Abstract
This work investigated the ion exchange technique for selective separation of rare earth elements (REE) from acid mine drainage (AMD), using different column systems, pH values, and eluent concentrations. Systematic analysis of pH and eluent concentration showed that an initial pH of 6.0 and 0.02 mol L−1 NH4EDTA are the optimal conditions, achieving 98.4% heavy REE purity in the initial stage (0 to 10 bed volumes). This represents a 32-fold increase compared to the original AMD (6.7% heavy REE). The speciation of REE and impurities was determined by Visual Minteq 4.0 software using pH 2.0, which corresponds to the pH at the inlet of the fractionation column. Under this condition, La and Nd and the impurities (Ca, Mg, and Mn) remained in the fractionation column, while Al was partially retained. In addition, the heavy REE (Y and Dy) were mainly in the form of REE-EDTA complexes and not as free cations, which made fractionation more feasible. The fractionation column minimized impurities, retaining 100% of Ca and 67% of Al, generating a liquor concentrated in heavy REE. This sustainable approach adopted herein meets the critical needs for scalable recovery of REE from diluted effluents, representing a circular economy strategy for critical metals.
1. Introduction
Given the growing demand for rare earth elements (REE), particularly for clean energy applications, the search for processes that recover these strategic metals efficiently and cheaply has increased significantly worldwide [1,2,3]. In this context, secondary sources containing these elements are essential, as investing in these sustainable resources can mitigate the supply risk. Important secondary sources are generated by mining companies, such as residues (tailings and waste rocks) and liquid effluents, such as acid mine drainage (AMD) [4,5].
The strategic relevance of REE is driving the exploration of secondary resources like AMD to diversify the supply chain beyond conventional mining [3,4]. Although REE concentrations in AMD are diluted, the vast volumes of this effluent imply that the total recoverable quantities are significant, providing a strong economic and environmental incentive for valorization [6,7,8]. However, the primary technical challenge is the extreme dilution of REE (µg to mg L−1) amidst a significant excess of impurities like iron and aluminum. Conventional pretreatment via fractional precipitation, while effective for bulk iron removal, fails to recover REE selectively. This is because of the overlapping pH ranges of precipitation of REE and aluminum, which leads to significant REE loss through co-precipitation and adsorption [9,10]. In addition, the effluent is too diluted for other methods like solvent extraction and precipitation using oxalic acid, as both methods become economically and technically unviable [11,12].
In this context, ion exchange offers a strategic solution to selectively concentrate REE from these large, diluted volumes into a minor, high-value liquor [11,12,13]. However, this merely shifts the bottleneck to the critical step of fractionation, separating valuable REE from each other and residual impurities. Current research is restricted to low-efficiency eluents, such as inorganic acids, which cannot achieve commercial-grade purity. Therefore, a clear need exists for an integrated process that combines high-efficiency concentration with selective fractionation. This study was designed to address this specific gap.
The ion exchange technique is successfully used for the concentration/purification of certain metallic elements; however, it is still incipient for REE. The solvent extraction technique is currently commercially used, despite being environmentally questionable. Studies to concentrate REE by ion exchange are available in the literature [11,12,13], but ion exchange for REE fractionation, especially in the presence of significant impurity content, is limited to elution by inorganic acids, which does not show the desired effectiveness. Shokobayev et al. [14] used NH4NO3 and HNO3 solutions to elute REE from sulfonic resins. However, as these eluent solutions must be at high concentration to be effective, i.e., between 7 and 8 mol·L−1, they can be used only in the broader context of REE elution, as they do not perform fractionation. On the other hand, elution with NH4EDTA (or Na2EDTA), which occurs through the complexation of the REE, has shown promising results in increasing the selectivity and/or fractionation of REE [15].
Moore et al. [16] investigated the elution with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) in a chromatography system composed of columns containing sulfonic resin loaded with REE, followed by fractionation columns containing iminodiacetic resin. Erbium was used as a retainer ion, and the process achieved up to 99% purity for specific REE with a significant reduction in separation time. In addition, 92% of EDTA and 94% of REE were recovered by precipitation. José et al. [17] used NH4EDTA to elute REE in a two-column system with cationic resin. The system effectively separated REE into fractions of heavy (Gd, Dy, and Y) and light (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm) elements. Still, there was no satisfactory fractionation of all the elements, especially light elements. Fernandez et al. [18] investigated the separation of REE by chromatography, using EDTA as the mobile phase. It was demonstrated that the speciation and charge of the REE-EDTA complexes undergo significant changes with pH, significantly affecting selectivity and elution efficiency. At pH 3.5, the light and medium REE complexes presented a charge of approximately −2, while at pH 6.5 the charge was −1 and up to −3 at pH 9.5, while the heavy REE complexes maintained a charge of −1. Ding et al. [19] proposed a two-zone ligand-assisted displacement chromatography for separating a mixture of Dy, Nd, and Pr using EDTA as an eluent and copper as a retention ion. In the first zone, high-purity Nd was obtained with a yield of 78%. The second zone, designed to separate the mixed bands from the first, produced all three REE with high purity and yield. Recycling the Nd/Pr and Dy/Nd mixed bands of Zone II increased the overall yield to over 99% for all three REE. Although effective, adding a new metallic element, such as copper, requires supplementary purification steps to remove this ion from the process, increasing its complexity and cost. This consideration is particularly relevant for AMD because operational simplicity and minimization of additional chemical load are desirable when dealing with large volumes of diluted and complex solutions.
EDTA and its salts are a central strategy in the selective elution of REE in chromatography processes [20,21,22]. The ability of EDTA to form stable complexes is crucial for the successful separation of REE. The efficiency of the process is directly linked to experimental conditions, particularly pH, which directly impacts the speciation and charge of REE-EDTA complexes and, consequently, fractionation. The studies mentioned above highlighted the relevance of optimizing EDTA elution conditions and chromatographic system design for efficient fractionation of REE.
