Reservoir Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in the Shimentan Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
Abstract
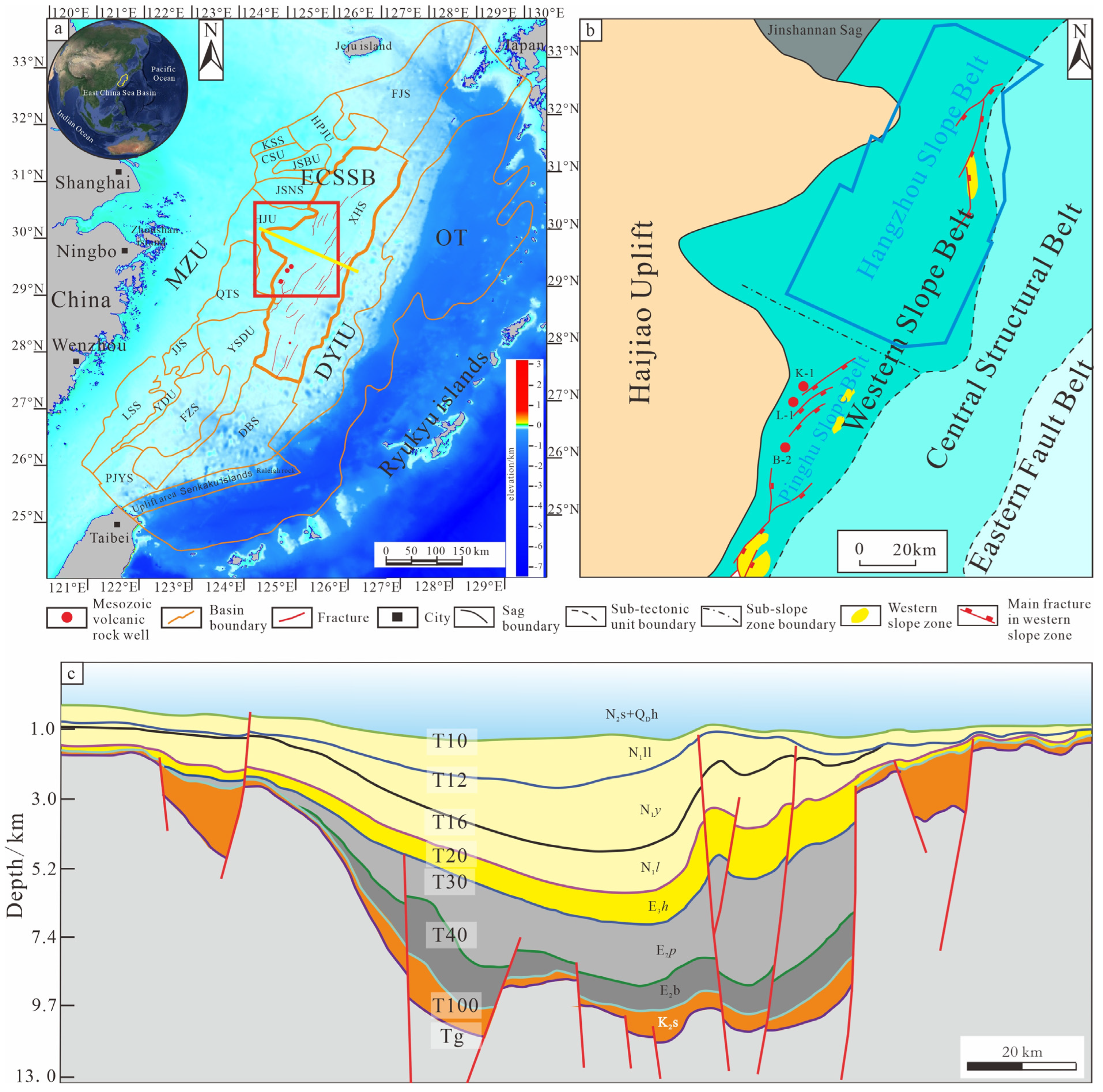
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting

3. Data and Methods
3.1. Thin Section Microscopy
3.2. Major Element Analysis
3.3. Coherence Cube Attribute Analysis
3.4. Dip Angle Attribute Analysis
3.5. Waveform Classification
4. Lithological Characteristics
4.1. Lithologic Composition
4.2. Well Logging Characteristics
5. Characteristics of Volcanic Facies
5.1. Classification of Volcanic Facies
5.1.1. Extrusive Facies
5.1.2. Eruptive Facies
5.1.3. Effusive Facies
5.2. Characteristics of Seismic Facies
6. Characteristics of Volcanic Edifices
6.1. Types of Volcanic Edifices
6.1.1. Stratified Volcanic Edifice (SVE)
6.1.2. Pseudostratified-Massive Volcanic Edifice (PSMVE)
6.1.3. Massive Volcanic Edifice (MVE)
6.2. Seismic Facies Characteristics of Volcanic Edifices
7. Interpretation of Volcanic Edifices and Volcanic Facies
7.1. Interpretation of Volcanic Conduits
7.2. Interpretation of Volcanic Edifices
7.3. Interpretation of Volcanic Facies
7.4. Analysis of Reservoir Potential
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schutter, S.R. Hydrocarbon occurrence and exploration in and around igneous rocks. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 214, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Meng, F.C.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.T. Discussion on the formation mechanism ofvolcanic oil and gas reservoirs. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.F.; Tian, Z.W.; Gao, Y.F.; Dai, X.J. Review of volcanic reservoir geology in China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 232, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Yang, H.F.; Wang, Q.B.; Shan, X.L.; Zhu, H.T.; Tang, H.F.; Hou, M.C.; Liu, X.J. Progress in exploration of volcanic oil and gas reservoirs. Earth Sci. 2025, 50, 363–376. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.Q. Volcanic rocks as prolific gas reservoir: A case study from the Qingshen gas field in the Songliao Basin, NE China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2008, 25, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhao, W.Z.; Jia, C.Z.; Zhu, R.K.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, X.J. Formation and distribution of volcanic hydrocarbon reservoirs in sedimentary basins of China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2008, 35, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.H.; Yin, C.H.; Liu, J.J.; Zhu, Y.K.; Lu, J.M.; Li, J.H. Formation mechanism of in-situ volcanic reservoirs in eastern China: A case study from Xushen gasfield in Songliao Basin. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2998–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Xu, C.Q.; Huang, Z.; Shan, X.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Yi, J. Enhanced Formation Conditions of the Large-Scale Volcanic Reservoir in the BZ8-3S Large Volcanic Structure in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2025, 50, 388–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Jin, L.C.; Lei, D.W.; Jia, X.Y.; Wang, C.M. Seismic Response Feature and Distribution Law of Carboniferous Volcanic Rock in Beisantai Uplift. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2008, 30, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, A.; Nicol, A.; Barrier, A.; Wang, H. Paleogeography and volcanic morphology reconstruction of a buried monogenetic volcanic field (part 2). Bull. Volcanol. 