Pore Evolution Characteristics and Accumulation Effect of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Gas Reservoirs in Northeastern Sichuan Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
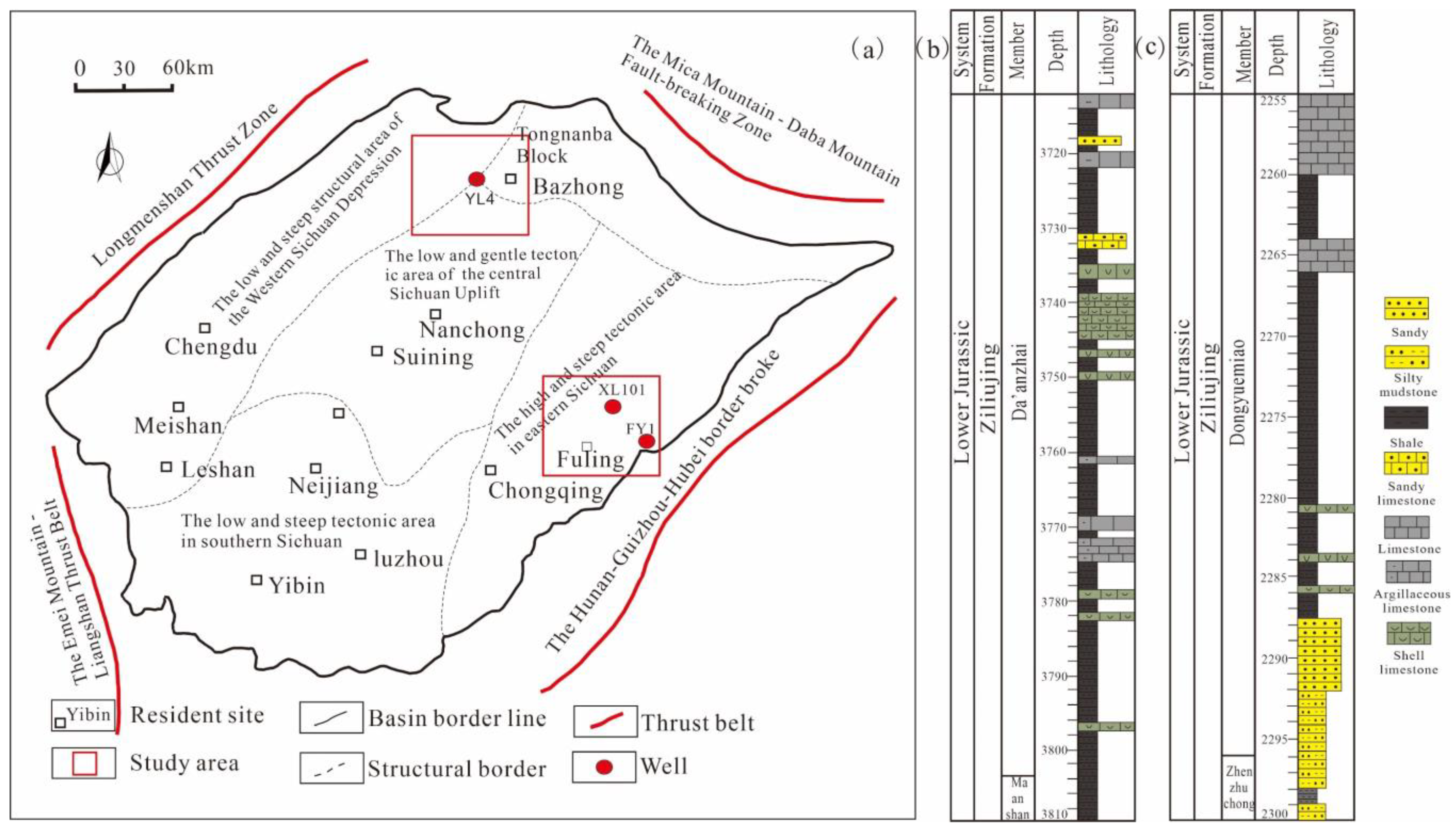
2. Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Samples
3.2. Experimental Methods
3.2.1. Thermal Simulation Experiment
3.2.2. Adsorption–Mercury Porosimetry Experiment
4. Results
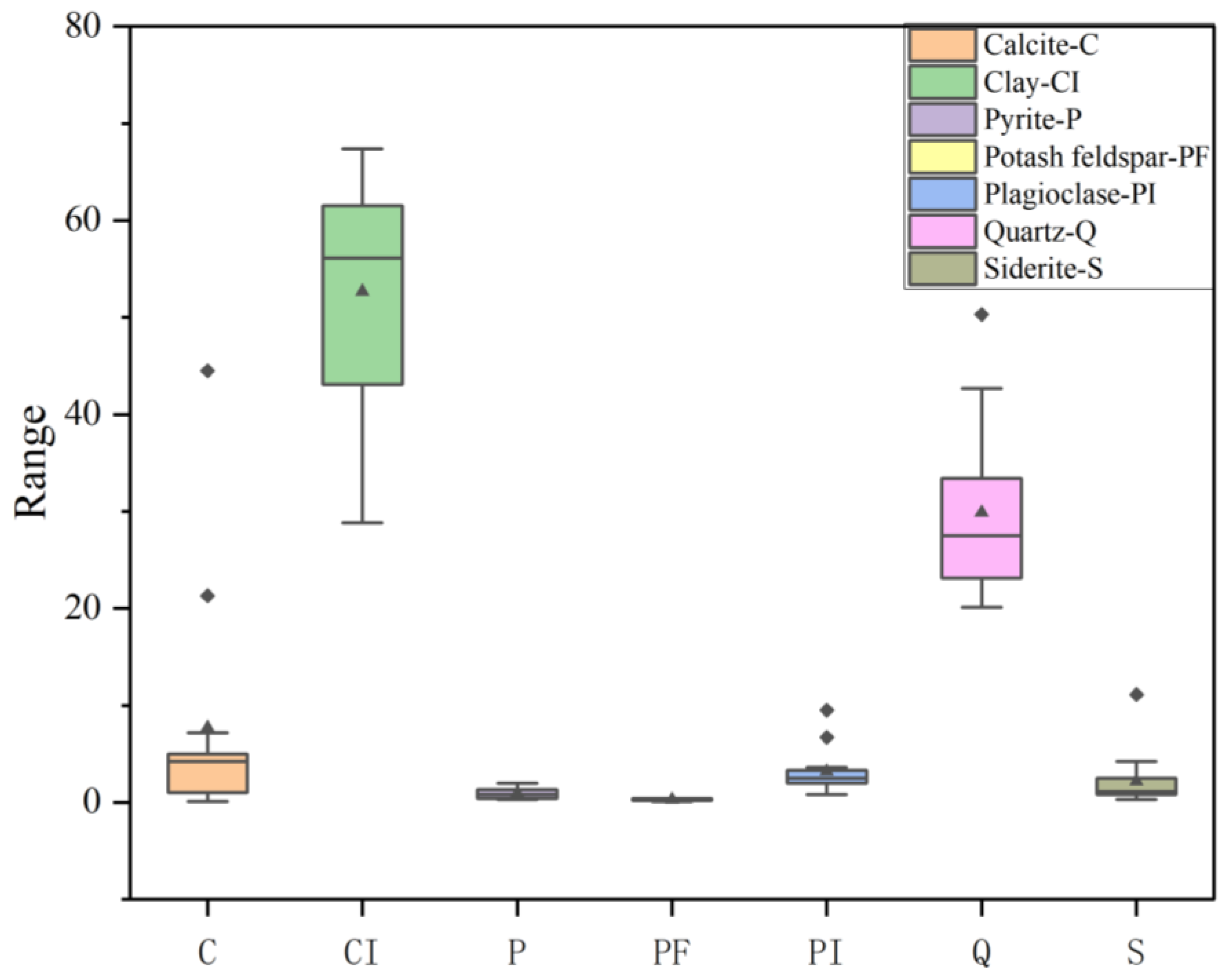
4.1. Organic Geochemistry and Mineral Composition Characteristics
4.1.1. Mineral Components