The present study investigated the fractionation of REE from an AMD sample, using a two-column system filled with ion exchange resin. In this system, the fractionation column was saturated with ammonium ion (NH4+), which is a component present in the NH4EDTA eluent, and did not introduce a new metal to the system, making the process potentially more direct and with less impact on the subsequent steps. The fractionation between light and heavy REE was evaluated by investigating the effect of pH and NH4EDTA concentration on selective elution. In addition, a better understanding of the fractionation mechanism was sought, aiming to improve the separation of REE and the removal of the main impurities present in AMD, such as Al and Ca, efficiently and sustainably.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acid Mine Drainage (AMD)
A sample of approximately 200 L of acid mine drainage (AMD) was obtained from a decommissioned uranium mine in Brazil [17]. Before column experiments, the sample was vacuum filtered using quantitative filter paper (85 g m−2, porosity of 25 µm), passed through a fixed bed filled with granular coal (>300 μm) to remove organic matter [23], then homogenized. An aliquot was taken and sent for chemical analysis by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), manufactured by SPECTRO Analytical Instruments, Kleve, Germany. The physicochemical analysis of the acid effluent sample is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical characterization of acid mine drainage (AMD).
The absence of uranium in the effluent is because the AMD is subjected to industrial pretreatment specifically engineered to eliminate uranium (U) and iron (Fe), as described in the work in [17].
2.2. Eluent Solution
The NH4EDTA eluent solution was prepared by dissolving anhydrous ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (H4EDTA, formula C10H16N2O8, free-flowing, Redi-Dri, purity > 98%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in 1.0 mol L−1 ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 28–30%) solution under continuous stirring and heating on an electric hot plate at 150 °C. The solution was then transferred to a volumetric flask, in which the pH was adjusted to 6.0 (HCl) or 8.5 (NH4OH), and the volume was completed with MILLI-Q deionized water.
2.3. Ion Exchange Resin
In the loading and elution experiments, the ion exchange resin Lewatit MDS 200 H, supplied by Lanxess Company (Cologne, Germany), was used. It is a strongly acidic, gel-type cation exchange resin in its H form, with styrene matrix, total capacity 2.3 eq·L−1, density 1.2 g·mL−1, water retention 48% to 53%, operating pH range 2 to 14, and operating temperature maximum 120 °C, according to the manufacturer’s specifications [24]. The selected resin, Lewatit® MDS 200 H, is a robust and recyclable material, as specified by its manufacturer [24]. It presents high chemical stability across the entire pH range (0–14) and thermal stability for operations up to 140 °C, although contact with strong oxidizing agents should be avoided. Physically, it is a mechanically robust material with high resistance to bead fracture. For recyclability, the manufacturer confirms that the resin can be regenerated using either hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4), with a recommended minimum contact time of 20 min.
2.4. Loading Experiments
A glass column with an internal diameter of 11 mm was packed with 6.25 or 12.5 g of Lewatit MDS 200 H resin (dry basis), obtaining beds of 8.0 mL or 15.5 mL, respectively, and the final packed bed lengths were 8.4 cm and 16.3 cm. The column was fed with AMD solution by a peristaltic pump (WATSON MARLOW, QDOS 30), with downflow, flow rates of 0.78 ± 0.01 mL∙min−1 (8 mL column) and 01.50 ± 0.01 mL∙min−1 (15.5 mL column), and a residence time of 10.2 min. The effluent samples were collected using an AMARSHAN—FRAC 900 fraction collector (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden) at time intervals and sent for analysis. After the experiment, the resin bed was washed with deionized water and a water level approximately 3 cm above the bed was kept until the start of the elution experiments. The average loading of the columns was QREE = 0.458 mmol∙g−1 for REE and Qimpurities = 1.39 mmol∙g−1 for impurities.
2.5. Elution Experiments
Experiments were performed in two different arrangements: (i) a single-column system and (ii) a two-column system connected in series. In the single-column arrangement, elution was conducted directly in the loading column (LC) after loading. In the arrangement with two columns in series, the effluent from the LC column was transferred directly to the top of the second column, called the fractionation column (FC), through peristaltic pumps. The FC was filled with Lewatit® MDS 200 H resin previously converted to the ammoniacal form NH4+. The resin activation was performed by percolating a 10% (v/v) NH4OH solution according to the methodology described by José et al. [17]. The flow rate of the NH4EDTA solution was maintained at 0.37 ± 0.02 mL·min−1 for the 8.0 mL column and 0.78 ± 0.02 mL·min−1 for the 15.5 mL column, resulting in an average residence time of 23 ± 1 min, and T 25 °C. Beds of the columns were LC = 8 mL or 15.5 mL and FC = 15.5 mL. Eluate was collected by an AMARSHAN— FRAC 900 fraction collector for both systems. The column system configurations are shown in Figure 1.
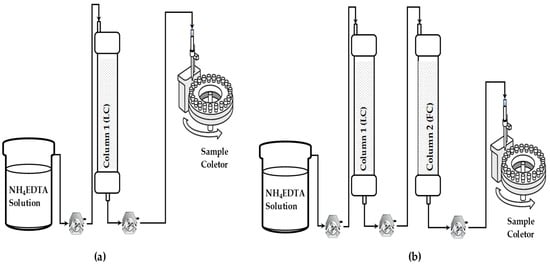
Figure 1.
Elution systems. (a) Single-column system (loading column (LC)) and (b) two-column system connected in series (loading column (LC) + fractionation column (FC)).
2.6. Chemical Analyses
The REE and impurity concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES; model SPECTRO ARCOS manufactured by SPECTR in Kleve, Germany) with an axial configuration, crossflow nebulizer, and wavelength range of 130 (160)–770 nm [17]. A multielement standard solution was used to construct the calibration, giving each REE element a linear range as a response. The precision and accuracy were also adjusted, with the standard deviation less than 3% and the quantification limits (LOQ) being 0.10 mg∙L−1 for REE.
