A Review on Lithium Extraction Processes from Spodumene and Resource Utilization of the Generated Lithium Slag
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Lithium Resources
2.1. Forms of Lithium
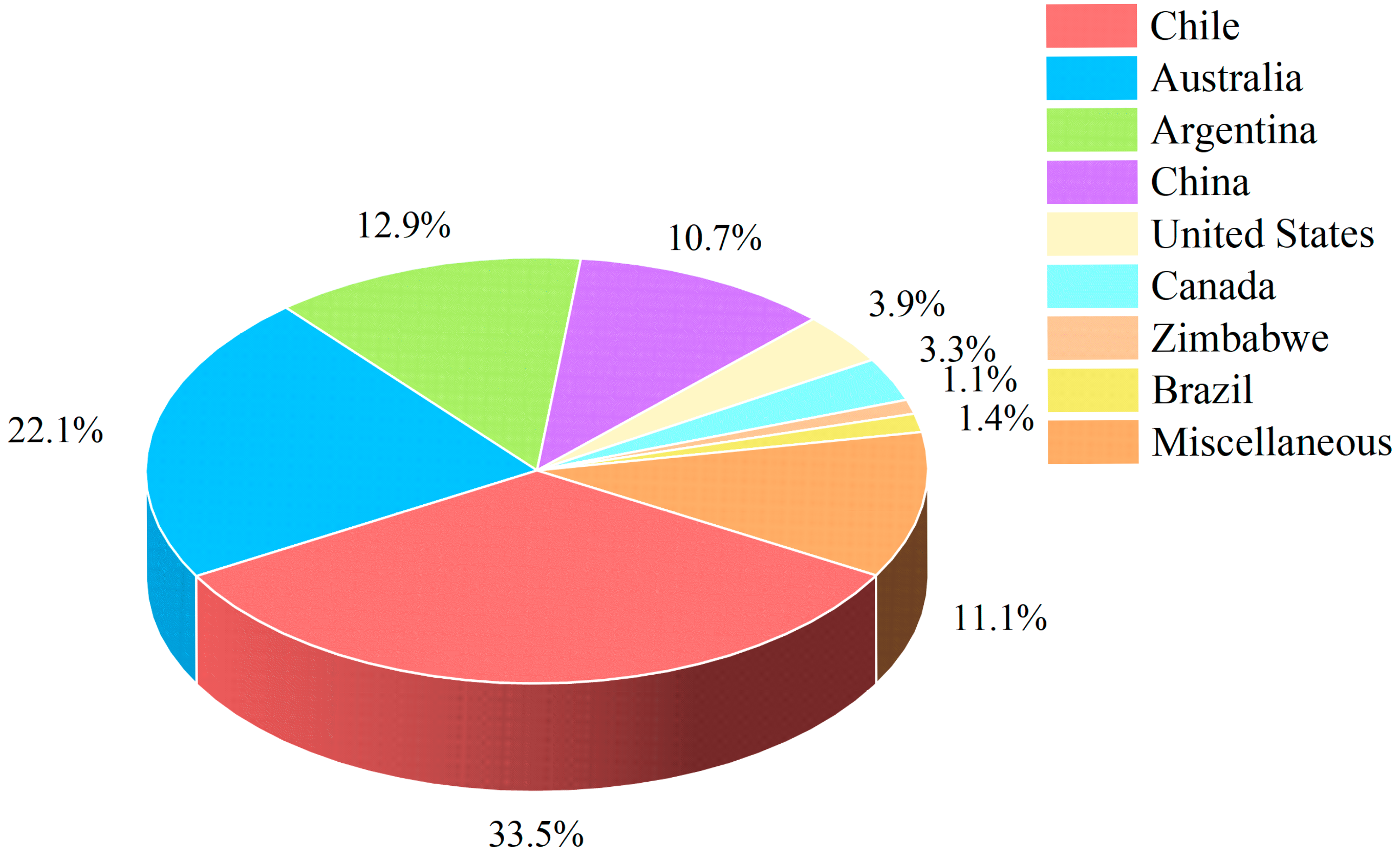
2.2. The Distribution of Spodumene Ore
3. The Main Source of Lithium Slag
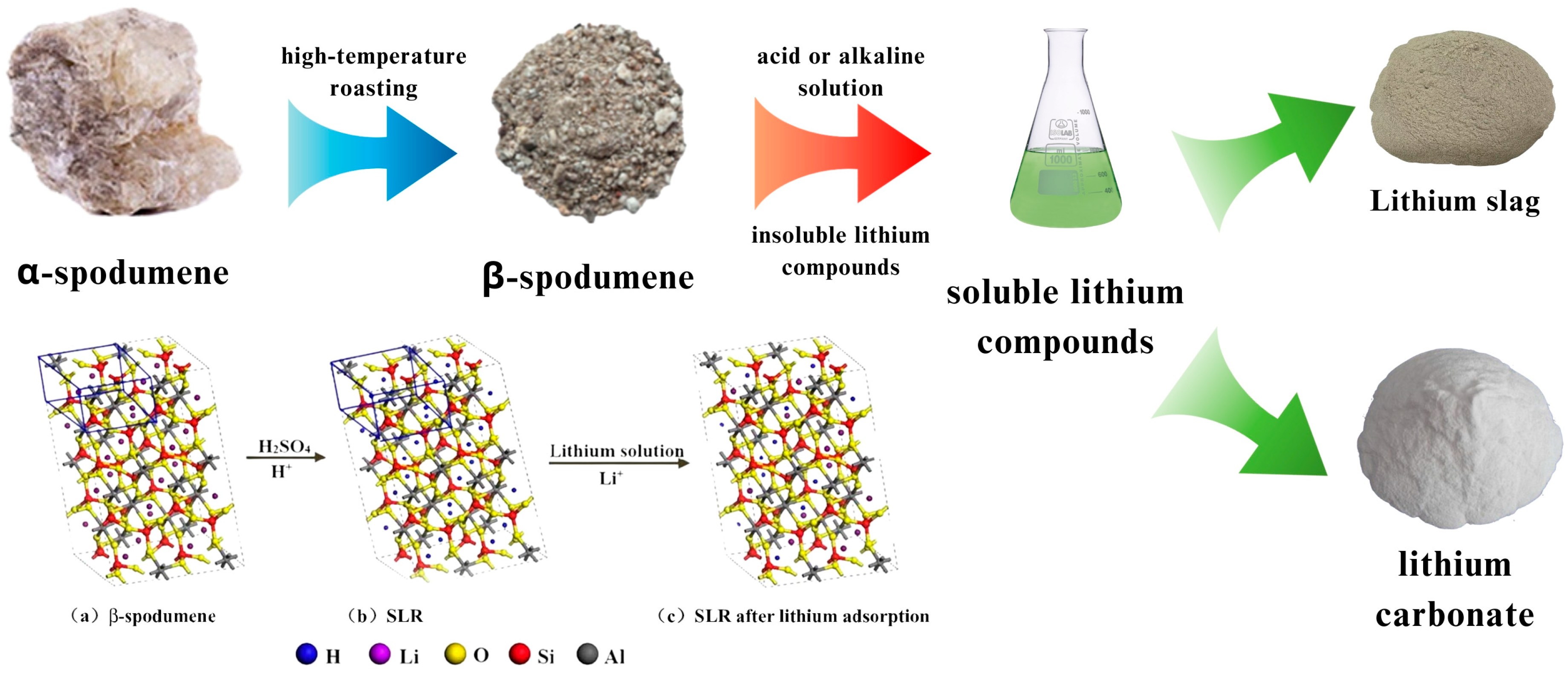
3.1. Acid Process
3.2. Alkali Method
3.3. Salt Roasting Method
3.4. Chlorination Method
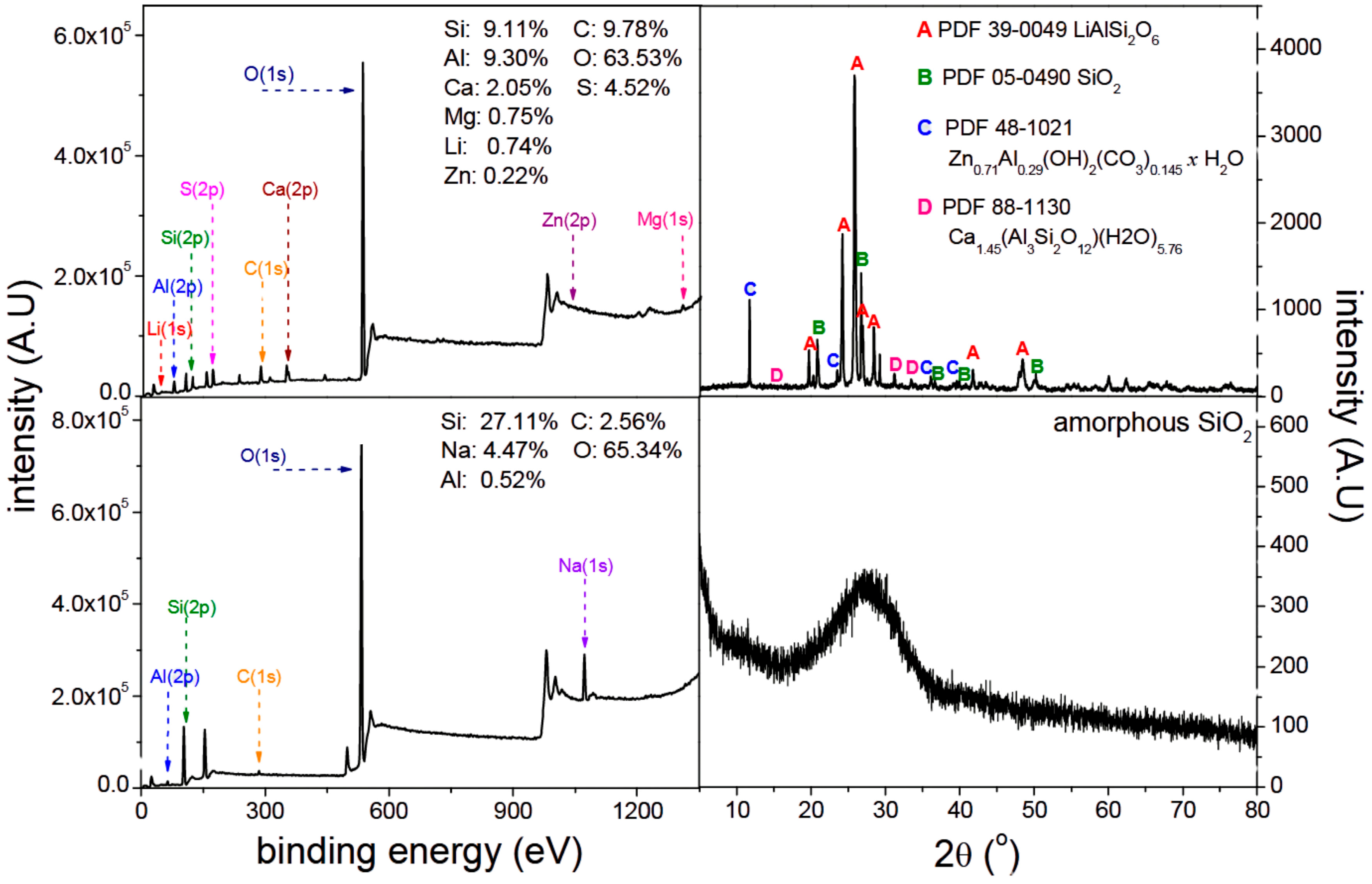
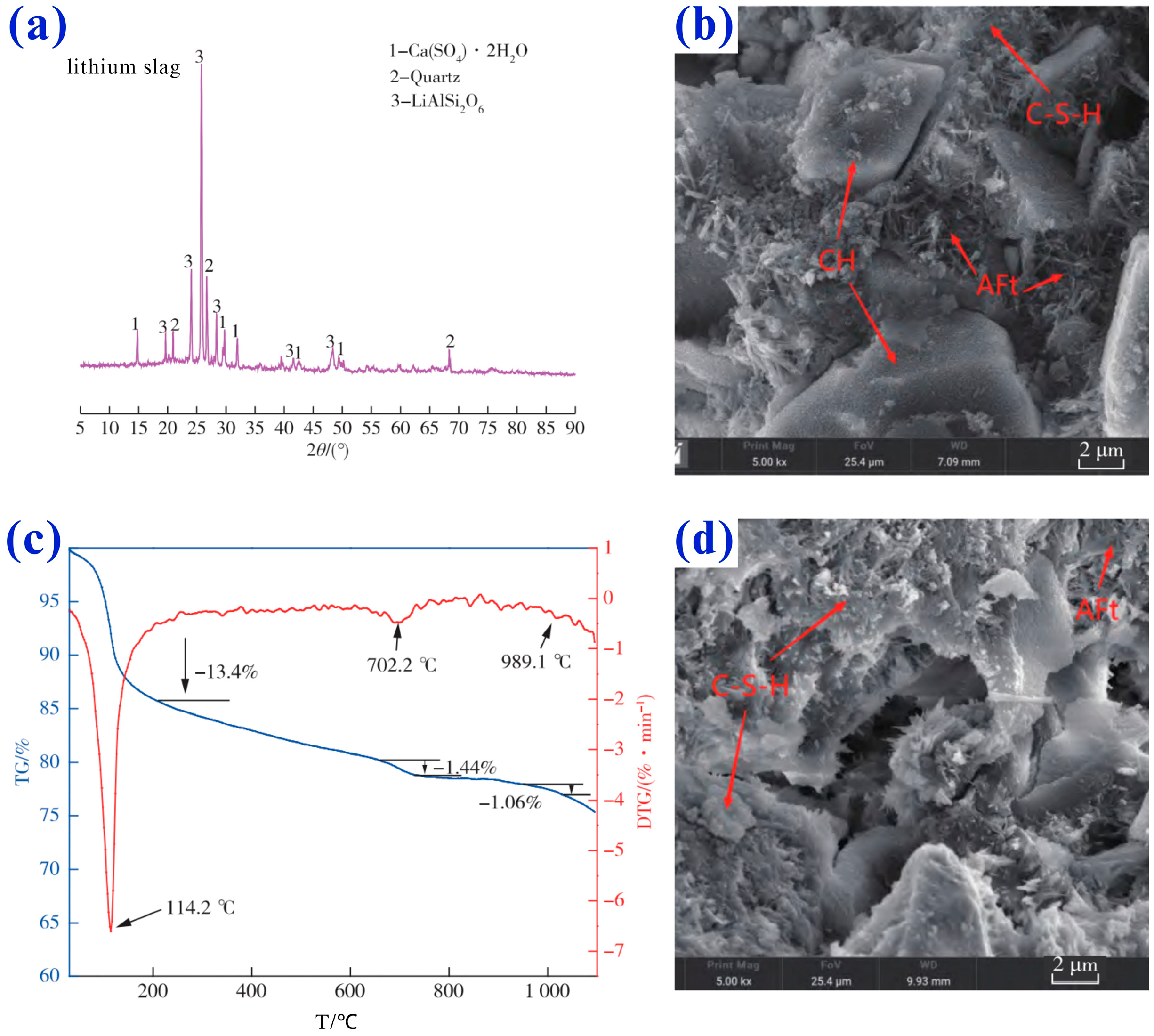
4. Chemical Composition and Mineralogical Characterization of Lithium Slag
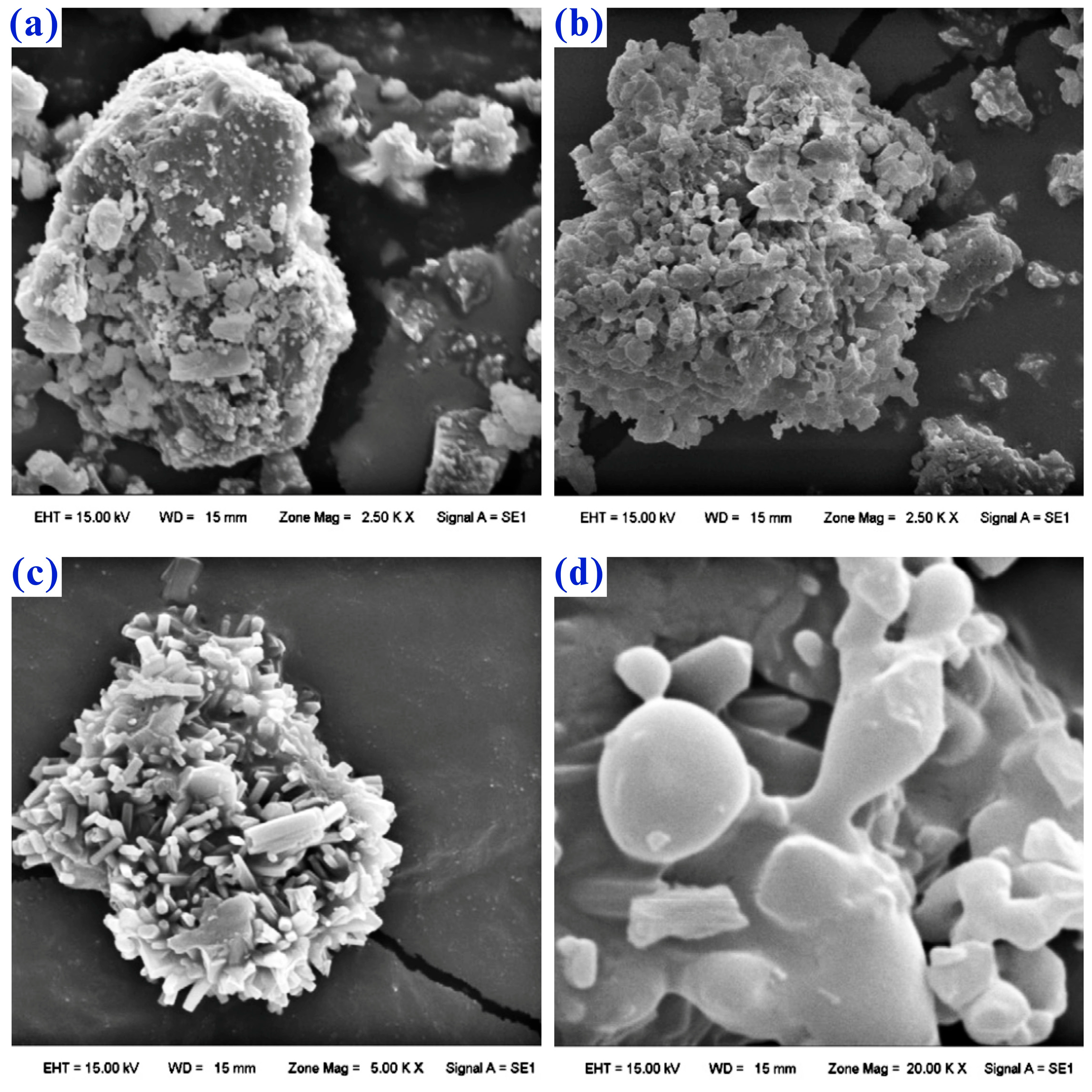
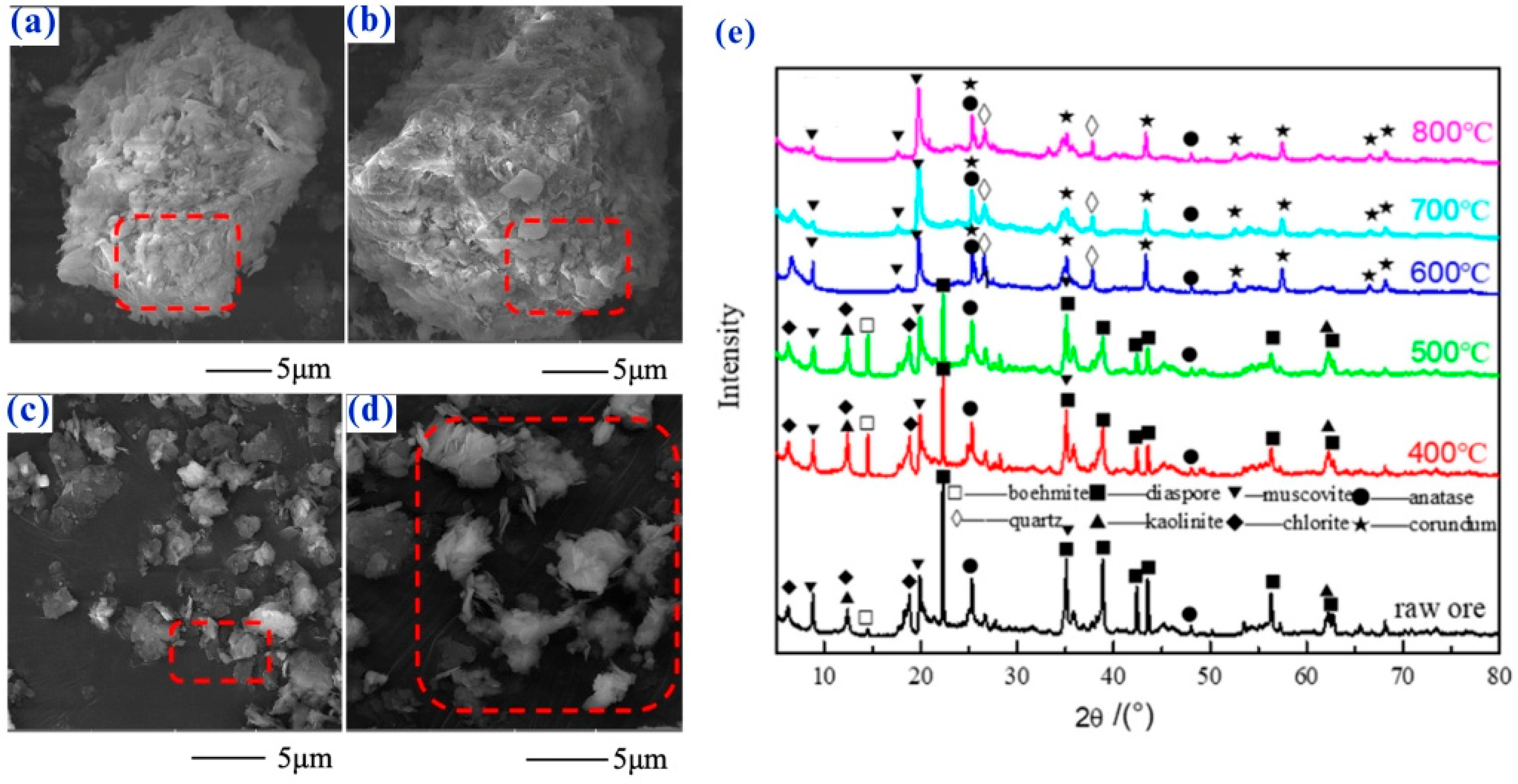
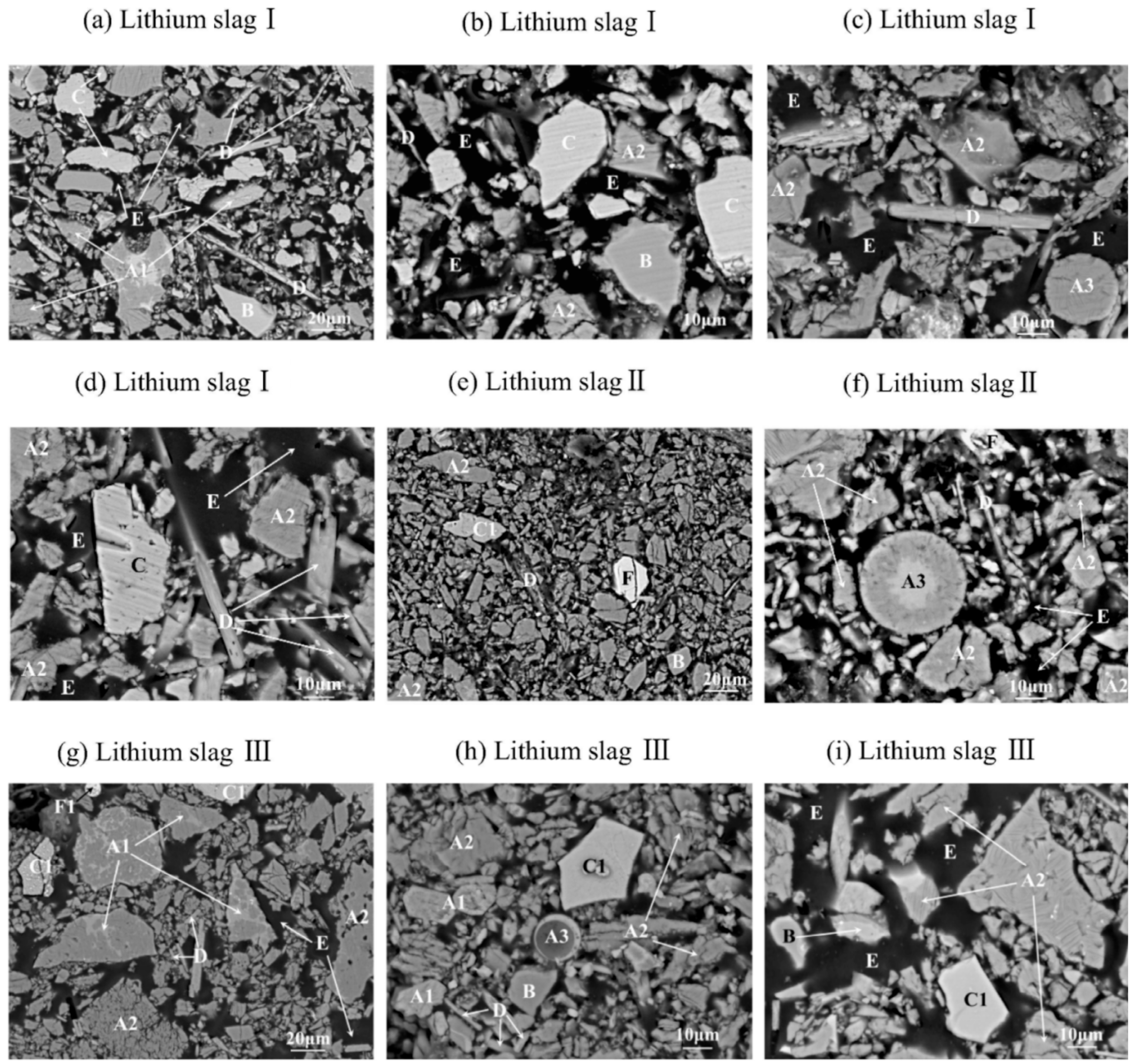
4.1. Mineralogical Characterization of Lithium Slag
4.2. Chemical Composition of Lithium
5. Resource Utilization Scheme of Lithium Slag
5.1. Gypsum
5.2. Silicon–Aluminum Powder
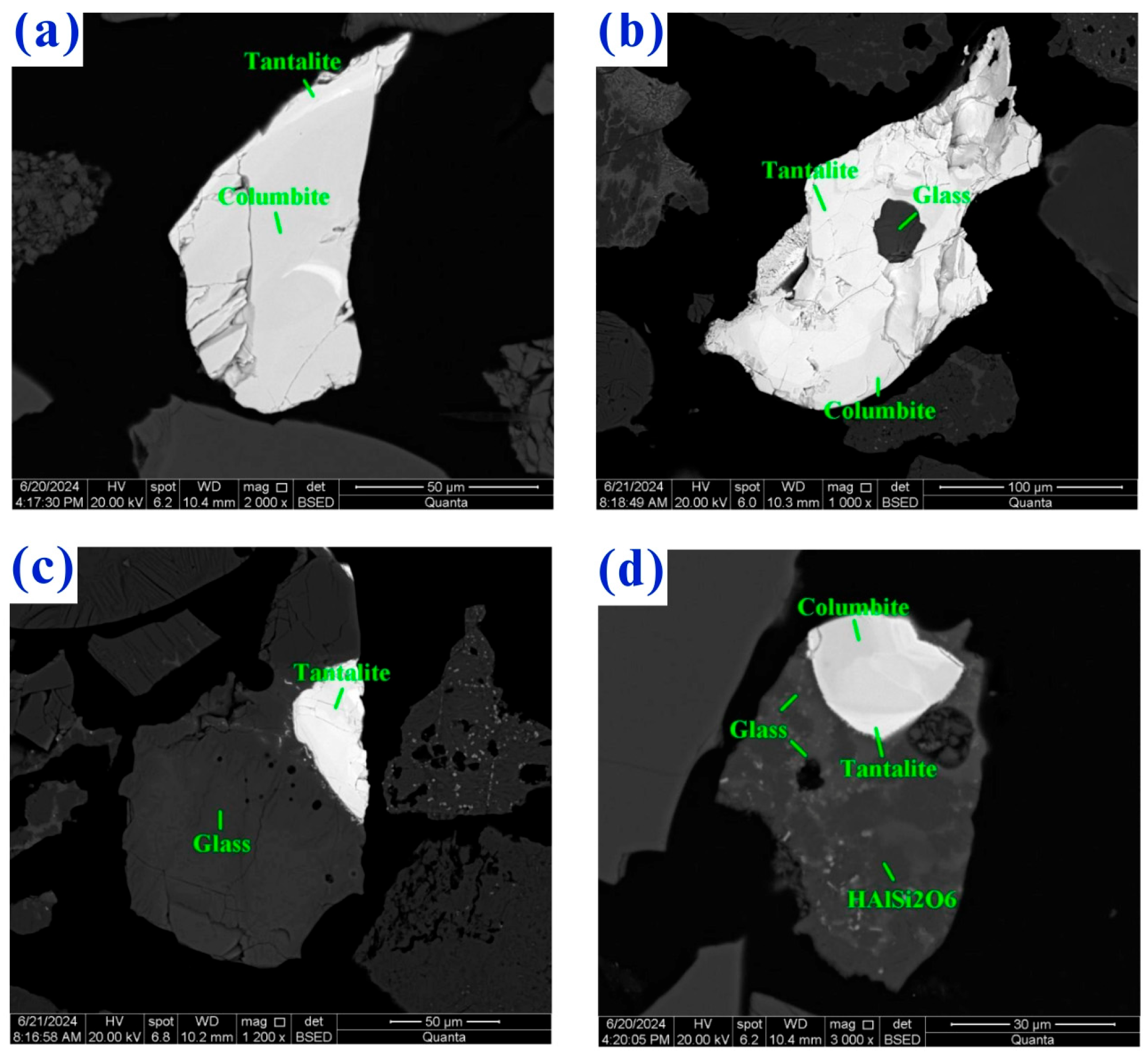
5.3. Fine-Grained Tantalum Concentrate Sludge
5.4. Challenges Faced by the Application of the Lithium Slag Resource
6. Conclusions and Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, R.Q. Research on the Synergistic Effect of Continuous Mergers and Acquisitions of Enterprises from the Perspective of Resource Allocation—Take Tianqi Lithium as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi University of Finance & Economics, Taiyuan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.Y. Synthesis of Aluminum Salt Adsorbent by Solvothermal/Hydrothermal Method and Its Lithium Extraction Performance. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.L.; Cao, Z.Q.; Liu, R.Q.; Song, Y.F.; Sun, W. Advances in Spodumene Beneficiation and Metallurgical Technologies. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2025, 77, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Sun, X. Lithium Material Flow Analysis in International Trade: A Life Cycle Perspective. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 35, 1362–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, K.; Hansdóttir, S.T.; Habib, H. Critical Metals for Electromobility: Global Demand Scenarios for Passenger Vehicles, 2015–2050. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.-M. Is Lithium the New Gold? Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dai, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, S. Research and Exploration Progress on Lithium Deposits in China. China Geol. 2020, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.Q.; Zhou, N.; Nouman, N.M.; Cui, L.; Yin, C.X. Classification and Progress of Extraction Technologies for Nonferrous Metal Resources. Sci. China Chem. 2025, 68, 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Yue, B.; Meng, B.B.; Cheng, L.Y.; Zhang, M.Y. Physicochemical Properties Analysis of Leaching Slag Generated in the Process of Lithium Salt Production from Lepidolite. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2025, 19, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.Z.; Lin, L.P.; Cheng, S.P.; Wang, X.; Guobiao, L.; Wang, D. Research Progress on the Preparation of Lithium Slag Lightweight Aggregate. Mod. Chem. Res. 2025, 15, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Yang, S.Q.; Che, C.Y.; Ma, R.T. Research on the Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Alkali-Activated Lithium Slag-Based Composite Paste Backfill Material Using RSM-BBD. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2025, 42, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.M.; Sun, J.R.; Liu, C.P.; Xian, W.; Wang, W.Q.; Luo, L.T.; Li, S. Study on Sintering Behavior and Properties of Lithium Slag-Based Foamed Ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 617, 122499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.L.; Li, J.R. A Brief Analysis of China’s Industrial Solid Waste Resources and Phosphogypsum Utilization Policy. Chem. Eng. Manag. 2025, 13, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Wu, S.M.; Chen, L.T.; Fan, H.S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zeng, L.X. Multiple Yolks-Shell Cobalt Phosphosulfide Nanocrystals Encapsulating into Rich Heteroatoms Co-Doped Carbon Frameworks for Advanced Sodium/Potassium Ion Batteries. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Li, Z.; Jin, R.; Li, Y.; Shuming, R.A.N. Lithium Resources in Brine of China’s Sea Salt Field Operations. Acta Geol. Sin. (Eng.) 2016, 90, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F. Extracting Lithium from Salt-Lake Brine. Nat. Chem. Eng. 2024, 1, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Zhong, Y.C.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, S.C.; Qu, T. Review of Technologies to Extract Lithium from Hard Rock Lithium Minerals. Miner. Eng. 2025, 232, 109577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Tong, X.; Xie, X.; Song, Q.; Fan, P.Q. Review of the Research on the Development and Utilization of Clay-Type Lithium Resources. Particuology 2024, 87, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chai, G.L.; Zhang, Y.H. Research Progress on Lithium Extraction from Salt-Lake Brine. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 148, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Discussion on Rational Development of Lithium Resources in Qinghai Salt Lake. Qinghai Sci. Technol. 2017, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.A.; Clavijo, A.; Lorca, M.; Andrade, M.O. Bringing the State Back in the Lithium Triangle: An Institutional Analysis of Resource Nationalism in Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2024, 20, 101534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.H.; Du, X.H.; Wang, G.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H. Preparation and Adsorption Performance Study of H2TiO3 Lithium Ion Sieve with Industrial Metantitanic Acid as Raw Materia. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2021, 4, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, M.P. The Research of Chinese Salt Lake Organisms: History, Status and Expectation. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2014, 88, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Hu, Y.F.; Shen, L.J.; Liu, W.P.; Jiao, J.; Jiao, P.C.; Liu, C.L. Santosh Pathways and Mechanisms of Lithium Enrichment in Brine Deposits: Geochemical and Isotopic Evidence from the Bieletan Section in the Qaidam Basin, Northwestern China. J. Earth Sci. 2024, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, C.; Urrutia, J.; Godfrey, L.; Jódar, J.; Pereira, M.; Villarroel, C.; Durán, C.; Soto, I.; Lam, E.J.; Gómez, L. An Evaluation of the Brine Flow in the Upper Part of the Halite Nucleus of the Salar de Atacama (Chile) through an Isotopic Study of δ 18 O and δ2H. Water 2024, 16, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, S.X.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Li, S.W.; Yin, S.H.; Zhang, L.B.; Jiang, X.B.; Zhou, G.L.; Zhang, N. Lithium Extraction from Salt Lake Brines with High Magnesium/Lithium Ratio: A Review. Env. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucrecia López Steinmetz, R.; Salvi, S.; García, M.G.; Arnold, Y.P.; Béziat, D.; Franco, G.; Constantini, O.; Córdoba, F.E.; Caffe, P.J. Northern Puna Plateau-Scale Survey of Li Brine-Type Deposits in the Andes of NW Argentina. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.T.; Han, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Tran, T. Recovery of Magnesium from Uyuni Salar Brine as Hydrated Magnesium Carbonate. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.N.; Zhang, T.A.; Pan, X.J.; Zhang, J.J. Eco-Friendly Extraction of Magnesium and Lithium from Salt Lake Brine for Lithium-Ion Battery. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.J.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.D.; Hao, Y.; Li, W. Study on Natural Evaporation Process of Longmucuo Brine. AMR 2013, 807–809, 2408–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yue, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H. Study on Adsorption Extraction Process of Lithium Ion from West Taijinar Brine by Shaped Titanium-Based Lithium Ion Sieves. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Hu, S.F.; Wang, C.X.; Duan, H.H.; Xiang, X. Highly Efficient Separation of Magnesium and Lithium and High-Valued Utilization of Magnesium from Salt Lake Brine by a Reaction-Coupled Separation Technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6618–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Bu, L.; Zheng, M. Lithium Resources Industrialization of Salt Lakes in China: A Case Study of the Xitaijinaier Salt Lake and the Zabuye Salt Lake. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2010, 31, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, B.; Makuei, F.; Albijanic, B.; Dyer, L. The Beneficiation of Lithium Minerals from Hard Rock Ores: A Review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessemond, C.; Lajoie-Leroux, F.; Soucy, G.; Laroche, N.; Magnan, J.-F. Spodumene: The Lithium Market, Resources and Processes. Minerals 2019, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Zhu, T.; Chen, X.S.; Liu, H.B.; He, G.S. Improving China’s Global Lithium Resource Development Capacity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 938534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Alexopoulos, I.; Pantelaki, O.; Karmali, V.; Komnitsas, K. Advances in Mineral Processing of Hard-Rock Lithium Ores: A Comprehensive Review. Min. Metall. Explor. 2025, 42, 1251–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R.D.; Newsome, L.; Falagan, C.; Karen, A. Hudson Edwards Bioleaching of Lithium from Jadarite, Spodumene, and Lepidolite Using Acidiothiobacillus Ferrooxidans. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1467408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maistry, N.; Singh, A. HLS Testwork on Spodumene and Lepidolite Samples to Determine Maximum Achievable Lithium Upgrade. Minerals 2025, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.K.; Liu, Z.K.; Wang, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Hou, D.B.; He, M.Y.; Zhou, J.D.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Rao, H.H.; et al. Research Progress on the Important Characteristics, Metallogenic Conditions and Formation Mechanism of Clay-Type Lithium Deposits and Resource Extraction Technology. J. Salt Lake Res. 2025, 33, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.D.; Liu, Y.B.; Ma, B.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Efficient Lithium Extraction from Low-Grade Clay-Type Lithium Ore via Nitric Acid Pressure Leaching. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.H.; Yang, W.L. Spatial-Temporal Pattern Evolution of Global Lithium Trade Network and China ’s Status from the Perspective of Industrial Chain. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. Financ. Econ. 2025, 23, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Wu, Q. Analysis of Potash Supply and Demand in China from 2024 to 2035: Based on the Study of Geological Characteristics of Mineral Deposits. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, D.H.; Yan, K.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, Y.T. Main Types, Distribution, Development and Utilization of Lithium Deposits in China. Geol. China 2024, 51, 811–832. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Xing, E.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Che, D.; Bu, L.; Han, J.; Ye, C. Classification and Mineralization of Global Lithium Deposits and Lithium Extraction Technologies for Exogenetic Lithium Deposits. China Geol. 2023, 6, 547–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.P.