Contribution of Sessile Acidophiles on Chalcopyrite Bioleaching Under Controlled Redox Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
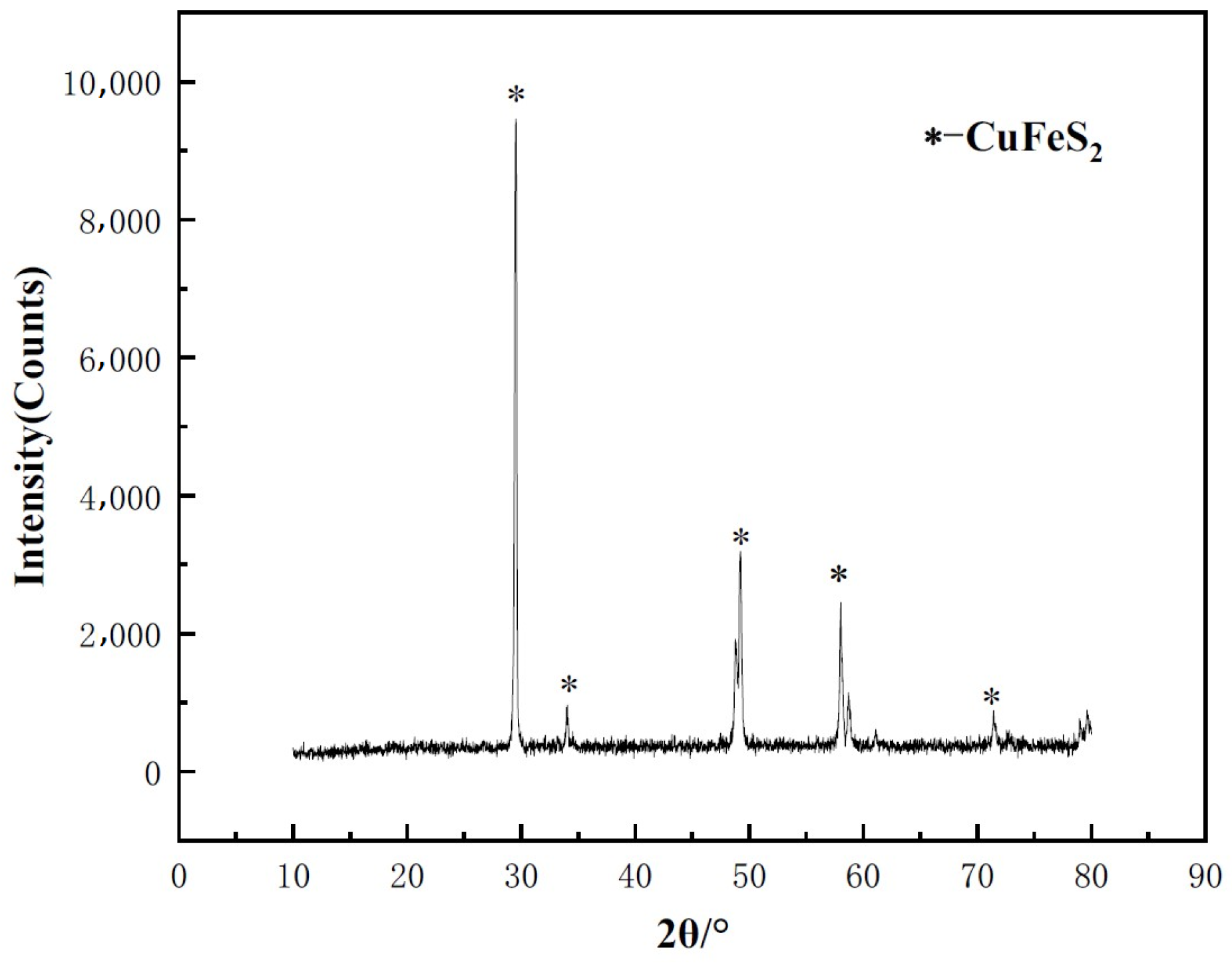
2.1. Samples and Microbes
2.2. Apparatus and Batch Experiments
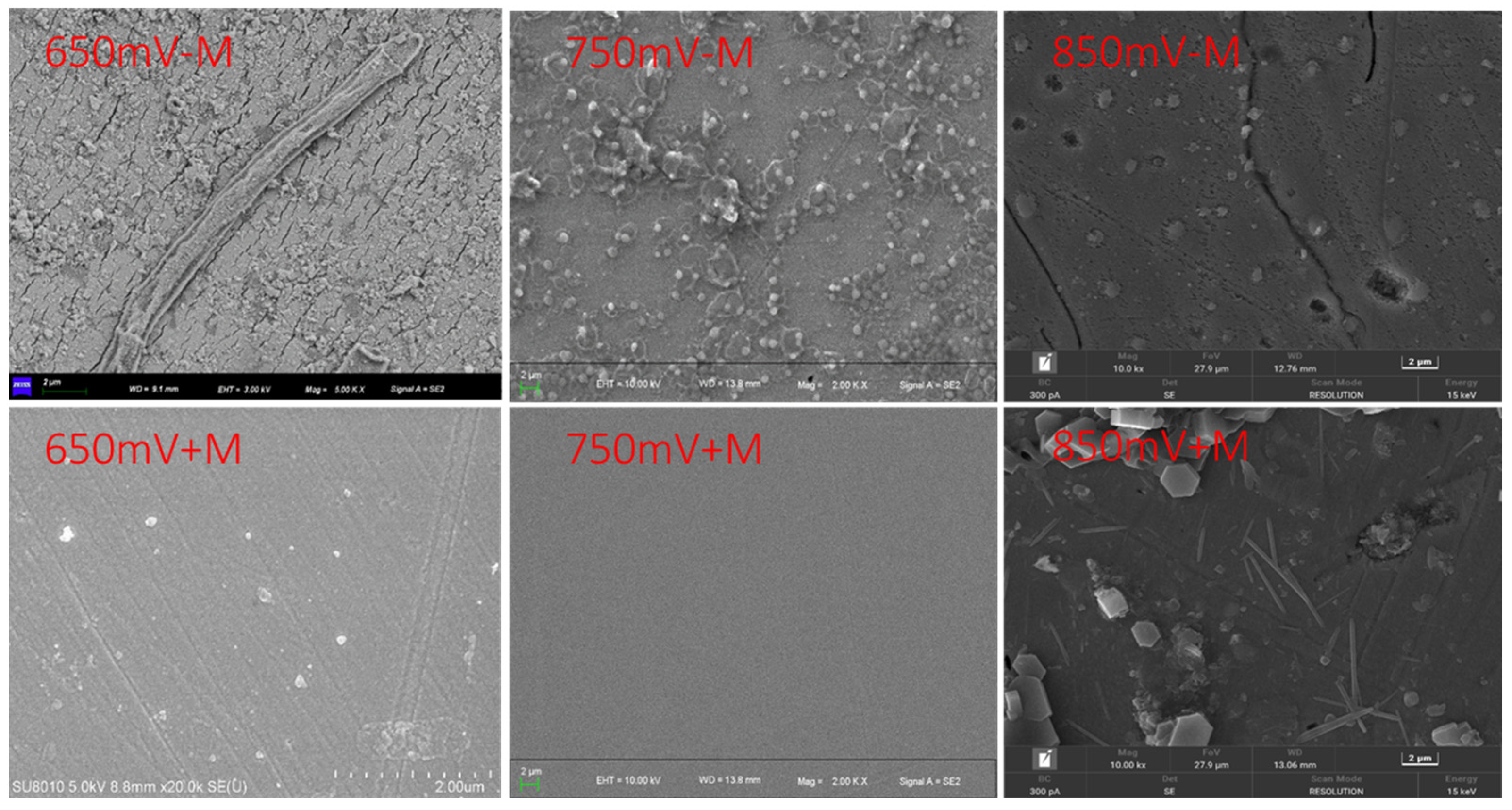
2.3. Surface Morphology by SEM
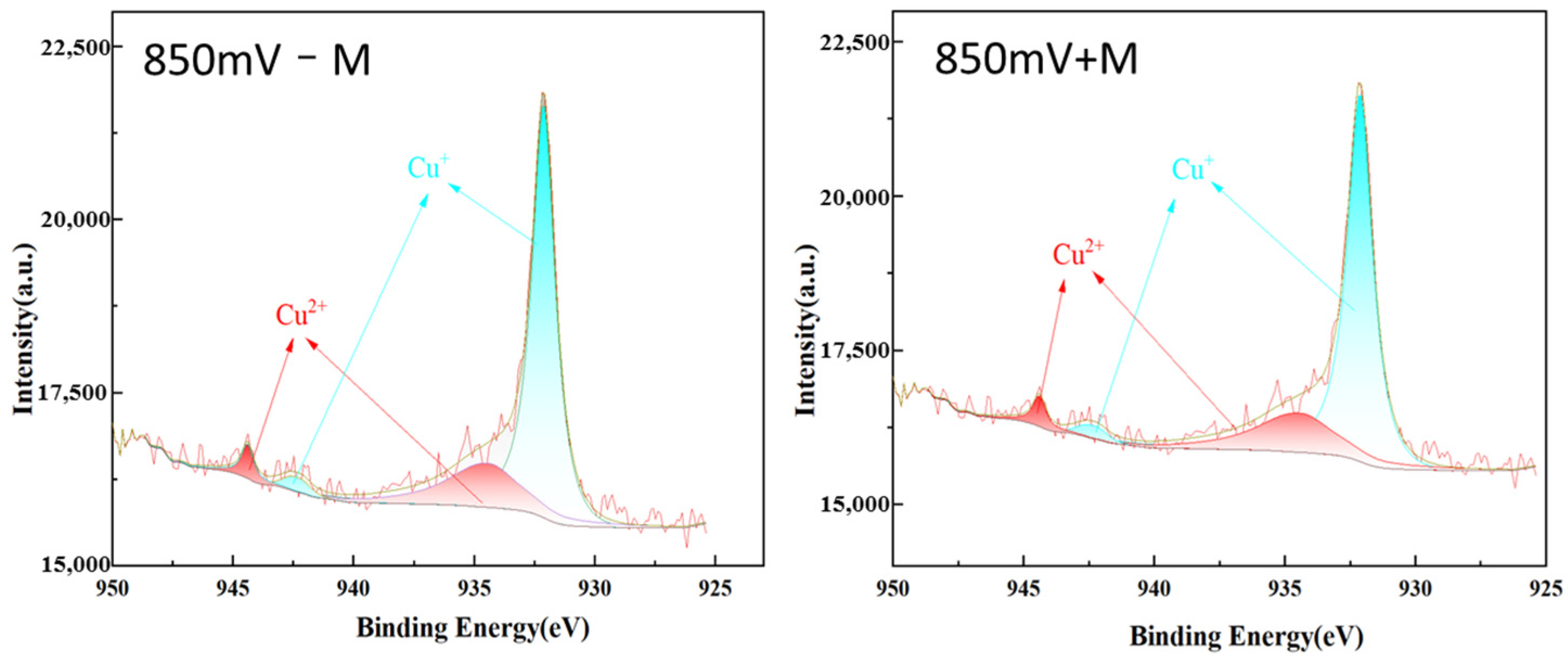
2.4. Surface Components by XPS
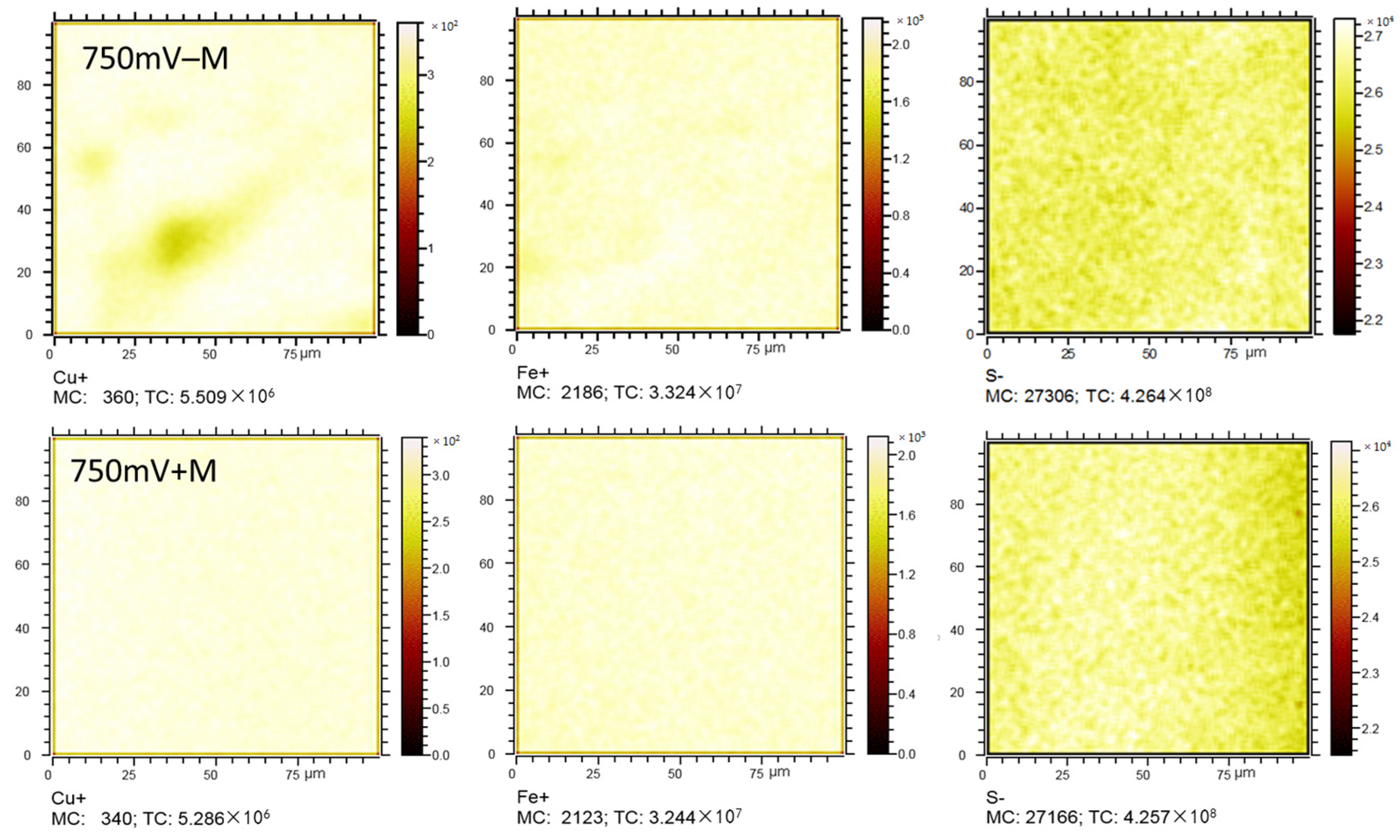
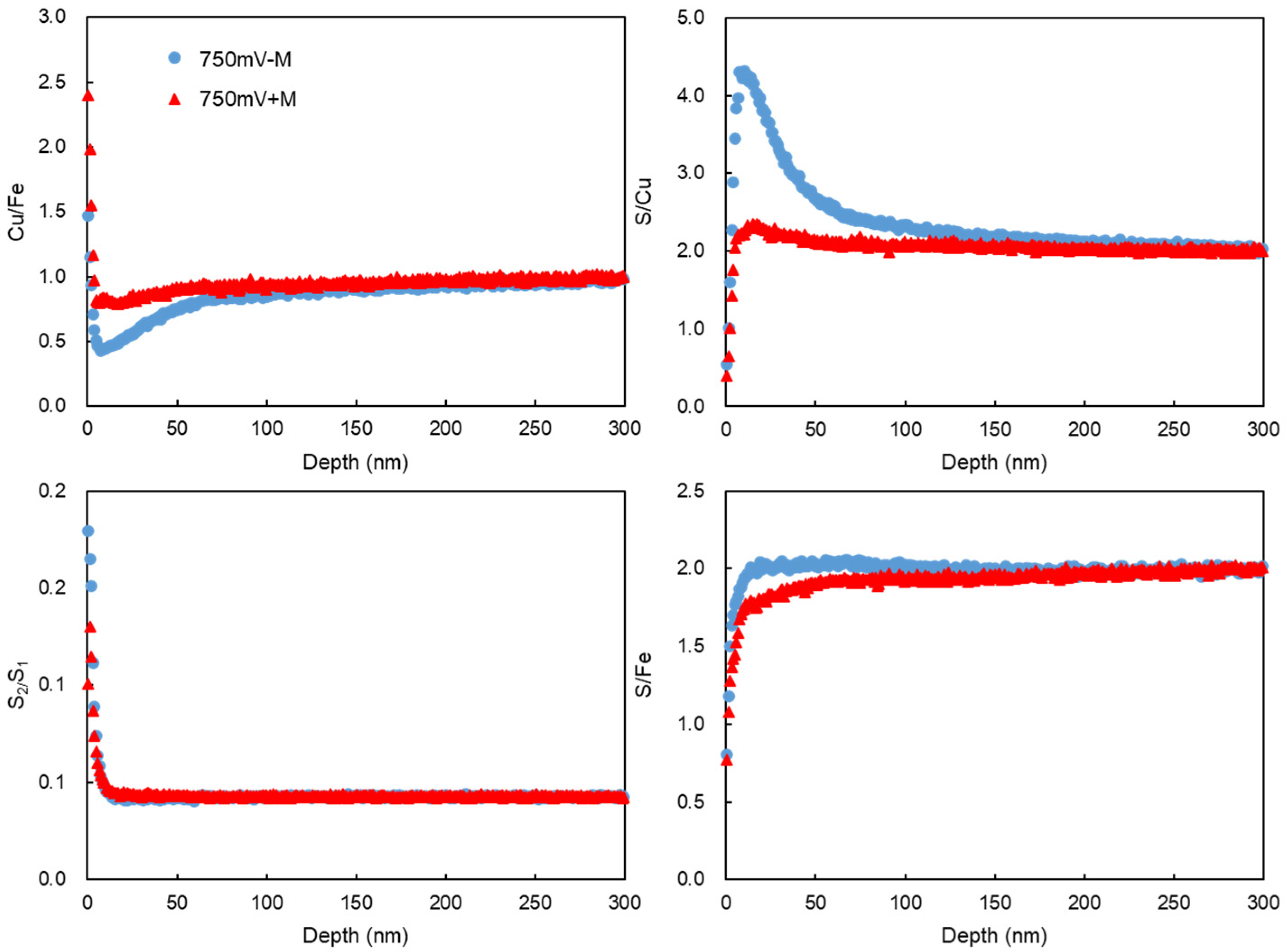
2.5. Copper, Iron, and Sulfur Distributions by Tof-SIMS
2.6. Quantification of Elemental Sulfur by HPLC Assay
2.7. Microbial Community Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of Oxidized Chalcopyrite Cube Surface
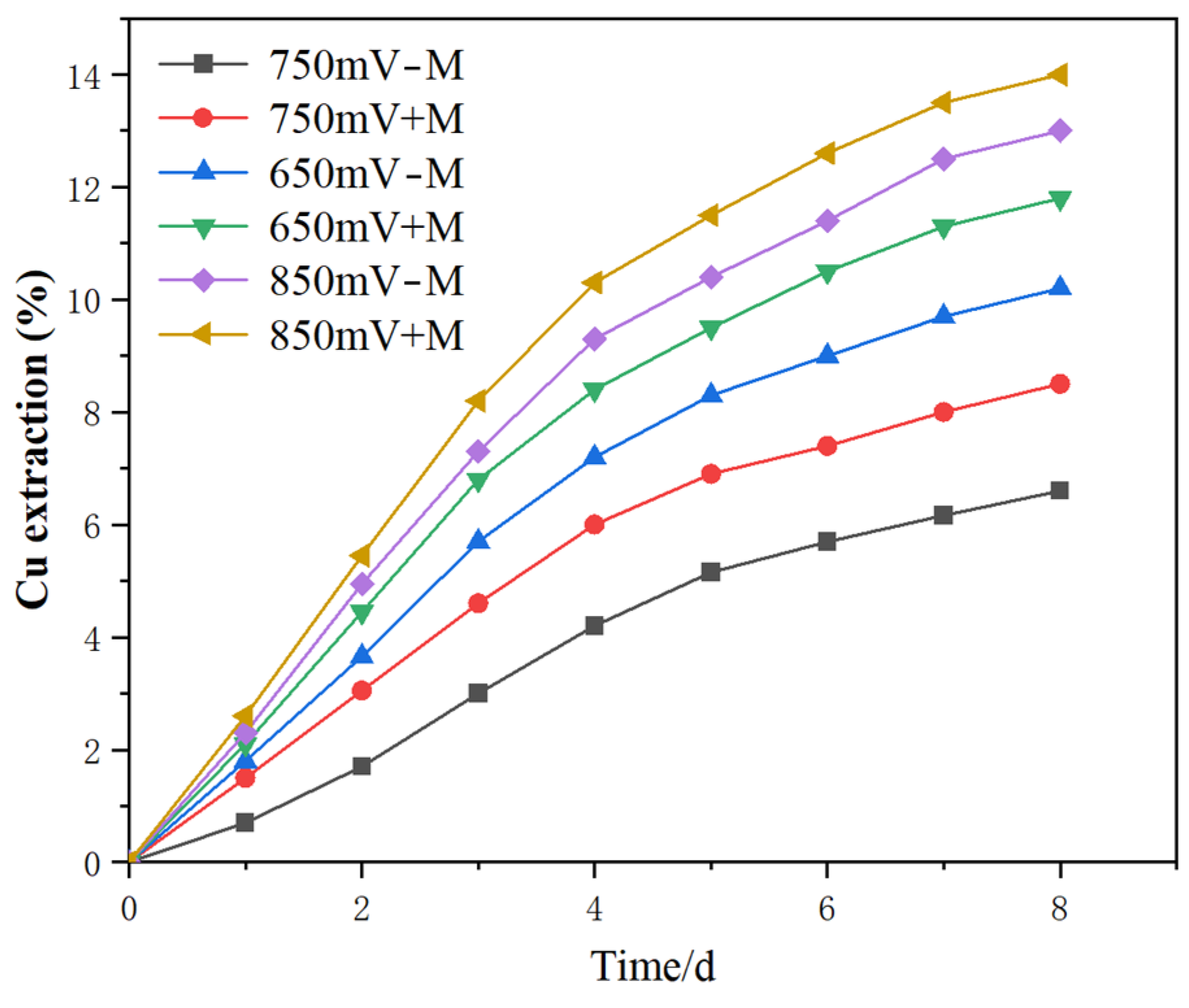
3.2. Copper Leaching Kinetics
3.3. Chalcopyrite Residue Surface Component Assay
3.4. Chalcopyrite Elemetal Distribution Assay by ToF-SIMS
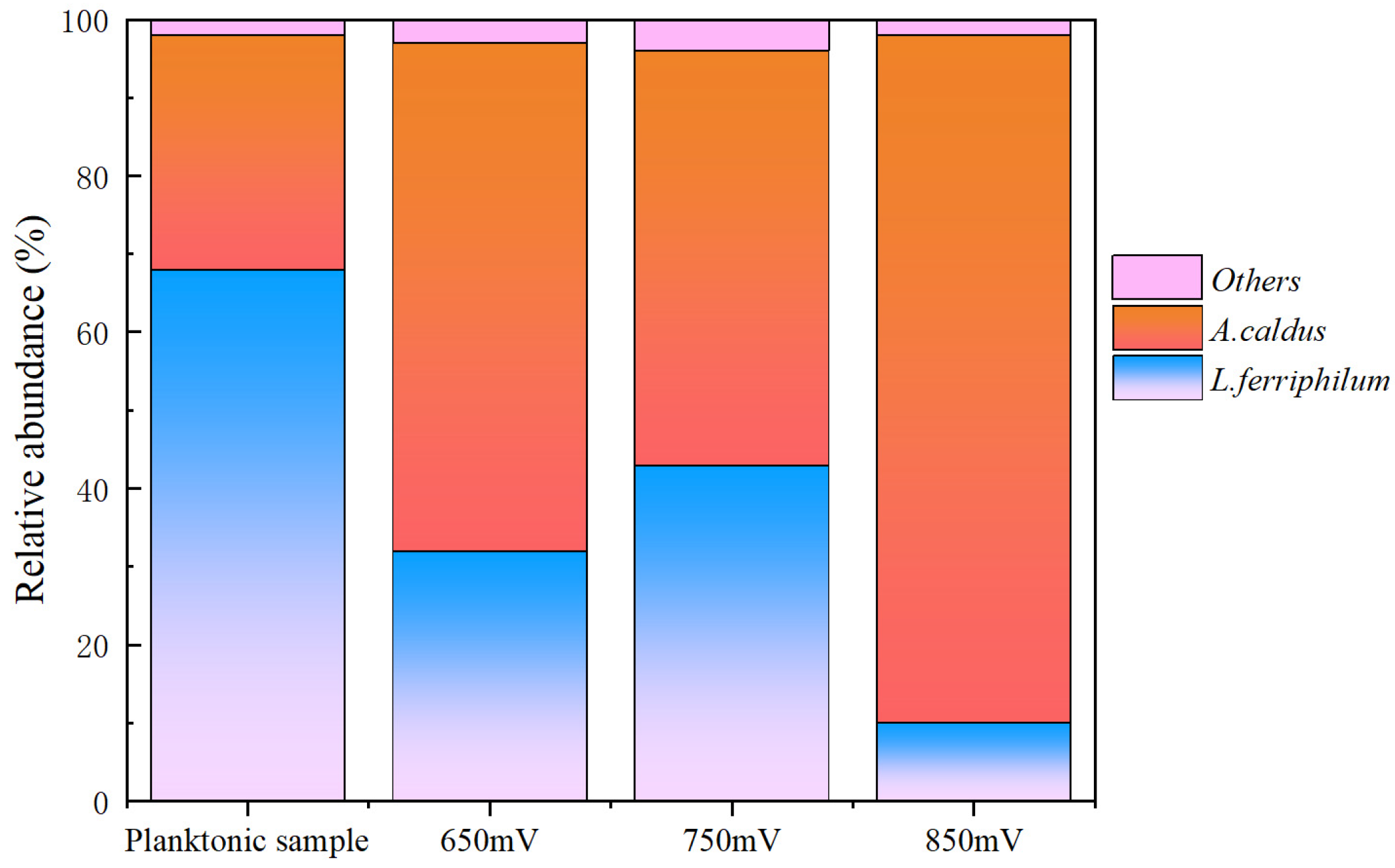
3.5. Microbial Community in Chalcopyrite Residue
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Z.H.; Chao, C.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Heise, C.; Sabzehei, K.; Asselin, E.; Dixon, D.G.; Mora, N. New perspective on the depassivation mechanism of chalcopyrite by ethylene thiourea. Miner. Eng. 2023, 204, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Y.; Li, H.D.; Wei, Q.; Qin, W.Q.; Yang, C.R. Effects of redox potential on chalcopyrite leaching: An overview. Miner. Eng. 2021, 172, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, F.F.; Schippers, A. Progress in bioleaching: Part B, applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 5913–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez-Yevenes, L.; Malverde, S.; Quezada, V. A sustainable bioleaching of a low-grade chalcopyrite ore. Minerals 2022, 12, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, M.; Schippers, A.; Hedrich, S.; Sand, W. Progress in bioleaching: Fundamentals and mechanisms of microbial metal sulfide oxidation—Part A. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6933–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Xie, L.; Han, L.B.; Wang, X.G.; Wang, J.M.; Zeng, H.B. In-situ probing of electrochemical dissolution and surface properties of chalcopyrite with implications for the dissolution kinetics and passivation mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tan, Q.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Gao, H.S.; Ruan, R. Sulfide mineral dissolution microbes: Community structure and function in industrial bioleaching heaps. Green Energy Environ. 2019, 4, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Yang, H.Y.; Luan, Z.C.; Sun, Q.F.; Ali, A.; Tong, L.L. Leaching of chalcopyrite under bacteria-mineral contact/noncontact leaching model. Minerals 2021, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yuan, W.B.; Jin, K.; Zhang, Y.S. Control of the redox potential by microcontroller technology: Researching the leaching of chalcopyrite. Minerals 2021, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Jozsa, P.G.; Sand, W. Sulfur chemistry in bacterial leaching of pyrite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.P.; Ehrlich, H.L. Microbial formation and degradation of minerals. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1964, 6, 153–206. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, Y.A.; Elzeky, M.A. Bioleaching of nonferrous sulfides with adapted thiophilic bacteria. Chem. Eng. J. 1990, 44, B31–B40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jia, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Tan, Q.Y.; Niu, X.P.; Leng, X.K.; Ruan, R.M. Limited role of sessile acidophiles in pyrite oxidation below redox potential of 650 mV. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.X.; Jia, Y.; Tan, Q.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Ruan, R.M. Contributions of microbial “contact leaching” to pyrite oxidation under different controlled redox potentials. Minerals 2020, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, W.; Gehrke, T.; Jozsa, P.G.; Schippers, A. (Bio) chemistry of bacterial leaching—Direct vs. indirect bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.X.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, H.P.; Tan, Q.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Jiang, C.Y.; Ruan, R.M. Evidence of weak interaction between ferric iron and extracellular polymeric substances of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Sand, W. Bacterial leaching of metal sulfides proceeds by two indirect mechanisms via thiosulfate or via polysulfides and sulfur. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.M.; Liu, Z.R.; Liao, W.Q.; Cheng, J.J.; Wu, X.L.; Qiu, G.Z.; Shen, L. Distribution and content changes of extracellular polymeric substance and iron ions on the pyrite surface during bioleaching. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2023, 30, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Chen, D.F.; Gao, H.S.; Ruan, R.M. Characterization of microbial community in industrial bioleaching heap of copper sulfide ore at Monywa mine, Myanmar. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Tan, Q.Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Feng, X.L.; Ruan, R.M. Industrial heap bioleaching of copper sulfide ore started with only water irrigation. Minerals 2021, 11, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.P.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Xia, L.Y.; Li, L.; Sun, H.Y.; Ruan, R. Correlation of surface oxidation with xanthate adsorption and pyrite flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 495, 143411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.T.; Liao, R.; Yang, B.J.; Yu, S.C.; Wu, B.Q.; Hong, M.X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.B.; Gan, M.; Jiao, F.; et al. Role and maintenance of redox potential on chalcopyrite biohydrometallurgy: An overview. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2020, 27, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Tan, Q.Y.; Jia, Y.; Shu, R.B.; Zhong, S.P.; Ruan, R.M. Pyrite oxidation in column at controlled redox potential of 900 mV with and without bacteria. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 4279–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Qian, L.; Sun, M.L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, J.; Kim, H.; Qiu, G.Z. The dissolution and passivation mechanism of chalcopyrite in bioleaching: An overview. Miner. Eng. 2019, 136, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E. Elemental sulfur formation during the ferric-chloride leaching of chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 1990, 23, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Pan, Y.G.; Xue, J.Y.; Sun, Q.F.; Su, G.Z.; Li, X. Comparative XPS study between experimentally and naturally weathered pyrites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8750–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okibe, N.; Johnson, D.B. Biooxidation of pyrite by defined mixed cultures of moderately thermophilic acidophiles in pH-controlled bioreactors: Significance of microbial interactions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Tao, X.X.; Cai, P. Study of formation of jarosite mediated by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in 9K medium. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2009, 1, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.L.; Gu, G.H.; Wang, X.H.; Yan, W.; Qiu, G.Z. Study on the jarosite mediated by bioleaching of pyrrhotite using Acidthiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biosci. J. 2017, 33, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Singru, R.M.; Biswas, A.K. Study of the roasting of chalcopyrite minerals by Fe-57 Mossbauer spectroscopy. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.L.; Ou, Y.; Tan, J.X.; Wu, F.D.; Sun, J.; Miao, L.; Zhong, D.L. Effect of EPS on adhesion of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on chalcopyrite and pyrite mineral surfaces. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisener, C.G.; Smart, R.S.C.; Gerson, A.R. Kinetics and mechanisms of the leaching of low Fe sphalerite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, R.C.; Lu, X.C.; Lu, J.J.; Li, C.X.; Li, J. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Miner. Eng. 2013, 53, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.C.; Zhang, L.J.; Xiang, W.L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, R.C. Collaborative effects of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and ferrous ions on the oxidation of chalcopyrite. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.S.; Qiu, Y.K.; Huang, Z.Z.; Yin, Y.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhu, D.Q.; Tong, Y.J.; Yang, H.L. The adaptation mechanisms of Acidithiobacillus caldus CCTCC M 2018054 to extreme acid stress: Bioleaching performance, physiology, and transcriptomics. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna, L.G.; Cardenas, J.P.; Covarrubias, P.C.; Haristoy, J.J.; Flores, R.; Nunez, H.; Riadi, G.; Shmaryahu, A.; Valdes, J.; Dopson, M. Architecture and gene repertoire of the flexible genome of the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Feng, X.; Liang, Y.L.; Xiao, Y.H.; Hao, X.D.; Yin, H.Q.