Abstract
High quality natural zeolites may have insecticidal effects and could be used for pest control. We determined the mineralogical and chemical composition of four representative samples of zeolite-rich rocks (zeot1–zeot4) collected from north-eastern Greece and their oviposition deterrent effect for the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae (Rossi) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Samples zeot1–zeot4 contain 54–70 wt.% clinoptilolite (HEU-type zeolite) and are free of fibrous minerals. Regarding the chemical composition, samples zeot1–zeot4 contain SiO2 between 64.29 (zeot4) and 68.03 wt.% (zeot3). The values of the sorption ability ranged from 134 to 195 meq/100 g, and the specific surface area ranged from 6.5 to 8.4 cm2/g. In addition, the concentration of toxic heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Se, V, and Zn) is very low and within the acceptable limits for the food sector. When females of the olive fruit fly had access to olive fruits treated with aqueous suspensions of zeot1–zeot4, a significant oviposition deterrent effect was observed. The highest oviposition deterrent effect was observed after the application of zeot3 on the olive fruits, i.e., the mean number of eggs laid by 5 females on the treated and non-treated (control) olive fruits after 8 days was 43.1 and 172.3, respectively. Among the tested zeolites, zeot3 had the highest levels of HEU-type zeolite (clinoptilolite), SiO2, Si, and Ca and the strongest sorption ability and specific surface area. The zeolites oviposition deterrent effect found in our experiments can be attributed to the creation of a thin layer (hymen) of natural zeolite on the surface of the olive fruits which inhibits females landing and egg laying. The oviposition deterrent effect of high-quality Greek zeolites with unique characteristics, if verified with field experiments, could improve the effective control of the olive fruit fly.
1. Introduction
Natural zeolites belong to a wide range of crystalline hydrated aluminosilicate mi-croporous minerals, which have, as their main property, the reversible dehydration and removal of water without destroying their crystal structure [1,2,3]. Zeolites are a class of microporous materials with outstanding properties because of their large pore volume, high surface area, and thermal stability [4]. Regarding their structure, they consist of three-dimensional networks of silica [SiO4] and alumina [AlO4] tetrahedra units, which are linked together by sharing all oxygen atoms, forming channels containing exchangeable cations (potassium, sodium, calcium, etc.), and water molecules [5,6,7]. Their crystal structure consists of five distinct extra-framework positions in which cations are exchanged. The positions of these extra-framework cations and water molecules bound within the crystal framework of the mineral, depend on the nature of the cations involved in the ion exchange [8,9].
In nature, about 67 types of zeolites are found, while more than 200 types of zeolites can be obtained synthetically [10]. Zeolite-rich rocks correspond to a rock containing significant amounts of one or more types of zeolites, and has specific mineralogical, chemical, morphological, and radiological characteristics (natural radionuclides in zeolite-rich rocks). Through the process of diagenesis and under special conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure, pH, salinity), mainly volcanic materials can be completely or partially converted into zeolite or zeolites in different environments. Under these conditions, occurrences in mafic volcanic rocks without economic value can be found, while deposits of sedimentary origin can be formed during diagenesis [11].
Among various types of zeolites, HEU-type zeolites (clinoptilolite-heulandite) are the most common, and are of great economic interest. Structurally, they are characterized by the presence of tabular crystals (usually 1–100 μm in size), and micro/nano-pores in a three-dimensional framework of channels with 10- and 8-membered rings [10,12]. Zeolite-rich rocks containing significant amounts of HEU-type zeolites (clinoptilolite-heulandite), have remarkable properties, resulting in high efficiency in numerous applications. The most important quality characteristics for environmental, agricultural, and industrial uses are highlighted by their complete chemical and mineralogical composition. According to the Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 651/2013 [13], the main properties of clinoptilolite of sedimentary origin as a feed additive for all animal species are the high content of clinoptilolite (≥80 wt.%), the low content of clay minerals ≤ 20 wt.%, and it is free of fibers and quartz. Concerning the various applications of the HEU-type zeolite, zeolite-rick rocks should show a low content of trace elements (mainly heavy metals) and radionuclides, high porosity, a high sorption ability, and the clinoptilolite should be rich in K and Ca. In addition, zeolite-rich rocks should not contain fibrous zeolites (erionite, mordenite, roggianite, scolesite, natrolite, mesolite, ferrierite), and quartz. The fibrous zeolites (erionite, mordenite, roggianite, mazzite), and to a lesser extent, quartz, are mainly toxic, carcinogenic, and highly pathogenic for animals and humans, mainly by inhalation [14,15,16,17,18].
High-quality zeolite-rich rocks, and synthetic zeolites, are widespread worldwide for their use in agriculture. They have been extensively used in industry as separation agents, absorbents, and ion exchangers, and also as agents for the removal of heavy metals and ammonium from fresh water [18,19,20,21,22,23]. As non-toxic, ecologically advantageous, and affordable materials, they are appropriate for agricultural uses in animal as well as plant production [24,25,26].
In pest control, zeolite-rich rocks exhibit insecticidal properties by adhering to insects’ bodies, causing epicuticle abrasion or disrupting it through lipid adsorption. Both mechanisms lead to rapid water loss and dehydration-induced death [27,28]. Studies have confirmed the effectiveness of natural zeolites against various crop pests, including Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), Oryzaephilus surinamensis (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Silvanidae), and Tribolium confusum (Jacquelin du Val) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), which infest stored grains and flour [29,30]. Additionally, natural zeolite has proven highly toxic to Sitophilus zeamais (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and other beetle pests in stored wheat [31,32].
The olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae (Rossi) (Diptera: Tephritidae) is the most injurious olive pest, and has been mainly recorded in the Mediterranean region, but also in Central and South Africa, the Near and Middle East, and Central America and California [33,34]. The adult female attacks olive fruits by laying her eggs inside them, causing severe losses in olive production [35,36]. The newly hatched larva feeds upon the fruit mesocarp, forming tunnels inside the drupe and destructing the pulp, which enables infestation by fungi and bacteria [37,38,39]. Consequentially, there is a severe reduction in the quality of all olive products, since these become unsuitable for consumption [36]. The loss in olive industry production due to this pest, can be as high as 30% [38].
The control of the olive fruit fly is mainly based on the application of many insecticides cover or bait sprays, which very often results in the development of olive fruit fly resistant populations, failure of effective control, and the presence of chemical residues in olive oil [40,41]. As a result, there is a growing need for safer and more sustainable alternatives such as kaolin, diatomaceous earth (DE), and natural zeolites which have shown promising insecticide activity against a wide range of insect pests [42,43,44,45]. Their mode of action involves damaging the insect epicuticle through abrasion or absorption of lipids, leading to dehydration and death [27,28]. Additionally, these materials may provide protection against microbial infestations and have demonstrated efficacy across several insect pests [27,46,47].
