Abstract
Strategic lithium resources are critical to national security and have attained heightened importance in contemporary geopolitical, economic, and military contexts. Persistent geochemical anomalies of lithium were first identified in coal-bearing claystones of the Middle Jurassic Xishanyao Formation at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine in the southern Junggar Basin, Xinjiang. In this study, a suite of analytical techniques, including X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy, time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry, and sequential chemical extraction, was employed to investigate the provenance, depositional environment, and modes of lithium occurrence in the claystone. Results indicated that the claystone at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine was dominated by moderately felsic rocks. The notable enrichment of lithium in the Liuhuanggou coal mine claystone indicates favorable metallogenic potential. Lithium was primarily hosted in the aluminosilicate-bound fraction with inorganic affinity and was structurally incorporated within clay minerals, such as kaolinite, illite, and Fe-rich chlorite (chamosite). Lithium-rich claystone was deposited under intense chemical weathering conditions in a transitional, slightly brackish environment characterized by elevated temperatures and low oxygen levels. These findings advance our understanding of sedimentary lithium mineralization mechanisms and offer direct practical guidance for lithium resource exploration and metallogenic prediction in the Xinjiang region, thereby supporting the development of efficient extraction technologies.
1. Introduction
Amid the global energy transition and pursuit of green, sustainable development, lithium (Li), often referred to as “white oil”, has become a cornerstone of the new energy industry [1]. With China’s lithium resource dependence exceeding 60%, the rapid expansion of the new energy sector has intensified the risk of supply chain bottlenecks [2]. Moreover, the non-renewable nature of lithium combined with the global oligopolistic structure of the lithium industry has rendered it one of China’s most critically scarce strategic minerals [3]. Therefore, urgent efforts are required to discover new lithium resources and advance fundamental research on lithium utilization, which is vital for ensuring national resource security.
Globally, lithium resources are classified into three primary types: brine, hard rock, and sedimentary clay deposits. Currently, brine and hard rock lithium resources dominate commercial extraction, whereas clay-associated lithium deposits remain unexplored owing to their relatively recent discovery. Efficient development of sedimentary lithium resources holds substantial potential for expanding China’s lithium reserves and alleviating domestic supply constraints [4]. The occurrence mode of lithium directly dictates the difficulty and complexity of extraction technologies and also significantly influences the estimation of lithium reserves and resources. Therefore, elucidating its occurrence mode is a critical prerequisite for the development and utilization of lithium resources [5].
In sedimentary lithium deposits, lithium exists primarily in three forms: surface-adsorbed, ion-exchangeable, and structurally bound. Among these, ion-exchangeable and structurally bound forms dominate, with minor occurrences as discrete mineral phases. Lithium may occur in the interlayer sites of clay minerals or within pseudohexagonal cavities in the tetrahedral sheets. Charge balance is achieved when substitution of silicon by aluminum creates structural vacancies that are filled by lithium ions, resulting in unpaired isomorphic substitution. Additionally, clay mineral surfaces provide two types of adsorption sites: basal planes and edge sites. The basal planes are composed of Si–O bonds or hydroxyl groups, whereas the edge sites are covered with chemisorbed water that exhibits acid-base activity due to broken Si(Al)–OH bonds. This surface water can generate variable charge, thereby influencing mineral surface complexation. In addition to adsorbed forms, lithium may migrate into the octahedral sheets of clay minerals and be hosted in structural positions [6]. Cui et al. [7] investigated carbonate clay-type lithium deposits in Southwest China using SEM-EDS and ion beam TOF-SIMS, revealing that lithium predominantly occurred in an adsorbed state within Mg-rich clay minerals. TEM-EDS analysis identified montmorillonite and cookeite as the principal Li-bearing phases. Lithium has been hypothesized to be initially incorporated into montmorillonite during weathering and sedimentation and subsequently retained in cookeite during diagenesis. Zhao et al. [8] reported the high cookeite abundance in the No. 15 coal seam of the Wangtaipu Mine, Jincheng Coalfield, based on the SEM-EDS data. TOF-SIMS analysis further confirmed that lithium was primarily hosted within the cookeite structure. Tang et al. [9] utilized lithium isotope data to demonstrate that illite and kaolinite were the primary Li-hosting minerals in the ore-bearing claystone sequences of the Xinmin bauxite deposit in northern Guizhou. In addition, the enrichment of key metals such as Li in clay stone is influenced by multiple factors, including sediment provenance and depositional environment [9]. Elements such as Al, Ti, rare earth elements (REEs), Th, Sc, and high field strength elements are effective indicators of sediment source regions [10,11]. Certain trace elements also exhibit high sensitivity to changes in depositional conditions, serving as reliable proxies for reconstructing paleo-depositional environments [12].
Systematic studies of the Jurassic strata in the Junggar Basin began in the 1960s and 1970s. The Jurassic formations along the southern margin of the basin experienced multiple episodes of tectonic activity, leading to significant spatial and temporal variations in sediment supply systems [13,14]. However, specific provenance analyses of the Xishanyao Formation at the Liuhuangou Coal Mine are lacking, and existing studies present divergent interpretations of provenance along the southern margin. Thus, investigating the provenance and depositional environment of the claystones in this region provides critical insights into ore genesis and metallogenic patterns, thereby offering important guidance for mineral exploration and development [15].
China hosts extensive coal-bearing sequences, with lithium-enriched coal seams documented in the Carboniferous-Permian strata of northern China and in the Late Permian and Late Triassic formations in southern regions [16]. Although these lithium resources are generally low-grade, they have considerable potential for further exploitation. Recently, lithium-enriched horizon has been identified in the Middle Jurassic Xishanyao Formation within the coal-bearing claystones of the Liuhuanggou area of Xinjiang. The lower member of the Xishanyao Formation represents the major coal-bearing stratum in the Middle Jurassic. However, the provenance, depositional environment, and mode of occurrence of lithium in these claystones remain poorly constrained. Thus, this study focuses on the coal-bearing claystones of the lower member of the Xishanyao Formation (J2x1) at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine. We examined their mineralogical assemblages and geochemical characteristics, including their major and trace element compositions, to assess their provenance, lithium occurrence modes, and depositional environment. These results provide critical insights into the metallogenic processes of sedimentary lithium systems and offer a scientific foundation for future resource exploration and comprehensive utilization strategies.
