Challenges and Opportunities for the Development of Urban Mining in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What is the current state of knowledge production regarding urban mining in Brazil, and how does it compare with international trends?
- What are the main technological routes being explored or required for urban mining in Brazil, and what are the challenges for their effective appropriation in the national context?
- To what extent is the current Brazilian legislation effective in driving urban mining, and what are the main legal and regulatory obstacles that need to be overcome?
- How do the challenges and opportunities for urban mining in Brazil compare with those observed in the European context, considering their distinct socioeconomic and environmental drivers?
2. Methodology
2.1. Eligibility Criteria (PRISMA Item 6)
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy (PRISMA Items 7 and 8)
2.3. Selection of Sources of Evidence (PRISMA Item 9)
2.4. Data Charting and Synthesis of Results (PRISMA Items 10, 11, 13)
3. Fundamentals of Urban Mining
4. Processes Used in Urban Mining
4.1. Hydrometallurgy
4.1.1. Leaching
4.1.2. Precipitation
4.1.3. Solvent Extraction
4.1.4. Electrodeposition
4.2. Pyrometallurgy
4.3. Biohydrometallurgy
4.4. Comparative Analysis Between the Processes
5. Perspectives of Urban Mining: A Comparison Between Brazil and the European Union Context
6. Knowledge Production and Technological Appropriation on Urban Mining in Brazil
7. Legal Dimension of Urban Mining: Effectiveness of Brazilian Legislation and Obstacles to Overcome
Critical Discourse Analysis
8. Conclusions
9. On the Use of Artificial Intelligence
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver Nanoparticles |
| ATPS | Aqueous Two-Phase Systems |
| CDA | Critical Discourse Analysis |
| CDW | Construction and Demolition Waste |
| CE | European Conformity |
| DEMATEL | Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory |
| DESs | Deep Eutectic Solvents |
| EEC | European Economic Community |
| ELV | End-of-Life Vehicles |
| EU | European Union |
| FAAS | Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| ILs | Ionic Liquids |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LCD | Liquid Crystal Display |
| LEDs | Light Emitting Diodes |
| LIBS | Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy |
| MCDA | Multi-Criteria Decision Aid |
| MNHM | Magnetic Nanohydrometallurgy |
| MRRJ | Metropolitan Region of Rio de Janeiro |
| NCA | Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum |
| PARAFAC | Parallel Factor Analysis |
| PCBs | Printed Circuit Boards |
| NSWP | National Solid Waste Policy |
| PPILs | Pseudo-Protic Ionic Liquids |
| REEs | Rare Earth Elements |
| RLSs | Reverse Logistics Systems |
| RoHS | Restriction of Hazardous Substances |
| RPMs | Rare and Precious Metals |
| SCFE | Supercritical Fluid Extraction |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SWT | Supercritical Water Technology |
| TSS | Tin Stripping Solution |
| USW | Urban Solid Waste |
| WEEE | Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment |
| WPCBs | Waste Printed Circuit Boards |
References
- Erdiaw-Kwasie, M.O.; Abunyewah, M.; Baah, C. A systematic review of the factors—Barriers, drivers, and technologies—Affecting e-waste urban mining: On the circular economy future of developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazançoglu, Y.; Ada, E.; Ozturkoglu, Y.; Ozbiltekin, M. Analysis of the barriers to urban mining for resource melioration in emerging economies. Resour. Pol. 2020, 68, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, P.; Ncube, A.; Casazza, M.; Passaro, R. Toward circular and socially just urban mining in global societies and cities: Present state and future perspectives. Front. Sustain. Cities 2022, 4, 930061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, Y.A.; Govindan, K.; Sasongko, N.A.; Hasibuan, Z.A. The critical success factors for sustainable resource management in circular economy: Assessment of urban mining maturity level. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 469, 143084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro-Salim, O. Urban mining of e-waste management globally: Literature review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 9, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udage Kankanamge, A.K.S.; Erdiaw-Kwasie, M.O.; Abunyewah, M. Towards a Taxonomy of E-Waste Urban Mining Technology Design and Adoption: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunseitan, O.A.; Schoenung, J.M.; Saphores, J.D.M.; Shapiro, A.A. The electronics revolution: From e-wonderland to e-wasteland. Science 2009, 326, 670–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Paterok, K.; Banerjee, A.; Saluja, M.S. Potential and relevance of urban mining in the context of sustainable cities. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2017, 29, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.H.; Giese, E.C.; Ribeiro-Duthie, A.C.; Lins, F.A.F. Sustainability and the circular economy: A theoretical approach focused on e-waste urban mining. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contador, L.S.; Freire, L.S.; Xavier, L.H. Paradoxes of electronic waste reverse logistics and urban mining in Brazil. Rev. Tecnol. Soc. 2022, 18, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Yamamoto, T.; McDonald, R.; D’Angelo, E.; Althaf, S.; Bel, G.; Deubzer, O.; Fernandez-Cubillo, E.; Forti, V.; et al. International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR). Global E-waste Monitor. 2024. Available online: https://ewastemonitor.info/the-global-e-waste-monitor-2024/ (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABNT NBR 10004; Resíduos Sólidos—Classificação. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2004.
