A Mineralogical Perspective on Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Extraction from Drill Cuttings: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and the Flow of the Review
3. Mineral Host Phases in REEs and Its Relevance to Drill Cuttings
3.1. Global Geological Sources of REEs: Deposit Types and Mineral Hosts
| Deposit Location | Deposit Type (Appx. REE Content %) * | Main REEs | REE-Host Minerals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayan Obo, China | Carbonatite/hydrothermal (3%–12%) | La, Ce, Nd | bastnasite, parasite, monazite |
| Mountain Pass, USA | Carbonatite (8.9%) | LREE | bastnasite |
| Mount Weld, Australia | Laterite/Carbonatite (~30%) | LREE | apatite, monazite, synchysite, churchite |
| Illimaussaq, Denmark | Peralkaline igneous (1%–3%) | La, Ce, Nd, HREE | eudialyte, steenstrupine |
| Pilanesberg, South Africa | Peralkaline igneous (0.2%–0.5%) | Ce, La | eudialyte |
| Steenkampskraal, South Africa | Vein (~17%) | La, Ce, Nd | monazite, apatite |
| Hoidas Lake, Canada | Vein (1.5%–5.5%) | La, Ce, Pr, Nd | apatite, allanite |
| Thor Lake, Canada | Alkaline igneous (1%–2.5%) | La, Ce, Pr, Nd, HREE | bastnasite |
| Strange Lake & Misery Lake, Canada | Alkaline igneous/hydrothermal (1%–2%) | La, Ce, Nd, HREE | gadolinite, bastnasite |
| Nolans Bore, Australia | Vein (2%–4%) | La, Ce, Nd | apatite, allanite |
| Norra Kärr, Sweden | Peralkaline igneous (0.6%–1%) | La, Ce, Nd, HREE | eudialyte |
| Khibina & Lovenzero, Russia | Peralkaline igneous (0.7%–1.2%) | LREE + Y, minor HREE | eudialyte, apatite |
| Nkwombwa Hill, Zambia | Carbonatite (1.5%–2.5%) | LREE | monazite, bastnasite |
| Kagankunde, Malawi | Carbonatite (2%–3%) | LREE | monazite-Ce, bastnaesite-Ce |
| Tundulu, Malawi | Carbonatite (2%–3%) | LREE | synchesite, parasite, bastnasite |
| Songwe, Malawi | Carbonatite (1%–2%) | LREE, Nd | synchesite, apatite |
| Ion Adsorption Deposits, China | Ion adsorption (soil) (0.05%–0.2%) | La, Nd, HREE | clay minerals |
| Maoniuping, China | Carbonatite (3%–4%) | LREE | bastnasite |
| Dong Pao, Vietnam | Carbonatite (4%–6%) | LREE | bastnasite, parisite |
3.2. Unconventional and Secondary Sources of REEs
3.2.1. Ion-Adsorption Clays
3.2.2. Black Shales and Organic-Rich Mudstones
3.2.3. Coal and Coal Byproducts
3.2.4. Phosphogypsum, AMD, and Metallurgical Slags
| Source | Typical Host Minerals/Associations | REE Grade | Enrichment Type | Key Advantages | Main Challenges | Approx. Recovery Potential (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion-Adsorption Clays | Kaolinite, halloysite, illite; REEs loosely adsorbed | 200–1000 ppm | HREE-enriched | Low energy input, environmentally benign | Heterogeneous mineralogy; shallow resource base | 60%–90% (High) |
| Black Shales/Organic-Rich Mudstones | Organic matter, aluminosilicates, apatite | 100–500 ppm | LREE & sometimes HREE | Vast distribution, shallow depth, co-recovery with hydrocarbons | Low grade; REEs strongly bound; redox-sensitive | 30%–60% (Moderate but scalable) |
| Coal & Coal Byproducts (e.g., Fly Ash) | Kaolinite, illite, amorphous phases, organics | 100–800 ppm (can exceed 1000 ppm in ash) | LREE-dominant | Abundant waste material, good leachability in ash | Highly variable mineralogy and feedstock quality | 40%–80% (up to 90% in fly ash)—Moderate to High |
| Phosphogypsum, AMD, Metallurgical Slags | Apatite, jarosite, amorphous/oxide-bound REEs | 50–300 ppm (up to 1 wt% in slags) | Mostly LREE | Dual benefit of resource recovery and environmental remediation | Toxicity, regulation, process residue management | 20%–60%, Moderate depending on feed quality |
3.3. Modes of REE Occurrence Based on Mineralogical Association
3.3.1. Ion-Adsorbed REEs
3.3.2. Mineral-Hosted REEs
3.3.3. REEs in Amorphous, Organic, or Colloidal Associations
3.4. Mineralogical Controls on REE Recovery: Why It Matters in Drill Cuttings
3.5. Mineralogical Forms of REEs Encountered in Drill Cuttings
3.5.1. Weathered Granitic and Clay-Rich Sediments: Ion-Adsorbed REEs
3.5.2. Carbonatites, Pegmatites, and Metamorphosed Terranes: Structurally Bound REEs
3.5.3. Black Shales and Organic-Rich Mudstones: Mixed and Amorphous REE Associations
3.5.4. Coal Seams and Fly Ash: Organically and Colloidally Bound REEs
3.5.5. Stability of REE-Host Minerals During Drilling: Challenges and Data Gaps
4. Synthesis and Analysis of Prior Studies on REE Recovery from Drill Cuttings
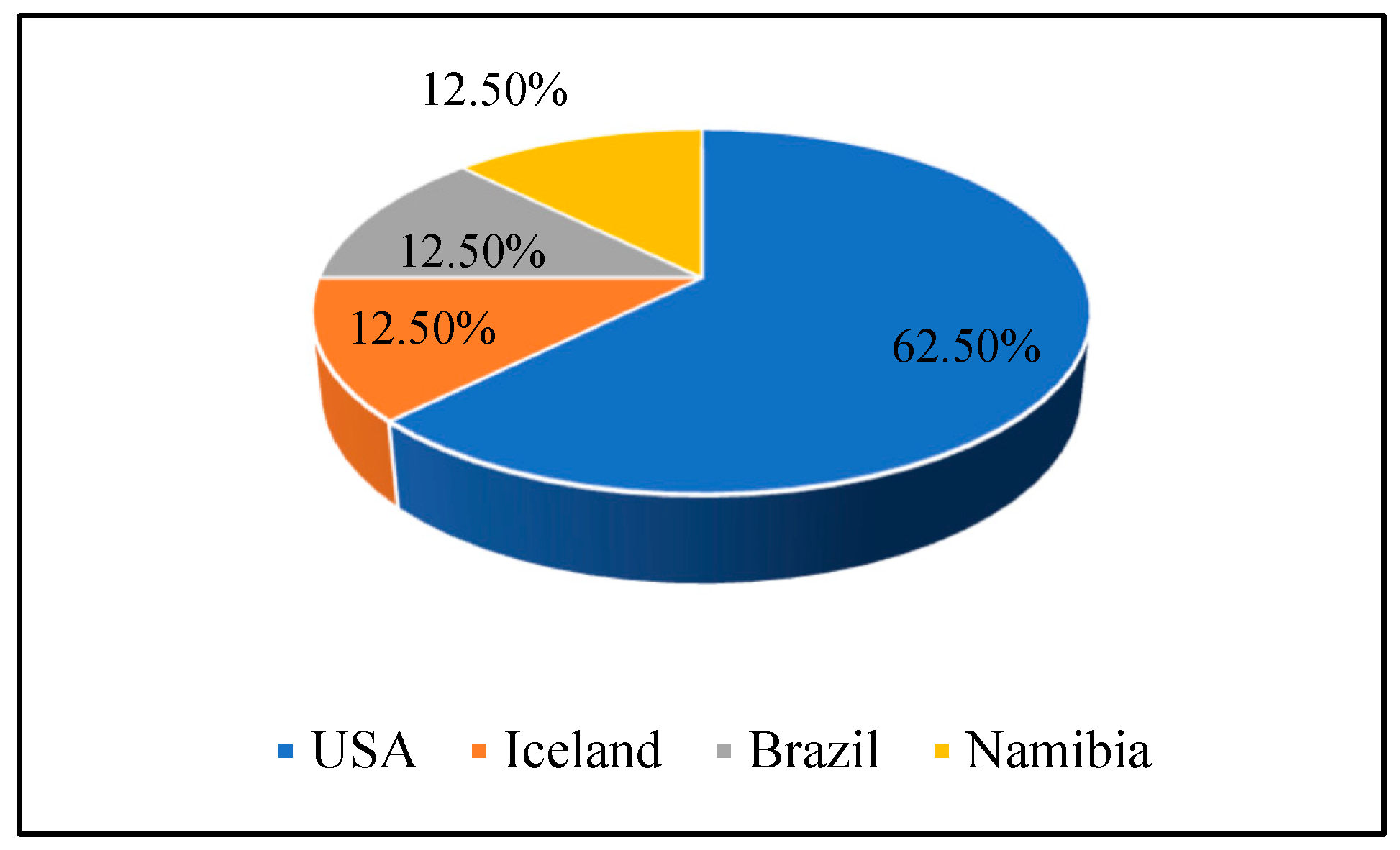
4.1. Geographical Trends in REE in Drilling Cutting Related Studies
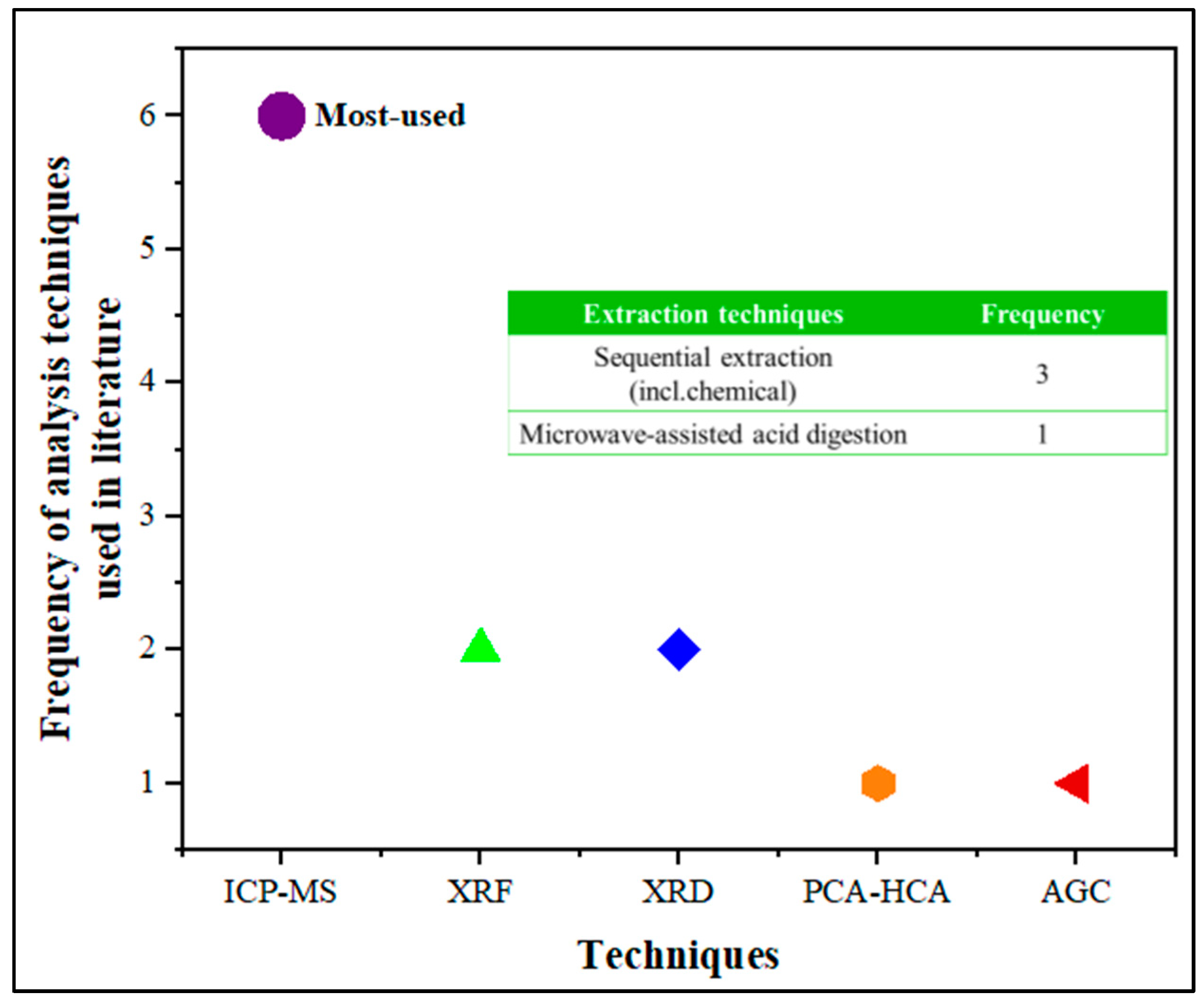
4.2. Extraction and Characterization Techniques
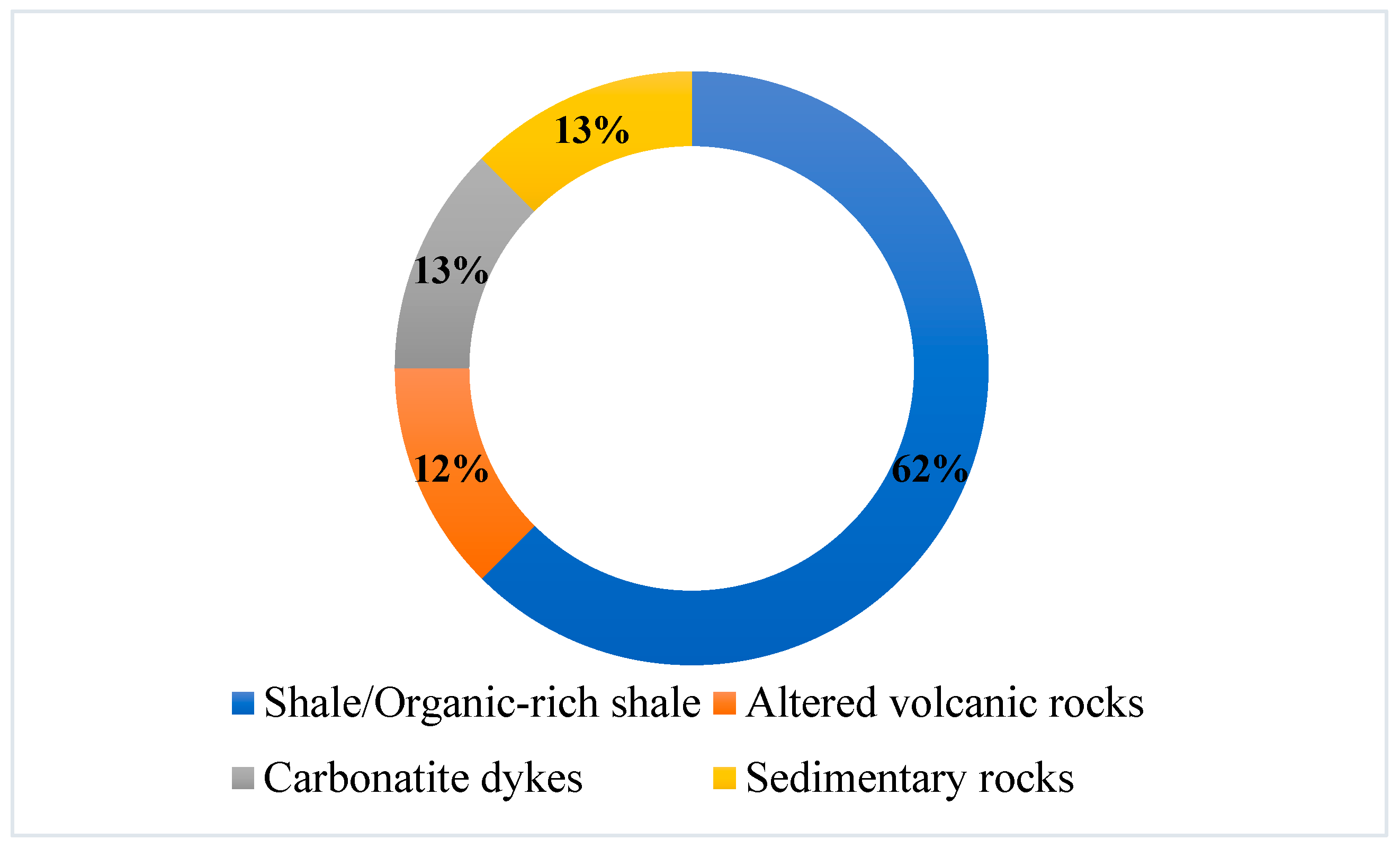
4.3. Type of Drilling Cutting Studied
4.4. Occurrence of REEs in Drilling Cuttings
4.5. Host Minerals vs. Lithology
4.6. Reliance on Core Samples vs. Drill Cuttings: Implications for REE Recovery
4.7. Limitations in Analytical Techniques Used in Previous Studies
4.8. Oversights in Existing Leaching Approaches for REEs from Drill Cuttings
4.9. Drilling Fluids and Their Influence on REE-Bearing Minerals
4.9.1. Fluid–Mineral Interactions in REE-Rich Formations
4.9.2. Mechanical Dispersion and Particle Loss
4.9.3. REE Leaching into Fluids vs. Preservation in Cuttings
| Research Group | Aspect | Impact on REEs Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Bamforth et al. (2024) [143] | pH Effect | Altered pH can destabilize REE-hosting minerals like monazite and apatite, leading to REE mobilization or deposition. |
| Madruga et al. (2018) [144] | Ionic Strength | Increased ionic strength induces cation exchange, mobilizing surface-adsorbed REEs from clay minerals. |
| Morariu et al. (2022) [145] | Clay Dispersion | Enhanced clay dispersion increases fine particle suspension and it can be deduced that REE-rich fines through solids control systems. |
| Fontana et al. (2020) [18] | Physical Particle Loss | Mechanical dispersion can entrain REE-hosting particles, reducing solid-phase REE yield in cuttings. |
| Rasool et al., 2024 [146] | Green Fluids (NADES/ILs) | Based on properties of NADES, REE can extracted in-situ with proper modification. |
| Fontana et al. (2020) [18] | REE Leaching into Fluid | Loosely bound REEs are susceptible to leaching into drilling fluids, though this phenomenon is rarely quantified in field studies. |
| Lopano et al., 2022 [124] | REE Preservation in Cuttings | Preservation of REEs in cuttings is favored in minerals like monazite; however, drilling fluid chemistry significantly influences this retention. |
5. Leaching and Characterization Techniques of REEs: Mineralogy Based Overview
5.1. Acid Leaching
5.2. Chemical Sequential Extraction
5.3. Microwave-Assisted Leaching
5.4. Bioleaching
5.5. Hybrid and Green Approaches
5.6. ICP-MS: The Benchmark for Quantification
5.7. ICP-OES and AAS: Less Sensitive Alternatives
5.8. XRD and SEM-EDS: Residual Solid Phase Analysis
5.9. PCA and HCA: Multivariate Interpretation Tools
5.10. Sequential Extraction and Speciation Studies
5.11. Solid–Liquid Partitioning and Mass Balance Considerations
6. Potential for Real-Time or Near-Drill Site REE Assessment
6.1. Shifting Toward On-Site Critical Element Screening
6.2. Mud-Logging as a Screening Tool for REEs
6.3. Portable Spectroscopy Tools: XRF, LIBS, and ICP-OES
6.4. Integration into Exploration and Resource Workflows
7. Qualitative Assessment of Economic Viability and Deployment Models
7.1. Resource Potential vs. Ore-Grade Feedstock
7.2. Cost Drivers in Drill Cuttings-Based Recovery
7.3. Recovery Limitations and Variability Challenges
7.4. Value Opportunities and Strategic Advantages
7.5. Scenario-Based Qualitative Assessment
8. Decision Tree Based on Mineral Host Phase in Drill Cuttings
9. Challenges and Future Directions
9.1. Challenges
9.2. Future Directions for Research and Development
