Abstract
The Baijianshan deposit is the sole skarn Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field, Xinjiang, China. Its ore genesis remains controversial, which hinders understanding of the relationship between skarn-type Zn-Cu and adjacent epithermal Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn mineralization and consequently impedes further regional exploration. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating on zircons from the granite and granite porphyry from the mining area yielded ages of 311 ± 1.7 Ma and 312 ± 1.6 Ma, respectively. The corresponding zircon εHf(t) values and TDM ages are 8.7–9.9 and 624–555 Ma for the granite, and 7.2–9.9 and 673–552 Ma for the granite porphyry. These granites are metaluminous, high-K calc-alkaline I-type granites, with high LREE/HREE ratios (4.92–9.03) and pronounced negative Eu anomalies. They are enriched in K, Th, U, Zr, and Hf, with significant depletions in Sr, P, and Ti. Combined geological and geochemical evidence indicate that these Late Carboniferous granites were derived from the juvenile crustal and formed in subduction-related back basin. Two-phase aqueous inclusions in the ore-bearing quartz and calcite have homogenization temperatures ranging from 117 to 207 °C and 112 to 160 °C, respectively, with the salinities in the ranges of 0.18~7.17 and 0.53~5.26 wt% NaCl eq. The S and Pb isotopic compositions of sulfides in the ores indicate that the ore-forming metals were sourced from the medium-acidic magmatite. The δ18OH2O and δDH2O values of hydrothermal fluids range from −6.97% to −5.84% and −106.8% to −99.6%, respectively, suggesting that the ore-forming fluids originated from the mixing of magmatic and meteoric water. Fluid mixing and corresponding conductive cooling were identified as the principal mechanism triggering the metallic mineral precipitation. The Baijianshan skarn Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit shares contemporaneous magmatic-mineralization ages and analogous material sources with the epithermal polymetallic deposits in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field, collectively constituting a unified skarn-epithermal metallogenic system. This hypothesis indicates that the deep parts of the epithermal deposits within the Yamansu volcanic rocks possess potential for exploring the porphyry-skarn-type deposits.
1. Introduction
In terms of the porphyry ore system, deposits of different end-members are the products of hydrothermal processes at different evolutionary stages and varying distances from the center of the causative intrusion [1,2,3,4,5]. These deposits comprise the porphyry-type mineralization formed by the hydrothermal fluids exsolved from the deep magma chambers, high- or intermediate-sulfidation epithermal deposits formed by the mixing of magmatic fluids and meteoric water, as well as low-sulfidation epithermal deposits formed by the magma-driven circulating meteoric water distal to the porphyries [1,5]. As another intrusion-related end-member in the porphyry ore system, the skarn deposits are defined as orebodies typically occurring within skarns and adjacent metasomatic rocks at the contact zones between aluminosilicate rocks (e.g., intrusions, volcanic rocks, and migmatites) and carbonates or other calcareous wall-rocks. These deposits form primarily through contact metasomatic reactions driven by the high-temperature hydrothermal fluids, generating both proximal Cu-Au skarns and distal Au/Zn-Pb skarn deposits [6,7,8,9]. Therefore, the mineralization processes of different deposit types within porphyry metallogenic systems and their temporal–spatial and genetic relationships can provide theoretical guidance for mineral exploration targeting in the mining districts [10,11,12,13,14,15].
The Xiaoshitouquan ore field is located in the eastern segment of the Harlik island arc belt (HIAB), Chinese Eastern Tianshan [16,17,18]. Since 1987, Team 704 of the Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources has conducted mineral exploration in this district through geological reconnaissance, follow-up of geochemical anomalies, and deep drilling. These efforts have discovered numerous epithermal Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposits (e.g., Qiongkuduke, Tongshan, Huangcaogou, and Xiaoshitouquan), as well as the Baijianshan skarn-type Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit [19,20,21]. All these epithermal deposits occur within the volcanic–volcaniclastic rocks of the Lower Carboniferous Yamansu Formation. Fluid inclusion and stable isotope analyses have been conducted on the epithermal deposits in the previous studies, preliminarily clarifying the ore genesis and mineralization process [22,23,24]. However, as a representative skarn deposit in the Xiaobaishitou ore field, the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit has received insufficient attention. Current research on this deposit is limited to geological characteristics and exploration targeting [25,26,27]. As a consequence, magmatism-mineralization age, sources of ore-forming fluids and metals, as well as metal precipitation mechanism remain unclear. This knowledge gap constrains the understanding of its genesis and regional metallogeny, thus hindering the deep/peripheral and regional-scale exploration.
Thus, this study presents an integrated investigation on the petrography, whole-rock geochemistry, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopes for the intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan deposit to constrain the timing of magmatism and mineralization, petrogenesis, and tectonic setting. Additionally, fluid inclusion and S-Pb-H-O isotopic analyses have been conducted in this study, aiming to constrain the sources of ore-forming fluids and metals, precipitation mechanism and ore genesis. These findings provide critical insights for further prospecting in the Baijianshan area and elsewhere in the region.
2. Regional Geology
The Tianshan orogenic belt, as a key component of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, has an ongoing debate regarding its formation time. Some scholars propose that it started from the Early Permian [28], whereas others advocate for the Early Triassic [29]. Nevertheless, it is generally accepted that its formation was shaped by a combination of microcontinental collision and island arc accretion [30]. Based on the distribution of ophiolite belts, fault systems, and metamorphic rocks, the Tianshan region can be divided into three secondary units, including Northern, Central, and Southern Tianshan [29]. Northern Tianshan is predominantly characterized by the Devonian-Carboniferous calc-alkaline volcanic-sedimentary rocks, whereas Central and Southern Tianshan are distinguished by the pre-Cambrian crystalline basement and passive continental margin sediments. Eastern Tianshan refers to the eastern part of Central and Northern Tianshan [31]. It can be further subdivided into the Bogda–Harlik Belt, Danan Lake–Jueluotage Belt, and Central Tianshan Block (Figure 1a).
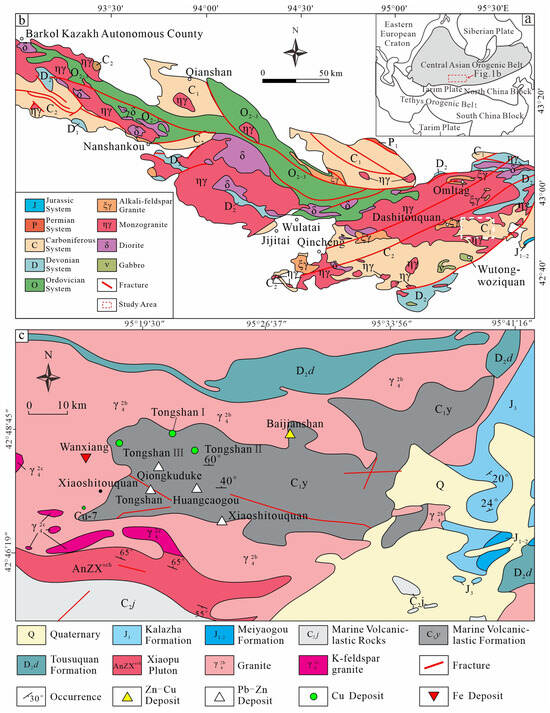
Figure 1.
(a) Tectonic framework of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt [32], (b) simplified geological map of the HIAB (modified from [32]), and (c) geological map of the Xiaoshitouquan ore field (modified from [23]).
The Lower Carboniferous Yamansu Formation volcanic rocks are widespread in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field (Figure 1b). This stratigraphy represents a volcanic-sedimentary sequence of marine–continental transition, including tuff, tuffaceous sandstone, conglomerate, marble, and volcanic breccia. The thickness exceeds one kilometer, reflecting multi-phase faulting and central composite volcanic eruptions [20]. The regional structure generally exhibits a NW–SE trend. Secondary NW-trending faults, developed on both the northern and southern flanks, combine with NE-trending left-lateral strike-slip faults to form a conjugate shear zone [23]. The faults in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field are primarily oriented in a near-EW direction, with secondary faults trending near SN (Figure 1c). The stratigraphy as a whole exhibits near-SE trending compound anticline. The magmatic activity shows multiple phases [32,33,34]. Early Paleozoic (446–440 Ma) mafic-intermediate rocks (such as diorite and hornblende diorite) mark the initiation of subduction. Carboniferous (~350 Ma) diorite intrusions reflect the upwelling of mantle-derived melts during the subduction process. Large-scale Latest Carboniferous to Early Permian (299–296 Ma) felsic intrusions (biotite granite, potassium-feldspar granite) were widely emplaced and formed in a post-collisional extensional setting, covering more than 50% of the regional area.
3. Ore Deposit Geology
The exposed strata within the mining area are dominated by the second subgroup of the Lower Carboniferous Yamansu Formation (C1y2), consisting of marine–continental transitional facies volcanic clastic rocks, limestones, and marbles. Influenced by the magmatic intrusion, these strata have undergone varying degrees of thermal contact metamorphism, forming hornfels zones and marble + skarn zones with thicknesses of 30–50 m. The marble + skarn zones are closely associated with the Zn-Cu polymetallic orebodies (Figure 2). The structures within the mining area are dominated by two fault sets: an approximately east–west trending set and a northeast trending set. These faults are commonly observed within the gabbro in the northwestern part. Acid, intermediate-acid, and basic intrusive rocks are exposed within the mining area, intruding into the Lower Carboniferous Yamansu Formation. The rock types mainly include granite, granite porphyry, granodiorite, diorite, and gabbro (Figure 3).
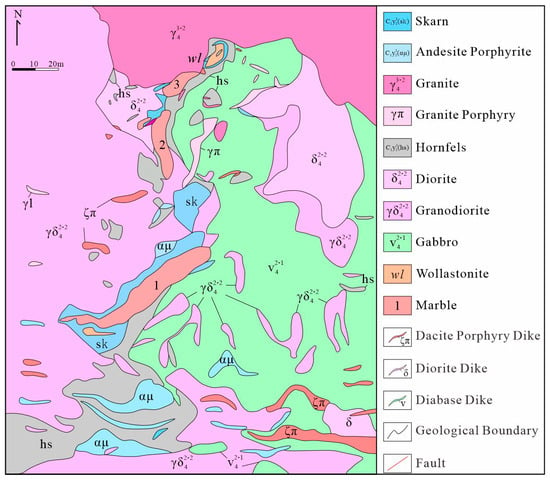
Figure 2.
Geological map of the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit [34].

Figure 3.
Field geological photographs and hand specimen photomicrographs of intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit. (a,b) Contact boundary between granite and skarn at Baijianshan; (c) flesh-red granite; (d,f) mineral composition predominantly quartz, K-feldspar, and plagioclase, with minor hornblende; (e) brownish-red granite porphyry.
Three zinc polymetallic orebodies (Zn-I, Zn-II, and Zn-III) and one copper polymetallic orebody (Cu-I) have been delineated in the mining area. The proven and probable reserves of Pb, Zn, and Cu are 302 t, 12,211 t, and 88 t, respectively. All the orebodies occur at depth and are controlled by the contact zone between the granitic intrusion and surrounding carbonates (Figure 4). As the largest Zn orebody, the Zn-I orebody has a length of 300 m and an inclined dip length of up to 178 m. The dip direction of this orebody ranges from 95° to 165°, with a dip angle of 38° to 63°. The Zn grade ranges from 0.56% to 35.44% (average 2.93%). The Cu-I orebody is located below the Zn-I orebody, with a length of approximately 75 m and a width of 50 m. The Cu grade ranges from 0.22% to 1.03% (average 0.49%).