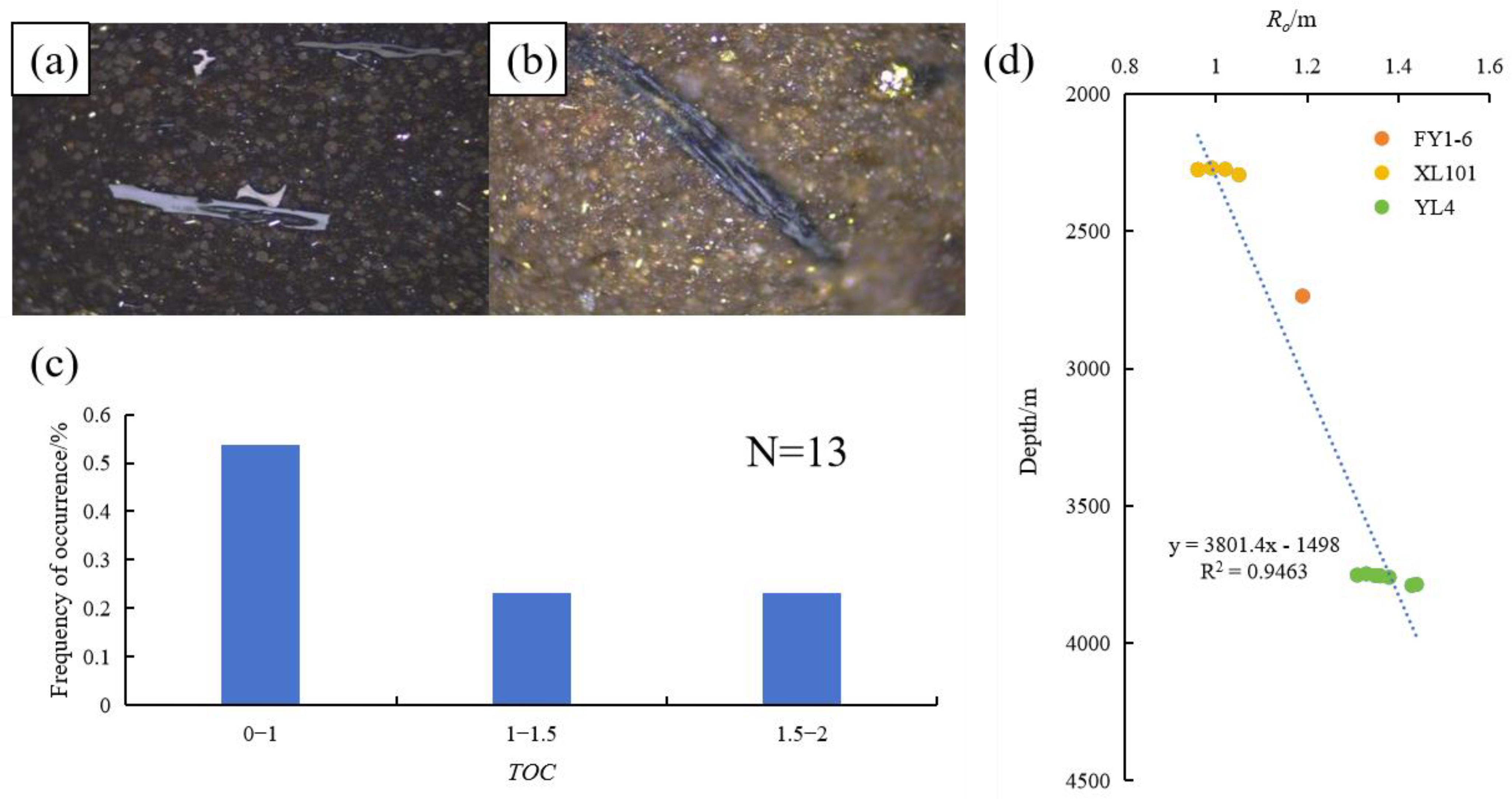
4.1.2. Geochemical Characteristics
4.2. Reservoir Pore Type
4.2.1. Organic Pores
4.2.2. Mineral Matrix Pores
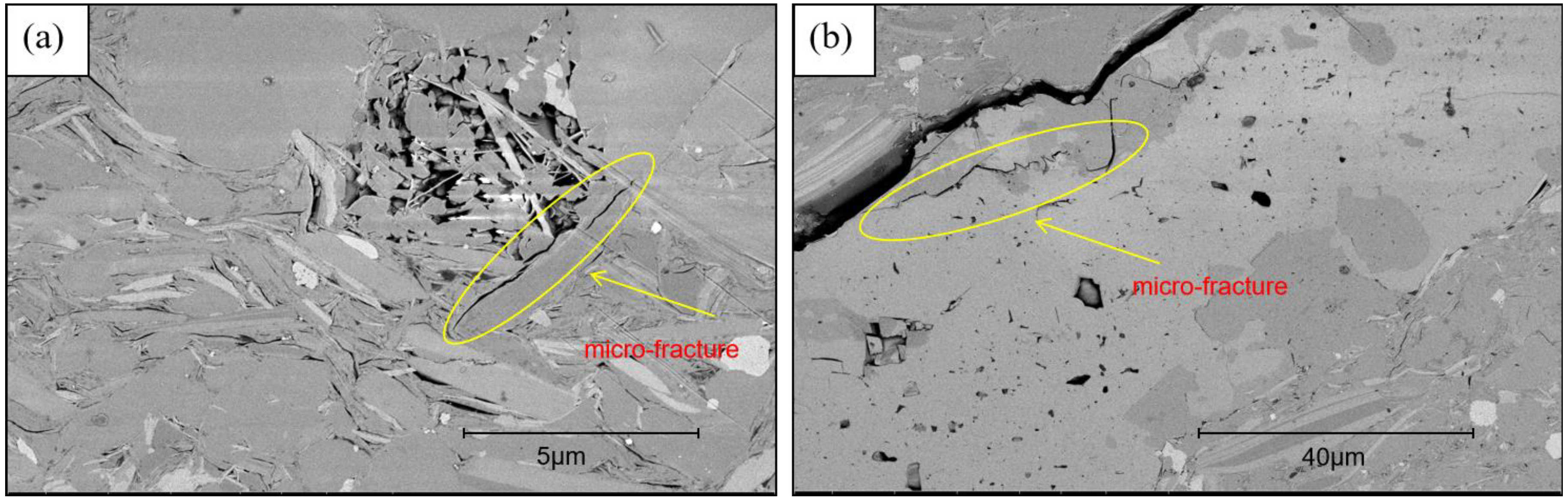
4.2.3. Microfractures
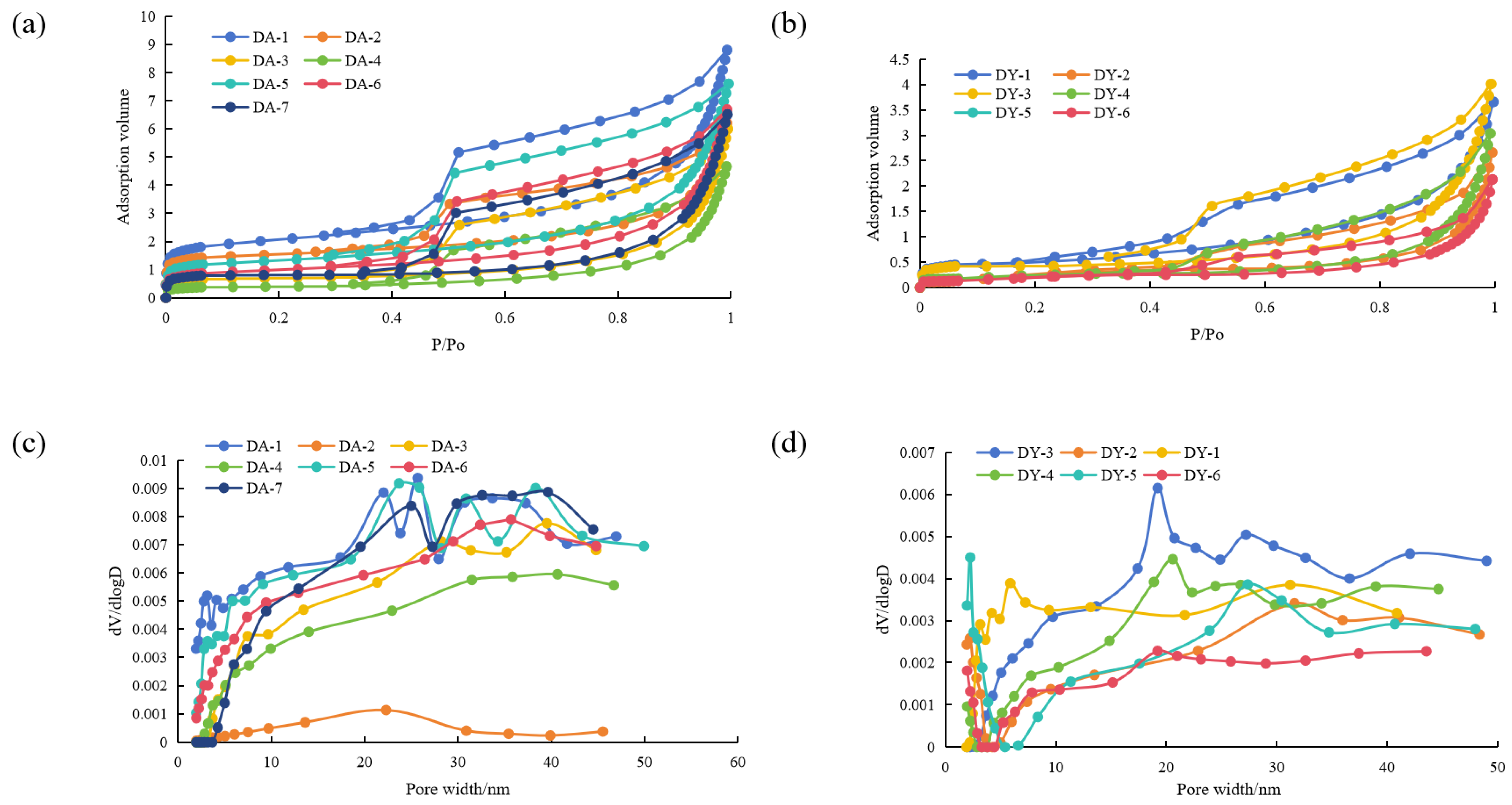
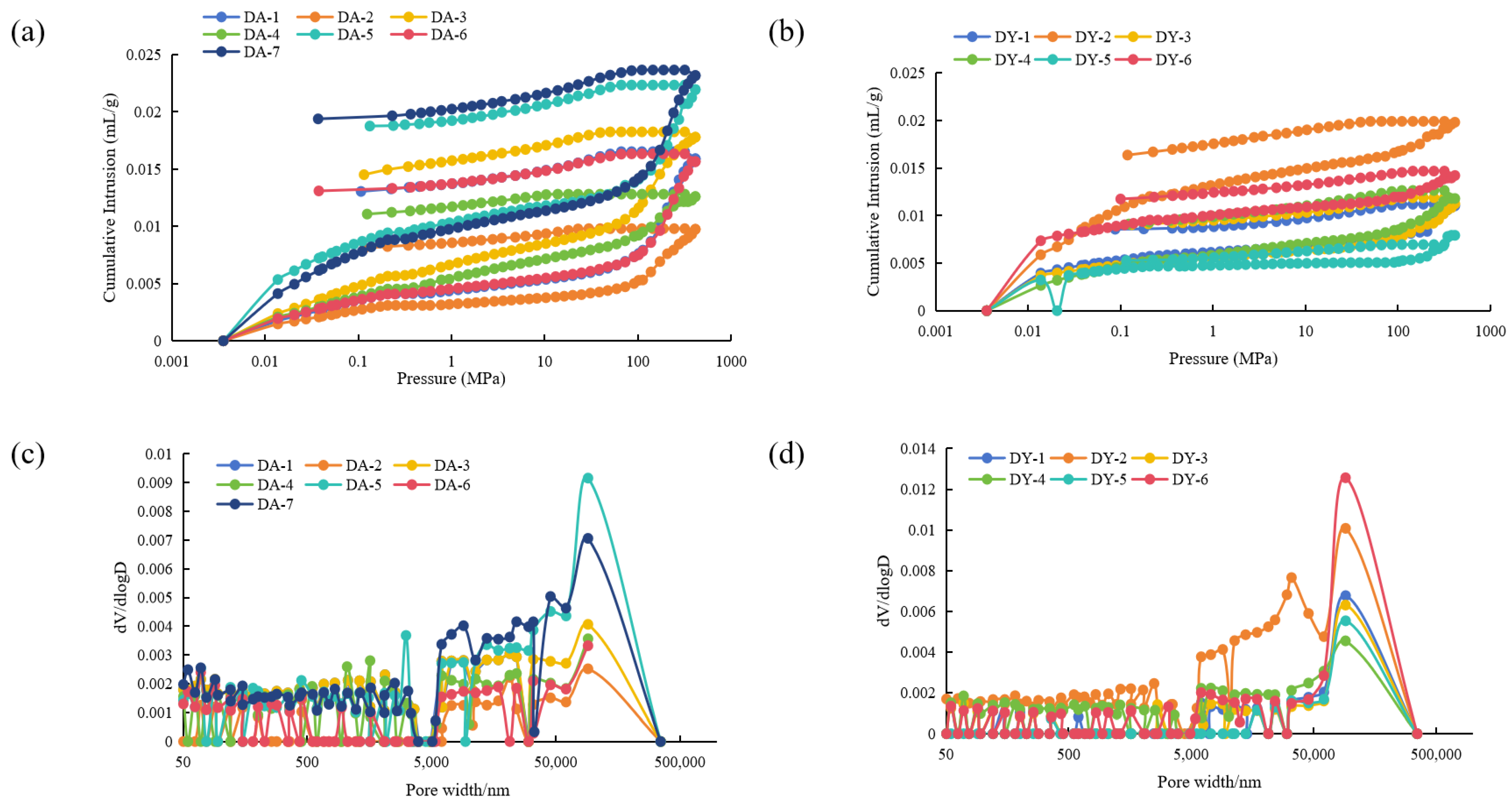
4.3. Full Aperture Experiment of Adsorption-Mercury Injection Joint Measurement of Shale Reservoir
4.3.1. Micropore and Mesopore Characteristics
4.3.2. Macropore Characteristics
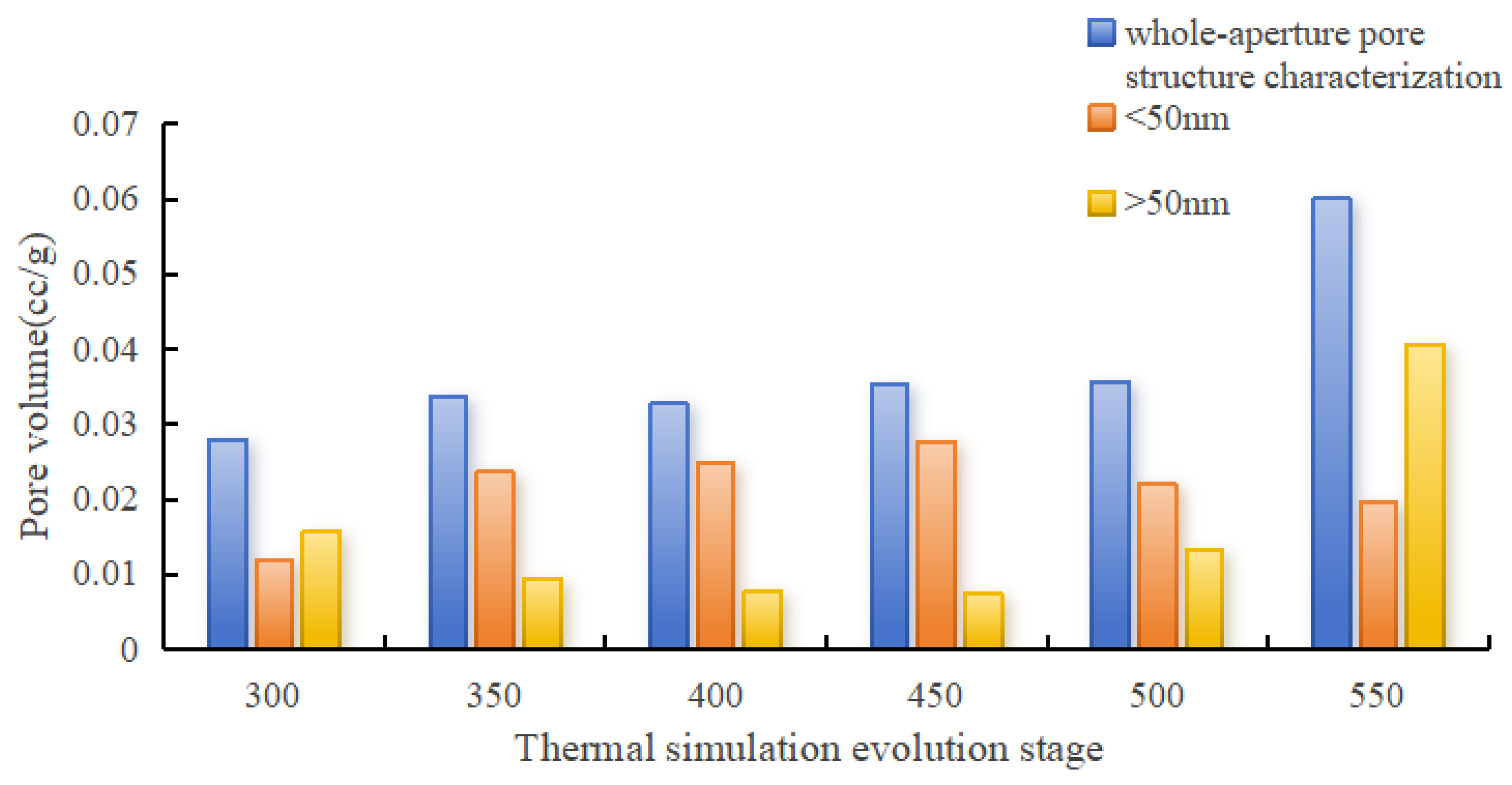
4.3.3. Comprehensive Comparison of Full Aperture Distribution
5. Discussion
