Formation Mechanism of Granitic Basement Reservoir Linked to Felsic Minerals and Tectonic Stress in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
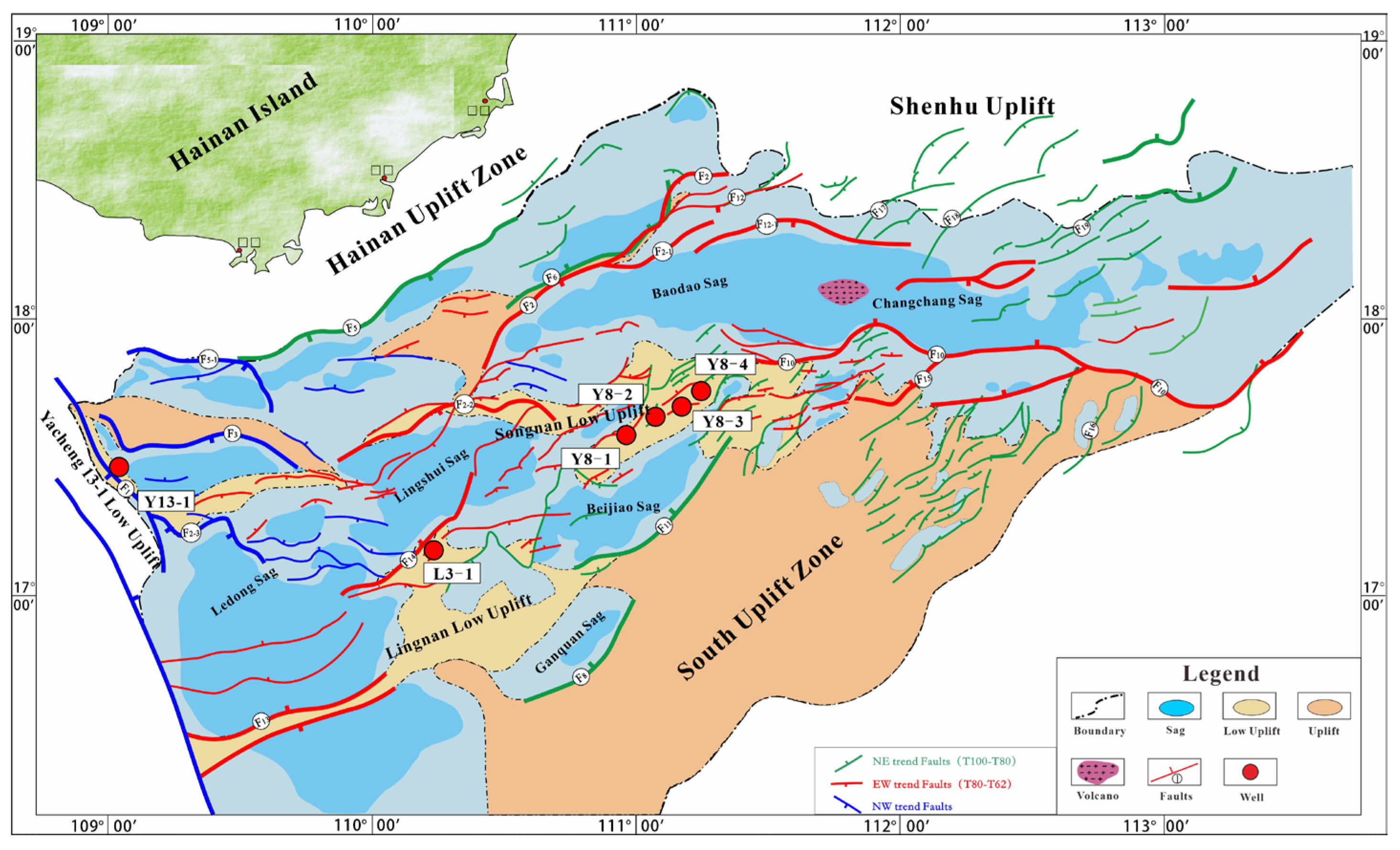
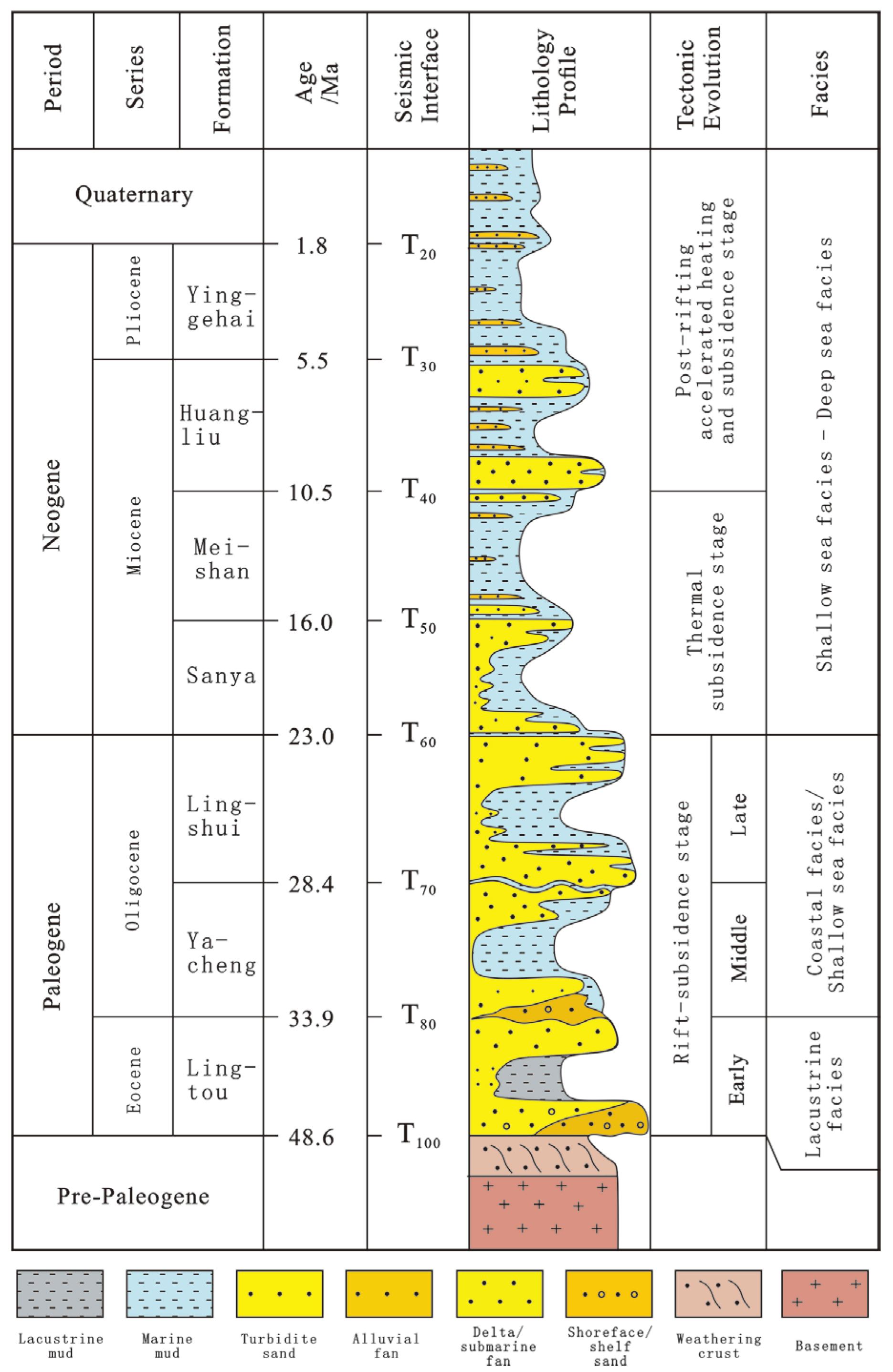
2. Geological Setting
3. Methods
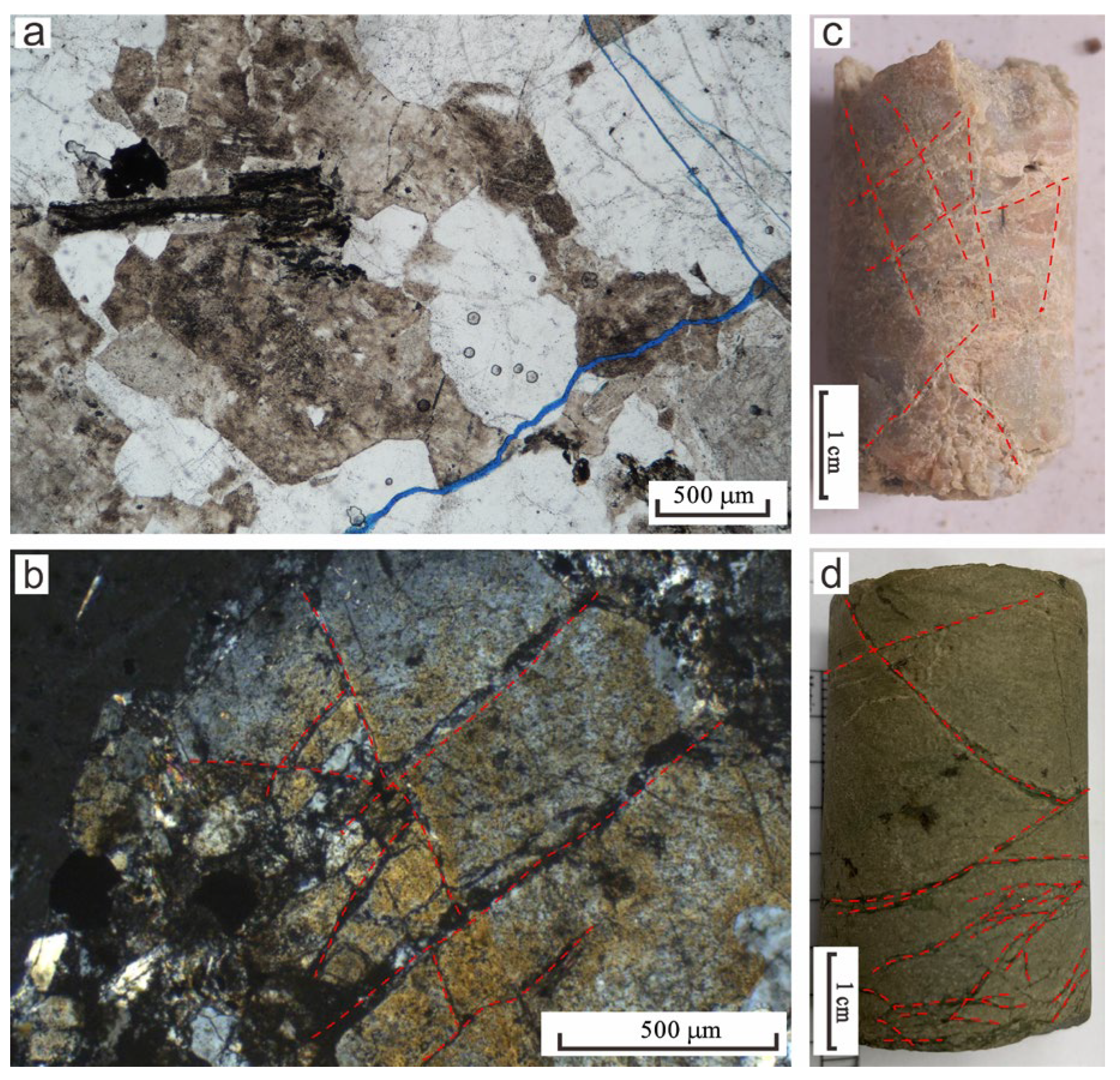
3.1. Microscopic Analysis of Thin Sections
3.2. Seismic Structure Interpretation
3.3. Well Logging Data Analysis
3.3.1. Statistics of Fracture Characteristic Elements
3.3.2. Geological Data from Drilling Wells
4. Results
4.1. Lithology and Fracture Characteristics
- (1)
- Granodiorite: The buried hill granodiorite in the Qiongdongnan Basin is widely developed. It is developed in Well L3-1 (depth of 4235~4244 m) and Well Y13-1 (depth of 3606~3620 m). Its microscopic characteristics are as follows: with a granite structure, the mineral composition is mainly plagioclase, alkaline feldspar, quartz, a small amount of biotite, muscovite, and iron; the rock contains multiple directional micro-cracks and is mostly filled with pyrite, and local mineral particles are broken in a network.
