Evolution of the Ore-Bearing Fluid of Alin Sb–Au Orebodies in Shuixie Cu–Co Orefield, SW China: Constraints on the Rare Earth Element and Trace Element Components of Auriferous Pyrite and Host Rock
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Regional Geological Background
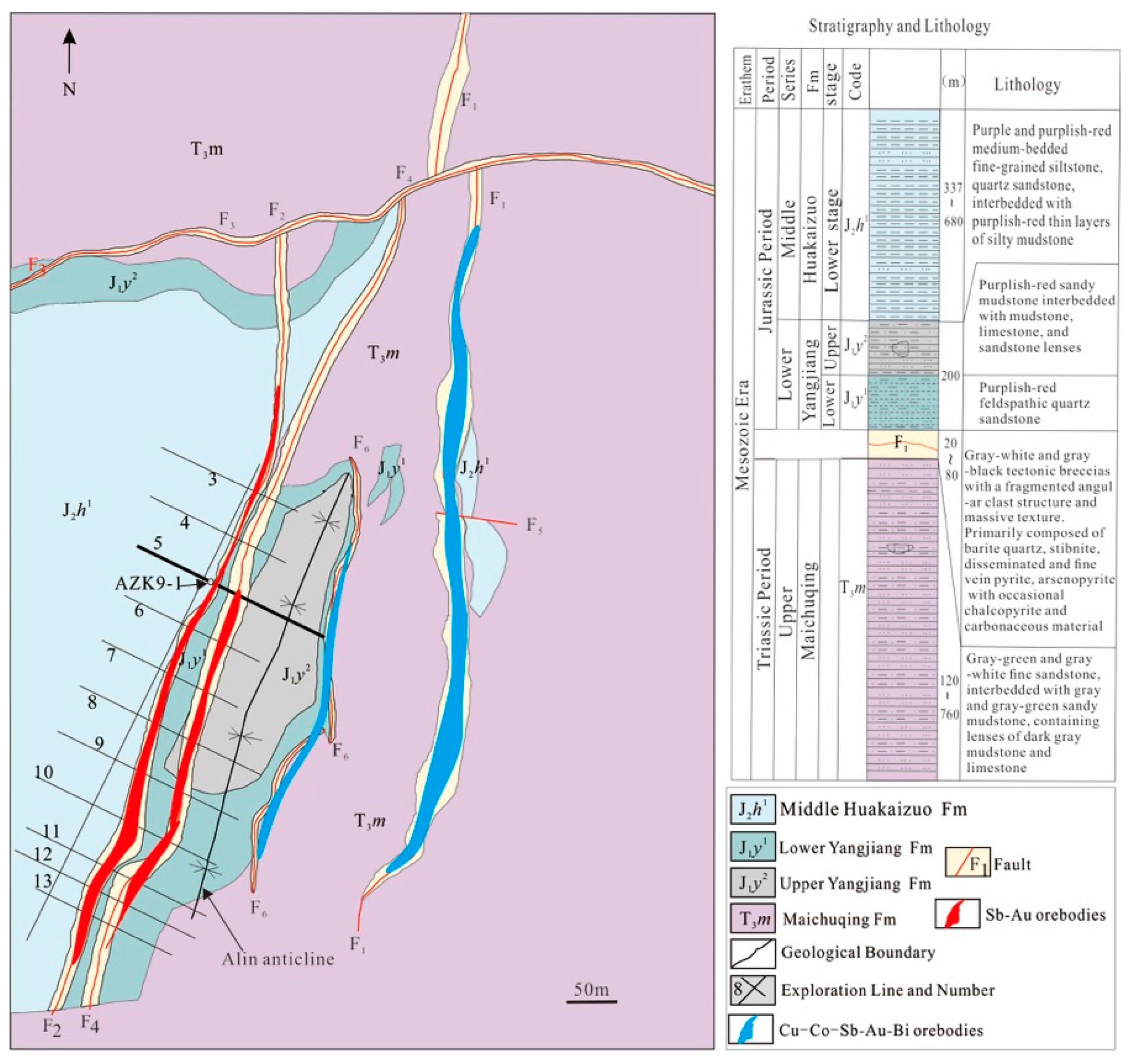
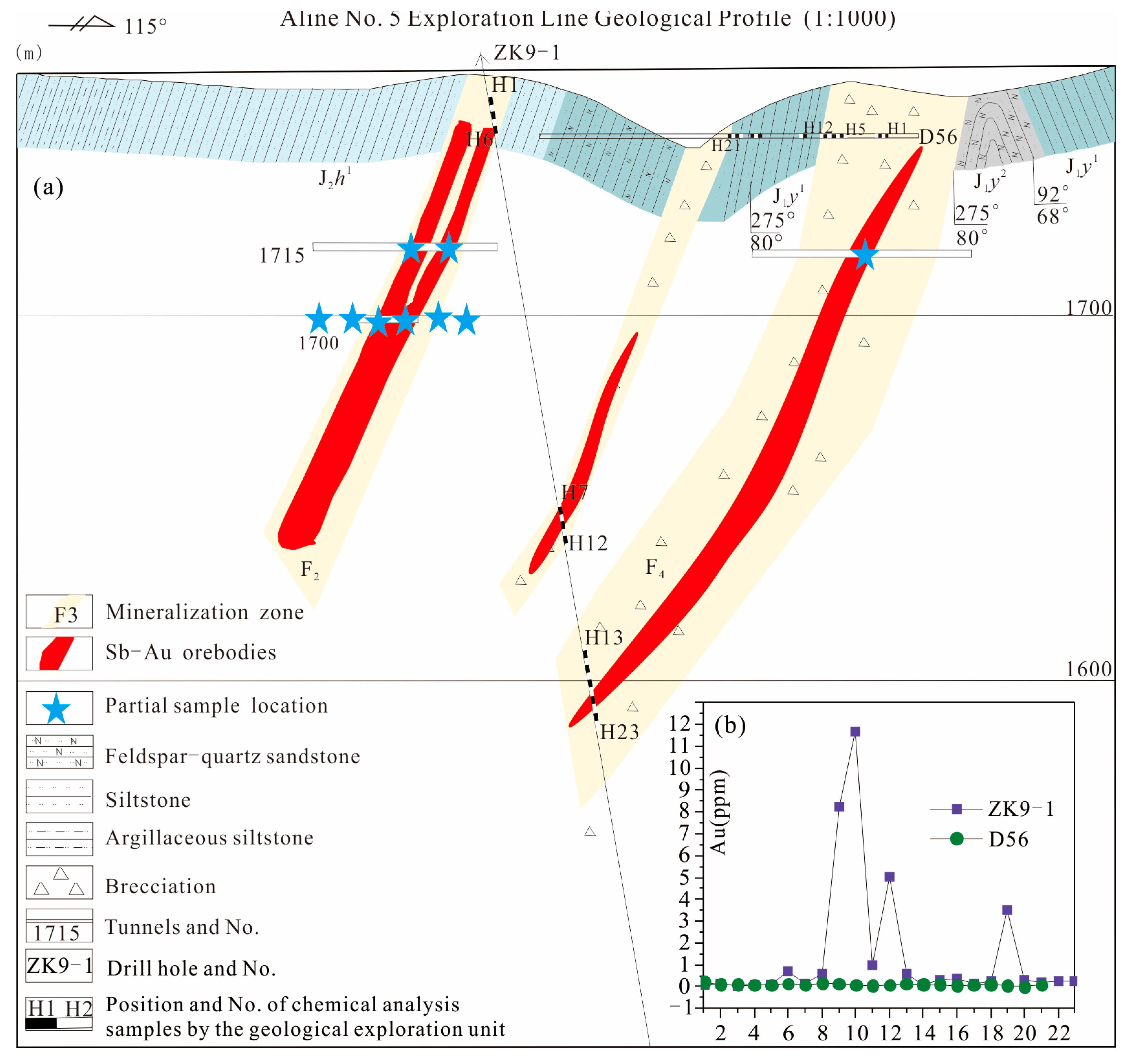
2.2. Deposit Geology