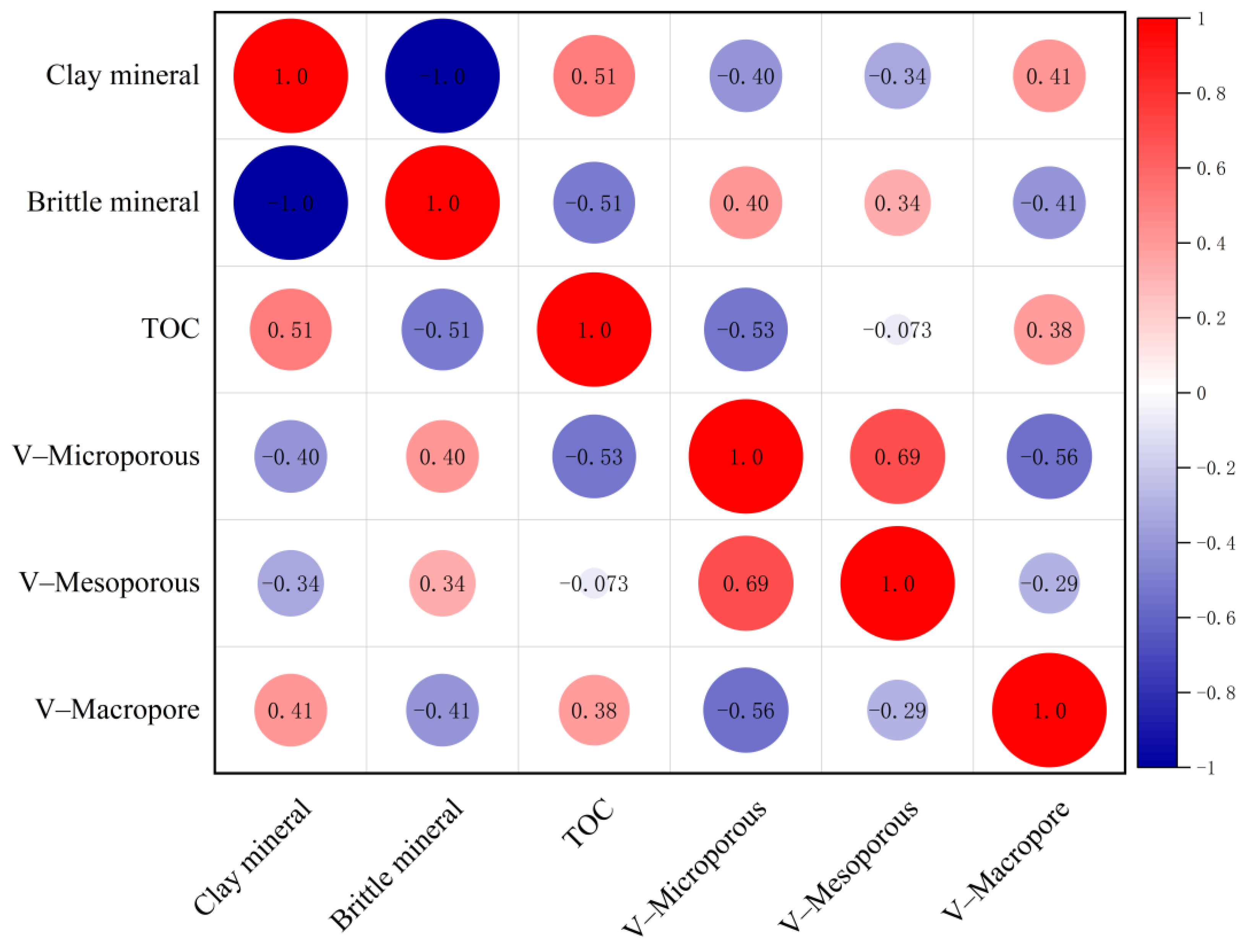
5.1. Effect of Hydrocarbon Generation and Mineral Composition on Pore Development of Continental Shale Reservoir
5.1.1. Differentiation Control of Mineral Composition on Pore Development
- (1)
- Clay minerals control the development of meso–macropores
- (2)
- Brittle minerals (quartz and carbonate) control the development of micro–mesopores
- (3)
- The evolution of organic matter has a dynamic adjustment effect on pores
5.1.2. Two-Stage Driving of Hydrocarbon Generation on Pore Evolution
5.2. Effect of Diagenesis on Pore Development of Continental Shale Reservoir