- ABNT NBR 16156; Resíduos de Equipamentos Eletroeletrônicos—Requisitos Para Atividade de Manufatura Reversa. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013.
- ABNT NBR 15833; Manufatura Reversa—Aparelhos de Refrigeração. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018.
- ABNT NBR IEC 63000; Documentação Técnica Para a Avaliação de Produtos Elétricos e Eletrônicos Com Relação à Restrição de Substâncias Perigosas (RoHS). ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019.
- União Europeia. Conselho. Diretiva 75/442/CEE, de 15 de Julho de 1975, Relativa aos resíduos. In Jornal Oficial das Comunidades Europeias, L 194; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- União Europeia. Conselho. Diretiva 91/156/CEE, de 18 de Março de 1991, Que Altera a Diretiva 75/442/CEE relativa aos resíduos. In Jornal Oficial das Comunidades Europeias, L 78; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- União Europeia. Parlamento Europeu. Conselho. Diretiva 2006/12/CE, de 5 de abril de 2006, relativa aos resíduos. In Jornal Oficial da União Europeia, L 114; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- União Europeia. Parlamento Europeu. Conselho. Diretiva 2008/98/CE, de 19 de novembro de 2008, relativa aos resíduos e que revoga certas Diretivas. In Jornal Oficial da União Europeia, L 312; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- União Europeia. Parlamento Europeu. Conselho. Diretiva 2012/19/UE, de 4 de julho de 2012, relativa a resíduos de equipamentos elétricos e eletrónicos (REEE). In Jornal Oficial da União Europeia, L 197; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil. Lei nº 12.305, de 2 de Agosto de 2010. Institui a Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos; Altera a Lei no 9.605, de 12 de Fevereiro de 1998; e Dá Outras Providências. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, DF, 03 Ago. 2010. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2007-2010/2010/lei/l12305.htm (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Brasil. Decreto nº 10.240, de 12 de Fevereiro de 2020. Acordo Setorial Para Implementação de Sistema de Logística Reversa de Produtos Eletroeletrônicos e Seus Componentes de Uso Doméstico. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2019-2022/2020/decreto/D10240.htm (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Brasil. Decreto nº 10.657, de 24 de março de 2021. Institui a Política de Apoio ao Licenciamento Ambiental de Projetos de Investimentos Para a Produção de Minerais Estratégicos—Pró-Minerais Estratégicos, Dispõe Sobre Sua Qualificação no Âmbito do Programa de Parcerias de Investimentos da Presidência da República e Institui o Comitê Interministerial de Análise de Projetos de Minerais Estratégicos. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2019-2022/2021/Decreto/D10657.htm (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Brasil. Decreto nº 10.936, de 12 de Janeiro de 2022. Regulamenta Dispositivos da Lei nº 12.305, de 2 de Agosto de 2010, Que Institui a Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2019-2022/2022/decreto/d10936.htm (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Brasil. Decreto nº 11.413, de 13 de Fevereiro de 2023. Institui o Certificado de Crédito de Reciclagem de Logística Reversa, o Certificado de Estruturação e Reciclagem de Embalagens em Geral e o Certificado de Crédito de Massa Futura, no Âmbito dos Sistemas de Logística Reversa de Que Trata o Art. 33 da Lei nº 12.305, de 2 de Agosto de 2010. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2023-2026/2023/Decreto/D11413.htm (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Fairclough, N. Critical Discourse Analysis: The Critical Study of Language; Longman: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, A.B., Jr.; Martins, F.P.; Cezarino, L.O.; Liboni, L.B.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. The sustainable development goals, urban mining, and the circular economy. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2023, 16, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.H.; Ottoni, M.; Abreu, L.P.P. A comprehensive review of urban mining and the value recovery from e-waste materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Q.; Chiang, J.F.; Li, J. Recovery of rare and precious metals from urban mines—A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, M.L.; Rizki, I.N.; Ullah, N. Recent advances in urban mining technology: A focus on electronic waste recycling potential in Indonesia. Clean. Waste Syst. 2025, 10, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunsu, C.; Petranikova, M.; Gergorić, M.; Ekberg, C.; Retegan, T. Reclaiming rare earth elements from end-of-life products: A review of the perspectives for urban mining using hydrometallurgical unit operations. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.F.; Pereira, M.M.; Leão, V.A. Acid Leaching of Rare Earth Elements Present in Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment: A Brief Review. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2022, 14, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, S.; Panghal, A.; Majid, I.; Mallick, S. Urban mining: Recovery of metals from printed circuit boards. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 9731–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodius, D.; Gandha, K.; Mudring, A.V.; Nlebedim, I.C. Sustainable Urban Mining of Critical Elements from Magnet and Electronic Wastes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Patel, A.; Kumar, S.; Pau-Loke, S. Urban mining of obsolete computers by manual dismantling and waste printed circuit boards by chemical leaching and toxicity assessment of its waste residues. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, A.B., Jr.