3. Sample and Analytical Methods
3.1. LA-ICP-MS Analysis
3.2. Trace Element Analysis of Whole Rock
4. Results
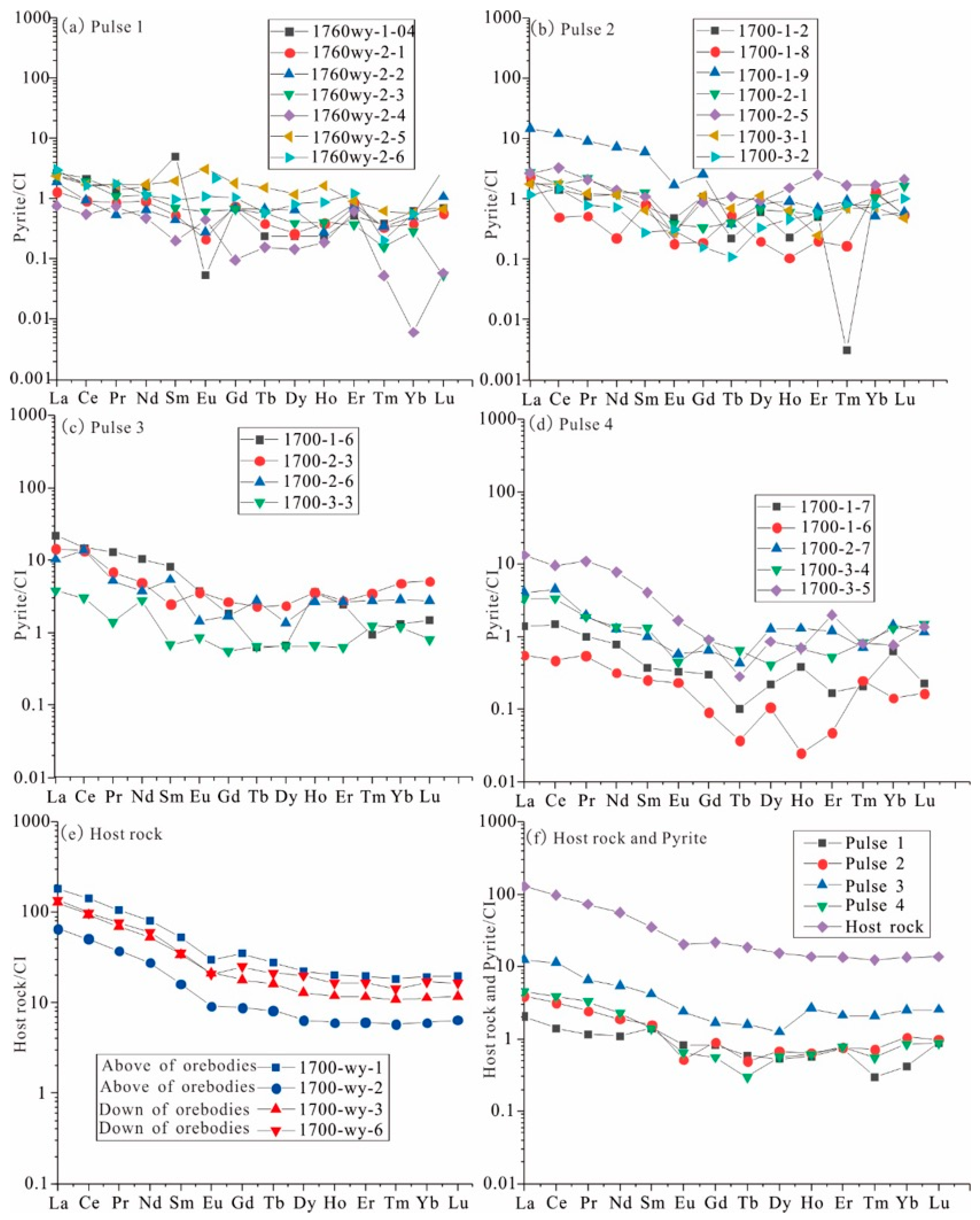
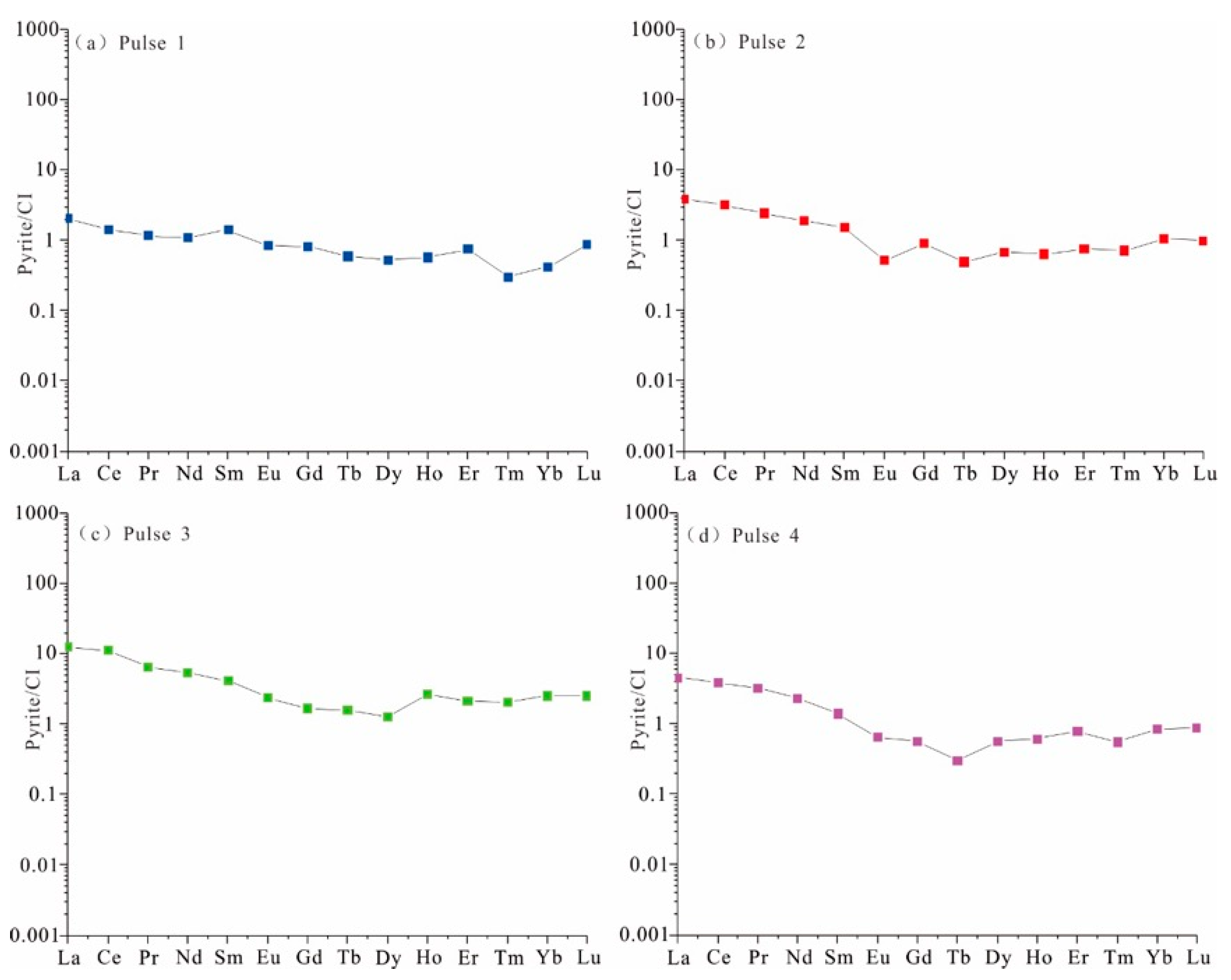
4.1. Rare Earth Elements