2.7. Thermodynamic Analysis: REE-Impurity-EDTA-H2O System
The thermodynamic stability of REE complexes and EDTA impurities in the elution systems was evaluated through speciation curves obtained through the Visual Minteq 4.0 software. The values of the formation constants to perform the thermodynamic calculations are presented in Table 2. These values were manually included in the software database [25].

Table 2.
Formation constants (log β) for the metallic complexes with EDTA and HEDTA.
3. Results
3.1. Loading of REE and Impurities
The column loading experiments were based on the REE loading profiles for the Lewatit® MDS 200 H resin reported by José and Ladeira [17] and José et al. [36]. The authors demonstrated that a desorption phenomenon of the heavier REE occurs, mainly for Sm, Gd, Dy, and Y, and the appearance of peaks above the feed line characterizes it. This phenomenon was attributed to the greater affinity of the resin for the light REE, mainly La, compared to the heavier REE [36]. Therefore, to avoid losses due to the desorption of these elements, the loading was interrupted around 630 BV, and the curves are shown in Figure 2. It can be noted that there was no desorption of REE, except Y and Dy, with Dy reaching saturation at 615 BV with 1% desorption, and for Y, the saturation occurred at 558 BV with a desorption of 6.5%.
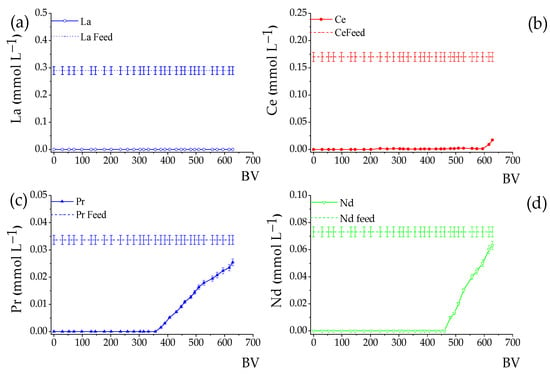
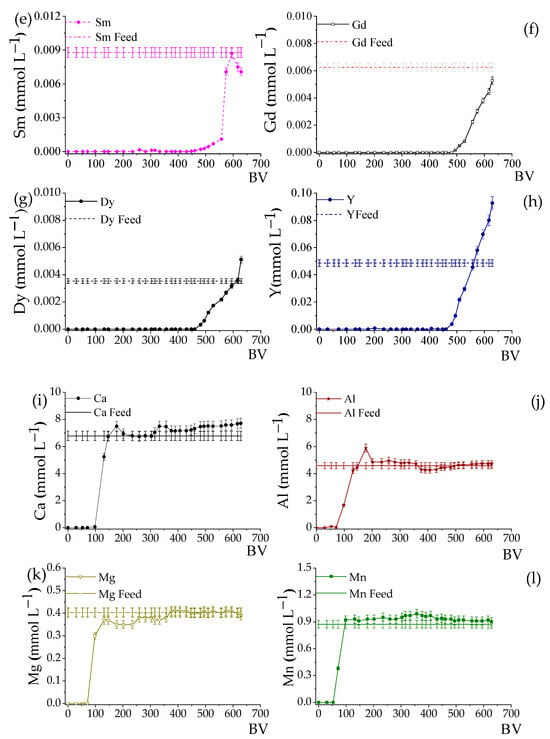
Figure 2.
REE loading profiles on Lewatit® MDS 200 H resin using AMD. Initial pH 3.50, LC = 8.0 mL; Residence time: 10.4 min, T 25 °C. The solid horizontal line represents the REE concentration in the feed solution. The subfigures detail the profiles for: (a–h) total Rare Earth Elements (REEs); (i–l) main impurities (Al, Ca, Mg, Mn).
Table 3 shows the amount of REE adsorbed after percolation of the AMD solution through columns of 8 and 15.5 mL bed volumes. Approximately 0.50 mmol∙g−1 of REE was adsorbed, with 24.0% of LREE (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm) and 2.1% of HREE (Gd, Dy, and Y) related to the total metals adsorbed. The adsorption efficiency for LREE varied from 78.2% for Sm to 100.0% for La, and for HREE, it varied between 75.2% for Y and 91.8% for Gd. The total REE loading (QREE) was 0.458 mmol∙g−1 (67 mg g−1). The results demonstrate a greater affinity of Lewatit resin for LREE compared to HREE, which agree REE with previous studies conducted under similar conditions [17,36,37].

Table 3.
Data on the loading of metals present in AMD by the Lewatit MDS 200 H resin.
Figure 2i–l also show the loading curves for Ca, Al, Mg, and Mn, which are considered the main impurities in AMD (Table 1). These elements tend to occupy a large part of the active sites of the resin, reducing the REE loading and directly affecting the composition of the eluate. It is noted that the breakpoint of the impurities occurs at BVs lower than the REE and that the loading curves present similar behaviors, i.e., after 100 BV, they reach rapid saturation. The total loading of the impurities was 1.39 mmol∙g−1 (49 mg g−1), representing 73.8% of the total amount of metals adsorbed, mainly Ca and Al. According to José et al. [17] and José et al. [34], the Lewatit MDS 200 H resin prefers REE, especially the light ones, to the detriment of impurities (Ca, Al, Mg, and Mn). However, given the high concentration of impurities in AMD, mainly Al, several studies have suggested selective precipitation of this element as pretreatment (increasing the pH or adding a precipitating agent) to minimize its impact on the adsorption process by ion exchange [36].