2. Geological Setting
The Liuhuanggou Coal Mine is located within the Urumqi foreland depression zone of the North Tianshan Fold Belt, characterized by NE-trending anticlines, synclines, and thrust faults (Figure 1). The regional tectonic framework exhibits multiphase superposition, high structural intensity, and complexity. Since the Cenozoic, oblique convergence between the Indian and Eurasian plates has driven strong compression, uplift, and deformation in the Junggar Basin and Tianshan Mountains, resulting in a reactivated orogenic belt and the formation of an asymmetric basin with elevated southern margins [17]. The northern Tianshan piedmont hosts three E-W trending imbricate thrust-fold belts and a corresponding foreland basin. The Liuhuanggou lies within the eastern segment of the first-order structural unit (Kala’za Anticline) [18], which experienced (1) initial deformation during the Late Mesozoic, (2) prolonged exhumation and slope reworking prior to the Pliocene, and (3) intense Neogene uplift that exposed certain portions of the Jurassic coal-bearing strata. Subsequent polyphase tectonic activity further generated second- and third-order structural belts.
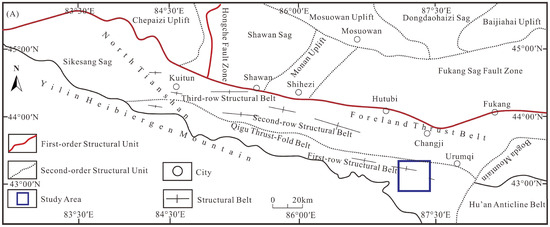
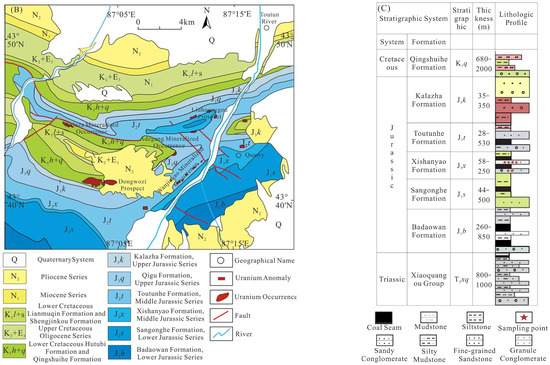
Figure 1.
Geological map of the Liuhuanggou area. (A) Structural Division Map of the Southern Junggar Basin; (B) Geological Map of the Southern Junggar Basin; (C) Stratigraphic Column of the Jurassic Coal Measures. (modified after [17,19]).
In the study area, the Jurassic System maintains an angular unconformity with the overlying Cretaceous strata, while the Triassic System is in unconformable contact with the overlying Jurassic Series [20]. The Middle Jurassic (J2) comprises the Xishanyao Formation and the Toutunhe Formation. The Xishanyao Formation, which serves as the primary coal-bearing stratum, consists of a lithological assemblage including conglomerate, coarse-grained sandstone, sandstone, siltstone, mudstone, carbonaceous mudstone, and coal seams. The majority of its workable coal seams are concentrated in the middle to lower sections of the coal-bearing segment. This study focused on coal seams Nos. 9–15 within the lower member of the Middle Jurassic Xishanyao Formation (J2x1). The immediate roof lithology is mudstone, and the floor lithology consists of mudstone or claystone. Seam thickness ranges from 7.41 to 13.03 m, with an average of 10.05 m, making them a regionally extensive, stable, and mineable coal resource.
3. Sampling and Analytical Strategies
3.1. Sample Preparation Procedures
Samples were obtained from coal-bearing strata (Nos. 9–15) within the Middle Jurassic Xishanyao Formation, comprising six specimens: ND1–ND4 from the roof strata and ND5–ND6 from the floor strata. Claystone samples were immediately sealed in argon-flushed containers to prevent oxidation and contamination. Sample preparation involved initial crushing using a DF-4 electromagnetic vibratory disk mill, followed by fine grinding in an agate mortar. The homogenized material was subsequently sieved to obtain solid powders with particle sizes less than 74 μm (200 mesh).
3.2. Experimental Methodology
X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF, ARL 9900, Applied Research Laboratories S.A., Geneva, Switzerland) was employed to determine major elements in claystone samples pressed into tablets with a boric acid backing substrate. Sequential scanning was applied, yielding relative standard deviations (RSD) of ≤1% for major elements. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Thermo Fisher iCAP Qc, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to analyze trace elements in claystone samples. The samples were digested using a high-pressure microwave digestion system with a mixture of 5 mL 40% HF, 2 mL 65% HNO3, and 1 mL 30% H2O2. The digested solutions were calibrated against a multi-element standard. The method achieved detection limits of ≤0.5 ppt for light trace elements such as Li, with precision (RSD) of ≤3%.
X-ray diffraction (XRD, Aolong Radiative Instrument Group Co., Ltd., Dandong, China) analysis was performed on an AL-Y300 diffractometer operated at 30 kV and 25 mA. Measurements were carried out from 7° to 70° (2θ) at a scan speed of 0.05°/s, with angular repeatability and minimum step size of 0.001°. Scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS, ZEISS Sigma 300, Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany) was employed for mineral observation. A through-lens detector (TLD) was used to efficiently collect secondary electrons (SE) and backscattered electrons (BSE). The working distance ranged from 5 to 8.5 mm, the acceleration voltage was set between 2 and 20 kV, and magnification varied from 100 to 2000×. The secondary electron image resolution was ≤1.5 nm.
The surface elemental composition and spatial distribution of the samples were characterized using Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS, model TOF.SIMS 5-100, IONTOF, Münster, Germany), which offers high surface sensitivity ranging from ppm to ppb levels. The specific parameters were as follows: a primary ion beam of Bi3++ at 30 keV with a 45° incidence angle, scanning an area of 100 μm × 100 μm; positive secondary ions were collected within a mass range of 0–900 amu. A Gas Cluster Ion Beam (GCIB) at 10 keV with a 45° incidence angle was used for sputtering, with a sputtering rate of approximately 0.15 nm/s.
Sequential chemical extraction experiments (SCEE) were conducted to determine lithium speciation in coal-bearing claystones from the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine, following an adapted six-step procedure based on Riley et al. (Figure 2) [21]. Each step targeted operationally defined fractions: (1) Water-soluble fraction: 2.5 g of <75 μm sample was agitated with 50 mL ultrapure water at 60 °C for 24 h, centrifuged (4000 rpm, 15 min), and the supernatant collected. The residue was washed three times, the leachate diluted to 100 mL, and the solid dried at 85 °C (Residue I). (2) Ion-exchangeable fraction: Residue I was extracted with 50 mL of 1 mol/L ammonium acetate under identical conditions to yield Residue II. (3) Carbonate-bound fraction: Residue II was treated with 50 mL of 3 mol/L HCl, following the same protocol, producing Residue III. (4) Sulfide-bound fraction: Residue III was extracted using 50 mL of 2 mol/L HNO3 under consistent conditions, yielding Residue IV. (5) Silicate-bound fraction: Residue IV was digested with 25 mL concentrated HF at 60 °C for 5 h in PTFE, evaporated near-dryness at 180 °C, re-dissolved in 5% HNO3, and centrifuged to obtain Residue V. (6) Residual fraction: 0.05 g of Residue V was digested in PTFE vessels via microwave-assisted acid digestion using 5 mL concentrated HNO3, 4 mL HF, and 1 mL H2O2. After complete digestion and evaporation to dryness, the residue was diluted to 100 mL for subsequent analysis.