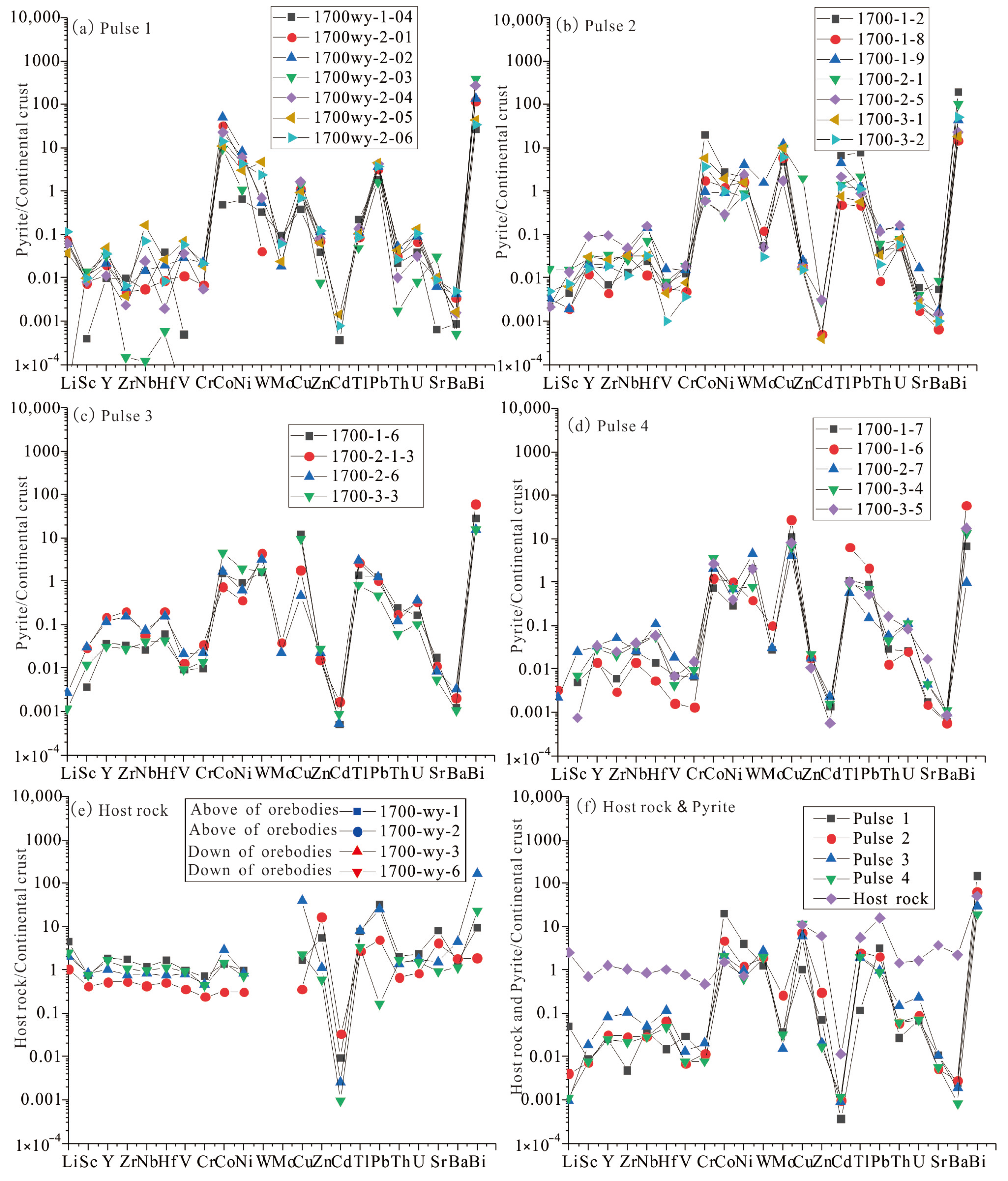
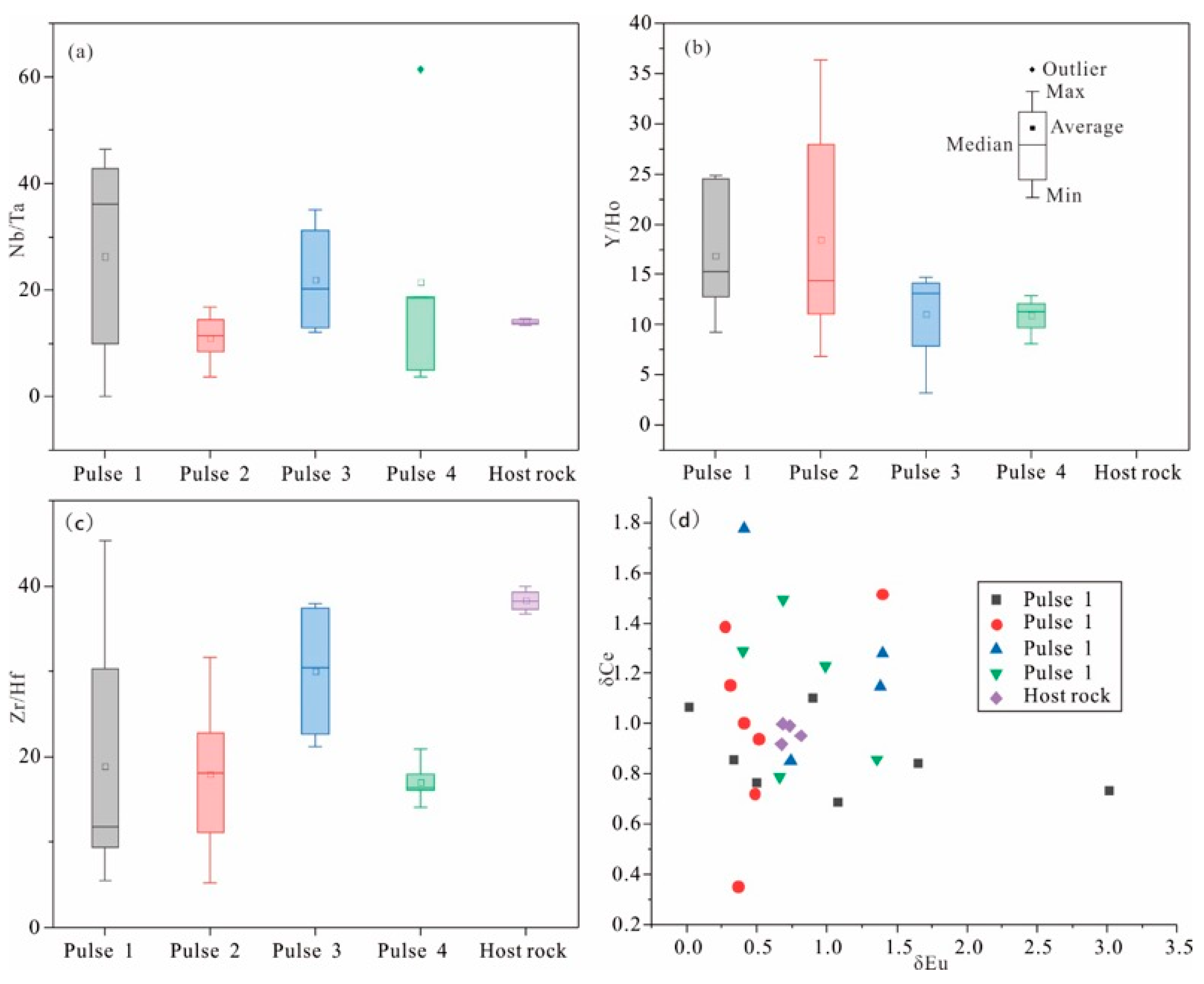
4.2. Trace Elements
5. Discussion
5.1. The Composition of Ore-Forming Fluid
5.2. Evolution of Ore-Bearing Fluid
6. Conclusions
- The ore-forming fluids were low in Cl− and F−, but enriched by sulfur-loving elements such as Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Bi and iron-group elements such as Co.
- The physical and chemical conditions during mineralization were marked by a reducing environment. Initially, the temperature decreased from pulse 1 to pulse 4, and then increased again.