3.2. Effect of pH on REE Fractionation in a Single-Column System
Figure 3 shows the REE elution curves for NH4EDTA at an initial pH of 6.0 and 8.5. The bands were separated at pH 6.0 (Figure 3a,c), indicating a fractionation between HREE and LREE in the first BVs. The elution of light elements, mainly Ce and La, started last, and for 0.01 M NH4EDTA, the elution of La began after the elution of the other REE had already finished. The percentage of La eluted was 3.5%, for Ce it was 78%, and for the other elements, elution was close to 100% (Table 4). Since La, together with Ce, are the elements most adsorbed on the Lewatit MDS 200 H resin (Table 4), this fact is quite relevant for the fractionation, since it led to the separation of La and part of the Ce from the other REE. Regarding the fractionation of REE at pH 8.5 (Figure 3b,d), the elution peaks occurred at lower BV values, and the Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd, Dy, and Y bands were relatively close. Those elements were almost completely eluted below 14 BV, showing an insignificant fractionation of REE. From 14 to 50 BV, the eluate was basically composed of La and Ce. Generally, at pH 6.0, the profiles were more elongated, and the elution was completed around 60 BV, while the elution at pH 8.5 finished close to 50 BV, implying a 20% smaller volume of eluent. Although the HREE elution peaks occurred at the beginning of the curve for both pH values, fractionation was favored at pH 6, but at pH 8.5, the peaks of REE were much higher.
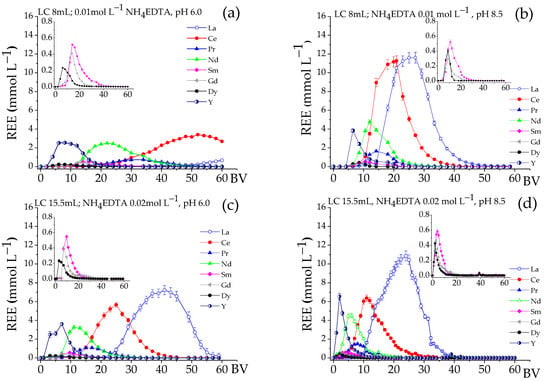
Figure 3.
Elution profiles for REE adsorbed on Lewatit MDS 200 H resin at different pH levels. Residence time: 21.3 min, T 25 °C. Profiles (a,b) initial LC = 8 mL; NH4EDTA = 0.01 mol∙L−1. Profiles (c,d) initial LC = 15.5 mL; NH4EDTA = 0.02 mol∙L−1.

Table 4.
Concentration of REE and corresponding BV at the peak of the elution profiles from Figure 3 and total elution (%).
In summary, the results presented by the single-column system demonstrated a clear principle: decreasing the initial eluent pH from 8.5 to 6.0 significantly enhanced the fractionation between HREE and LREE, particularly enabling the near-total separation of La and Ce. Thus, the elution performed with 0.02 mol L−1 solution and pH 6.0 provided a satisfactory fractionation between HREE and LREE and produced a concentrated solution proper for the subsequent steps.
3.3. Effect of the Fractionation Column on REE Elution
A two-column elution system has been studied when effective separation of the REE bands is needed [16,17,38,39]. Using a single-column system (Figure 3), elution at pH 6.0 successfully separated the HREE and LREE bands. However, a fractionation column was tested here to obtain a more concentrated eluate without sacrificing band separation. Figure 4 shows the effect of adding a fractionating column filled with NH4+ on the REE elution profile using NH4EDTA 0.02 mol∙L−1 at pH 6.0. Table 5 presents the elution data based on Figure 4. Comparing the REE elution profiles in Figure 4a,b, the addition of a fractionation column improved REE separation, especially at the start of the elution where HREE appeared. This is because the fractionation column interacted more with the LREE elements, delaying their elution and causing a slight separation between Y and Nd, as Nd’s elution was postponed. Nd began eluting around 5 BV in the single-column system, but in the two-column system, it started around 12 BV. Although the eluate was more diluted, the two-column setup was more effective for fractionating rare earth elements (REE). To highlight this benefit, fractions of 10 BVs of eluate were collected up to 40 BV for both systems (Figure 4a,b), and the composition of the REE in each fraction was analyzed without considering impurities, as shown in Figure 5.
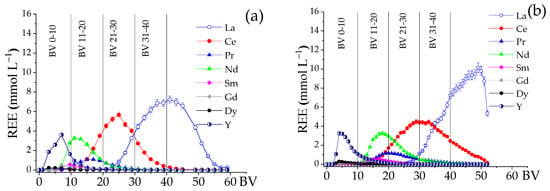
Figure 4.
Effect of the fractionation column on the elution of REE and impurities. (a) Single-column system (LC = 15.5 mL) and (b) two-column system (LC = 15.5 mL and FC = 15.5 mL pre-saturated resin NH4+). Eluent 0.02 mol∙L−1 NH4EDTA; initial pH 6.0, T 25 °C. Residence time: 21.3 min.

Table 5.
Concentration of REE and impurities at the elution peak (Figure 6). Elution 0.02 mol·L−1 NH4EDTA, pH 6.0.
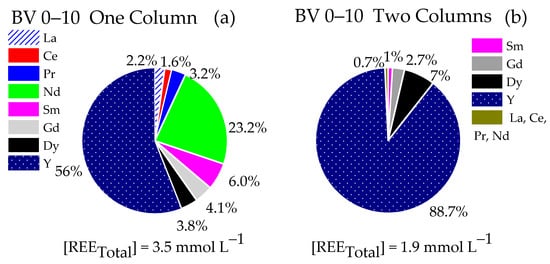
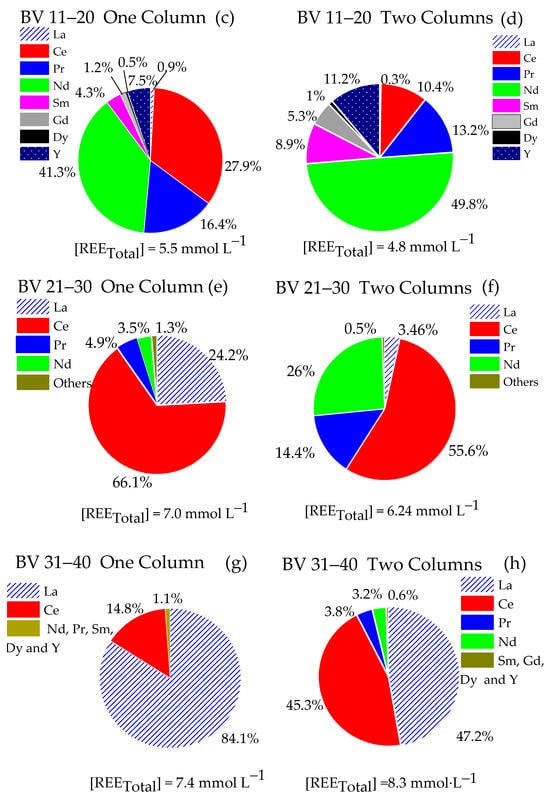
Figure 5.