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Cobalt Recovery from Li-Ion Battery Recycling: A Critical Review. Metals 2021, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, L.; Amato, A.; Fonti, V.; Ubaldini, S.; De Michelis, I.; Kopacek, B.; Vegliò, F.; Beolchini, F. Cross-current leaching of indium from end-of-life LCD panels. Waste Manag. 2015, 42, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.P.; Benvenuti, J.; Espinosa, D.C.R. A review of the current progress in recycling technologies for gallium and rare earth elements from light-emitting diodes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.A.G.; Caldas, M.P.K.; Moraes, V.T.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Recovering metals from motherboard and memory board waste through sulfuric leaching. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Singh, K.K.; Singh, R. Hydrometallurgical recovery of manganese and nickel and isolation of tantalum from obsolete tantalum capacitor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Tran, N.T.T.; Song, M.H.; Pham, T.P.T.; Yun, Y.S. Thiosulfate-based leaching for eco-friendly urban mining: Recent developments and challenges. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, J.; Tan, Q.; Liu, L.; Dong, Q. Green Process of Metal Recycling: Coprocessing Waste Printed Circuit Boards and Spent Tin Stripping Solution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, M.P.K.; Martins, T.A.G.; Moraes, V.T.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Synthesis of Ag nanoparticles from waste printed circuit board. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.M.N.O.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Botelho Júnior, A.B.; Tenório, J.A.S. NCA Type Lithium Ion Battery: A Review of Separation and Purification Technologies for Recycling Metals. J. Sustain. Metall. 2024, 10, 1036–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunsu, C.; Menard, Y.; Eriksen, D.Ø.; Ekberg, C.; Petranikova, M. Recovery of critical materials from mine tailings: A comparative study of the solvent extraction of rare earths using acidic, solvating and mixed extractant systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Olea, F.; Sepúlveda, R.; Castillo, J.; Cabezas, R.; Merlet, G.; Romero, J. Possibilities and challenges for ionic liquids in hydrometallurgy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrachart, G.; Couturier, J.; Dourdain, S.; Levard, C.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents. Processes 2021, 9, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J.; Robla, J.I. Solvent extraction in the recovery of metals from solutions: Entering the third decade of XXI century. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 265, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Anawati, J.; Azimi, G. Urban mining of terbium, europium, and yttrium from real fluorescent lamp waste using supercritical fluid extraction: Process development and mechanistic investigation. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Ramírez, C.; Janssen, C.H.C. Pseudo-Protic Ionic Liquids for the Extraction of Metals Relevant for Urban Mining. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Valderrama, M.I.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Montiel-Hernández, J.F.; Rivera-Landero, I.; Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Arenas-Flores, A. Urban Mining and Electrochemistry: Cyclic Voltammetry Study of Acidic Solutions from Electronic Wastes (Printed Circuit Boards) for Recovery of Cu, Zn, and Ni. Metals 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Han, J.I.; Hong, Y.; Yavuz, C.T. Energy-efficient electrochemical recovery of gold enabled by a thiourea-based electrolyte system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.F.; Malpass, A.C.G.; Malpass, G.R.P. Recycling of Printed Circuit Boards for Cooper Extraction: A Review of the Methods Employed. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2024, 16, 456–471. [Google Scholar]
- Nithya, R.; Sivasankari, C.; Thirunavukkarasu, A. Electronic waste generation, regulation and metal recovery: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1347–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. A review of current progress of recycling technologies for metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, E.; Barmak, K.; West, A.C.; Park, A.H.A. Advancements in the treatment and processing of electronic waste with sustainability: A review of metal extraction and recovery technologies. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Kumar, S. Metallurgical processes unveil the unexplored “sleeping mines” e- waste: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32359–32370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M. Recovery of metals and nonmetals from electronic waste by physical and chemical recycling processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.; He, H.; Frost, K.; Nauyen, B.H.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Schoenung, J.M. Comparative life cycle assessment of copper and gold recovery from waste printed circuit boards: Pyrometallurgy, chemical leaching and bioleaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Joo, S.H.; Nersisyan, H.H.; Kong, M.S.; Lee, J.W.; Park, K.W.; Lee, J.H. Reduction Kinetics of Zinc Powder from Brass Converter Slag by Pyrometallurgical Method Using Hydrogen Gas. KONA Powder Part. J. 2016, 33, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y. Recycling and recovery of spent copper–indium–gallium–diselenide (CIGS) solar cells: A review. Int. J. Miner., Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, M.; Shetty Kodialbail, V.; Saidutta, M.B. Performance of Fluidized-Bed Bioreactor in Copper Bioleaching from Printed Circuit Boards using Alcaligenes aquatilis. Waste Biomass Valor. 2024, 15, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, É.F.; Cesa Rovaris, B.; Valerio, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Hotza, D. Bioleaching of Printed Circuit Board Waste to Obtain Metallic Nanoparticles. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Kumar, S. Exploring bioleaching potential of indigenous Bacillus sporothermodurans ISO1 for metals recovery from PCBs through sequential leaching process. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.P.; Bismarck, A. Mycomining: Perspective on fungi as scavengers of scattered metal, mineral, and rare earth element resources. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, S.; Props, R.; Fitts, J.P.; Smet, R.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Vital, M.; Pieper, D.H.; Vanhaecke, F.; Boon, N.; Hennebel, T. Platinum Recovery from Synthetic Extreme Environments by Halophilic Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giese, E.C. E-waste mining and the transition toward a bio-based economy: The case of lamp phosphor powder. MRS Energy Sustain. 2022, 9, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Holuszko, M.; Espinosa, D.C.R. E-waste: An Overview on Generation, Collection, Legislation and Recycling Practices. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.B.R.; Bezerra, A.K.L.; Moita Neto, J.M.; Silva, E.A. Mining Law: In Search of Sustainable Mining. Sustainability 2021, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, P. Mineral Resource Governance in the 21st Century and a Sustainable European Union. Miner. Econ. 2021, 34, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedam, V.V.; Raut, R.D.; Jabbour, A.B.L.S.; Agrawal, N. Moving the Circular Economy Forward in the Mining Industry: Challenges to closed-loop in an emerging economy. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhofer, S.; Steuer, B.; Ramusch, R.; Beigl, P. WEEE management in Europe and China—A comparison. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, H.; Wagner, M.; Baldé, C.P.; Martínez, L.H.; Huisman, J.; Dewulf, J. What gets measured gets managed—Does it? Uncovering the waste electrical and electronic equipment flows in the European Union. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.; Johnson, M.; Fitzpatrick, C. Enabling preparation for re-use of waste electrical and electronic equipment in Ireland: Lessons from other EU member states. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, M.; Bergmann, G.; Schelte, N.; Severengiz, S. Closing the loop of small WEEE—Life cycle based approach for the evaluation of end-of-life strategies on the example of coffee machines. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2024, 23, 200220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Conheça a Linha do Tempo da Tragédia de Mariana (MG). Publicado em 25/10/2024. Available online: https://www.gov.br/planalto/pt-br/repactuacao-do-acordo-do-rio-doce/conheca-a-linha-do-tempo-da-tragedia-de-mariana-mg (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste Mismanagement in Developing Countries: A Review of Global Issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, F., Jr.; de Sales, L.; Yoshida, A.; Terazono, A.; Tembresa, J. Urban Mining from a Circularity Perspective. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 468, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.A.; Ramakrishna, S. A Comprehensive Analysis of E-waste Legislation Worldwide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14412–14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoni, M.; Dias, P.; Xavier, L.H. A Circular Approach to the E-waste Valorization Through Urban Mining in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 120990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.L. Unequal Geographies of Urban Mining: E-waste Management in London, Sao Paulo and Accra. Environ. Plann. E Nat. Space 2022, 6, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.B.R.; da Silva, E.A. Environmental Licensing in Brazilian’s Crushed Stone Industries. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 71, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.B.R.; Silva, E.A.; Moita Neto, J.M. Sustainable Development Goals in Mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, V.; Gomes, H.I.; Santos, R.; Toller, S.; Vitale, L. Urban Mining of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Residues with Emphasis on Bioleaching Technologies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 59128–59150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragazzi, M.; Fedrizzi, S.; Rada, E.C.; Ionescu, G.; Ciudin, R.; Cioca, L.I. Experiencing Urban Mining in an Italian Municipality Towards a Circular Economy Vision. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Raspall, F.; Fearnley, L.; Silva, A. Urban Mining in Buildings for a Circular Economy: Planning, Process and Feasibility Prospects. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejaswini, M.; Pathak, P.; Gupta, D.K. Sustainable Approach for Valorization of Solid Wastes as a Secondary Resource Through Urban Mining. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlezak, S.L.; Styer, J.E. Inclusive Urban Mining: An Opportunity for Engineering Education. Mining 2023, 3, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica—ANEEL. Micro e Minigeração Distribuída de Energia Elétrica Cresceu 8,85 GW Em 2024, 2025. Available online: https://www.gov.br/aneel/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2025/micro-e-minigeracao-distribuida-de-energia-eletrica-cresceu-8-84-gw-em-2024 (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Green Eletron. Resíduos Eletrônicos no Brasil—2023. 2023. Available online: https://greeneletron.org.br/download/RELATORIO_DADOS_2023.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Xavier, L.H.; Ottoni, M.; Lepawsky, J. Circular economy and e-waste management in the Americas: Brazilian and Canadian frameworks. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.P.