Indication of REEs, Fe, and Mn Composition Typomorphism of Calcite in Metallogenic Fracture Zones with Respect to Local Tectonic Stress Fields: A Case Study of the Qingshan Lead–Zinc Deposit in Northwest Guizhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Geological Features
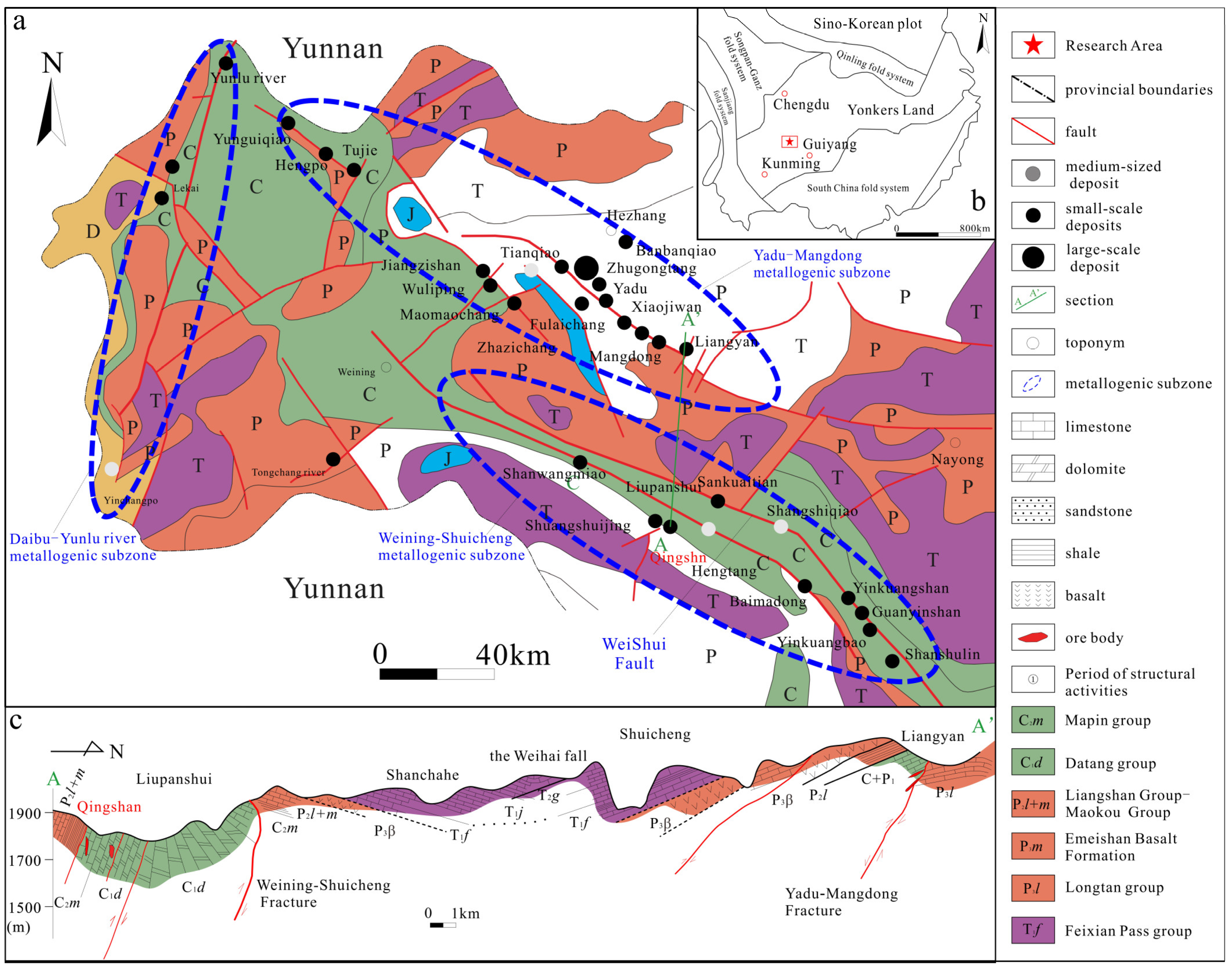
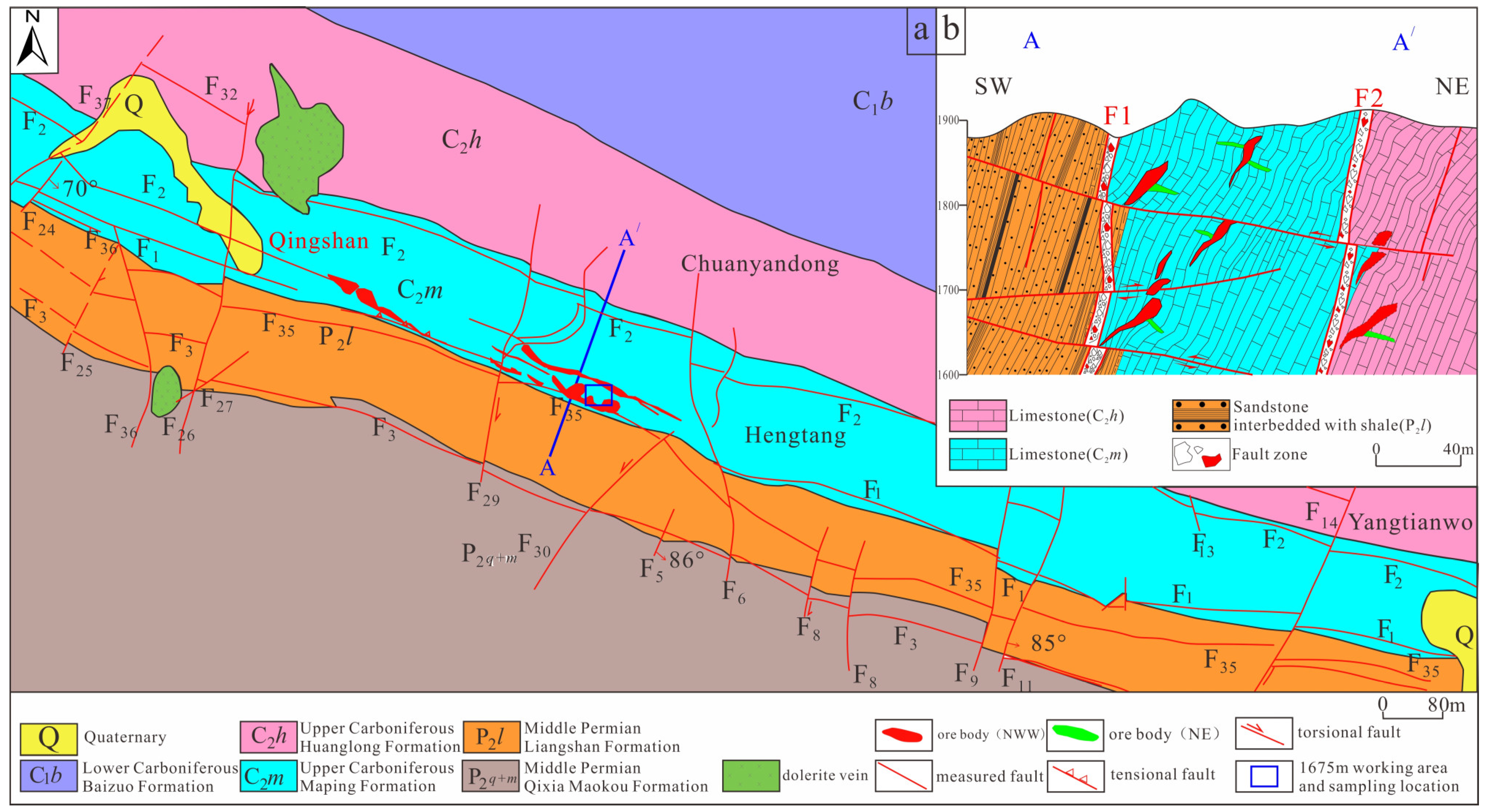
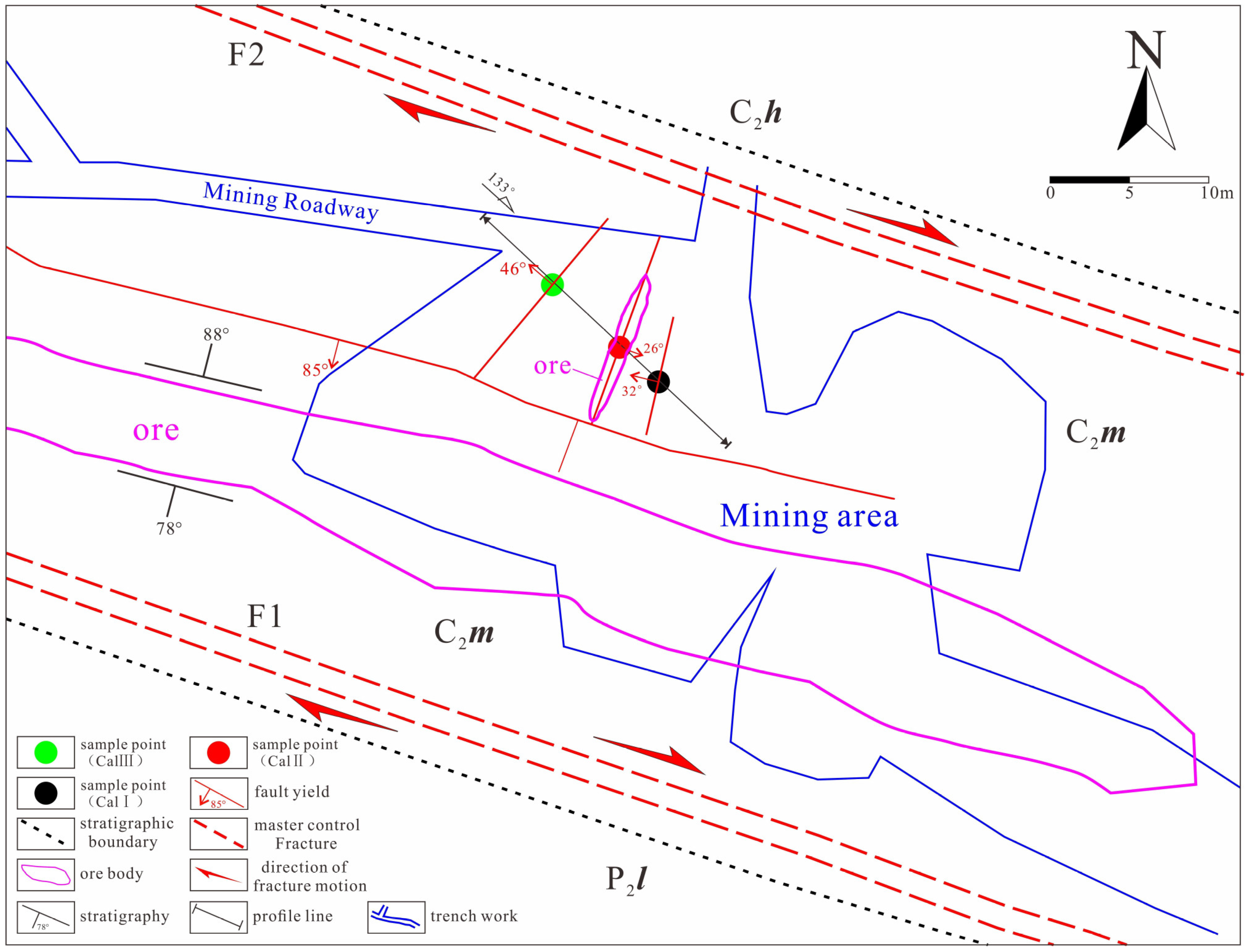
3. Geological Characteristics of the Ore Deposit
4. Sample Collection and Test
4.1. Sample Collection and Description
4.2. The Mineral Assemblage at the Microscale