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, X.D. Co-culture microorganisms with different initial proportions reveal the mechanism of chalcopyrite bioleaching coupling with microbial community succession. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, L.A.; Watling, H.R.; Watkin, E.L.J. Microbial population dynamics of inoculated low-grade chalcopyrite bioleaching columns. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Z.; Feng, S.S.; Tong, Y.J.; Yang, H.L. Enhanced “contact mechanism” for interaction of extracellular polymeric substances with low-grade copper-bearing sulfide ore in bioleaching by moderately thermophilic Acidithiobacillus caldus. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xia, J.L.; Yang, Y.; Nie, Z.Y.; Zheng, L.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Peng, A.A.; Tang, L.; Qiu, G.Z. Sulfur oxidation activities of pure and mixed thermophiles and sulfur speciation in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3877–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, B.J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.K.; Zhang, R.Y.; Sand, W. Comparative analysis of attachment to chalcopyrite of three mesophilic iron and/or sulfur-oxidizing acidophiles. Minerals 2018, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Chen, M.; Zou, L.C.; Shu, R.B.; Ruan, R.M. Study of the kinetics of pyrite oxidation under controlled redox potential. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

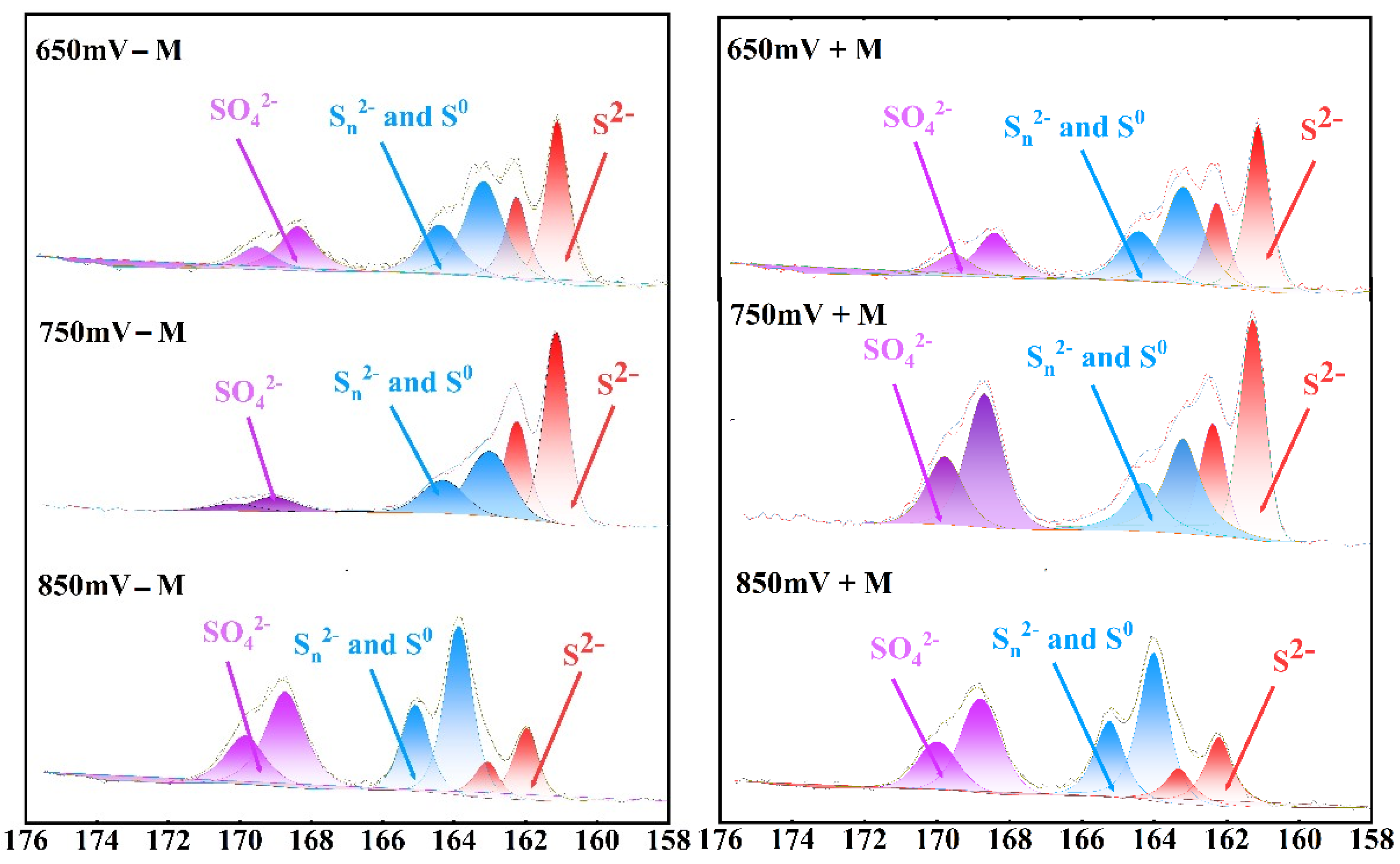
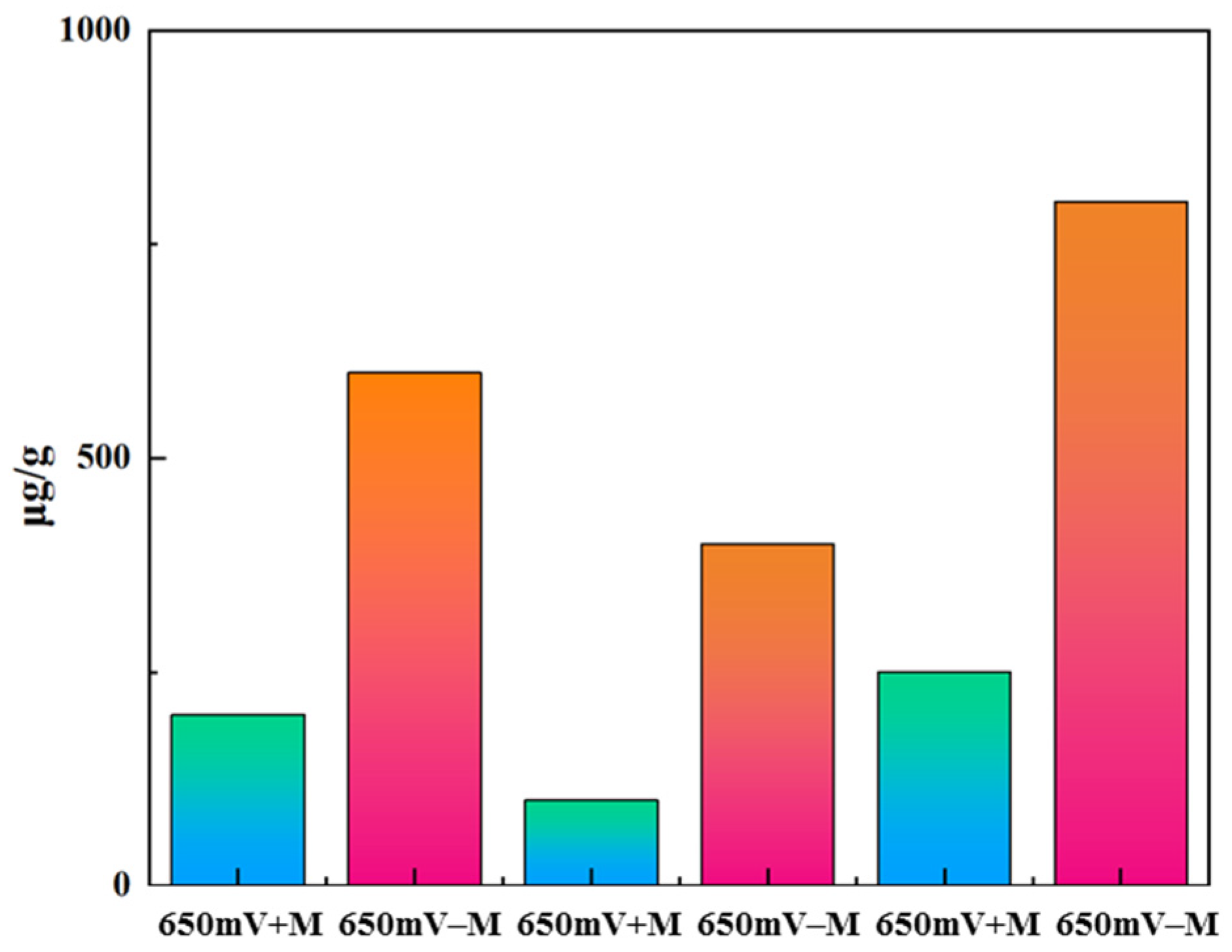

| 650 mV − M | 650 mV + M | 750 mV − M | 750 mV + M | 850 mV − M | 850 mV + M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | % | % | % | % | % | % |