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Chemical Exploratory Analysis of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (Icp Oes): Data Treatment and Elements Correlation. Detritus 2020, 13, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.P.; Pereira-Filho, E.R.; Bro, R. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) spectra interpretation and characterization using parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC): A new procedure for data and spectral interference processing fostering the waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) recycling process. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Vinhal, J.T.; Oliveira, R.P.; Coleti, J.L.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Characterization of end-of-life LEDs: Mapping critical, valuable and hazardous elements in different devices. Waste Manag. 2022, 151, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, L.F.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Vaccari, M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Botelho Junior, A.B. Characterization of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Recycling Perspective towards Circular Economy. Minerals 2024, 14, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Neto, J.F.; Souza, A.P.S.; Silva, M.M.; Santos, S.M.; Florencio, L. Critical barriers to material recovery from e-waste in Brazil. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annoni, R.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Silva, A.M.; Assunção, M.C.; Franco, M.B.; Souza, W. Light emitting diode waste: Potential of metals concentration and acid reuse via the integration of leaching and membrane processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespanhol, M.C.; Patrício, P.R.; Silva, L.H.M.; Vargas, S.J.R.; Rezende, T.C.S.; Campos, R.A. A Sustainable Methodology to Extract Bismuth from Secondary Sources. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespanhol, M.C.; Fontoura, B.M.; Quintão, J.C.; Silva, L.H.M. Extraction and purification of gold from raw acidic electronic leachate using an aqueous biphasic system. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 115, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.M.; Almeida, S.N.; Toma, H.E. Magnetic Nanohydrometallurgy Applied to Lanthanide Separation. Minerals 2020, 10, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrós, W.M. Gravity Concentration in Urban Mining Applications—A Review. Recycling 2023, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, P.S.S.; Domingues, A.S.; Palomero, J.P.G.; Cenci, M.P.; Kasper, A.C.; Dias, P.R.; Veit, H.M. c-Si PV module recycling: Analysis of the use of a mechanical pre-treatment to reduce the environmental impact of thermal treatment and enhance materials recovery. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.B.; Souza, G.B.M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Pavão, L.V.; Alonso, C.G.; Cabral, V.F.; Cardozo-Filho, L. Simultaneous recycling of waste solar panels and treatment of persistent organic compounds via supercritical water technology. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimassoni, Y.S.; Lima, M.T.W.D.C.; Yamane, L.H.; Siman, R.R. The recovery of rare earth elements from waste electrical and electronic equipment: A review. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 222, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.P.; Garcia, J.A.; Souza, R.G.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Indium Recovery from End-of-Life E-Waste: Important Details Related to Spectroanalytical Determination and Recycling Viability. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2024, 35, e-20230201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.D.; Schreiber, D.; Jahno, V.D. Circular Economy and Buildings as Material Banks in Mitigation of Environmental Impacts from Construction and Demolition Waste. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, Z.M.G.; Piao, Z.; Vasconcelos, K.L.; Poulikakos, L.D.; Bernucci, L.L.B. Comparative environmental performance of pavement structures considering recycled materials and regional differences. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, L.D.; Pasquini, E.; Tusar, M.; Hernando, D.; Wang, D.; Mikhailenko, P.; Pasetto, M.; Baliello, A.; Falchetto, A.C.; Miljković, M.; et al. RILEM interlaboratory study on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures modified with polyethylene waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.L.M.; Silva, M.M.; Santos, S.M. Forecasting of secondary lead recovery from motorcycle batteries in Brazil: A contribution to waste management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 106260–106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Almeida, F.S.; Carvalho, R.B.; Santos, F.S.; Souza, R.F.M. On the Hibernating Electronic Waste in Rio de Janeiro Higher Education Community: An Assessment of Population Behavior Analysis and Economic Potential. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.G.F.; Silva, W.D.O.; Fontana, M.E.; Levino, N.; Guarnieri, P. A GIS-based multi-criteria approach for identifying areas vulnerable to subsidence in the world’s largest ongoing urban socio-environmental mining disaster. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2024, 19, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, R.; Ottoni, M.; Barros, J.; Santos, M.A. Assessment of the waste management reporting in the electricity sector. Clean. Responsible Consum. 2021, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. Lei nº 9.605, de 12 de Fevereiro de 1998. Dispõe sobre as sanções penais e administrativas derivadas de condutas e atividades lesivas ao meio ambiente, e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, DF, 13 Fev. 1998. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/LEIS/L9605.htm (accessed on 30 May 2025).

