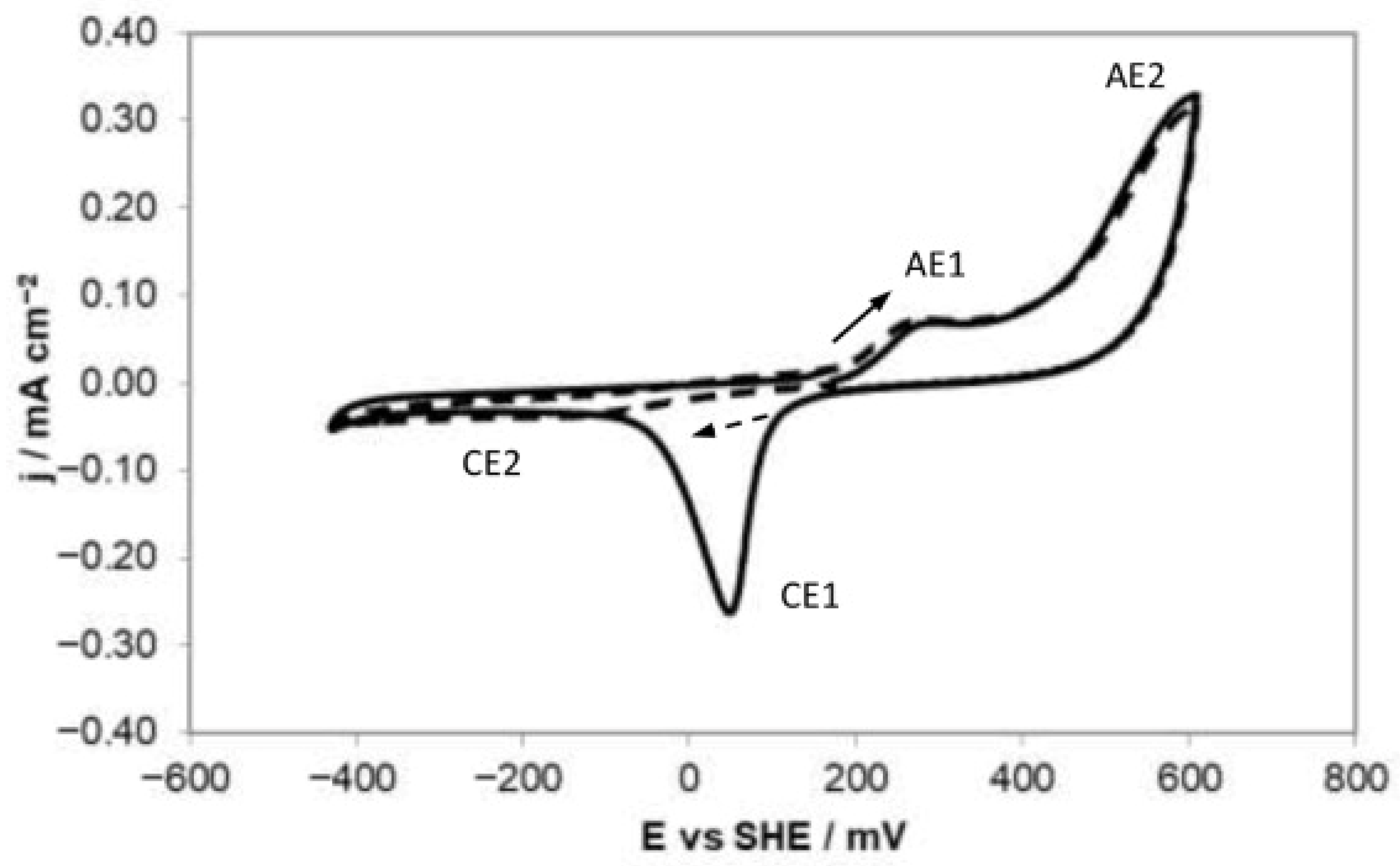
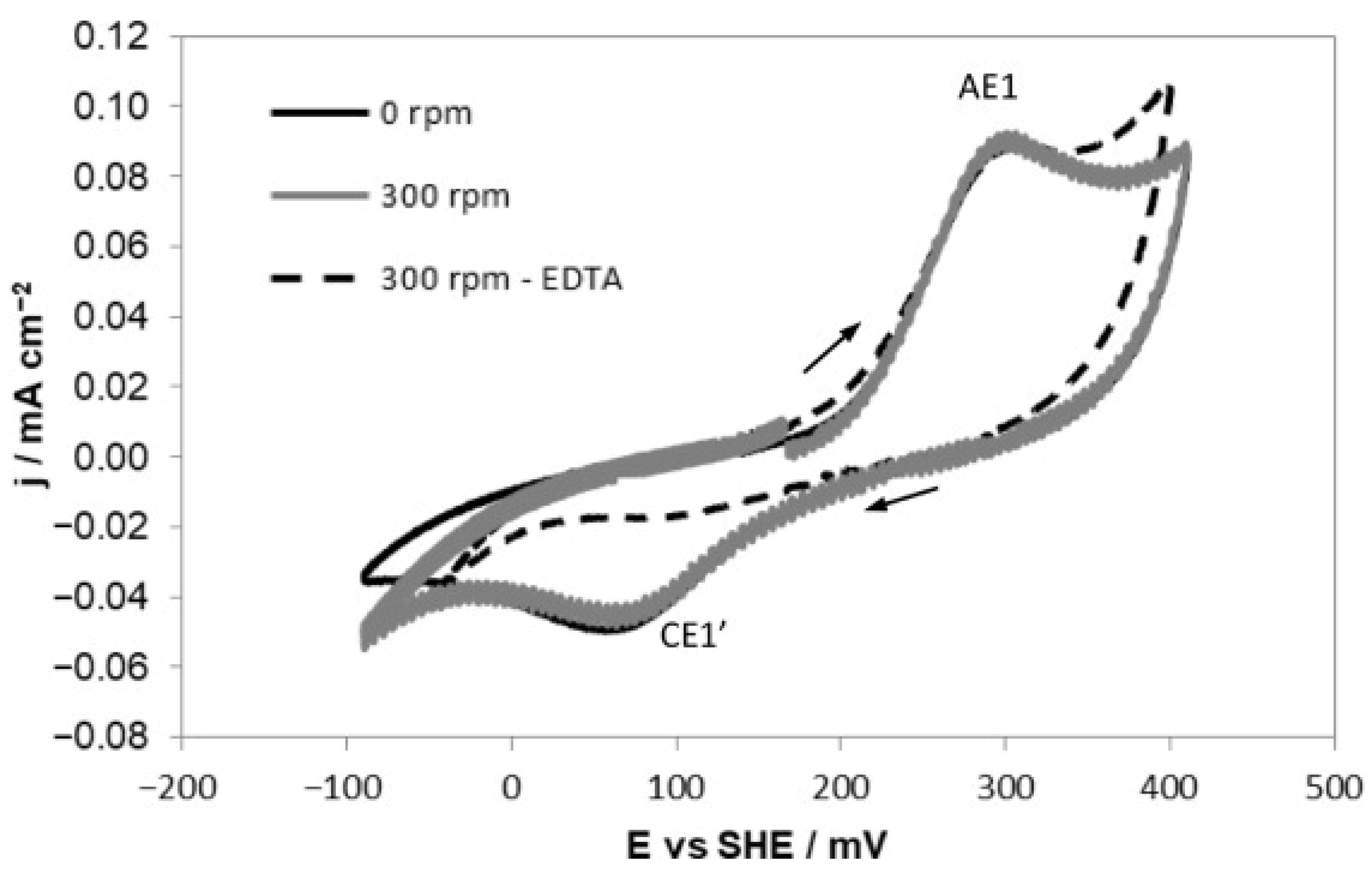
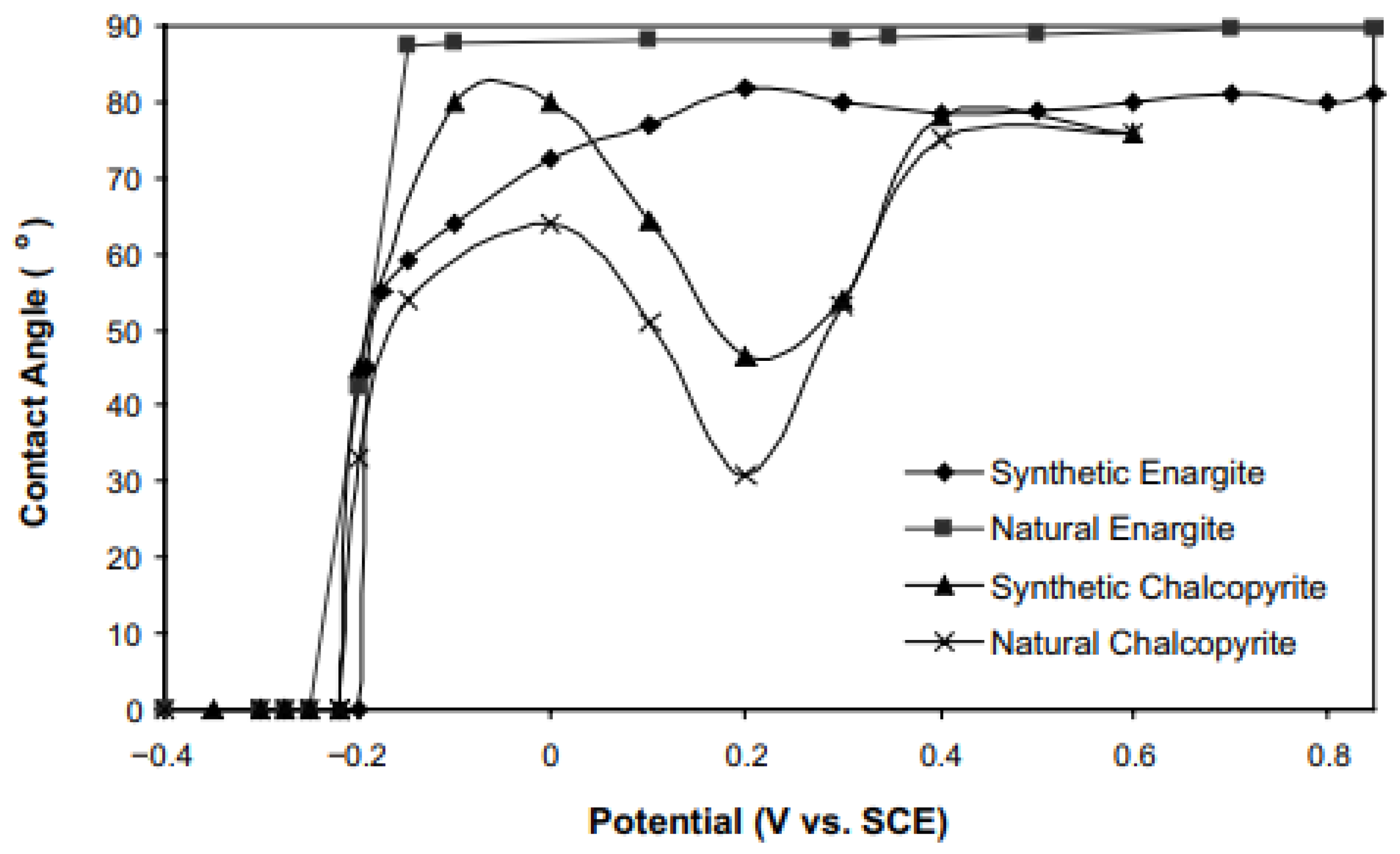






| Source | Reagents | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|
| [62] | NaCN, KMnO4 | NaCN and KMnO4 depress enargite and chalcopyrite but cause significant copper losses (45%). |
| [56] | Na2S, MAA | MAA allows the separation of 50% of the arsenic without affecting the buoyancy of the chalcopyrite. |
| [63] | NaCN, KMnO4, Na2S | NaCN achieved the best Cu-As separation with 55.2% Cu recovery and minimal As content. KMnO4 and Na2S were less effective. |