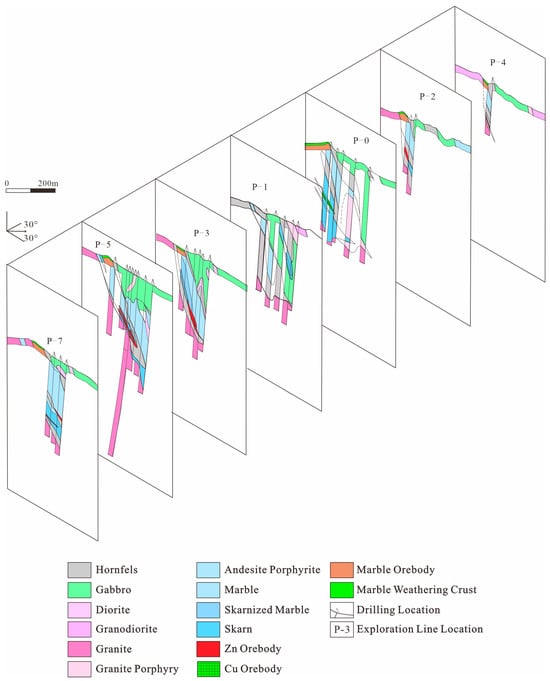
Figure 4.
Composite section of the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit [34].
The textures of ores mainly comprise fine-vein, net-vein, disseminated, nodular, and spotted (Figure 5). The primary metallic minerals include chalcopyrite, galena, sphalerite, and pyrite, with a small amount of ilmenite and magnetite. The non-metallic minerals mainly consist of garnet, pyroxene, wollastonite, quartz, and calcite (Figure 6). The hydrothermal alteration is characterized by skarnization, carbonation, and chloritization. Carbonation primarily occurs as light-colored calcite veins, accompanied by minor sulfides. The orebodies are situated in the contact zones between intrusion and marble and are related to carbonation, skarnization, and chloritization.

Figure 5.
Hand specimen photographs of representative ores from the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit. (a) Sparse sphalerite in garnet matrix, (b) honey-colored wollastonite, (c) calcite replacing early-stage epidote, (d) paragenetic pyrite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena overprinted by later quartz-calcite veinlets, (e) honey-colored and milky calcite replacing epidote, (f) intergrown specularite and epidote replaced by quartz, (g) quartz-pyrite vein crosscutting pyritized wallrock, (h) oxidized pyrite exhibiting tarnish in wollastonite matrix, and (i) quartz-pyrite vein replacing early skarn minerals.
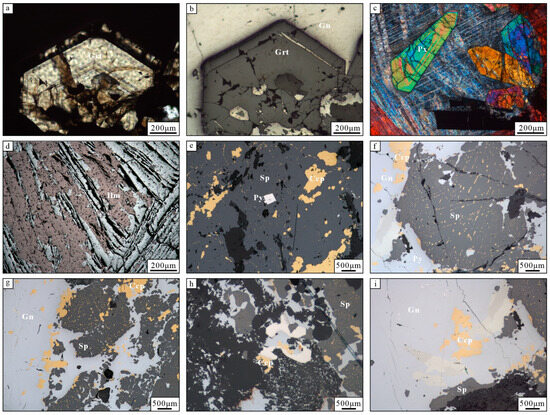
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs of the mineral from the Baijianshan Zn-polymetallic deposit. (a) Zoned garnet exhibiting pale-yellow to white coloration, (b) zoned garnet under cross-polarized light, (c) the pyroxene was enclosed by calcite in the late stage of mineralization, (d) specularite partially altered to ilmenite, (e) sphalerite replacing chalcopyrite with euhedral pyrite grains, and (f–i) paragenetic association of sphalerite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, and galena; sphalerite and chalcopyrite occur as solid solution texture with minor Bi-bearing minerals in galena.
Based on the mineral assemblages, ore textures, vein crosscutting relationships, and alteration types, the mineralization process of the Baijianshan deposit is divided into five stages (Figure 7). The prograde skarn stage (I) is characterized by the occurrence of garnet, wollastonite, and pyroxene. The garnet shows yellow-white in color, with medium-grained euhedral crystal structure (Figure 5a and Figure 6a,b). The pyroxene is encased by later calcite (Figure 6c). The retrograde skarn stage (II) is characterized by the occurrence of yellowish-green epidote aggregates and crosscut by late-stage quartz-sulfide veins (Figure 5c). The oxide stage (III) comprises abundant magnetite and ilmenite (Figure 6d). Magnetite is commonly iron-gray in color, with a metallic luster. It is commonly intergrown with ilmenite and replaces the early-stage garnet (Figure 6d). The early quartz-sulfide stage (IV) is characterized by the occurrence of quartz and metallic sulfides such as pyrite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena (Figure 5d–i). Pyrite is typically pale yellow and exhibits euhedral to subhedral texture (Figure 6e). Chalcopyrite is strongly associated with galena and sphalerite, forming a solid solution within sphalerite (Figure 6e–i). The late quartz-carbonate stage (V) is characterized by the occurrence of calcite. Calcite is the dominant gangue mineral and the fills cavities left by skarn mineral assemblages (Figure 5e).
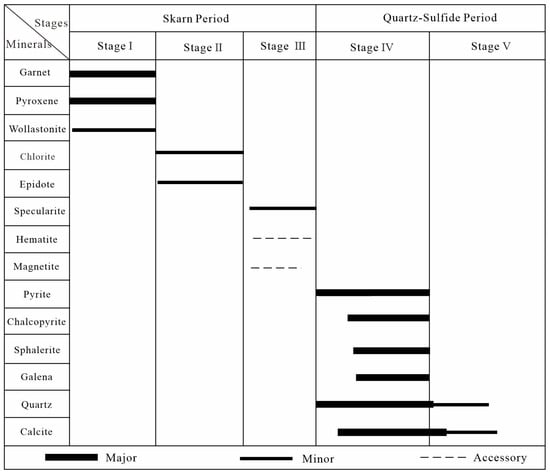
Figure 7.
Paragenetic sequence of ore and gangue minerals in the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit.
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
Sixty ore and host rock samples were taken from the outcrops and drill hole at the Baijianshan mining area. Samples of granite porphyry and granite specific sampling locations are shown in Figure 2. The granite displays a flesh-red color with medium- to fine-grained granitic texture and massive structure. Mineral composition is primarily K-feldspar (40%), plagioclase (30%), and quartz (20%), with minor hornblende (7%) and chlorite (3%, Figure 3c). The granite porphyry exhibits a brownish-red color with porphyritic texture and massive structure. Phenocrysts consist predominantly of feldspar (20%) and quartz (13%), with minor hornblende (10%) and pyroxene (7%). The matrix is composed of feldspar (25%) and quartz (25%, Figure 3d). Polished thin sections were made from both host rock samples and Zn-Cu ores of different hydrothermal stages. Subsequently, a total of sixteen samples with typical mineral assemblages were selected for further analysis of mineralogy, fluid inclusions, isotopes, and elemental geochemistry.
4.1. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating
Zircons of the causative intrusions in the Baijianshan mining area were separated and selected for the U-Pb dating, including the granite and granite porphyry. In situ U–Pb dating of zircon was carried out using the LA-ICP-MS method at the Analytical Laboratory Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology. Analyses used a Coherent (Dieburg, Germany) Geolas 193 laser-ablation system coupled with Thermo Scientific (Bremen, Germany) HR-ICP-MS, with 24–32 μm spots, 6 Hz pulse rate, and 7 J/cm2 energy density. Helium carrier gas was mixed with argon before entering the ICP-MS. Standard NIST SRM 610 [35] optimized the machine and calibrated trace elements. Zircon 91500 [36,37] served as the U-Th-Pb isotopic external standard, while Plešovice zircon [38] was the monitoring standard. Each analysis included 20 s gas-blank and 40 s sample data acquisition, with zircon 91500 repeated every six analyses for Pb/U fractionation and drift correction. Data were processed using ICPMSDataCal [39] for concordia diagrams.
4.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements Analyses
For the whole-rock major-trace element analyses, 7 samples of granite porphyry and 7 samples of granite were selected. Fresh whole-rock samples were crushed in a steel jaw crusher and powdered to <200 mesh using an agate mill. The major and trace elements analysis was completed by Chengdu Nanda Company, Chengdu, China. Major element compositions were determined using Rigaku (Tokyo, Japan) ZSX Primus III+ X-ray fluorescence spectrometers with accuracy better than 5%. Samples were placed in a Li2B4O7 solution at a ratio of 1:10 and melted at a temperature of 1150–1250 °C. The melted sample was made into a glass disk. Trace elements were analyzed on a Perkin-Elmer (Singapore) NexION 1000G ICP-MS, with an analytical accuracy of better than 5%–8%. Sample powders were digested using an HF + HNO3 mixture in high-pressure Teflon bombs at 185 ± 5 °C for 48 h. The USGS standard GSP-2 [40] were used for calibration of element concentrations of the unknowns.
4.3. In-Situ Zircon Hf Isotopes Analyses
In situ Hf isotope analysis of zircons was conducted at Analytical Laboratory Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology using a Coherent (Germany) Geolas 193 laser-ablation system coupled with Nu Plasma Ⅱ MC-ICP-MS, with analytical parameters set at 44 μm spot size, 10 Hz pulse rate, and 10 J/cm2 energy density. Helium carrier gas mixed with argon and trace nitrogen was applied to enhance Hf sensitivity. Zircon 91500 [41] served as the external standard, analyzed every ten samples alongside Plešovice zircon [37] as an unknown. The n(176Hf)/n(177Hf) ratio for 91500 and Plešovice zircon was 0.2822779 and 0.2824571. Isobaric interference corrections utilized were 176Lu/177Hf via 175Lu (176Lu/175Lu = 0.02655 [42] and 176Yb/177Hf via 173Yb (176Yb/173Yb = 0.79381; [43]). Mass fractionation was corrected exponentially using 179Hf/177Hf = 0.7325 [42] and 173Yb/171Yb = 1.132685 [43].
4.4. Fluid Inclusion Microthermometry
Quartz and calcite from the main-ore stage were prepared to observe fluid inclusions. Microthermometry of fluid inclusions was conducted on a Linkam THMSG600 heating–freezing system at the College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Chengdu University of Technology. Heating and freezing protocols followed Roedder (1984) [44]. The thermocouples were calibrated by measuring the melting temperatures of pure water (0.0 °C) and pure CO2 (−56.6 °C) using synthetic fluid inclusions. The measurement accuracy of phase transitions in fluid inclusions was ±0.2 °C for temperatures below 0 °C, ±0.5 °C between 0 °C and 100 °C, and ±2 °C between 100 °C and 600 °C. Heating and cooling rates were controlled at 20 °C/min during heating or freezing processes most of the time, and were reduced to ±0.2 °C for ice-melting temperature and ±2 °C for homogenization (Th, L + V → L).
4.5. Stable Isotope Analysis
In situ sulfur isotope microanalysis by LA-MC-ICP-MS was conducted at Createch Testing (Tianjin) Technology Co., Ltd, Tianjin, China. Analyses employed a Thermo Scientific (Bremen, Germany) Neptune Plus multi-collector ICP-MS coupled with a RESOlution SE 193 nm solid-state laser system (Applied Spectra, West Sacramento, CA, USA). Target areas were selected based on post-scan imagery, with sulfide ablation performed using a spot diameter adjustable between 10 and 150 μm (30 μm for sphalerite; 20 μm for pyrite). Ablation parameters included an energy density of 3 J/cm2 and a repetition rate of 5 Hz. Ablated aerosols were transported via high-purity He carrier gas to the MC-ICP-MS. 32S and 34S were measured using Faraday cups, with 0.131 s integration time per 200 data cycles (total acquisition time ≈ 27 s). Before analysis, instrument parameters were optimized using sulfide reference materials. To minimize matrix effects, matrix-matched sulfide standards were applied with a standard-sample-standard bracketing protocol for mass bias correction.