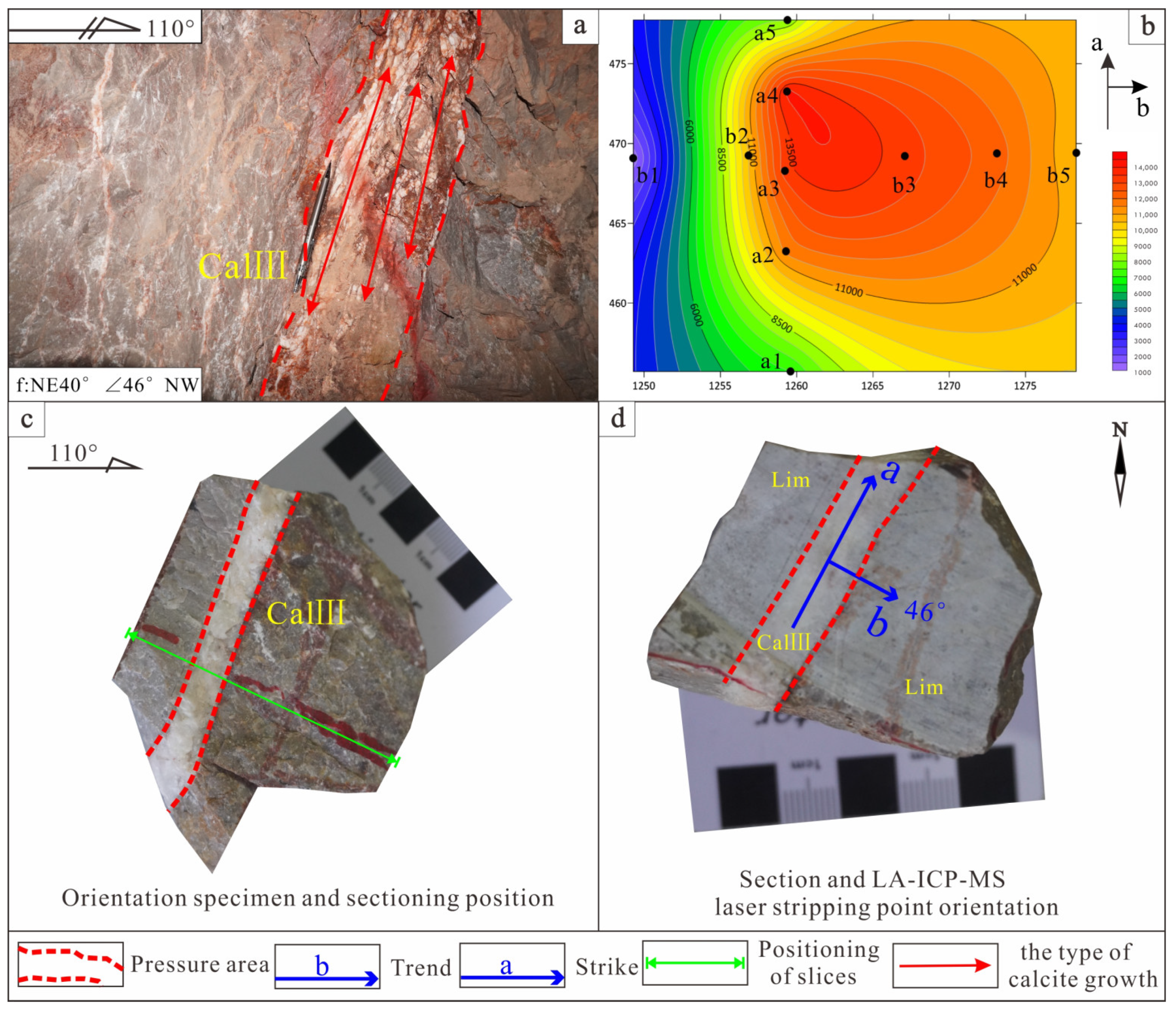
4.3. Sample Test
5. Results
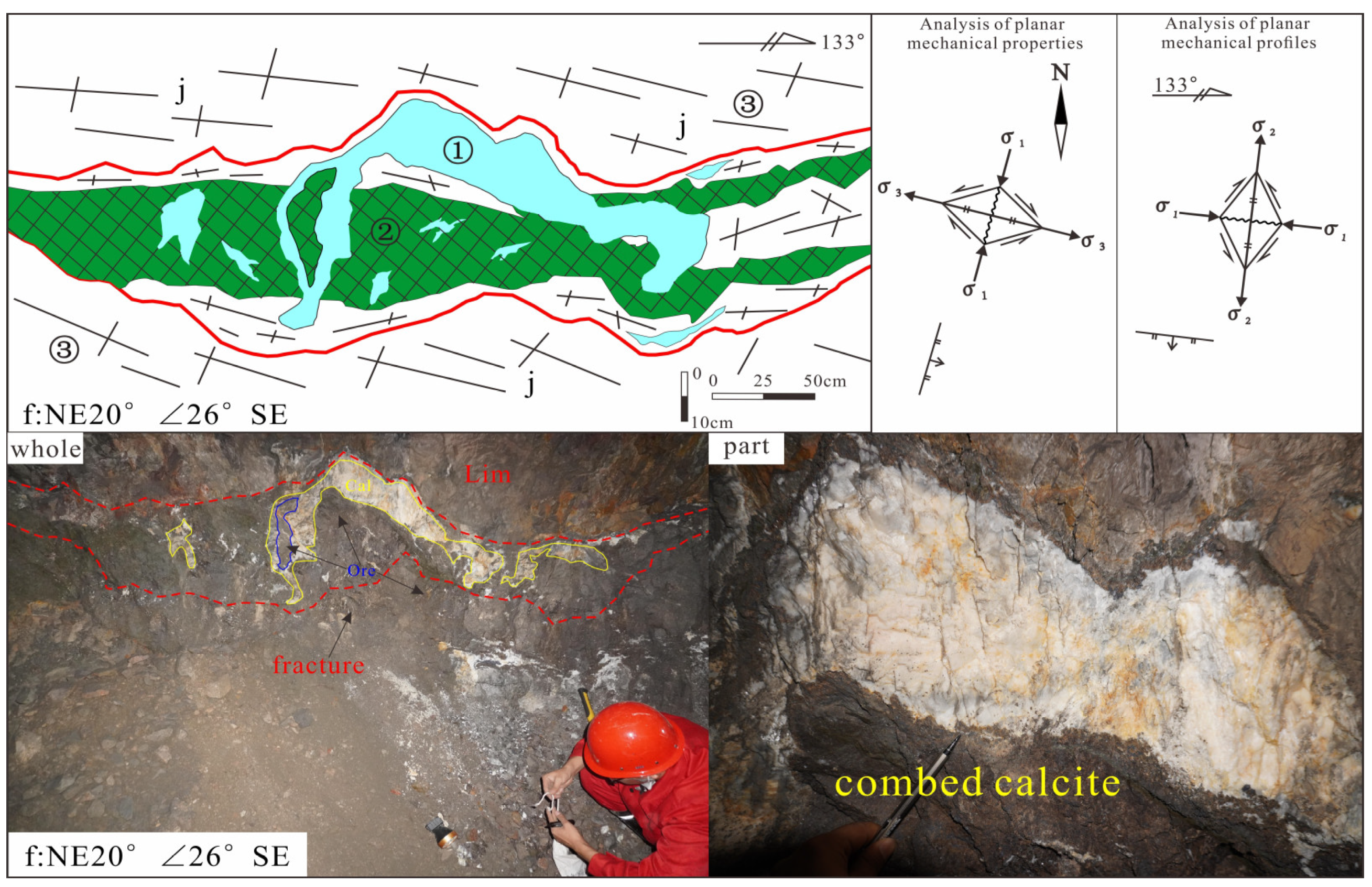
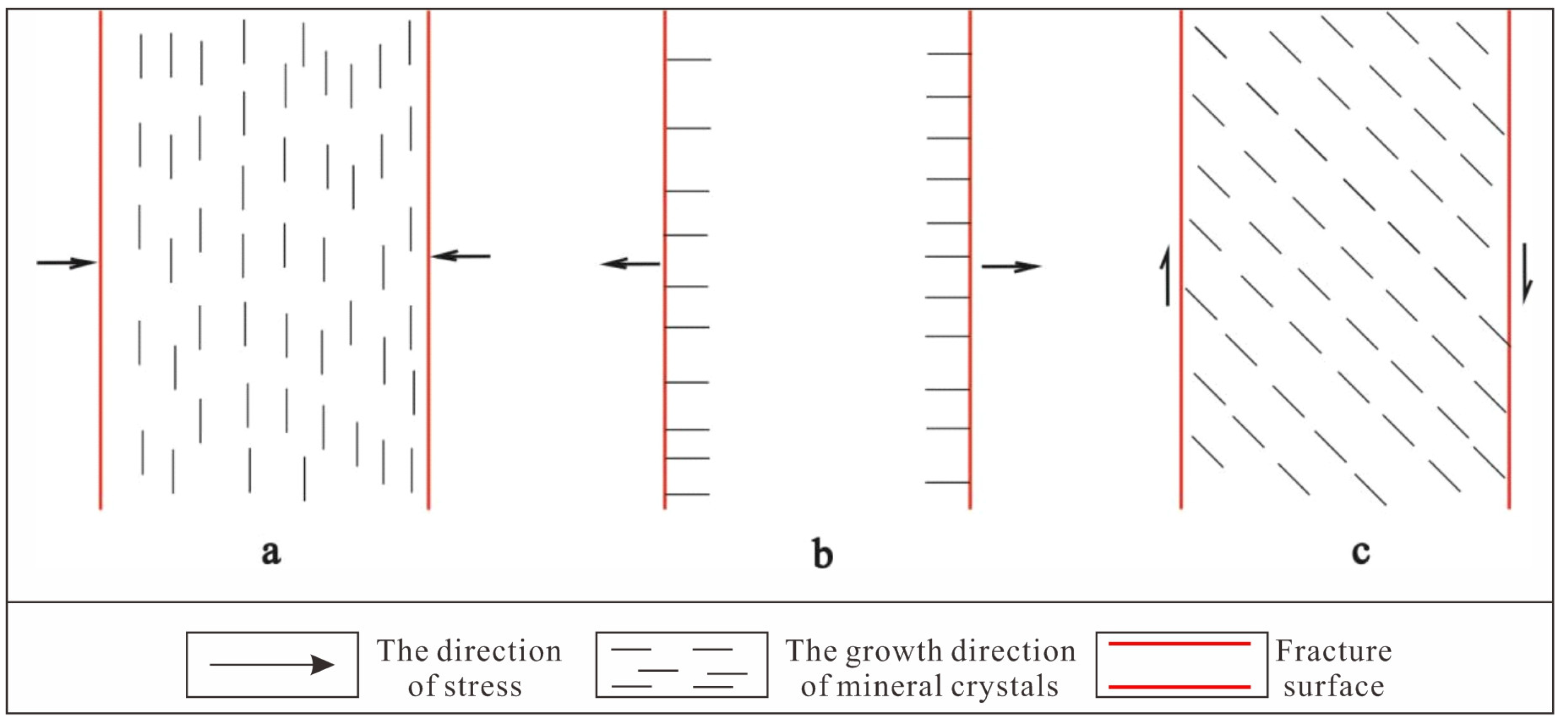
5.1. Analysis of the NE Fault Structure
5.1.1. Action Characteristics of Torsional Stress
5.1.2. Action Characteristics of Tensile Stress
5.1.3. Action Characteristics of Compressive Stress
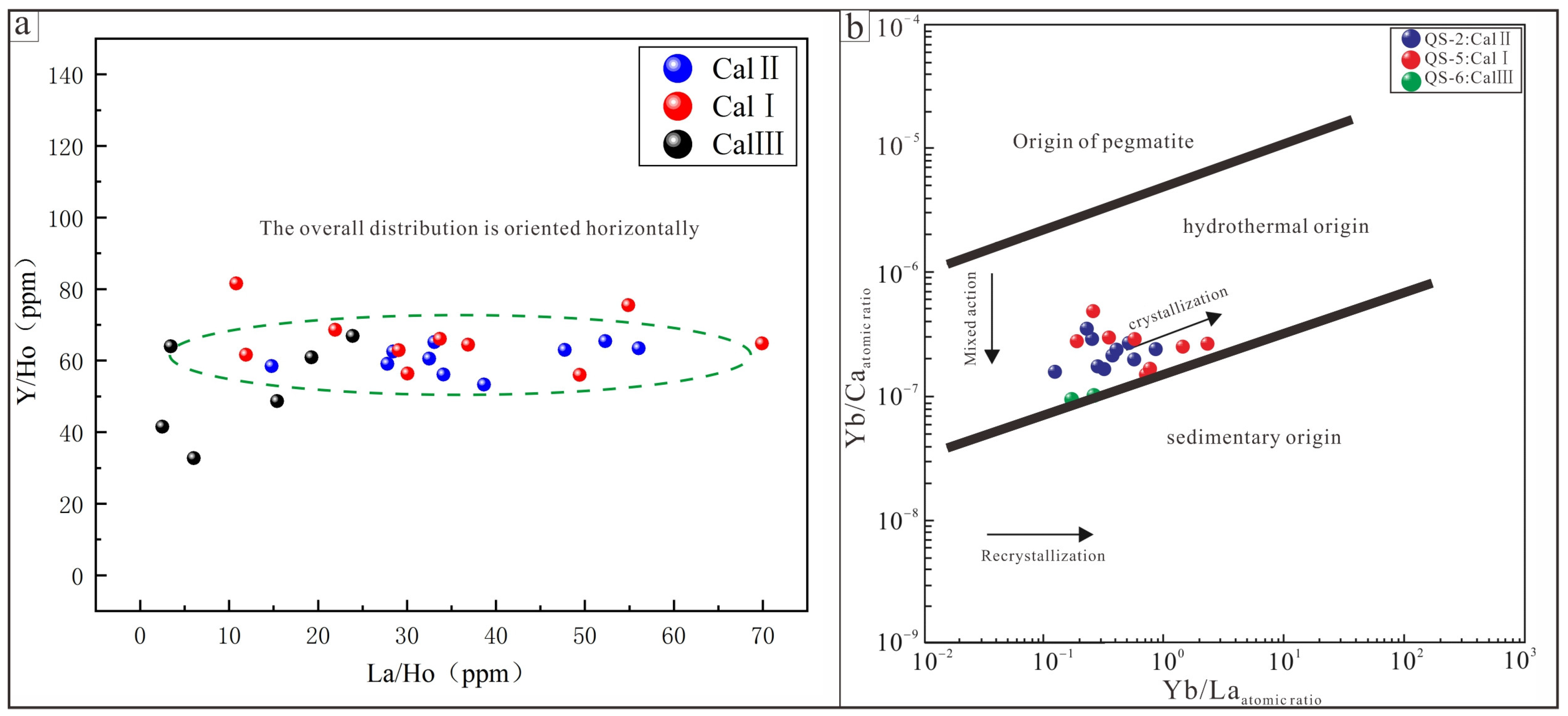
5.2. Calcite REE Characterization
- CalII had the highest total amount of rare earth elements (ΣREE = 16.44–55.41 × 10−6), with obvious fractionation of light and heavy