The discovery of new products such as natural zeolites for the control of the olive fruit fly is of great importance for the protection of olive production. This present study investigates the mineralogical and chemical composition of four different zeolite-rich rocks originated from north-eastern Greece and their oviposition deterrent effect on females of the olive fruit fly B. oleae.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Mineralogical and Chemical Characterization
2.1.1. Sampling and Mineralogical Characterization
Four representative samples of zeolite-rich rocks (samples zeot1, zeot2, zeo3, zeot4) were collected from specific layers of the volcaniclastic deposits of Petrota of the Evros Region, in northern Greece (Figure 1). The basin of the Evros River, in the Greek territory, was shaped by Tertiary tectonic subsidence, which was formed by marginal faults in the massif of Rhodope. At the beginning of the Quaternary, the post-Alpine Thrace Basin was formed, unconformably over-lying the Alpine basement and filled with molassic sediments. The basement of the area consists of metamorphic rocks such as gneisses, chlorite-amphibolitic gneisses, and lens-shaped bodies of Mesozoic marble. These rocks are strongly deformed due to the Alpine orogeny [48,49,50,51].
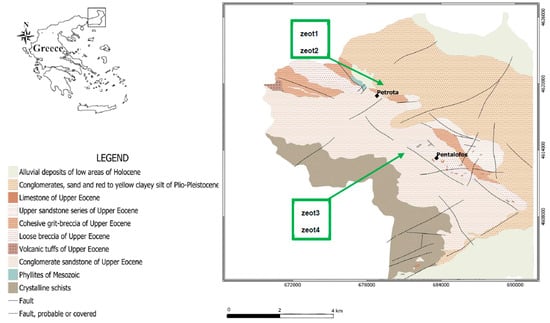
Figure 1.
Geological map of the sampling (zeot1–zeot4) area in the Evros basin, Thrace provenance.
The volcaniclastic rocks of Petrota were locally affected by hydrothermal alterations, which is why they contain zeolites, with clinoptilolite being the main representative [52].
Various opinions prevail regarding the diagenesis model. According to Tsirambides et al. [50], the presence of clinoptilolite indicates that the volcanic material was altered in a low-salinity environment. Aleksiev and Djourova [53] found that the alteration of tuffs, leading to the formation of zeolites, was caused by the ingress of meteoric and seawater into the hot ignimbrites. Tsolis-Katagas and Katagas [54] proposed that the authigenic pyritic minerals formed due to burial diagenesis at a temperature range of 84–91 °C.
The samples were studied in their bulk form, ground (<125 μm), and homogenized. All samples were grounded further for mineralogical and chemical analysis, while thin sections were prepared for study under microscope.
The mineralogical composition of the samples includes the microscopic study and the X-ray diffraction method (XRD). From the representative samples (zeot1–zeot4), polished thin sections were prepared to determine their petrographic, morphological, and chemical characteristics under a polarizing and scanning electron microscope. From each sample, a small representative amount was crushed and grounded in an agate mortar, until it became homogeneous.
The bulk mineralogy of the samples was determined with X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, using a Bruker D8 Advance equipped with DaVinci diffractometer, using a strip silicon detector (LynxEye XE-T, (1D mode) (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany)), anti-scatter slit 18 mm and divergence slit 17 mm. It used Ni-filtered CuKα1 radiation, 40 KV, and 40 mA. Random powder mounts of samples were scanned with 0.019° step size and 0.25 s counting time per step. Results were evaluated using DIFFRAC. EVA v7.1® using the database of ICDD (PDF4-2023-2024) (International Centre for Diffraction Data, Newtown Square, PA, USA) provided by Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany.
The mineral phases were quantified using a Rietveld-based refinement routine using the TOPAS 6.0® (2016) software (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). The routine is based on the calculation of a single mineral-phase pattern according to the crystalline structure of the respective mineral, and the refinement of the pattern using a non-linear least squares routine. The quantification errors performed without an internal standard and calculated for each phase were estimated to be ~1% [55].
2.1.2. Sorption Ability and Binding Capacity
The ion exchange capacity (sorption ability) of each sample was measured according to the Ammonium Acetate Saturation (AMAS) method [56]. A 1N solution of ammonium acetate (CH3COONH4) is prepared, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 7.0. For each <63 μm particle size fraction, four individual samples weighing 100–150 mg each are prepared and placed in 15 mL test tubes. Then, 10 mL of the CH3COONH4 solution is added to each tube, followed by vigorous manual agitation for a few seconds. The tubes are then placed on a rotary shaker for 24 h. Subsequently, centrifugation is carried out at 1500 rpm for 4 min, the supernatant is decanted, and a fresh 10 mL of CH3COONH4 solution is added following the same procedure. This saturation process is repeated for a total of 10 days [57]. The sorption mechanisms differ according to the way the metal up-take arises from the aqueous solution. The sorption can be presented as absorption that occurs as ion exchange in layered and micro/nanoporous minerals, as adsorption that is represented by inner and outer sphere surface complexation and as surface re/co-precipitation [58].
For the measurement of binding capacity, a JENWAY 3340 Ion/pH Meter (Cole-Parmer Ltd., Vernon Hills, IL, USA), combined with an ammonia electrode of the ORION type was used. The exchange capacity of the sample (CEC) is given by the formula CEC = (M × V/W) × 100 (meq/100 g), where M is the indication of the ion meter in moles/liter, V is the volume (in liters) of the nitrogen-free water added, and W is the initial weight (in grams) of the sample. For each material under examination, four values are obtained, from which the mean between the smallest and largest value is calculated. From this value and the other two remaining values, a weighted mean is derived, representing the binding capacity of the tested sample. The method was certified using standard mixtures of amorphous and crystalline phases, with a typical deviation found to be 5 meq/100 g [59].
2.1.3. Specific Surface Area
The specific surface area of each sample was measured via the BET method, using a specific surface area device Quantachrome Nova 2000e surface area and pore size analyzer (Anton Paar QuantaTec Inc., Boynton Beach, FL, USA). With the nitrogen adsorption–desorption method, the surface area can be measured for pulverized solids and porous materials. This is achieved by determination of the amount of a gas adsorbed as a mono-layer on its sample solid. Sorption takes place near or at the boiling point of the adsorbate gas. Since the surface area covered by each adsorbed molecule of gas is known, the surface area of the material can be calculated from the number of molecules adsorbed, that is, from the amount of adsorbed gas at specific conditions of adsorption [60].
