Effects of Superfine Cement on Fluidity, Strength, and Pore Structure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill
Abstract
1. Introduction
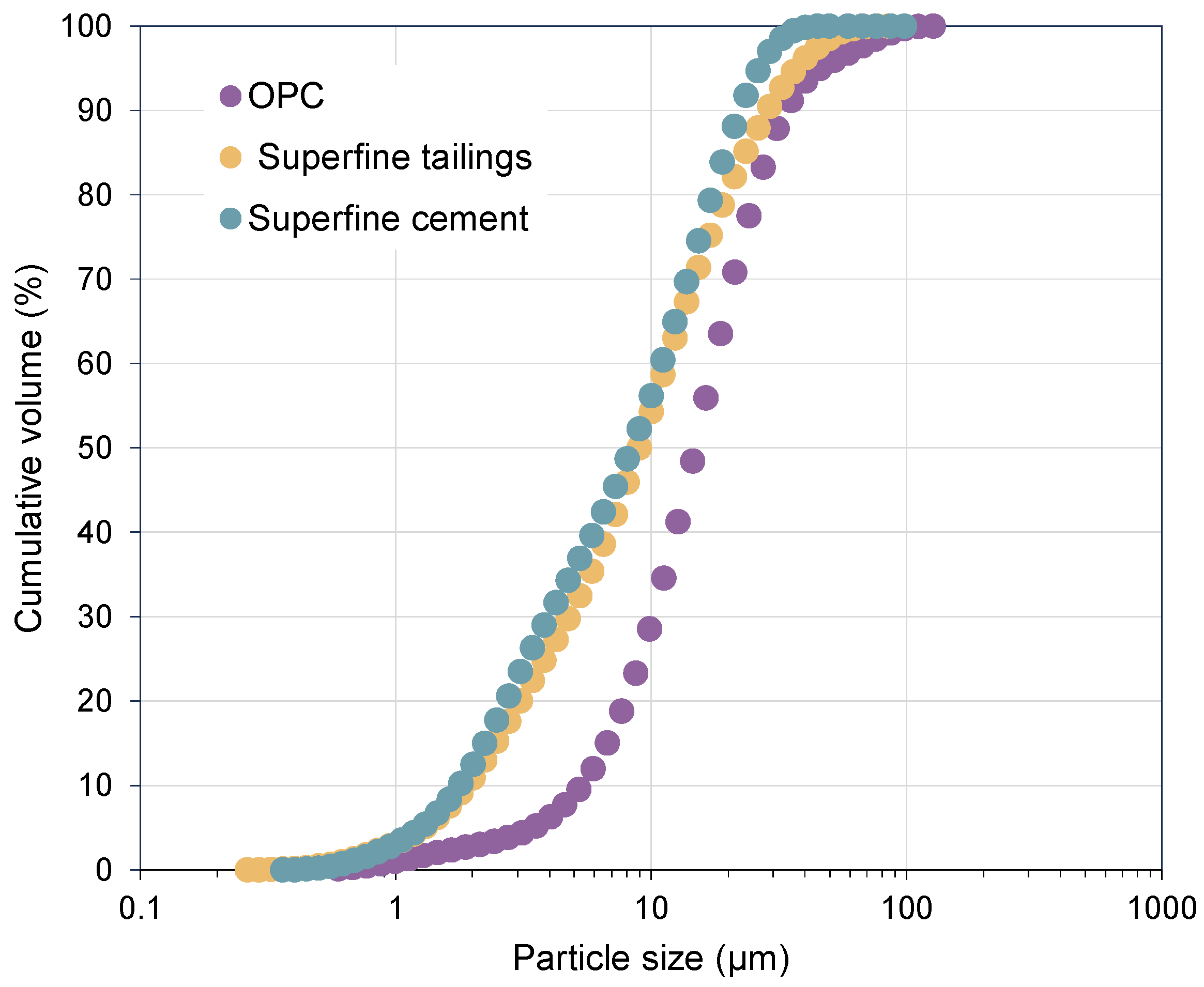
2. Raw Materials and Sample Preparation
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Fluidity Test