In situ lead isotope analyses of sulfides were conducted using a Thermo Fisher Scientific (Bremen, Germany) Neptune Plus MC-ICP-MS with a Coherent (Germany) Geolas HD excimer ArF laser-ablation system at Wuhan Sample Solution Analytical Technology Co., Ltd, Wuhan, China. Laser parameters were dynamically optimized: spot diameters (44–90 μm) adjusted in real time based on Pb signal intensity, pulse frequencies (4–10 Hz) modulated to maintain constant ablation rates, and fluence fixed at 5 J/cm2. The gas flow protocol employed He as the primary transport medium, with post-ablation mixing of Ar to enhance plasma stability. Further details on the in situ Pb isotopic ratio analysis were provided by [45].
Hydrogen (δD) and oxygen (δ18O) isotope analyses of quartz separates from the quartz-sulfide veins were conducted at Createch Testing (Tianjin) Technology Co., Ltd., China, using a Finnigan MAT 253 mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). The δD values of fluid inclusions in minerals were analyzed using the Zn reduction method [46]. Oxygen gas was produced from the samples reacting with BrF5 in externally heated nickel reaction vessels [47]. The H-O isotope results are reported relative to the Standard Mean Ocean Water (SMOW) with the precisions of ±1‰ for δD and ±0.2‰ for δ18O, respectively.
5. Results
5.1. Zircon U-Pb Ages
Zircon U-Pb dating results are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The analyzed zircons are colorless or light yellow, and are mainly short- to long-prismatic in shape, exhibiting high euhedrality and few fractures. Cathodoluminescence images show that most zircons are dark grayish-black and exhibit distinct magmatic oscillatory zoning, indicating typical magmatic zircons (Figure 8a,b).
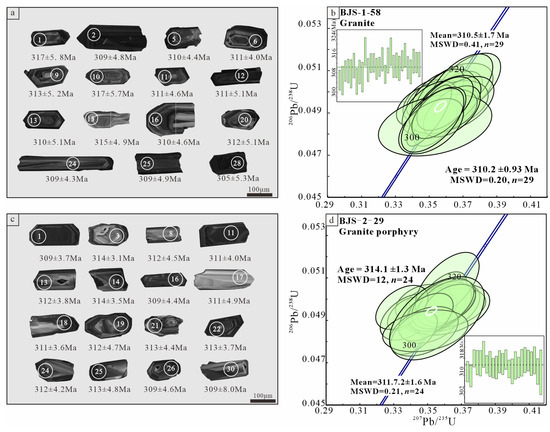
Figure 8.
(a) representative cathodoluminescence images of zircon grains from the granite, (b) LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon concordia diagrams for the granite from Baijianshan, (c) representative cathodoluminescence images of zircon grains from the granite porphyry, (d) LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon concordia diagrams for the granite porphyry from Baijianshan.
Zircons of granite (BJS-1-58) exhibit grain sizes of 400–1200 μm with aspect ratios of 2:1–7:1 (Figure 8b). Analytical results show Th = (53.66–452.81) × 10−6, U = (140–789) × 10−6, and Th/U ratios of 0.30–0.63. Thirty spot analyses yielded 29 concordant data points, producing a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 311 ± 1.7 Ma (MSWD = 0.41) and a concordia age of 310 ± 0.9 Ma (MSWD = 0.20).
Zircons from granite porphyry (BJS-2-29) range from 350 to 700 μm in size with aspect ratios of 2:1–4:1 (Figure 8d). Measured compositions include Th = (31.73–553.22) × 10−6, U = (90–726) × 10−6, and Th/U = 0.29–0.76. Twenty-four zircon grains were analyzed, and these zircons yield a weighted mean 206Pb/238U age of 312 ± 1.6 Ma (MSWD = 0.21) and a concordia age of 314 ± 1.3 Ma (MSWD = 12).
5.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements Compositions
Major and trace element data of the two intrusive from the Baijianshan deposit are presented in Supplementary Table S2. The granite exhibits high silica content (SiO2 = 73.79–76.86 wt%), potassium-rich (K2O = 3.30–4.35 wt%), alkali-rich (7.25–8.27 wt%), calcium-poor (CaO = 0.91–1.97 wt%), magnesium-poor (MgO = 0.06–0.19 wt%), low Fe2O3 content (1.34–2.77 wt%), and low Al2O3 content (10.5–12.65 wt%). The K2O/Na2O ratio ranges from 0.76 to 1.73 (average 1.28). All sample points lie within the granite field in the TAS diagram (Figure 9a). The A/CNK and A/NK values range from 1.00 to 1.10 and 1.14 to 1.40, respectively, and all samples fall within the peraluminous series field and plot on the I-type granite side (Figure 9b). The samples exhibit low Mg# values (19.47–28.56), and the Rittmann index (σ) are 1.65–2.18, classifying them as calc-alkaline rocks. In the w(K2O) versus w(SiO2) diagram, the samples mainly plot within the high-K calc-alkaline series field (Figure 9c). In the w(SiO2) versus AR diagram, the samples fall into the alkaline-calc-alkaline series field (Figure 9d).
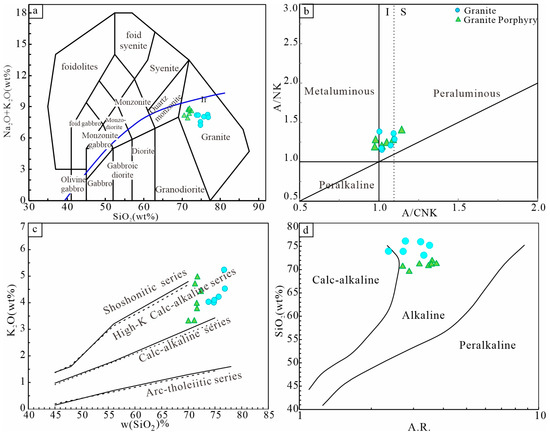
Figure 9.
TAS classification and rock series discrimination diagrams of the typical intrusive rock from Baijianshan: (a) TAS classification [48]; (b) A/CNK vs. A/NK [49]; (c) SiO2 vs. K2O [50]; (d) SiO2 vs. A.R. [51].
The granite porphyry samples exhibit relatively high SiO2 content with a narrow range (70.26%–72.63%). Key compositional features include w(Al2O3) = 14.07–15.78 wt% (average 14.86), w(K2O + Na2O) = 7.95–9.14 wt% (average 8.66), w(Fe2O3) = 2.17–3.18 wt% (average 2.52), w(MgO) = 0.36–0.52 wt% (average 0.41), and w(TiO2) = 0.22–0.37 wt% (average 0.37). The w(K2O + Na2O) ranges from 7.95% to 9.14% (average 8.64%), while the w(K2O)/w(Na2O) varies between 0.68 and 1.22 (average 0.92). These rocks show high total alkali content with comparable potassium and sodium levels, indicating slight sodium enrichment. The A/CNK and A/NK values range from 0.95 to 1.14 (average 1.03) and 1.17 to 1.41(average 1.26), respectively. The samples display low Mg# values (20.19–25.48) and Rittmann index (σ) values ranging from 2.32 to 2.82, primarily classifying as calc-alkaline rocks. In TAS, w(K2O)-w(SiO2), A/NK-A/CNK, and w(SiO2)-AR diagram, plots consistently classify the rocks as metaluminous high-K calc-alkaline series, plotting on the I-type granite field (Figure 9).
The total rare earth elements (REEs) in the Baijianshan granite are relatively low, with ∑REE = (133.94–189.15) ×10−6, (La/Yb)N = 3.51–8.79, and LREE/HREE = 4.92–9.03, showing a significant light–heavy rare earth element fractionation. The chondrite-normalized REE pattern shows LREE enrichment with a distinct negative Eu anomaly. (δEu = 0.23–0.41, Figure 10a). In the trace element spider diagram, it shows notable depletion in Ba, Nb, Sr, P, and Ti, with a slight enrichment in Zr and Hf, and clear enrichment in K, Th, and U (Figure 10b).
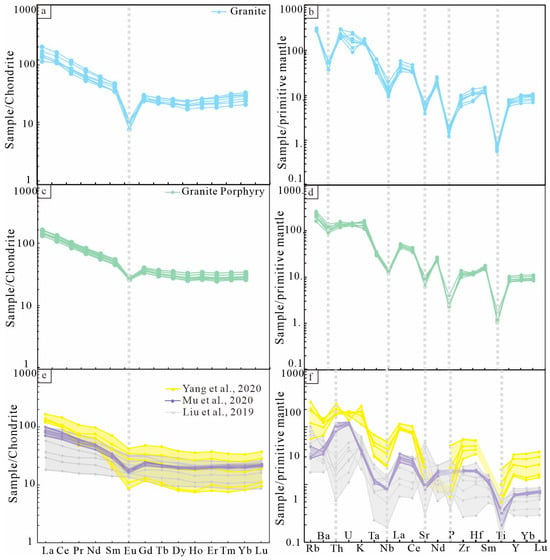
Figure 10.
(a) chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granite from Baijianshan area; (b) primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams of granite from Baijianshan area; (c) chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granite porphyry from Baijianshan area; (d) primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams of granite porphyry from Baijianshan area; (e) chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Yamansu volcanic rocks; (f) primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams of the Yamansu volcanic rocks. Normalizing values from [51]. Data are from [52,53,54].
The ∑REE in the granite porphyry is (160.13–198.25) × 10−6, (La/Yb)N = 4.79–5.62, and LREE/HREE = 5.31–5.88, with a noticeable light–heavy rare earth element fractionation. In the REE chondrite-normalized diagram, it also exhibits a right-leaning pattern (Figure 10c) with a negative europium anomaly (δEu = 0.56–0.75). In the trace element spider diagram, it shows strong depletion in Ba, Nb, Sr, P, and Ti, with slight enrichment in Zr and Hf, and noticeable enrichment in K, Th, and U (Figure 10d).
The trace element compositions of the two types of rocks show both differences and similarities. The granite exhibits a more pronounced negative europium anomaly compared to the granite porphyry. Both rocks are enriched in K, Th, U, Zr, and Hf and depleted in Sr, P, and Ti.
5.3. Zircon Hf Isotopes Compositions
This study conducted Lu-Hf isotopic analysis on geochronological samples from the Baijianshan granite (BJS-1-58) and granite porphyry (BJS-2-29) based on zircon U-Pb geochronology, with a total of 19 analysis points. The Hf isotope parameters were calculated using the weighted average age, and the data are presented in Supplementary Table S3. The n(176Hf)/n(177Hf) ratio for the granite ranges from 0.282807 to 0.282857, with zircon εHf(t) values ranging from +8.7 to +9.9, corresponding to a two-stage model age (TDM2) of approximately 624 to 555 Ma. The n(176Hf)/n(177Hf) ratio for the granite porphyry ranges from 0.282781 to 0.282856, with zircon εHf(t) values of +7.2 to +9.9, corresponding to a two-stage model age (TDM2) of approximately 673 to 552 Ma.
5.4. Fluid Inclusions
Based on petrographic observations, numerous fluid inclusions have been identified within quartz and calcite from the late quartz-sulfide stage of the Baijianshan Zn-polymetallic deposit. These inclusions are primarily classified by origin as primary and secondary inclusions. Based on phase state and composition at room temperature (25 °C), primary inclusions are classified into aqueous liquid-vapor inclusions and aqueous monophase inclusions (Figure 11). Quartz predominantly hosts aqueous liquid-vapor inclusions with sizes ranging from 1–5 μm (minor populations reaching ~10 μm), exhibiting vapor-to-liquid ratios (V/L) of 5%–10% and diverse morphologies including ellipsoidal, elongated, and irregular forms. In calcite, fluid inclusions occur exclusively as aqueous liquid-vapor types, typically distributed in clusters with subrounded, elongated, and irregular morphologies. These calcite-hosted inclusions display sizes concentrated within 1–5 μm and V/L ratios of 5%–30% (Figure 11).
