Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
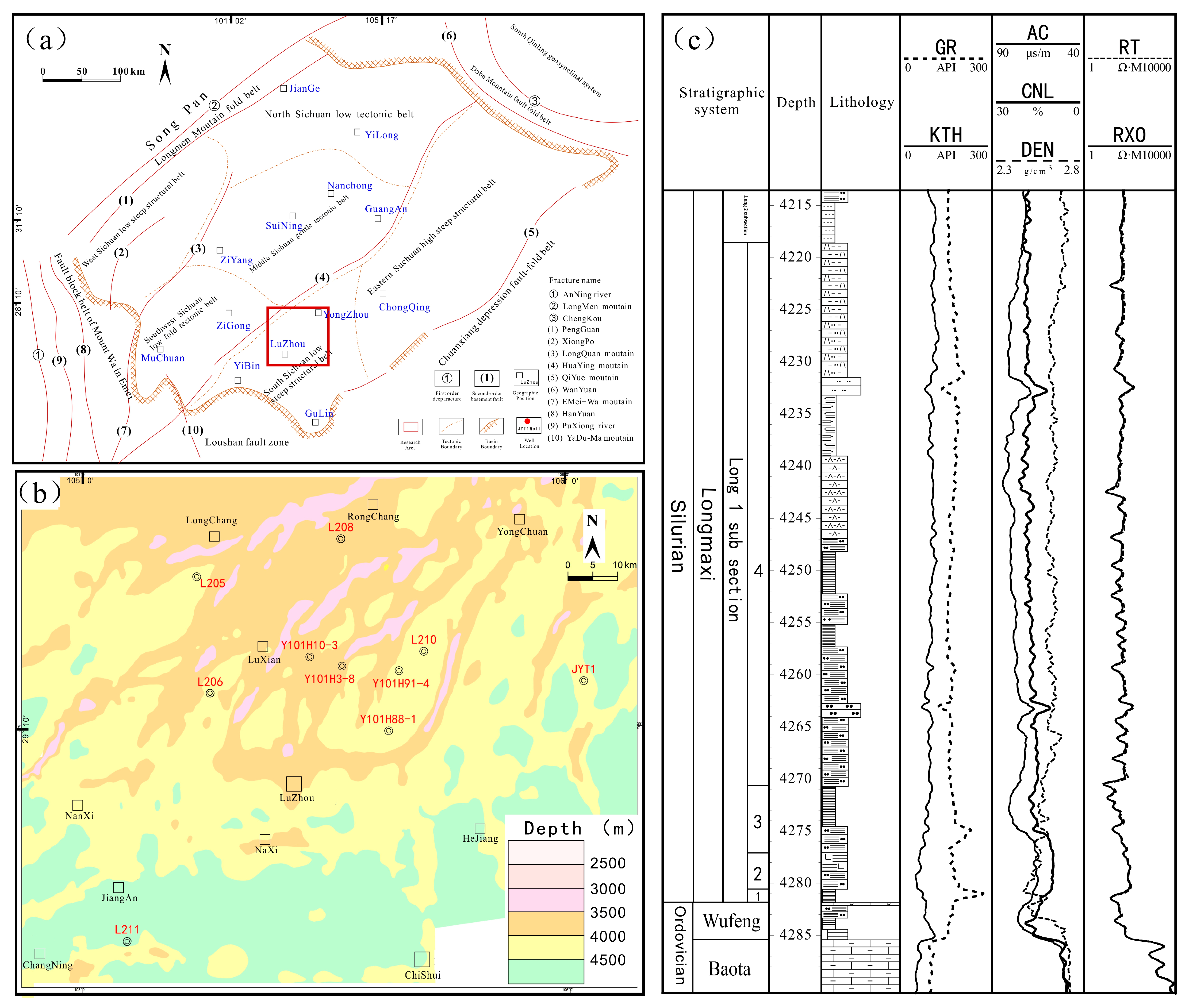
2. Geologic Background
3. Experiments
3.1. Total Organic Carbon Content Analysis
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Mpas
3.4. Low Pressures Nitrogen Adsorption
3.5. High Pressure Hg Injection
4. Results
4.1. TOC and Mineral Composition
4.2. Pore Structure
5. Discussion
5.1. Phenomena and Characterization of PS
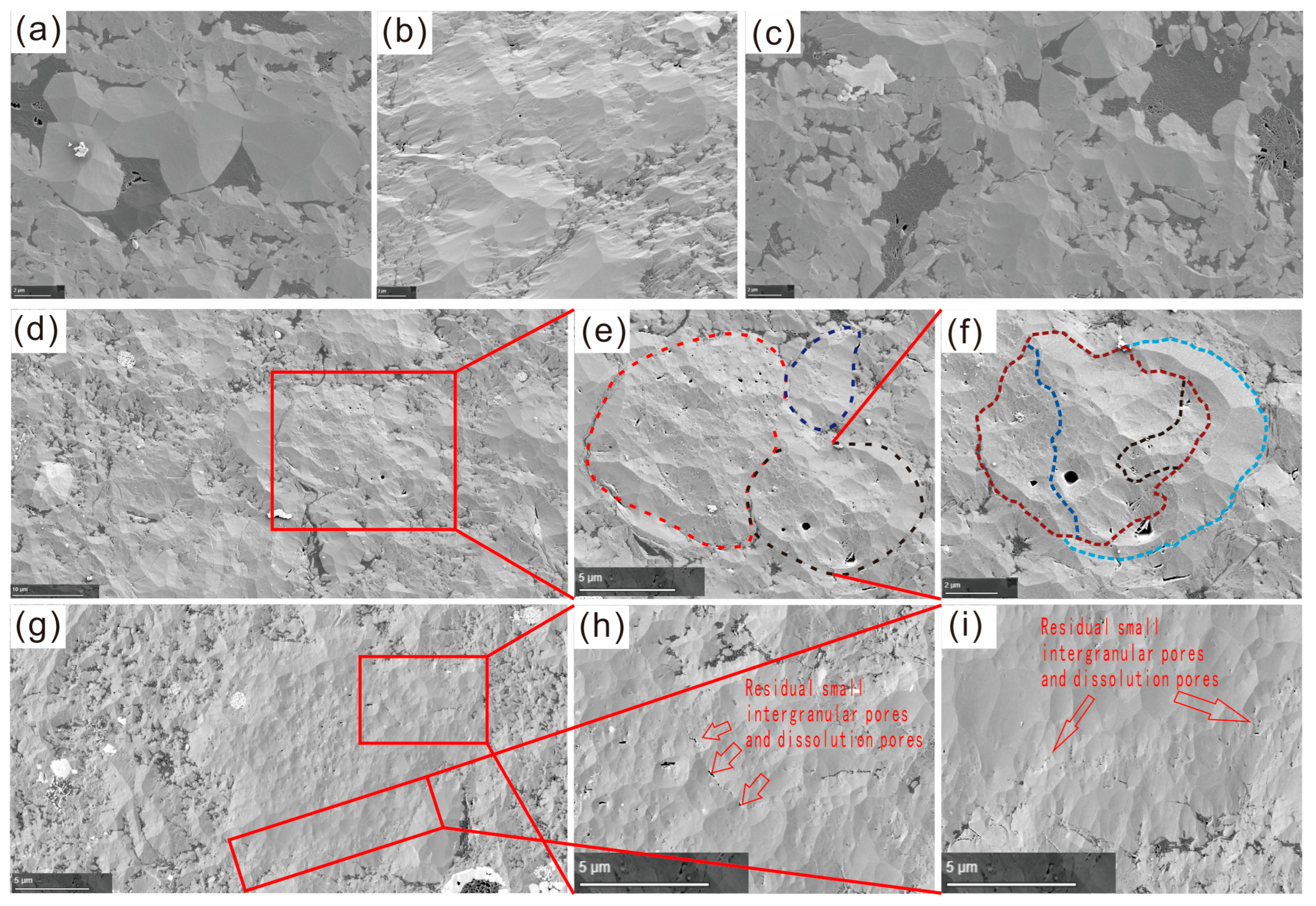
5.1.1. PS Characteristics
- (1)
- Some particle contour shapes no longer exist
- (2)
- Discontinuous Sutures and Increased Particle Size