- (1)
- Compaction action
- (2)
- Clay mineral transformation
- (3)
- Dissolution
5.3. Source–Reservoir Evolution Process and Accumulation Effect of Continental Shale
- (1)
- Early Jurassic: Organic matter enrichment and reservoir prototype formation
- (2)
- Cretaceous: Hydrocarbon generation–diagenesis synergy and key period of hydrocarbon accumulation
- (3)
- Cenozoic: Structural adjustment and current gas reservoir pattern finalization
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The continental shale reservoirs in northeastern Sichuan are dominated by mesopores (10–50 nm), followed by macropores (5–50 μm), and micropores (<2 nm) account for the lowest proportion. Clay minerals and calcite synergistically control pore development: Interlayer pores (2–10 nm) of clay minerals contribute to high specific surface area, while calcite dissolution forms macropores. The “clay-carbonate synergistic pore-increasing” model was established to reveal the differential control of mineral assemblages on pore type and distribution, providing a mineralogical basis for “dessert” prediction.
- (2)
- Thermal simulation experiments show that the pore evolution has a threshold effect of 450 °C (corresponding to Ro ≈ 2.0%). Below 450 °C, the liquid product of hydrocarbon generation fills the pores, the micropore volume decreases, and the total pore volume decreases. Above > 450 °C, the organic matter is cracked to form shrinkage cracks (1–5 μm) and nanopores (10–50 nm), and the macropore volume increases. The two-stage dynamic characteristics of the pore evolution of continental shale are clarified, which provides theoretical support for the evaluation of deep shale gas reservoirs.