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diao, H.; Yang, H.; Tan, T.; Ren, G.; You, M.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Bai, Y.; Xia, S.; Song, S. Navigating the rare earth elements landscape: Challenges, innovations, and sustainability. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursunoglu, N.; Kursunoglu, S. The Importance of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) for Energy Transition. In Proceedings of the 4th International Batman Energy Summit, Batman, Turkey, 24–25 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Balaram, V. Sources and applications of rare earth elements. In Environmental Technologies to Treat Rare Earth Elements Pollution: Principles and Engineering; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; Volume 113, pp. 75–113. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, W.L.; Kotter, R.; Özuyar, P.G.; Abubakar, I.R.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Matandirotya, N.R. Understanding rare earth elements as critical raw materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. Global potential of rare earth resources and rare earth demand from clean technologies. Minerals 2017, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating rare earth element availability: A case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, R.; Cook, D.R. Rare earths: A review of the landscape. MRS Energy Sustain. 2018, 5, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushyantha, N.; Batapola, N.; Ilankoon, I.; Rohitha, S.; Premasiri, R.; Abeysinghe, B.; Ratnayake, N.; Dissanayake, K. The story of rare earth elements (REEs): Occurrences, global distribution, genesis, geology, mineralogy and global production. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifle, D.; Sverdrup, H.; Koca, D.; Wibetoe, G. A simple assessment of the global long term supply of the rare earth elements by using a system dynamics model. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2013, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Du, X.; Graedel, T. Uncovering the global life cycles of the rare earth elements. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratiotou Efstratiadis, V.; Michailidis, N. Sustainable recovery, recycle of critical metals and rare earth elements from waste electric and electronic equipment (circuits, solar, wind) and their reusability in additive manufacturing applications: A review. Metals 2022, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaustad, G.; Williams, E.; Leader, A. Rare earth metals from secondary sources: Review of potential supply from waste and byproducts. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costis, S.; Mueller, K.K.; Blais, J.-F.; Royer-Lavallée, A.; Coudert, L.; Neculita, C.M. Review of Recent Work on the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Secondary Sources; INRS, Centre–Eau Terre Environnement: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, F.; He, J. Geochemistry and origin of rare earth elements (REEs) in the Shengli River oil shale, northern Tibet, China. Geochemistry 2011, 71, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, O.; Biggart, K.; Dewing, K. Rare Earth Element (REE) Content of Shale, Coal and Coal Byproducts, and Potential for Canadian REE Supply: A Literature Review and Initial Assessment; Geological Survey of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.; Surkova, T.Y.; Azlan, M.; Yulusov, S.; Sukurov, B.; Yessimova, D. Black shale ore of Big Karatau is a raw material source of rare and rare earth elements. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 205, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Peng, B.; Juhasz, A.; Hu, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, X. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during black shale weathering: Implications from acid rock drainage and sequential extraction study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, K.B.; Araujo, R.G.O.; de Oliveira, F.J.; Bascuñan, V.L.; de Andrade Maranhão, T. Rare earth elements in drill cutting samples from off-shore oil and gas exploration activities in ultradeep waters. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poduval, A.; Brownlow, J.; Jew, A. Searching for “Gold” in Wells: Converting Drill Cuttings into a Commodity by Identifying and Extracting Critical Minerals. In SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference; URTEC: Houston, TX, USA, 2024; p. D011S006R002. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, A.S.; Stewart, R.J.; Schliephake, K. A review of the current options for the treatment and safe disposal of drill cuttings. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepovitsyn, A.; Lebedev, A. Drill cuttings disposal efficiency in offshore oil drilling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillon, A.; Vidalie, J.-F.; Hamzah, U.S.; Suripno, S.; Hadinoto, E.K. Drilling and waste management. In SPE International Conference and Exhibition on Health, Safety, Environment, and Sustainability? SPE: Richardson, TX, USA, 2002; p. SPE-73931-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, N.K.; De Vivo, B.; Salminen, R. Rare Earth Elements: The role of geology, exploration, and analytical geochemistry in ensuring diverse sources of supply and a globally sustainable resource. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 133, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lučić, M.; Vdović, N.; Bačić, N.; Mikac, N.; Dinis, P. Disentangling the influence of lithology and non-provenance factors on the geochemistry of rare earth elements: A study of fine-grained sediments from the Sava River headwaters (Slovenia, Croatia). J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3704–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.; Hall, G.; Reimann, C.; Siewers, U. Distribution of rare earth elements in crystalline bedrock groundwaters: Oslo and Bergen regions, Norway. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.W.; Greaves, C.; Lawson, R.; Hayes, S.; Boyle, F. Options for the recycling of drill cuttings. In SPE Health, Safety, Security, Environment, & Social Responsibility Conference-North America; SPE: Richardson, TX, USA, 2003; p. SPE-80583-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Zepf, V.; Zepf, V. Rare Earth Elements: What and where they are. In Rare Earth Elements: A New Approach to the Nexus of Supply, Demand and Use: Exemplified Along the Use of Neodymium in Permanent Magnets; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, M.; Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. REE mineralogy and resources. In Handbook on the physics and chemistry of Rare Earths; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands,, 2016; Volume 49, pp. 129–291. [Google Scholar]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Zhou, X. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements in natural terrestrial waters: A review of what is currently known. Chin. J. Geochem. 1997, 16, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Jowitt, S.M.; Mudd, G.M.; Haque, N. A detailed assessment of global rare earth element resources: Opportunities and challenges. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1925–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangsy-Kania, S.; Flouros, F. Rare earth elements as a huge economic challenge for the future of green economy. In Proceedings of the 40th International Business Information Management Association Conference, Virtual, 23–24 November 2022; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Van Acker, K.; Blanpain, B.; Mishra, B.; Apelian, D. Rare-earth economics: The balance problem. Jom 2013, 65, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Hong, F.; Yin, M.