- (3)
- Intergranular Dissolution and Organic Matter Filling
5.1.2. Quantitative Characterization of PS
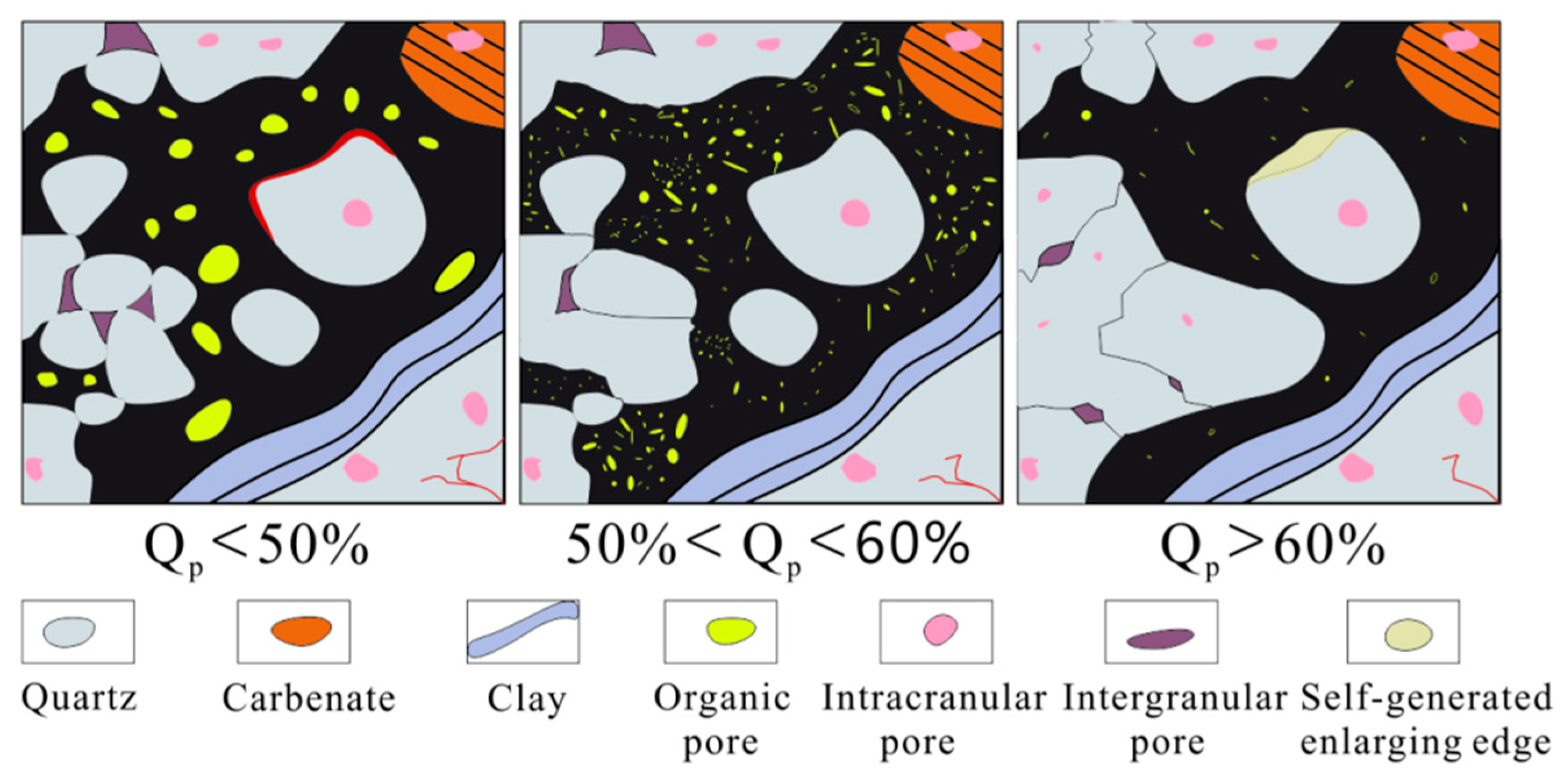
5.2. Characteristics of Shale Reservoirs with Different PS Intensities
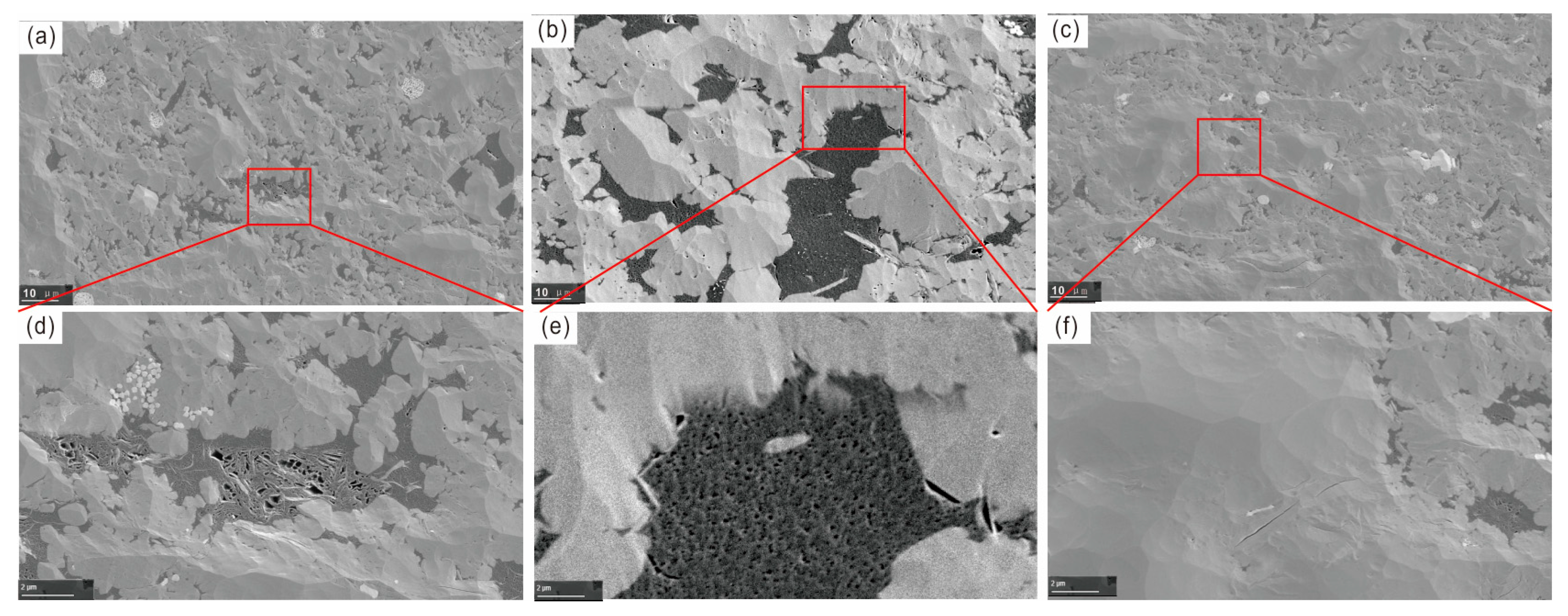
5.2.1. Fabric Characteristics of Shale Reservoirs Under Different PS Intensities
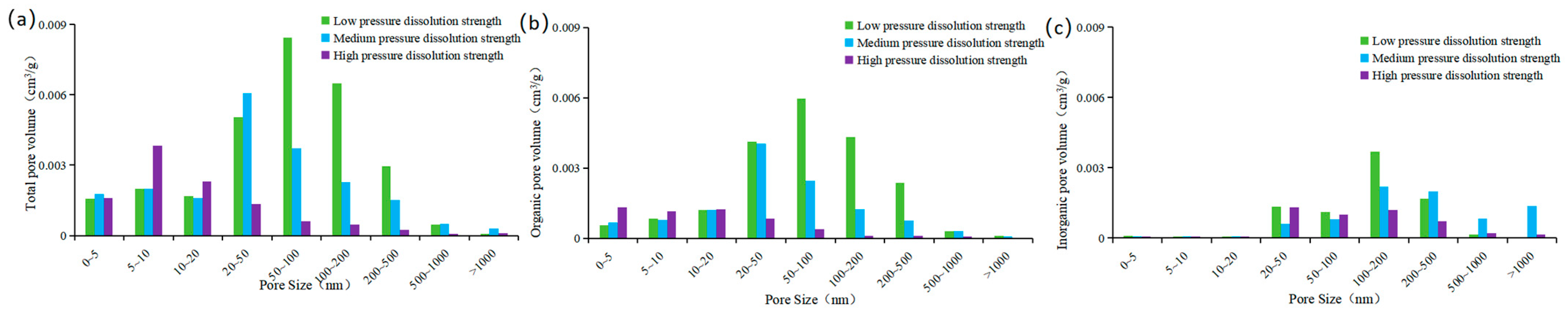
5.2.2. Micro-Pore Structure Characteristics of Shale Reservoirs Under Different PS Intensities
5.3. Influencing Factors of PS
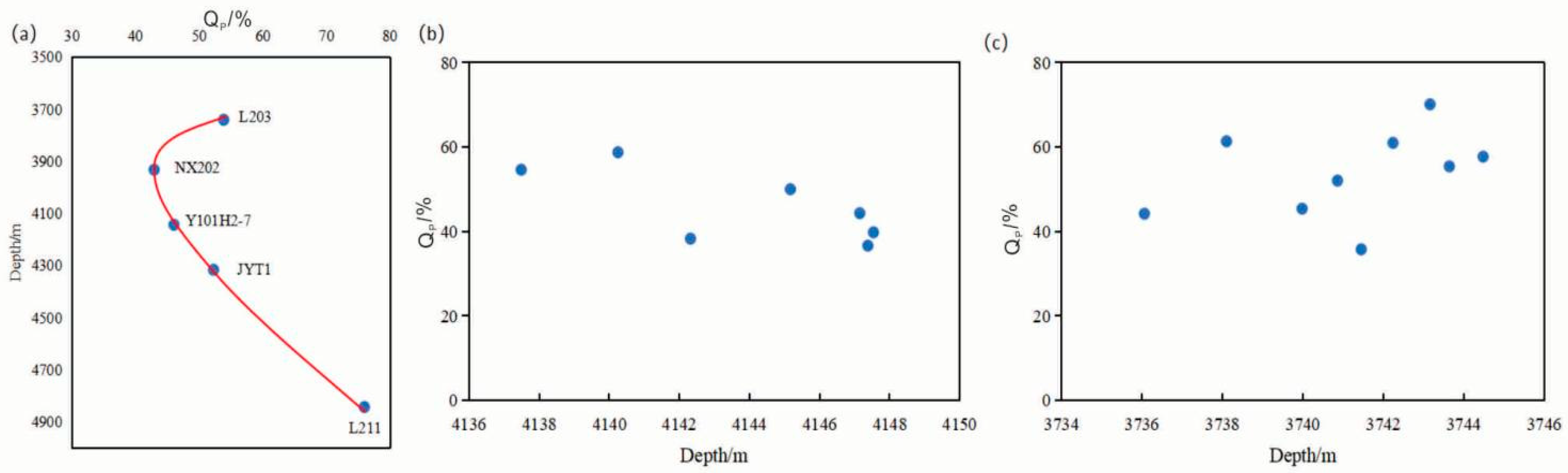
5.3.1. Burial Depth
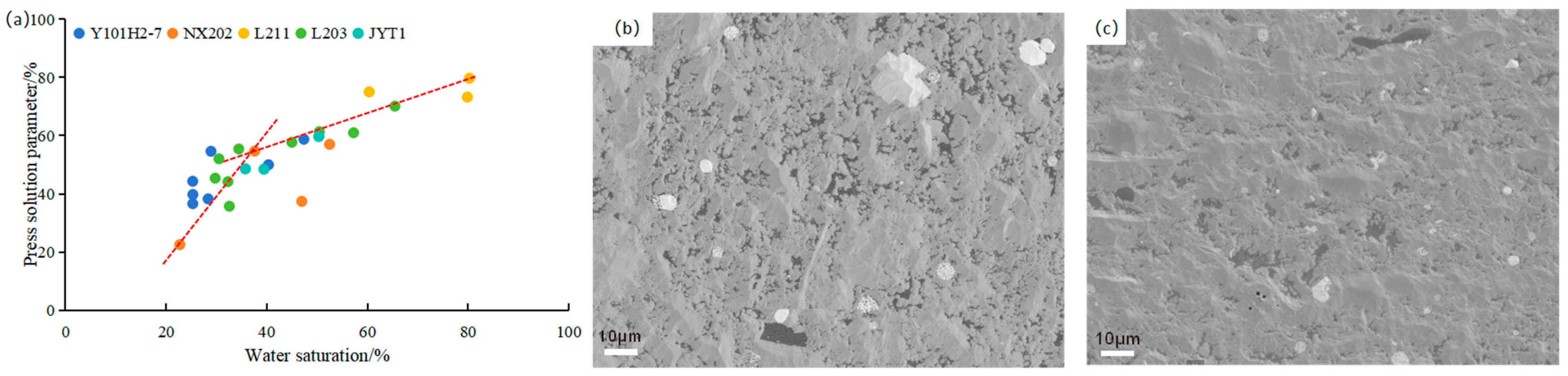