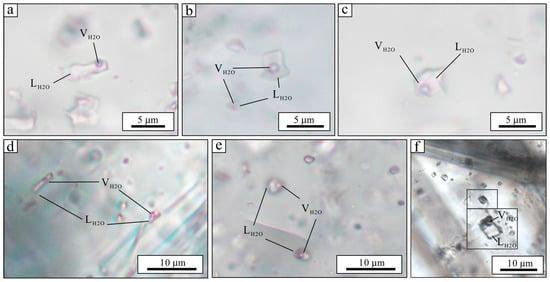
Figure 11.
Photomicrographs of representative fluid inclusions from different stages in the he Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit. (a–c) Microscopic images of aqueous liquid-vapor fluid inclusions in quartz; (d–f) microscopic images of aqueous liquid-vapor fluid inclusions in calcite.
Homogenization temperatures were measured for large-diameter primary aqueous liquid-vapor inclusions in quartz and calcite. The microthermometry data of fluid inclusions are summarized in Supplementary Table S4 and shown in Figure 12. Quartz-hosted inclusions in late quartz-sulfide stage homogenize at temperatures from 117 to 207 °C (average 157 °C). The Tm,ice vary from −4.5 to 0.5 °C (average −1.6 °C), corresponding to the salinities of 2.6–9.9 wt% NaCl eq (average 5.9 wt% NaCl eq). Microthermometric analysis of aqueous liquid-vapor inclusions in calcite yielded homogenization temperatures of 112 to 160 °C (average 143 °C), final ice-melting temperatures of −5.26 to −0.53 °C (average −1.8 °C), and calculated salinities of 0.53–5.26 wt% NaCl eq. (average 3.00 wt% NaCl eq).
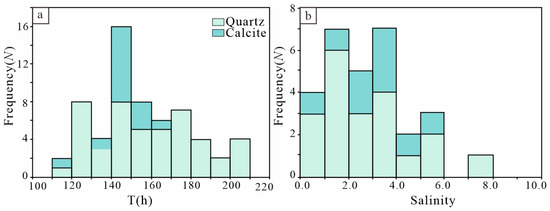
Figure 12.
(a) Histograms of the homogenization temperatures; (b) histograms of the salinities of fluid inclusions in the ore-stage quartz and calcite from Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit.
5.5. S-Pb-H-O Isotopic Compositions
Results of in situ sulfur isotope analysis for metallic sulfides, including pyrite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena from the Baijianshan Zn-Cu deposit are presented in Supplementary Table S5. The δ34S values of hydrothermal sulfides in ore range from −4.16‰ to 6.86‰ (average 3.90‰). Sulfur isotope compositions exhibit distinct ranges across sulfide species: Pyrite δ34S values range from −4.16‰ to 1.71‰ (average −1.31‰), while sphalerite displays higher values between 4.76‰ and 6.25‰ (average 5.69‰). Chalcopyrite yields a narrow isotopic range of 6.10–6.39‰ (average 6.22‰), with galena showing intermediate values from 4.22‰ to 6.86‰ (average 5.01‰).
The in situ Pb isotopic data of hydrothermal sulfides from the Baijianshan deposits are listed in Supplementary Table S6. In situ lead isotopic measurements of galena from this deposit yielded characteristic ratios approximating 206Pb/204Pb = 18.119, 207Pb/204Pb = 15.541, and 208Pb/204Pb = 37.901.
The δ18Oquartz and δDH2O values of quartz-sulfide veins from the Baijianshan deposits are listed in Supplementary Table S7. The δ18Oquartz values of quartz range from 8.68% to 9.81%. The δ18OH2O values obtained from this study were calculated using the quartz–water fractionation equation (1000lnαQ-W = 3.38 × 106/T2 − 3.40 [46]) and based on an average homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions of 153 °C. The calculated δ18OH2O values range from −6.97‰ to −5.84‰, and the measured δDH2O-VSMOW values range from −106.80‰ to −99.63‰.
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Magmatism and Mineralization
The oldest magmatic event in the HIAB occurred in the Middle Ordovician of the Early Paleozoic, related to the Early Paleozoic island arc evolution [16,55,56,57]. In the HIAB, the outcropped Middle Ordovician to Early Silurian amphibolite and medium-basic lava have formation ages concentrating between 469 and 447 Ma [16,26,33,56,58]. Magma activity in the Late Paleozoic was extremely intense within the study area, and many intrusions have now been dated with precise and reliable zircon ages (Supplementary Table S8). During the Carboniferous, large-scale intermediate-acid magmatic activity occurred in the HIAB, yielding U-Pb ages ranging from 352 to 330 Ma [34]. The zircon U-Pb ages of A-type granite and alkaline granite from the Nanshankou area are 352–351 Ma and 331 ± 2 Ma [59,60], respectively. The volcanic rocks are primarily andesites and rhyolites from the Yamansu Formation, with zircon ages ranging from 348 to 334 Ma [53,61]. Additionally, zircon ages of rhyolites and andesites from the Yamansu volcanic rocks in the southern part of Aqi Mountain are 324 ± 2 Ma and 319 ± 1 Ma, respectively [62]. The LA–ICP-MS zircon U–Pb age data of basalts and skarns from Yamansu skarn iron deposit yield ages of 324.4 ± 0.94 and 323.47 ± 0.95 Ma, respectively [62]. Previous studies have reported zircon ages for Late Carboniferous intrusions in the HIAB ranging from 320 to 307 Ma [21,32,63,64,65,66]. During the Early Permian, the region experienced widespread magmatic activity with zircon ages predominantly ranging from 298 to 288 Ma [67,68,69,70,71]. Recently, an amphibolite-peridotite dike was discovered in the Qincheng, Hami, with three sets of zircon U-Pb ages [72]: 298.4 ± 1.7 Ma, 297.7 ± 1.6 Ma, and 295.5 ± 1.6 Ma.
The weighted average zircon age obtained in this study for the granite in the Baijianshan mining area is 311 ± 1.7 Ma, which is closely consistent with that of the granite porphyry (312 ± 1.6 Ma). In the Xiaoshitouquan area, the zircon ages of granitic porphyry, monzogranite, and biotite granite from the Qiongkuduke Ag polymetallic deposit are 312 ± 1.7 Ma, 320 ± 1.5 Ma, and 314 ± 2.8 Ma, respectively [21]. These ages are consistent with the age range of the intrusions in the Baijianshan area. Currently, there are no reports on the metallogenic age of skarn-type and epithermal deposits in the study area. Therefore, the crystallization age of causative granite and the eruption age of hosting volcanic rocks are approximated as the metallogenic age. It is inferred that the metallogenic age of these deposits should be the same as or slightly later than the intrusive and eruptive ages. On the other hand, the metallogenic age of the Baijianshan skarn Zn-Cu deposit is roughly the same as that of the epithermal deposits in the Xiaoshitouquan area (e.g., Qiongkuduke and Tongshan).
6.2. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Causative Granitoids
6.2.1. Petrogenetic Types
Granites are traditionally divided into the I-type, S-type, M-type, and A-type based on the nature of source rocks and geological setting [73,74]. Determining the rock type of granite requires a comprehensive analysis of petrographic evidence [73]. The Baijianshan granites exhibit no observed A-type granite diagnostic alkaline mafic minerals such as riebeckite-arfvedsonite, aegirine-aegirine-augite, or fayalite [74]. In terms of trace elements, they exhibit relatively low concentrations of high field strength elements such as Ga, Zr, and Nb with the values of Zr + Nb + Ce + Y all below the lower limit of A-type granites, leading to the conclusion that it does not belong to the A-type granite category [75].
The Baijianshan granites contain approximately 5% hornblende; thus, they are preliminarily classified as I-type granite based on petrography. According to the previous studies, typical S-type granites are strongly peraluminous rocks that develop minerals such as cordierite and muscovite, with an A/CNK value significantly greater than 1.1 [76]. The two types of granites in the Baijianshan area have A/CNK < 1.1, classifying them as sub-aluminous to weakly peraluminous rocks. The dark minerals are primarily biotite and amphibole, and there is a positive correlation between Rb and Th. The magma source area is likely to be weakly peraluminous or sub-aluminous, which is distinctly different from the characteristics of S-type granites.
Previous studies have further confirmed that P2O5 decreases progressively during the evolution of I-type granitoid magmas, whereas it increases during the evolution of S-type granitoid magmas [77,78]. In the SiO2-P2O5 diagram, all the samples exhibit a clear negative correlation between SiO2 and P2O5, displaying typical characteristics of I-type granites. The granites in the Baijianshan mining area are high-silica, sub-aluminous to peraluminous, and belong to the calc-alkaline to alkaline series. Both petrographic and geochemical characteristics indicate that these rocks are I-type granites.
6.2.2. Source of Magmas
In situ zircon Lu-Hf isotopes can provide detailed records of isotopic composition changes during magma mixing and differentiation, and serve as an effective isotopic tracer method for identifying mantle magma end-members in terms of discriminating the magma source region [79,80]. Generally, higher εHf(t) values and corresponding younger model ages suggest that the granite may originate from the mixing of mantle material within the continental crust or the recycling of newly formed crust [81,82]. In contrast, lower εHf(t) values and corresponding older model ages indicate that the granite may have originated from deep melting or re-melting of ancient crust. I-type granites can be formed by the addition of mantle-derived material during crustal remelting [83,84], or by partial melting of mafic igneous or metamorphic rocks within the crust [85].
In this study, the εHf(t) values of the Baijianshan granites range from 8.7 to 9.9 and 7.2 to 9.9, respectively, with corresponding two-stage model ages (TDM2) being 808–693 Ma and 863–694 Ma. It is noteworthy that magmatic rocks in the Eastern Tianshan, regardless of lithology or age, consistently show positive Hf isotope values. For example, the εHf(t) values of the Xiaopu pluton and the Qincheng pluton (320–316 Ma) in the HIAB range from +8.0 to +13.8 and +10.8 to +16.7, respectively, with corresponding Hf model ages ranging from 822 to 450 Ma and 641 to 268 Ma, indicating that young crust served as the main source of the granite generation [66]. In addition, the εHf(t) values and TDM2 ages of the Omoertag alkaline granite (289 Ma) range from +8.7 to +12.5 and 600 to 430 Ma, respectively, suggesting that they may have been generated by partial melting of juvenile crust derived from depleted mantle material that had undergone crustal evolution [70]. Forming in the late stage of Early Carboniferous, alkali-feldspar granite from Nanshankou had εNd(t) values ranging from 5.66 to 6.12 and the Nd model ages are 600–620 Ma, which suggests that the magma may originate from the young crust [59]. Granitic intrusions at Balikun formed in the Early Permian (284–288 Ma) have variable Nd (εNd(t) = +1.92–+6.03) isotope compositions and young TDM model ages (0.56–0.75 Ga) suggest that they were derived from juvenile crustal sources, probably earlier arc intrusion.
The Baijianshan granites exhibit positive εHf(t) values and their similar crustal model ages (863–693 Ma), suggesting the young crust served as the main source for the granite generation. Combined with the occurrence of mafic rocks in the region, these young materials may be genetically linked to neoteric mantle-derived mafic underplating magmatism.
The intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan mining area show depletions in P, Ti, Nb, and Ta, indicating characteristics of continental crust (Figure 10b,d). The Sr contents in the granites and granite porphyries from the Baijianshan mining area are relatively low (80.9–217 ppm; average 144 ppm), which lie within the range between the depleted mantle (20 ppm) and lower crust (290 ppm) [86]. It is significantly lower than that of the enriched mantle (~1100 ppm; [87]), suggesting that these granites cannot be the product of partial melting of enriched mantle. Experimental petrological studies have shown that the Mg# of granites can be used to reflect the contribution of magma source region. Mg# values less than 40 represent melts derived from mafic lower crust, while Mg# values greater than 40 reflect melts predominantly sourced from the mantle [88]. The Mg# values of the Baijianshan granites range from 14.8 to 35.3 (with an average of 23.4), indicating no contribution of mantle-derived magma. In conclusion, the formation of the Baijianshan granites is mainly related to the juvenile lower crust, accompanied by the contribution of some mantle materials.
Ba is an element that is highly enriched in the subduction zone fluids, whereas Th is relatively inert in aqueous fluids [89]. Therefore, the high Ba/Th ratios (>300) typically indicate a significant contribution from subduction zone fluids to the magma source region [89]. The Ba/Th ratios of the granite porphyries and granites in the Baijianshan area range from 59.6 to 74.6 (average 64.6) and 10.2 to 23.2 (average 17.2), respectively. The relatively low Ba/Th ratios suggest that the contribution of subduction zone fluids to the magma source region is not significant. Generally, if the magma is formed by partial melting of the mantle influenced by the subduction plate fluids, it typically has a higher Sr/Ce ratio (>20) [90]. However, the Baijianshan granites exhibit relatively low Sr/Ce ratios ranging from 2.7 to 23.5 (average 10.9), indicating that the contribution of subduction zone fluids to the source region magma is not significant. In the magmatic arc environment, the addition of subducted sediments and slab-derived fluids to the magma can be identified through the mass fraction of Th values and the (Th)/(Ce), (Th)/(Yb), (Sr)/(Nd), and (Sr)/(Th) ratios [91]. Magmas that incorporate sediments typically have high Th and Ce contents and (Th)/(Yb) values, whereas the magmas influenced by slab-derived fluids tend to have high Sr contents. As seen from the (Sr)/(Th)-(Th)/(Ce) and (Sr)/(Nd)-(Th)/(Yb) diagrams, it is evident that the Baijianshan granites resulted from the incorporation of subducted sediments (Figure 13).
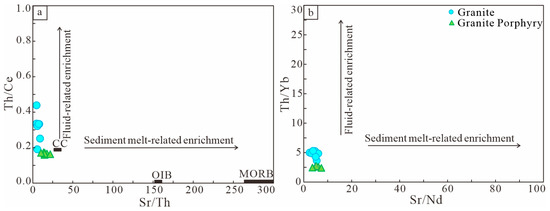
Figure 13.
Diagrams of (a) Sr/Th vs. Th/Ce; (b) diagrams of Sr/Nd vs. Th/Yb [91].
6.2.3. Fractional Crystallization
As the SiO2 content increases, the TiO2, Al2O3, TFeO, MgO, and P2O5 contents of the Baijianshan granites show a systematic decrease (Figure 14), indicating that these variations may be related to the fractional crystallization of dark-colored minerals (such as pyroxene, amphibole), Fe-Ti oxides, feldspar, and apatite. The samples exhibit varying degrees of negative anomalies in Ba, Sr, and Eu, suggesting the fractional crystallization of plagioclase and potassium feldspar during the magma evolution [73,92]. The depletion of P and Ti may be associated with the limited fractional crystallization of apatite and Ti-oxide minerals, while the low MgO and FeOT characteristics probably reflect the separation crystallization of magnesium-iron minerals (e.g., biotite).
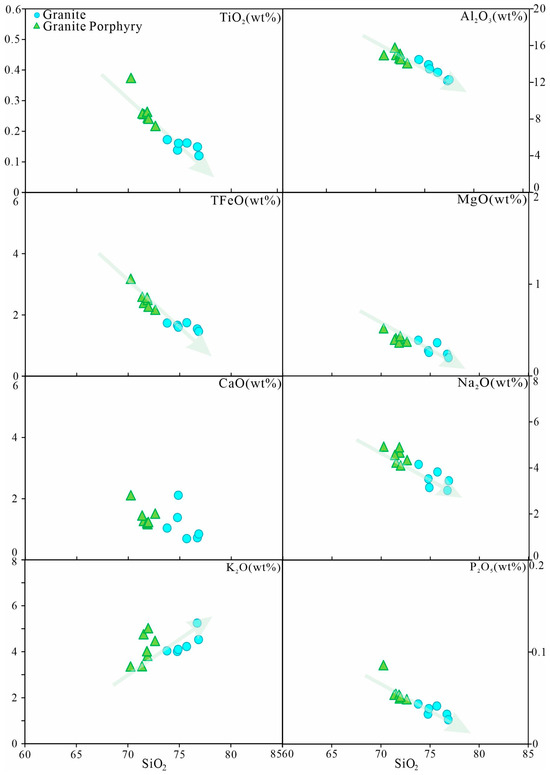
Figure 14.
Harker diagrams of major elements of intrusive rock from Baijianshan.
6.2.4. Tectonic Setting
Currently, there is significant debate regarding the genesis and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic intrusive rocks in the HIAB, with four main viewpoints being proposed: (1) continental rift [58,93], (2) back-arc basin [59,63,94,95], (3) island arc [65,96,97], and (4) post-collision [98,99]. During the Silurian-Carboniferous period (440–310 Ma), large-scale intermediate to acidic island arc magmatic activities occurred in the Halrik Mountains [16,55,62,99]. The tectonic evolution of the Halrik Mountain subduction-related orogenic belt generally underwent four stages: (1) the oceanic basin contraction–back-arc extension stage (Carboniferous), (2) oceanic basin closure–arc (continent)-continent collision stage (Late Carboniferous), (3) post-collision–extension and compression stage (Early Permian to Middle Jurassic), and (4) intracontinental–compression and recompression stage (Late Middle Jurassic to Late Cenozoic) [64].
The elemental geochemical characteristics of granite can reflect the tectonic environment in which it was formed [48,100,101]. The Baijianshan granites are enriched in large ion lithophile elements such as Rb, K, and Th, and depleted in high field strength elements such as Nb, Sr, and Ti, which is similar to the geochemical characteristics of typical island arc magmatic rocks. Moreover, Baijianshan granites are classified as I-type granite which is generally formed in the subduction setting. In the trace element Ta-Yb and Rb-(Y+Nb) tectonic discrimination diagrams, most samples fall into the volcanic arc granite area, with a small number falling into the post-collision granite and intraplate granite field (Figure 15a,b). The magma source region of Baijianshan granites may be strongly influenced by subduction processes.
The gneissoid-biotitic granite (311 ± 9 Ma) at Xiaopu formed in the extensional setting of back-arc [63]. The granite at Xiaopunan (312 ± 2 Ma) considered that the Omltag rock mass magma is formed in the island arc environment before the collision and is the product of the collision compression extension transition of the Hallik orogenic belt [102]. The granite from the Qiongkuduke Ag-Pb-Zn deposit (314–312 Ma) was formed in an island arc setting induced by the subduction of the Kanggurtag Ocean basin during the Late Carboniferous [21]. Previous studies suggest that the collision time in the Halrik area occurred approximately during the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian (310–289 Ma) [67,69,98,100]. The newly obtained zircon U-Pb ages of the Baijianshan granites in this study are 312–311 Ma, indicating that these granites formed in an extensional tectonic setting of back-arc basin during the subduction processes. In addition, the Baijianshan skarn deposit and epithermal deposits in the region have roughly contemporaneous mineralization ages [21,23]. Epithermal deposits generally form in subduction and back-arc extension tectonic settings rather than in a collisional setting, which also supports the formation of regional magmatic rocks in a subduction tectonic background.
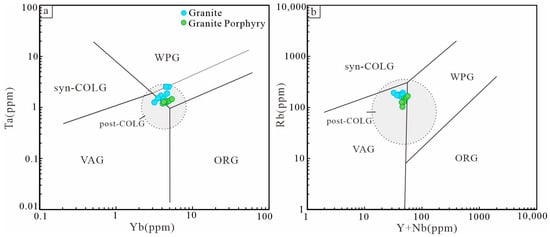
Figure 15.
Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Baijianshan granites: (a) Ta/Yb diagrams; (b) Rb/(Y+Nb) diagrams [48,103]. IAG: island arc granitoid; CAG: continental arc granitoid; CCG: continental collision granitoid; POG: post-orogenic granitoid; RRG: rift-related granitoid; CEUG: continental epeirogenic uplift-related granitoid; VAG: volcanic arc granitoid; syn—COLG: syn–collision granitoid; WPG: within-plate granitoid; ORG: ocean ridge granitoid; post—COLG: post-collision granitoid.
6.3. Source of Ore-Forming Components
The orebodies of the Baijianshan deposit are directly hosted in the skarns, which are in close contact with intermediate-acidic magmas. A large amount of garnet, wollastonite, and pyroxene are developed in the ores at early stage. In addition, the specularite and ilmenite in the oxide stage and quartz, calcite pyrite, and chalcopyrite in the quartz-sulfide stage are commonly observed. Such mineral assemblages show a typical alteration series of skarn-type deposits [6,7,8,9]. Therefore, the occurrence of orebodies and mineral assemblages indicate that the early ore-forming fluids may originate from the magmatic fluids, with progressive addition of meteoric water with time. Fluid inclusions are direct samples of ore-forming fluids preserved in minerals, which cannot only reflect the nature and evolution of ore-forming fluids, but also indicate the source of ore-forming fluids [44,104,105]. Abundant bi-phase aqueous inclusions are developed in the ore-stage quartz and calcite. The ore-forming fluids in the last stage belong to low-temperature (150–200 °C), low-salinity (0.18–7.17 wt% NaCl eq), and low-density (0.85–2.35 g/cm3) H2O-NaCl system, indicating the addition of meteoric water in the later stage. The H-O isotopic compositions of fluid inclusions can also effectively reflect the source of ore-forming fluids [46,106]. All the data points of H-O isotopic of ore-forming fluids in stage IV are located within the area between the meteoric water line and magmatic water in the H-O isotopic diagram (Figure 16), similar to that of typical skarn-type deposits in China, such as the Arqiale deposit (δ18OH2O = −5.2–−0.7‰, δDV-SMOW = −128—−109‰; [107]), the Xiaoyangchong iron deposit (δ18OH2O = −2.28–2.29‰, δDV-SMOW = −93.3–−74.4‰; [108]), and the Songyuan deposit (δ18OH2O = −6.39–1.41‰, δDV-SMOW = −85.6–−64.9‰; [108]). Accordingly, the observed H-O isotopic compositions for Baijianshan likely result from the mixing of magmatic fluids with meteoric water. Based on the geological, fluid inclusion, S-Pb isotopic compositions of sulfides and H-O isotopic compositions of quartz, it is believed that the early ore-forming fluids of the Baijianshan deposit were mainly magmatic fluids, and gradually mixed with meteoric water as the ore-forming process progressed, and eventually gradually transitioned to be dominated by meteoric water.
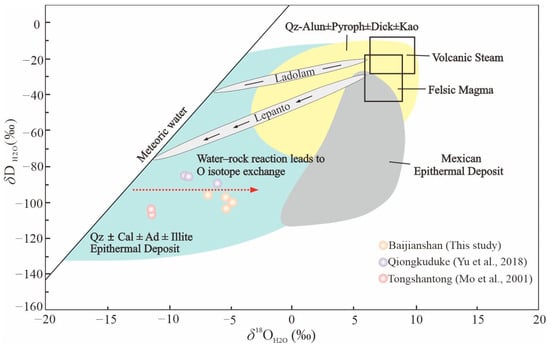
Figure 16.