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Zhao, G.; Wong, J.W. Structural differences between light and heavy rare earth elment binding chlorophylls in naturally grown fern Dicranopteris linearis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005, 106, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battsengel, A.; Batnasan, A.; Narankhuu, A.; Haga, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Shibayama, A. Recovery of light and heavy rare earth elements from apatite ore using sulphuric acid leaching, solvent extraction and precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Honghui, H.; Bai, T.; Jiang, S. Geochemistry of monazite within carbonatite related REE deposits. Resources 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S. The Solubility of Monazite in Carbonate Melts at Upper Mantle and Crustal Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, J. Extraction and separation of heavy rare earth elements: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergoric, M.; Ekberg, C.; Steenari, B.-M.; Retegan, T. Separation of heavy rare-earth elements from light rare-earth elements via solvent extraction from a neodymium magnet leachate and the effects of diluents. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xu, C.; Shi, A.; Smith, M.P.; Kynicky, J.; Wei, C. Origin of heavy rare earth elements in highly fractionated peraluminous granites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 343, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.-C.; Chen, W.-Q. Supply and demand conflicts of critical heavy rare earth element: Lessons from gadolinium. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Kim, K.-H.; Uchimiya, M.; Kwon, E.E.; Jeon, B.-H.; Deep, A.; Yun, S.-T. Global demand for rare earth resources and strategies for green mining. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Lyons, M. Critical Materials for the Energy Transition: Rare Earth Elements; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K.R.; Van Gosen, B.S.; Foley, N.K.; Cordier, D. The principal rare earth elements deposits of the United States: A summary of domestic deposits and a global perspective. In Non-Renewable Resource Issues: Geoscientific and Societal Challenges; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 131–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhanheng, C. Global rare earth resources and scenarios of future rare earth industry. J. Rare Earths 2011, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Z.; Jowitt, S.M.; Mudd, G.M.; Haque, N. Assessing rare earth element mineral deposit types and links to environmental impacts. Appl. Earth Sci. 2013, 122, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.; Nash, G.; Hadler, K.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Anderson, C.; Wall, F. Zeta potentials of the rare earth element fluorcarbonate minerals focusing on bastnäsite and parisite. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, J.J.; Smalley, R.G. Bastnasite. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1945, 30, 601–615. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, B.; Kylander-Clark, A.; Holder, R. REE partitioning between monazite and garnet: Implications for petrochronology. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2019, 37, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, C.J.; Harlov, D.E.; Budzyń, B. Experimental metasomatism of monazite and xenotime: Mineral stability, REE mobility and fluid composition. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 99, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engi, M. Petrochronology based on REE-minerals: Monazite, allanite, xenotime, apatite. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2017, 83, 365–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, J.M.; Spear, F.S.; Wark, D.A. Electron microprobe analysis of REE in apatite, monazite and xenotime: Protocols and pitfalls. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 48, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, D. Pb and rare earth element diffusion in xenotime. Lithos 2006, 88, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, G.; Andrehs, G.; Rhede, D. Crystal chemistry of monazite and xenotime from Saxothuringian-Moldanubian metapelites, NE Bavaria, Germany. Eur. J. Mineral. 1996, 8, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieré, R.; Sorensen, S.S. Allanite and other REE-rich epidote-group minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2004, 56, 431–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal, J. Rare earth element deposits of alkaline igneous rocks. Resources 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Jha, M.K.; Kumar, J.R.; Lee, J.Y. Process development to recover rare earth metals from monazite mineral: A review. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, P.L.; Duncan, R.K. Evaluation of rare earth element deposits. Appl. Earth Sci. 2014, 123, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. Characteristics and Genesis of Ion Adsorption-Type Rare Earth Element Deposits; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bustillo Revuelta, M.; Bustillo Revuelta, M. Mineral deposits: Types and geology. In Mineral Resources: From Exploration to Sustainability Assessment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 49–119. [Google Scholar]
- Castor, S.B. Rare earth deposits of North America. Resour. Geol. 2008, 58, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, Z.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Rare Earth Element Deposits in China; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jaireth, S.; Hoatson, D.M.; Miezitis, Y. Geological setting and resources of the major rare-earth-element deposits in Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 62, 72–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voncken, J.; Voncken, J. The ore minerals and major ore deposits of the rare earths. In The Rare Earth Elements: An Introduction; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 15–52. [Google Scholar]
- Barakos, G.; Mischo, H.; Gutzmer, J. How potential mines can connect to the global REE market. Min. Eng. 2018, 70, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- García, M.V.R.; Krzemień, A.; del Campo, M.Á.M.; Álvarez, M.M.; Gent, M.R. Rare earth elements mining investment: It is not all about China. Resour. Policy 2017, 53, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Hughes, A.; Lim, S.; Vernon, C. Rare earth elements: Overview of mining, mineralogy, uses, sustainability and environmental impact. Resources 2014, 3, 614–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B.A.; Alam, M.S.; Flynn, S.L.; Chen, N.; Hao, W.; Ramachandran Shivakumar, K.; Swaren, L.; Gutierrez Rueda, D.; Konhauser, K.O.; Alessi, D.S. Rare earth element adsorption to clay minerals: Mechanistic insights and implications for recovery from secondary sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7217–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, A.M.; Smith, M.P.; Finch, A.A.; Estrade, G.; Villanova-de-Benavent, C.; Nason, P.; Marquis, E.; Horsburgh, N.J.; Goodenough, K.M.; Xu, C.; et al. Adsorption of rare earth elements in regolith-hosted clay deposits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.A.; Papangelakis, V.G. Recovery of rare earth elements adsorbed on clay minerals: I. Desorption mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 117, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; He, H.; Xin, C.; Zhu, J.; Xinghu, W.; Zhu, R.; Wang, H. Understanding the role of natural clay minerals as effective adsorbents and alternative source of rare earth elements: Adsorption operative parameters. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, D.-H.; Liu, C.-Q.; Shields-Zhou, G.A.; Jiang, S.-Y. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of black shale and kerogen in the early Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Guizhou province, South China: Constraints for redox environments and origin of metal enrichments. Precambrian Res. 2013, 225, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, Y.N.; Eder, V.G.; Al’bina, G.Z.; Krasavchikov, V.O. Models of the REE distribution in the black shale Bazhenov Formation of the West Siberian marine basin, Russia. Geochemistry 2010, 70, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffmann, A.K.; Littke, R.; Rippen, D. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Mississippian and Lower Pennsylvanian black shales at the northern margin of the Variscan Mountain Belt (Germany and Belgium). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Torres, M.; McManus, J.; Algeo, T.J.; Hakala, J.A.; Verba, C. Controls on rare earth element distributions in ancient organic-rich sedimentary sequences: Role of post-depositional diagenesis of phosphorus phases. Chem. Geol. 2017, 466, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Deng, Y.; Mao, G.Z. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of the Upper Triassic mudstones in the southern Ordos Basin, Central China. Geol. J. 2015, 50, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, P.; Maity, S.; Mishra, S.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Dusane, C.; Pillai, A.S.; Kumar, A.V. Estimation of rare earth elements in Indian coal fly ashes for recovery feasibility as a secondary source. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.; Kolker, A. Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Coal Fly Ash; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 2327–6932. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Komorek, J.; Białecka, B.; Nowak, J.; Klupa, A. Assessment of the potential of polish fly ashes as a source of rare earth elements. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 124, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, R.K.; Hower, J.C.; Dwyer, G.S.; Hsu-Kim, H. Trends in the rare earth element content of US-based coal combustion fly ashes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahorava, V.; Bazhko, V.; Freeman, M. Viability of phosphogypsum as a secondary resource of rare earth elements. In Proceedings of the XXVIII International Mineral Processing Congress Proceedings, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 September 2016; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, F.; Yu, W.; Yin, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, R.A. A critical review of the enhanced recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Molecules 2023, 28, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermassi, M.; Granados, M.; Valderrama, C.; Ayora, C.; Cortina, J.L. Recovery of rare earth elements from acidic mine waters: An unknown secondary resource. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liang, X.; Cheng, H. Review of rare earth element (REE) adsorption on and desorption from clay minerals: Application to formation and mining of ion-adsorption REE deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 157, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.; Papangelakis, V. An overview of rare-earth recovery by ion-exchange leaching from ion-adsorption clays of various origins. Mineral. Mag. 2016, 80, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, X. Study on rare earth resources potential and industrial development in Myanmar. China Min. Mag. 2023, 32, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.J.; Lin, A.; Li, X.-L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; Ma, G.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, B. Mineralization of ion-adsorption type rare earth deposits in Western Yunnan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; O’Rielly, D.; Wilson, R.; Das, K.; Wade, B. Mineral chemistry of rare earth element (REE) mineralization, Browns Ranges, Western Australia. Lithos 2013, 172, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobev, S.; You, T.-S.; Suen, N.-T.; Saha, S.; Greene, R.; Paglione, J. Synthesis, structure, chemical bonding, and magnetism of the series RE LiGe2 (RE = La–Nd, Sm, Eu). Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, P. REE (Y), Nb, and Ta enrichment in pegmatites and carbonatite-alkalic rock complexes. In Lanthanides, Tantalum and Niobium: Mineralogy, Geochemistry, Characteristics of Primary Ore Deposits, Prospecting, Processing and Applications Proceedings of a workshop in Berlin, November 1986; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 103–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Fan, H.-R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, K.-F.; She, H.-D. Carbonatite-related REE deposits: An overview. Minerals 2020, 10, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, M.; Porwal, A.; González-Álvarez, I. Targeting REE deposits associated with carbonatite and alkaline complexes in northeast India. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catrouillet, C.; Guenet, H.; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.; Dia, A.; LeCoz, M.B.; Deville, S.; Lenne, Q.; Suko, Y.; Davranche, M. Rare earth elements as tracers of active colloidal organic matter composition. Environ. Chem. 2019, 17, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Dahlqvist, R.; Turner, D.; Stolpe, B.; Larsson, T.; Ingri, J.; Andersson, P. Colloidal rare earth elements in a boreal river: Changing sources and distributions during the spring flood. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3261–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, M.; Wiche, O. Rare earth elements (REE): Origins, dispersion, and environmental implications—A comprehensive review. Environments 2024, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzov, S.; Finkelman, R.B.; Il’enok, S.; Maslov, S.; Mezhibor, A.; Blokhin, M. Modes of occurrence of rare-earth elements (La, Ce, Sm, Eu, Tb, Yb, Lu) in coals of northern Asia. Solid Fuel Chem. 2019, 53, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.A.; Vignati, D.A.; Hissler, C. Contrasting distribution of REE and yttrium among particulate, colloidal and dissolved fractions during low and high flows in peri-urban and agricultural river systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickov, I.V.; Lim, A.G.; Vorobyev, S.N.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Colloidal associations of major and trace elements in the snow pack across a 2800-km south-north gradient of western Siberia. Chem. Geol. 2022, 610, 121090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A.; Davranche, M.; Molénat, J. Colloidal control on the distribution of rare earth elements in shallow groundwaters. Aquat. Geochem. 2010, 16, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-R.; Liu, W.-S.; Zhang, M.; Jin, C.; Ding, K.-B.; Baker, A.J.; Qiu, R.-L.; Tang, Y.-T.; Wang, S.-Z. Organic-mineral colloids regulate the migration and fractionation of rare earth elements in groundwater systems impacted by ion-adsorption deposits mining in South China. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Gałuszka, A. The characteristics, occurrence, and geochemical behavior of rare earth elements in the environment: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 429–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, P.; Wei, G.; Yang, Y.; Ji, S.; Ma, L.; Zhou, J.; Tan, W.; Zhu, J.; Takahashi, Y. Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements (REEs) in ion-adsorption-type REE deposits: Constraints of an iron (hydr) oxide-clay mineral composite. Am. Mineral. 2025, 110, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, G.; Saneie, R.; Abdollahi, H.; Ebrahimi, E.; Rezaei, A.; Mohammadkhani, M. Application of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as a green lixiviant for extraction of rare earth elements from caustic-treated monazite concentrate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, R.; Sreenivas, T.; Kumar, M.A.; Singh, D. Recovery of rare earth elements from coal flyash using deep eutectic solvents as leachants and precipitating as oxalate or fluoride. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 214, 105952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.H.; Ahmad, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Ali, H.; Bajwa, N.T. In-House Synthesis and Characterization of Vitamin C and Glycerine Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent. Key Eng. Mater. 2024, 1003, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Han, H.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, T. Differential leaching mechanisms and ecological impact of organic acids on ion-adsorption type rare earth ores. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, P.L. The role of fluids in the formation of rare earth element deposits. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.; Koeberl, C. Mineralogical and chemical composition and distribution of rare earth elements in clay-rich sediments from central Uganda. Geochem. J. 2001, 35, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Ishihara, S. REE mineralization of weathered crust and clay sediment on granitic rocks in the Sanyo Belt, SW Japan and the Southern Jiangxi Province, China. Resour. Geol. 2008, 58, 373–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, H.Z.; Al Hossain, A.; Islam, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Yu, M. Geochemistry of Core Sediments From the Southeast Coast of Bangladesh: Constraints on Chemical Weathering, Paleoenvironmental Conditions, Provenance, and Tectonic Setting. Geol. J. 2025, 60, 1252–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Niu, Y.; Romer, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Li, W. High silica leucogranites result from sedimentary rock melting—Evidence from trace elements and Nd-Hf-B isotopes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2025, 26, e2024GC012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batapola, N.; Dushyantha, N.; Premasiri, H.; Abeysinghe, A.; Rohitha, L.; Ratnayake, N.; Dissanayake, D.; Ilankoon, I.; Dharmaratne, P. A comparison of global rare earth element (REE) resources and their mineralogy with REE prospects in Sri Lanka. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 200, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, I.A.; Stepanov, A.S.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Murphy, D.; Mavrogenes, J.; Allen, C.; Chen, W.; Bottrill, R. Complex REE systematics of carbonatites and weathering products from uniquely rich Mount Weld REE deposit, Western Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, S.; Filer, J. Assessing the impact of black shale processes on REE and the U–Pb isotope system in the southern Appalachian Basin. Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Groppo, J.G.; Henke, K.R.; Hood, M.M.; Eble, C.F.; Honaker, R.Q.; Zhang, W.; Qian, D. Notes on the potential for the concentration of rare earth elements and yttrium in coal combustion fly ash. Minerals 2015, 5, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Huang, R.; Tang, Y. Comprehensive understandings of rare earth element (REE) speciation in coal fly ashes and implication for REE extractability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, C.; Tang, M.; Cao, S.; Hu, T.; Ji, W.; Luo, Y.; Wen, M.; Zhang, N. Modes of occurrence of rare earth elements in coal fly ash: A case study. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9738–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, N.; Engi, M.; Gnos, E.; Jakob, V.; Liechti, A. Monazite analysis; from sample preparation to microprobe age dating and REE quantification. Schweiz. Mineral. Und Petrogr. Mitteilungen 2000, 80, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Andrehs, G.; Heinrich, W. Experimental determination of REE distributions between monazite and xenotime: Potential for temperature-calibrated geochronology. Chem. Geol. 1998, 149, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A. Drill Cutting and Core Major, Trace and Rare Earth Element Anlayses from Wells RN-17B and RN-30, Reykjanes, Iceland; USDOE Geothermal Data Repository (United States); University of California Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Agrawal, V.; Sharma, S. Association of Rare Earths in Different Phases of Marcellus and Haynesville Shale: Implications on Release and Recovery Strategies. Minerals 2022, 12, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucman, M. Sustainable Critical Element Recovery Based on Advanced Geochemical Characterization; National Energy Technology Laboratory: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://netl.doe.gov/sites/default/files/2021-09/PIOGA_Stuckman2021.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Lopano, C. Beneficial Reuse of Drill Cuttings; National Energy Technology Laboratory: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://netl.doe.gov/sites/default/files/netl-file/22RS-25_Lopano.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Stuckman, M.Y.; Lopano, C.L.; Berry, S.M.; Hakala, J.A. Geochemical solid characterization of drill cuttings, core and drilling mud from Marcellus Shale Energy development. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 68, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczok, M.; Stuckman, M.; Xiong, W.; Brandi, M.; Lopano, C. Characterization of Oil and Gas Drill Cuttings for Critical Mineral Recovery and Reuse Potential as Soil Supplements; National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL): Pittsburgh, PA, USA; Morgantown, WV, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- E-Tech Resources Inc. Diamond Drilling Intersects Thick, Rare Earth Element (REE) Mineralisation, Open at Depth and Along Strike at Eureka. Available online: https://etech-resources.com/diamond-drilling-intersects-thick-rare-earth-element-ree-mineralisation/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Peelman, S.; Sun, Z.H.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Leaching of rare earth elements: Review of past and present technologies. In Rare Earths Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Keon, N.; Swartz, C.; Brabander, D.; Harvey, C.; Hemond, H. Validation of an arsenic sequential extraction method for evaluating mobility in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Akhmadiyeva, N.; Abdulvaliyev, R.; Abhilash; Meshram, P. Overview on extraction and separation of rare earth elements from red mud: Focus on scandium. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. Case studies of radioactivity of drilling mud for in situ leaching uranium mining in China. J. Environ. Radioact. 2022, 251, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Shuai, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Extraction of rare earth elements from a contaminated cropland soil using nitric acid, citric acid, and EDTA. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Repo, E.; Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yin, D.; Sillanpää, M. An EDTA-β-cyclodextrin material for the adsorption of rare earth elements and its application in preconcentration of rare earth elements in seawater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.-C.; Wen, S.-M.; Wang, Y.-J.; Cao, Q.-B.; Zhao, W.-J. Dissolution kinetics of cerussite in an alternative leaching reagent for lead. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Rashchi, F.; Mostoufi, N. Kinetics of leaching: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, E.; Howe, J.; Shimmield, G.; Cummings, D.; Carroll, J. Contaminant Leaching from Drill Cuttings Piles of the Northern and central North Sea: A Review; Center for Coastal & Marine Sciences: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 1999; 49p. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, K.A.; Byrne, R.H.; Schijf, J. Sorption of yttrium and rare earth elements by amorphous ferric hydroxide: Influence of pH and ionic strength. Mar. Chem. 2006, 99, 128–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Effects of redox potential and pH value on the release of rare earth elements from soil. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, P.; Sposito, F.; Inguaggiato, C.; Zuddas, P.; Inguaggiato, S.; Venturi, M. Zr, Hf and REE distribution in river water under different ionic strength conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermassi, M.; Granados, M.; Valderrama, C.; Skoglund, N.; Ayora, C.; Cortina, J.L. Impact of functional group types in ion exchange resins on rare earth element recovery from treated acid mine waters. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwewa, B.; Tadie, M.; Ndlovu, S.; Simate, G.S.; Matinde, E. Recovery of rare earth elements from acid mine drainage: A review of the extraction methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiravi, M.; Ackah, L.; Guru, R.; Mohanty, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L. Chemical extraction of rare earth elements from coal ash. Miner. Metall. Process. 2017, 34, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, T.G.; Xia, F.; Tiddy, C.J.; González-Álvarez, I.; Brugger, J.; Hu, S.-Y.; Schoneveld, L.E.; Pearce, M.A.; Putnis, A. High-Grade REE accumulation in regolith: Insights from supergene alteration of an apatite-rich vein at the Kapunda Cu mine, South Australia. Miner. Depos. 2024, 59, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, L.Y.; da Camara, P.C.; Marques, N.d.N.; Balaban, R.d.C. Effect of ionic strength on solution and drilling fluid properties of ionic polysaccharides: A comparative study between Na-carboxymethylcellulose and Na-kappa-carrageenan responses. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morariu, S.; Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M. Rheological investigation of polymer/clay dispersions as potential drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.H.; Ahmad, M. Revolutionizing shale drilling with potassium chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvent as an additive. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2024, 14, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Li, Q.; Honaker, R.; Zhang, W. Acid leaching recovery and occurrence modes of rare earth elements (REEs) from natural kaolinites. Miner. Eng. 2022, 175, 107278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Chakladar, S.; Mohanty, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Jha, M. Review on the environment friendly leaching of rare earth elements from the secondary resources using organic acids. Geosyst. Eng. 2022, 25, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Stuckman, M.; Howard, B.H.; Bank, T.L.; Roth, E.A.; Macala, M.K.; Lopano, C.; Soong, Y.; Granite, E.J. Application of sequential extraction and hydrothermal treatment for characterization and enrichment of rare earth elements from coal fly ash. Fuel 2018, 232, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R.M.; Sahuquillo, A.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F. Comparison of single and sequential extraction procedures for the study of rare earth elements remobilisation in different types of soils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, J.R.; Davidson, C.M. Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst 2008, 133, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittermüller, M.; Saatz, J.; Daus, B. A sequential extraction procedure to evaluate the mobilization behavior of rare earth elements in soils and tailings materials. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.; Panda, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Parhi, P. Ultrasound and Microwave assisted leaching of neodymium from waste magnet using organic solvent. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzen, E.M.; Kingston, H.S. Comparison of microwave-assisted and conventional leaching using EPA method 3050B. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 4316–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarifar, D.; Daryanavard, M.; Sheibani, S. Ultra fast microwave-assisted leaching for recovery of platinum from spent catalyst. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; Kingman, S. Microwave-assisted leaching—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.J.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Deady, E.A.; Gregory, S.P. Comparison of three approaches for bioleaching of rare earth elements from bauxite. Minerals 2020, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Pan, J.; Dong, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C. Bioleaching of rare earth elements: Perspectives from mineral characteristics and microbial species. Minerals 2023, 13, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Fordjour, E.Y.; Yang, X. Bioleaching of rare earth elements challenges and opportunities: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L. Role of microorganisms in bioleaching of rare earth elements from primary and secondary resources. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Becker, T.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L. Microbial contact enhances bioleaching of rare earth elements. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 3, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.K.; Gupta, A.; Ramteke, P.; Sahoo, H.; Sengupta, A. Biosorption-a green method for the preconcentration of rare earth elements (REEs) from waste solutions: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Adidharma, H.; Radosz, M.; Wan, P.; Xu, X.; Russell, C.K.; Tian, H.; Fan, M.; Yu, J. Recovery of rare earth elements with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4469–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Yin, S. Sustainable green production: A review of recent development on rare earths extraction and separation using microreactors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 17616–17626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoy, L.; Xu, J.; Kulkarni, Y.; Huang, C.-H. Ionic liquid recovery of rare-earth elements from coal fly ash: Process efficiency and sustainability evaluations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11824–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, I. Determination of rare earth elements concentrations in natural waters—A review of ICP-MS measurement approaches. Talanta 2021, 221, 121636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaliannejad, R.; Aghahoseini, M.; Amini, M.K. Determination of rare earth elements in uranium materials by ICP-MS and ICP-OES after matrix separation by solvent extraction with TEHP. Talanta 2021, 222, 121509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wei, W.; Yang, Y.-H.; Romer, R.L.; Wu, S.-T.; Wu, T.; Zhong, L.-F. Accurate determination of ultra-trace rare earth elements by LA-ICP-MS/MS and its application to cassiterite for effective elimination of Gd and Tb false positive anomalies. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2024, 39, 2992–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gui, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; He, M.; Hu, B. Trace rare earth elements analysis in atmospheric particulates and cigar smoke by ICP-MS after pretreatment with magnetic polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1324, 343003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potanin, E. Analysis of the separation of gadolinium isotopes by the ICR method. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2008, 34, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xue, S.; Majoros, M.; Collings, E.W.; Sumption, M.D. FEM Modelling of Current Sharing in Tape Stack Cables; Influence of ICR, ITR, Defect Number, and Thermal Boundary Conditions. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2025, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Titova, S.A.; Kruglova, M.P.; Stupin, V.A.; Manturova, N.E.; Silina, E.V. Potential Applications of Rare Earth Metal Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavković-Beškoski, L.; Ignjatović, L.; Bolognesi, G.; Maksin, D.; Savić, A.; Vladisavljević, G.; Onjia, A. Dispersive solid–liquid microextraction based on the poly (HDDA)/graphene sorbent followed by ICP-MS for the determination of rare earth elements in coal fly ash leachate. Metals 2022, 12, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losev, V.N.; Buyko, O.V.; Borodina, E.V.; Zhizhaev, A.M.; Samoilo, A.S. Preconcentration and ICP-OES determination of rare earth elements using silicas chemically modified with aminophosphonic groups in fossil raw materials. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 7523–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; Xie, J.; Han, J.; Zhao, X. Crystallization properties of magnesium aluminosilicate glass-ceramics with and without rare-earth oxides. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 419, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Chiang, Y.W.; Santos, R.M. X-ray diffraction techniques for mineral characterization: A review for engineers of the fundamentals, applications, and research directions. Minerals 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pourret, O.; Guo, H.; Martinez, R.E.; Zouhri, L. Impact of hydrous manganese and ferric oxides on the behavior of aqueous rare earth elements (REE): Evidence from a modeling approach and implication for the sink of REE. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, H.; Mueller, J.; Bruncks, N.; Lauke, H.; Pickardt, J.; Schwarz, H.; Eckart, K. Organometallic compounds of the lanthanides. Part 17. Tris [(tetramethylethylenediamine) lithium] hexamethyl derivatives of the rare earths. Organometallics 1984, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Ji, H.; Deng, S.; Jiang, L. XRD and TEM analyses of a simulated leached rare earth ore deposit: Implications for clay mineral contents and structural evolution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Rare earth elements (REEs) recovery from coal waste of the Western Kentucky No. 13 and Fire Clay Seams. Part I: Mineralogical characterization using SEM-EDS and TEM-EDS. Fuel 2022, 307, 121854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ao, X.; Liang, L.; Mao, X.; Guo, Y. Recovery of rare earth elements from sedimentary rare earth ore via sulfuric acid roasting and water leaching. J. Rare Earths 2025, 43, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.E.; Kaya, O.; Stopic, S.; Gürmen, S.; Friedrich, B. NdFeB magnets recycling process: An alternative method to produce mixed rare earth oxide from Scrap NdFeB magnets. Metals 2021, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Hou, H.; Liang, H.; Chen, K.; Chen, X. Raman spectroscopy study of phosphorites combined with PCA-HCA and OPLS-DA models. Minerals 2019, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, J.; Huang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, X.; Mo, M.; Tan, S.; Tong, H. CNHO and mineral element stable isotope ratio analysis for authentication in tea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 91, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, A.; Mutić, J.; Lučić, M.; Vesković, J.; Miletić, A.; Onjia, A. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Followed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry and Multivariate Profiling of Rare Earth Elements in Coffee. Foods 2025, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Noble, A.; Vass, C.; Ziemkiewicz, P. Speciation of rare earth elements in acid mine drainage precipitates by sequential extraction. Miner. Eng. 2021, 168, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Öhlander, B.; Ingri, J.; Thunberg, J. Solid speciation and fractionation of rare earth elements in a spodosol profile from northern Sweden as revealed by sequential extraction. Chem. Geol. 1999, 160, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Green, T.H. Apatite/liquid partition coefficients for the rare earth elements and strontium. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 56, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B. Two-liquid partition coefficients: Experimental data and geochemical implications. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 56, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, A.J. A review of experimental studies of crystal/liquid trace element partitioning. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 743–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varhaug, M. Mud logging. Oilfield Rev. 2016, Volume 28, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Blue, D.; Blakey, T.; Rowe, M. Advanced mud logging: Key to safe and efficient well delivery. In Offshore Technology Conference; OTC: Houston, TX, USA, 2019; p. D032S058R003. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, J.; Arunkumar, T.; Ravipati, S.V.S.D.; Varma, S.S. XRD investigation of biodegradable magnesium rare earth alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 4676–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honaker, R.; Hower, J.; Eble, C.; Weisenfluh, J.; Groppo, J.; Rezaee, M.; Bhagavatula, A.; Luttrell, G.; Bratton, R.; Kiser, M. Laboratory and bench-scale testing for rare earth elements. Cell 2014, 724, 554–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Crocombe, R.A. Portable spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 1701–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocombe, R.A.; Leary, P.E.; Kammrath, B.W. Portable Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.; Carvalho, C.; Soares, A.; Souza, A.; Bastos, E.; Guimarães, E.; Santos, J.; Carvalho, T.; Calderari, V.; Marinho, L. Physical and chemical characterization of drill cuttings: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneller, F.; Kalf, D.; Weltje, L.; Van Wezel, A. Maximum Permissible Concentrations and Negligible Concentrations for Rare Earth Elements (REEs); National Institute for Public Health and the Environment Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Okwousah, C.S. Oil and Gas Marginal Field Techno-Economics. Ph.D. thesis, Cranfield University, Bedford, UK,, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nader, F.H. Multi-Scale Quantitative Diagenesis and Impacts on Heterogeneity of Carbonate Reservoir Rocks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jowitt, S.M. Mineral economics of the rare-earth elements. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.H.; Thompson, K.A.; Ma, L.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Luu, S.T.; Duong, M.T.N.; Kernaghan, A. Toward the circular economy of Rare Earth Elements: A review of abundance, extraction, applications, and environmental impacts. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L.; Coe, N.M. Critical mineral strategies in Australia: Industrial upgrading without environmental or social upgrading. Resour. Policy 2024, 91, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Keenan, R. Critical mineral sustainable supply: Challenges and governance. Futures 2023, 146, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Junet, A.; Guilleux, C.; Poszwa, A.; Devin, S.; Sarala, P.; Pospiech, S.; Middleton, M.; Pinheiro, J.-P. New methodological approach for deep penetrating geochemistry and environmental studies, Part 1: On-site soil extraction of trace and rare earth elements. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2024, 24, geochem2023-056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, P.; Deshpande, K.; Jawadand, S.; Dora, M.; Selokar, A.; Daware, G.; Sahu, M.; Nandi, A.K.; Randive, K. Innovative Technologies for Recycling and Extraction of REE Check for updates. In Current Trends in Mineral-Based Products and Utilization of Wastes: Recent Studies from India: Prospects and Challenges of Mineral Based Products and Utilization of Wastes for the ‘Make in India’Initiative, Nagpur November 10–11, 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Leich, A. Eudialyte Geochronology: Investigating the Timing of Ree Mineralization in the Grenville Province. Master’s Thesis, Boston College, Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Pei, J.; Yin, S.; Li, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L. Leaching behaviour of rare earth elements from low-grade weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore using magnesium sulfate. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Huang, L.; Gao, G.; Yang, R.; Xiao, Y. Recovery of rare earths from ion-absorbed rare earths ore with MgSO4-ascorbic acid compound leaching agent. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Rezaei Azizi, M.; Calagari, A.A.; Cheshmehsari, M. Rare earth element geochemistry and tetrad effects of the Dalir phosphatic shales, northern Iran. Neues Jahrb. Für Geol. Und Paläontologie Abh. 2017, 286, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, T.; Sarapää, O. Clay and clay mineralogy. In Physical-Chemical Properties and Industrial Uses; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2008; pp. 11–65. [Google Scholar]


| Mode of Occurrence | Host Medium | Extractability | Example Deposits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ion-adsorbed | Clays (kaolinite, halloysite) | Easy (mild leaching) | South China lateritic clays |
| Mineral-hosted (crystalline) | Monazite, bastnäsite, xenotime | Hard (acid/roasting) | Mountain Pass, Bayan Obo |
| Organic/amorphous-bound | Coal, black shale, Fe-Mn oxides | Moderate (oxidation) | Appalachian coals, fly ash |
| Lithology | Dominant REE-Host Phases | REE Type | Bonding Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weathered Granites/Ion-Clay Zones | Ion-adsorbed REEs on kaolinite, halloysite, illite | HREE > LREE | Weak electrostatic adsorption |
| Carbonatites/Pegmatites/Plutonics | Monazite, bastnäsite, xenotime, allanite | LREE > HREE | Crystal lattice substitution (Ca2+, Th4+) |
| Black Shales/Organic Mudstones | Organically-bound REEs, phosphate microfossils, clays | Mixed LREE & HREE | Organo-metallic complexation, interlayer sorption |
| Coal Seams/Fly Ash | Amorphous aluminosilicates, Fe–Mn oxides, organic matter | Mixed (varies) | Variable: adsorption, chelation, occlusion |
| Marine Shales/Siliciclastic Sediments | Ion-adsorbed + interlayered REEs on smectite/illite clays | Variable (often HREE) | Weak ionic and surface bonding |
| Thermally Altered Zones/Alterites | Secondary phosphates, altered monazite, poorly crystalline oxides | LREE > HREE | Recrystallized or amorphous lattice |
| Research Group | Extracted Material Type | Basin/Region | Lithology Type | REE Host Phases Identified | Analytical Methods Used | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fowler & Zierenberg (2015) [121] | Drill cuttings and core samples | Reykjanes Peninsula, Iceland | Altered tholeiitic basalts (volcanic rocks) | Not mineral-speciated; implied REE association with clays, zeolites, and sulfates | XRF, ICP-MS | Vertical variation in REE content linked to hydrothermal alteration; LREE enrichment in altered zones |
| Bhattacharya et al. (2022) [122] | Core samples | Appalachian Basin (Marcellus), Haynesville Basin | Organic-rich black shale | Acid-soluble (carbonates, phosphates); minor organics and silicates | Sequential extraction, XRD, ICP-MS | Whole-rock REEs: 295–342 ppm; Haynesville higher than Marcellus; low extraction due to clay-bound REEs |
| Stuckman et al. (2021) [123] | Drill cuttings | Various U.S. Basins | Shale formations | Not specified | Advanced geochemical characterization techniques | Explored potential recovery of critical minerals, including REEs, from shale gas drill cuttings; emphasized sustainable recovery methods |
| Lopano et al. (2022) [124] | Drill cuttings | Various U.S. Basins | Shale formations | Not specified | Geochemical characterization | Developed novel treatments for optimizing drill cuttings for use as soil amendments; evaluated potential recovery of critical metals, including REEs, from waste materials across U.S. basins |
| Fontana et al. (2020) [18] | Drill cuttings | Offshore Brazil (Ultradeep waters) | Sedimentary rocks from offshore drilling | Not specified | Microwave-assisted acid digestion, ICP-MS, PCA, HCA | REE concentrations varied with depth; Ce, La, Nd, Sm, and Eu up to mg/kg levels; identified three sample groups based on REE composition; suggested drill cuttings as potential alternative REE source |
| Stuckman et al. (2019) [125] | Drill cuttings, core samples, and drilling mud | Marcellus Shale, USA | Organic-rich black shale | Not specified | Sequential chemical extraction, XRD, ICP-MS | Identified concentrations of REEs and other critical minerals; provided insights into their distribution and potential environmental impacts |
| Barczok et al. (2024) [126] | Drill cuttings and core samples | Various U.S. Basins | Shale formations | Not specified | Sequential extraction, ICP-MS | Identified concentrations of REEs and other critical minerals; developed a four-step sequential extraction process; demonstrated potential for converting drill cuttings into soil supplements |
| E-Tech Resources Inc. (2022) [127] | Drill cuttings and core samples | Eureka Project, Namibia | Carbonatite dykes | Monazite | XRF, ICP-MS | Intersected significant REE mineralization, including 8.2 m at 2.6% TREO from 83 m depth; mineralization open at depth and along strike |
| * Lithology | La | Ce | Nd | Pr | Sm | Eu | Dy | Y | Tb | Gd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shale/Organic-rich shale |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
| Sedimentary rocks (offshore) |  |  |  |  |  | |||||
| Carbonatite dykes |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Altered volcanic rocks |  |  |  |  |
| Lithology | Ion-Adsorbed Clays | Monazite | Xenotime | Organic Matter | Fe-Mn Oxides | Apatite | Zeolites Amorphous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shale/Organic-rich shale |  |  /minor /minor |  |  |  |  /minor /minor |  |
| Sedimentary rocks (offshore) |  /moderate /moderate |  /trace /trace |  | maybe |  |  |  |
| Carbonatite dykes |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Altered volcanic rocks |  /weak /weak | maybe |  |  |  /weak /weak |  |  |
| Scenario | Key Assumptions | Viability Summary |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Centralized Pilot Plant with Acid Leaching |
|
|
| 2. Field-Integrated Portable Unit |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasool, M.H.; Ridha, S.; Ahmad, M.; Shamsuddun, R.A.B.; Zahoor, M.K.; Khan, A. A Mineralogical Perspective on Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Extraction from Drill Cuttings: A Review. Minerals 2025, 15, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050533
Rasool MH, Ridha S, Ahmad M, Shamsuddun RAB, Zahoor MK, Khan A. A Mineralogical Perspective on Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Extraction from Drill Cuttings: A Review. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasool, Muhammad Hammad, Syahrir Ridha, Maqsood Ahmad, Raba’atun Adawiyah Bt Shamsuddun, Muhammad Khurram Zahoor, and Azam Khan. 2025. "A Mineralogical Perspective on Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Extraction from Drill Cuttings: A Review" Minerals 15, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050533
APA StyleRasool, M. H., Ridha, S., Ahmad, M., Shamsuddun, R. A. B., Zahoor, M. K., & Khan, A. (2025). A Mineralogical Perspective on Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Extraction from Drill Cuttings: A Review. Minerals, 15(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050533