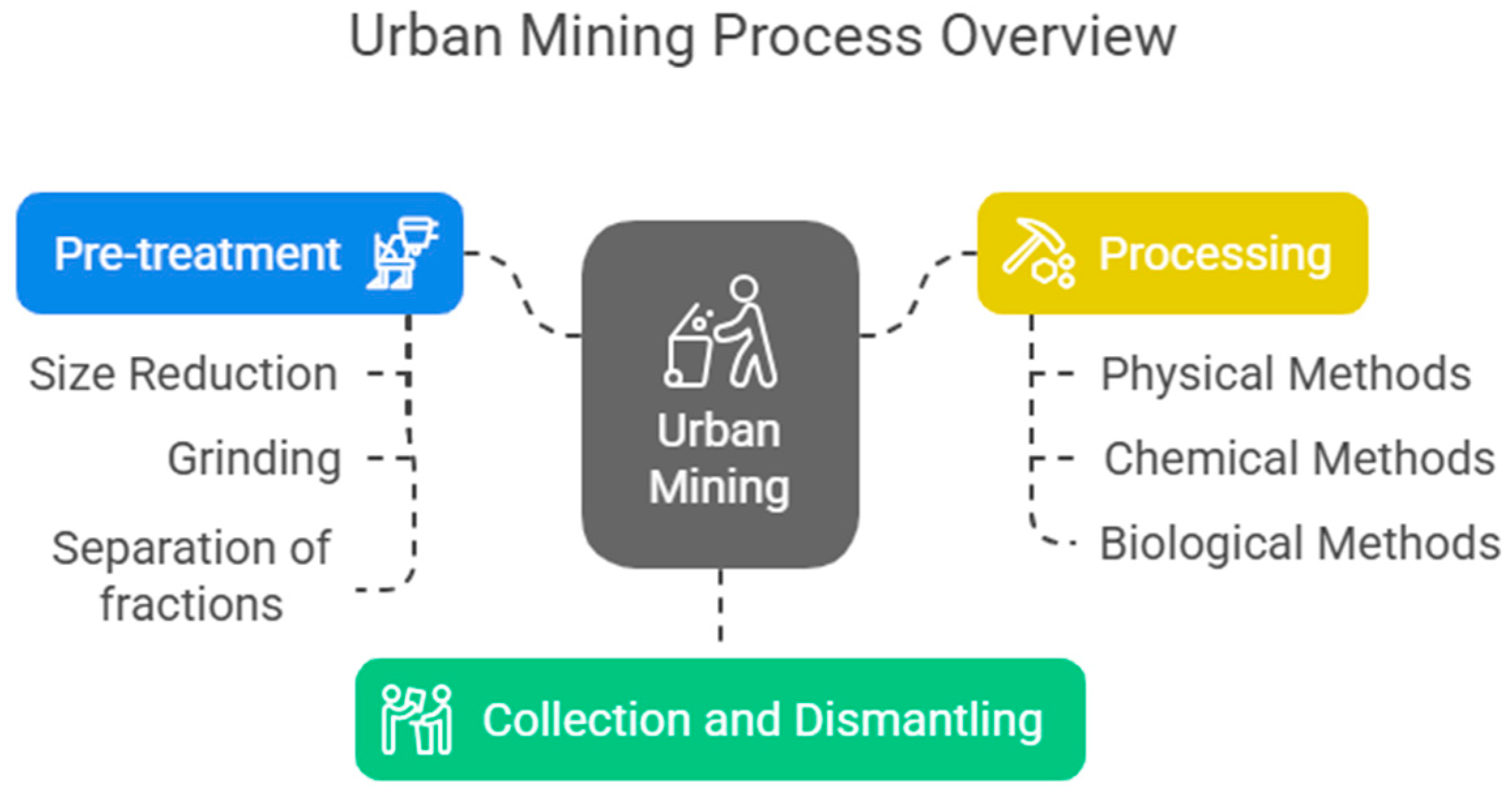


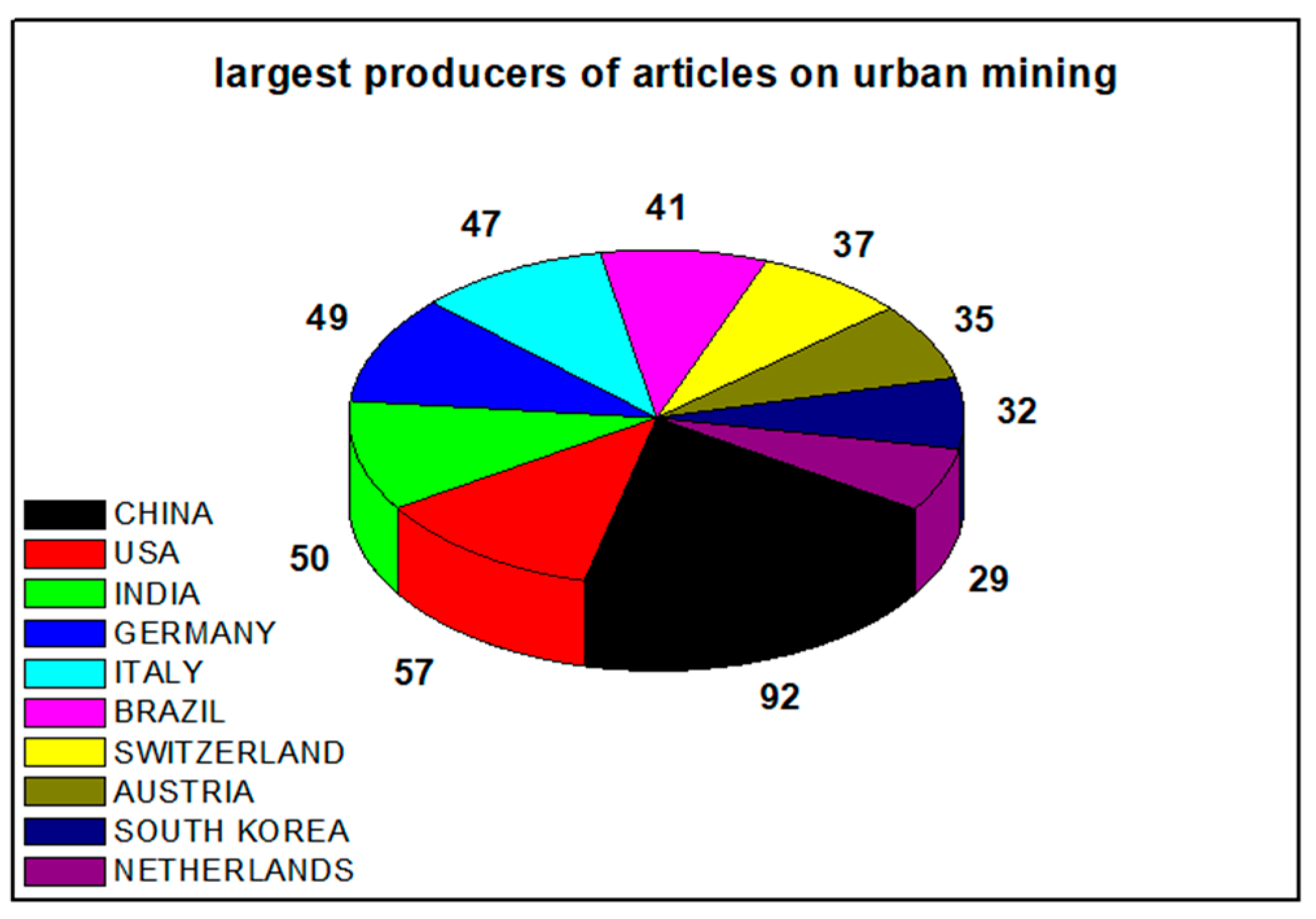
| Keywords | Records Obtained 1 |
|---|---|
| “urban mining” and “hydrometallurgy” | 27 |
| “urban mining” and “pyrometallurgy” | 9 |
| “urban mining” and “biohydrometallurgy” | 10 |
| “urban mining” and filtering the results by Countries/Regions: “Brazil” | 41 |
| Characteristic | Conventional Mining | Urban Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Resources | Mineral deposits (ores) located in the Earth’s crust, generally in remote and specific areas. | Waste and discarded products in urban areas, including electronic waste, construction and demolition waste, end-of-life vehicles, and urban solid waste. |
| Environmental Impact | Destruction of ecosystems, deforestation, soil and water pollution, waste generation (tailings and sterile material), landscape alteration. | Reduced pressure on natural resources, decreased pollution, lower energy consumption, reduced volume of waste sent to landfills, recovery of degraded areas. |
| Location | Generally in rural or remote areas, often in regions of great biodiversity or environmental importance. | Predominantly in urban and peri-urban areas, close to consumption and waste generation centers. |
| Complexity | Complex extraction, beneficiation, and refining processes, which require large investments in infrastructure and technology. | Complex processes of collection, sorting, dismantling, separation, and refining, which require cutting-edge technologies and efficient logistics. The heterogeneous composition of waste is a major challenge. |
| Regulation | Rigorous environmental legislation, complex environmental licensing, requirements for the recovery of degraded areas, need for constant monitoring. | Legislation under development, need for specific regulation for the sector, definition of responsibilities, incentives for recycling and reverse logistics, combating informality. |