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J. The New Discoveries of Saline Lakes and Geothermal Ore Deposits on the Qinghai-Tlbet Plateau. Acta Geosci. Sin. 1990, 11, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Fu, J.J.; Li, Y. Super Large Lithium and Boron Deposit in Jadar Basin, Serbia. Geol. Rev. 2015, 61, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, C.; Xu, H. Analysis of the global lithium resource distribution and potential. China Min. Mag. 2015, 24, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.J. Demand Forecast and Supply Analysis of Critical Mineral Required by New Energy Vehicles. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Hong, T.; Gao, H.H.; Wei, P.T. ‘Lithium’ Unlocks Future Energy Passwords. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2022, 41, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, X.J.; Fei, G.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Cai, Y.H. Process Mineralogy Characteristics of Lijiagou Pegmatite Spodumene Deposit, Sichuan, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.P.; Liu, L.; Ding, G.F. Present Situation and Development Trend of Lithium Resources in the World. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2019, 39, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Si, X.; Xu, S.P.; Wang, J.Z. Rational Thoughts on Lithium Resources Development and Utilization under New Energy Background. Resour. Ind. 2024, 26, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, L.B.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, Y.L.; Dan, Y.; Zhao, P.; He, Y.; et al. Review: The Formation, Characteristics, and Resource Utilization of Lithium Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.F.; Gu, D.L.; Lin, G.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H.Y. Recovery of Lithium from a Synthetic Solution Using Spodumene Leach Residue. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 177, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M. Froth Flotation of Spodumene from Spodumene-Bearing Pegmatite Ores: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; Nitou, M.V.M.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, L.F.; Nie, J.L.; Niu, Y.H.; An, L.; Lv, W.Q. Li-Ion Transport in Solid-State Electrolyte of Li1-xAl1-xSi2+xO6: An Ab Initio Study. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Ma, B.Z.; Lü, Y.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. A Review of Lithium Extraction from Natural Resources. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.H.; Yang, Y.K.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Han, G.H.; Cao, Y.J. Research Progress of Lithium ExtractionTechnology from Spodumene and Crystal Transformation. Nonferrous Met. (Extr. Metall.) 2024, 2, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
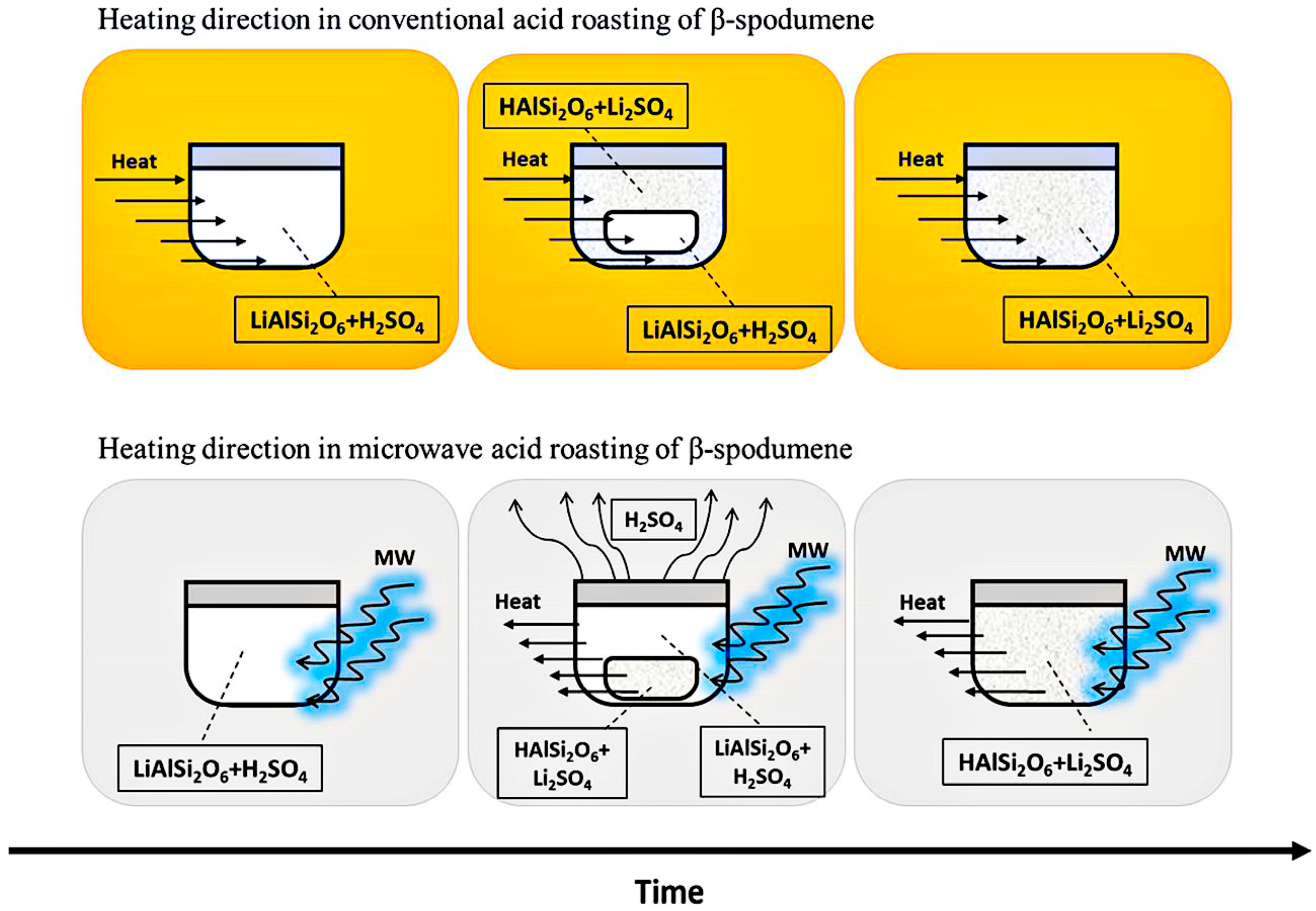
