Solvent Extraction of Critical Minerals from the Leachate of High-Nickel Black Mass Using Nickel-Preloaded Extractants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solvent Extraction Chemicals
2.2. Experimental and Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Extraction of Al, Cu, and Mn with Ni-Preloaded D2EHPA
3.1.1. Preloading Behavior of Co and Ni in D2EHPA
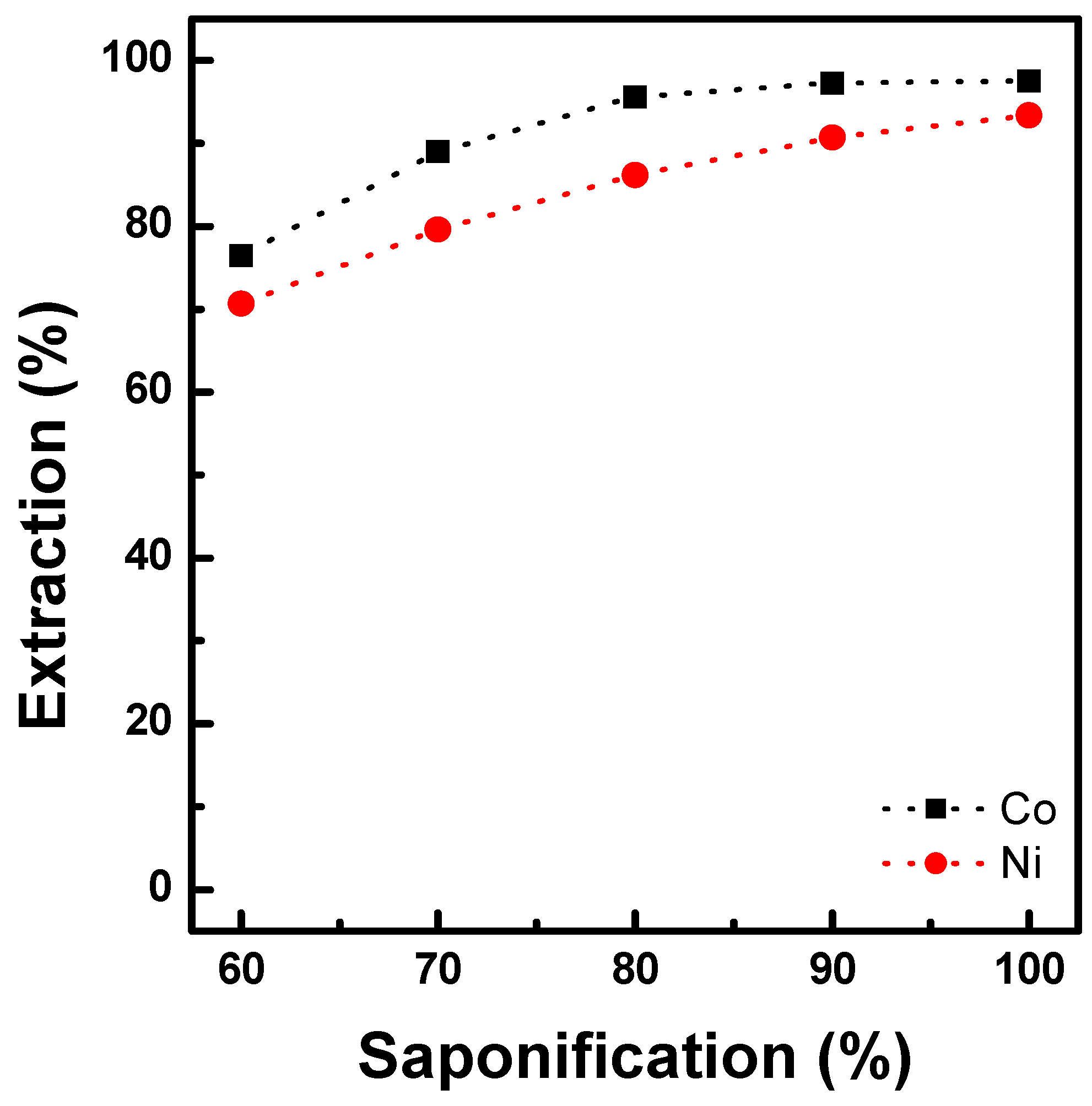
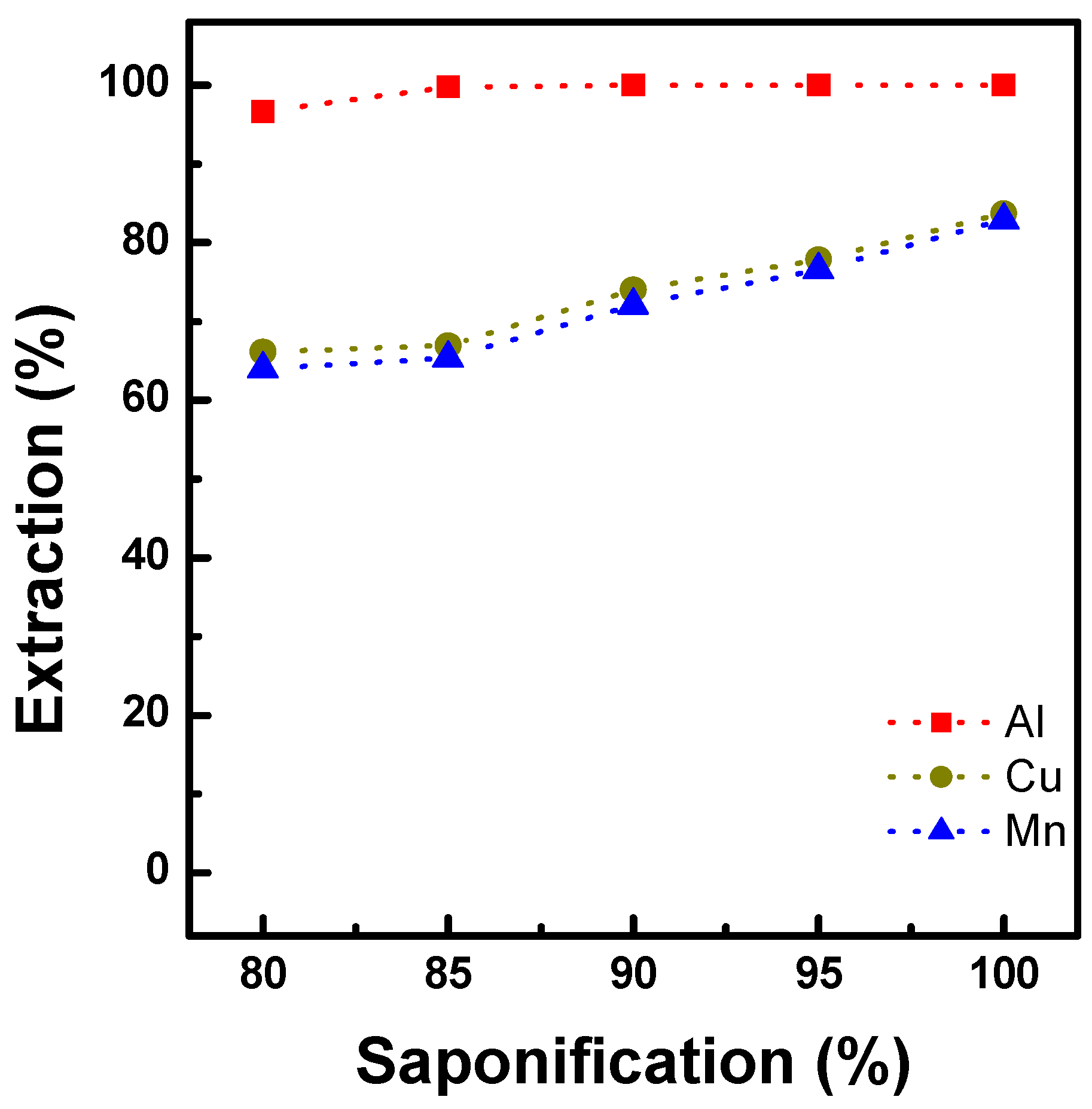
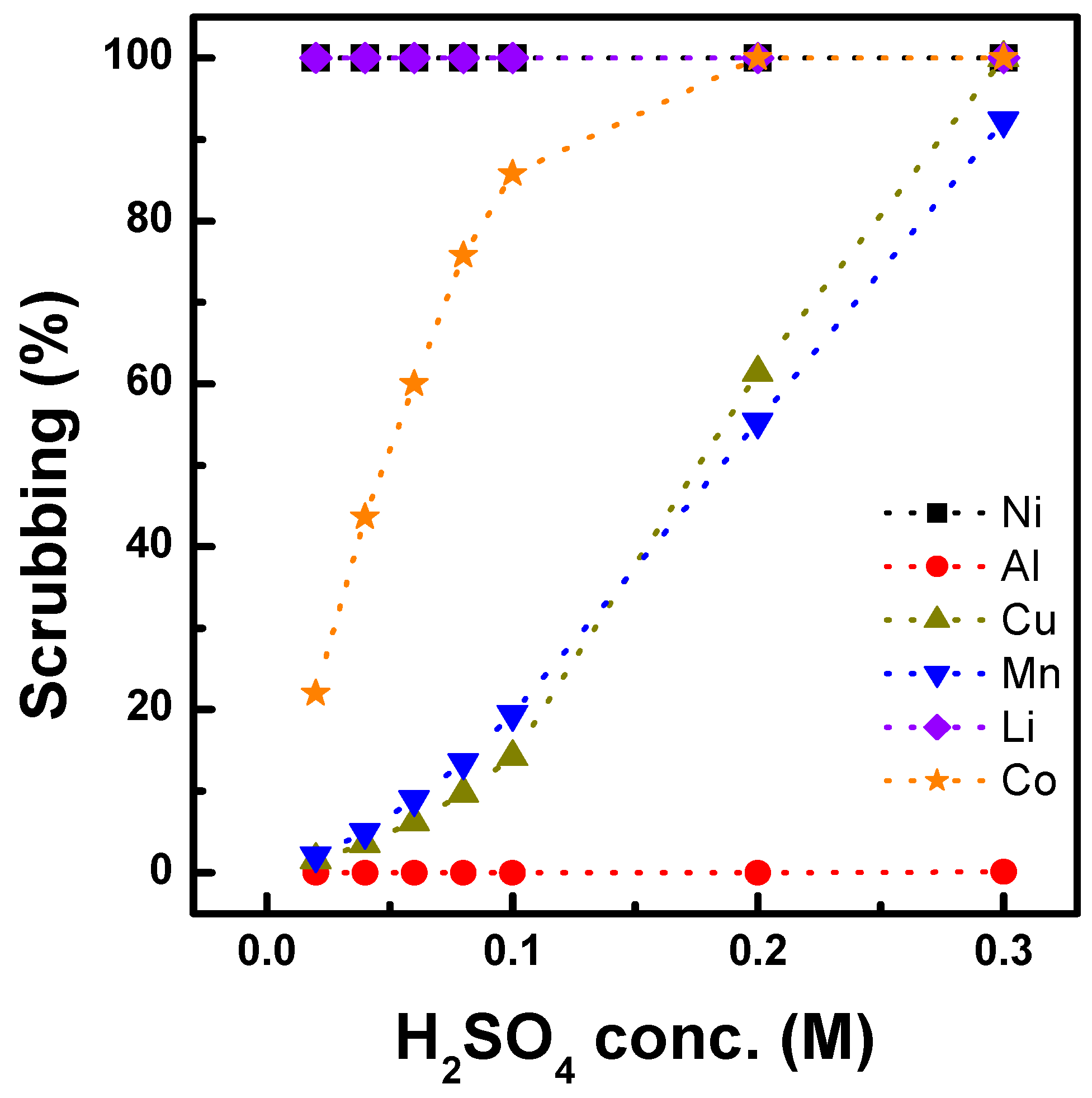
3.1.2. Extraction Behavior of Al, Cu, and Mn with Ni-D2EHPA
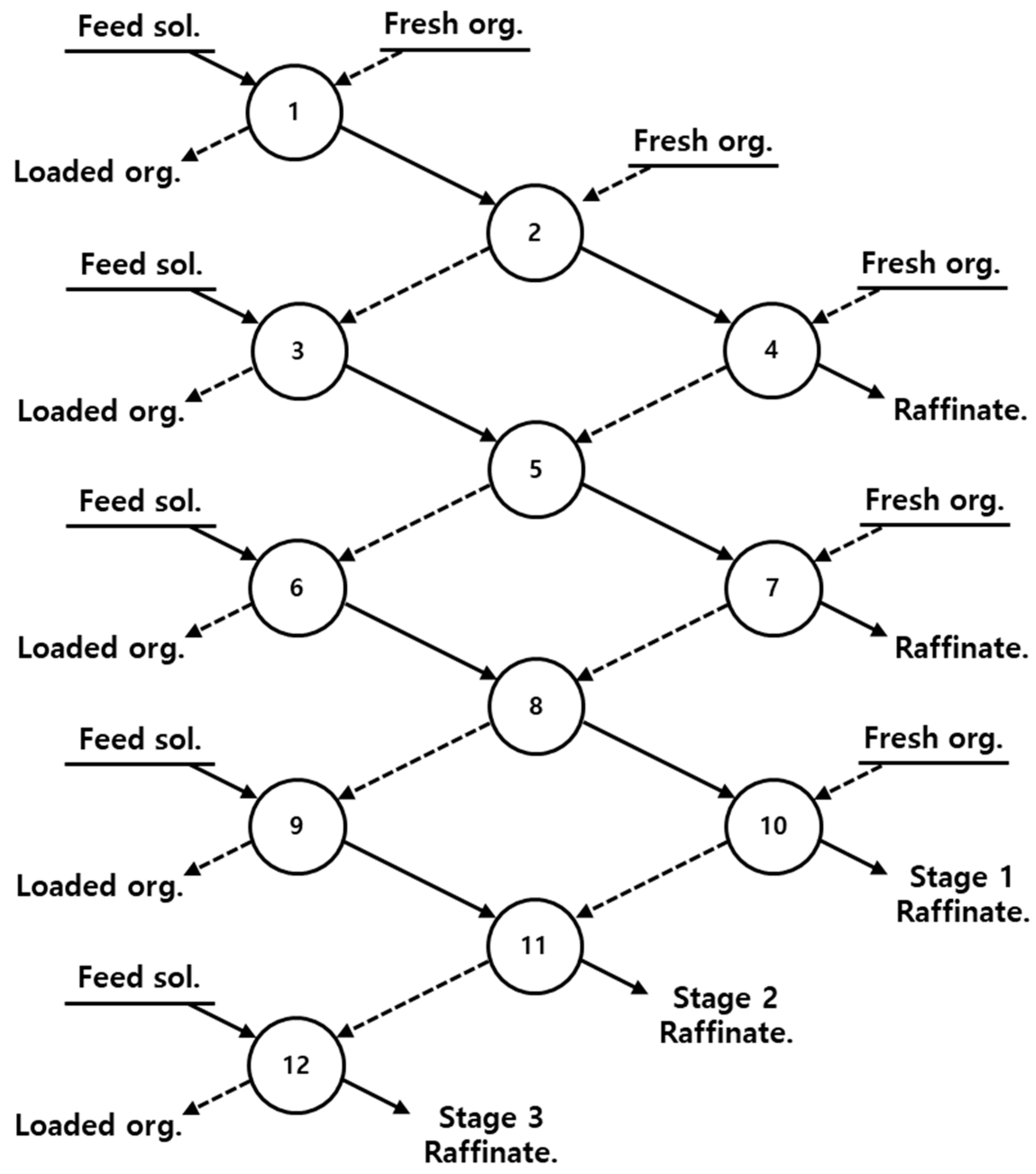
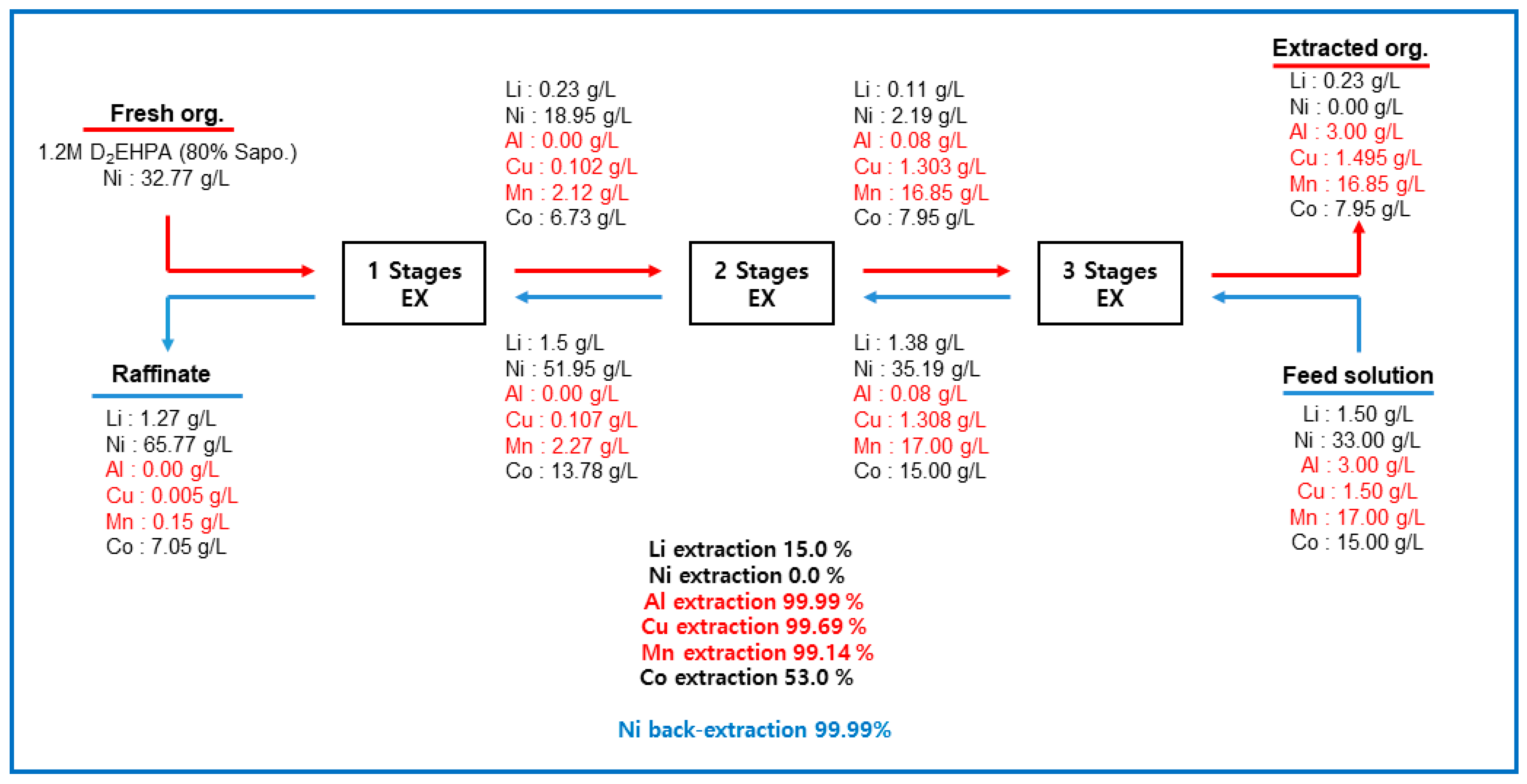
3.1.3. Three-Stage Batch Simulation of Solvent Extraction by Ni-D2EHPA
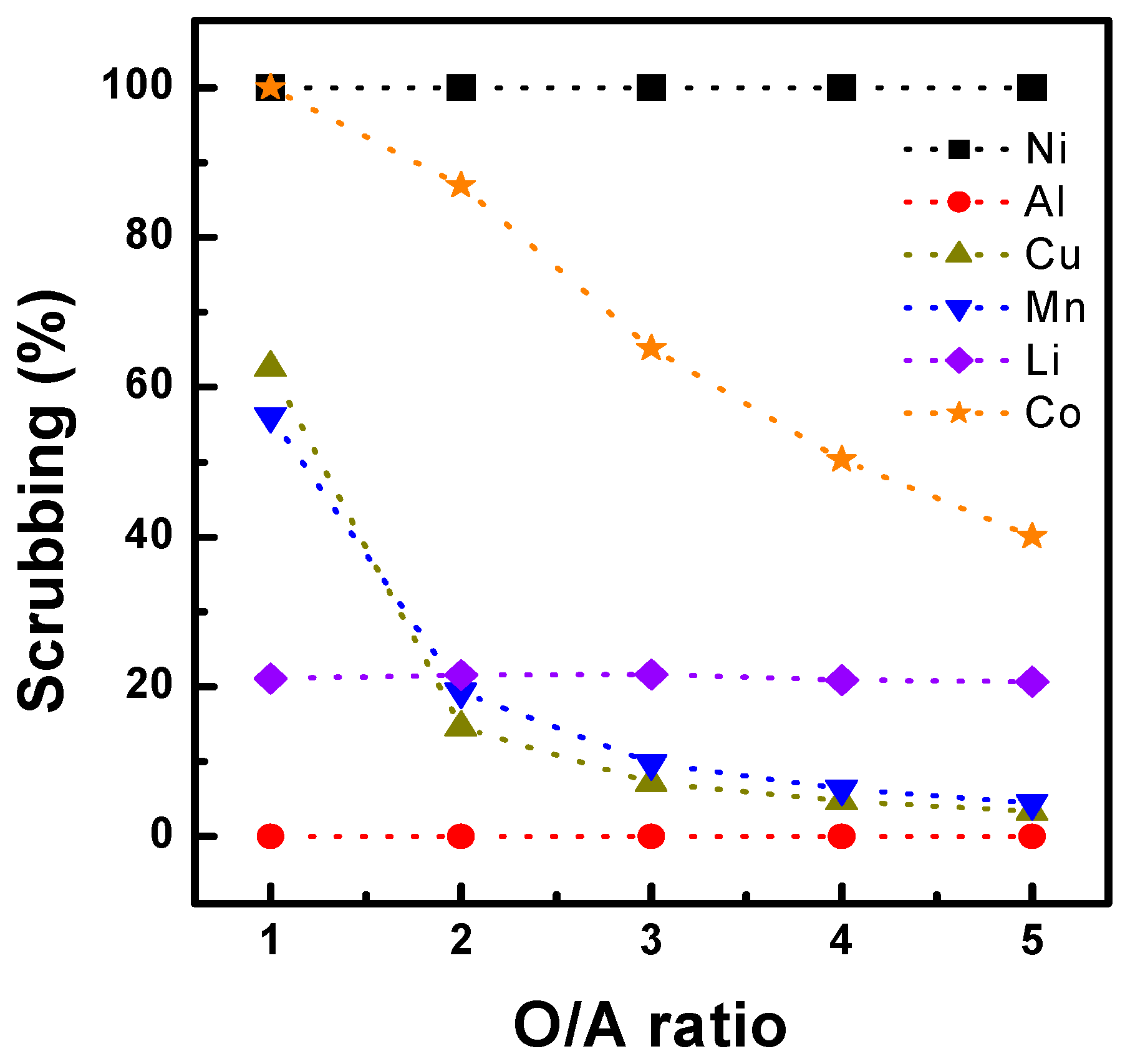
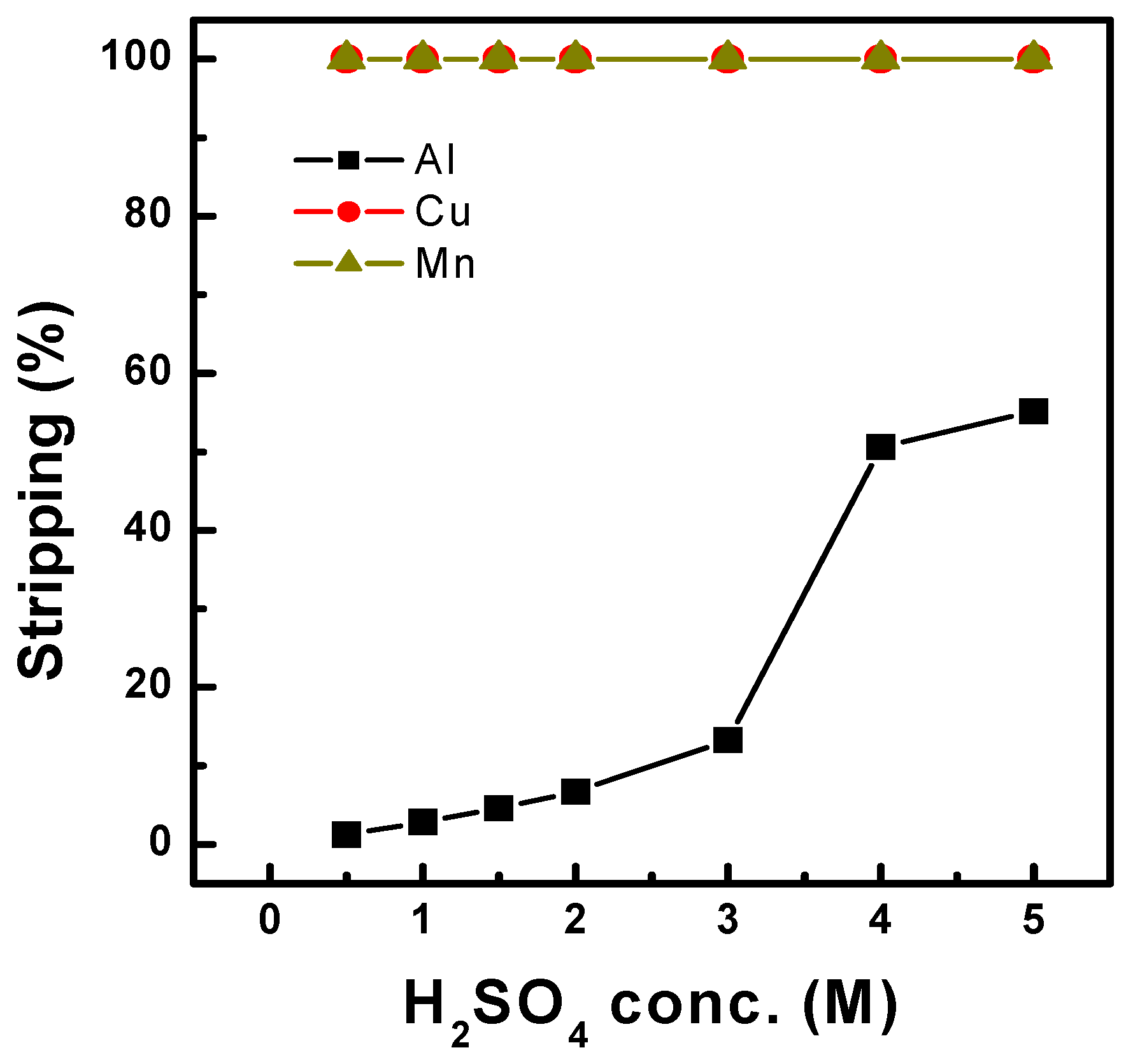
3.1.4. Scrubbing and Stripping Behavior After Extraction with Ni-D2EHPA
3.2. Extraction of Co with Ni Preloaded PC88A
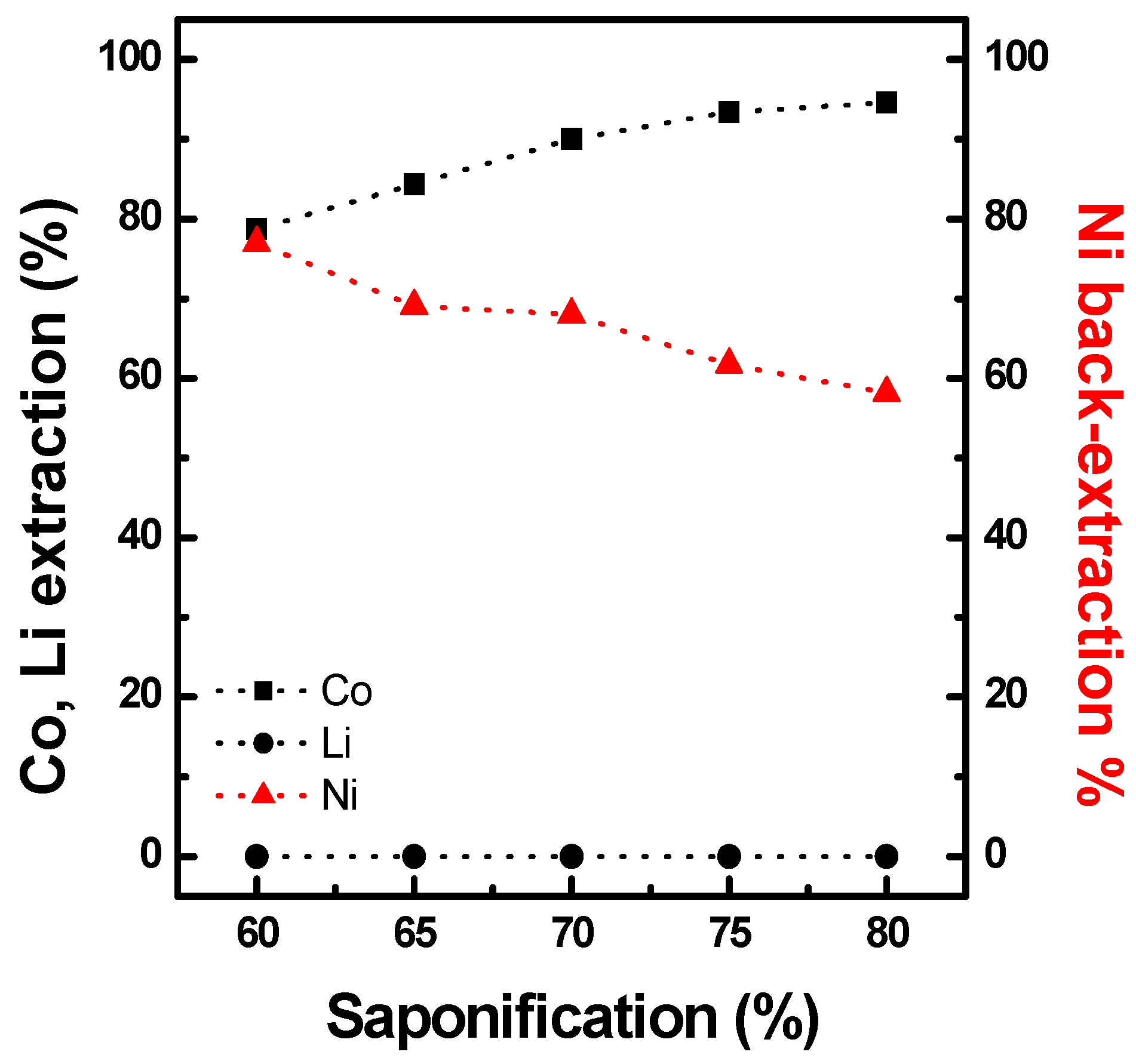
3.2.1. Preloading of Ni in PC88A
3.2.2. Extraction of Co with Ni-PC88A
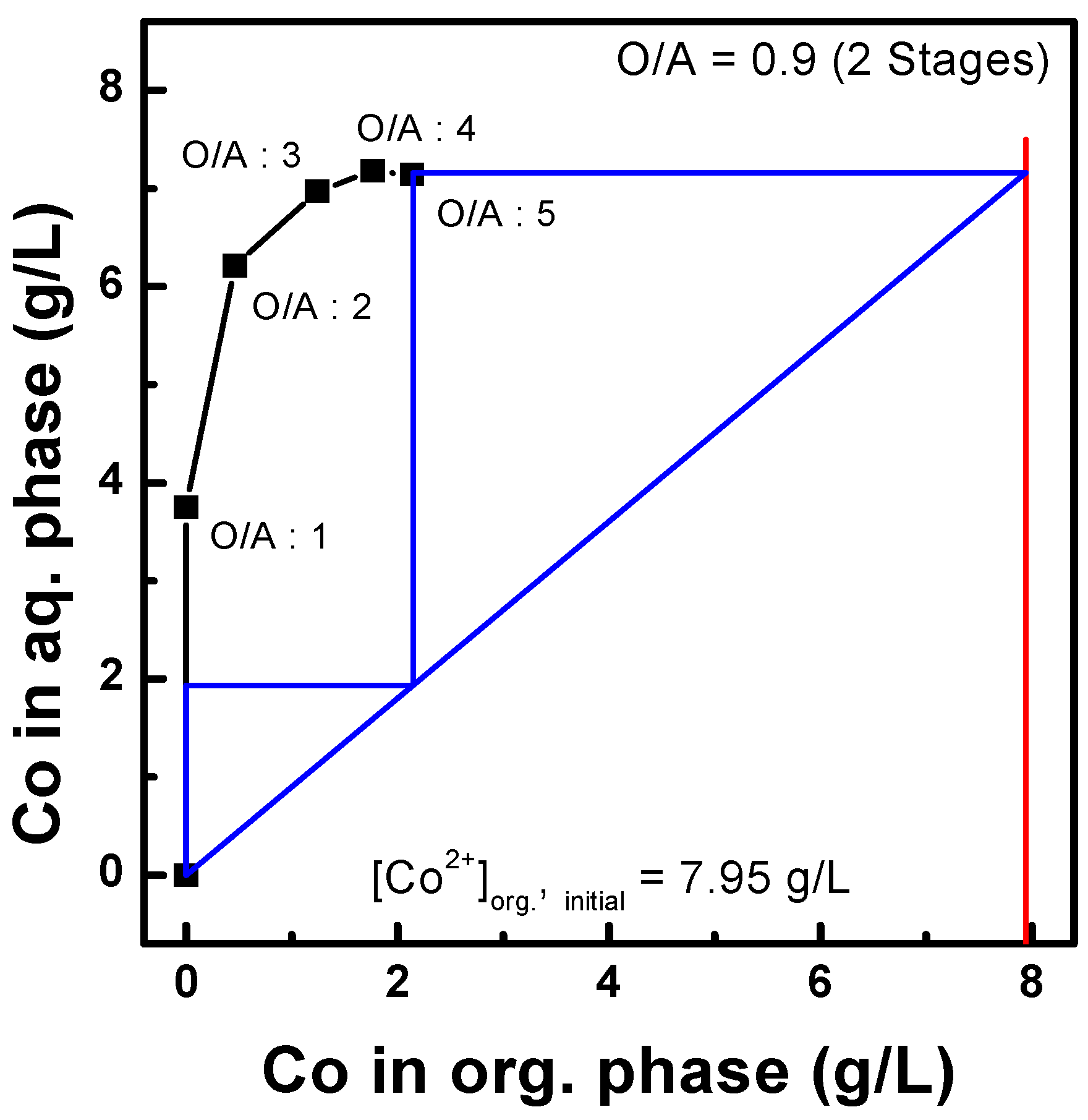
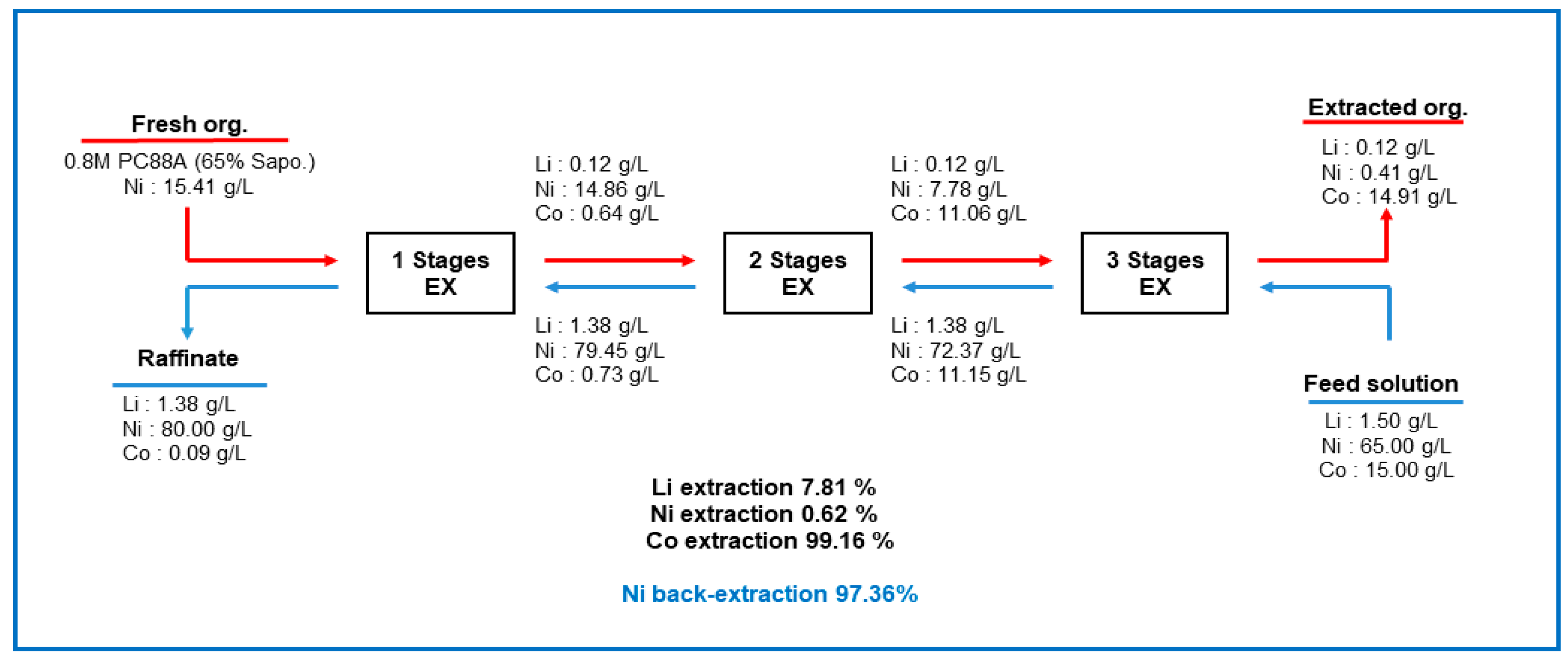
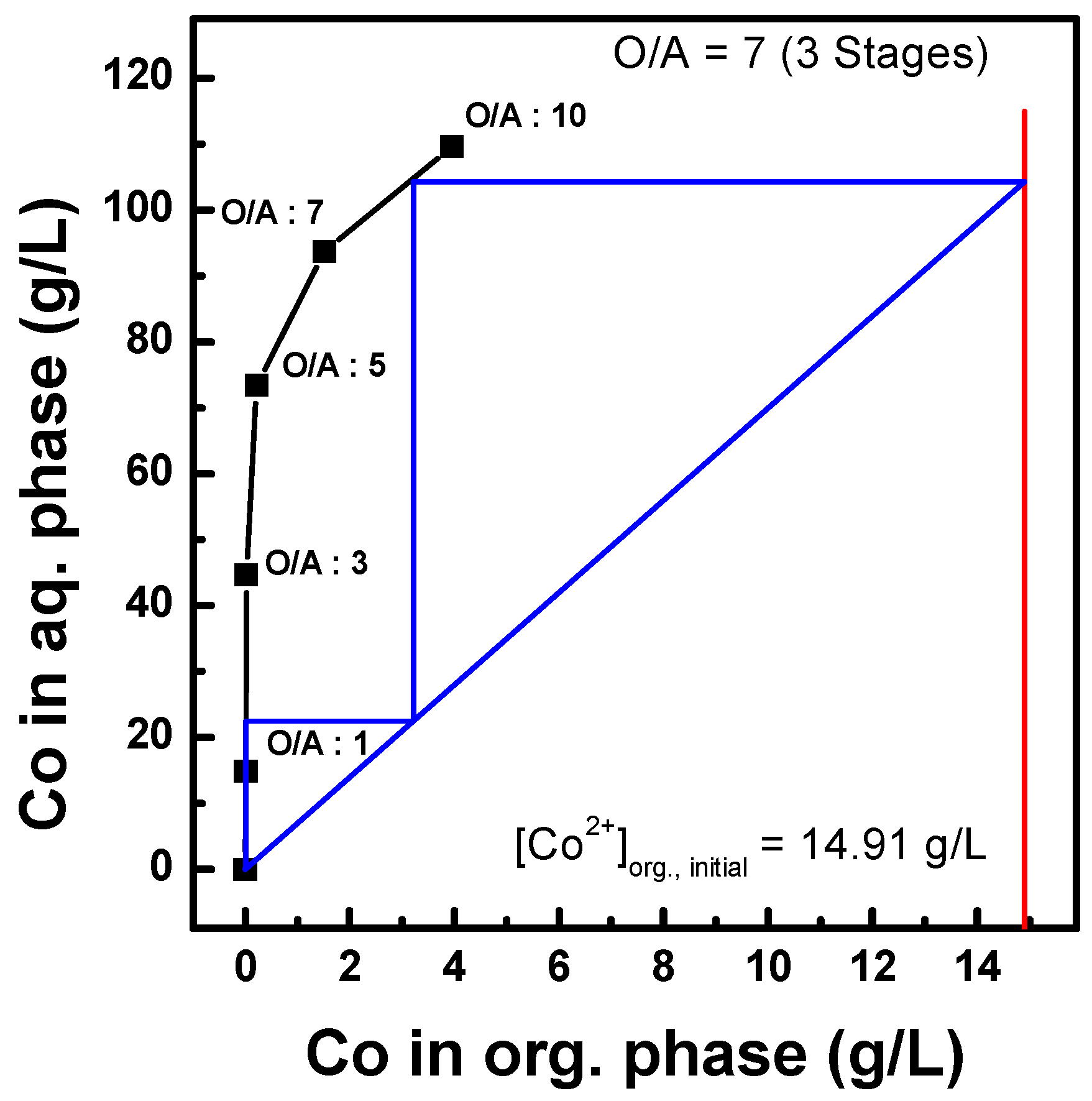
3.2.3. Three-Stage Batch Simulation of Solvent Extraction by Ni-PC88A