| Economy | Traditional sector, with a large impact on the global economy, job creation, and foreign exchange earnings, but also with negative externalities (environmental and social costs). | Growing sector, with the potential to generate green jobs, reduce dependence on imports, boost technological innovation, and promote the circular economy. |
| Challenges | Resource depletion, social conflicts, environmental impacts, increasing extraction costs, rigorous environmental regulations. | Efficient selective collection, separation technologies, reverse logistics, traceability of materials, economies of scale, public awareness, specific regulations, combating informality. |
| Perspectives | Development of more sustainable mining technologies, recovery of degraded areas, corporate social responsibility. | Expansion of selective collection, development of advanced recycling technologies, promotion of the circular economy, creation of markets for recycled materials, public awareness. |
| Characteristic | Brazil | Europe/European Union |
|---|---|---|
| Main Drivers and Primary Focus | Reduction of waste volume in landfills; social inclusion of the informal workforce. | Resource scarcity; circular economy goals; security of critical metals supply. |
| Legislative Framework | National Solid Waste Policy (PNRS) and decrees: legal framework under development, with gaps in implementation, enforcement, and clarity of responsibilities. | More advanced and harmonized legislative framework (WEEE, RoHS Directives, Circular Economy Package), focusing on Extended Producer Responsibility; Variation in effectiveness among member states. |
| Infrastructure | Lack of adequate selective collection and processing infrastructure; logistics challenges (continental dimensions). | More developed and formalized collection and recycling infrastructure, despite challenges in meeting collection targets. |
| Technology and Innovation | Significant technological barriers; initial processing primarily local, export of noble-metal-rich components; growing research and development phase. | Investment in advanced recycling technologies and value chain creation; technological mastery and pursuit of strategic autonomy. |