- The temperature increase during pulse 4 may have resulted from the influx of Sb-bearing high-temperature hydrothermal fluids, causing a metasomatic effect.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Z.Q.; Zaw, K.; Pan, G.T.; Mo, X.X.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Y.Z.; Li, X.Z. Sanjiang Tethyan metallogenesis in SW China: Tectonic setting, metallogenic epochs and deposit types. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 31, 48–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Barosh, P.J.; Wu, Z.H. Vast early Miocene lakes of the central Tibetan Plateau. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2008, 120, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Yang, L.F.; Zhang, R.; Du, B.; Shi, K.X. Tectonic–fluid–mineral system in the Lanping basin, Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 1957–1977, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.J.; Xue, C.D.; Wei, A.Y.; Wang, W.; Li, G. Discovery of gold deposit in the Shuixie Zhifanghe copper–cobalt district in Yongping County, western Yunnan Province, SW China. Geol. China 2024, 51, 2, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Xue, C.D.; Feng, Z.J.; Wang, W.; Wei, A.Y. In situ elemental and sulfur isotopic variations of Au–bearing iron–sulfides from newly unearthed Alin gold deposit in the Shuixie Cu–Co orefield (Western Yunnan Province), SE Tibet: Insights into enrichment processes of invisible gold. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 178, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Sun, D.S.; Chang, L.; Zang, W.S.; Wang, J.; Lu, A.H. Morphogenesis of Pyrite. Geoscience 1987, 1, 60–76, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Xu, T.; Lu, Q.T.; Zheng, M.; Bai, Z.M. The fine upper crustal stracture below the Qin-Hang and Wuyishan metallogenic belts revealed by double beamforming ambient noise tomgraphy. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 65, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.S.; Chen, G.Y. Morphogenesis of Pyrite. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 1987, 3, 139–140, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 1–510. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Christopher, S.; Stephen, L. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.; Hollit, C.; Maslennikov, V.; Meffre, S.; Gilbert, S.; Bull, S.; Scott, R.; Emsbo, P.; Thomas, H.; et al. Gold and trace ele ment zonation in pyrite using a laser imaging technique: Implic ations for the timing of gold in orogenic and Carlin-style sedi ment hosted deposits. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 635–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.Z.; Hua, R.M.; Gao, J.F.; Li, W.; Zhao, K.; Long, G.; Lu, H. Existing forms of REE in gold bearing pyrite of the Jinshan gold deposit, Jiangxi Province, China. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, J.; Cornell, D.H.; Theart, H.F.J. Rare-earth element and isotopic evidence for the genesis of the Prieska massive sulfide deposit, South Africa. Econ. Geol. 1989, 84, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.X.; Liu, H.D.; Hou, J.H.; Wang, Q.H.; Chen, H. The rare earth elements and trace elements of gold–bearing pyrite from Jiangjiayao gold deposit, Shandong Province. Geol. China 2020, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.N.; Yan, Z.; Xue, C.D.; Xin, D.; Dong, M.M. India indenting Eurasia: A brief review and new data from the Yongping Basin on the SE Tibetan Plateau. Geosciences 2021, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.N.; Dong, M.M.; Xue, C.D. Coherent chemical variation trends of the 55–25 Ma magmatic rocks in SE Tibet: N–S direction lithospheric stretching of Eurasia during early stage of India–Eurasia Collision. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 1283–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.J.; Yang, T.N.; Xue, C.D.; Xin, D.; Yan, Z.; Liao, C.h.e.n.; Han, X.u.e.; Xie, Z.P.; Xiang, K. Complete deformation history of the transition zone between oblique and orthogonal collision belts of the SE Tibetan Plateau: Crustal shortening and rotation caused by the indentation of India into Eurasia. J. Struct. Geol. 2022, 156, 104545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resource Reserves Verification Report of Xiaotuanshan from Shuixie Copper–Cobalt Deposit, Yongping County, Yunnan Province; Yongping Mining Co., Ltd.: Dali, China, 2023; (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Zong, K.Q.; Klemd, R.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.Y.; Guo, J.L.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.M. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900 Ma) high–grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB). Precambrian Res. 2017, 290, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Chen, H.H.; Hu, S.H. “Wave” Signal–Smoothing and Mercury–Removing Device for Laser Ablation Quadrupole and Multiple Collector ICPMS Analysis: Application to Lead Isotope Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Gunther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA−ICP−MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; McDonough, W.F. Magmatism in ocean basin. In Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Ocean Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes; Saunders, A.D., Norry, M.J., Eds.; Geological Socity London Special Publish: London, UK, 1989; Volume 42, pp. 313–345. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Luo, T.C.; Zhang, B.R.; Zhang, H.F.; Han, Y.W.; Zhao, Z.D.; Hartmut, K. Texture and composition of Eastern China crust. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1999, 29, 204–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.W.; Ma, Z.D.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, B.R.; Li, F.L.; Gao, S.; Bao, Z.Y. Geochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 1–370, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Huang, D.Y.; Pu, W.M. On the geological characteristics and genesis of Shuixie copper deposit in Yongping. Yunnan Geol. 1994, 13, 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, H.L.; Li, J.K.; Li, J.L.; Wang, G.Q. Evolution of ore fluid of the Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong: Constraints on REE and trace element component of auriferous pyrite. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2518–2532, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Oreskes, N.; Einaudi, M.T. Origin of rare earth element–enriched hematite breccias at the Olympic Dam Cu–U–Au–Ag deposit, Roxby Downs, South Australia. Econ. Geol. 1990, 85, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, H. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction–zone fluids. Nature 1996, 380, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wu, L.L.; Uttly, P.J.; Norman, T.; Zheng, J.M.; Qin, Y.Z. REE features of arsenian pyrite and vein quartz and their fulid inclusions in Jingfeng (Liannigou) gold deposit, Guizhou provice, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, M.H.; Dong, Q.J.; Huang, Q.W. Trace Elements Features of the Vein Quartzs, Arsenian Pyrites and Their Fluid Inclusions in Jinfeng (Lannigou) Gold Deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Geol. J. China Univ. 2009, 15, 506–516, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J.F.; Li, Y. A study of minor elements in minerals from polymetallic deposits in the central part of the da hinggan mountains. Miner. Depos. 1999, 34, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Ge, W.S.; Ding, H.; Chen, J.; Jia, H.X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.R. Geochemical Characteristics of REE and Trace Elements of Pyrite: Constraint on the Ore–Forming Fluid of the Lvyuan Gold Deposit, Eastern Junggar. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2017, 36, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare–earth element behaviours in fluorine–rich hydrothermal fluids. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1995, 119, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaxley, G.M.; Green, D.H.; Kamenetsky, V. Carbonatitemetasomatism in the Southeastern Australian Lithosphere. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Q.H.; Yan, M.C. Applied Geochemistry Element Abundance Pamphlet; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 8–114, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Barrat, J.A.; Zanda, B.; Moynier, F.; Bollinger, C.; Liorzou, C.; Bayon, G. Geochemistry of CI chondrites: Major and trace elements, and Cu and Zn isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Ru, S.; Xue, C.; Wang, W. Evolution of the Ore-Bearing Fluid of Alin Sb–Au Orebodies in Shuixie Cu–Co Orefield, SW China: Constraints on the Rare Earth Element and Trace Element Components of Auriferous Pyrite and Host Rock. Minerals 2025, 15, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050491
Li G, Ru S, Xue C, Wang W. Evolution of the Ore-Bearing Fluid of Alin Sb–Au Orebodies in Shuixie Cu–Co Orefield, SW China: Constraints on the Rare Earth Element and Trace Element Components of Auriferous Pyrite and Host Rock. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050491
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guo, Shanshan Ru, Chuandong Xue, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Evolution of the Ore-Bearing Fluid of Alin Sb–Au Orebodies in Shuixie Cu–Co Orefield, SW China: Constraints on the Rare Earth Element and Trace Element Components of Auriferous Pyrite and Host Rock" Minerals 15, no. 5: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050491
APA StyleLi, G., Ru, S., Xue, C., & Wang, W. (2025). Evolution of the Ore-Bearing Fluid of Alin Sb–Au Orebodies in Shuixie Cu–Co Orefield, SW China: Constraints on the Rare Earth Element and Trace Element Components of Auriferous Pyrite and Host Rock. Minerals, 15(5), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050491