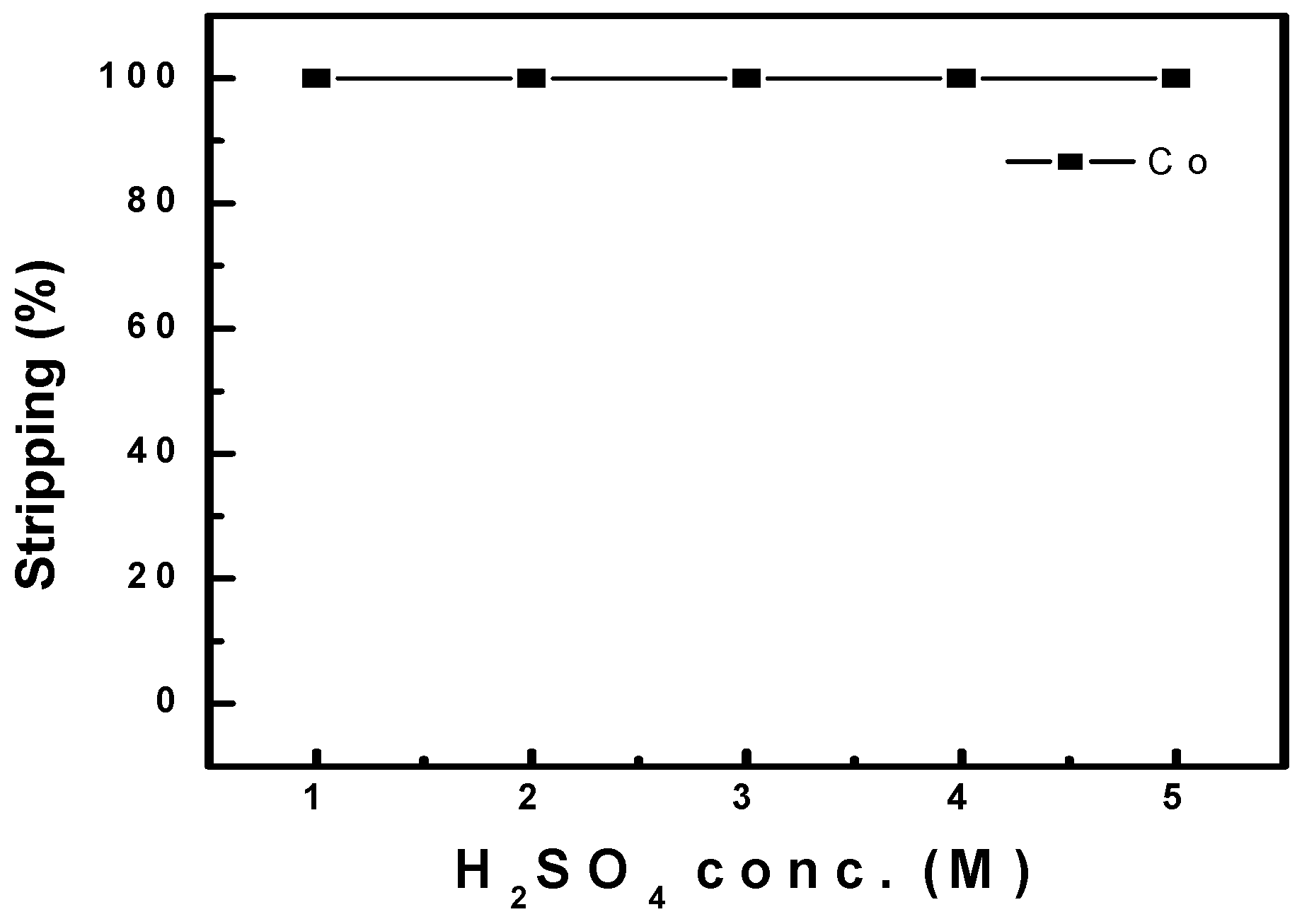
3.2.4. Stripping of Co After Extraction with Ni-PC88A
3.3. Overall Process Flowsheet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibra, E.M.; Connelly, E.; Dhir, S.; Drtil, M.; Henriot, P.; Hwang, I.; Le Marois, J.-B.; McBain, S.; Paoli, L.; Teter, J. Global EV Outlook 2022: Securing Supplies for an Electric Future; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Pohl, O.; Bhatt, A.I.; Collis, G.E.; Mahon, P.J.; Rüther, T.; Hollenkamp, A.F. A review on battery market trends, second-life reuse, and recycling. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 167–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimäki, H.; Karhu, M.; Kotilainen, J.M.; Sairinen, R.; Jokilaakso, A.; Lassi, U.; Huttunen-Saarivirta, E. Sustainability of the use of critical raw materials in electric vehicle batteries: A transdisciplinary review. Environ. Chall. 2024, 16, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Li, J. An overview of global power lithium-ion batteries and associated critical metal recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, H.; Hassan, E.; Frisone, D.; Amiriyan, M.; Farahati, R.; Farhad, S. Recycling