- (2)
- Monzonitic granite: The monzonitic granite in the buried hill of the Qiongdongnan Basin is widely developed. It is developed in Well Y8-1 (depth 2922~3054 m), Well Y8-2 (depth 3354~3492 m), Well Y8-3 (depth 2834 m~2986 m), Well Y8-4 (depth 2890~2939 m), Well L3-1 (depth 4328~4338 m), and Well Y13-1 (depth 3570~3610 m). The microscopic characteristics comprise a granite structure, mainly composed of plagioclase, alkaline feldspar, quartz, a small amount of biotite (less than 5%), and iron; biotite and plagioclase are mostly euhedral and subhedral, and alkaline feldspar and quartz are mostly subhedral and anhedral. The weathering of plagioclase is strong, and the surface clay and sericite are present. Alkaline feldspar is mainly striped feldspar, and the surface is clean; a small amount of quartz is granular, with a gray–white interference color and wavy extinction; black mica is brown scaly; iron is granular opaque; the rock develops multiple directional micro-cracks which are partially filled with pyrite, and the crystals are locally fractured, forming a network.
- (3)
- Syenite: The syenite in the buried hill of the Qiongdongnan Basin is less widely distributed. It is mainly found in Well Y8-1 (depth of 2974 m) and Well Y8-2 (depth of 3490 m). Its microscopic characteristics comprise a granite structure, mainly composed of alkaline feldspar and plagioclase and a small amount of quartz and biotite, epidote, and opaque minerals. Clayization is mostly developed on the surface of feldspar, and calcite vein filling can be seen.
- (4)
- Granite: Buried hill granites are widely distributed in the Qiongdongnan Basin. They are developed in Well Y13-1 (depth 3650~3690 m) and Wells Y8-3 and Y8-4 (depths 2897 m and 2969~2972.25 m). Its microscopic identification features are as follows: granite structure, massive structure; the main minerals are feldspar, quartz, and a small amount of biotite; this type of feldspar contains plagioclase and alkali feldspar. Plagioclase occurs as subhedral crystals, exhibiting polysynthetic twinning. It is predominantly altered to sericite and clay minerals, with minor alteration along crystal margins where the original cleavages and boundaries remain relatively preserved. The crystals consist of quartz, striped feldspar, orthoclase, and mica. Some crystals are altered; for example, orthoclase was altered to hydromica and kaolinite. Most of the mica is altered, and some is altered into chlorite.
- (5)
- Diabase: Diabase in the Qiongdongnan Basin is found in the basement of Well L3-1. It is developed as interlayers. The microscopic characteristics comprise a diabase structure, and the mineral composition is mainly plagioclase, pyroxene, and a small amount of quartz; plagioclase is subhedral; it can be seen that some feldspars are filled with pyroxene in the triangular framework formed by disorderly arrangement, and pyroxene is colorless–light yellow, with high protrusions. A small amount of quartz is granular, characterized by a gray–white interference color, with wavy extinction.