- (3)
- The Cretaceous is the key period of hydrocarbon accumulation. Hydrocarbon generation and dissolution diagenesis synergistically form high porosity and permeability reservoirs, and free gas accounts for more than 70%. The Cenozoic tectonic fine-tuning (uplift amplitude < 1000 m) maintains the integrity of the gas reservoir and forms a vertical differentiation pattern of “upper adsorption and lower free”. A dynamic accumulation model of “early rich source–Cretaceous high-quality reservoir–Freshman strong guarantee” is proposed, and the spatial and temporal coupling mechanism of structure–hydrocarbon generation–preservation is clarified, which guides the exploration to give priority to the development area of dissolution pores in the Da’anzhai section and the structural stability zone with Ro between 0.7% and 1.33%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Nie, H. Exploration potential of shale gas resources in china. Nat. Gas Ind. 2008, 28, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Strategic Conception of Accelerating Shale Gas Resources Investigation and Exploration and Development in China. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 2010, 31, 135–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Gao, B.; Zhao, J. Shale gas enrichment and high yield control factors of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in southeastern Sichuan Basin. Geol. Front. 2016, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Li, X.; Li, K.; He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W. Shale gas exploration and development in the Sichuan Basin: Progress, challenge and countermeasures. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, N.; Luo, Z. Technical status and challenges of shale gas development in Sichuan Basin, China. Petroleum 2015, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, Z.; Lai, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; He, J.; Zou, G.; Wang, P.; Li, Z. Brittleness characteristics and controlling factors of continental shale in the Da ‘anzhai Member of the Lower Jurassic Ziliujing Formation in northeastern Sichuan. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 366–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.J.K.; Bustin, R.M. Characterizing the shale gas resource potential of Devonian–Mississippian strata in the Western Canada sedimentary basin: Application of an integrated formation evaluation. AAPG Bull. 2008, 92, 87–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Dong, D.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Cheng, K. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and resource potential of shale gas in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2010, 37, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Gao, S.; Huang, J.; Guan, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Discussion on the exploration & development prospect of shale gas in the Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2015, 2, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Feng, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P. Source-reservoir characteristics and coupling evaluations for the Lower Jurassic lacustrine shale gas reservoir in the Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.-H.; Tang, X.-L.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.-X.; Yang, P.-P.; Yang, X.; Li, W.-B.; Hao, J. The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Deng, B.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y. Current situation, potential and prospect of shale gas exploration and development in Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 42–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Yu, R.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Kang, L.; Zhao, S. Prospects and challenges of shale gas development in China. Pet. Sci. Bull. 2023, 8, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, R.; Shen, B.; Wang, G.; Wan, C.; Wang, Q. Geological characteristics, resource potential, and development direction of shale gas in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2025, 52, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Nie, H. Geological characteristics of continental shale gas reservoir in the Jurassic Da’anzhai member in the northeastern Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Jarvie, D.M. Morphology, Genesis, and Distribution of Nanometer-Scale Pores in Siliceous Mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett Shale. J. Sediment. Res. 2009, 79, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q. Microscopic pore structure characteristics and controlling factors of Longmaxi Formation shale in Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2014, 34, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Ji, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, P. Characteristics of Microscopic Pore Structures and Their Effect Impacts on Methane Adsorption Capacity in Continental Shales. J4 2016, 22, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Jin, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, T.; Wang, G. Pore structure characteristics of shale reservoirs in Ziliujing Formation, Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 909–918. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Qi, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, F. Characteristics of Microscopic Pore Structures and Its Influencing Factors of the Qiongzhusi Formation Shales in the Southern Sichuan Basin. Acta Metall. Sin. 2018, 24, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Qu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yu, C. Differences of shale pore structure characteristics under different tectonic deformation in Fuling shale gas field. Acta Pet. Sin. 2025, 46, 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Shao, X.; He, W. Visualization of dynamic micro-migration of shale oil and investigation of shale oil movability by NMRI combined oil charging/water flooding experiments: A novel approach. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 165, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, R. Implications from marine shale gas exploration breakthrough in complicated structural area at high thermal stage: Taking Longmaxi Formation in welI JY1 as an example. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Duan, J.; Ji, C.; Duan, H. Discovery and theoretical and technical innovations of Yuanba gas field in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, G. An overview of the geology and production of the Fuling shale gas field, Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Geosci. 2020, 1, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z. Pore Structure and Gas Content Characteristics of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Reservoirs in Northeast Sichuan, China. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Jin, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Investigating the Pore Structure Characteristics and Reservoir Capacities of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Reservoirs in the Northeastern Sichuan Basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 886907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Liang, J. Geological conditions and accumulation patterns of shale gas accumulation in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations of Baima Syncline, Fuling Gas Field, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2024, 35, 1656–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Che, S.Q. Selection evaluation of shale gas in Pingqiao block of Fuling Gas Field. Pet. Geol. Eng. 2022, 36, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q. Formation conditions and exploration direction of shale gas in Fuling artesian well group, Sichuan Basin. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 43, 757–764. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.T.; Han, H.; Bai, W.H.; Xiao, S.; Wu, W.; He, C.; Wang, Y. Resource evaluation and favorable area optimization of shale oil and shale gas in the Da’anzhai member northeast Sichuan Basin, China. World Pet. Ind. 2024, 31, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Fu, X. Re-evaluation of continental shale gas exploration potential in Yuanba area. Sichuan Geol. J. 2020, 40, 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zou, H.; Hao, F.; Li, P.; Yang, S.; Song, Y. Discussion on reservoir characteristics and ultra-tight genesis of Xujiahe Formation in Yuanba area, Northeast Sichuan. Geology 2017, 91, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z. Natural gas exploration model of shallow tight sandstone in western Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 1997, 17–20+5+21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Peng, H. Characteristics of multi-source petroleum systems in Sichuan basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2002, 29, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, K.; Tang, Y.; Yang, F.; Mei, L.; Shen, C. Critical Tectonic Periods and the Response of Gas Accumulation in Non-Marine Tight Sandstone Reservoir in Yuanba-Tongnanba Area, Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 756–772. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Xuan, Q.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X. Pore structure evolution characteristics of continental shale in China as indicated from thermal simulation experiments. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 2159–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21650.2-2008; Pore Size Distribution and Porosity of Solid Materials by Mercury Porosimetry and Gas Adsorption—Part 2: Analysis of Mesopores and Macropores by Gas Adsorption. Chinese Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- NB/T 14008-2015; Analysis of Full-Scale Pore Size Distribution of Shale Both by Mercury Porosimetry and Adsorption. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Jiang, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, Z. Pore Structure and Gas-Bearing Properties of Typical Marine and Continental Shale Reservoirs in China; Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Xue, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Chang, J.; et al. Controlling factors of marine shale gas differential enrichment in southern China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z. Geological factors controlling shale gas enrichment and high production in Fuling shale gas field. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, D.; Shu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, A.; Wei, X.; Ni, K.; Zhao, P. Exploration, development, and construction in the Fuling national shale gas demonstration area in Chongqing: Progress and prospects. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2023, 10, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. Hydrocarbon accumulation characte-ristics and main controlling factors for Permian Maokou Formation in Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2022, 44, 639–646. [Google Scholar]




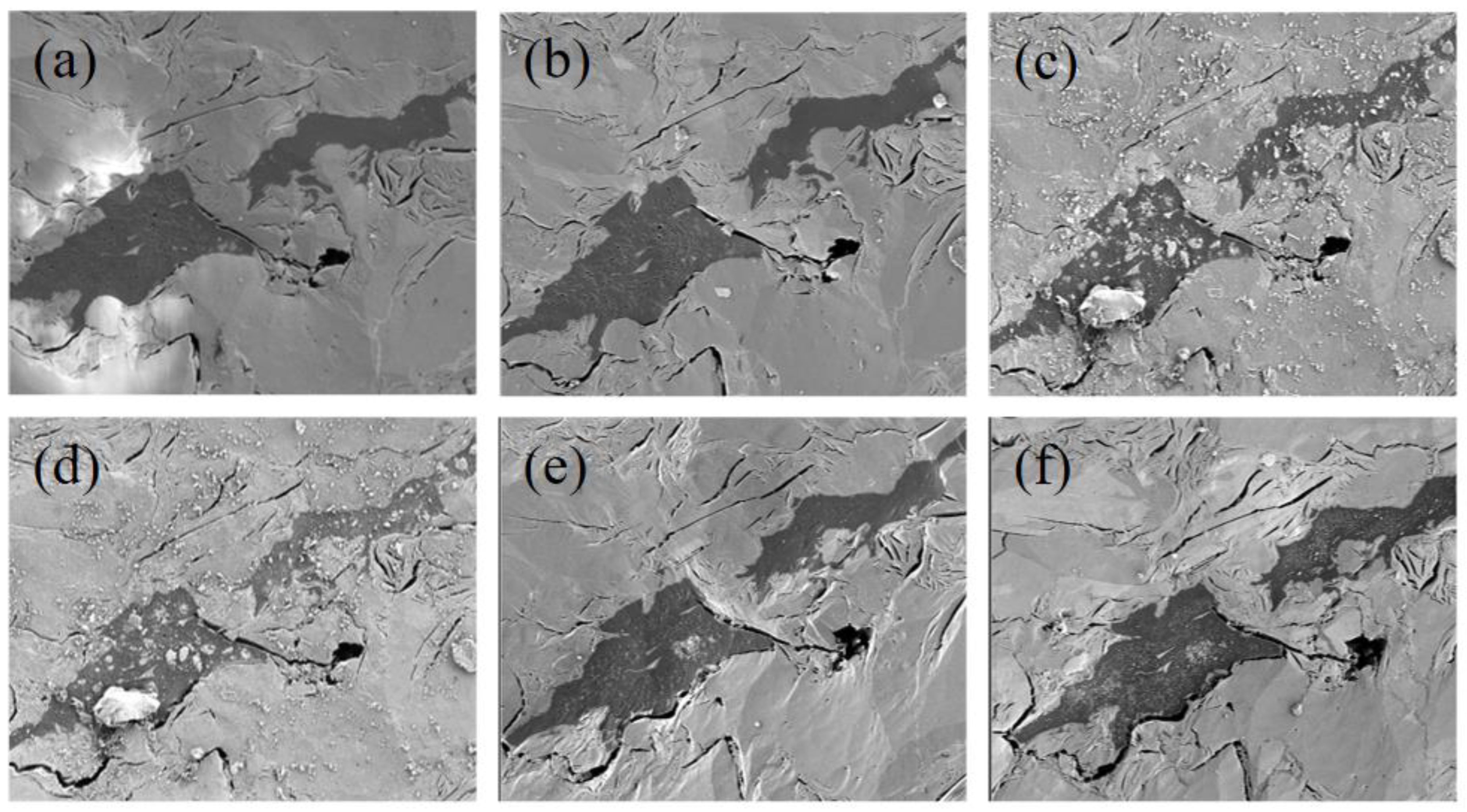

| Thermal Simulation Experiment Temperature Point/°C | Original Sample | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 550 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ro/% | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.15 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 3.1 |
| Mature stage of organic matter | Mature | High maturity | Over-mature | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Pore Evolution Characteristics and Accumulation Effect of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Gas Reservoirs in Northeastern Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060650
He X, Jiang T, Jiang Z, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang D. Pore Evolution Characteristics and Accumulation Effect of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Gas Reservoirs in Northeastern Sichuan Basin. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060650
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xinyi, Tao Jiang, Zhenxue Jiang, Zhongbao Liu, Yuanhao Zhang, and Dandan Wang. 2025. "Pore Evolution Characteristics and Accumulation Effect of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Gas Reservoirs in Northeastern Sichuan Basin" Minerals 15, no. 6: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060650
APA StyleHe, X., Jiang, T., Jiang, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., & Wang, D. (2025). Pore Evolution Characteristics and Accumulation Effect of Lower Jurassic Continental Shale Gas Reservoirs in Northeastern Sichuan Basin. Minerals, 15(6), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060650