5.3.2. Water Saturation
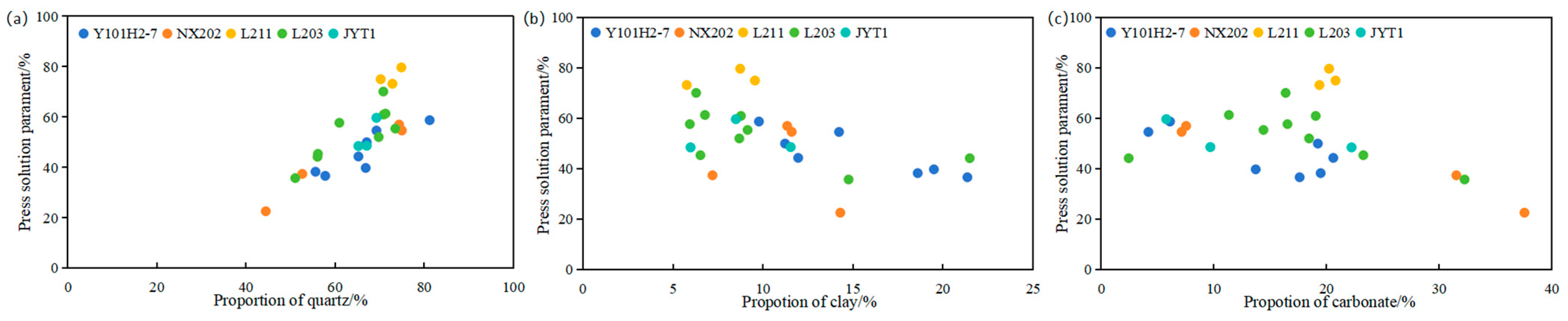
5.3.3. Mineral Composition
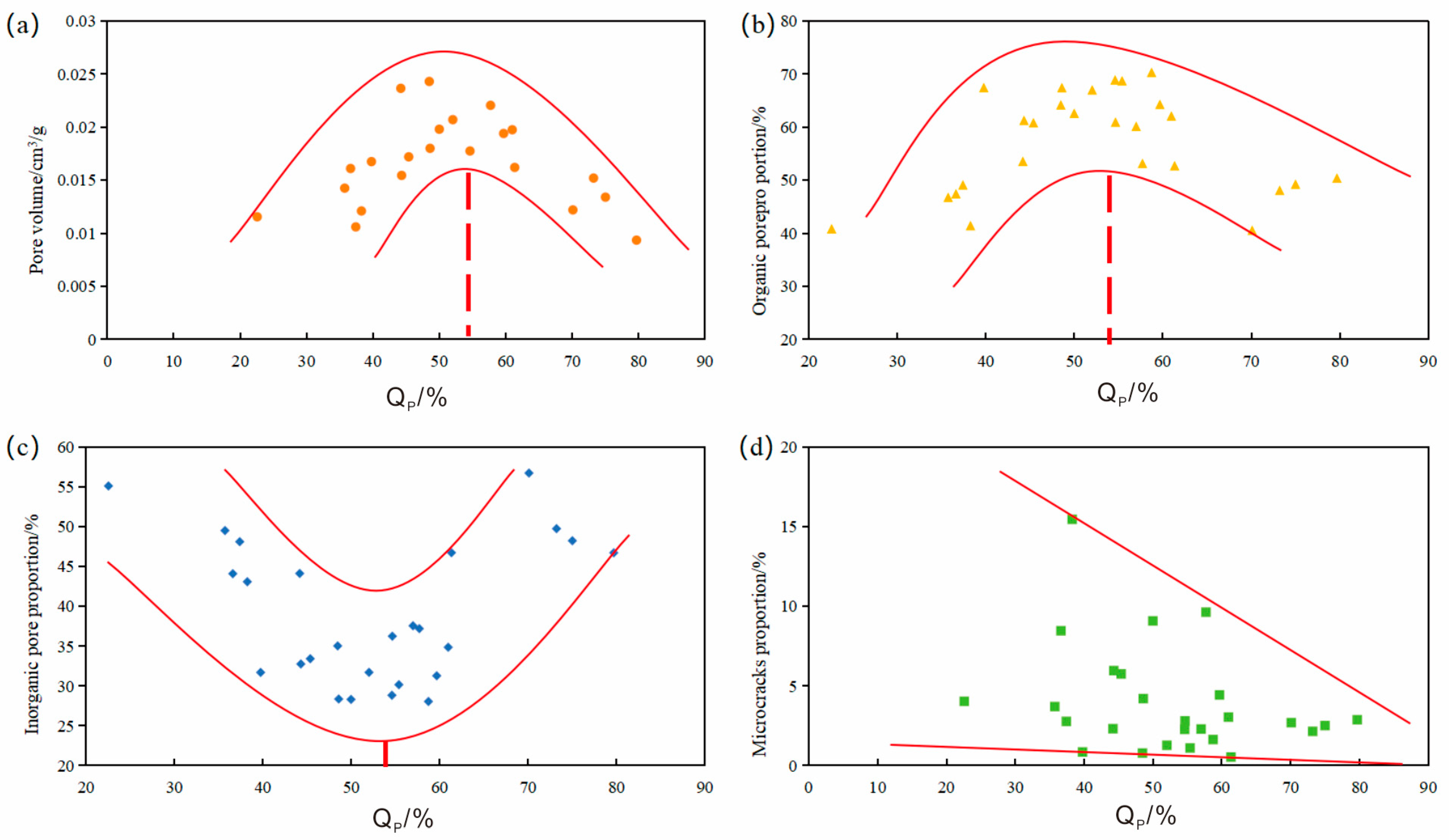
5.4. Effect of PS on Pore Development of Shale Reservoir
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- PS is prevalent in the Longmaxi Formation, exhibiting distinct characteristics: portions of particle profiles in shale reservoir have vanished, resulting in a consolidated shale mass. Large-grained minerals display intermittent sutures while maintaining mineral particle outlines, with a noticeable increase in particle size. The boundaries between residual and adjacent particles feature intergranular dissolution cavities, some of which are occupied by organic matter.
- (2)
- Based on the primary mineral content of shale reservoirs and the mineral components influenced by PS, a semi-quantitative method was established, which relies on quartz mineral composition and particle size analysis for PS intensity (Qp). The PS in Longmaxi shale reservoirs exhibits significant variation, with parameters ranging from 20% to 70%. Using statistical methods and mineral micro-distribution characteristics, the intensity of PS is categorized into three types: low (Qp < 50%), medium (50% < Qp < 60%), and high (Qp > 60%).
- (3)
- As burial depth, temperature, and pressure increase, the PS of the Longmaxi Formation shale reservoir becomes stronger. Water saturation is positively correlated with PS parameters. Notably, when water saturation exceeds 40%, PS becomes more pronounced, potentially due to the influence of diagenetic fluids on clay transformation and feldspar alteration. Additionally, an increase in quartz content, particularly cryptocrystalline quartz, enhances PS, whereas an increase in clay mineral content diminishes it.