2.1.4. Chemical Analysis
Representative polished thin sections were prepared and observed under a scanning electron microscope for the analysis of morphological and chemical characteristics of the contained zeolite, by the SEM-EDS (EDXS) method. The scanning electron microscope is a Jeol JSM-840 type (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a LINKAN 10,000 microanalysis system and operates with a voltage of 15 kV, electron beam intensity < 3 nA, and a diameter of 1 μm. Corrections were made using the ZAF-4/FLS software provided by LINK. To minimize the volatilization of alkali metal ions in the zeolite framework, the electron beam spot size was enlarged, and the counting time decreased. Different minerals (micas, carbonates, and feldspars) and pure metals were used as probe standards. SEM analysis provided an accurate chemical formula for zeolite (several readings were taken for the studied zeolite and the average chemical formula was calculated). Clinoptilolite is member of the heulandite group, which belongs to natural zeolites. The structure of zeolites that belong to the heulandite group have pores defined by 8- to 10-member rings, whereas the clinoptilolite pore structure is defined by 10-membered rings [61]. The ratio of Si/Al in clinoptilolites ranges between 4.25 and 5.25. The calculation of the chemical formula was on the model Na6Al6Si30O72·24H2O on the basis of 72 oxygen and 24 water molecules [62].
2.1.5. X-Ray Fluorescence Study (XRF)
Considering the study on toxicity of chemical elements (mainly heavy metals), X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyses were carried out using a Bruker S1 TITAN handheld XRF analyzer for elemental analysis, having as an excitation source a miniaturized 50 kV X-ray tube, and a silicon source (<145 eV) with a beam diameter of 5 mm (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). For the analysis, the built-in method of analysis “Geoexploration” was used, which is a factory setting for soil analysis (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). The analysis process was carried out in three energy ranges (15, 30, and 50 kV) where each one lasts 30 s (in total measuring 90 s), and the determination results were demonstrated as Average Value ± SD [63]. The elemental analysis, which results from its application of the “Geoexploration” method, is corrected using reference curves from certified standard samples (CRMs) in order to minimize the errors.
2.2. Determination of Oviposition Deterrent Effect
We evaluated the oviposition deterrent effect of zeot1–zeot4 for females of the olive fruit fly B. oleae under laboratory conditions. For the experiments, we used females from a laboratory colony of B. oleae which was established with adults emerged from field infested olive fruits collected in Kassandra, Chalkidiki, Νorthern Greece, and maintained in the laboratory in wooden cages with wire-screen sides at 25 ± 1 °C, relative humidity (RH) 65 ± 1%, and a photoperiod of 16L:8D, as described by Kovaiou et al. [64]. The experimental olive fruit flies were second-generation descendants of the stock colony females. They were reared from egg to pupae in olive fruits that were collected in early August, and maintained at 5 ± 1 °C for approximately 2–3 months in glass jars, before being offered to the stock flies for oviposition.
Each sample was ground in a mechanical agate mortar for 10 min, and then placed in a sieve shaker, which consists of a set of sieves with the aperture size ranging from 100 to 63 μm, for 15 min. The desired material of <63 μm (powder form) grain size distribution was collected, and the process was repeated until the entire quantity of our samples was sieved.
The processed zeot1–zeot4 samples were dissolved in tap water (5 g zeot1–zeot4 powder/100 mL water), forming aqueous suspensions. Olive fruits used in the experiments as oviposition substrates were collected during August from Chalkidiki, Νorthern Greece, and maintained at 5 °C for approximately 2 months, before their use in the experiments. For the experiments, olive fruits were immersed in the zeot1–zeot4 aqueous suspensions in glass jars for 20 s. For the control, the olive fruits were immersed in water. After immersion, the olive fruits were allowed to dry on the surface of a metal sieve, and then were transferred to a plexiglass cage (20 × 20 × 20 cm) with five 10 days old, mated females of B. oleae. Subsequently, we scored the number of oviposition holes on the surface of the olive fruit, every 2 days (for a period of 8 days) under a stereoscope (Zeiss Stemi 305®, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany). In each treatment and the control, there were four replicates (cages with 5 fruits and 5 adult females). All experiments were performed in a climatic room under a temperature of 25°C, photoperiod of 16L:8D, and RH ranging from 50 to 55%.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
To evaluate the oviposition-deterrent effect of zeot1–zeot4 samples on B. oleae, ANOVA was conducted within the General Linear Models (GLM) framework. Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) were identified using the Student–Newman–Keul’s test, while Levene’s test assessed variance homogeneity. Normality of residuals was tested with the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. If variance heterogeneity was significant, log transformation was applied; if criteria for parametric analysis remained unsatisfied, the Kruskal–Wallis test and Mann–Whitney U test were used. A t-test compared oviposition holes between treated and control olives under varying conditions at 2, 4, 6, and 8 days. All tests were conducted at α = 0.05, using IBM SPSS Statistics 24.0.
3. Results
3.1. Mineralogical and Chemical Characterization
3.1.1. Mineralogical Characterization
The microscopic study showed the presence of porphyroblastic texture. Samples zeot1–zeot4 of Petrota, contain clinoptilolite (HEU-type zeolite), feldspars (K-feldspar + plagioclase), quartz, cristobalite, micas, ±chlorite, fragments, and amorphous/vitreous mass (Figure 2).
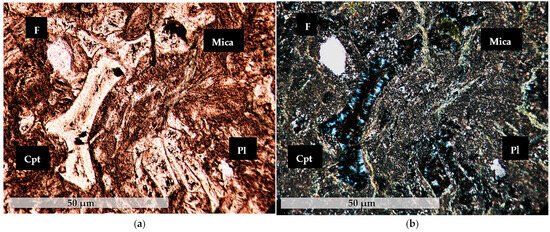
Figure 2.
Representative photograph of zeolite-rich rock sample zeot3 under a polarizing microscope. Cpt: Clinoptilolite, F: K-Feldspar, Pl: Plagioclase, Mica, (a) N//, (b) N⊥.
The semi-quantitative mineralogical composition of the samples studied is presented in Table 1, while their XRD patterns are shown in Figure 3. Clinoptilolite and micas constitute the microporous minerals of the zeolite-rich rocks. The non-microporous minerals found in each sample are quartz, feldspars, and cristobalite.

Table 1.
Mineralogical composition (wt.%), sorption ability (meq/100 g), and specific surface area (cm2/g) of the studied zeolite-rich rock samples.