2019, 81, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.E.; Schofield, N.; Brown, D.J.; Jolley, D.W.; Reid, A. 3D seismic imaging of the shallow plumbing system beneath the Ben Nevis Monogenetic Volcanic Field: Faroe–Shetland Basin. J. Geol. Soc. 2017, 174, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessler, A.M.; Lowe, D.R. Initial generation of sand across climate zones of the Mojave, Sierra Nevada, and Klamath Batholiths in California, U.S.A. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 348, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruski, C.I. Seismic recognition of igneous rocks of the Deepwater Taranaki Basin, New Zealand, and their distribution. New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 2020, 63, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Single, R.T.; Jerram, D.A. The 3D facies architecture of flood basalt provinces and their internal heterogeneity: Examples from the Palaeogene Skye Lava Field. J. Geol. Soc. 2004, 161, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planke, S.; Symonds, P.A.; Alvestad, E.; Skogseid, J. Seismic volcanostratigraphy of large-volume basaltic extrusive complexes on rifted margins. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 19335–19351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Wang, P.J.; Song, L.Z.; Zhang, H.H.; Yuan, W.; Yang, D. Seismie volcanostratigraphy of Yingcheng formationin the Songliao basin, Cretaceous, NE China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.F.; Hu, J.; Li, J.H.; Chen, M.F.; Gao, Y.F. Geological significances of typical seismie facies of volcanic rocks of the rifted period in Songliao Basin, NE China. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 53, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.F.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, H.C.; Hu, J.; Dai, X.J.; Goh, T.L.; Miao, M.; Xu, B.Y. Possible geological interpretation of the volcanic seismic facies based on volcanostratigraphy elements: A case analysis of the Yingcheng Formation in the Changling Fault Depression, Songliao Basin, NE China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 225, 211668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.J.; Tang, H.F.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, P.J.; Xu, C.M.; Kong, T.; Zhao, T.L.; Wang, P.J. Facies Architecture Model of the Shimentan Formation Pyroclastic Rocks in the Block-T Units, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin, and its Exploration Significance. Acta Geol. Sin.—Engl. Ed. 2019, 93, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Tang, H.F.; Wang, P.J.; Xu, H.Y.; Zhao, P.J. Characteristics of volcanic reservoirs in Cretaceous Shimentan Formation in Xihu Sag. China Offshore Oil Gas 2025, 37, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Xu, H.Z.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wang, J.; He, X.J. Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China Sea basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 675–691. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.L.; Zhong, K.; Fu, X.W.; Chen, C.F.; Zhang, M.Q.; Gao, S. The formation and evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: A new view. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 89–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.; Yu, Y.X.; Liu, J.S.; Jiang, Y.M.; Tang, X.J.; Chen, S.; Yu, L. Main controlling factors of the central inversional structure belt and the development of Ningbo anticline in Xihu sag, East China Sea Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.J.; Zhong, R.