| [58] | MAA | MAA reduces xanthate adsorption on enargite without affecting chalcopyrite. Pre-aeration improves selective flotation. |
| [59] | MAA | At pH 10.0 with 2.5 kg/t MAA, 55% recovery is obtained. Higher doses reduce the depressive effect of MAA. |
| [6] | MAA | The formation of MgNH4AsO4-6H2O was not observed. In addition, Mg has no passivating effect under alkaline conditions. |
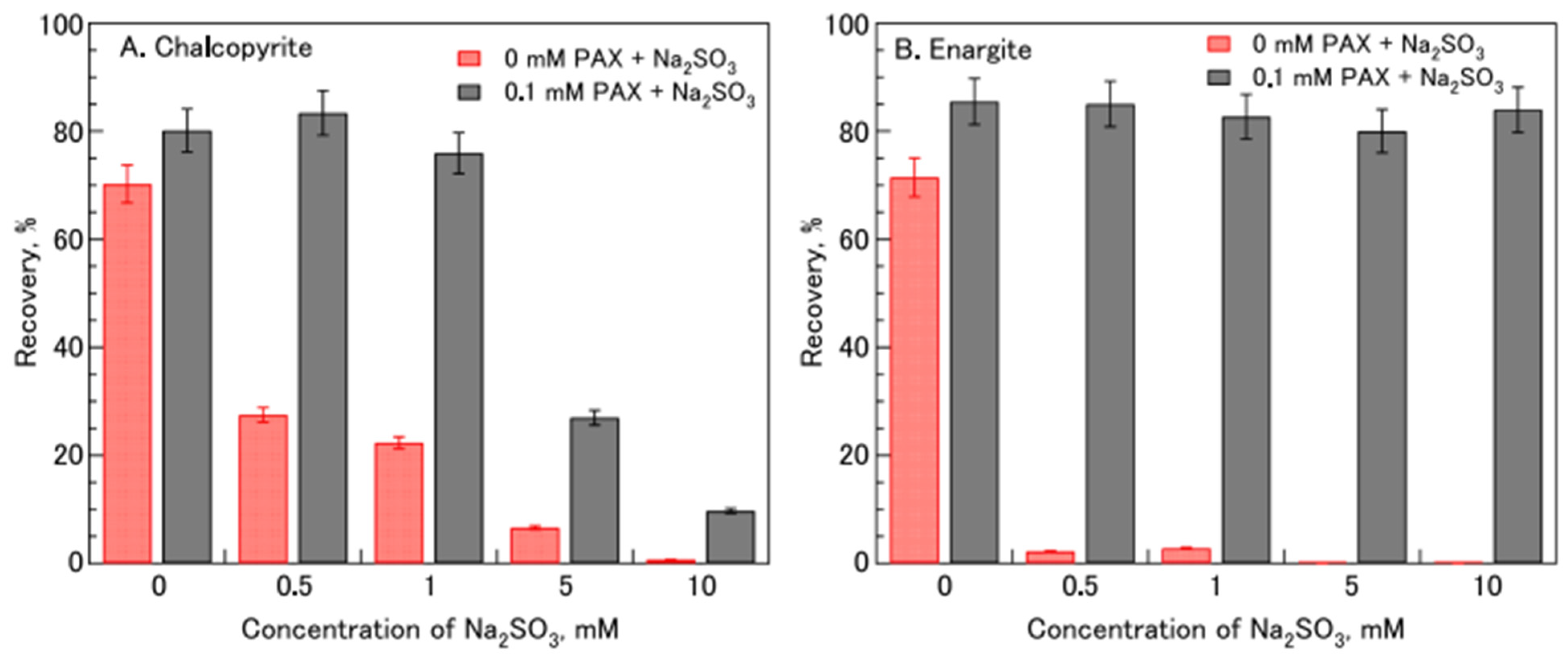
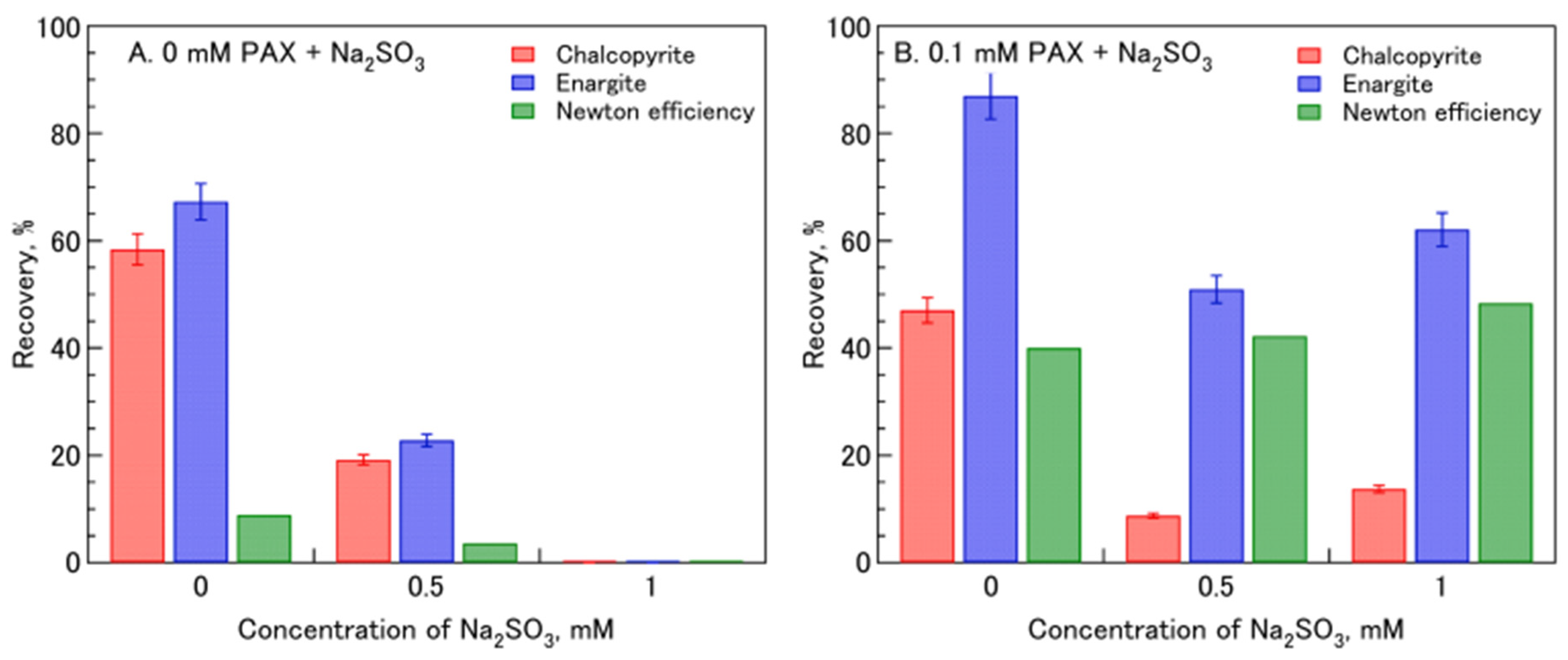
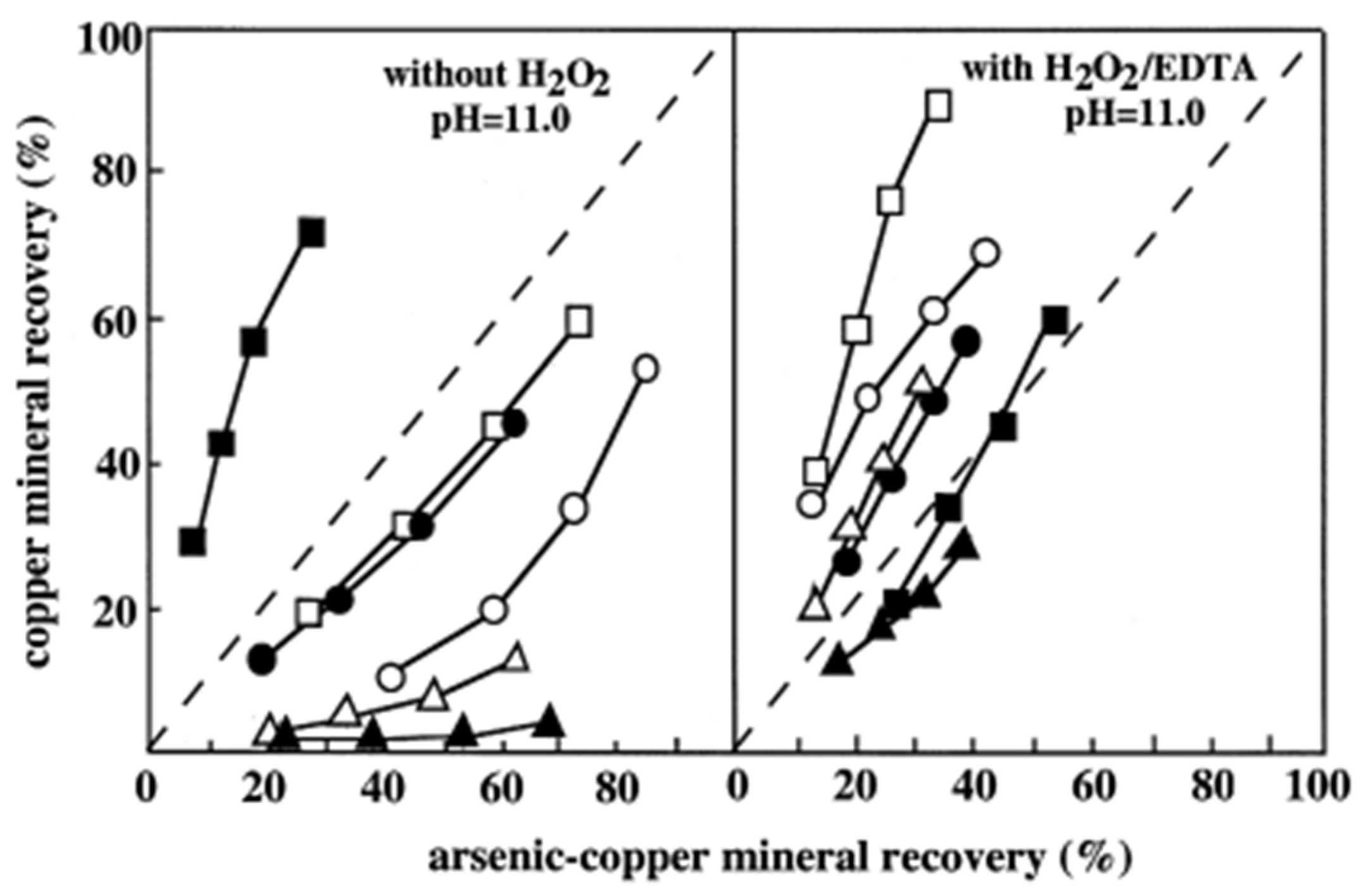
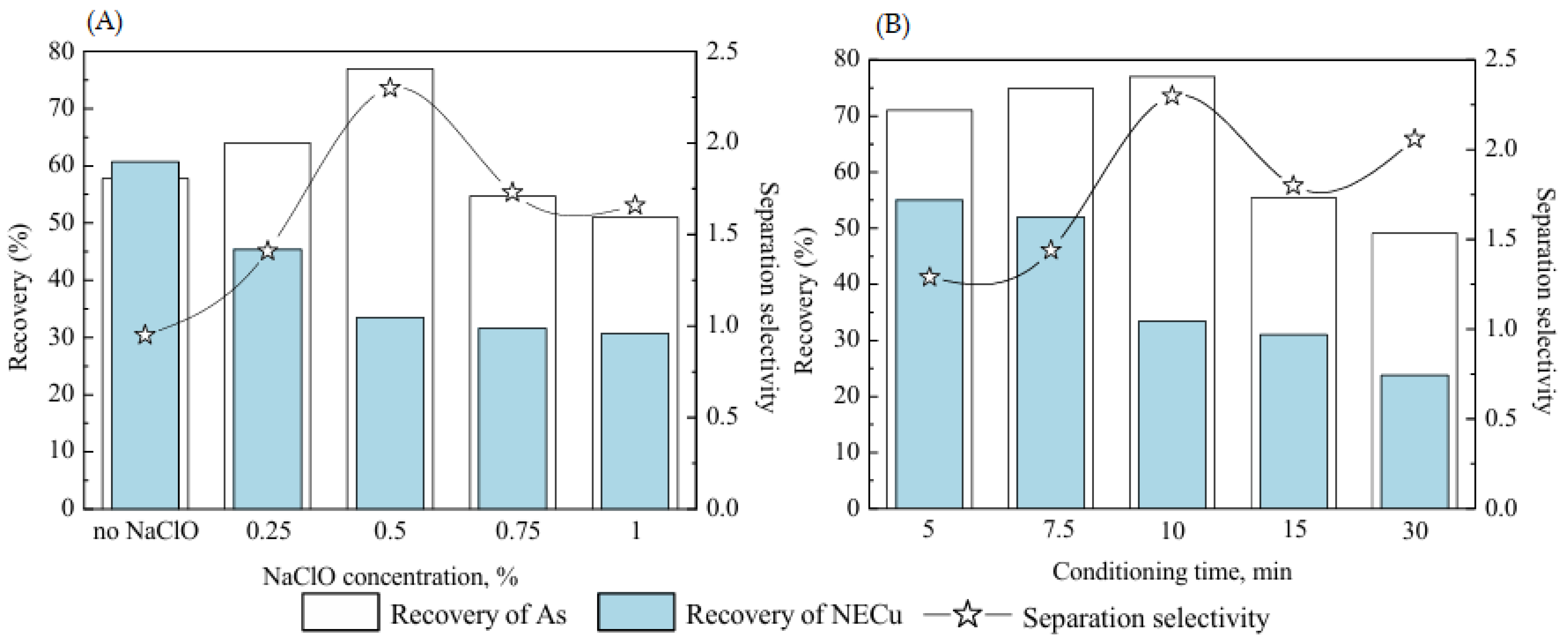
| [64] | Na2SO3, PAX | Na2SO3 enhances the selective flotation of enargite in the presence of PAX, while depressing chalcopyrite in mixed systems. |