δDH2O versus δ18OH2O plot of ore-forming fluids of the typical deposits in Xiaoshitouquan ore field [109]. The H-O isotopic data of Qiongkuduke and Tongshantong from [22,23].
Sulfur in the ore-forming fluids commonly have four sources: deep magmatic/mantle (generally δ34S ≈ −3‰ to 3‰; [110]), seawater sulfate (generally δ34S ≈ 20 ± 10‰; [111]), sedimentary reduced sulfur (generally δ34S as low as −40‰; [112]), and mixed sources (generally with a wide δ34S range). The in situ δ34S values of sulfides from the Baijianshan deposit exhibit a wide range from −4.16‰ to 6.86‰ (average 3.90‰). Given that the analyzed sulfides were not from the same sample, this variation may be attributed to differing contributions of heavy sulfur isotopes from the host strata, rather than disequilibrium sulfur isotope fractionation. Although the δ34S values of sulfides vary greatly, it may still effectively indicate the source of sulfur. The ores in the Baijianshan deposit contain abundant sulfides and minor sulfosalt minerals, without sulfate minerals, indicating reducing ore-forming environment [113,114]. Under the reducing environment, the δ34S values of sulfides are approximately equal to the total sulfur isotopic compositions (δ34SΣS) of the ore-forming fluids [113,114]. The in situ δ34S values of sulfides from the Baijianshan deposit are close to those of magmatic sulfur and significantly differ from those of seawater and biogenic sulfur (Figure 17). Given the direct occurrence of Zn-Cu orebodies within the contact zone between skarn and granites, it is suggested that the sulfur in the ore-forming fluids primarily originated from the magmatic sources. In addition, the in situ Pb isotopic date of galena in the ores are located within the area between the mantle and orogenic evolution curve (Figure 18), indicating that the lead originated from a mixed source of the mantle and crust. Combined geology and S-Pb isotopic data indicate that the ore-forming metals at Baijianshan were mainly derived from medium-acidic magmatic rocks, with a minor contribution from the host rocks.
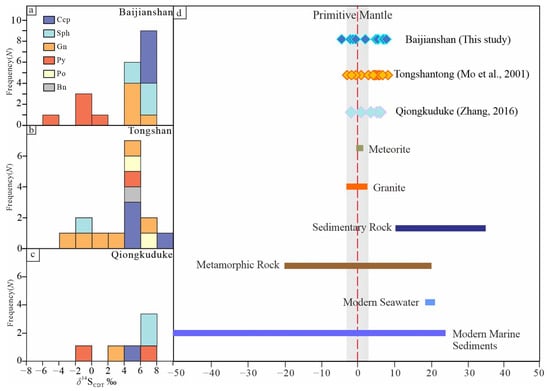
Figure 17.
(a) Frequency histogram of values of δ34S of the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit; (b) Frequency histogram of values of δ34S of the Tongshan Cu deposit; (c) Frequency histogram of values of δ34S of the Qiongkuduke Ag deposit; (d) The Zn-Cu-Ag polymetallic deposit in Xiaoshitouquan ore field with those from different natural geological settings. The ranges for natural geological settings are taken from [112]. For data of Qiongkuduke and Tongshantong from [22,115].
6.4. Precipitation Mechanism
Fluid boiling, fluid mixing, and water–rock reactions commonly alter the physicochemical properties (e.g., T, pH and fO2) of ore-forming fluids [116,117]. These processes are generally considered to be the principal mechanisms for the enrichment and precipitation of metallic minerals [118,119,120]. Regarding the skarn-type deposits, metal precipitation caused by fluid boiling and mixing is widely accepted [120,121]. For the skarn deposits containing low-temperature metallic minerals, the mixing between the magmatic fluids with high temperatures and salinities and groundwater/meteoric water with low temperatures and salinities is generally recognized as the key factor controlling the mineral precipitation [122,123,124]. The ore-forming elements of the Baijianshan deposit are dominated by Zn, accompanied by Cu, Ag, and Pb, which implies that the fluid mixing may have played a significant role in the precipitation of ore materials [122,123,124]. The ore-forming fluids during the main stage belong to low-temperature and low-salinity H2O-NaCl system. This indicates that the influx of meteoric water into the mineralization system likely triggered metal precipitation. In addition, the H-O isotopic compositions of ore-forming fluids during the mineralization stage also indicates the involvement of meteoric water into the hydrothermal system. Therefore, integration of geological, fluid inclusion, and H-O isotopic compositions indicates that the mixing of magmatic-hydrothermal and meteoric water reduces the stability of metal complexes and causes the precipitation of ore-forming elements [125,126]. In fact, the mixing of magmatic fluids with meteoric water has been widely recognized as the critical precipitation mechanism in studies of numerous skarn deposits [107,127,128,129]. According to the results from fluid inclusion and H-O isotope, Altunbey and Kilic [127] demonstrated that the ore-forming fluids in the Cavuslu iron deposit in eastern Turkey formed by mixing magmatic fluids and meteoric water during the retrograde alteration stage. The importance of fluid mixing in the metal precipitation has also been demonstrated for the Jiawula large Pb-Zn-Ag deposit in the Great Hinggan Mountains of Inner Mongolia and the Mengya’a Pb-Zn Deposit in Tibet [128,129]. Moreover, similar observations have been reported for the Arqiale skarn deposit in Western Tianshan, where previous studies also attribute the primary cause of ore precipitation to the mixing of magmatic fluids and meteoric water [107].
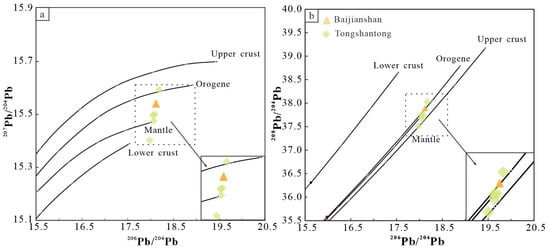
Figure 18.
Plumbotectonic model for galen from the Baijianshan Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit and Tongshantong deposits [130]. (a) 207Pb/204Pb−206Pb/204Pb model; (b) 208Pb/204Pb−206Pb/204Pb model.
6.5. Ore-Forming Process and Implications for Exploration
The HIAB is located in the eastern part of the Late Paleozoic Bogda-Halik Cu-Au-Ag polymetallic mineralization belt. It is a continental margin arc system formed during the subduction and consumption of the Paleo-Asian Ocean plate [28,29]. The Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Halik area was accompanied by multiple episodes of magmatic activity [16,56,58,59,66,68,69,70]. The small-scale intrusive rocks were mainly formed during the Late Ordovician to Early Silurian, in an island arc environment, resulting from the northward subduction of the Kanggurtage Ocean basin plate [16,26,33,55]. The widely distributed granites and potassic granites formed in the Late Carboniferous (320–308 Ma) back-arc basin during subduction [32,63]. Intense magmatic activity occurred during the Early Permian (290–270 Ma) and formed in a post-collisional extensional tectonic environment, leading to the development of complex rock types (Figure 19a).
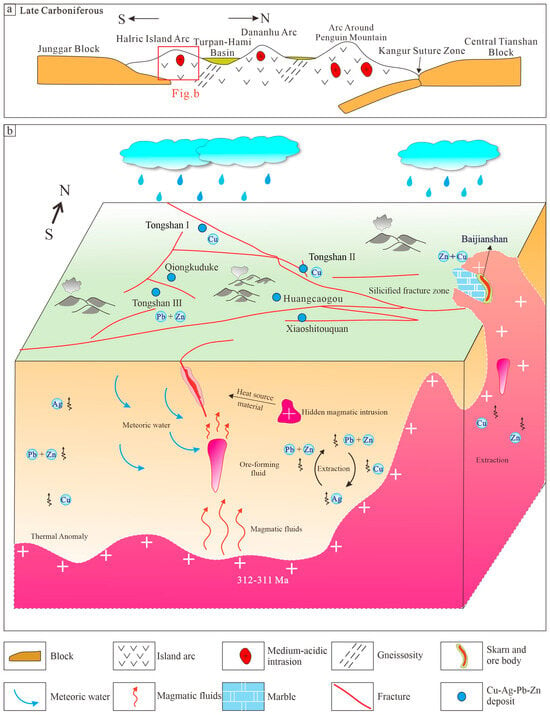
Figure 19.
(a) A schematic diagram for the Late Carboniferous tectonic evolution of the Harlik, Eastern Tianshan, (b) plumbotectonic model for sulfides from the Baijianshan and Tongshantong deposits in Xiaoshitouquan ore field.
In the Late Carboniferous collisional–extensional stage, deep faults were activated, intruding residual magma from the chamber to form mineralized Mesozoic intermediate-acidic granites. The magmatic hydrothermal fluids exsolved from the crystallized granites migrated into the contact zone between the Baijianshan granite and carbonates, forming the prograde skarn assemblages (garnet–tremolite–silica) and later retrograde skarn assemblages. The ore-forming elements in the high-temperature and high-salinity magmatic fluids migrated as Cl− complexes. with the hydrothermal system evolves, the meteoric water percolating along faults mixes with deep magmatic fluids, leading to major changes in the physical and chemical parameters of the ore-forming fluids. On the one hand, due to the sudden drop in temperature (quartz-sulfide stage homogenization temperature: 150–200 °C) and dilution of salinity (0.18–7.17 wt% NaCl eq), the stability of metal complexes was destroyed. On the other hand, the pH of ore-forming fluids increased due to the neutralization of acidic fluids by the carbonate host rocks, further promoting the precipitation of sulfides (Figure 19b).
The Baijianshan deposit has a close genetic relationship with the regional intermediate-acidic magmatic rocks. This study reveals that the formation age of the regional magmatic rocks is Late Carboniferous (314–310 Ma), which can approximately represent the age of Zn-Cu mineralization. This age is consistent with those of epithermal polymetallic deposits in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field. In addition, the Baijianshan deposit has a similar ore-forming element combination (Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag) and consistent H-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions to the adjacent epithermal polymetallic deposits, indicating that these deposits have similar sources of ore-forming fluids and material. In summary, the Baijianshan skarn Zn-Cu deposit and numerous epithermal Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposits (e.g., Qiongkuduke, Tongshantong, Huangcaogou, and Xiaobaishitou) in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field constitute a skarn-epithermal ore system (Figure 19b). The volcanic rocks in the Xiaoshitouquan ore field, located in the eastern part of the HIAB, are less eroded and has preserved a relatively complete epithermal system, during which silicification, sericite alteration, and vein-like Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn orebodies are widely developed (Figure 19b). To the northeast of this area, the large-scale exposure of the Halilik granite and occurrence of skarn mineral assemblages indicate a highen degree of erosion. Therefore, there is good potential to explore porphyry-skarn Cu polymetallic deposits at the deep part of the identified epithermal deposits within the Yamansu volcanic rocks. Furthermore, more attention should also be paid to the skarn-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposits in the contact zone between the Halilik granite and carbonates or calcareous volcanic rocks.
7. Conclusions
1. The granite and granite porphyry within the Baijianshan deposit yielded zircon U-Pb ages of 312–311 Ma. The granites at Baijianshan exhibit characteristic features of I-type granites. The magmas were primarily derived from the juvenile crust. These granites were formed in subduction-related back-arc basin.
2. The ore-forming fluids were dominated by the magmatic fluids at the early stage, with progressive input of meteoric water over time. The S-Pb isotopic compositions suggest that the ore-forming metals were sourced from medium-acidic magmatic rocks, with a minor contribution from the host rocks. Fluid mixing acts as the key mechanism triggering the precipitation of metallic minerals.