Composition of the eluate fractions. (a,c,e,g) Single-column system (LC = 15.5 mL) and (b,d,f,h) two-column system (LC and FC 15.5 mL pre-saturated NH4+). 0.02 mol∙L−1 NH4EDTA, pH 6.0. Residence time: 21.3 min, T 25 °C.
Comparing the composition of the fraction 0–10 BV for both systems (Figure 5a and Figure 6b), a significant enrichment of HREE, particularly Y (88.7%) and Dy (7%), was noticed for the two-column system, whose total concentration of REE in the eluate was 1.85 mmol∙L−1, consisting of 98.4% of HREE. For the single-column system, the total concentration of REE in the eluate was 3.4 mmol∙L−1, with 63.8% of HREE (Gd, Dy, and Y) and 36.2% of LREE (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm). The predominant HREE in the single-column system was Y (56%), and the principal LREE was Nd (23.2%).
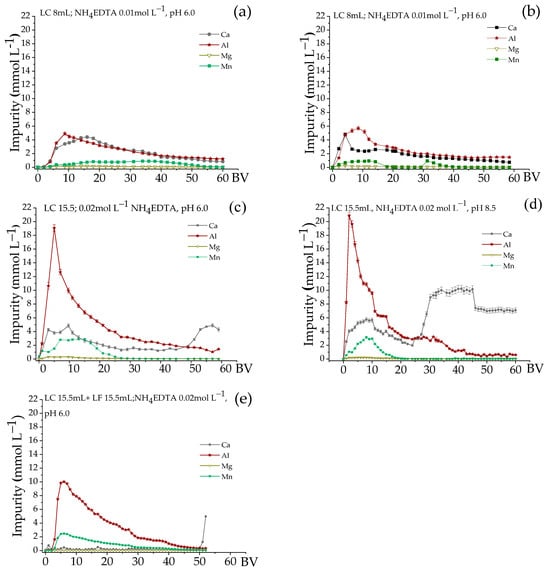
Figure 6.
Elution of impurities for single- and two-column systems. Residence time: 21.3 min, T 25 °C. (a) pH 6.0 and (b) pH 8.5, NH4EDTA 0.01 mol∙L−1, LC = 15.5 mL. (c) pH 6.0 and (d) pH 8.5, NH4EDTA 0.02 mol∙L−1, LC = 15.5 mL. (e) pH 6.0, NH4EDTA 0.02 mol∙L−1, LC and FC = 15.5 mL.
For the 11–20 BV fraction (Figure 5c and Figure 6d), the REE concentration in the eluate was 5.5 mmol∙L−1 for the single-column system to 4.0 mmol∙L−1 for the two-column system. Nd was the predominant element in both systems, varying from 41% to 50% of the total REE for the single-column system and with the fractionation column, respectively. The retention, especially of Ce, by the fractionation column favored the enrichment of this fraction in Sm, Gd, and Dy, whose percentages practically doubled.
Regarding fraction 21–30 BV, although both systems presented similar total REE concentrations in the eluate (approximately 6.5 mmol∙L−1), the single-column system generated a liquor with a higher concentration of La and Ce (87.6% of the total REE), with the remainder practically composed of Nd and Pr (10.8%). In the two-column system, the retention of HREE was reduced compared to light elements, such as La and Ce, as the percentage of both elements in the liquor was approximately 57.9%, evidencing the preferential retention of LREE by the fractionation column. Nd and Pr totaled 37.3%.
The 31–40 BV fraction from the single-column system (Figure 5g) showed a liquor with a REE concentration of 7.4 mmol∙L−1, composed mainly of 18.9% Ce and 79.6% La, totaling 98.5% of these elements. The remainder of this fraction comprised 1.5% Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd, Dy, and Y. The two-column system (Figure 5h) showed a similar pattern, with La and Ce representing 92.5% of the total REE and a liquor concentration slightly higher (8.3 mmol·L−1). The significant predominance of La and Ce for both systems suggests an affinity of these elements for the resin. The strong interaction of LREE with the fractionation column, especially at acidic pH (close to 2.6), is probably due to the speciation of La and Ce, which contributes to their preferential interaction compared to HREE (Silva et al., 2024) [38].
These studies demonstrate that while EDTA-based chromatography is a potent tool, its optimization is governed by a central conflict between maximizing fractionation selectivity and maintaining an economically viable concentration of the liquor. Adding columns to enhance fractionation, as pointed out by Silva et al. [38], leads to the counterproductive dilution of the product. In addition, the eluate is also more diluted because of optimizing chemical parameters, such as reducing the EDTA concentration to enhance fractionation. This generates an intricate optimization environment in which the disadvantage of dilution rapidly cancels the marginal advantage of any single strategy.
3.4. Elution Profiles of Impurities for Single-Column and Two-Column Systems
According to Table 3, the number of impurities (Ca, Al, Mg, and Mn) adsorbed by the cationic resin represents 74%, and the remaining 26% are REE. Therefore, it is expected that the eluate contains high concentrations of impurities. Figure 6 shows the elution of impurities at different pH values and eluent concentrations for both systems. The data related to these elution profiles are presented in Table 6. For NH4EDTA 0.01 mol·L−1 (Figure 6a,b), the elution of Ca and Al showed similar behaviors, with high concentrations of these metals at the beginning of the process and then a gradual decrease. The elution of Ca varied between 20 and 25%, Al was around 30%, and Mg was not very expressive. Mn was eluted between 45 and 85%, and the best elution occurred at pH 6.0.