| [66] | Ca-lignosulfonate, CaO, activated carbon | Differential adsorption of Ca-lignosulfonate on enargite surfaces selectively depresses enargite over covellite. Bench-scale tests combining reagent removal with activated carbon, pH adjustment using CaO, and Ca-lignosulfonate depression produced low-As copper concentrates (As 0.57%) and arsenic-rich fractions. |
| Source | Research Objectives | Main Results |
|---|---|---|
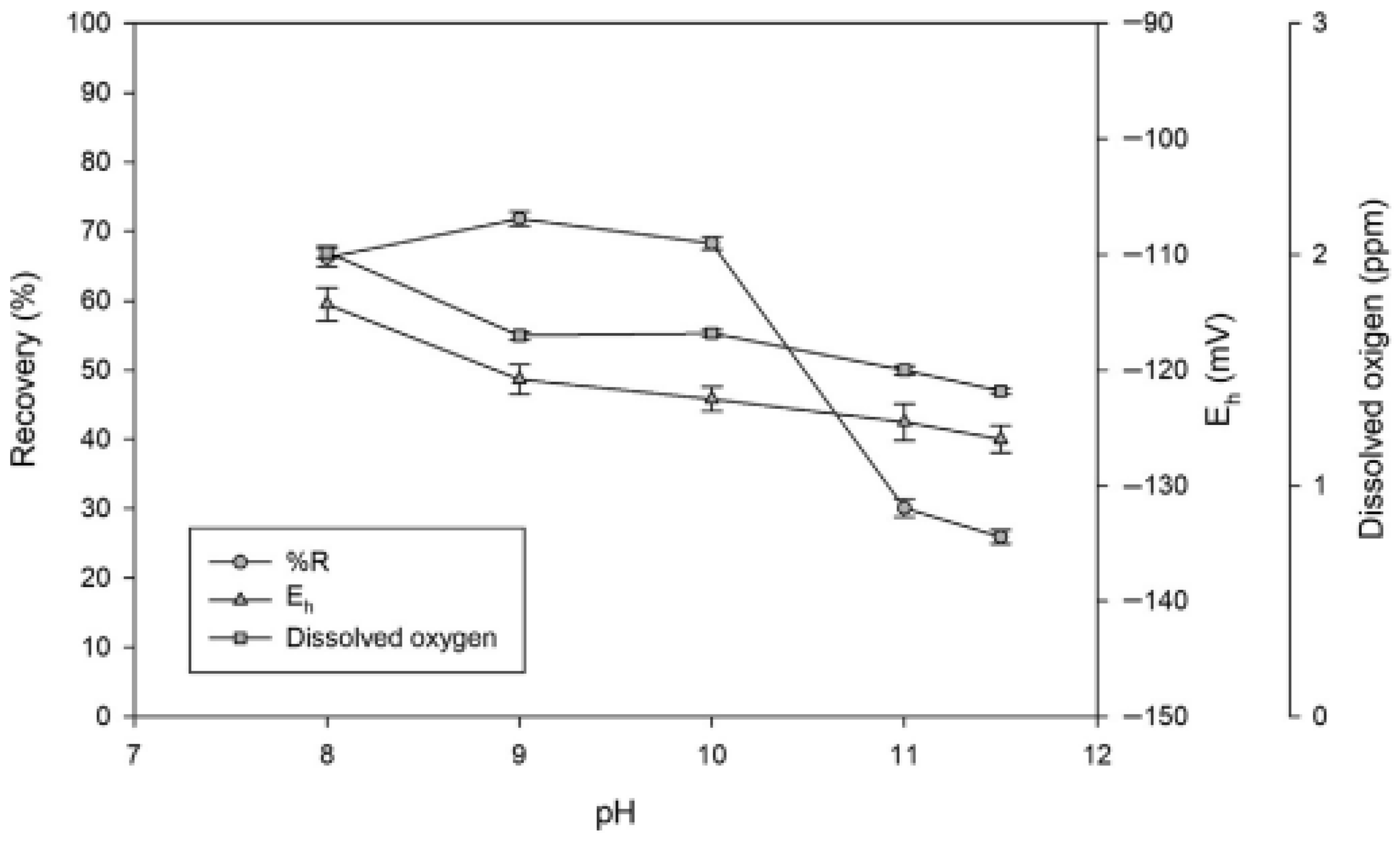
| [68] | Evaluate the floatability of enargite as a function of pulp potential using hydrogen peroxide and sodium sulfide. | Enargite