rare earth elements, where the light rare earth elements were the most enriched (LREE = 14.42–47.25 × 10−6), with LREE/HREE (mean) = 6.40 and (La/Yb)N (mean) = 28.24, and the pattern of the rare earth element partitioning was right-dipping, with negative Eu anomaly (δEu = 0.58–1.03) and weak negative Ce anomaly (δCe = 0.5–0.63).
- The total amount of REEs in CalI (ΣREE = 1.41–28.93 × 10−6) was enriched in light rare earth elements, with LREE/HREE (mean) = 5.48 and (La/Yb)N (mean) = 23.75, and the pattern of rare earth element partitioning was right-dipping, with maximum negative Eu anomaly (δEu = 0.26–1.09) and weak Ce anomaly (δCe = 0.43–0.55).
- CalIII had relatively low total rare earth elements (ΣREE = 2.03–4.68 × 10−6), was enriched in light rare earth elements, with LREE/HREE (mean) = 3.92 and (La/Yb)N (mean) = 6.19, and weak Eu (δEu = 0.5–1.46) and Ce (δCe = 0.56–0.70) anomalies.
5.3. Calcite Fe, Mn Elemental Characteristics
- CalII had the highest Fe + Mn content of 2186.69 × 10−6;
- CalI had a moderate Fe + Mn content of 1066.96 × 10−6;
- CalIII had the lowest Fe + Mn content of 904.31 × 10−6.