Table 6.
Elution percentages for the impurities.
Figure 6c,d show that with the increase in NH4EDTA concentration to 0.02 mol∙L−1, the elution of Al occurred simultaneously with the elution of HREE. According to Table 2, among the impurities, Al presented the highest complexation constant for EDTA; therefore, the increase in the EDTA concentration tended to favor Al elution. At pH 6.0, the elution was extended to 60 BV, while at pH 8.5, the elution was practically completed at 45 BV. Mn was eluted entirely, regardless of the pH, while Mg did not show significant elution. For Ca, the increase in the eluent concentration did not have a significant impact at pH 6.0, remaining around 25%. However, at pH 8.5, the elution of Ca was greatly favored and reached 63.7% (Table 6).
Figure 6e shows that the fractionation column retained all Ca and Mg, and, despite the higher eluent concentration, the complete separation of these impurities from the REE fractions was obtained. Regarding Al, a partial retention resulted in a significant decrease in its concentration in the eluate in the first BV. This result is relevant for the 0–10 BV fraction (Figure 5) because fractions richer in HREE can be obtained due to the lower presence of Al. The total Al elution passed from 65% in the single-column system to 33% in the two-column system (Table 6). There was no significant change in the amount of Mn eluted; however, its elution extended throughout the process.
3.5. Influence of the pH That Enters the Fractionation Column
Figure 7 shows the pH profiles of the eluate for the single-column and two-column systems. It is seen that when the eluent left the first column and entered the fractionation column, the pH was close to 2.0. The pH decrease, initially at 8.5 or 6.0, occurred because as the metal-EDTA complexes formed, H+ was released [17,40]. At low pH, forming metal complexes with a higher formation constant is preferential [41,42,43].
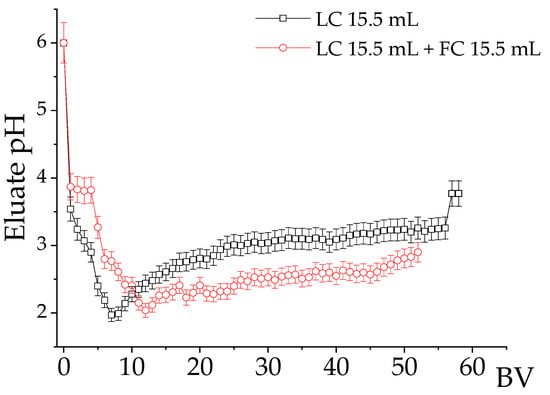
Figure 7.
pH profile of the eluate during elution experiments. Residence time 21.3 min. NH4EDTA = 0.02 mol∙L−1, initial pH 6.0, T 25 °C. NH4EDTA 0.02 mol∙L−1. FC activated with NH4+.
Some works in the literature propose that in AMD, most of the REE and Al cations are in the forms REE-SO4+ and Al-SO4+ [44,45], while a smaller part will be adsorbed as REE3+ or Al+3 [35,37]. Therefore, the reactions of complexation of the metals adsorbed on the resin, followed by the deprotonation of the EDTA species, follow the sequences described in Reactions (1)–(3):
where M denotes the metal cations adsorbed onto the resin (REE or impurities), m is the metal charge, and n is the number of protons associated with EDTA.
[R-SO3-M(SO4)] + (HnEDTA) = [R-SO3−] + M-EDTA− + SO42− + nH+,
[(R-SO3)m-M] + (HnEDTA) = [mR-SO3−] + M-EDTA−(4−m) + nH+,
[(R-SO3)m-M] + (H3EDTA) = [mR-SO3−] + M-HEDTA−(3−m),
In Table 4, EDTA elution is mainly based on the differences between the complexation constants of REE and impurities [15,17,36]. However, the complexation may not be selective if there is an excess of EDTA in the eluent. The changes in speciation as a function of pH of a 0.02 mol∙L−1 NH4EDTA solution containing REE (La, Nd, Dy, and Y) and impurities (Ca and Al) are shown in Figure 8, where the data correspond to the concentration values of the elements in BV 7 (Figure 4a and Figure 6c), where a peak in the metal concentration and a decrease in pH to around 2.4 were observed.
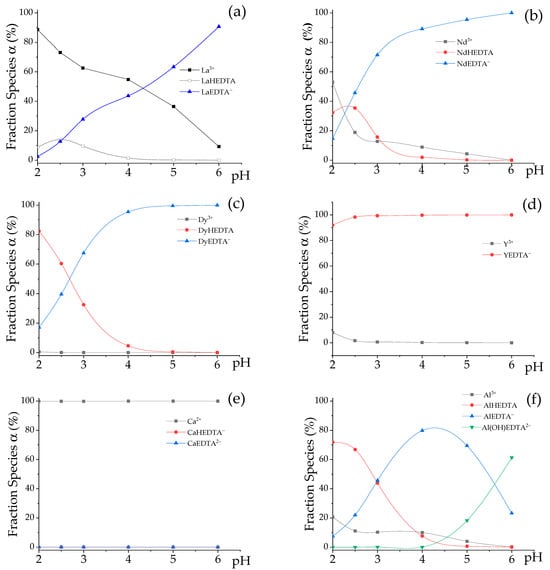
Figure 8.
Distribution diagram as a function of pH for metal-EDTA-H2O systems constructed via computer simulation by Visual Minteq 4.0 software. REE, mmol·L−1 = La 0.14, Ce 0.06, Pr 0.01, Nd 0.03, Sm 0.01, Gd 0.01, Dy 0.22, Y 2.60. Impurities, mmol·L−1 = Ca 3.80, Al 19.07, Mg 0.28, Mn 1.51; pH = 2.4. (Speciation of the main Rare Earth Elements La (a); Nd (b); (c) Dy and (d) Y and Speciation of the main impurities: (e) Ca and (f) Al.