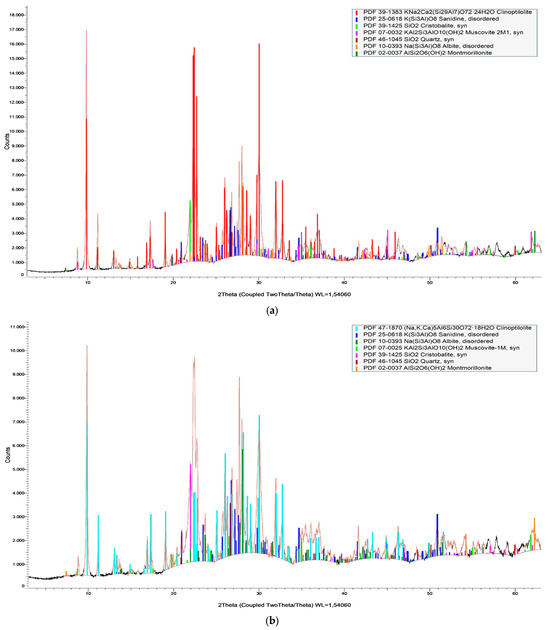
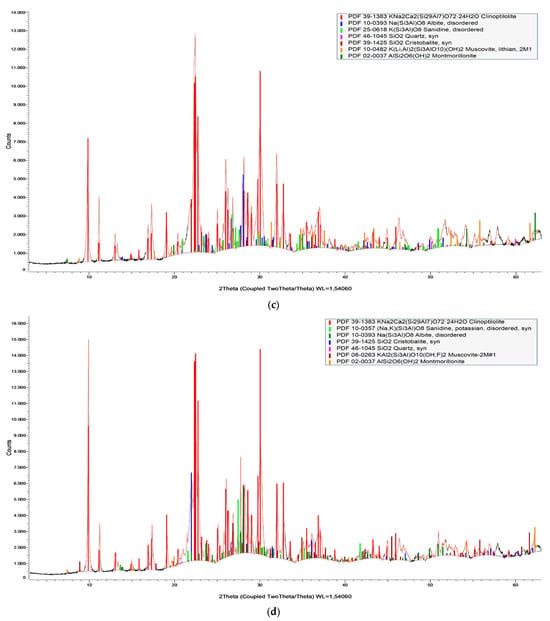
Figure 3.
X-ray Powder Diffraction pattern of zeolite-rich rock samples (a) zeot1, (b) zeot2, (c) zeot3, and (d) zeot4.
According to the mineralogical results, the contained clinoptilolite and micas + clay minerals are the consisting parts of the microporous minerals of the zeolite-rich bearing rock. Additionally, the non-microporous minerals were found to be feldspars (K-feldspars + plagioclase) and quartz + cristobalite.
According to Cook et al. [65] and Moore and Raynolds [66], the qualitative analysis of the examined samples was evaluated using the database of ICDD PDF4+ (PDF2023-2024) provided by Bruker. In detail, the zeolite content, characterized as clinoptilolite, was determined by the characteristic peak at d-spacing ~9.9 Å, micas from the peak at d-spacing at 4–12.6° 2θ, K-feldspars from the peak at d-spacing at 3.26–3.21, feldspars from the peak at d-spacing at 3.21–3.17 Å, quartz from the peak at d-spacing at 4.26 Å–3.34 Å–1.81 Å, and cristobalite from the peak at d-spacing at 4.15 Å.
The amorphous (volcanic glass) content of the studied samples was determined using the fitting method on the broad background hump between 10° and 20° 2θ in the powder XRD trace [67].
3.1.2. Sorption Ability and Binding Capacity
The measured sorption ability of the samples (AMAS method) is presented in Table 1. The theoretical CEC of the samples was calculated using the values of 2.54 meq/g for clinoptilolite (Table 2) [61,68]. Also, the expected CEC of the samples was calculated from the total extra-framework cations that were measured by SEM-EDS (results presented inTable 3) [69]. The extra-framework cations of sample zeot1 are Mg 9.45 meq/100 g, Ca 40.72 meq/100 g, Na 73.09 meq/100 g, K 103.63 meq/100 g; of sample zeot2 are Mg 49.92 meq/100 g, Ca 117.24 meq/100 g, Na 17.78 meq/100 g, K 45.76 meq/100 g; of sample zeot3 are Mg 46.55 meq/100 g, Ca 131.53 meq/100 g, Na 23.28 meq/100 g, K 44.71 meq/100 g; and for sample zeot4, Mg 1.45 meq/100 g, Ca 57.28 meq/100 g, Na 48.58 meq/100 g, and K 107.32 meq/100 g.

Table 2.
CEC and sorption ability (meq/100 g) of the studied zeolite-rich rock samples. (Cpt: Clinoptilolite).
The measured sorption ability of the samples is close to the expected CEC which implies that the main process that controls the sorption procedure of the samples is the ion exchange [69].
3.1.3. Specific Surface Area
The specific surface area is an important characteristic of natural materials rich in zeolites and is particularly useful for their adsorptive and catalytic properties. The BET specific surface area was calculated according to the procedure defined by Rouquerol et al. [70], and is presented in Table 1. No significant change in the specific surface area was observed between the samples, with the highest value observed in zeot3.
3.1.4. Chemical Analysis
According to Table 3, the Si/Al ratio calculated from 4.42 (zeot4) to 4.64 (zeot2), and consequently, all the zeolites contained in the studied samples can be classified as HEU-type clinoptilolites (Si/Al > 4), having K, Na, Ca, and Mg as exchangeable cations [71,72].

Table 3.
Chemical composition wt.% and the formula of the HEU-type zeolites contained in the studied Greek zeolite-rich rocks.
Table 3.
Chemical composition wt.% and the formula of the HEU-type zeolites contained in the studied Greek zeolite-rich rocks.
| Major Oxides (wt.%) | Formula Based on 72 Oxygens | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | zeot1 | zeot2 | zeot3 | zeot4 | Samples | zeot1 | zeot2 | zeot3 | zeot4 |
| SiO2 | 65.09 | 66.68 | 68.03 | 64.29 | Si | 29.87 | 29.75 | 30.80 | 29.52 |
| Al2O3 | 13.11 | 12.85 | 12.31 | 12.22 | Al | 6.51 | 6.40 | 6.77 | 6.67 |
| Fe2O3tot | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | Fe3+ | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| MnO | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | Mn | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| MgO | 0.18 | 0.92 | 0.14 | 0.09 | Mg | 0.13 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.02 |
| CaO | 0.96 | 3.60 | 3.50 | 1.89 | Ca | 0.56 | 1.55 | 1.78 | 0.79 |
| SrO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | Sr | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| BaO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | Ba | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Na2O | 2.15 | 0.61 | 0.35 | 1.44 | Na | 2.01 | 0.47 | 0.63 | 1.34 |
| K2O | 4.48 | 2.20 | 2.54 | 5.10 | K | 2.85 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 2.96 |
| H2O | 13.96 | 13.07 | 13.00 | 14.85 | H2O | 22.23 | 19.30 | 19.99 | 23.23 |
| Total | 99.98 | 99.97 | 99.92 | 99.94 | Si/Al | 4.58 | 4.64 | 4.54 | 4.42 |
Zeot1 has K and Na as the main exchangeable cations, and its chemical formulae based on 72 oxygens is K2.8Na2.0Ca0.5Mg0.1Al6.5Si29.9O72·22H2O. Zeot2 has Ca and K as the main exchangeable cations, and its chemical formulae based on 72 oxygens is Ca1.5K1.2Mg0.7Na0.5Al6.4Si29.7O72·19H2O. Zeot3 has Ca as the main exchangeable cation, and its chemical formulae based on 72 oxygens is Ca1.8K1.2Mg0.6Na0.6Al6.7Si30.8O72·20H2O. Zeot4 has K as the main exchangeable cation, and its chemical formulae based on 72 oxygens is K3.0Na1.3Ca0.8Al6.7Si29.5O72·23H2O.