6. Discussion
6.1. The Indicative Significance of REE in Calcite
6.1.1. Characterization of REE Partitioning Patterns in Calcite
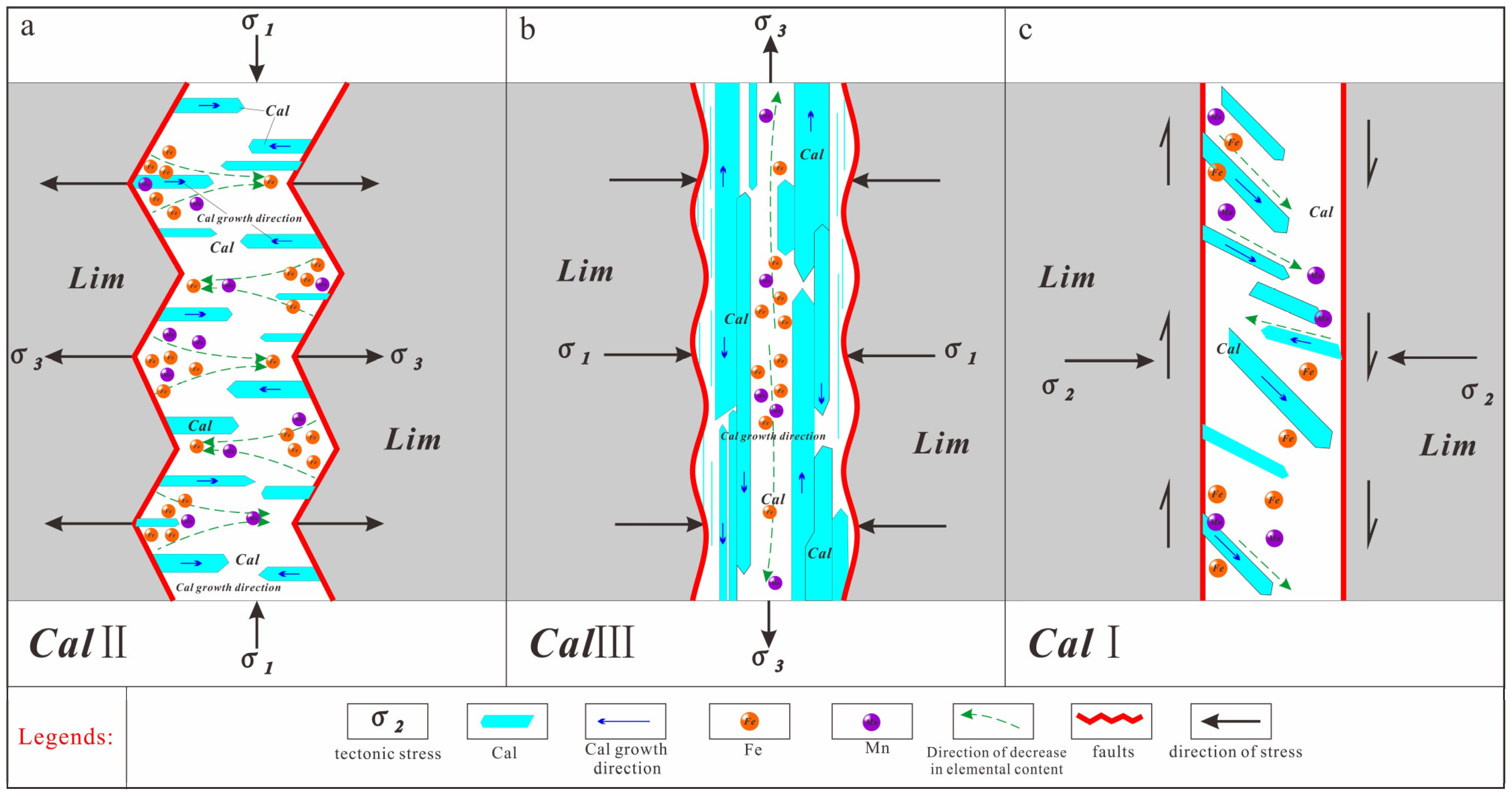
6.1.2. Causes of the Three Types of Calcite
6.2. Calcite Fe and Mn Elemental Variations
6.3. Interpretation of the Ore Deposit Within the Tectonic Setting
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, R.S.; Wang, M.Z.; Jing, Z.G.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.Y. Ore-controlling mechanism of NE-trending ore-forming structural system at Zn-Pb polymetallic ore concentration area in northwestern Guizhou. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 850–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.H.; Han, R.S.; Wang, F.; Wang, M.Z.; He, Z.; Zhou, W.; Luo, D. Structural ore−controlling mechanism of the Qingshan lead−zinc deposit in northwestern Guizhou, China and its implications for deep prospecting. Geol. China 2024, 51, 399–425. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.C.; Han, R.S. Theory and Method of Ore-Field Geomechanics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.S.; Zhao, D. Research methods for the deep extension pattern of rock/ore-controlling structures of magmatic-hydrothermal ore deposits-a preliminary study. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 420–437. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Ruan, W.L.; Jing, Z.G.; Zhang, M.H.; Gun, M.S. Characteristics and geological significance of trace element composition of pyrite in Qingshan lead-zinc deposit in northwest Guizhou Province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2023, 43, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.G. Ore-Controlling Factors, Metallogenic Rules and Prospecting Prediction of Lead and Zinc Deposits in Northwest Guizhou; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.G.; Huang, Z.L. Study on controlling ore factors of Pb-Zn deposits and prospecting model in the area of southwestern Guizhou. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2008, 28, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Han, R.S.; Li, W.B.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhang, Z.L.; Ma, D.Y. Geochemistry and Ore-Formation of the Huize Giant Lead-Zinc Deposit, Yunnan Province, China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 77–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Gu, X.C.; Wen, S.M.; Han, R.S.; Shen, R. Effect of Emeishan basalt in northeast Yunnan on lead and zinc mineralization. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2012, 26, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Geochemistry and Geochronology of Multi-Generation Garnet: New Insights on the Genesis and Fluid Evolution of Prograde Skarn Formation. Geosci. Front. 2022, 14, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.S.; Liu, C.Q.; Huang, Z.L.; Li, Y. Characteristics of ore-controlling structures and REE composition of fault rocks in Huize lead-zinc deposit, Yunnan. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 20, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.L.; Li, W.B.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Han, R.S.; Liu, C.Q. REE Geochemistry of Calcites from Fault Zone of Huize Superlarge Pb-Zn Deposits in Yunnan Province. Miner. Depos. 2003, 22, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Han, R.S.; Wang, J.S.; Ren, T. REE Geochemical Characteristics in Lehong Large Lead-Zinc Deposit, Northeastern Yunnan Province, China. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2017, 37, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A. The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: 2. Theoretical predictions of speciation in hydrothermal solutions to 350 °C at saturation water vapor, pressure. Chem. Geol. 1990, 82, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Mucci, A. Partitioning of rare earth elements (REEs) between calcite and seawater solutions at 25 °C and 1 atm, and highdissolved REE concentration. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimstidt, J.D.; Balong, A.; Webb, J. Distribution of trace elements between carbonate minerals and aqueous solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Möller, P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 45, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SubÍas, I.; Fernández-Nieto, C. Hydrothermal events in the Valle de Tena (Spanish Western Pyrenees) as eviden ced by fluid inclusions and trace-element distribution from fluorite deposits. Chem. Geol. 1995, 124, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Y.; Bi, X.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Peng, J.T.; Li, H.; Li, D.H.; Zhu, C.S. REE, Mn, Fe, Mg and C, O isotopic geochemistry of calcites from Furong tin deposit, South China: Evidence for the genesis of the hydrothermal ore-forming fluids. Resour. Geol. 2010, 60, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q. Study of thermoluminescence(tl) of quartz and calcite in the Xitieshan Pb-Zn deposit. Miner. Resour. Geol. 1996, 10, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, A.Y.; Xue, C.D.; Hong, T.; Luo, D.F.; Li, L.R.; Wang, F.; Zhou, G.M.; Liu, X. The alteration-mineralization zoning model for the Maoping lead-zinc deposit northeastern Yunnan Province: Evidence from alternation-lithofacies mapping. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2012, 31, 723–735. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, M.L.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.D.; Li, R. The mineralizing fluid property reflected by gochemical characteristics of calcite in polymetallic deposit. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2012, 27, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Song, Y.C.; Zhuang, L.L.; Huang, S.Q.; Hu, G.; Huang, G.; Tian, L.D.; Yue, L.L. Trace elemental compositions of ore-related hydrothermal calcite for Mississippi Valley-type deposit: A case study of the Duocaima giant Pb-Zn deposit, Qinghai, China. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2023, 42, 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Ma, K.Z.; Xie, X.Y.; Han, Z.H. Geochemical and geological significance of hydrothermal calcite from Nibao gold deposit in Guizhou Province. Miner. Depos. 2020, 39, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Han, Z.C.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, G.C. REE, Fe and Mn Contents of Calcites and Their Prospecting Significance for the Banqi Carlin-type Gold Deposit in Southwestern China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2018, 42, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.R. Rare earth elements in foraminifera tests. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1985, 73, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.R.; Elderfield, H. Rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in ferromanganese oxide coatings of Cenozoic foraminifera from the Atlantic Ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, J.C. The chemistry and sulfur isotope composition of massive sulfide and associated deposits on Green Seamount, eastern Pacific. Econ. Geol. 1988, 83, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Koschinsky, A.; Dulski, P.; Hein, J.R. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Yelken, M.A.; Gaudette, H.E.; Stetzenbach, K.J. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in hypersaline and dilute acidic natural terrestrial waters: Complexation behaviour and middle rare earth element enrichment. Chem. Geol. 1996, 133, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Nozaki, T.; Osawa, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ono, R. Rare earth, major and trace elements in the Kunimiyama ferromanganese deposit in the northern Chichibu belt, Central Shikoku, Japan. Resour. Geol. 2005, 55, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, J.; Meisser, N. Manganese-rich assemblages in the Barrhorn Unit, Turtmanntal, Central Alps, Switzerland. Can. Mineral. 2006, 44, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.G.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.L.; Danyushevskiy, L. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China:A LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovsky, V.Y.; Gamyanin, G.N.; Polufuntikova, L.I. Structures, mineralogy, and fluid regime of ore formation in the polygenetic Malo-Taryn gold field, Northeast Russia. Russ. J. Pac. Geol. 2015, 9, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

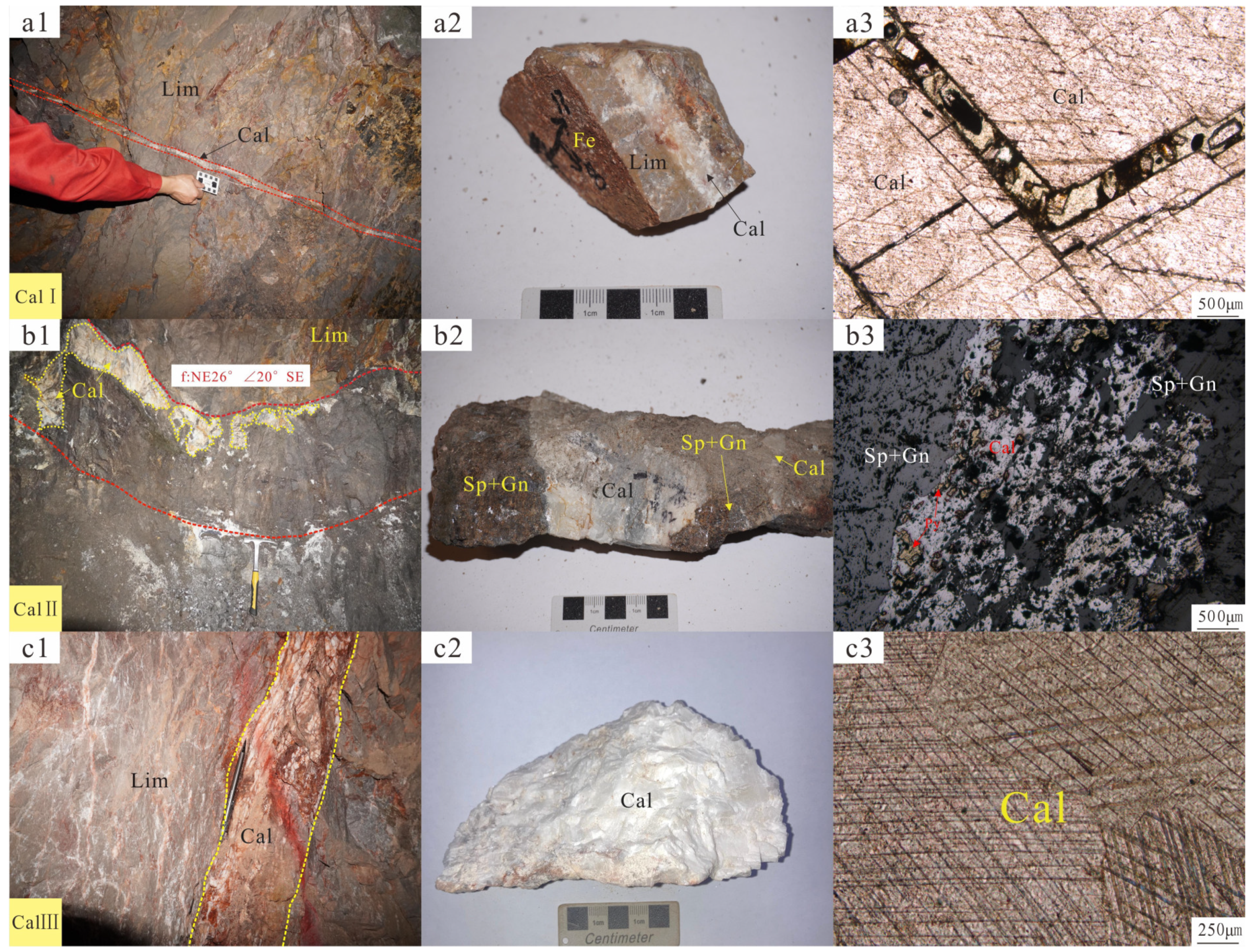




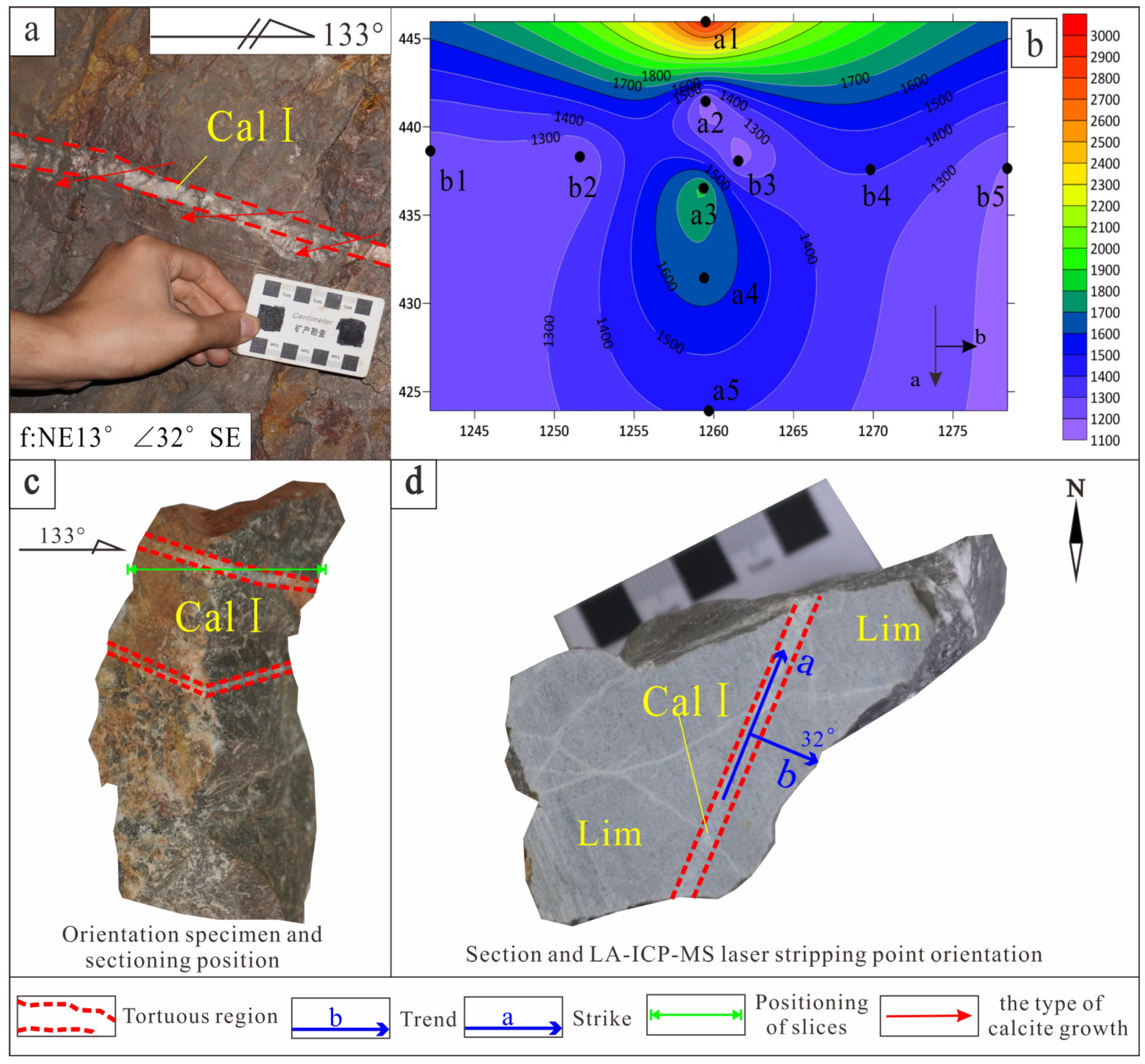