- Salakjani, N.K.; Singh, P.; Nikoloski, A.N. Acid Roasting of Spodumene: Microwave vs. Conventional Heating. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Han, S.H.; Sagzhanov, D.; Vaziri Hassas, B.; Slawecki, T.M.; Agrawal, D.; Akbari, H.; Mensah-Biney, R. Microwave-Assisted Calcination of Spodumene for Efficient, Low-Cost and Environmentally Friendly Extraction of Lithium. Powder Technol. 2022, 397, 116992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ma, S.Y.; Hu, P.; Wang, J.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Luo, S.S. A Method of Extracting Lithium by Microwave Acid Roasting and Mechanical Ball Milling. U.S. Patent Application No. CN119307715A, 12 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.C.; Xie, R.Q.; Tong, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.H. Extract Lithium from Clay-Type Lithium Ore by Mixed Acid and Its Mechanism. Particuology 2024, 91, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.N.; Guo, T.F.; Wen, H.J.; Luo, C.G.; Cui, Y.; Du, S.J.; Wang, N. Leaching Efficiency of Sulfuric Acid on Selective Lithium Leachability from Bauxitic Claystone. Miner. Eng. 2020, 145, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.; Mohammadi-Jam, S.; Li, R.H.; Liang, J.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Kökkılıç, O.; Omelon, S.; Waters, K.E. Preliminary Investigation into Lithium Extraction by Phosphoric Acid Leaching of Spodumene. Miner. Eng. 2024, 209, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.G.; Liang, S.; Deng, X.X.; Zhang, B.Y.; Xu, C.; Tu, M.J.; Gao, Y.B.; Zhan, B.X.; Chang, L.J. A Method for Efficient Extraction of Lithium from Spodumene Clinker and Preparation of Low Iron and Low Sulfur Silicon Aluminum Powder. U.S. Patent Application No. CN118792502A, 17 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, L.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Dong, H.B. Production and Market Situation of Lithium Hydroxide in China. China Nonferrous Met. 2009, 17, 74–75. [Google Scholar]
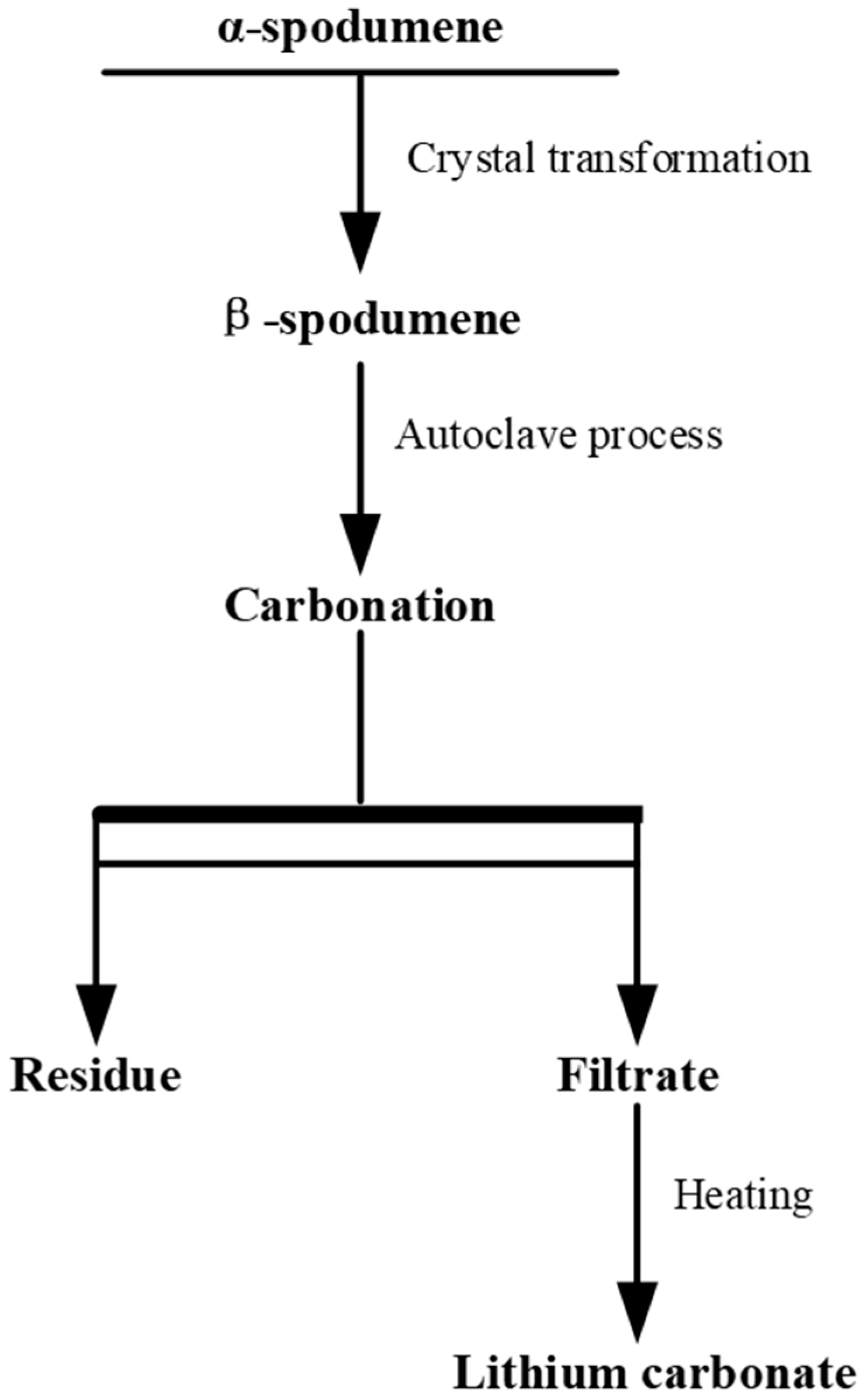
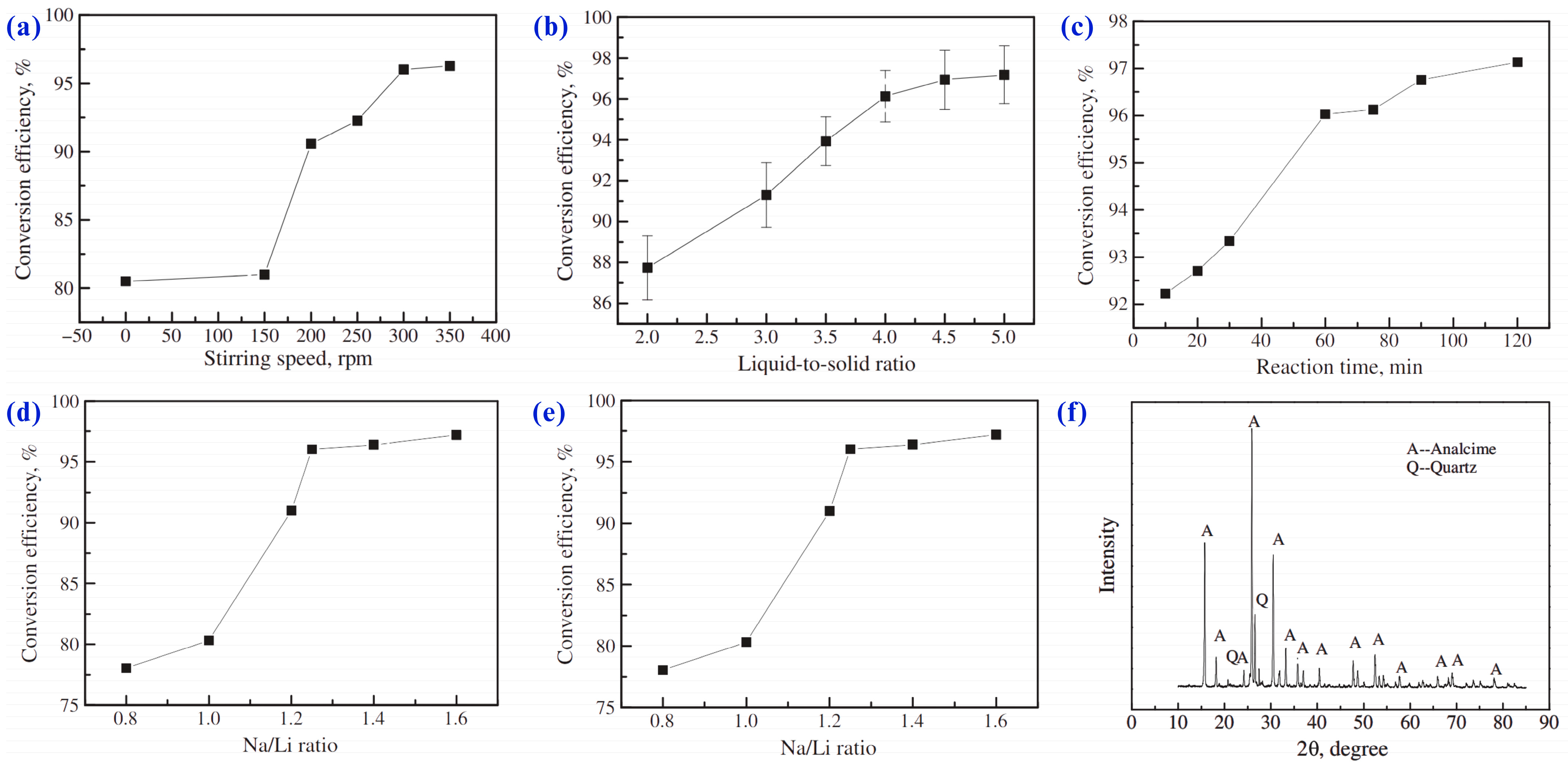
- Chen, Y.; Liao, T.; Chen, B.Z.; Tian, Q.Q. Extraction of Lithium from Spodumene by Sodium Carbonate Autoclave Process. Nonferrous Met. (Extr. Metall.) 2011, 9, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.Q. Extraction of Lithium Carbonate from Spodumene Ore. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Subasinghe, H.C.S.; Rezaee, M. Direct Lithium Extraction from α-Spodumene Using NaOH Roasting and Water Leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Tan, X.M.; Liu, W.Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.Z. Current Status and Research Progress of Lithium Extraction Technology from Ore. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2020, 40, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Qiu, S.B.; Sun, T.Y.; Zhu, M.Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.G. A Method for Producing Lithium Sulfate Solution by Spodumene Sulfate Roasting Method. CN114507779A, 9 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Samoilov, V.I.; Kulenova, N.A.; Sheregeda, Z.V.; Gadylbekova, L.G.; Agapov, V.A.; Shushkevich, L.V. Integrated Processing of Spodumene in Hydrometallurgy. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2008, 81, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cheng, S.Q.; Qi, Z.P. A Method for Extracting Lithium from Spodumene by Salt Gypsum Assisted Sulfate Method. CN119082493A, 4 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.Q.; Chen, B.Z.; Shi, X.C.; Liao, T. Preparation of Lithium Carbonate from Spodumene by a Sodium Carbonate Autoclave Process. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
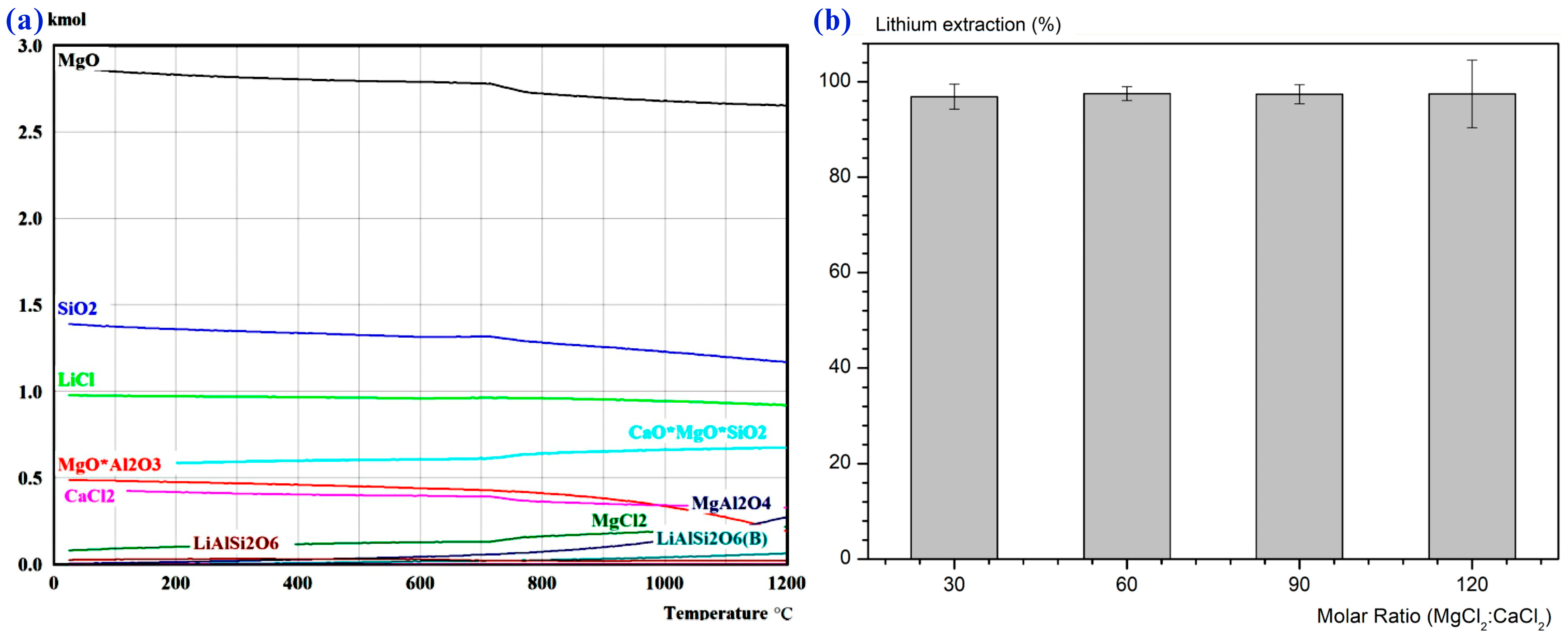
- Barbosa, L.I.; Valente, G.; Orosco, R.P.; González, J.A. Lithium Extraction from β-Spodumene through Chlorination with Chlorine Gas. Miner. Eng. 2014, 56, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.G.; Ni, C.Q.; Zhong, H.; Xie, Y.Q. A Method of Mechanical Activation Enhanced Chlorination Roasting of Spodumene for Water Leaching of Lithium. CN118272671A, 29 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, P.F.A.; Brigido, C.R.D.S.; Pinto, C.P.; França, S.C.A.; Rosales, G.D. Extracting Lithium from Brazilian α-Spodumene via Chlorination Roasting. Mining 2025, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Wang, D.M.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, D.P.; Liu, Z. Micro-Morphology and Phase Composition of Lithium Slag from Lithium Carbonate Production by Sulphuric Acid Process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.B.; Zhang, X.; He, X.Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Deng, X.F.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.B. Utilization of Lithium Slag by Wet-Grinding Process to Improve the Early Strength of Sulphoaluminate Cement Paste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.X.; Wu, D.F.; Yan, L.L.; Zhou, Y. Recycling of Spodumene Slag: Preparation of Green Polymer Composites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36942–36953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S.; Liu, H.; Duan, P.; Ruan, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ge, W. The Effects of Lithium Slag on Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers Designed by Response Surface Method (RSM). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.P.; Hu, K.J.; Yuxian, K.; Yan, X.Y.; Li, J.Y. Research Progress on Activation Technology and Mechanism of Lithium Slag. Mod. Min. 2024, 40, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Yu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y. Research Progress on Recycling Technologies of Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Materials. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2025.