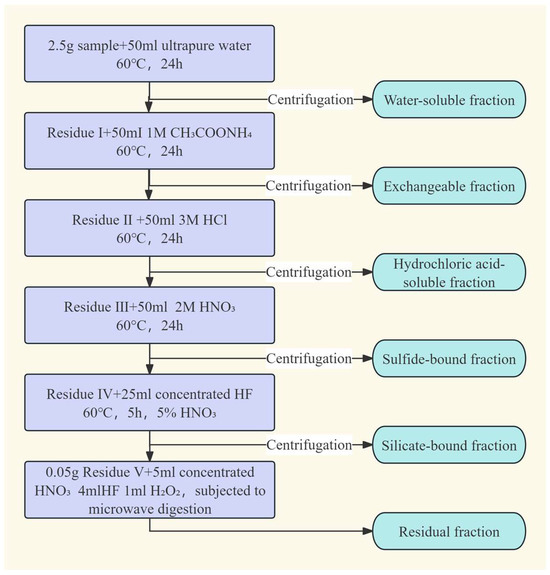
Figure 2.
Flowchart of sequential chemical extraction procedure. (modified after [21]).
4. Results and Data Interpretation
4.1. Elemental Geochemistry
Based on their concentration in coal, elements can be classified into two categories: major elements (content > 0.01%) and trace elements (content < 0.01%) [22]. Investigating the geochemical characteristics of these major and trace elements provides critical insights into sediment provenance, reconstructs peat-forming environments, and elucidates geological evolutionary processes [10]. As revealed in Table 1, the major element oxide concentrations in the claystone from the Xishanyao Formation in the Xinjiang Liuhuanggou Coal Mine are dominated by SiO2 (64.36%), Al2O3 (28.38%), and K2O (2.16%), suggesting the probable presence of abundant aluminosilicate minerals. Other oxides were present in decreasing order of abundance as follows: Fe2O3 (1.69 wt%) > TiO2 (1.33 wt%) > Na2O (0.78 wt%) > MgO (0.75 wt%) > CaO (0.14 wt%). Notably, sample ND1 exhibited the highest SiO2 content (71.13 wt%), whereas ND6 (a floor stratum sample) recorded the highest Al2O3 concentration (44.21 wt%). As shown in Table 2, the contents of trace elements in the claystone of the Xishanyao Formation from the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine are presented. The average lithium (Li) content is 75.3 μg/g, with a maximum value of 155.9 μg/g, significantly higher than the average upper continental crust (UCC) value of 20 μg/g [11]. Additionally, several other elements, including V, Cr, Ga, Zr, Nb, Mo, Cd, In, Hf, Ta, W, Pb, Th, and U, were present in concentrations above the average UCC values (Table 2).

Table 1.
Major element concentrations (wt%) in claystone samples.

Table 2.
Trace element concentrations (μg/g) in claystone samples.
The concentration coefficient (CC) proposed by Dai et al. [23] was applied to evaluate the degree of element enrichment in claystone. CC is defined as the ratio of the trace element concentration in a sample to its corresponding background value. This coefficient was used to assess the enrichment or depletion levels of trace elements in coal-bearing samples. The classification scale for CC is as follows: CC < 0.5, depletion; 0.5 ≤ CC < 2, normal levels; 2 ≤ CC < 5, slight enrichment; 5 ≤ CC < 10, enrichment; 10 ≤ CC < 100, significant enrichment; and CC ≥ 100, abnormal enrichment. As shown in Figure 3, the enrichment pattern of trace elements in the roof and floor claystones of the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine is illustrated. Based on the CC distribution diagram (Figure 3A), Li (CC = 2.13) and Cd (CC = 2.07) were slightly enriched in the claystone roof of the Xishanyao Formation at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine. Notably, in the floor strata, the average Li content reached 140.94 μg/g, corresponding to enrichment (CC = 7.05) (Figure 3B). In addition, Ga, Zr, Nb, In, Hf, Ta, W, Th, and U also exhibited slight enrichment.
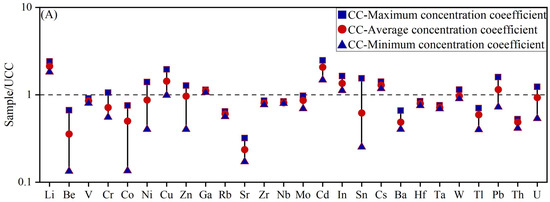
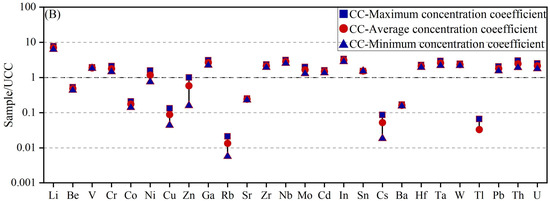
Figure 3.
Trace element enrichment coefficient diagram for claystone roof and floor samples. (A) Samples ND1–ND4; (B) Samples ND5 and ND6.
4.2. Mineralogical Characteristics
Integrated XRD analyses (Figure 4) indicated that the roof claystones of the Xishanyao Formation were primarily comprising dolomite, illite, quartz, and kaolinite (Figure 4A), whereas the floor strata were dominated by quartz and kaolinite (Figure 4B). SEM-EDS mapping (Figure 5) revealed a more diverse mineral assemblage, including quartz, kaolinite, dolomite, illite, chlorite group minerals, K-feldspar, zircon, calcite, pyrite, rutile, ilmenite, chromite, albite, and sphene. Notably, the prominent XRD peaks of kaolinite, illite, and quartz, coupled with their widespread presence in the SEM images, suggest that these minerals could be principal hosts of lithium.
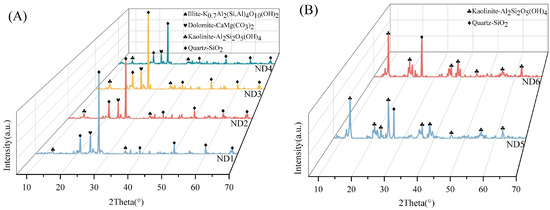
Figure 4.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) pattern. (A) Samples ND1–ND4; (B) Samples ND5 and ND6.