| Sample Number | Sample Location | Fracture Mechanical Properties of Sampling Site | Sample Occurrence | Color | Type | Formation Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QS-2 | 1675 m | Tension | Comb-like | White | Fault zone | Main metallogenic stage (CalII) |
| QS-3 | ||||||
| QS-4 | ||||||
| QS-5 | 1675 m | Torsion | Veinlet | White | Fault zone | Early metallogenic stage (CalI) |
| QS-6 | ||||||
| QS-7 | 1675 m | Compression | Lath | Pink | Fault zone | Late metallogenic stage (CalIII) |
| QS-8 | ||||||
| QS-9 |
| Sample Number | Typology | La | Ge | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QS-2 | CalII | 9.33 | 9.81 | 1.75 | 7.23 | 1.37 | 0.28 | 1.53 | 0.20 | 1.19 | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 12.85 | 33.81 | 29.77 | 4.04 | 7.36 | 27.84 | 0.58 | 0.60 |
| 6.95 | 7.92 | 1.55 | 6.14 | 1.29 | 0.34 | 1.71 | 0.20 | 1.29 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 14.77 | 28.81 | 24.19 | 4.62 | 5.23 | 11.53 | 0.69 | 0.59 | ||
| 5.66 | 4.44 | 0.77 | 3.11 | 0.57 | 0.24 | 0.86 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 6.40 | 16.44 | 14.78 | 1.67 | 8.87 | 81.16 | 1.03 | 0.52 | ||
| 4.34 | 3.97 | 0.87 | 3.96 | 0.99 | 0.28 | 1.45 | 0.21 | 1.21 | 0.29 | 0.84 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 17.16 | 18.97 | 14.42 | 4.54 | 3.17 | 7.82 | 0.72 | 0.50 | ||
| 15.26 | 14.13 | 2.91 | 12.22 | 2.11 | 0.62 | 2.97 | 0.36 | 2.42 | 0.46 | 1.28 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 30.06 | 55.41 | 47.25 | 8.16 | 5.79 | 22.72 | 0.75 | 0.52 | ||
| 10.33 | 11.04 | 2.00 | 8.03 | 1.49 | 0.42 | 1.79 | 0.25 | 1.57 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 17.01 | 38.61 | 33.32 | 5.29 | 6.30 | 19.34 | 0.79 | 0.59 | ||
| 7.79 | 8.86 | 1.55 | 6.91 | 1.55 | 0.34 | 1.80 | 0.21 | 1.25 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 14.52 | 31.56 | 27.00 | 4.56 | 5.92 | 19.86 | 0.62 | 0.63 | ||
| 6.27 | 6.61 | 1.13 | 5.33 | 1.34 | 0.29 | 1.44 | 0.19 | 1.10 | 0.22 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 13.79 | 24.82 | 20.97 | 3.86 | 5.44 | 20.91 | 0.63 | 0.61 | ||
| 10.78 | 10.62 | 1.86 | 7.89 | 1.57 | 0.31 | 1.75 | 0.19 | 1.12 | 0.23 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.04 | 14.22 | 37.30 | 33.04 | 4.26 | 7.75 | 29.67 | 0.58 | 0.58 | ||
| 11.93 | 11.78 | 2.03 | 8.23 | 1.74 | 0.39 | 1.82 | 0.22 | 1.27 | 0.23 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 14.93 | 40.52 | 36.10 | 4.42 | 8.17 | 41.61 | 0.67 | 0.59 | ||
| QS-5 | CalI | 2.16 | 1.96 | 0.43 | 1.94 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.81 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.04 | 11.19 | 10.03 | 7.28 | 2.75 | 2.64 | 4.46 | 1.09 | 0.50 |
| 3.62 | 2.84 | 0.60 | 2.57 | 0.60 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 6.80 | 12.24 | 10.35 | 1.88 | 5.50 | 12.31 | 0.64 | 0.47 | ||
| 1.70 | 1.34 | 0.26 | 1.19 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 1.92 | 5.32 | 4.68 | 0.64 | 7.27 | 64.75 | 0.30 | 0.49 | ||
| 7.86 | 6.72 | 1.60 | 6.88 | 1.62 | 0.33 | 1.70 | 0.20 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 13.73 | 28.93 | 25.01 | 3.92 | 6.37 | 36.21 | 0.62 | 0.47 | ||
| 3.19 | 2.67 | 0.49 | 2.15 | 0.48 | 0.12 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 6.89 | 10.82 | 9.10 | 1.73 | 5.27 | 14.08 | 0.68 | 0.52 | ||
| 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 2.09 | 1.41 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 2.49 | 4.97 | 0.26 | 0.55 | ||
| 7.04 | 5.52 | 1.24 | 5.10 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 9.69 | 22.92 | 20.13 | 2.78 | 7.23 | 35.25 | 0.65 | 0.46 | ||
| 7.85 | 4.72 | 0.93 | 3.70 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 0.09 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 7.28 | 20.25 | 18.01 | 2.24 | 8.04 | 31.45 | 0.76 | 0.43 | ||
| 3.40 | 2.83 | 0.55 | 2.62 | 0.46 | 0.14 | 0.72 | 0.09 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 6.67 | 11.83 | 10.02 | 1.82 | 5.52 | 18.51 | 0.77 | 0.51 | ||
| 2.81 | 2.74 | 0.63 | 3.19 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.92 | 0.12 | 0.63 | 0.13 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 8.81 | 12.50 | 10.19 | 2.31 | 4.42 | 15.47 | 0.65 | 0.50 | ||
| QS-6 | CalIII | 1.21 | 1.22 | 0.21 | 1.01 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 3.31 | 4.68 | 3.88 | 0.80 | 4.88 | 10.50 | 0.57 | 0.59 |