- (4)
- In deep shale reservoirs, PS is a common phenomenon, yet intense PS hinders pore development. As PS intensity increases, quartz particles in the shale reservoir fuse, compressing the original intergranular pores and organic matter. This leads to the reduction, deformation, or even elimination of organic pores, and a decrease in intergranular pores. Consequently, the proportion of total pore volume and organic pore surface ratio in the shale reservoir initially increases and then decreases. This underscores that a quartz content exceeding 70% in shale reservoirs is detrimental to pore development. Therefore, when the quartz content in Longmaxi formation shale reservoirs surpasses 70%, there is a significant risk associated with shale gas exploration and development.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, S.W.; Shi, Z.S.; Zhang, L.F. Deep shale gas in China: Geological characteristics and development strategies. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Nie, H.K.; Dang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, G.R.; Li, W.P.; Lu, Z.Y. Shale Gas Exploration and Development in China: Current Status, Geological Challenges, and Future Directions. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6359–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, G.S.; Wu, J.F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.T. Deep shale gas exploration and development in the southern Sichuan Basin: New progress and challenges. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2023, 10, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.K.; Jin, Z.J.; Li, P.; Katz, B.J.; Dang, W.; Liu, Q.Y.; Ding, J.H.; Jiang, S.; Li, D.H. Deep shale gas in the Ordovician-Silurian Wufeng–Longmaxi formations of the Sichuan Basin, SW China: Insights from reservoir characteristics, preservation conditions and development strategies. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 244, 105521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Wu, Y.H.; Liang, X.; Jiang, Z.X.; Wang, G.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Duan, X.G.; Gong, H.J. Control effect of formation water on shale gas enrichment in the background of strike-slip fault activity in western Chongqing. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2023, 42, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Gao, P.; Hu, D.F.; Liu, R.B.; Li, G.; Lu, C.G.; Zhou, Q. Water distribution in pore systems and its influences on gas-bearing property of deep shale: A case study of the Longmaxi Formation in the Luzhou area, southern Sichuan Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 163, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Wu, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.X.; Xia, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, J.J. Microscopic occurrence and movability mechanism of pore water in deep shale gas reservoirs: A typical case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Luzhou block, Sichuan Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 151, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garum, M.; Glover, P.W.J.; Lorinczi, P.; Micklethwaite, S.; Hassanpour, A. Integration of multiscale imaging of nanoscale pore microstructures in gas shales. Energy Fuel 2021, 35, 10721–10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, B.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Scale-span pore structure heterogeneity of high volatile bituminous coal and anthracite by FIB-SEM and X-ray μ-CT. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 81, 103443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.M.; Hu, Q.H.; Cheng, H.F.; Ilavsky, J.; Kuzmenko, I.; Shang, F.H.; Liu, L.F. Pore structure and wettability of Bossier shale, East Texas, United States: Insights from integrated porosimetry, scattering, and imbibition approaches. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 11042–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, S.D.; Wang, R.C.; Wu, J.Q.; Li, Z.; Song, Y. Multifractal characteristics on pore structure of Longmaxi shale using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 241, 213176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M.; Zou, J.; Gentzis, T.; Rezaee, R.; Bubach, B.; Carvajal-Ortiz, H. Multifractal analysis of gas adsorption isotherms for pore structure characterization of the Bakken Shale. Fuel 2018, 219, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Nie, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Jiang, S.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, P.; Chen, Z. Pore-scale mechanisms and characterization of light oil storage in shale nanopores: New method and insights. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nie, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, C.; Cao, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, P. Differences in Pore Type and Pore Structure between Silurian Longmaxi Marine Shale and Jurassic Dongyuemiao Lacustrine Shale and Their Influence on Shale-Gas Enrichment. Minerals 2023, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Harris, N.B. The effect of thermal maturity on porosity development in the Upper Devonian–Lower Mississippian Woodford Shale, Permian Basin, US: Insights into the role of silica nanospheres and microcrystalline quartz on porosity preservation. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 217, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Ye, Y.H.; Liu, S.G.; Ran, B.; Deng, B.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Yong, Z.; Sun, W. Characterization and evolution of nanoporosity in superdeeply buried shales: A case study of the Longmaxi and Qiongzhusi shales from MS well #1, North Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Jin, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liu, K.; Jin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Nie, H.; Du, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, R. Mineral composition and seal condition implicated in pore structure development of organic-rich Longmaxi shales, Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, P. The main geological factors controlling the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale gas content. AAPG Bull. 2022, 106, 2073–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, R.; Hao, F.; Engelder, T.; Yi, J.; Zhang, B.; Shu, Z. Complex rotation of maximum horizontal stress in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale on the eastern margin of the Sichuan Basin, China: Implications for predicting natural fractures. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.F.; Liu, Z.J.; Qiang, W.A.; Wei, F.B.; Tao, Y.U. Analysis and thinking of the difference of Wufeng–Longmaxi shale gas enrichment conditions between Dingshan and Jiaoshiba areas in southeastern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 31, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Xiao, X.M.; Hu, D.F.; Lash, G.; Liu, R.B.; Cai, Y.