4.2. Structural Characteristics
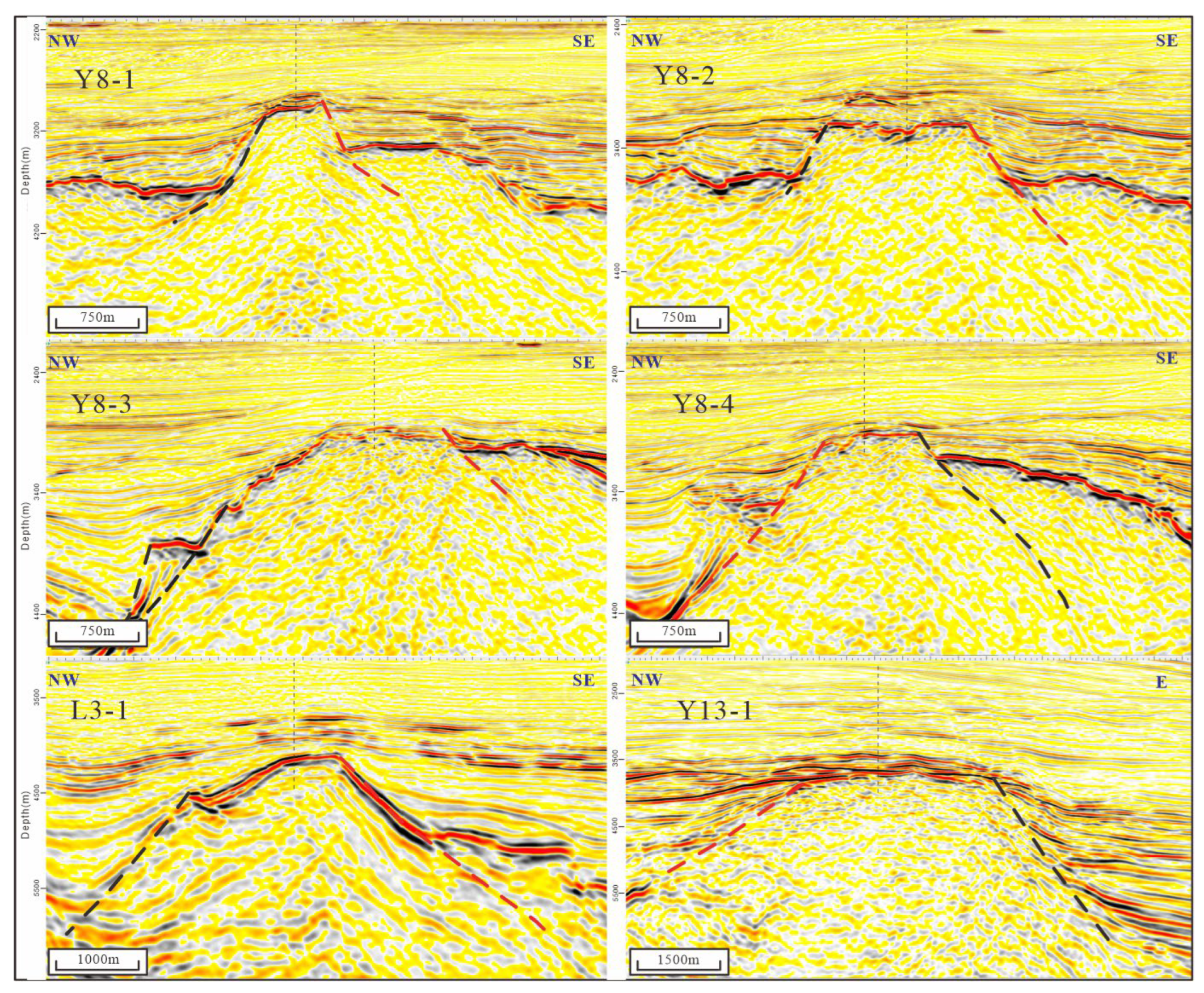
4.2.1. Structural Elements of the Buried Hill Boundary Fault
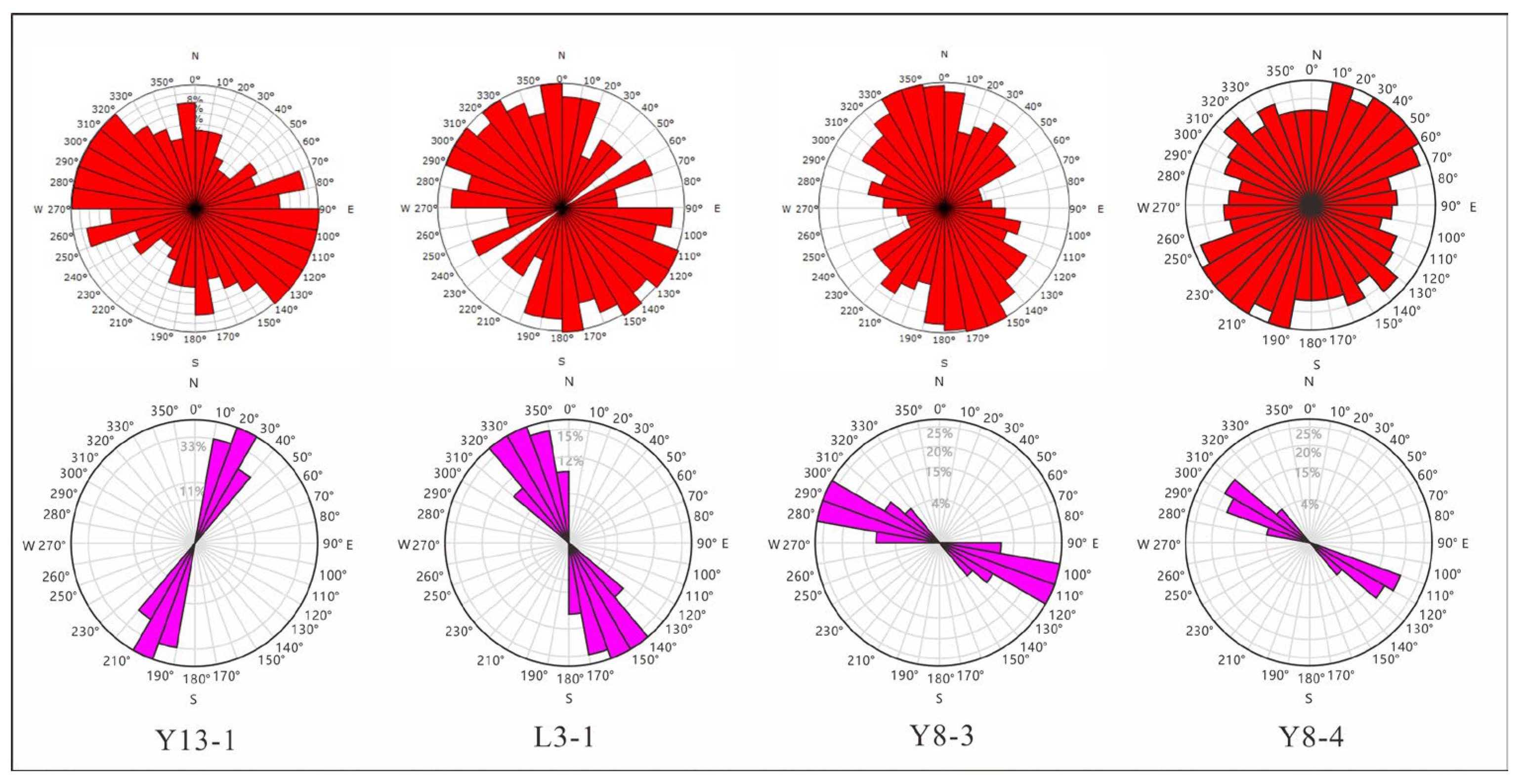
4.2.2. Fracture Occurrence Interpretation from Imaging Logging
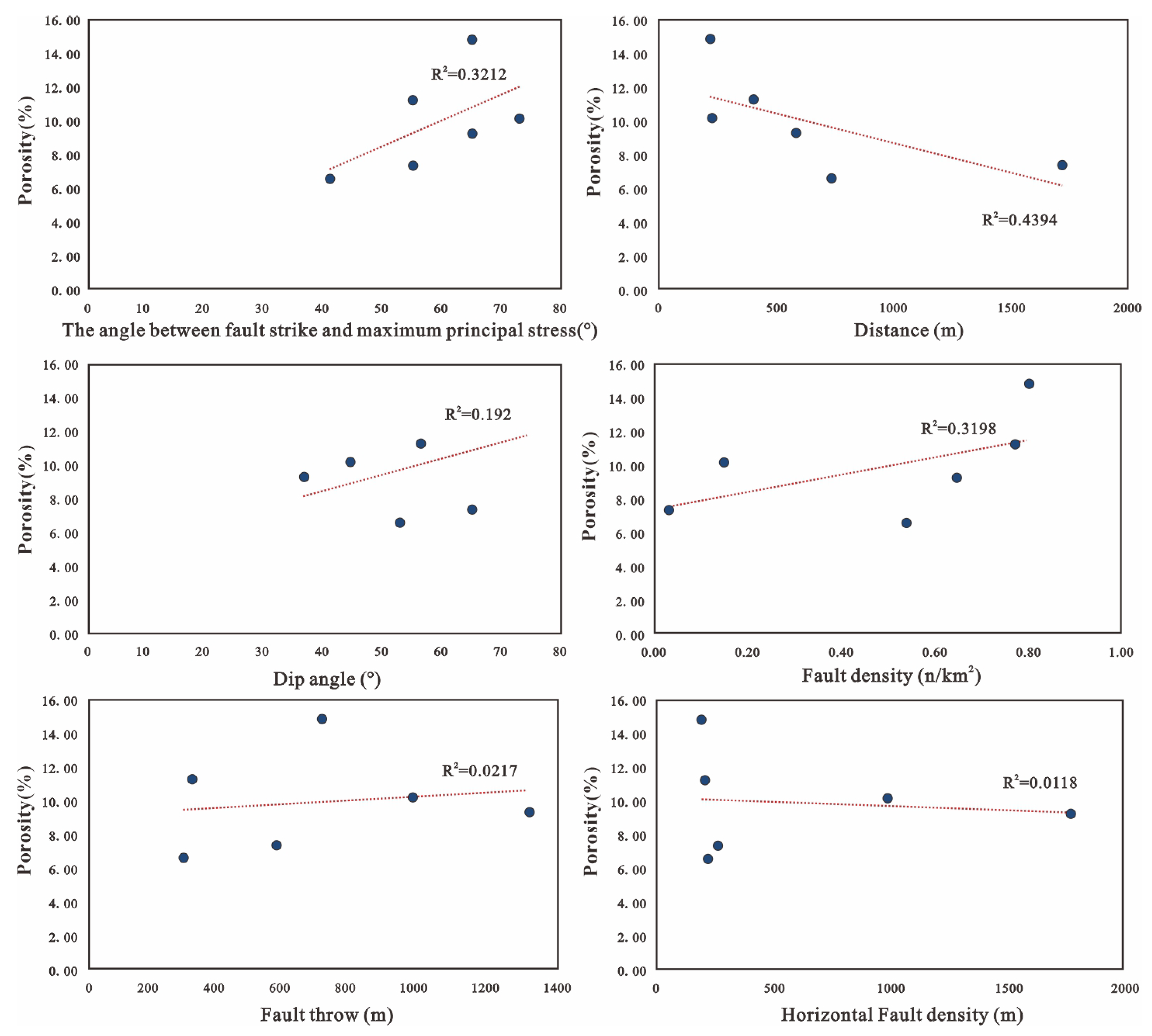
4.3. The Physical Properties of the Basement Reservoir and Its Zoning
5. Discussion
5.1. The Felsic Minerals Contributing to Brittleness and Solubility
5.2. Fracture Formation Linked to Multi-Stage Tectonic Activities
5.3. The Formation Mechanism of the Basement Reservoir
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, S. Reflected buried hills and their importance in petroleum geology. Econ. Geol. 1922, 17, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H. Buried Hill Reservoir and Petroleum System in Rift Basin; Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 1998; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, L.R.; Wen, Z.X.; Wang, Z.M.; He, Z.J.; Song, C.P.; Liu, X.B. Resource potential, giant discoveries, and implications of ancient hydrocarbon plays worldwide. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, R.C.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, B.Q.; Guo, Y.H. Major controls on natural gas accumulations in deep-buried hills in Bozhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. J. China Univ. Pet. Ed. Nat. Sci. 2017, 41, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Zhou, J.X.; Yang, H.F.; Ye, T. New fields, new type sand resource potentials of oil-gas exploration in Bohai Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 45, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.W.; Xu, C.G.; Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; Su, W. Reservoir forming mechanism of Penglai 9-1 granite buried-hills and its oil geology significance in Bohai Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2017, 38, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.A.; Li, H.Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, Q.S.; Cui, H.Z. Recognition of oil and gas accumulation of Mesozoic covered buried hills in Bohai sea area and the discovery of BZ 13-2 oilfield. China Offshore Oil Gas 2021, 33, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Wang, Q.B.; Feng, C.; Ye, T.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.W.; Zhou, L. Formation Conditions and Geological Significance of Large Archean Buried Hill Reservoirs in Bohai Sea. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 1534–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.C.; Zhou, J.X.; Yang, H.F.; Guan, D.Y.; Su, W.; Ye, T.; Zhao, J.D. Discovery of large-scale metamorphic buried-hill oilfield in Bohai Bay Basin and its geological significance. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1587–1598,1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.; Lv, D.Y.; Yi, J.; Shan, X.L.; Zhang, J.R.; Liu, X.J.; Gao, F.H.; Wang, W.; Ren, S.Y.; Xu, H.J. Lithology characteristics, genesis and reservoir significance of metamorphic rocks in the Archean buried hill of Bozhong sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Case studies of Bozhong19-6 structural area and Anziling area. Acta Pet. Sin. 2024, 46, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Zhang, G.C.; Huang, S.B.; Shan, X.L.; Li, J.H. Formation of large- and medium-sized Cretaceous volcanic reservoirs in the offshore Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Xu, C.Q.; Huang, Z.; Shan, X.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Yi, J. Enhanced formation conditions of the large-scale volcanic reservoir in the BZ8-3S large volcanic structure in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2024, 50, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M. Reservoir Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Mesozoic Granite Buried-Hill in Songnan Low Uplift, Qiongdongnan Basin. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.L.; Xu, C.G.; Yi, J.; Niu, C.M.; Hao, G.L.; Guo, J.N.; Yan, B. Mesozoic Magmatic Activities and Hydrocarbon Accumulationsin Magmatic Buried Hills in Typical Offshore Oil and Gas Basins of China. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2024, 54, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, D.; Okla, T. A few notes on the future work of the petroleum geologist in the mid-continent oil fields. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1917, 75, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, C.C.; Gus, H.G. Stratigraphic and tectonic framework of Libya: Abstract. AAPG Bull. 1966, 50, 608. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.P.; Naylor, W.V. History of oil development in Libya. AAPG Bull. 1966, 50, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, F.T.; Weeger, A.A. Sirte Basin and Tertiary Niger Delta Basin in Africa; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Areshev, E.G.; Dong, T.L.; San, N.T. Reservoirs in fractured basement on the continental shelf of southern Vietnam. J. Pet. Geol. 1992, 15, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Nguyen, T.B.N.; Lee, W.K. A review of geological characteristics and improved oil recovery for a high temperature fractured basement reservoir, Vietnam. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2014, 36, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Cuong, T.X.; Warren, J.K. Bach ho field, a fractured granitic basement reservoir, Cuu Long Basin, offshore SE Vietnam: A “buried-hill” play. J. Pet. Geol. 2009, 32, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, X.H.; Xu, G.S.; Liu, P.B.; Gao, K.S.; Guan, D.Y. Characteristics and controlling factors of reservoirs in Penglai 9-1 largescale oilfield in buried granite hills, Bohai Sea. Oil Gas Geol. 2015, 36, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yang, Y.; You, C. Base rock weathering crusts and petroleum accumulation in Dongping area, Qaidam Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2019, 39, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Cai, J.J.; Wan, Q.H.; Gao, X.; Yan, P. Reservoir condition analysis of a buried granite hill in the Huizhou depression and its petroleum geological significance. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2019, 39, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.X.; Shi, H.S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.D. Great discovery and significance of new frontier exploration in Huizhou sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.C.; He, X.H.; Jin, Q.Y.; Cao, H.Y.; He, L.W.; Que, Y.Y.; Chen, A.Q. Factors controlling the formation and distribution of Mesozoic buried hill reservoirs in the Qiongdongnan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Xu, S.; Mao, X.; Zhong, J.; Jiao, Y.; Xiong, X. Reservoir Characteristics and Genetic Mechanisms of the Mesozoic Granite Buried Hills in the Deep-water of the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; You, L.; Mao, X.L.; Zhong, J.; Wu, S.J. Reservoir Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Granite Buried Hill in Songnan Low Uplift, Qiongdongnan Basin. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.Y.; Gan, J.; Jiao, X.Y.; Hu, Q.W.; Chen, Y. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factor of buried hill of Lingnan Low Uplift in deep water area of Qiongdongnan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Hou, M.C.; Wu, K.Q.; Xiong, F.H.; You, L.; Li, C.X.; Wang, W.B. Permian-Triassic felsic magmatism in the Qiongdongnan Basin: Implications for the tectonic properties and evolution of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2024, 40, 2450–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xiong, F.H.; Chen, A.Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.B.; Hou, M.C. Granitic magmatism and tectonic evolution in Qiongdongnan basin and their constraints on the properties of buried hill reservoirs. Geol. Bull. China 2024, 43, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Q.; Chen, A.Q.; Hu, L.; Hou, M.C.; You, L.; He, X.H.; Cao, H.Y.; Que, Y.Y.; Xiong, F.H.; Wang, W.B. Combined control mechanism of weathering and tectonics for basement granite of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2024, 46, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, Q.W.; Wang, S.Y.; Jiang, R.F.