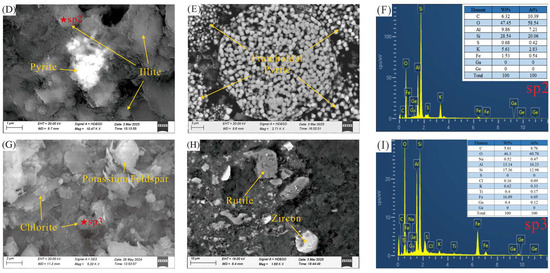
Figure 5.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of clay-hosted lithium ores. (A) SEM images of kaolinite and rutile in sample ND6; (B) SEM images of chromite, quartz, and rutile in sample ND6; (C) EDS spectra from Spot 1; (D) SEM images of pyrite and illite in sample ND1; (E) SEM image of framboidal pyrite in sample ND2; (F) EDS spectra from Spot 2; (G) SEM images of potassium feldspar and chlorite in sample ND5; (H) SEM images of rutile and zircon in sample ND6; (I) EDS spectra from Spot 3.
In sample ND6 exhibiting the highest lithium content, kaolinite displayed a characteristic lamellar morphology, primarily occurring as irregular flakes. Some flakes showed curled edges and were stacked into book-like aggregates. These crystals were small, uniformly distributed, and occasionally clustered into massive compact structures (Figure 5A). The quartz exhibits an irregular granular morphology with moderate to good roundness (Figure 5B), typically indicative of transport by geological agents such as wind or flowing water [24]. In sample ND1, illite appeared as flaky or layered matrices enveloping pyrite (Figure 5D). Scanning electron microscopy observations reveal that the dominant iron mineral in the samples is pyrite. In sample ND1, it occurs as aggregates embedded within illite (Figure 5D). This type of pyrite is interpreted to have formed during the syngenetic stage, where limited sulfate availability resulted in slow growth rates, preventing the development of massive aggregates. Alternatively, in sample ND2, pyrite is present as characteristic spherical framboidal aggregates. These consist of numerous fine-grained euhedral pyrite microcrystals densely packed into well-rounded clusters with finely textured surface protrusions. The microcrystals are relatively uniform in size, and the aggregates range from several to tens of micrometers in diameter (Figure 5E), representing typical authigenic fine-grained pyrite assemblages.
Additional identified phases included rutile, chromite, and zircon. Chromite and zircon were observed as accessory minerals scattered within the matrix as stellate grains and fine detrital clasts (Figure 5B,H). EDS analysis (Figure 5I) indicated a Si/Al atomic ratio of approximately 1.27 (typically chlorite) and a notably high Fe content (16.09 wt%), exceeding that of typical clay minerals. The low concentrations of Ca and K excluded the possibility of illite or Fe-bearing silicates, thereby identifying the mineral as Fe-rich chlorite (Figure 5G). The oolitic texture and dominance of Fe2+, coupled with undetectable Mg levels, suggested its identification as chamosite. Integrated SEM observations confirmed that the roof and floor samples ND1, ND5, and ND6 with elevated lithium contents were composed primarily of clay minerals (illite and kaolinite), along with quartz, rutile, pyrite, and minor amounts of chlorite (Figure 5).
4.3. Characterization of Element Occurrence Modes
TOF-SIMS offers high sensitivity and depth resolution for localized ion detection, enabling elemental and isotopic analyses at the ppm level. This technique facilitates chemical distribution mapping across a wide range of materials and elements, including lithium [6]. In this study, TOF-SIMS was employed to characterize lithium distribution in high-Li samples. As shown in Figure 6, Al and Si dominated the scanned region, indicating that clay minerals were the primary constituents of sample ND5. Li enrichment was spatially correlated with the Al-Si-K distributions and co-localized with Fe-Mg hotspots, suggesting that Li was primarily hosted in K-bearing and Fe/Mg-rich clay minerals. In contrast, Li exhibited minimal correlation with Ca or Ti, thereby excluding pyrite (FeS2), rutile (TiO2), and dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) as significant lithium hosts. Figure 7 further illustrates that in sample ND6, Li hotspots were aligned with Si and Al distributions, definitively identifying aluminosilicate minerals as the principal lithium-bearing phases.
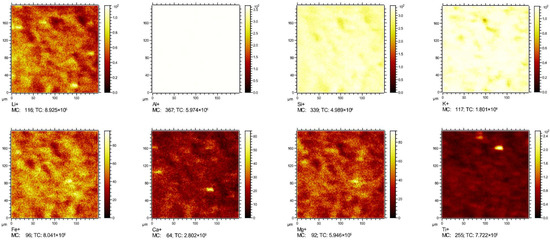
Figure 6.
TOF-SIMS positive secondary ion images of Li, Al, Si, K, Fe, Ca, Mg, and Ti in ND5.
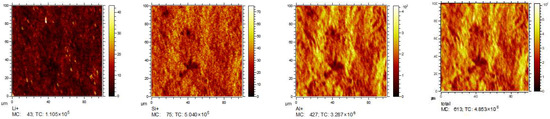
Figure 7.
TOF-SIMS positive secondary ion images of Li, Si, Al, and total ions in ND6.
Sequential chemical extraction results (Table 3) indicated a pronounced inorganic affinity for lithium in claystone samples ND1–ND6. The aluminosilicate-bound fraction was dominant, ranging from 34.35% to 70.77% (average: 52.37%), with the highest proportions observed in floor strata samples ND5 and ND6. Despite minor variations among samples, this form consistently represents the principal mode of Li occurrence. The organic-bound fraction was the secondary form, accounting for 21.22% to 39.17% (average: 30.86%), with elevated values in roof samples ND2 and ND4. This distribution pattern implies that organic matter may contribute to lithium enrichment via complexation mechanisms. The HCl-soluble and water-soluble fractions were comparatively minor, averaging 7.17% and 7.05%, respectively. Ion-exchangeable and sulfide-bound forms were present only in trace amounts, with averages of 1.36% and 1.19%, respectively. Notably, in the high-lithium samples ND5 and ND6, water-soluble and ion-exchangeable lithium together accounted for less than 1%, highlighting the dominance of more stable binding states.

Table 3.
Relative mass fractions (%) of lithium occurrence phases in Liuhuanggou claystones.