| 0.74 | 0.99 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 3.23 | 3.74 | 2.96 | 0.78 | 3.79 | 4.86 | 0.66 | 0.66 | ||
| 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 3.21 | 3.07 | 2.17 | 0.90 | 2.42 | 4.08 | 0.55 | 0.59 | ||
| 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1.43 | 2.03 | 1.61 | 0.41 | 3.89 | 8.85 | 1.46 | 0.70 | ||
| 1.04 | 1.22 | 0.25 | 0.93 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 2.80 | 4.79 | 3.80 | 0.99 | 3.83 | 5.58 | 0.50 | 0.59 | ||
| 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.41 | 2.17 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 4.72 | 3.27 | 1.00 | 0.56 | ||
| WY-1 | Perimeter rock (limestone) | 1.86 | 2.71 | 0.56 | 1.52 | 0.26 | 0.059 | 0.31 | 0.047 | 0.37 | 0.071 | 0.27 | 0.027 | 0.22 | 0.034 | 4.07 | 8.32 | 6.97 | 1.35 | 5.17 | 6.06 | 0.64 | 0.65 |
| WY-2 | 2.32 | 3.28 | 0.62 | 1.95 | 0.37 | 0.082 | 0.46 | 0.083 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.036 | 0.3 | 0.042 | 4.97 | 10.47 | 8.62 | 1.85 | 4.66 | 5.55 | 0.61 | 0.67 | |
| WY-3 | 6.15 | 7.05 | 1.42 | 5.55 | 1.01 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 0.21 | 1.28 | 0.3 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 11.5 | 26.47 | 21.39 | 5.08 | 4.21 | 5.13 | 0.56 | 0.58 | |
| WY-4 | 0.66 | 1.82 | 0.32 | 0.7 | 0.11 | 0.024 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.028 | 0.2 | 0.033 | 2.36 | 4.52 | 3.63 | 0.88 | 4.12 | 2.37 | 0.55 | 0.97 | |
| WY-5 | 2.11 | 3.13 | 0.84 | 1.46 | 0.27 | 0.074 | 0.41 | 0.062 | 0.38 | 0.099 | 0.38 | 0.035 | 0.29 | 0.046 | 4.57 | 9.59 | 7.88 | 1.70 | 4.63 | 5.22 | 0.68 | 0.58 | |
| WY-6 | 3.32 | 3.3 | 1 | 2.81 | 0.55 | 0.11 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.76 | 0.19 | 0.6 | 0.092 | 0.66 | 0.083 | 9.23 | 14.22 | 11.09 | 3.13 | 3.55 | 3.61 | 0.57 | 0.44 | |
| WY-7 | 1.68 | 2.13 | 0.67 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 0.061 | 0.3 | 0.041 | 0.31 | 0.086 | 0.37 | 0.049 | 0.34 | 0.061 | 4.61 | 7.518 | 5.96 | 1.56 | 3.83 | 3.54 | 0.80 | 0.49 |
| Sample Number | Typology | Fe | Mn | Fe + Mn | Fe + Mn Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QS-2 | CalII | 1361.18 | 479.91 | 1841.08 | 2186.69 |
| 1341.32 | 439.43 | 1780.75 | |||
| 1329.19 | 543.06 | 1872.25 | |||
| 1324.63 | 1845.42 | 3170.05 | |||
| 1517.42 | 2425.59 | 3943.01 | |||
| 1343.03 | 558.60 | 1901.62 | |||
| 1322.21 | 770.87 | 2093.08 | |||
| 1298.94 | 422.68 | 1721.62 | |||
| 1340.93 | 513.97 | 1854.91 | |||
| 1241.81 | 446.67 | 1688.48 | |||
| QS-5 | CalI | 905.07 | 60.06 | 965.13 | 1066.96 |
| 923.67 | 141.57 | 1065.24 | |||
| 1205.53 | 71.31 | 1276.84 | |||
| 931.71 | 28.91 | 960.62 | |||
| QS-6 | CalIII | 881.64 | 24.81 | 906.45 | 904.31 |
| 885.68 | 16.49 | 902.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Han, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, L. Indication of REEs, Fe, and Mn Composition Typomorphism of Calcite in Metallogenic Fracture Zones with Respect to Local Tectonic Stress Fields: A Case Study of the Qingshan Lead–Zinc Deposit in Northwest Guizhou, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030292
Zhao X, Han R, Zhang Y, Wang M, Wang L. Indication of REEs, Fe, and Mn Composition Typomorphism of Calcite in Metallogenic Fracture Zones with Respect to Local Tectonic Stress Fields: A Case Study of the Qingshan Lead–Zinc Deposit in Northwest Guizhou, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030292
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaotong, Runsheng Han, Yan Zhang, Mingzhi Wang, and Lei Wang. 2025. "Indication of REEs, Fe, and Mn Composition Typomorphism of Calcite in Metallogenic Fracture Zones with Respect to Local Tectonic Stress Fields: A Case Study of the Qingshan Lead–Zinc Deposit in Northwest Guizhou, China" Minerals 15, no. 3: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030292
APA StyleZhao, X., Han, R., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., & Wang, L. (2025). Indication of REEs, Fe, and Mn Composition Typomorphism of Calcite in Metallogenic Fracture Zones with Respect to Local Tectonic Stress Fields: A Case Study of the Qingshan Lead–Zinc Deposit in Northwest Guizhou, China. Minerals, 15(3), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030292