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, C.; Tian, L.X.; Zhang, C.M.; Bian, K.G. Origin of the overpressure and hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of bedrock buried hills in the deepwater area, Qiongdongnan Basin. Earth Sci. 2023, 50, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Guo, L.L.; Wang, G.Z.; Hui, G.G.; Santosh, M.; Somerville, I.D.; Cao, X.Z.; Li, Y. Plate tectonic control on the formation and tectonic migration of Cenozoic basins in northern margin of the South China Sea. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Zeng, Q.B.; Yang, H.Z.; Guo, S.; Zhong, K. Structural characteristics of central depression belt in deep-water area of the Qiongdongnan Basin and the hydrocarbon discovery of Songnan low bulge. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.F.; Li, C.; Chen, G.J.; Zhang, G.C.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.T.; Zhou, Q.S. Zircon U–Pb age constraints on the provenance of Upper Oligocene to Upper Miocene sandstones in the western Qiongdongnan Basin, South China sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 126, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.L.; Wang, G.C. New venture of exploration of pre-cenozoic oil and gas in Chinese offshore areas. Earth Sci. Front. 2000, 7, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, L.R.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, R.C.; Wei, X.D.; Shrivastava, C. Precambrian basement reservoirs: Case study from the northern Bongor Basin, the Republic of Chad. AAPG Bull. 2018, 102, 1803–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wei, A.J.; Sun, Z.; Gao, K.S.; Cheng, Q. The reservoir characteristics and their significance for deliverability in metamorphic granite buried hill: A case study from the JZS oil field in the Liaodong Bay Basin, NE China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.S.; Chen, X.J.; Liao, G.L.; Peng, Z.C. Zonation characteristics of the granite basement buried hill in Yongle 8 area of Qiongdongnan basin. China Offshore Oil Gas 2023, 35, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.J.; Zhu, C.B.; Chen, X.J.; Chen, P.; Tan, B.; Xiong, Y.X.; Guo, S.S.; Jiang, N. Reservoir Interpretation of Intrusive Rock Buried-Hill with Mud-Logging Data while Drilling—Taking the Y Area in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea as an Example. Energies 2022, 15, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.Y.; Lv, D.Y.; Yi, J.; Shan, X.L.; Liu, X.J.; Zhu, B.H.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.C. Classification and Quantitative Characterization of Archean Metamorphic Buried Hill Reservoirs in the Bohai Sea. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 35193–35206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.C.; Yang, D.S.; Guo, S.; Wang, L.; Lü, C.F. The formation of oil and gas in basement buried hills with its model of three-element controlling reservoir and the frontiers of deep water oil and gas exploration in the northern South China Sea. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 2045–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Tang, H.F. Characteristics of Weathering Reservoirs and Differences in Fracture Formation in the Weathering Crust of the Pre-Cenozoic Basement of Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.G.; Du, X.F.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, W.; Hao, T.W. Formation mechanism of hnigh-quality dep buriedhil reserroir of Archaean metamorphic rcks and its significance in petroleum exploration in Bohai Sea area. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 235–247+294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Wang, Q.B.; Liu, X.J.; Zhao, M.; Hao, Y.W. Characteristics and developing patterns of gneiss buried hill weathering crust reservoir in the sea area of the Bohai Bay basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, K.; Wang, G. Distribution features and main controlling factors of volcanic buried hill reservoirs in carboniferous basement of Junggar Basin. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.G.; Chen, H.D. Reservoir-forming rules and main controlling factors of Archean buried hill reservoir of middle to northern Liaoxi Uplift in Liaodong Bay area in Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2024, 46, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.R.; Zhang, L.L.; Wu, Z.; Xie, S.W.; Zhao, J.W.; Lu, F.R.; Liang, C.; Pan, J.; Huang, L. Distribution laws of intensively weathering and leached zones in deep-water buried hills of the Pearl River Mouth Basin and their controlling factors. Nat. Gas Ind. 2024, 44, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, G.J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.C. Characteristics and main controlling factors of structural fracture development in deep buried hill reservoirs of basement metamorphic rocks:a case study of B block, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2024, 46, 799–811. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.F.; Liu, H.M.; Cao, Z.X.; Tian, M.R.; Tang, D.; Ma, S.K. Main Controling Factors of Archaeozoic Weathering Crust Reservoir: With Jiyang and Luxi Area as an Example. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2015, 45, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.M. Characteristics and Control Factors of Archean Buried-Hill Metamorphic Fractured Reservoirs in the BZ19-6 Structural Region, Bozhong Sag. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, A.Q.; Niu, C.M.; Wang, Q.B.; Guo, L.L. Characteristics and vertical zonation of large-scale granitic reservoirs, a case study from Penglai oil field in the Bohai Bay Basin, North China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 8109–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Niu, C.M.; Wei, A.J. Characteristics and genetic mechanism of large granitic buried-hill reservoir, a case study from PengLai oil field of Bohai Bay Basin, north China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 189, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, A.Q.; Hou, M.C.; Niu, C.M.; Wang, Q.B. Characteristic of the Bodong segment of the Tanlu Fault Zone, Bohai sea area, eastern China: Implications for hydrocarbon exploration and regional tectonic evolution. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, A.Q.; Niu, C.M.; Wang, Q.B.; Hou, M.C. Characteristics, controlling factors and petroleum geologic significance of fractures in the Archean crystalline basement rocks: A case study of the South Jinzhou oilfield in Liaodong Bay depression, North China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xu, G.S.; Zhou, W.; Liang, J.J.; Xu, F.H.; He, S. Predicting Granitic Buried-Hill Reservoirs Using Seismic Reflection data—A Case Study from the Bongor Basin, Southwestern Chad. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 949660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Shan, X.L.; Yi, J.; Xu, P.; Ren, S.Y.; Niu, P.H. Development mechanism of metamorphic fractured reservoirs in the Bozhong area, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications from tectonic and magmatic hydrothermal activities. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 229, 212030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Wu, S.Q. Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Granite Weathering Crust of Songnan Low Uplift, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Minerals 2024, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, A.Q.; Yang, H.F.; Huang, Z.; Luo, J.; Hou, M.C. Tectonism and fracture-related dissolution induced the formation of the large-scale metamorphic granite reservoir: Implications from Bozhong 26–6 Precambrian bedrock trap, offshore Bohai Bay basin, Northern China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.L.; Wang, P.J.; Wu, J.F.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, W.Y.; Lang, Y.Q. Distribution of the Mesozoic in the continental margin basins of the South China Sea and its petroliferous significance. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.L.; Wang, P.J.; Zhang, G.C.; Wang, W.Y. Characteristic of regional fractures in South China Sea and its basement tectonic framework. Prog. Geophys. 