The SEM back-scattered images showing the microstructure of clinoptilolite tabular crystals, in zeolite-rich rock samples are shown in Figure 4.
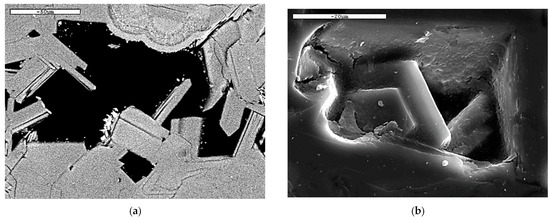
Figure 4.
SEM back-scattered images showing the microstructure of clinoptilolite tabular crystals in zeolite-rich rock samples zeot3 (a) and zeot4 (b).
3.1.5. X-Ray Fluorescence Study (XRF)
XRF results for the zeolite-rick rock samples evidenced the existence of the following minor elements: As, Ba, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Se, V, and Zn. The average concentrations of heavy metals for three measurements of each of the samples are given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Heavy metals content (mg/kg) in the studied Greek natural zeolite-rich rocks, and their detection limits, using certified reference materials (CRMs) from our department.
As a complementary chemical analysis, the determination of Cr(VI) (hexavalent chromium)—a toxic and hazardous form of chromium—was carried out using spectrophotometry with the diphenylcarbazide (DPC) method, measured at 525 nm with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. In this approach, Cr(VI) reacts with diphenylcarbazide in an acidic medium to form a pink–violet complex, whose color intensity correlates with the concentration of hexavalent chromium. The resulting complex is then quantified using a UV–VIS spectrometer at 540 nm. The results showed that Cr6+ concentrations in all four tested samples were below the detection limit (<1 ppb), indicating the absence of detectable levels of Cr(VI).
3.2. Oviposition Deterrent Effect of zeot1–zeot4
After their application as aqueous suspensions on the surface of olive fruits, all the tested zeolites (zeot1–zeot4) caused a significant reduction in the oviposition holes compared to the control, and therefore, had a notable oviposition deterrent effect on egg laying. As shown in Table 5, the tested zeolites had a variable oviposition deterrent effect on females of the olive fruit fly. The highest oviposition deterrent effect was observed after the application of zeot3 on the olive fruits (mean number of eggs laid on the olive fruit after 8 days: 43.1 compared to the non-treated olive fruits (Control: 172.3) (Table 5). The lowest oviposition deterrent effect was determined after the application of zeot4 or zeot2, with zeot1 having an intermediate effect.

Table 5.
Mean (±SE) number of B. oleae eggs (oviposition holes) laid by 5 females in olive fruits immersed in 5% zeolites aqueous solutions and water (control) after 2, 4, 6, and 8 days of maintenance at a temperature of 25 °C, photoperiod of 16L:8D, and relative humidity 50–55%.
This variable oviposition deterrent effect of the tested zeolites could be due to their unique mineralogical and chemical characteristics. The mineralogical composition of zeot3 is characterized by the highest quantities of HEU-type zeolite (clinoptilolite) and microporous minerals (Table 1), the highest sorption ability and specific area (Table 2). The chemical composition of zeot3 is characterized by the highest concentration of SiO2, Si, and Ca (Table 3).
Figure 5 shows the substantial reduction in oviposition holes on olive fruit after the application of zeot3.

Figure 5.
Oviposition deterrent effect of zeot3 on females of the olive fruit fly. Olive fruits were maintained in cages with 5 adult females of the olive fruit fly for 8 days at 25 °C and 16L:8D. The black spots on the surface of the fruits are the oviposition holes on (a) olive fruits treated with zeot3, (b) control (non-treated olive fruits).
4. Discussion
Our results show that clinoptilolite-rich rocks with unique characteristics, when applied as aqueous suspensions on the olive fruits, have a strong oviposition deterrent effect on B. oleae adult females, and cause a significant reduction in the number of oviposition holes on the olive fruits. This oviposition deterrent effect may be due to the prevention of females landing on the fruit surface, which is caused by the formation of a thin zeolite layer.
We found that the mineralogical and chemical composition of the tested zeolites may have a significant impact on effectiveness as an insect deterrent, particularly with respect to the olive fruit fly. Specifically, varying concentrations of zeolite (clinoptilolite) in samples zeot1–zeot4, with the highest levels found in sample zeot3, appear to affect the oviposition deterrent effect. The zeolites have unique structural properties that allow them to act as an ion-exchanger and molecular sieve, making them useful for a variety of industrial and environmental applications [8,9]. Particularly, the ability of clinoptilolite to absorb and remove volatile organic compounds that attract the olive fruit fly to olive trees, appears to be a possible mechanism responsible for its oviposition deterrent properties. In our experiments, the thin zeolite layer formed on the olive fruit surface after application created a porous coating. This physical barrier may interfere with the olive fly’s ability to recognize or access the olive fruit surface and lay its eggs.
However, it is important to note that the use of zeolite-rich rock as an insect deterrent, should be carefully evaluated to ensure that any potential toxic effects on humans and animals, are minimized. The primary characteristics of zeolite-rich rocks include a high concentration of HEU-type zeolite (clinoptilolite–heulandite), along with minimal levels of trace elements. Our current findings from the toxicity assessment of undesirable chemical elements (heavy metals) indicate that all the samples of natural zeolite-rich rocks exhibit extremely low concentrations. In particular, the levels of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, Se, V, and Zn fall below the maximum permissible limits set for the food sector according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations—FAO; the World Health Organization—WHO; European Union [73,74]. The Cr content in zeot3, specifically Cr(VI) (hexavalent chromium), was found to be below the detection limit (<1 ppb), while all measured heavy metals, including lead, were within acceptable safety limits. Therefore, these elements are unlikely to contribute significantly to the material’s efficacy, which is more likely related to its mineralogical and physicochemical characteristics.
Moreover, it is mandated that zeolite-rich rocks do not contain fibrous zeolites (e.g., erionite, mordenite, roggianite, mazzite). In particular, the presence of fibrous zeolites can be dangerous for both the operator and the consumer [14,15,16,17,18]. In our investigation, it is worth mentioning that the samples we examined are devoid of any fibrous minerals and contain low amounts of quartz (<10%). This implies that our zeolite-rich rocks can be considered safe for both processing and utilization.