| Informal Sector Integration | Prominent presence of informal collectors; need for inclusive approaches and formalization. | Predominantly formalized sector; challenges in uniform policy implementation. |
| Public Awareness | Low public awareness regarding correct WEEE disposal. | Growing consumer awareness and pressure for responsible practices. |
| Economic and Fiscal Incentives | Logistics costs and lack of specific fiscal incentives as barriers. | Pursuit of strengthening economic autonomy and reducing ecological footprint; creation of markets for recycled materials. |
| Year | Approach |
|---|---|
| 1970 | Europe: Directive 75/442/CEE—prioritization of waste elimination |
| 1990 | Directive 91/156/CEE—introduction of the paradigm of integrated management and prevention at the source |
| 2006–2008 | Directive 94/62/CE—specific directives for packaging Consolidation and improvement of the legal framework (Directive 2006/12/CE and Waste Framework Directive 2008/98/CE) |
| 2008 | Incorporation of the principles of the circular economy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moita Neto, J.M.; Leal, R.C.; Araújo, N.L.d.S.; da Silva, E.A. Challenges and Opportunities for the Development of Urban Mining in Brazil. Minerals 2025, 15, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060593
Moita Neto JM, Leal RC, Araújo NLdS, da Silva EA. Challenges and Opportunities for the Development of Urban Mining in Brazil. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060593
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoita Neto, José Machado, Régis Casimiro Leal, Nivianne Lima dos Santos Araújo, and Elaine Aparecida da Silva. 2025. "Challenges and Opportunities for the Development of Urban Mining in Brazil" Minerals 15, no. 6: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060593
APA StyleMoita Neto, J. M., Leal, R. C., Araújo, N. L. d. S., & da Silva, E. A. (2025). Challenges and Opportunities for the Development of Urban Mining in Brazil. Minerals, 15(6), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060593