5. Discussion
5.1. Sedimentary Provenance Analysis
Provenance characteristics are a primary factor controlling trace element concentrations in sedimentary rocks [25]. During weathering, transport, and deposition, elements such as Al, Ti, Zr, Nb, and Hf exhibit low mobility, making them reliable indicators for inferring source rock composition. Two principal methods are commonly employed for provenance discrimination: Sahraeyan and Bahrami [26] proposed a discriminant function diagram based on major elements to classify four source rock types—mafic (P1), intermediate (P2), felsic (P3), and quartzose recycled (P4) [27]; while Dai et al. introduced the Al2O3/TiO2 ratio as a geochemical indicator, with value ranges of 3–8, 8–21, and 21–70 corresponding to sediments derived from mafic, intermediate, and felsic igneous rocks, respectively [28]. As shown in Figure 8, the Al2O3/TiO2 ratios in claystones from the Xishanyao Formation at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine ranged from 16.14 to 28.01, with an average of 23.79. These values indicate that the source rocks were predominantly intermediate to felsic in composition. Notably, samples with higher lithium concentrations fell within the range characteristic of intermediate rocks, suggesting a potential link to weathering of such lithologies. To further constrain the provenance, an Al2O3/TiO2 vs. Sr/Y plot was used (Figure 9), which also indicated a dominant granitic or rhyolitic (felsic) source.
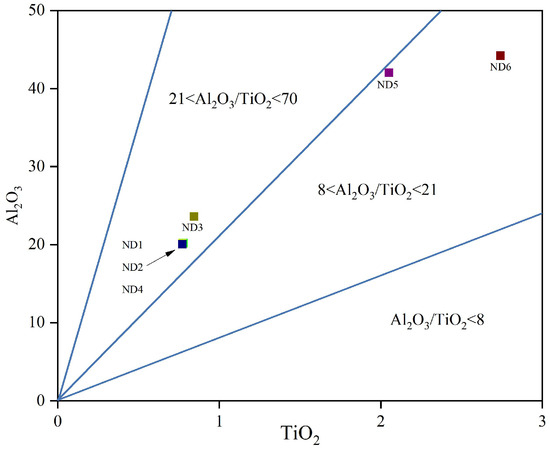
Figure 8.
Al2O3/TiO2 in claystone at the top and bottom plates (modified after [29]).
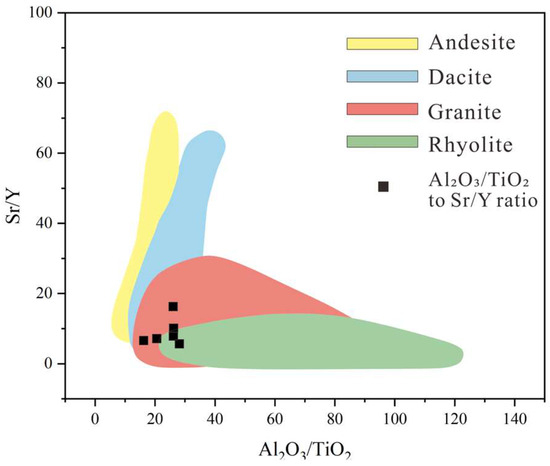
Figure 9.
Al2O3/TiO2-Sr/Y binary distribution diagram. (modified after [29]).
Rare earth elements (REEs) have short residence times in seawater. They are rapidly incorporated into detrital minerals and suspended particulate matter without significant fractionation, thus effectively preserving the geochemical signature of their source regions. This property makes REEs particularly valuable for sediment provenance studies [30]. Therefore, REE characteristics are widely used in provenance analysis. In this study, REE data from the claystone samples were normalized to UCC values using a standard UCC normalization scheme (Figure 10) [11,19]. The overall REE distribution patterns were similar across samples, exhibiting a left-skewed trend indicative of heavy rare earth element (HREE) enrichment. In samples ND1–ND4, light rare earth elements (LREEs) showed mild depletion, whereas HREEs were relatively flat to slightly enriched. In contrast, samples ND5 and ND6 exhibited LREE depletion and more pronounced HREE enrichment. Europium (Eu) typically exhibits negative anomalies in coal-bearing rocks derived from acidic to intermediate-acidic terrestrial sources. However, positive Eu anomalies may occur under the influence of high-temperature hydrothermal fluids or reducing environments [31]. In this study, the average δEu value was 0.76 (δEu = EuN/EuN* = EuN/(0.67 × SmN + 0.33 × TbN; N, Standardization [32]), indicating a negative Eu anomaly. This suggests that the claystone was primarily influenced by terrestrial clastic input, likely derived from weathered intermediate–felsic rocks. Additionally, Vos et al. [33] demonstrated that quartz formed in high-energy eolian sands exhibits improved roundness with increasing transport distance. As shown in Figure 5B, the presence of well-rounded quartz grains suggests a relatively long distance from the sediment source area.
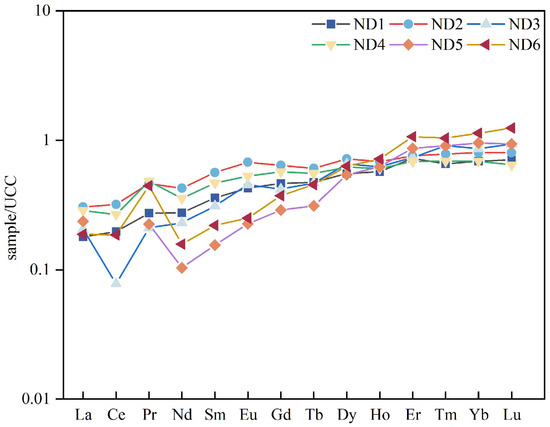
Figure 10.
Upper continental crust (UCC)-normalized rare earth element distribution patterns. (modified after [19,24]).
The Th/Sc ratio can be used to infer the nature of source rocks [34]. Typically, Th/Sc > 1 indicates acidic rock, 0.6 < Th/Sc < 1 indicates neutral rock, and Th/Sc < 0.6 indicates basic rock. In claystone seams Nos. 9–15, the Th/Sc ratios ranged from 0.41 to 2.07, with an average of 0.96. This also indicates that the material composition of the claystone was primarily neutral and acidic, with an overall neutral character.
Comprehensive analysis indicates that the provenance of the claystones from the Xishanyao Formation in the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine is dominated by intermediate to felsic rocks. These findings are consistent with previous studies which concluded that the Middle Jurassic strata along the southern margin of the Junggar Basin were largely sourced from intermediate to felsic rocks in the northern Tianshan Mountains [19].