floats without a collector under oxidizing conditions and it is depressed under reducing conditions. Maximum recovery occurs between 150 and 270 mV/SHE. |
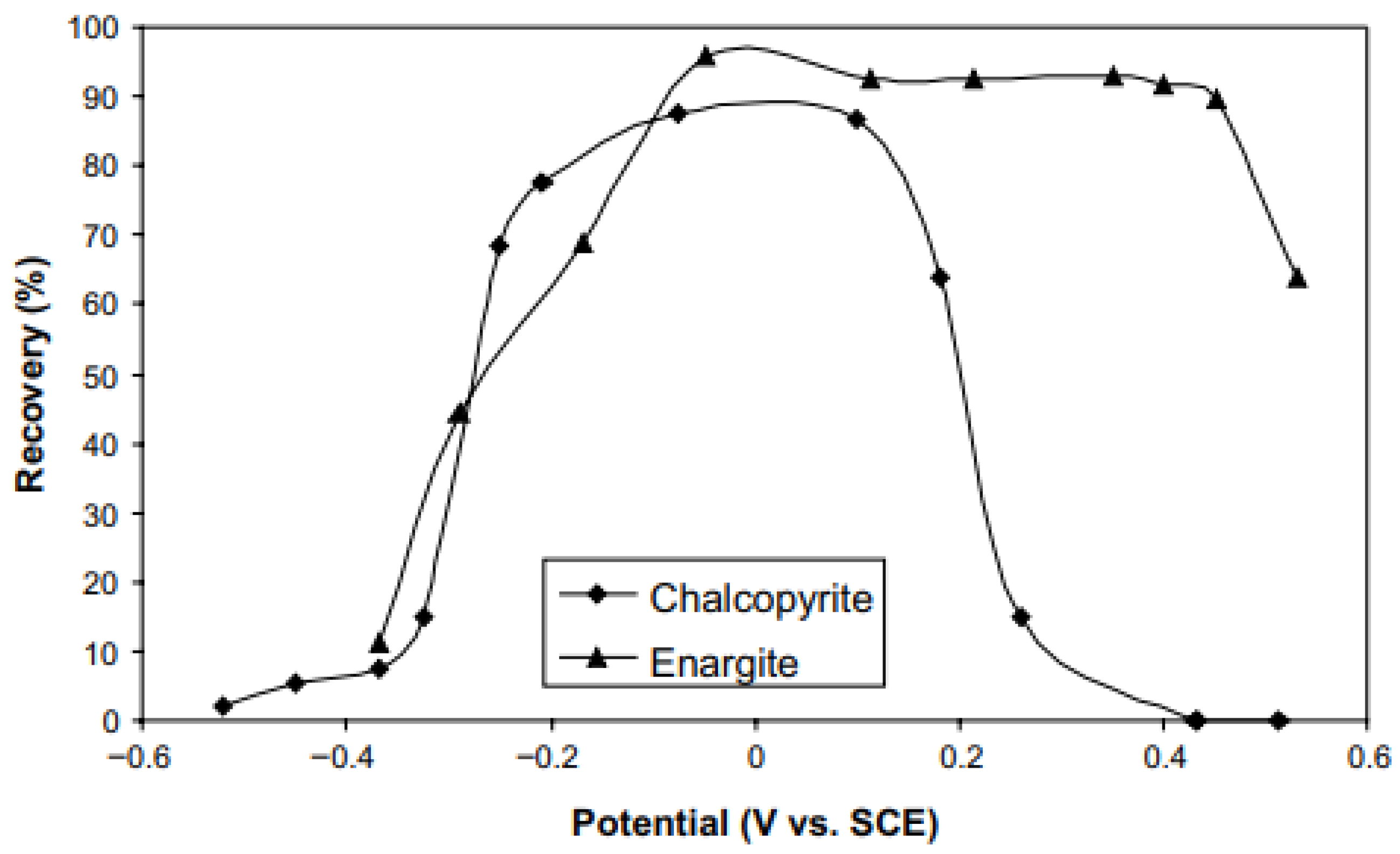
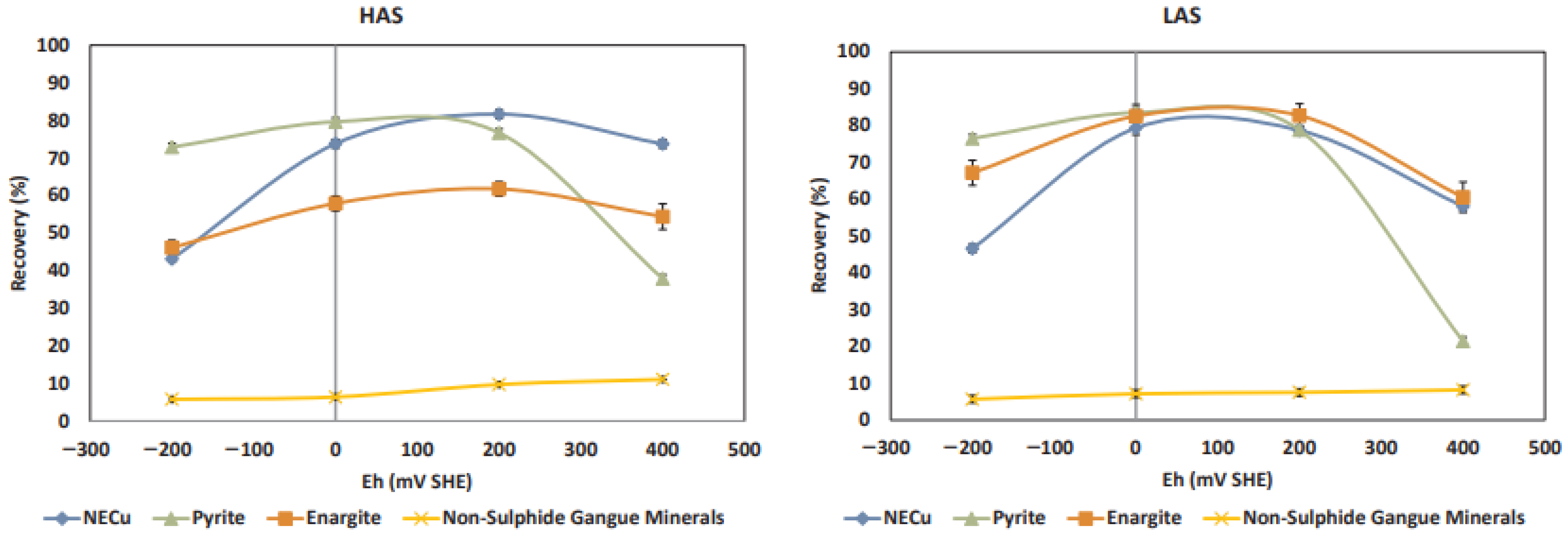
| [8] | Analyze the floatability of enargite and chalcopyrite in simple and mixed- mineral systems under different potentials. | Enargite floatability remains stable between −100 and 450 mV/SHE, decreasing outside this range. |
| [74] | Evaluate the flotation range of enargite using different collectors, comparing PAX and NaEtX. | It expands the flotation range of enargite with PAX compared to NaEtX. |