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, B.Y.; Yuan, T.; Liu, S.Y. Effect of silica diagenesis on porosity evolution of deep gas shale reservoir of the Lower Paleozoic Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Sichuan Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 145, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Nie, S.; Li, H.; Radwan, A.E.; Pan, Q.C.; Shi, X.C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Guo, Y. Quantitative prediction and spatial analysis of structural fractures in deep shale gas reservoirs within complex structural zones: A case study of the Longmaxi Formation in the Luzhou area, southern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 263, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Jiang, Z.X.; Wei, F.B.; Yuan, T.; Li, F. Shale gas accumulation mechanism of deep-buried marine shale of Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeast Sichuan Basin. Pet. Res. 2025, 10, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Wirth, R.; Schreiber, A.; Schulz, H.; Horsfield, B. Formation of nanoporous pyrobitumen residues during maturation of the Barnett Shale (Fort Worth Basin). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Jin, Z.J.; Jin, Z.K.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Du, W.; Yan, C.; Geng, Y. Mineral types and organic matters of the Ordovician-Silurian Wufeng and Longmaxi shale in the Sichuan Basin, China: Implications for pore systems, diagenetic pathways, and reservoir quality in fine-grained sedimentary rocks. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 86, 655–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; He, S.; Chen, M.; Hou, Y.; Guo, X.; Wei, C.; Han, Y.; Yang, R. Quartz types and origins in the paleozoic Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, Eastern Sichuan Basin, China: Implications for porosity preservation in shale reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 106, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; He, Q.; He, S.; Zhai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Wei, C.; Hou, Y.; Guo, X. Quartz types, origins and organic matter-hosted pore systems in the lower cambrian Niutitang Formation, middle yangtze platform, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 123, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliken, K.T.; Olson, T. Silica diagenesis, porosity evolution, and mechanical behavior in siliceous mudstones, Mowry Shale (Cretaceous), Rocky Mountains. USA. J. Sediment. Res. 2017, 87, 366–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yi, Y.; Dang, F.; Ye, Y. Characterization of quartz in the Wufeng Formation in northwest Hunan Province, south China and its implications for reservoir quality. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.S.; Demicco, R.V. Earth Surface Processes, Landforms and Sediment Deposits; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; p. 830. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Hammes, U. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, X.; Luo, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zhong, K.; Wu, J. Mineral Composition of Prospective Section of Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale in Luzhou Shale Play, Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, J.; Liang, X.; Shi, X.; Bao, S.; Wu, W.; Xu, L.; Tang, X.; Han, Y. Characteristics, formation mechanism and geological implications of high water-cut shale gas reservoirs in western Chongqing area. Nat. Gas Ind. 2024, 44, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, K.; Guo, W. Biogenic silica and organic carbon fluxes provide evidence of enhanced marine productivity in the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian of South China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 534, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyberg, B.; Jahren, J.; Winje, T.; Bjørlykke, K.; Faleide, J.I.; Marcussen, Ø. Quartz cementation in Late Cretaceous mudstones, northern North Sea: Changes in rock properties due to dissolution of smectite and precipitation of micro-quartz crystals. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowey, P.J.; Taylor, K.G. Extensive authigenic quartz overgrowths in the gasbearing Haynesville-Bossier Shale, USA. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 356, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Jansa, L.; Li, J.; Song, J.; et al. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 213, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, S.C.; Liu, S.B.; Zhang, H. Determination of organic-rich shale pore features by mercury injection and gas adsorption methods. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 3, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.F.; Kong, D.T.; Liu, H.Q. Pore structure of shale from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Duan, X.; Liu, Q.; Blach, T.P.; Ostadhassan, M.; Liu, B.; Ji, Y.; Hu, Q.; Pan, Z. The importance of pore-fracture connectivity in overmature marine shale for methane occurrence and transportation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 157, 106495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Cheng, P.; Tian, H.; Gai, H.; Xiao, X. Distribution and occurrence of pore water and retained oil in nanopores of marine-terrestrial transitional shales during oil generation and expulsion: Implications from a thermal simulation experiment on shale plug samples. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 150, 106125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Rong, H.; Chen, S.J.; Tang, Y.G.; Deng, Y. Diagenesis and reservoir property variations of tight sandstone with burial depths ranging from shallow to ultra-deep in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2024, 11, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Z.; Cai, J.G.; Long, S.X.; Gao, B.; Feng, D.J.; Peng, Z.Y.; Zeng, X. The Control of Diagenesis and Mineral Assemblages on Brittleness of Mudstones. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 758046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yu, B.; Ruan, Z.; Bai, C.; Shen, Z.; Löhr, S.C. Diagenesis and fluid evolution in the third member of the Eocene Shahejie Formation, Bonan Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 128, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, R.; Aharonov, E.; Koehn, D.; Gratier, J.-P.; Ebner, M.; Baud, P.; Rolland, A.; Renard, F. Stylolites: A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 114, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midtbø, R.E.A.; Rykkje, J.M.; Ramm, M. Deep burial diagenesis and reservoir quality along the eastern flank of the Viking Graben: Evidence for illitization and quartz cementation after hydrocarbon emplacement. Clay Miner. 2000, 35, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, S.P.; Loucks, R.G.; Day-Stirrat, R.J. Impact of regional variation in detrital mineral composition on reservoir quality in deep to ultra deep lower Miocene sandstones, western Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 35, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Li, R.X.; Jiang, Z.X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Investigation of variation in shale gas adsorption capacity with burial depth: Insights from the adsorption potential theory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 73, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Hu, Q.H.; Barber, T.J.; Bleuel, M.L.; Anovitz, M.; Littrell, K. Quantifying fluid-wettable effective pore space in the Utica and Bakken oil shale formations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Xiao, X.M.; Tian, H.; Gai, H.F.; Zhou, Q.; Li, T.F.; Fan, Q.Z. Differences in the distribution and occurrence phases of pore water in various nanopores of marine-terrestrial transitional shales in the Yangquan area of the northeast Qinshui Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 137, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, X.F.