Although there are no relevant references in the literature, the calculation of the amorphous materials in all the samples studied was measured. In most previous studies regarding the use of zeolite-rich rocks in agriculture, the content of amorphous materials was not included in the mineralogical composition. This resulted in an overestimation of the percentages of the crystalline phases of the remaining minerals. Consequently, in our research, the percentages of clinoptilolite in each sample are 54–70 wt.%
To our knowledge, this is the first instance where the deterrent properties of zeolite-rich rock have been investigated for controlling B. oleae in olive fruits. The utilization of zeolite-rich rock as a natural insect deterrent has been increasingly studied, owing to its potential as an environmentally friendly and sustainable substitute for chemical pesticides. Recent research has demonstrated the insecticidal effects of zeolite-rich rocks on various stored-product in-sects, including S. oryzae infesting stored wheat and rice seeds and T. castaneum affecting stored flour [29,32]. Moreover, natural clinoptilolite has exhibited high mortality rates in other stored-product pests like O. surinamensis and T. confusum [28]. Studies have also shown natural zeolite to be highly toxic to the maize weevil S. zeamais and three other beetle pests infesting stored wheat [31,32].
Previous studies of our group have shown that a high-quality Greek clinoptilolite-rich rock has a high insecticidal activity for the bruchid Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae), under different temperature and RH conditions [27]. Additionally, Kovaiou et al. [64] tested the oviposition deterrent effect of a Greek clinoptilolite-rich rock (70 wt.% clinoptilolite, 18 wt.% amorphous material, 7 wt.% feldspars, 4 wt.% cristobalite, and 1 wt.% quartz), against B. oleae. The oviposition deterrent effect for the olive fruit fly was very high under a series of tested temperatures (17 °C, 20 °C, 25 °C, and 30 °C) and RHs (23%, 33%, 55%, 75%, and 94%). Moreover, the residual effectiveness of the zeolite after uniform water spraying remained high, comparable to that of the pyrethroid insecticide Decis® (deltamethrin) (Bayer AG, Leverkusen, Germany) [64]. Furthermore, apart from HEU-type zeolites, analcime has also been studied for its oviposition deterrent effect, with an equally effective action [75].
The deterrence of oviposition may also arise from alterations in the emitted fruit’s volatile compounds [39,41] and coloration [76], both of which play a substantial role in egg production and influence the behavior of the olive fruit fly.
It is known that zeolite-rich rocks, and generally inert dusts, such as diatomaceous earth (DE) and kaolin, are insecticidally effective by partially removing the insect’s outer cuticle (epicuticule) through abrasion by hard non-sorptive particles or by disrupting the epicuticle via adsorption of epicuticular lipids to sorptive particles [46]. Both processes induce rapid water loss from the insect’s body and cause death by desiccation [28]. According to Eroglu et al. [77], the structure of the dust, the species of insects, and the environmental conditions are three basic parameters that affect the efficacy of zeolite-rich rocks and other inert dusts, regarding their insecticidal evaluation. Moreover, specific dust properties, such as the size and shape of the dust particles, content of silica and alumina (Si/Al ratio), sorption ability, framework structure, can also be affective concerning the insecticidal potential [78,79,80,81].
While the use of zeolite-rich rock as a natural insect deterrent has shown promising results, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action, and to optimize its mineralogical and chemical composition to enhance its effectiveness, while minimizing any potential negative effects on the environment. Future experiments are necessary in order to confirm the results of the laboratory experiments in field conditions, as well as the possibility of the wide application of zeolite-rich rocks, especially with very high contents of clinoptilolite, for the protection of olive oil production from the olive pest. Additional studies may also investigate the potential use of zeolite-rich rock in combination with other natural deterrents, such as essential oils, to enhance its effectiveness. Nevertheless, the potential of zeolite-rich rocks as an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides for controlling olive fruit fly infestations is an exciting area of research that warrants continued investigation.
5. Conclusions
Clinoptilolite-rich rocks are widespread worldwide for their use in agriculture, as non-toxic, ecologically advantageous, and affordable materials. We found that among the four different Greek zeolite-rick rocks tested (zeot1–zeot4), the one with specific mineralogical and chemical characteristics had the highest oviposition deterrent effect against the olive fruit fly B. oleae (zeot3). The mineralogical composition of zeot3 is characterized by the highest quantities of HEU-type zeolite (clinoptilolite) (70 wt.%), the highest sorption ability (195 meq/100 g), and the highest specific surface area (8.4 cm2/g). The chemical composition of zeot3 is characterized by the highest concentration of SiO2, Si, and Ca. This deterrent effect can be mainly attributed to the creation of a thin layer (hymen) of natural zeolite on the surface of the fruits and the unique characteristics of the tested zeolites.
Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind the deterrent effect of zeolite-rich rocks on B. oleae, as well as their efficacy under field conditions. Zeolites represent a promising avenue for the development of environmentally friendly and sustainable pest control strategies in olive production. Its unique mineralogical and chemical composition, combined with its natural abundance and low toxicity, makes it a potential alternative to traditional chemical insecticides.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K., N.K., S.K.K., N.A.K. and A.F.; Methodology, D.K., N.K., A.F. and N.A.K.; Software, S.K.K., A.K. and C.M.; Validation, D.K., N.K., N.A.K., A.F., S.K.K. and A.K.; Formal analysis, D.K., S.K.K. and A.K.; Investigation, D.K., N.K., N.A.K., A.F., S.K.K., A.K. and C.M.; Resources, D.K., N.K. and N.A.K.; Data curation, S.K.K. and A.K.; Writing—original draft preparation, S.K.K. and A.K.; Writing—review and editing, S.K.K., A.K., C.M., N.K. and D.K.; Visualization, S.K.K. and A.K.; Supervision, D.K., N.K. and N.A.K.; Project administration, D.K. and N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is part of the research of the first author, S.K. Kovaiou, which is financed by the Special Account for Research Funds AUTH, Grant No. 679423.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reasons.
Acknowledgments
This present study was conducted in interdisciplinary collaboration with the Laboratory of Mineralogy and Petrology, the School of Geology, and the Laboratory of Applied Zoology and Parasitology, School of Agriculture, of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece. The authors thank L. Papadopoulou, School of Geology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, for her assistance regarding SEM-EDS (EDXS) analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this work has not been published previously, and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. All the authors approve its publication in your journal.