5.2. Lithium Occurrence Mechanisms
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminosilicates that typically exhibit particle sizes smaller than 2 μm and layered structures composed of alternating Al-O octahedral and Si-O tetrahedral sheets [35]. The predominant clay mineral assemblages in Chinese coal-bearing strata consist of kaolinite, chlorite, and illite [36,37]. Lithium within these minerals exists primarily in the adsorbed or structurally bound states. (i) Adsorbed Li+ is located on external surfaces or interlayer sites. These sites carry negative charges arising from Al3+-for-Si4+ substitutions in the tetrahedral sheets and Mg2+/Fe2+-for-Al3+ substitutions in the octahedral sheets. Charge compensation through Li+ adsorption facilitates its extraction via dilute acid leaching. (ii) Structurally bound Li+ can be incorporated into the silica tetrahedral or alumina octahedral lattices, rendering it resistant to ion-exchange extraction. In tetrahedral sheets, Si4+ may be replaced by coupled Al3+ + Li+ substitutions, where Li+ occupies adjacent structural voids, such as ditrigonal cavities. Alternatively, Li+ may engage in coupled substitutions with Mg2+/Fe2+-for-Al3+ in octahedral sheets or directly replace Al3+ at Al-octahedral sites [38].
XRD and SEM analyses revealed that the claystone from the Liuhuanggou Coal-bearing strata was primarily composed of quartz and clay minerals. Kaolinite and illite were identified as the dominant phyllosilicates, with minor chlorite also present. All clay minerals exhibited typical layered silicate structures.
Stepwise chemical extraction (SCEE) is widely employed for the quantitative determination of trace element occurrence modes in coal, relying on the differential leaching capacities of specific reagents to characterize the elemental distribution [39]. The integrated extraction results (Figure 11) indicated that lithium in the Liuhuanggou Coal-bearing claystone predominantly existed in aluminosilicate-bound forms, suggesting a strong inorganic affinity. The secondary organic-bound fraction implies potential lithium-organic associations, possibly due to hydrothermal Li incorporation into organic substrates [40]. The minimal proportions of water-soluble and ion-exchangeable fractions (<1%) reflected poor leachability, excluding the presence of free ions or surface-adsorbed Li. These findings suggest that lithium is primarily structurally bound within mineral lattices, necessitating lattice disruption for effective extraction.
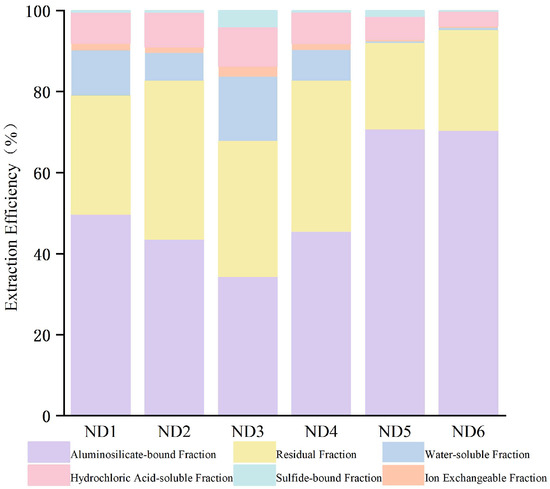
Figure 11.
Lithium leaching efficiency during sequential extraction from roof and floor samples.
TOF-SIMS analysis confirmed that lithium occurred predominantly within the aluminosilicate phases. Positive-ion mapping of sample ND5 revealed a strong spatial correlation between Li+ enrichment and Si-Al-K distributions, indicating preferential Li association with K-bearing clay minerals. Combined with the XRD and SEM results, these findings identify illite as the principal Li-hosting phase. Additionally, Li+ enrichment showed spatial co-localization with Fe and Mg, with a stronger correlation to Fe. SEM observations suggest that Li may also be incorporated into Fe-rich chlorite (e.g., chamosite). However, the low Mg content of oolitic chlorite precluded its detection by EDS. Sample ND6 provided direct mineralogical evidence of Li residing in kaolinite, which was consistent with the XRD and SEM results. Integrated analyses confirmed that structurally bound lithium primarily resided in (i) kaolinite, (ii) illite (confirmed by XRD, SEM, TOF-SIMS, and stepwise extraction), and (iii) Fe-rich chlorite, identified as chamosite (confirmed by SEM, TOF-SIMS, and stepwise extraction results).
5.3. Depositional Environment Reconstruction
5.3.1. Paleosalinity Variations
Paleosalinity has been recognized as a critical factor governing lithium enrichment in claystones [41]. The Mg/Al ratio (m = 100 × MgO/Al2O3) and Sr/Ba ratio serve as robust proxies for paleosalinity reconstruction [42]. Specifically, m > 10 indicates marine saline conditions; 1 ≤ m ≤ 10 reflects brackish transitional environments; and m < 1 denotes terrestrial freshwater settings. Similarly, Sr/Ba > 1 indicates marine conditions, 0.6 < Sr/Ba < 1 indicates brackish settings, and Sr/Ba < 0.6 indicates freshwater environments. As shown in Figure 12A, the claystones from the Xishanyao Formation have an average m value of 3.3 (ranging from 0.33 to 5.03), indicating a brackish marine–continental transitional environment. The average Sr/Ba ratio is 0.54, with lithium-rich samples ND5 and ND6 exhibiting Sr/Ba values between 0.9 and 1, suggesting a freshwater to transitional slightly saline depositional setting. Furthermore, the concentrations of Li, Ni, Ga, and Sr serve as sensitive indicators of paleosalinity [43]. A Li content greater than 150 μg/g suggests a saline (marine) environment, while values below 90 μg/g are indicative of freshwater (continental) conditions. As listed in Table 2, the average Li content in the claystones is 75.3 μg/g (range: 36.5–155.9 μg/g). Collectively, these geochemical proxies suggest that the Xishanyao Formation claystones were deposited in a transitional, slightly saline paleoenvironment.
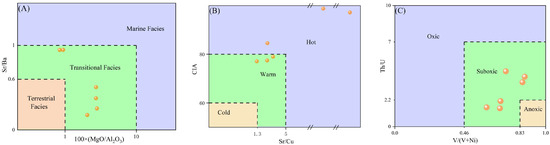
Figure 12.
Paleoenvironmental proxies. (modified after [38]). (A) Paleosalinity indicators. (B) Paleoclimate indicators. (C) Paleoredox indicators.
5.3.2. Paleoclimate
Paleoclimate is a fundamental determinant of sedimentary system dynamics that can regulate weathering intensity and rates. Quantitative reconstruction of paleoclimatic conditions can be achieved using elemental proxies [44]. The Sr/Cu ratio functions as a sensitive paleotemperature indicator, with values > 5.0 indicating hot, 1.3–5.0 warm, and <1.3 cold conditions. In this study, an average Sr/Cu ratio of 18.32 suggested a hot paleoclimate (Figure 12B). The Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA), which is controlled by both temperature and humidity, is also widely used to assess paleoclimate and chemical weathering intensity. CIA values > 80 typically reflect hot and humid conditions with intense weathering; values between 60 and 80 indicate warm and humid conditions with moderate weathering; and values < 60 correspond to cold and arid conditions with weak weathering. The mean CIA value of 85.7 in the study area further supports the interpretation of a hot and humid paleoclimate with intense weathering, which is consistent with the Sr/Cu-based inference.