and Reusing Copper and Aluminum Current-Collectors from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies 2022, 15, 9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.A.; Prados, L.M.Z.; Majuste, D.; Mansur, M.B. Hydrometallurgical separation of aluminium, cobalt, copper and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.; Heo, W.; Kim, B. The Enhancement of Recycling Processes Efficiency of Lithium Ion Batteries; A Review. Resour. Recycl. 2024, 33, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Q. Pretreatment options for the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Cao, H.; Sun, Z. A mini-review on metal recycling from spent lithium ion batteries. Engineering 2018, 4, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, S.; Wesselborg, T.; Kaukinen, A.; Sainio, T. Removal of iron, aluminium, manganese and copper from leach solutions of lithium-ion battery waste using ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, L.; Frank, J.; Elwert, T. Industrial recycling of lithium-ion batteries—A critical review of metallurgical process routes. Metals 2020, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Kim, S.-B.; Chae, J.-G. Adsorption of Ni (II), Co (II), and Mg (II) from Sulfuric Acid Solution by Diphonix Resin for the Utilization of Laterite Ore. J. Miner. Soc. Korea 2010, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Agatzini-Leonardou, S.; Dimaki, D. Recovery of Nickel and Cobalt from Low-Grade Nickel Oxide Ores by the Technique of Extraction in Heaps Using Dilute Sulphuric Acid at Ambient Temperature. Greek Patent GR1001555, 22 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, B.; Muir*, D. Pressure acid leaching of nickel laterites: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metullargy Rev. 2000, 21, 527–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Son, S.H.; Park, S.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, B.Y.; Lee, M.S. Study on selective lithium leaching effect on roasting conditions of the waste electric vehicle cell powder. Resour. Recycl. 2019, 28, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Dorfling, C.; Eksteen, J. Evaluating a solvent extraction process route incorporating nickel preloading of Cyanex 272 for the removal of cobalt and iron from nickel sulphate solutions. Miner. Eng. 2012, 27, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Separation