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; He, X.J.; Dai, Y. Segmentation and Genetie Mechanism of Pinghu Fault Zone in Xihu Sag Slope Area, East China Sea Basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2024, 54, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Zou, W.; Liu, J.S.; Tang, X.J.; He, X.J. Genetic Mechanism of Inversion Anticline Structure at the End of Miocene inXihu Sag, East China Sea: A New Understanding of Basement Structure Difference. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 968–979. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, B.; Sun, A.; Guo, T. Risk assessment of mantle-derived CO2 in the East China Sea basins, China. AAPG Bull. 2023, 107, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahraa, A.; Ghosh, D. Seismic Waveform Classification of Reservoir Properties Using Geological Facies Through Neural Network; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.C.; Zhang, T.; Tang, H.F.; Lu, B.L.; Dong, Z. Integrated Identification of Lithology Using Seismic and Magnetic Anomaly Data for Granite and Gneiss Basement: A Case Study of the LiShui Depression in the East China Sea Basin. Minerals 2023, 13, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.F.; Bian, W.H.; Wang, P.J.; Gao, Y.F.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.S. Classification and Model of Volcanie Facies in the Basin. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2023, 53, 1651–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Neuendorf, K.K.E.; Mehl, J.P., Jr.; Jackson, J.A. Glossary of Geology; American Geological Institute: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2011; p. 800. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.H.; Li, F.; Shen, Y.J.; Feng, T.H. The seismic reflection features of volcanic stratum and the seismic-geologicalinterpretation:The case study in Xujiaweizi faulted depression, Songliao basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.F.; Li, R.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Feng, X.H.; Wang, L.Y. Textural characteristics of volcanic strata and its constraint to impedance inversion. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 620–627. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.H.; Yin, C.H.; Qi, J.S.; Dong, J.H. Main factors controlling hydrocarbon accumulation in large volcanic gas fields: A case study of the Qingshen gas field in the Songliao basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.B.; Fan, X.P.; Leng, Q.L.; Zhang, T.T. Volcanic reservoir characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation control factors of rift depressions in southern Songliao Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.G.; Zhang, G.C.; Huang, S.B.; Shan, X.L.; Li, J.H. Formation of large-and medium-sized Cretaceous volcanic reservoirs in the offshore Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | LOI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-1-1 | 61.40 | 17.77 | 2.74 | 2.56 | 0.48 | 1.98 | 3.74 | 1.13 | 0.71 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 7.13 | 99.75 |
| K-1-2 | 60.04 | 18.41 | 2.66 | 2.73 | 0.46 | 2.21 | 3.95 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 7.62 | 99.77 |
| K-1-3 | 63.14 | 18.72 | 1.70 | 1.76 | 0.25 | 1.95 | 4.18 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 6.45 | 99.88 |
| K-1-4 | 63.49 | 17.06 | 3.96 | 1.98 | 0.54 | 1.74 | 3.23 | 1.73 | 0.58 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 5.60 | 100.01 |
| L-1-1 | 66.14 | 16.13 | 2.87 | 1.53 | 1.47 | 0.63 | 2.72 | 4.26 | 0.97 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 2.93 | 99.87 |