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, J.; Sun, F.R.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Water adsorption and its impact on the pore structure characteristics of shale clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 155, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.F.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, K.L.; Shi, J.T.; Yang, L.; Feng, D.; Zhang, T.; Yu, P.L. Water distribution characteristic and effect on methane adsorption capacity in shale clay. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, X.M.; Wei, Q.; Cheng, P.; Tian, H. Occurrence of irreducible water and its influences on gas-bearing property of gas shales from shallow Longmaxi formation in the Xishui area, Guizhou, southern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 654136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Dong, D.Z.; Qi, L.; Shen, Y.F.; Jiang, C.; He, B.W. Basic features and evaluation of shale gas reservoirs. Nat. Gas Ind. 2010, 30, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Dong, D.Z.; Li, J.Z.; Wang, S.J.; Li, X.J.; Wang, L.; Cheng, K.M.; Huang, J.L. Reservoir characteristics of shale in Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, southern Sichuan. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.Z.; Dong, D.Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Sun, S.S.; Zhang, S.R.; Guo, W. Types of biogenic quartz and its coupling storage mechanism in organic-rich shales: A case study of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yan, D.T.; Zhuang, X.G.; Liu, Z.X.; Li, B.Q.; Wei, X.S.; Xu, H.W.; Li, D.W. Origin of quartz in the lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in south Hubei Province, upper Yangtze platform. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 96, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.T.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.L.; Feng, Z.H.; Deng, C.; Bai, Y.B.; Shao, H.M.; Yan, M.; Tan, Z. Effects of smectite-illitization and hydrocarbon generation on the pore structure: A case study from the continental shales in China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2026, 15, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Song, M.; Zhong, K.; Xu, J. Types and formation mechanisms of authigenic quartz in the Late Paleozoic alkaline lacustrine shales, NW China. Sediment. Geol. 2025, 482, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, P.; Li, P.; Ding, J.; Sun, C.; Zhai, C.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Z.; Dang, W. Quartz types, formation mechanism, and its effect on shale oil and gas enrichment: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2025, 261, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Liu, B.; Dong, D.; Lu, B.; Yawar, Z.; Chen, Z.; Schieber, J. Silica diagenesis in the lower paleozoic Wufeng and Longmaxi formations in the Sichuan Basin, south China: Implications for reservoir properties and paleoproductivity. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 121, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Samples | Depth/m | TOC/% | Water Saturation/% | Porosity/% | Organic Pore Ratio/% | Inorganic Pore Ratio/% | Microcracks Ratio/% | Quartz Ratio/% | Carbenate Ratio/% | Clay Ratio/% | Average Particle Size of Quartz/μm | Mean Particle Size of Mineral/μm | Pore Volume/cm3/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y101H-1 | 4137.49 | 4.05 | 28.94 | 3.55 | 68.91 | 28.82 | 2.27 | 69.28 | 4.19 | 14.23 | 1.74 | 1.19 | 0.01775 |
| Y101H-2 | 4147.15 | 7.32 | 25.31 | 5.09 | 61.29 | 32.75 | 5.96 | 65.24 | 20.61 | 11.96 | 1.31 | 1.35 | 0.01545 |
| Y101H-3 | 4145.17 | 3.98 | 40.35 | 3.96 | 62.62 | 28.3 | 9.08 | 67.10 | 19.24 | 11.23 | 1.86 | 1.09 | 0.01980 |
| Y101H-4 | 4140.25 | 4.59 | 47.38 | 2.56 | 70.33 | 28.04 | 1.63 | 81.22 | 6.11 | 9.78 | 2.25 | 1.21 | 0.01280 |
| Y101H-5 | 4142.32 | 4.76 | 28.37 | 6.42 | 41.46 | 43.08 | 15.46 | 55.6 | 19.49 | 18.60 | 1.47 | 1.19 | 0.01210 |
| Y101H-6 | 4147.38 | 3.32 | 25.32 | 4.22 | 47.45 | 44.09 | 8.46 | 57.79 | 17.62 | 21.36 | 1.34 | 1.48 | 0.01610 |
| Y101H-7 | 4147.54 | 4.32 | 25.34 | 5.35 | 67.46 | 31.69 | 0.85 | 66.87 | 13.72 | 19.50 | 1.13 | 1.33 | 0.01675 |
| NX202-8 | 3938.39 | 2.69 | 46.97 | 5.12 | 49.12 | 48.11 | 2.77 | 52.64 | 31.54 | 7.20 | 1.33 | 1.31 | 0.01060 |
| NX202-9 | 3936.92 | 3.51 | 22.75 | 4.31 | 40.86 | 55.11 | 4.03 | 44.45 | 37.59 | 14.30 | 1.11 | 1.53 | 0.01155 |
| NX202-10 | 3931.95 | 3.8 | 37.61 | 2.86 | 60.96 | 36.24 | 2.80 | 74.98 | 7.14 | 11.60 | 1.66 | 1.21 | 0.01430 |
| NX202-11 | 3923.66 | 4.65 | 52.49 | 2.91 | 60.16 | 37.55 | 2.29 | 74.36 | 7.54 | 11.35 | 2.76 | 1.37 | 0.00955 |
| L211-12 | 4833.45 | 3.94 | 80.25 | 1.87 | 50.41 | 46.71 | 2.87 | 74.87 | 20.24 | 8.74 | 2.87 | 1.41 | 0.00935 |
| L211-13 | 4853.80 | 4.23 | 60.35 | 2.68 | 49.26 | 48.23 | 2.51 | 70.23 | 20.81 | 10.00 | 2.94 | 1.42 | 0.01340 |
| L211-14 | 4841.79 | 4.05 | 79.85 | 3.04 | 48.11 | 49.75 | 2.14 | 72.87 | 19.38 | 5.77 | 2.91 | 1.44 | 0.01520 |
| L203-15 | 3740.86 | 5.57 | 30.52 | 4.14 | 67.03 | 31.70 | 1.27 | 69.79 | 18.46 | 8.69 | 1.85 | 1.08 | 0.02070 |
| L203-16 | 3742.24 | 4.96 | 57.25 | 3.95 | 62.11 | 34.85 | 3.04 | 70.90 | 19.05 | 8.78 | 2.39 | 0.94 | 0.01975 |
| L203-17 | 3743.16 | 4.98 | 65.46 | 2.44 | 40.58 | 56.73 | 2.69 | 70.83 | 16.38 | 6.29 | 2.23 | 0.87 | 0.01220 |
| L203-18 | 3744.48 | 4.44 | 45.00 | 4.41 | 53.18 | 37.19 | 9.63 | 60.96 | 16.54 | 5.94 | 2.19 | 0.88 | 0.02205 |
| L203-19 | 3743.64 | 4.98 | 34.45 | 2.44 | 68.75 | 30.15 | 1.10 | 73.52 | 14.41 | 9.15 | 1.95 | 1.44 | 0.01220 |
| L203-20 | 3741.45 | 3.29 | 32.59 | 5.85 | 46.79 | 49.51 | 3.70 | 51.06 | 32.27 | 14.76 | 1.29 | 1.19 | 0.01425 |
| L203-21 | 3739.98 | 3.75 | 29.77 | 6.44 | 60.84 | 33.41 | 5.75 | 56.15 | 23.28 | 6.53 | 1.27 | 1.10 | 0.01720 |
| L203-22 | 3738.1 | 5.25 | 50.45 | 2.24 | 52.74 | 46.73 | 0.53 | 71.32 | 11.34 | 6.78 | 2.29 | 1.05 | 0.01620 |
| L203-23 | 3736.06 | 4.29 | 32.30 | 4.73 | 53.57 | 44.12 | 2.31 | 56.05 | 2.44 | 21.49 | 1.36 | 1.03 | 0.02365 |
| JYT1-24 | 4319.55 | 7.03 | 50.35 | 3.88 | 64.30 | 31.27 | 4.43 | 78.03 | 5.78 | 8.50 | 1.89 | 1.19 | 0.01940 |
| JYT1-25 | 4317.23 | 5.1 | 39.46 | 4.86 | 64.2 | 35.02 | 0.78 | 61.45 | 22.23 | 5.98 | 1.42 | 1.26 | 0.0243 |
| JYT1-26 | 4313.04 | 4.34 | 35.76 | 3.6 | 67.45 | 28.35 | 4.2 | 69.99 | 9.69 | 11.54 | 1.22 | 1.23 | 0.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, D.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, C.; Qiu, X.; Wen, R.; Hu, Q. Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121241
Liang D, Fu Y, Jiang Y, Luo C, Qiu X, Wen R, Hu Q. Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121241
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Demin, Yonghong Fu, Yuqiang Jiang, Chao Luo, Xunxi Qiu, Ran Wen, and Qinhong Hu. 2025. "Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121241
APA StyleLiang, D., Fu, Y., Jiang, Y., Luo, C., Qiu, X., Wen, R., & Hu, Q. (2025). Quantitative Characterization of Deep Shale Gas Reservoir Pressure-Solution and Its Influence on Pore Development in Cases of Luzhou Area in Sichuan Basin. Minerals, 15(12), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121241