References
- Holmes, D. Industrial Minerals and Rocks; Braun-Brumfield, Inc.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1994; pp. 1129–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Abu Zeitoun, E.; Alassmy, Y.A.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Sebakhy, K.O. Impact of Synthesis Parameters on the Crystallinity of Macroscopic Zeolite Y Spheres Shaped Using Resin Hard Templates. Crystals 2024, 14, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar Pour, Z.; Abduljawad, M.M.; Alassmy, Y.A.; Alnafisah, M.S.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Sebakhy, K.O. Synergistic Catalytic Effects of Alloys of Noble Metal Nanoparticles Supported on Two Different Supports: Crystalline Zeolite Sn-Beta and Carbon Nanotubes for Glycerol Conversion to Methyl Lactate. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.M. Zeolites and zeolite-like materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehakova, M.; Čuvanová, S.; Dzivak, M.; Rimár, J.; Gaval’Ová, Z. Agricultural and agrochemical uses of natural zeolite of the clinoptilolite type. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.; Singh, D.N. A review on synthesis, characterization and industrial applications of fly-ash zeolites. J. Mater. Educ. 2011, 33, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Natural vs. synthetic zeolites. Crystals 2020, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, T.; Gunter, M.E. Stepwise dehydration of heulandite-clinoptilolite from Succor Creek, Oregon, U.S.A.: A single-crystal X-ray study at 100 K. Am. Min. 1991, 76, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Gunter, M.E.; Armbruster, T.; Kohler, T.; Knowles, C.R. Crystal structure and optical properties of Na- and Pb-exchanged heulandite-group zeolites. Am. Min. 1994, 79, 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Colella, C. Natural zeolites. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 157, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A. An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves; Surface and Interface Analysis; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU). No 651/2013 of 9 July 2013 Concerning the Authorization of Clinoptilolite of Sedimentary Origin as a Feed Additive for All Animal Species and Amending Regulation (EC) No 1810/2005. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2013/651/oj/eng (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Davis, J.M. In vivo assays to evaluate the pathogenic effects of minerals in rodents. In Health Effects of Mineral Dusts; Guthrie, G.D., Jr., Mossman, B.T., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 28, pp. 471–487. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, K.E. In vitro evaluation of mineral cytotoxicity and inflammatory activity. In Health Effects of Mineral Dusts; Guthrie, G.D., Jr., Mossman, B.T., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 28, pp. 489–511. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.; Nolan, R.; Langer, A.; Cooper, W. Health effects of various mineral dusts other than asbestos. In Health Effects of Mineral Dusts; Guthrie, G.D., Jr., Mossman, B.T., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 28, pp. 361–407. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs: Arsenic, Metals, Fibers and Dusts. Volume 100C. A Review of Human Carcinogens; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Filippidis, A.; Tziritis, E.; Kantiranis, N.; Tzamos, E.; Gamaletsos, P.; Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, S. Application of Hellenic natural zeolite in Thessaloniki industrial area wastewater treatment. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 19702–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsishvili, G.V.; Andronikashvili, T.G.; Kirov, G.N. Natural Zeolites; Ellis Horwood Limited: Hertfordshire, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Filippidis, A.; Kantiranis, N. Experimental neutralization of lake and stream waters from N. Greece using domestic HEU-type rich natural zeolitic material. Desalination 2007, 213, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippidis, A.; Apostolidis, N.; Paragios, I.; Filippidis, S. Zeolites clean up. Indust. Miner. 2008, 487, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Filippidis, A.; Papastergios, G.; Kantiranis, N.; Filippidis, S. Neutralization of dyeing industry wastewater and sludge by fixation of pollutants in very high quality HEU-type zeolitic rock. J. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 2, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Papastergios, G.; Kantiranis, N.; Filippidis, A.; Sikalidis, C.; Vogiatzis, D.; Tzamos, E. HEU-type zeolitic rock in fixed bed columns as decontaminating agent for liquid phases. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 59, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.R.; Ming, D.W. Recent progress in the use of natural zeolites in agronomy and horticulture. In Natural Zeolites 93; Ming, D.W., Mumpton, F.A., Eds.; ICNZ: Brockport, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 477–490. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bekkum, H.; Flanigen, E.M.; Jansen, J.C. Introduction to Zeolite Science and Practice; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Colella, C. Application of natural zeolites. In Handbook of Porous Solids; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1156–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Floros, G.D.; Kokkari, A.I.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Kantiranis, N.; Damos, P.; Filippidis, A.; Koveos, D.S. Evaluation of the natural zeolite lethal effects on adults of the bean weevil under different temperatures and relative humidity regimes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, D.M.; Puterka, G.J.; Drake, S.R.; Unruh, T.R.; Knight, A.L.; Baherle, P. Particle film application influences apple leaf physiology, fruit yield, and fruit quality. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 126, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, G.G.; Marković, M.M.; Adamović, M.; Daković, A.; Golić, M.P.; Kljajić, P.J. Insecticidal potential of natural zeolite and diatomaceous earth formulations against rice weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbos, C.I.; Sakka, M.; Berillis, P.; Athanassiou, C.G. Insecticidal potential of zeolite formulations against three stored-grain insects, particle size effect, adherence to kernels and influence on test weight of grains. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2016, 68, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryadi, Y.; Syarief, R.; Hubeis, M.; Herawati, H. Effect of zeolite on the development of Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. In Stores Products Production, Proceedings of the 6th International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, Canberra, Australia, 17–23 April 1994; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kljajić, P.; Andrić, G.; Adamović, M.; Bodroža-Solarov, M.; Marković, M.; Perić, I. Laboratory assessment of insecticidal effectiveness of natural zeolite and diatomaceous earth formulations against three stored-product beetle pests. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2010, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, M.E.; Koveos, D.S. Inhibition of ovarian maturation in the olive fruit fly, Dacus oleae (Diptera: Tephritidae), under long photophase and an increase of temperature. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daane, K.M.; Johnson, M.W. Olive fruit fly: Managing an ancient pest in modern times. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koveos, D.S.; Tzanakakis, M.E. Effect of the presence of olive fruit on ovarian maturation in the olive fruit fly, Dacus oleae, under laboratory conditions. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1990, 55, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidi, N.; Gioti, A.; Wybouw, N.; Dermauw, W.; Ben-Yosef, M.; Yuval, B.; Vontas, J. Transcriptomic responses of the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae and its symbiont Candidatus Erwinia dacicola to olive feeding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koveos, D.S.; Tzanakakis, M.E. Diapause aversion in the adult olive fruit fly through effects of the host fruit, bacteria, and adult diet. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1993, 86, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskou, D.; Blekas, G.; Tsimidou, M. Olive oil composition. In Olive Oil; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2007; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkari, A.I.; Pliakou, O.D.; Floros, G.D.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Koveos, D.S. Effect of fruit volatiles and light intensity on the reproduction of Bactrocera (Dacus) oleae. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiro, R.; Casal, S.; Cunha, S.C.; Baptista, P.; Pereira, J.A. Olive volatiles from Portuguese cultivars Cobrançosa, Madural and Verdeal Transmontana: Role in oviposition preference of Bactrocera oleae (Rossi) (Diptera: Tephritidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkari, A.I.; Milonas, P.G.; Anastasaki, E.; Floros, G.D.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Koveos, D.S. Determination of volatile substances in olives and their effect on reproduction of the olive fruit fly. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Vayias, B.J.; Dimizas, C.B.