5.3.3. Paleoredox Conditions
The concentrations of V, Ni, Th, and U are considered reliable redox proxies during sediment deposition [45]. The V/(V + Ni) ratio distinguishes depositional environments as anoxic (>0.83), suboxic (0.46–0.83), or oxic (<0.46) [46]. A mean V/(V + Ni) value of 0.74 (range: 0.61–0.86) indicates the suboxic depositional conditions. Uranium is readily oxidized and mobile, with enrichment typically occurring under anoxic or suboxic conditions. In contrast, thorium exhibits limited mobility and strong sediment adsorption and enrichment under oxygenated conditions [47]. Thus, the Th/U ratio serves as an additional redox indicator: <2 indicates anoxic, 2.2–7 suboxic, and >7 oxic environments. A mean Th/U value of 2.93 further supports suboxic conditions (Figure 12C). Collectively, these redox proxies confirm that the Xishanyao Formation claystones were predominantly deposited under suboxic conditions.
Pyrite typically forms in anoxic aquatic environments or within shallow subsurface sediments. Coarse-grained, euhedral pyrite crystals often occur as sac-like aggregates or vein-type formations, which develop either within the pore spaces of sediments during diagenesis or through post-diagenetic hydrothermal alteration [48]. Furthermore, numerous studies have further demonstrated that the formation and morphology of framboidal pyrite can be closely associated with redox conditions, with such structures generally forming in suboxic to anoxic sulfidic environments [49]. The abundant framboidal pyrite observed in SEM-EDS analyses (Figure 5D,E) provides additional evidence supporting deposition under oxygen-deficient conditions.
6. Conclusions
Key conclusions from integrated analyses of elemental composition, occurrence modes, and depositional environments are as follows for the coal-bearing claystone of the Xishanyao Formation at the Liuhuanggou Coal Mine:
The claystone samples exhibit substantial lithium enrichment, with concentrations reaching up to 155.9 μg/g. This value significantly exceeds the average upper continental crust values, suggesting considerable potential industrial value. Major element oxides were dominated by SiO2, Al2O3, and K2O, consistent with a mineral assemblage primarily composed of clay minerals such as kaolinite and illite, which likely provided a host structure for lithium enrichment. Lithium was found to occur predominantly in an inorganic form bound within aluminosilicates, with both direct and indirect evidence confirming its structural incorporation into clay minerals, specifically kaolinite, illite, and Fe-rich chlorite (likely chamosite). Provenance analysis indicated derivation from intermediate to felsic rocks. The depositional environment was reconstructed as a slightly brackish transitional system, formed under a hot climate with intense chemical weathering and suboxic conditions—factors that collectively promoted Li mobilization and accumulation. This study provides the first systematic investigation of Li occurrence modes in this region, offering important implications for lithium prospecting and resource evaluation in similar coal-bearing sequences.
Author Contributions
J.L.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing—original draft preparation. B.W.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation. S.F.: Visualization, Supervision, Writing–review & editing, Validation, Funding acquisition. X.L.: Methodology, Writing–review & editing. W.W.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition. R.J.: Conceptualization, Methodology. K.C.: Software, Data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region science and technology plan project-Key laboratory open subject (Grant No. 2023D04056), the National Key Research & Development Program Project (Grant No. 2021YFC2902003), the Major Scientific and Technological Project in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2022A03014) and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Science and Technology Program Project—Key Research and Development Special Project (Grant No. 2023B03013-1), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42162017).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to all the editors and reviewers who have helped us to improve and publish this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Bo Wei was employed by the Yaxin Coalbed Methane Investment and Development (Group) Limited Liability Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Hussain, A.; Prakash, A.; Chaudhary, U.A.; Zahbi, M.; Yadav, M. Lithium: A Catalyst for Sustainable Industrial Evolution. Bulletin Pure Appl. Sci.-Math. 2024, 43, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Olivetti, E.A.; Ceder, G.; Gaustad, G.G.; Fu, X.K. Lithium-ion battery supply chain considerations: Analysis of potential bottlenecks in critical metals. Joule 2017, 1, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, A. The geopolitical risk and strategic uncertainty of green growth after the Ukraine invasion: How the circular economy can decrease the market power of and resource dependency on critical minerals. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2023, 3, 1099–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Zou, T.R.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, D.H.; Ding, X. The metallogenetic regularities of lithium deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2015, 89, 652–670. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, N.; Wei, Q.; Liu, J.J. Advance and prospect of researches on the mineralization of critical elements in coal-bearing sequences. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2024, 43, 49–63+5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.F.; Zhou, X.P. Research Progress on the Metallogenic Characteristics of Sedimentary Lithium Deposits and the Occurrence State of Lithium. Met. Mine 2024, 53, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wen, H.J.; Yu, W.X.; Luo, C.G.; Du, S.J.; Ling, K.Y.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.H. Study on the occurrence state and enrichment mechanism of lithium in lithium-rich clay rock series of the Daoshitou Formation of Lower Permian in Central Yunnan. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 2080–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.B.; Dai, S.F. Lithium resources in coal-bearing strata: Occurrence, mineralization, and resource potential. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Fu, Y.; Yan, S.; Chen, P.W.; Cao, C.; Guo, C.; Wu, P.; Long, Z.; Long, K.S.; Wang, T.S.; et al. The source, host minerals, and enrichment mechanism of lithium in the Xinmin bauxite deposit, northern Guizhou, China: Constraints from lithium isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Bechtel, A.; Eble, C.F.; Flores, R.M.; French, D.; Graham, I.T.; Hood, M.M.; Hower, J.C.; Korasidis, V.A.; Moore, T.A.; et al. Recognition of peat depositional environments in coal: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 219, 103383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Scientific Publications (Oxford): Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Morford, J.L.; Emerson, S. The geochemistry of redox sensitive trace metals in sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1735–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Luo, Z.J.; Wang, K.; Liu, K.; Ren, Y.; Deng, Y. Boundary Changes of Jurassic-Cretaceous Prototype Basin of Southern Junggar and Responses of Sedimentary Provenance and Depositional Systems. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.P.; Yu, X.H.; Li, S.L.; Li, S.L.; Chen, B.T.; Shan, X.; Wang, Z.X. Discussion on the Model of Braided River Transform to Meandering River:As an example of Toutunhe Formation in Southern Junggar Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2014, 32, 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, H.J.; Tao, N.; Xu, F.; Ye, Q. Mineralogical and geochemical investigations of the Li-rich clay strata from Central Yunnan, Southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 181, 106614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.J.; Xu, F.; Cui, L.; Wang, J.X.; Li, S.Y.; Zhao, Z.S.; Xiao, L.; Guo, Y.X.; Zhao, C.L. Geochemistry characteristics and resource utilization of strategically critical trace elements from coal-related resources. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.L.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Z.Q. Characteristics and geological significance of burnt rocks in Liuhuanggou area, along northern margin of Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2024, 51, 854–866+879. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Constraints of Petrogeochemical Characteristics of Jurassic Sandstone on Provenance and Paleoenvironment in the Southern Margin of Junggar Basin. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.C.; Li, C.F.; Wang, A.M. Hydrogeological conditions and their effect on the coalbed methane enrichment in Liuhuanggou area on the south margin of Junggar basin. Coal Geol. Explor. 2018, 46, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.P. Characterization of mineral-bearing petrology and posterozoic alteration in the Sulphur Gully mineralized zone at the southern margin of the Junggar Basin. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2013, 33, 205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Che, K.X. Elemental Geochemistry of Critical Metal in Coal and Retention Characteristics During Coal Combustion—A Case Study of Xinjing No. 8 Coal. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis and significance of mineral matter in coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xing, Y.W.; Zhang, W.G.; Song, W.J.; Wang, P.P. Enrichment of U–Se–Mo–Re–V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: Geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, B.C.; Sahu, B.K. Factor analysis of sphericity and roundness data of clastic quartz grains: Environmental significance. Sediment. Geol. 1974, 11, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Wang, W.F.; Bai, H.Y.; Lu, Q.F.; He, X.; Wang, W.L.; Shi, Z.L. Element geochemistry and uranium speciation characteristics of uranium-rich coal in Honghaigou mine, Yili basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Sahraeyan, M.; Bahrami, M. Geochemistry of sandstones from the Aghajari Formation, Folded Zagros Zone, southwestern Iran: Implication for paleoweathering condition, provenance, and tectonic setting. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 4, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.A.M.; Zaki, A.A.; Elwan, W.; El-Naggar, M.R.; Gouda, M.M. Experimental and modeling investigations of cesium and strontium adsorption onto clay of radioactive waste disposal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Xie, P.P.; Jia, S.H.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Yan, X.Y.; French, D. Enrichment of U-Re-V-Cr-Se and rare earth elements in the Late Permian coals of the Moxinpo Coalfield, Chongqing, China: Genetic implications from geochemical and mineralogical data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.H.; Wei, Y.C.; Qin, G.H.; Ning, S.Z.; Cao, D.Y.; Wang, A.W. Geochemistry, mineralogy, and coal petrology of No. 4 coal in Sandaoling Mine, Turpan-Hami Basin, northwest China: Provenance and peat depositional environment. Minerals 2023, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Weathering and global denudation. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Graham, I.T.; Ward, C.R.A. review of anomalous rare earth elements and yttrium in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.F. Geochemistry and Enrichment Genesis of High Alkali High Inertinite Coals from the Eastern Junggar Coalfield, Xinjiang; China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, K.; Vandenberghe, N.; Elsen, J. Surface textural analysis of quartz grains by scanning electron microscopy (SEM): From sample preparation to environmental interpretation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 128, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanzu, C.; Maboko, M.A.H.; Manya, S. Geochemistry of fine-grained clastic sedimentary rocks of the Neoproterozoic Ikorongo Group, NE Tanzania: Implications for provenance and source rock weathering. Precambrian Res. 2008, 164, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhou, X.P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.F. Geochemical features of lithium–rich bauxite from the Benxi Formation in Qinyuan County, Shanxi, China: Insights into their depositional environment and lithium enrichment. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 163, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Gu, L.D.; Seredin, V.V.; Liu, H.D.; Zhou, D.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zou, J.H.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the coal in the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, China: Further evidence for the existence of an Al (Ga and REE) ore deposit in the Jungar Coalfield. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 98, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Liu, L.S.; Kang, X.J.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.F. Enrichment of lithium in the claystone coal gangue from the Malan mine, Xishan Coalfield, Shanxi Province, Northern China. Geochemistry 2023, 83, 125972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.F.; Wu, Z.X. Lithium occurrence state and sedimentary environment of clay rocks in coal-bearing strata in southern Shanxi. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 2395–2408. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, K.W.; French, D.H.; Farrell, O.P.; Wood, R.A.; Huggins, F.E. Modes of occurrence of trace and minor elements in some Australian coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, T.R.; Coble, M.A.; Dilles, J.H. Hydrothermal enrichment of lithium in intracaldera illite-bearing claystones. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, R.L.; Meixner, A.; Hahne, K. Lithium and boron isotopic composition of sedimentary rocks—The role of source history and depositional environment: A 250 Ma record from the Cadomian orogeny to the Variscan orogeny. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Guo, S.B. Sedimentary response and restoration of paleoshoreline of Taiyuan-Shanxi Formations in North China basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 152, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.C.; Deng, X.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Tian, J.C.; Li, S.X.; You, J.Q. Geochemical Characteristics and Environmental Implications of Trace Elements of Zhifang Formation in Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2017, 35, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.R.; He, S.; He, Z.L.; Li, X.C.; Zhai, G.Y.; Huang, Z.Q. Petrographical and geochemical characterization of the Upper Permian Longtan formation and Dalong Formation in the Lower Yangtze region, South China: Implications for provenance, paleoclimate, paleoenvironment and organic matter accumulation mechanisms. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 139, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, R.S.; Liu, C.L.; Gong, H.W.; Dun, C.; Tong, C.; Chamssidini, L.G. Paleo-sedimentary environment in relation to enrichment of organic matter of Early Cambrian black rocks of Niutitang Formation from Xiangxi area China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 112, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Tian, J.C.; Wang, F.; Liang, Q.S.; Yang, T.; Kneller, B.; Liang, X.W. Sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment of black mudstones from the upper Triassic Chang-7 member in the Ordos Basin, Northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 224, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, R.W. Geochemical Prospecting for Thorium and Uranium Deposits; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.J.; Ulrich, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Trace element compositions of sulfides from Pb-Zn deposits in the Northeast Yunnan and northwest Guizhou Provinces, SW China: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analyses of sphalerite and pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Liu, J.S. A re-assessment of elemental proxies for paleoredox analysis. Chem. Geol. 2020, 540, 119549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).