and recovery of metal values from leaching liquor of mixed-type of spent lithium-ion batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 144, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Hydrometallurgical recovery of metal values from sulfuric acid leaching liquor of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sole, K.; Siwela, L.; Khuzwayo, N. Separation of manganese from cobalt by solvent extraction: Application to the recycling of spent cathode material from lithium-ion batteries. In Proceedings of the Battery Materials Conference 2022, Johannesburg, South Africa, 24–25 August 2022; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, S.; Ren, Z.; Huang, L.; Xu, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Cui, G. Electrolyte Engineering Toward High Performance High Nickel (Ni ≥ 80%) Lithium—Ion Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Seong, W.M.; Manthiram, A. Cobalt-free, high-nickel layered oxide cathodes for lithium-ion batteries: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 34, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, N.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.-I.; Kwon, K. Extraction strategies from black alloy leachate: A comparative study of solvent extractants. Batteries 2024, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Chernyaev, A.; Ossama, M.; Seisko, S.; Lundström, M. Leaching of NMC industrial black mass in the presence of LFP. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibaba.com. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Carson, I.; Tasker, P.A.; Love, J.B.; Moser, M.; Fischmann, A.J.; Jakovljevic, B.; Soderstrom, M.D.; Morrison, C.A. The supramolecular and coordination chemistry of cobalt (II) extraction by phosphinic acids. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Song, S.J.; Tran, T.T.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Co (II), Ni (II), and Cu (II) from Sulfuric Acid Solution by Solvent Extraction. Resour. Recycl. 2022, 31, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, T.; Kobayashi, T. X-ray absorption near edge structure simulation of LiNi0.5Co 0.2Mn0.3O2 via first-principles calculation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35655–35661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieceli, N.; Vonderstein, C.; Swiontekc, T.; Stopić, S.; Dertmann, C.; Sojka, R.; Reinhardt, N.; Ekberg, C.; Friedrich, B.; Petranikova, M. Recycling