3. The Baijianshan skarn Zn-Cu polymetallic deposit and the adjacent epithermal polymetallic deposits in the Xiaobaishitou ore field show close relationship in time, space, and genesis, collectively constituting a skarn-epithermal ore system. This hypothesis indicates that the deep parts beneath the epithermal deposits within the Yamansu volcanic rocks possess good potential for exploring the porphyry-skarn deposits.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15111107/s1, Table S1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for the studied intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan skarn deposit. Table S2. Whole-rock major (wt.%) and trace element (ppm) compositions of the intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan skarn deposit. Table S3. Zircon Hf isotopic data for the intrusive rocks from the Baijianshan skarn deposit. Table S4. Microthermometric and salinity data of fluid inclusions from the Pianyanzi Au deposit. Table S5. Sulfur isotope compositions of sulfides from the Baijianshan deposit. Table S6. Lead isotopic compositions of galena in Baijianshan deposit. Table S7. H-O isotopes of hydrothermal minerals from the Biajianshan deposit. Table S8. Zircon U-Pb ages of volcanic rocks in Harlik mountains, eastern of Xinjiang.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. and S.Z.; data curation, F.C.; formal analysis, S.Z. and J.W.; funding acquisition, B.H.; project administration, S.Z.; validation, J.W. and B.H.; visualization, D.Z. and B.H.; writing—original draft, F.C.; writing—review and editing, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Copper-Polymetallic Deposit Reconnaissance at Tongshan, Hami City, Xinjiang (Project No. K24-XJ015) and the Incremental Copper-Polymetallic Deposit Reconnaissance at Tongshan, Hami City, Xinjiang (Project No. K25-XJ071).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the Chengdu University of Technology for their guidance in the field.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry copper systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 150, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenquist, J.W.; Lowenstern, J.B. The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature 1994, 370, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P.; Spell, T.; Rameh, E.; Razique, A.; Fletcher, T. High Sr/Y Magmas Reflect Arc Maturity, High Magmatic Water Content, and Porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au Potential: Examples from the Tethyan Arcs of Central and Eastern Iran and Western Pakistan. Econ. Geol. 2012, 107, 295–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D.A.; Berger, V.L.; Menzie, W.D.; Berger, B.R. Porphyry copper deposit density. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.R.; Deyell, C.L.; Waters, P.J.; Gonzales, R.I.; Zaw, K. Evidence for magmatic-hydrothermal fluids and ore-forming processesin epithermal and porphyry deposits of the Baguio district, Philippines. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 1399–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, D.F. The Contact Metasomatic Magnetite Deposits of Southwestern British Columbia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbi, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.H.; Chang, Z.S.; Mavrogenes, J. Fluid compositions reveal fluid nature, metal deposition mechanisms, and mineralization potential: An example at the Haobugao Zn-Pb skarn, China. Geology 2021, 49, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiranen, T.; Poutiainen, M.; Mänttäri, I. Geology, geochemistry, fluid inclusion characteristics, and U-Pb age studies on iron oxide-Cu-Au deposits in the Kolari region, northern Finland. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 30, 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Lin, W.W.; Bi, C.S.; Li, D.X. Basic Geological Characteristics of Skarn Deposits of China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. 1986, 14, 59–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jenner, F.E.; O’Neill, H.S.C.; Arculus, R.J.; Mavrogenes, J.A. The magnetite crisis in the evolution of arc-related magmas and the initial concentration of Au, Ag and Cu. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 2445–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.D.; Liang, H.Y.; Ling, M.X.; Zhan, M.Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Ireland, T.R.; Wei, Q.R.; et al. The link between reduced porphyry copper deposits and oxidized magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 103, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, M. Copper enrichment in arc magmas controlled by overriding plate thickness. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Lu, Y.; Kemp, A.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z.; Duan, L. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones. Geology 2015, 43, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Groves, D.I.; Shu, Q.; Gao, L.; Yang, L.; Qiu, K.; Wang, C.; et al. Tibetan ore deposits: A conjunction of accretionary orogeny and continental collision. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Cao, K. Post-collisional porphyry copper deposits in Tibet: An overview. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 258, 104954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.G.; Tu, Q.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Ren, Y.; Li, S.L.; Dong, F.R. Preliminary determination of the Early Paleozoic magmatic arc in the Karlik Mountains, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China-Evidence from zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granite bodies in the Tashuihe area. Geol. Bull. China 2006, 25, 923–927. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, T.Y.; Xu, S.Q.; Li, P.; Chen, B.X. The Geologic Character and Tectonic Significance of Paleozoic Volcanic Rocks in the Harlik Mountains, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geol. 2013, 31, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Xu, X.Y.; Ma, Z.P.; Chen, J.L.; Cui, F.L.; Zhu, X.H.; Sun, J.M. Geochemistry and Tectonic Setting of the Early Carboniferous Volcanic Rocks in the Eastern Section of the Bogda Orogenic Belt in Xinjiang. Geol. Explor. 2015, 51, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T.H.; Qing, K.Z.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, X.D.; Hui, W.D. Geological characteristics and exploration prospect of copper and Multi-Metal deposits in Xiaoshitouquan District, Eastern Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geol. 2002, 20, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, B.; Zhang, L.C.; Xu, X.W.; Sun, H. Geochemical characteristics of volcanic, sub-volcanic rocks in Xiaoshitouquan copper polymetallic deposit, eastern Tianshan, and its metallogenie setting. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Mao, Q.G.; Yu, M.J.; Fang, T.H.; Cheng, F.W. Geochemical Characteristics and Zircon U-Pb Ages of the Magmatite in the Qiongdukuke Ag-Pb-Zn Polymetallic Deposit of Xinjiang. Geol. Explor. 2017, 53, 270–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, J.P.; Yi, S.K.; Wang, X.D.; Li, J.A. Study on geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of Tongshan copper polymetallic deposit, Xingjiang. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2001, 15, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Mao, Q.G.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, F.W.; Fu, W.W. Characteristics of Ore-Forming Fluids and Their Geological Significance of OiongkudukeAg-Polymetallic Deposit in the Xiaoshitouquan Area of Eastern Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 3100–3111+3125. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.W.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.W.; Dong, S.Y.; Huang, B.F.; Zhang, D.; Song, M.W.; Liao, Z.Y.; Peng, L. Trace element characteristics of hydrothermal minerals and the genesis of the Tongshan copper deposit in the Xiaoshitouquan area, East Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Mineral. Petrol. 2025, 45, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.Y.; San, J.Z.; Kang, F. Geological Characteristics and Preliminary Analysis of Prospecting Potential for the Baijianshan No. I Copper-Zinc Polymetallic Deposit, Hami City, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous. Xinjiang Non-Ferr. Met. 2009, 32, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.H.; Chen, B.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.L. Early Paleozoic subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the Harlik pluton, Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.Y. Geological Characteristics of the Baijianshan Zinc Polymetallic Deposit in Hami City, Xinjiang. Xinjiang Non-Ferr. Met. 2015, 38, 77–79+82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Shu, L.S.; de Jong, K.; Charvet, J.; Cluzel, D.; Jahn, B.M.; Chen, Y.; Ruffet, G. Structural and Geochronological Study of High—Pressure Metamorphic Rocks in the Kekesu Section (Northwestern China): Implications for the Late Paleozoic Tectonics of the Southern Tianshan. J. Geol. 2010, 118, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Hao, J.; Zhai, M.G. Accretion Leading to Collision and the Permian Solonker Suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the Central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics 2003, 22, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.M. The Central Asia orogenic Belt and Growth of the continental Crust in the Phanerozoic. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ. 2004, 226, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, J.B.; Li, D.D. Mineralogical characteristics and petrogenetic significance of the amphibole in the Weiya V-Ti-magnetite deposit in the eastern Tianshan. Miner. Explor. 2016, 7, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.H.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, X.; Xi, R.G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, K. Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of Late Carboniferous Leucogranites in Harlik Area, Eastern Tianshan. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; He, X.F.; Li, J.T.; Yang, P.T.; Liang, B.; Su, H.; Yang, Y.D.; Liu, Y.Z.; Dai, Z.H. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Signficances of the Qincheng Tianshengquan Pluton in the Harlik Orogen of Eastern Xinjiang. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 36, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.W.; Huang, B.F.; Che, C.; Wu, L.N.; Cheng, J.P.; Chen, M.X. Detailed Investigation Report: Baijianshan Marble Mine and Zinc Polymetallic Mine in Hami City, Xinjiang. 2016; 1–133, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Jochum, K.P.; Weis, U.; Stoll, B.; Kuzmin, D.; Yang, Q.C.; Raczek, I.; Jacob, D.E.; Stracke, A.; Birbaum, K.; Frick, D.A.; et al. Determination of Reference Values for NIST SRM 610–617 Glasses Following ISO Guidelines. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2011, 35, 397–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Hanchar, J.M.; Peck, W.H.; Sylvester, P.; Valley, J.; Whitehouse, M.; Kronz, A.; Morishita, Y.; Nasdala, L.; Fiebig, J.; et al. Further characterisation of the 91500 zircon crystal. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2004, 28, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Alle, P.; Corfu, F.; Quadt, A.V.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand. Newsl. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, C.G.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.H. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, W.; Weis, D.; Williams, G.; Hanano, D.; Kieffer, B.; Scoates, J. Complete Trace Elemental Characterisation of Granitoid (USGS G-2, GSP-2) Reference Materials by High Resolution Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2006, 30, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichert, T.J. The Hf isotopic composition of zircon reference material 91500. Chem. Geol. 2008, 253, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichert, T.J.; Chauvel, C.; Albarè, F. Separation of Hf and Lu for high-precision isotope analysis of rock samples by magnetic sector-multiple collector ICP-MS. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1997, 127, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.M.; Vervoort, J.D.; Hanchar, J.M. Guidelines for reporting zircon Hf isotopic data by LA-MC-ICPMS and potential pitfalls in the interpretation of these data. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedder, E. Fluid inclusions. Rev. Mineral. 1984, 12, 1–644. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.C.; Gunther, D.; Liu, Y.S.; Ling, W.L.; Zong, K.Q.; Chen, H.H.; Gao, S.; Xu, L. Direct lead isotope analysis in Hg-rich sulfides by LA-MC-ICP-MS with a gas exchange device and matrix-matched calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 948, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.L.; Shepherd, T.J.; Durham, J.J.; Rouse, J.E.; Moore, G.R. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal. Chem. 1982, 54, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.N.; O’Neil, J.R.; Mayeda, T.K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniar, P.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, R.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis. Geol. Mag. 1969, 106, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Chen, T.; Sang, M.S.; Zhang, Y.J. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and geological significance of the Yamanu Formation volcanic rocks in the eastern segment of the East Tianshan. West-China Explor. Eng. 2020, 32, 93–96, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Muzhapaer, M.; Gong, X.K.; Nijiati, A. Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Volcanic Rocks of the Lower Carboniferous Yamansu Formation in the Jueluotage Area. Xinjiang Geol. 2020, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Liao, Q.A.; Fan, G.M.; Nie, X.M.; Wang, F.M. The discovery and tectonic implication of Early Carboniferous post-collisional I-type granites from the south of Karamaili in eastern Junngar. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.C.; Zhong, L.; Li, L.Q. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of quartz diorite in the Koumenzi area, Karlik Mountains, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China, and its geological significance. Geol. Bull. China 2006, 25, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Wang, K.Z.; Sun, G.H.; Mo, S.G.; Li, W.Q.; Yang, T.N.; Gao, L.M. Paleozoic active margin slices in the southern Turfan-Hami basin: Geological records of subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean platein central Asianregions. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.T.; He, X.F.; Liu, L.; Yang, P.T.; Liang, B.; Su, H.; Yang, Y.D.; Han, H.M.; Liu, Y.Z.; Dai, Z.H. Ordovician Tectonic Evolution of Harlik in Eastern Tianshan of Xinjiang: Constraints from LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks. Geoscience 2017, 31, 460–473. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Liao, Q.A.; Xiao, D.; Luo, T.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.F.; Wang, G.C. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Early Carboniferous A-Type Grainte in Harlik, Xinjiang. J. Geomech. 2016, 22, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.F.; Zhao, H.; Guo, R.L.; Wang, G.C.; Liao, Q.A. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Implications of Early Carboniferous A-Type Granites in Harlik Area from the Eastern Tianshan. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 2245–2263. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Liao, Q.A.; Chen, J.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Guo, D.B.; Hu, Z.C. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Volcanic Rocks from Yamansu Formation in the Eastern Tianshan, and Its Geological Significance. Earth Sci. 2012, 37, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Yu, J.J.; Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cui, Y.C.; Yu, J.L. Geochronology, geochemistry and genesis of Yamansu Formation volcanic rocks of southern Aqi Mountain in Jueluotage tectonic belt, eastern Tianshan of Xinjiang. Glob. Geol. 2018, 37, 88–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, T.; Zhang, Z.C.; Santosh, M.; Encarnacion, J.; Zhu, J.; Luo, W.J. Geochronology and geochemistry of submarine volcanic rocks in the Yamansu iron deposit, Eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China: Constraints on the metallogenesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.H. Dissertation submitted to Chinese Academy of Geological Science for Doctoral Degree. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Shu, L.S.; Santosh, M.; Zhao, X.X. Island arc-type bimodal magmatism in the eastern Tianshan Belt, Northwest China: Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and implications for the Paleozoic crustal evolution in Central Asia. Lithos 2013, 168–169, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Tong, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, W. Zircon U-Pb ages, genetic evolution and geological significance of Carboniferous granites in the Harlik Mountain, East Tianshan, Xinjiang. Geol. Bull. China 2018, 37, 790–804. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Shu, L.S.; Zhu, W.B.; Wang, C.Y.; Ma, R.S. Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Rocks from the Harlik Metamorphic Belt in Eastern Xinjiang and Its Geological Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2002, 76, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.S.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Wu, C.Z.; Tang, J.H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Feng, H.; Lei, R.X. Petrologic characteristics, zircon geochronology of dioritic enclaves in Early Permian Badashi monzogranite of East Tianshan Mountains and their geological implications. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2009, 28, 299–315. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhang, K.H.; Zhou, J. Geochronology and Geochemistry Characteristics of the Early Permian Monzogranite and Dioritic Enclaves of East Tianshan and Their Tectonic Implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 2334–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhang, K.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhou, J. Characteristics, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Permian Omoertage alkaline granites in Harlik area, Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2016, 35, 929–946. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Xing, W.W.; Jia, H.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhao, Z.N.; Ma, M.L.; Guo, S.E. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Tectonic Significance of Southern Xiamaya Granite in Harlik Area, Dongtianshan Mountain. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 40, 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.L.; Ma, H.D.; Zhu, B.Y.; Qiu, L. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics, and tectonic implications of the early Permian ultrabasic dykes in the Harlik Mountain, east Tianshan, Xinjiang. J. Geomech. 2025, 31, 156–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yang, J.H.; Zheng, Y.F. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, B.W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos 1999, 46, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 1998, 45, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichavant, M.; Montel, J.M.; Richard, L.R. Apatite solubility in peraluminous liquids: Experimental data and an extension of the Harrison-Watson model. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh Earth Sci. 1992, 83, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, G.J.; Qi, C.S. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I- and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of subducted flat-slab? Lithos 2007, 96, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Gao, S. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 185–220. [Google Scholar]
- Benbassat, M.; Carlson, R.W.; Puri, V.K.; Davenport, M.D.; Schriver, J.A.; Latif, M.; Smith, R.; Portigal, L.D.; Lipnick, E.H.; Weil, M.H. Pattern-based interactive diagnosis of multiple disorders: The MEDAS system. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, 2, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.X.; Hou, Z.Q.; Niu, Y.L.; Dong, G.C.; Qu, X.M.; Zhao, Z.D.; Yang, Z.M. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet. Lithos 2007, 96, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.I.S.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Foster, G.L.; Paterson, B.A.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hergt, J.M.; Gray, C.M.; Whitehouse, M.J. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf-O Isotopes in Zircon. Science 2007, 315, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Richards, S.W. Geodynamic significance of S-type granites in circum-Pacific orogens. Geology. 2008, 36, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; Stephens, W.E. Origin of infracrustal (I-type) granite magmas. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh Earth Sci. 1988, 79, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, R.K.; Hart, S.R. Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 231, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhai, M.G. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic lamprophyre dykes from the Taihang Mountains, North China, and implications for the sub-continental lithospheric mantle. Geol. Mag. 2003, 140, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Encarnación, J.; Xue, C.J.; Duan, S.G.; Zhao, Z.D.; Liu, J.L. Petrogenesis of the Kekesai composite intrusion, western Tianshan, NW China: Implications for tectonic evolution during Late Paleozoic time. Lithos 2012, 146, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, J.D. Petrogenesis of the basalt-andesite-dacite association of Grenada, Lesser Antilles island arc, revisited. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1995, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Eggins, S. Subduction Zone Magmatism; Blackwell: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead, J.D.; Eggins, S.M.; Johnson, R.W. Magma Genesis in the New Britain Island Arc: Further Insights into Melting and Mass Transfer Processes. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 1641–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Liu, X.J.; Yu, L.J.; Yu, L.J.; Wang, J.G. Highly fractionated origin and magmtic-hydrothermal evolution of the Kampa leucogranites in the Tethyan Himalaya. Nanjing Univ. Nat. Sci. 2020, 56, 800–814. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.Q.; Xia, Z.C.; Xue, X.Y.; Li, X.M.; Ma, Z.P.; Wang, L.S. Carboniferous Tianshan igneous megaprovince and mantle plume. Geol. Bull. China 2004, 23, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Yuan, C.; Long, X.P.; Sun, M.; Huang, Z.Y.; Du, L.; Wang, X.Y. Carboniferous Bimodal Volcanic Rocks in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Evidence for Arc Rifting. Gondwana Res. 2017, 43, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, M.; Yuan, C.; Long, X.P.; Jiang, Y.D.; Li, P.F.; Huang, Z.Y.; Du, L. Alternating Trench Advance and Retreat: Insights from Paleozoic Magmatism in the Eastern Tianshan, Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Tectonics 2018, 37, 2142–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Badarch, G.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Qin, K.; Wang, Z. Palaeozoic Accretionary and Convergent Tectonics of the Southern Altaids: Implications for the Growth of Central Asia. J. Geol. Soc. 2004, 161, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Yang, H.; Jia, X.; Sang, M.; Abuduxun, N.; Liu, Y. Early Carboniferous Rifting of the Harlik Arc in the Eastern Tianshan (NW China): Response to Rollback in the Southern Altaids? Am. J. Sci. 2022, 322, 313–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Shu, L.S. Features of the post-colisional tectono-magmatism and geochronological evidence in the Harlik Mt., Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S.; Xiao, W.J.; Xu, Y.G.; Long, X.P.; Zhao, G.H. Post-Collisional Plutons in the Balikun Area, East Chinese Tianshan: Evolving Magmatism in Response to Extension and Slab Break-Off. Lithos 2010, 119, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Gu, L.X.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Wu, C.Z.; Tang, J.H.; San, J.Z.; Li, G.G.; Li, Z.H. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Permian alkaline granite and quartz-syenite assemblage in Harlik Mountains, XinJiang. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 3182–3196. [Google Scholar]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature. 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.T.; Ma, Y.C.; Li, S.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.J. Geochemical Characteristics and Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Omltag Massif in the Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Mineral. Petrol. 2020, 40, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.X.; Lu, H.Z. Validation and representation of fluid inclusion microthermometric data using the fluid inclusion assemblage (FIA) concept. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, G.X.; Steel-Maclnnis, M. Fluid Inclusions Studies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–412. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Grove, D.I. Orogenic gold: Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos 2015, 233, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.W.; Zou, H.; Bagas, L.; Shen, Y.F.; Shu, Z.P.; Su, J.; Liang, Q.D.; Wang, C.S.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, H. A newly identified Permian distal skarn deposit in the Western Tianshan, China: New evidence from geology, garnet U–Pb geochronology and S–Pb–C–H–O isotopes of the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 143, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Li, W.; Wang, K.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Han, C.S.; Yang, Y.L. Study of ore-forming fluid and ore forming age of skarn-type iron ore in the Fanchang area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 96, 1297–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Gu, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Song, M.; Shu, Z. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of tabei: A newly identified intermediate-sulphidation epithermal Pb-Zn deposit adjacent to low-sulphidation au deposit in the tulasu basin, Chinese western Tianshan. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussidon, M.; Lorand, J.P. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-eastern Pyrenees, France): Anion microprobe study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holser, W.T.; Kaplan, I.R. Isotope geochemistry of sedimentary sulfates. Chem. Geol. 1966, 1, 93–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, 2nd ed.; Barnes, H.I., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 509–567. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R. The Discussion of the Metallogenic Characteristics and Genesis of the QiongKuduke Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit in Hami, Xinjiang, China. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, S.E.; Ohmoto, H. Chemical evolution and mineral deposition in boiling hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Jones, A.E.; Bowell, R.J.; Migdisov, A.A. Gold in solution. Elements 2009, 5, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.X.; Liu, L.; Dong, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, K.; Li, B.H. Immiscibility during mineralization of Yinan Au-Cu-Fe deposit, Shandong Province: Evidence from fluid inclusions and H-O isotopes. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.Z. Fluids immiscibility and fluid inclusions. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Xie, G.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Zheng, J.H. Mineralogy, Fluid Inclusion, and Stable Isotope Studies of the Chengchao Deposit, Hubei Province, Eastern China: Implications for the Formation of High-Grade Fe Skarn Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 325–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Fan, H.R.; Pan, J.Y.; Chi, Z.; Cui, J.M. Progress and Prospect of Fluid Inclusion Research in the Past Decade in China (2011–2020). Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2021, 40, 802–818. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, D.F.; Wang, C.M.; Shen, D.L. Ore genesis of the Weibao lead-zinc district, Eastern Kunlun Orogen, China: Constrains from ore geology, fluid inclusion and iso-tope geochemistry. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 1209–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.C.; Deng, J.; Shu, Q.H.; Li, G.J.; Cui, X.L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.F. Geology, fluid inclusion and stable isotopes (O, S) of the Hetaoping distal skarn Zn-Pb deposit, northern Baoshan block, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 90, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.H.; Chang, Z.S.; Hammerli, J.; Lai, Y.; Huizenga, J.M. Composition and Evolution of Fluids Forming the Baiyinnuo’er Zn-Pb Skarn Deposit, Northeastern China: Insights from Laser Ablation ICP-MS Study of Fluid Inclusions. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Tan, J.; Qiu, K.F.; Fu, J.M.; Cheng, X.H.; Li, F.; Yang, X.L. Fluid Inclusion Characteristics of Zhouwu Cu-Polymetal Deposit, Yingde, Guangdong Province. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2017, 36, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Tan, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; He, D. Inclusion features and geological significance of the Tonglüshan skarn-type copper-iron (gold) deposit in Daye, Hubei. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Altunbey, M.; Kilic, A.D. Fluid inclusion and oxygen isotope studies in garnets related to cavuslu Skarn iron mineralization, East Turkey. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 149, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Gu, X.X.; Tang, J.X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, W.B.; Jing, L.B.; Xiang, H.Y. Source and characteristics of ore-forming fluids in the Mengya’a Pb-Zn deposit, Tibet. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2011, 38, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Duan, D.F.; Xiong, S.F. Fluid origin and evolution of the Ruanjiawan W-Cu-(Mo) deposit from the Edong District in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt of China: Constraints from fluid inclusions and H-O-C-S isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics-the model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).