| S22− | 53.88 | 52.04 | 56.85 | 52.40 | 17.27 | 21.01 |
| Sn2−/S0 | 39.12 | 28.7 | 34.66 | 25.65 | 45.76 | 34.86 |
| SO42− | 6.98 | 19.26 | 8.49 | 21.95 | 36.97 | 44.13 |
| 750 mV − M | 750 mV + M | |
|---|---|---|
| Species | % | % |
| FeS2 | 100 | 28.6 |
| FeSO4 | 0 | 71.4 |
| 850 mV + M | 850 mV − M | |
|---|---|---|
| Species | % | % |
| Cu+ | 76.05 | 77.46 |
| Cu2+ | 23.95 | 22.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Q.; Sun, H.; Jin, J.; Qu, J.; Ruan, R.; Zhang, C. Contribution of Sessile Acidophiles on Chalcopyrite Bioleaching Under Controlled Redox Potentials. Minerals 2025, 15, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050480
Yang Q, Jia Y, Zhang L, Tan Q, Sun H, Jin J, Qu J, Ruan R, Zhang C. Contribution of Sessile Acidophiles on Chalcopyrite Bioleaching Under Controlled Redox Potentials. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050480
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiru, Yan Jia, Luohu Zhang, Qiaoyi Tan, Heyun Sun, Jiaqi Jin, Jingkui Qu, Renman Ruan, and Chao Zhang. 2025. "Contribution of Sessile Acidophiles on Chalcopyrite Bioleaching Under Controlled Redox Potentials" Minerals 15, no. 5: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050480
APA StyleYang, Q., Jia, Y., Zhang, L., Tan, Q., Sun, H., Jin, J., Qu, J., Ruan, R., & Zhang, C. (2025). Contribution of Sessile Acidophiles on Chalcopyrite Bioleaching Under Controlled Redox Potentials. Minerals, 15(5), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050480