2015, 30, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.C. Tectonic evolution of deepwater area of northern continental margin in South China Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2010, 31, 528–533+541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.C.; Jia, Q.J.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, P.J.; Zhao, Q.L.; Sun, X.M.; Xie, X.J.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, W. On tectonic framework and evolution of the South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 4194–4215. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.B.; Liu, L.F.; Wu, K.Q.; Chen, S.P.; Jiang, X.; Hao, J. Control factors and comprehensive prediction of granite buried hill reservoirs in western segment of Shaleitian bulge, Bohai Sea. China Pet. Explor. 2017, 22, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, P.F.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, W.; Liu, R.J. New understanding and research directions of oil and gas accumulation in Paleozoic buried hills, Jiyang Depression. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2024, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barg, E.; Skar, Ø. Faults and fractures in the crust: Field observations and modeling approaches. J. Struct. Geol. 2005, 27, 1234–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Li, M.J.; Mu, H.Y. Depositional setting and enrichment mechanism of organic matter of lower cretaceous shale in ri-qing-wei basin in the central sulu orogenic belt. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 808916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, A.; Niu, C.; Luo, J.; Hou, M. A fracture-related deep Archean crystalline basement reservoir facilitated by thrusting and mineralogy: Newly discovered Bozhong 19-6 large gas field, offshore Bohai Bay Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2025, 109, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Well | Fault Strike | The Angle | Fault Dip | Dip Angle | Distance (m) | Horizontal Fault Throw (m) | Fault Throw (m) | Fault Density (n/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y8-1 | NE∠55° | 65 | ∠145° | 75 | 219 | 192 | 698 | 0.80 |
| Y8-2 | NE∠41° | 41 | ∠145° | 53 | 736 | 216 | 285 | 0.54 |
| Y8-3 | NE∠55° | 65 | ∠325° | 37 | 586 | 1772 | 1318 | 0.65 |
| Y8-4 | NE∠55° | 55 | ∠145° | 56 | 404 | 206 | 310 | 0.87 |
| L3-1 | NE∠48° | 73 | ∠138° | 44 | 226 | 987 | 970 | 0.15 |
| Y13-1 | NW∠330° | 55 | ∠240° | 65 | 1721 | 262 | 562 | 0.03 |
| Well | Weathering Fracture Zone Porosity (%) | Inner Crack Zone Porosity (%) | Whole Reservoir Porosity (%) | Net-to-Gross Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y8-3 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 9.5 | 0.7 |
| Y8-4 | 11.3 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 0.9 |
| Y8-1 | 14.9 | / | 14.9 | 0.65 |
| Y8-2 | 6.6 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 0.53 |
| L3-1 | 10.2 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 0.5 |
| Y13-1 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Zhou, T.; He, X.; Chen, Z.; Que, Y.; Chen, A.; Wang, W. Formation Mechanism of Granitic Basement Reservoir Linked to Felsic Minerals and Tectonic Stress in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Minerals 2025, 15, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050457
Hu Q, Zhou T, He X, Chen Z, Que Y, Chen A, Wang W. Formation Mechanism of Granitic Basement Reservoir Linked to Felsic Minerals and Tectonic Stress in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050457
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qianwei, Tengfei Zhou, Xiaohu He, Zhihong Chen, Youyuan Que, Anqing Chen, and Wenbo Wang. 2025. "Formation Mechanism of Granitic Basement Reservoir Linked to Felsic Minerals and Tectonic Stress in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea" Minerals 15, no. 5: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050457
APA StyleHu, Q., Zhou, T., He, X., Chen, Z., Que, Y., Chen, A., & Wang, W. (2025). Formation Mechanism of Granitic Basement Reservoir Linked to Felsic Minerals and Tectonic Stress in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Minerals, 15(5), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050457