- Yi, P.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.Q.; Yin, Z.G.; Deng, X.X. Test on Flotation Desulfurization of a Lithium Slag in Sichuan. Mod. Min. 2023, 39, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Lu, Z.Y.; Zhan, B.X.; Yang, F.Y.; Hou, L.; Chen, X.M.; Yu, Q.H.; et al. Performance and Hydration of Ternary Compound Cement by Using Lithium Slag, Limestone and Clinker. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xue, L.T.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, R.; Sun, X.C.; Wu, K.Z.; Chi, R.A. Experimental Study on Hydration Activity Modification of Fluorgypsum. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 44, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.G.; Wang, Z.M.; Liu, Y.C. Description of Revised"building Plaster"GB/T 9776—2008. New Build. Mater. 2009, 36, 13–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.Y. Study on Preparation and Key Properties of Composite Cementitious Material Containing Phosphogypsum. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Hu, B.; Shi, S. Preparation and Hydration Properties of Multi-Component Solid Waste Low Carbon Cementitious Materials Based on Gypsum and Slag. Nonferrous Met. (Extr. Metall.) 2024, 9, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhou, H.L.; Gong, D.D.; Reng, S.L.; Qian, H.L. Research Progress on Resource Utilization Technology of Lithium Smelting Slag. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2025, 15, 308–318. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Liao, S.Y.; Jiang, X.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Determination on Beryllium Content in Silicon-Aluminum Powder by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES). Yunnan Metall. 2024, 3, 155–160, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.W. Going Forward by ‘Green’ and Turning ‘Waste’ into Treasure. Mianyang Dly. 2024, 6, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Chen, S.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, H.F.; Wang, B. Study on the Microstructures and Thermophysical Properties of the Spacer Fibre Papers. China Pulp Pap. 2025, 44, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.N.; Hu, M.R.; Huang, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, Q.; Huang, S.X. Study on Lithium Silicon Aluminum Powder Replacing Pyrophyllite as Glass Fiber Raw Material. Fiber Glass 2025, 2, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Chen, B.; Li, Y.M.; Li, R.X. Effect of Ball Milling Time on the Microstructure and Properties of High-Silicon–Aluminum Composite. Materials 2023, 16, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.B.; Li, M.G.; He, X.Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.B. Preparation for Micro-Lithium Slag via Wet Grinding and Its Application as Accelerator in Portland Cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.X.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; He, Y.Q.; Yi, P.; Cahng, L.; Yin, Z.G. Experimental Study on Tantalum and Niobium Recovery from Lithium Slag Extracted from Sichuan Spodumene. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2025, 6, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Salt-Lake Brine | Li+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qarhan Salt Lake, China [24] | 3.279 | 108.5 | 0.763 | 2.281 | 0.107 | 6.39 |
| Atacama Salar Brine, Chile [25] | 3.02 | 17.6 | 28.2 | 61.9 | 0.41 | 37.9 |
| Olaroz Salar Brine, Argentina [27] | 1.01 | 2.00 | 6.22 | 98.85 | 0.51 | 10.07 |
| Uyuni Salar Brine, Bolivia [28] | 0.57 | 13.3 | 14.2 | 53.1 | 0.48 | 0.48 |
| Yiliping Salt Lake, China [29] | 0.33 | 26.29 | 15.11 | 78.02 | - | 25.50 |
| Longmucuo Salt Lake, China [30] | 0.865 | 75.41 | 15.59 | 11.10 | 0.12 | 25.9 |
| West Taijinar Salt Lake, China [31] | 0.784 | 60.58 | 16.00 | 21.01 | 0.185 | 25.08 |
| East Taijinar Salt Lake, China [32] | 6.75 | 85.47 | 7.69 | 10.42 | - | 29.58 |
| Zabuye Salt Lake, China [33] | 0.16 | 21.4 | 7.10 | 69.2 | 40.5 |
| Genetic Type | Research and Exploitation Degrees | Typical Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Salt-lake brine type | High degree of research and exploitation | Altiplano Lithium Triangle (Andes, South America), salt lakes on China’s Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, salt lakes in the southwestern U.S. |
| Deep brine type | Great potential, but a low degree of research | Cenozoic tectonic zone in the western Qaidam Basin, China; deep Triassic brine in Huangjinkou, Xuanhan, Sichuan Basin, China |
| Granite pegmatite type | High grades and extensively surveyed | Greenbushes lithium deposit (Australia), Altay deposit (Xinjiang, China), Jiajika and Maerkang deposits (Sichuan, China) |
| Granite type | Low grades, high exploitation costs | Brazilian granite lithium deposits |
| Pyroclastic weathered clay subtype | Formed by weathering and lithium enrichment of lithium-bearing pyroclastic rocks | Kings Valley (Nevada, U.S.), a valley in the south-central Mexican Plateau |
| Silico-aluminous clay type | Formed in the Neopaleozoic, widely distributed | Dazhuyuan deposit (Guizhou, China) |
| Coal-measure clay type | Widely distributed, low exploration degree | Jungar coal field (China), Ningwu coal field (Shanxi Province, China) |
| Component/Element | Acid Process Lithium Slag | Alkali Process Lithium Slag | Salt-Roasting Lithium Slag | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | ~60%–70% | ~58%–68% | ~62%–72% | Main component, exists in the amorphous phase and quartz; core raw material for silica-alumina micro-powder preparation |
| Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) | 15%–20% | 14%–18% | 16%–21% | Exists in the aluminosilicate phase; participates in hydration reactions when used as a cementitious material |
| Sulfur Trioxide (SO3) | ~9%–10% | ~10%–11% | ~8%–9% | Mainly exists in the form of (gypsum phase, CaSO4·2H2O); requires desulfurization for building material applications |
| Calcium Oxide (CaO) | 3%–5% | 4%–6% | 2%–4% | Derived from limestone neutralization (acid process) or alkali additives (alkali process); promotes hydration in cement systems |
| Magnesium Oxide (MgO) | 0.5%–1.2% | 0.3%–0.8% | 0.4%–1.0% | Trace impurity; low content, no significant impact on mainstream utilization |
| Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) | <0.5% | <0.5% | <0.5% | Trace impurity; controlled via magnetic separation in silica-alumina micro-powder production |
| Lithium Oxide (Li2O) | 0.1%–0.3% | 0.08%–0.25% | 0.12%–0.35% | Residual unextracted lithium; recyclable via advanced leaching technologies (e.g., bio-leaching) |
| Tantalum Pentoxide (Ta2O5) | 0.01%–0.03% | 0.008%–0.025% | 0.012%–0.032% | Exists in the tantalite-niobite phase; recoverable via Falcon centrifugal gravity separation + magnetic separation |
| Niobium Pentoxide (Nb2O5) | 0.005%–0.02% | 0.004%–0.018% | 0.006%–0.022% | Coexists with Ta; separation requires differential shaking table gravity separation due to similar chemical properties |
| Potassium Oxide (K2O) | 0.8%–1.5% | 0.5%–1.0% | 1.2%–2.0% | Higher in salt-roasting slag (from potassium sulfate additive); may affect concrete setting time |
| Sodium Oxide (Na2O) | 0.3%–0.8% | 1.0%–1.8% | 0.4%–0.9% | Higher in alkali-process slag (from sodium carbonate); improves the reactivity of silica-alumina components |
| Other Impurities (MnO, TiO2, etc.) | <0.5% | <0.5% | <0.5% | Trace elements; leaching concentration below hazardous waste limits, no environmental risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, Y.; Yan, W.; Deng, X.; Huang, S.; Sun, A.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, S.; Peng, W.; Wang, W.; Ge, P.; et al. A Review on Lithium Extraction Processes from Spodumene and Resource Utilization of the Generated Lithium Slag. Minerals 2025, 15, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101073
Bu Y, Yan W, Deng X, Huang S, Sun A, Guan Q, Zhou S, Peng W, Wang W, Ge P, et al. A Review on Lithium Extraction Processes from Spodumene and Resource Utilization of the Generated Lithium Slag. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101073
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Yongjie, Wenxuan Yan, Xingxing Deng, Sen Huang, Aihui Sun, Qingjun Guan, Shuang Zhou, Wenqing Peng, Weijun Wang, Peng Ge, and et al. 2025. "A Review on Lithium Extraction Processes from Spodumene and Resource Utilization of the Generated Lithium Slag" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101073
APA StyleBu, Y., Yan, W., Deng, X., Huang, S., Sun, A., Guan, Q., Zhou, S., Peng, W., Wang, W., Ge, P., & Yang, Y. (2025). A Review on Lithium Extraction Processes from Spodumene and Resource Utilization of the Generated Lithium Slag. Minerals, 15(10), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101073