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Papagregoriou, A.S.; Buchelos, C.T. Insecticidal efficacy of diatomaceous earth against Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Tribolium confusum du Val (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) on stored wheat: Influence of dose rate, temperature and exposure interval. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2005, 41, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari, N.; Prioli, C.; Martini, A.; Trotta, V.; Barionio, P. Insecticidal efficacy of a diatomaceous earth formulation against a mixed age population of adults of Rhyzopertha dominica and Tribolium castaneum as function of different temperature and exposure time. Bull. Insectology 2008, 61, 355–360. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=4743cfff8bc78d9f23d02cc53295e363fee54898 (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Arthur, F.H. Immediate and delayed mortality of Oryzaephilus surinamensis (L.) exposed on wheat treated with diatomaceous earth: Effects of temperature, relative humidity, and exposure interval. J. Stor. Prod. Res. 2001, 37, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, I.; Ulrichs, C. Action of amorphous diatomaceous earth against different stages of the stored product pests Tribolium confusum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), Sitophilus granarius (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2001, 37, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, C.; Someus, E.; Spanoghe, P. Potential and actual uses of zeolites in crop protection. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puterka, G.J.; Glenn, D.M.; Sekutowski, D.G.; Unruh, T.R.; Jones, S.K. Progress toward liquid formulations of particle films for insect and disease control in pear. Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mposkos, E. High-pressure metamorphism in gneisses and pelitic schists in the East Rhodope Zone (N. Greece). Miner. Petrol. 1989, 41, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mposkos, E.; Liati, A. Metamorphic evolution of metapelites in the high-pressure terrane of the Rhodope zone, Northern Greece. Can. Miner. 1993, 31, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirambides, A.; Filippidis, A.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A. Zeolitic alteration of Eocene volcaniclastic sediments at Metaxades, Thrace, Greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 1993, 7, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutles, T.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A.; Filippidis, A.; Tsirambides, A. Geology and geochemistry of the Eocene zeolitic-bearing volcaniclastic sediments of Metaxades, Thrace, Greece. Estudios Geol. 1995, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirov, G.N.; Filippidis, A.; Tsirambides, A.; Tzvetanov, R.G.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A. Zeolite-bearing rocks in Petrota area (Eastern Rhodope Massif, Greece). Geol. Rhodopica 1990, 2, 500–511. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksiev, B.; Djourova, E.G. On the origin of zeolite rocks. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 1975, 28, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Tsolis-Katagas, P.; Katagas, C. Zeolitic diagenesis of Oligocene pyroclastic rocks of the Metaxades area, Thrace, Greece. Miner. Mag. 1990, 54, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bish, D.; Post, J. Quantitative mineralogical analysis using the Rietveld full-pattern fitting method. Am. Min. 1993, 78, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, D.C.; Smith, B.F.L. Chemical analysis. In A Handbook of Determinative Methods in Clay Mineralogy; Wilson, M.J., Ed.; Blackie: Glasgow, UK, 1987; pp. 248–274. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Stamatakis, M.; Filippidis, A.; Squires, C. The uptake ability of the clinoptilolitic rocks of Samos Island, Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2004, 36, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G. Distinguishing adsorption from surface precipitation. In Geochemical Processes of Mineral Surfaces; Davis, J.A., Hayes, K., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 323, pp. 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Drakoulis, A.; Kantiranis, N.; Filippidis, A.; Sergiou, A. The uptake ability of amorphous-rich industrial materials from Milos Island. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference of the Committee for Economic Geology, Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Thessaloniki, Greece, 7–9 October 2005; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.; Datar, A.; Jeong, C.; Deng, X.; Chung, Y.G.; Lin, L.C. Surface area determination of porous materials using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method: Limitations and improvements. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 20195–20209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpton, F.A. Mineralogy and Geology of Natural Zeolites; Mineralogical Society of America: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1977; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gottardi, G.; Galli, E. General information on zeolites. Nat. Zeolites 1985, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wen, Y.; Chen, W.; Han, F.; Chang, G.; Yao, C. Effects of important factors on determination of metals in soil samples using hand-held X-ray fluorescence. In Sustainable Development of Water and Environment. ICSDWE 2021; Jeon, H.Y., Ed.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaiou, S.K.; Kokkari, A.; Floros, G.; Kantiranis, N.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Filippidis, A.A.; Koveos, D. Oviposition deterrent effect of a high-quality natural zeolite for the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae, under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. Insects 2024, 15, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, H.E.; Johnson, P.D.; Matti, J.C.; Zemmels, I. Methods of sample preparation and X-ray diffraction data analysis. In Initial Reports of the Deep-Sea Drilling Project; Hayes, D.E., Ed.; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 28, pp. 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.C.; Reynolds, R.C. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 1–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Stergiou, A.; Filippidis, A.; Drakoulis, A. Calculation of the percentage of amorphous material using PXRD patterns. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2004, 36, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock Forming Minerals, 2nd ed.; Longman: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Sikalidis, K.; Godelitsas, A.; Squires, C.; Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, A. Extra-framework cation release from heulandite-type rich tuffs on exchange with NH4+. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Llewellyn, P.; Rouquerol, F. Is the BET equation applicable to microporous adsorbents? Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.R.; Surdam, R.C. Diagenesis of volcanogenic sediments in a Tertiary saline lake; Wagon Bed Formation, Wyoming. Am. J. Sci. 1979, 279, 832–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, D.S.; Alberti, A.; Armbruster, T.; Artioli, G.; Colella, C.; Galli, E.; Grice, J.D.; Liebau, F.; Mandarino, J.A.; Minato, H.; et al. Recommended nomenclature for zeolite minerals: Report of the Subcommittee on Zeolites of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Canad. Miner. 1997, 35, 1571–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU). No 915/2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/915/oj/eng (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaiou, S.K.; Kokkari, A.; Mytiglaki, C.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Kantiranis, N. Zeolites in agriculture: Oviposition deterrent effect of Greek analcime-rich zeolite rock against the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae. In Proceedings of the International Conference of European Clay Groups Association-EUROCLAY 2023, Bari, Italy, 24–27 July 2023; Volume 9, pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyannos, B.I.; Kouloussis, N.A. Captures of the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae on spheres of different colours. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, N.; Sakka, M.K.; Emekci, M.; Athanassiou, C.G. Effects of zeolite formulations on the mortality and progeny production of Sitophilus oryzae and Oryzaephilus surinamensis at different temperature and relative humidity levels. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 81, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korunić, Z. Review: Diatomaceous earths, a group of natural insecticides. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1998, 34, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, B.; Roesli, R. Inert dusts. In Alternatives to Pesticides in Stored-Product IPM; Subramanyam, B., Hagstrum, D.W., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 321–380. [Google Scholar]
- Vayias, B.J.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Korunic, Z.; Rozman, V. Evaluation of natural diatomaceous earth deposits from south-eastern Europe for stored-grain protection: The effect of particle size. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Sehgal, B.; Subramanyam, B. Insecticidal potential of a synthetic zeolite against the cowpea weevil, Callosobruchus maculatus (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2017, 72, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).