| [75] | Investigate the separation of enargite from other copper minerals through pulp potential control. | The threshold flotation potential of enargite is −75 mV/SHE at pH 8.0 and −25 mV/SHE at pH 11.0. Its selective separation from chalcopyrite occurs at 0 mV/SHE (pH 8.0 or 11.0). |
| [76] | Analysis of the effect of pH and pulp potential on the flotation of metallic arsenic using ethyl xanthate. | Arsenic exhibited high floatability (up to 95% recovery in 8 min) with Aerofroth 65 and 40 g/t of PEX at pH 5.0–10.0. At pH 10.0, its flotation was efficient within a potential range of −300 to 225 mV/SHE. |
| [43] | Identify the formation of passivating layers in the flotation of arsenic at different potentials. | Identification of a Cu(OH)2 passivating layer at potentials <570 mV/SHE and elemental sulfur at potentials >760 mV/SHE. |
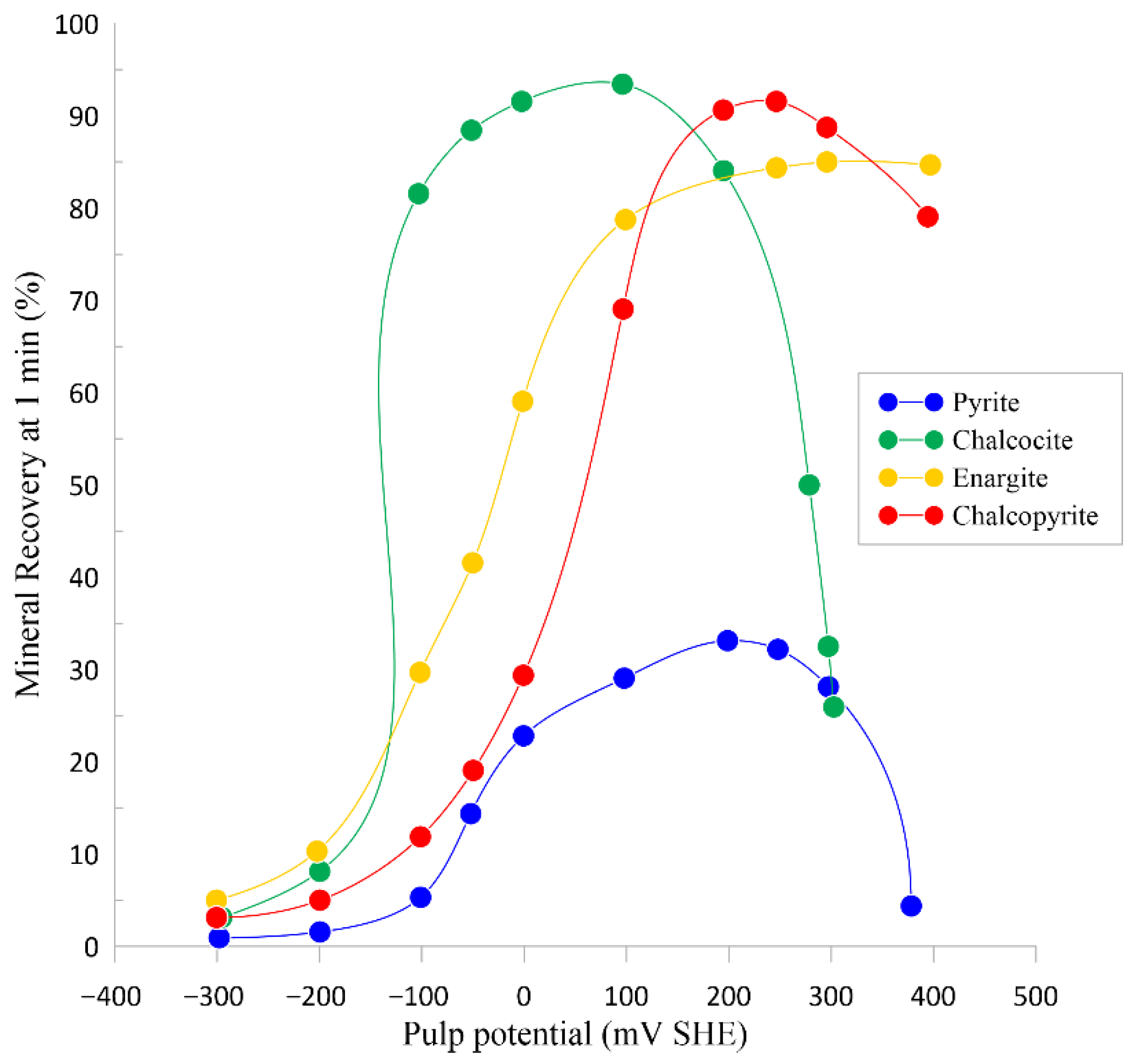
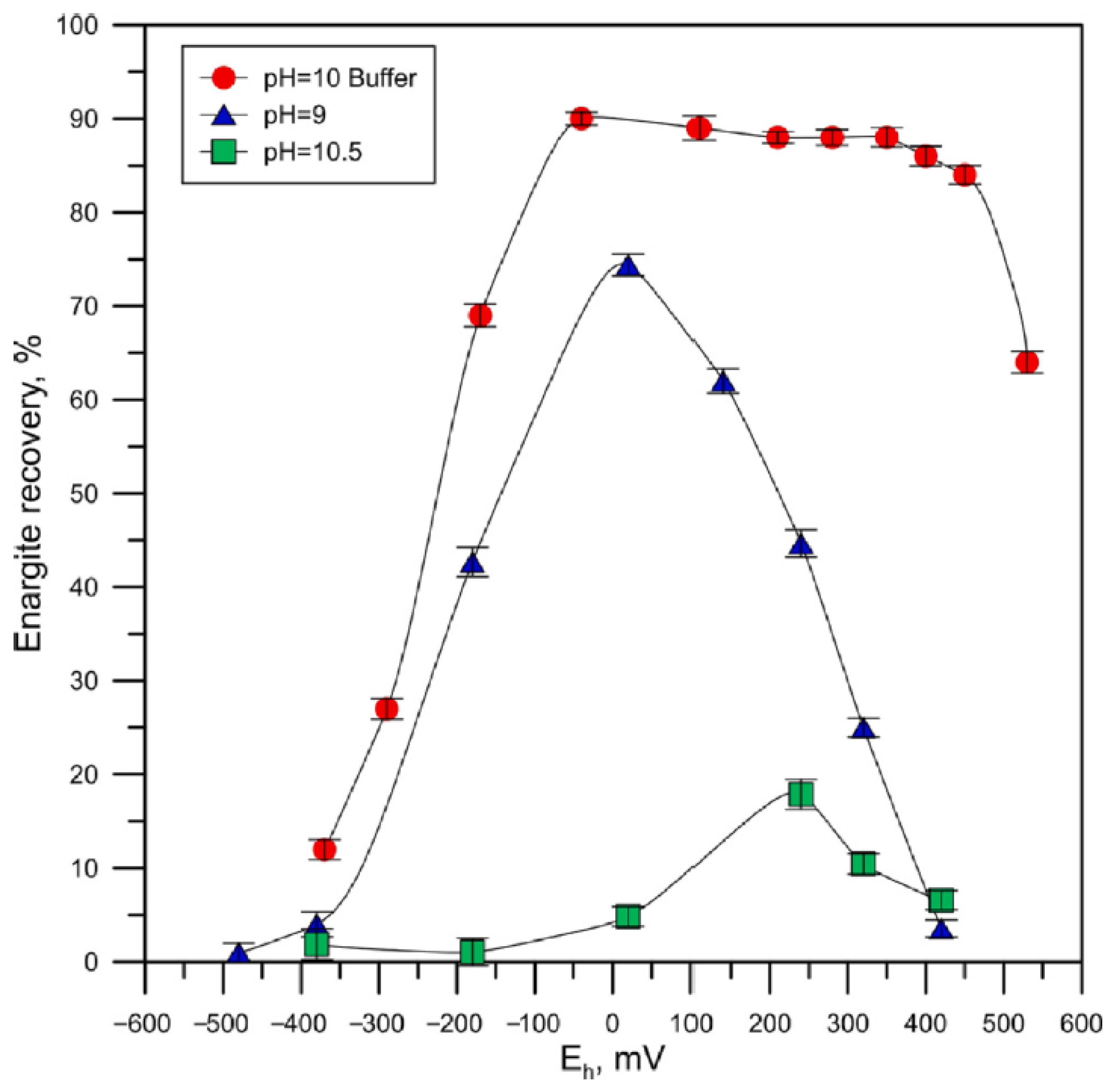
| [3,9] | Evaluate the floatability of enargite in high- and low-arsenic content samples under different pulp potentials. | Enargite exhibits a lower recovery at −200 mV/SHE and maximum recovery at 200 mV/SHE. |
| [82] | Analyze the galvanic interactions between enargite and pyrite and their impact on selective flotation. | Galvanic interactions with pyrite oxidize enargite, reducing its floatability and affecting selectivity. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda-Villagrán, P.; Yepsen, R.; Ramírez-Madrid, A.; Saavedra, J.H.; Gutiérrez, L. Review of Enargite Flotation—Part I: Surface Characterization and Advances in Selective Flotation. Minerals 2025, 15, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090971
Miranda-Villagrán P, Yepsen R, Ramírez-Madrid A, Saavedra JH, Gutiérrez L. Review of Enargite Flotation—Part I: Surface Characterization and Advances in Selective Flotation. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090971
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda-Villagrán, Pablo, Rodrigo Yepsen, Andrés Ramírez-Madrid, Jorge H. Saavedra, and Leopoldo Gutiérrez. 2025. "Review of Enargite Flotation—Part I: Surface Characterization and Advances in Selective Flotation" Minerals 15, no. 9: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090971
APA StyleMiranda-Villagrán, P., Yepsen, R., Ramírez-Madrid, A., Saavedra, J. H., & Gutiérrez, L. (2025). Review of Enargite Flotation—Part I: Surface Characterization and Advances in Selective Flotation. Minerals, 15(9), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090971