According to Figure 8a, at pH 2.0, approximately 90% of the La is in the form of La3+, which means that the fractionation column will largely retain it. With increasing pH, the subsequent formation of LaHEDTA and LaEDTA− occurs. Yu et al. (2025) [45], who also modeled this system, demonstrated that temperature significantly influences these La-EDTA equilibria. At pH 2.5, an elevation in temperature (from 25 to 45 °C) resulted in a decreased fraction of free La3+ and a concomitant increase in LaHEDTA, thereby altering the overall complexation constant. Although the present investigation was conducted under isothermal conditions at 25 °C, this observation underscores the potential role of temperature as a parameter for optimizing such separation processes. Between pH 4 and 5, the dominant species for lanthanum was LaEDTA−, which would not be completely retained. As for Nd, at pH 2.0 (Figure 8b), only approximately 53% was in the form of Nd3+, and the remainder was in the form of NdHEDTA and NdEDTA−. Regardless of the pH value, there was no significant concentration of Y3+ and Dy3+ cations in the outlet solution of the loading column (LC). Therefore, there will not be considerable retention of the heavy elements in the fractionation column (FC), which favors the separation of the HREE and LREE.
In the single-column system, the eluate pH varied between 2.0 and 2.3 for approximately 20 BV (Figure 7). In this condition, approximately 20% of the aluminum was in the form of Al3+, which should be retained by the cationic resin, justifying the partial retention of this impurity by the fractionation column. The remainder of the aluminum was partly in AlEDTA− (5%), and the majority (65%) was in the form of neutral AlHEDTA species that presented little interaction with the resin. This is consistent with the findings of Pinto et al. [46], who utilized the dissociation of Al-EDTA complexes at low pH (e.g., pH 1) to facilitate aluminum separation during nickel recovery from EDTA leachates. Ca2+ was the only stable calcium species and was completely retained.
4. Conclusions
The study showed that the pH and the concentration of the NH4EDTA played a significant role in REEs’ fractionation and elution percentage. Fractionation was more intense at pH 6.0, while increasing the NH4EDTA concentration favored elution efficiency, especially for LREE. The use of more concentrated NH4EDTA resulted in better-defined elution bands for HREE. At pH 6.0, there were significant gains in selectivity, mainly at the first 15 BV, and greater control over the elution of impurities, such as Al and Ca. The two-column system configuration proved efficient in separating HREE and LREE, allowing the production of purer fractions. The retention of impurities by the fractionation column reinforces its importance in improving the selectivity of the process. The two-column system filled with Lewatit MDS 200 H resin saturated with NH4+ showed superior performance to that achieved at pH 8.5 in terms of separation between LREE and HREE, reinforcing the relevance of chemical speciation and pH control for fractionation optimization. The fractionation column preferentially retained LREE, eluting HREE in the first fractions, especially yttrium (Y) and dysprosium (Dy). The two-column system for selective elution of REE present in diluted effluents, such as AMD, produced sustainably and economically specific fractions of REE oxides, as well as being applicable on an industrial scale, thus expanding the perspectives for selective fractionation processes of REE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.Q.L.; Methodology, C.S. and A.C.Q.L.; Validation, C.S.; Formal Analysis, C.S. and P.A.P.V.S.F.; Investigation, C.S.; Resources, A.C.Q.L.; Writing—Original Draft, C.S. and P.A.P.V.S.F.; Writing—Review & Editing, A.C.Q.L.; Supervision, A.C.Q.L.; Project Administration, A.C.Q.L.; Funding Acquisition, A.C.Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Brazilian institutions MCTI, CNPq, FAPEMIG, and FINEP and Transforma Project, RENOVAMin Project, INCT-Materia Project, GRANIOTER Project, and Regina Project.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feng, J.; Wu, X.; Gao, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhou, F.; Chi, R. Leaching Behavior of Rare Earth Elements and Aluminum from Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ore with Ammonium Formate Inhibitor. Minerals 2023, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagwar, P.P.; Iqbal, S.S.; Dutta, D. Sustainable recovery of rare Earth elements from industrial waste: A path to circular economy and environmental health. Waste Manag. Bull. 2025, 3, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otron, A.M.A.A.; Tran, L.H.; Blais, J.F. Mass balance and economic study of a treatment chain for nickel, cobalt and rare earth elements recovery from Ni-MH batteries. Environ. Technol. 2024, 46, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.O.S.; Talan, D. From Waste to Wealth: A Circular Economy Approach to the Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements and Battery Metals from Mine Tailings. Separations 2025, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, G.; Yuksekdag, A.; Kose Mutlu, B.; Koyuncu, I. A review of greener approaches for rare earth elements recovery from mineral wastes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 357, 124379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.; Ziemkiewicz, P.; Siefert, E. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Acid Mine Drainage Feedstocks. Apresentação, West Virginia University. 2025. Available online: https://wvwri.wvu.edu/files/d/94918daf-1eb3-4f49-88e4-2f9044e112d7/hoffman-ree-presentation-2025.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards zero-waste valorisation of rare-earth-containing industrial process residues: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifian, S.; Wang, L.N.H. Resin-based approaches for selective extraction and purification of rare earth elements: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Granados, M.; Valderrama, C.; Ayora, C.; Cortina, J.L. Recovery of rare earth elements from acidic mine waters: An unknown secondary resource. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2022, 810, 152258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Honaker, R.Q. Rare Earth Elements Recovery Using Staged Precipitation from a Leachate Generated from Coarse Coal Refuse. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 195, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Soldenhoff, K.; Ogden, M.D. Comparative study of the application of chelating resins for rare earth recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouardi, Y.; Virolainen, S.; Mouele, E.S.M.; Laatikainen, M.; Repo, E.; Laatikainen, K. The recent progress of ion exchange for the separation of rare earths from secondary resources—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 218, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhko, O.; van Deventer, J. Application of ion exchange technology for the upgrading and purification of the rare earth elements. In Proceedings of the Southern African Rare Earths 2nd International Conference 2024, Swakopmund, Namibia, 19–20 June 2024; The Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015; Volume 99, pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shokobayev, N.; Bouffier, C.; Dauletbakov, T.S. Rare earth metals sorption recovery from uranium in situ leaching process solutions. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Granados, M.; Valderrama, C.; Skoglund, N.; Ayora, C.; Cortina, J.L. Impact of functional group types in ion exchange resins on rare earth element recovery from treated acid mine waters. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.W.; Froisland, L.J.; Petersen, A.E. Rapid Separation of Heavy Rare-Earth Elements; Report of Investigations, 9564; Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- José, L.B.; Silva, G.C.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Pre-concentration and partial fractionation of rare earth elements by ion exchange. Miner. Eng. 2024, 205, 108477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.G.; Alonso, J.I.G. Separation of rare earth elements by anion-exchange chromatography using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as mobile phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1180, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; David, H.; Wang, N.-H.L. Two-zone ligand-assisted displacement chromatography for producing high-purity praseodymium, neodymium, and dysprosium with high yield and high productivity from crude mixtures derived from waste magnets. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3769–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, N.-H.L. Three-zone ligand-assisted displacement (LAD) chromatography method for producing high-purity neodymium, praseodymium, cerium, and lanthanum from mineral concentrates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 376, 133947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadeghsedghi, S.; Sauber, M.E.; Baghbanzadeh, M.; Dashtban Kenari, S.L.; Volchek, K.; Issa, S.; Mortazavi, S. Separation of rare earth elements using chelation-assisted electrodialysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Hao, H.; Guan, Z.; Wang, M.; Feng, Z.; Huang, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, C. One-stop decomplexation of Cu-EDTA and Cu capture in rare earth purification wastewater using NdFeB waste/H2O2 system: Performance, mechanism, and application. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 517, 163856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadani, M. Adsorption process modeling to reduce COD by activated carbon for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LANXESS Lewatit MDS 200 H [Internet]. Cologne: LANXESS Corporation; [cited 12 April 2025]. Available online: https://lanxess.com/en-us/products-and-brands/products/l/lewatit--mds-200-h (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Gustafsson, J.P. Visual MINTEQ 4.0 User Guide; Department of Sustainable Development, Environmental Science and Engineering, KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- CHEMPENDIX. Thermodynamic Data. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/chempendix/thermo (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Torres, J.; Kremer, C.; Kremer, E.; Domíguez, S.; Mederos Arrieta, M.A. The thermodynamics of the formation of Sm(III) mixed-ligand complexes carrying α-amino acids. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2003, 355, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikens, D.A.; Bahbah, F.J. Potentiometric characterization of aluminum aminopolycarboxylate chelonates. Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.S.S.; Ascenso, O.S.; Barros, M.T.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Pre-treatment of the paper pulp in the biodegradable chelating agents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Brien, R.D.; Summers, T.J.; Kaliakin, D.S.; Cantu, D.C. Correction: The solution structures and relative stability constant of lanthanide-EDTA complexes predicted from computation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 10263–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brücher, E.; Laurenczy, G. Aminopolycarboxylic of Rare Earths. 9. Kinetic Study of Exchange Reactions between Cerium (III)-Ethylenediaminetetraacetate Complex and Lead (II), Nickel (II) and Cobal(II) Ions. Inorg. Chem. 1983, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostromina, N.A.; Kholodnaya, G.S.; Kirillov, A.I. Investigation of praseodymium (3) complexing with ethylenediaminetetraacetate and diethylenetriaminepentaacetate. Koord. Khim. 1980, 6, 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Kolat, R.S.; Powell, J.E. The solid Rare Earth Chelates of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid. Inorg. Chem. 1961, 1, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, F.; De Stefano, C.; Gianguzza, A.; Piazzese, D.; Sammartano, S. Speciation of Poly-Amino Carboxylic Compounds in Seawater. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2003, 15, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Martell, A.E. NIST Critically Selected Stability Constants of Metal Complexes Database 46; Version 8.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2004. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/srd/46_8.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- José, L.B.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Recovery and separation of rare earth elements from an acid mine drainage-like solution using a strong acid resin. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.C.; Bertoli, A.C.; Duarte, H.A.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Recovery of rare earth elements from sulfate-rich acid mine water: Looking through the keyhole, the exchange reaction for cationic resin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.C.; Souza, C.; Ferreira, P.A.P.V.S.; Nazareth, L.P.T.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Effect of Fractionation Columns on the Elution of Rare Earth Elements Recovered from Acid Mine Drainage. Minerals 2024, 14, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.W. Selective Separation of Rare Earth Elements by Ion Exchange in an Iminodiacetic Resin. U.S. Patent No 6093376, 25 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jen, J.-F.; Chen, C.-S. Determination of metal ions as EDTA complexes by reversed-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1992, 270, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hamza, M.F.; Vincent, T.; Roux, J.-C.; Faur, C.; Guibal, E. Tuning the sorption properties of amidoxime-functionalized algal/polyethyleneimine beads for La(III) and Dy(III) using EDTA: Impact of metal speciation on selective separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zheng, X.; Ji, B.; Xu, Z.; Bao, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Mei, J.; Li, Z. Green recovery of rare earth elements under sustainability and low carbon: A review of current challenges and opportunities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H. Aluminium Speciation in Different Water Types. In Lake Gårdsjön: An Acid Forest Lake and Its Catchment; Ecological Bulletins: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1985; Volume 37, pp. 109–119. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20112940 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Hem, J.D. Graphical Methods for Studies of Aqueous Aluminum Hydroxide, Fluoride, and Sulfate Complexes; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1827-B; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, Z. Application of Temperature Regulation of Complex Stability Constants in Removal of Key Impurities from Lanthanum Oxide. J. Rare Earths, 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.S.S.; Sadeghi, S.M.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Separation and recovery of nickel, as a salt, from an EDTA leachate of spent hydrodesulphurization catalyst using precipitation methods. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).