| L-1-2 | 62.82 | 15.53 | 5.19 | 1.54 | 1.99 | 1.06 | 1.83 | 6.48 | 1.17 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 1.57 | 99.63 |
| L-1-3 | 61.91 | 17.41 | 3.72 | 1.41 | 2.05 | 1.35 | 2.85 | 3.38 | 1.04 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 4.38 | 99.74 |
| L-1-4 | 63.68 | 15.73 | 4.67 | 1.19 | 2.32 | 0.62 | 2.38 | 6.13 | 1.16 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 1.68 | 99.87 |
| L-1-5 | 64.55 | 15.57 | 2.93 | 1.41 | 1.95 | 1.17 | 1.93 | 6.46 | 1.25 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 2.11 | 99.64 |
| L-1-6 | 58.46 | 23.81 | 1.64 | 0.66 | 0.39 | 1.35 | 3.96 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 8.25 | 99.76 |
| L-1-7 | 65.03 | 14.92 | 3.99 | 1.50 | 1.80 | 1.01 | 1.63 | 6.52 | 1.19 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 1.86 | 99.73 |
| Facies | Subfacies | Microfacies | Lithology | Fabric and Structural Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusive | Subaerial lava dome | Core | Lava | Irregular columnar joints in the upper part; regular joints in the mid-lower sections |
| In situ autoclastic accumulation | Autoclastic and volcaniclastic breccia association | Massive structure, composed of in situ fragmented material | ||
| Eruptive | Pyroclastic flow | Proximal belt | Welded volcaniclastic breccia/tuff | Well-developed cross-bedding and pseudo-flow structures |
| Base surge | Proximal belt | Volcaniclastic breccia and tuff | Pseudo-flow structures, parallel bedding, cross-bedding, or graded bedding | |
| Distal belt | Tuff | Parallel, horizontal, and graded bedding | ||
| Effusive | Subaerial lava flow | Simple lava flow | Lava | Stratified stacking with vertical texture zoning: vesicular zone, dense core, and vesicle-rich top; accompanied by columnar and shrinkage joints |
| Facies | Geometry | Frequency | Amplitude | Continuity | Reflection Configuration Pattern | Seimic Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base surge | Tabular | High | Medium to strong | Semi-continuous to continuous | Parallel to subparallel reflection |  |
| Simple lava flow | Tabular to lenticular | Low | Medium to strong | Semi-continuous | Progradational reflection |  |
| Compound lava flow | Tabular to wedge-shaped | Low to medium | Medium to strong | Semi-continuous to discontinuous | Progradational reflection |  |
| Lava dome | Mound-shaped | Medium to high | Medium to weak (occasionally strong) | Discontinuous | Chaotic reflection |  |
| Volcanic conduit | Pipe-like | Medium to high | Medium to weak (occasionally strong) | Discontinuous | Chaotic reflection |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y. Reservoir Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in the Shimentan Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060647
Liu Y. Reservoir Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in the Shimentan Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060647
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang. 2025. "Reservoir Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in the Shimentan Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin" Minerals 15, no. 6: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060647
APA StyleLiu, Y. (2025). Reservoir Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Potential of Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in the Shimentan Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Minerals, 15(6), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060647