of Li-ion batteries from industrial processing: Upscaled hydrometallurgical treatment and recovery of high purity manganese by solvent extraction. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2023, 41, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu Cheng, M.H. Solvent Extraction Process for Recovering Nickel and Cobalt from Each Solutions. US20040050212A1, 18 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Lee, J.-c.; Jeong, J.; Kim, B.-S.; Pandey, B. Selective recovery of cobalt, nickel and lithium from sulfate leachate of cathode scrap of Li-ion batteries using liquid-liquid extraction. Met. Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Elements | Al (g/L) | Cu (g/L) | Mn (g/L) | Co (g/L) | Ni (g/L) | Li (g/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contents | 3.0 | 1.5 | 17.0 | 15.0 | 33.0 | 1.5 | 3.15 |
| Elements | Co (g/L) | Ni (g/L) | Li (g/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contents | 15.0 | 65.0 | 1.5 | 5.61 |
| Elements | Al | Cu | Mn | Co | Ni | Li |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contents (g/L) | 3.00 | 1.50 | 16.85 | 7.95 | 0.02 | 0.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Cho, Y.-C.; Hong, Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, G.-G.; Ahn, J. Solvent Extraction of Critical Minerals from the Leachate of High-Nickel Black Mass Using Nickel-Preloaded Extractants. Minerals 2025, 15, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111221
Ahn J, Kim K-H, Cho Y-C, Hong Y, Kim B, Lee G-G, Ahn J. Solvent Extraction of Critical Minerals from the Leachate of High-Nickel Black Mass Using Nickel-Preloaded Extractants. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111221
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Junmo, Ki-Hun Kim, Yeon-Chul Cho, Yeongran Hong, Byeongkyu Kim, Go-Gi Lee, and Jaewoo Ahn. 2025. "Solvent Extraction of Critical Minerals from the Leachate of High-Nickel Black Mass Using Nickel-Preloaded Extractants" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111221
APA StyleAhn, J., Kim, K.-H., Cho, Y.-C., Hong, Y., Kim, B., Lee, G.-G., & Ahn, J. (2025). Solvent Extraction of Critical Minerals from the Leachate of High-Nickel Black Mass Using Nickel-Preloaded Extractants. Minerals, 15(11), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111221