3.2. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) Test
3.3. Packing Density and Water Film Thickness (WFT) Test
3.4. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) Test
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Fluidity Characteristics of STCPB
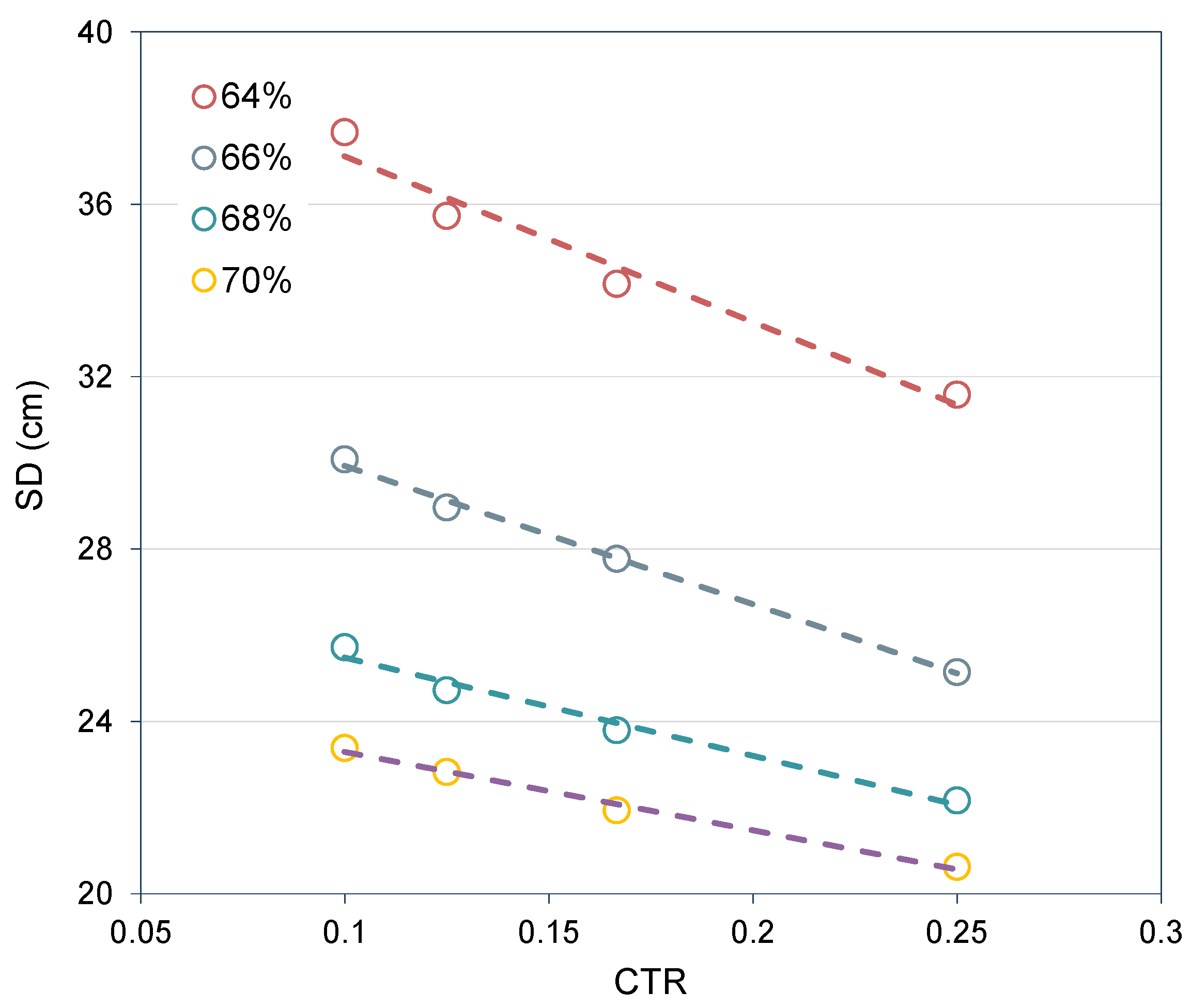
4.1.1. Effect of CTR
4.1.2. Effect of SC
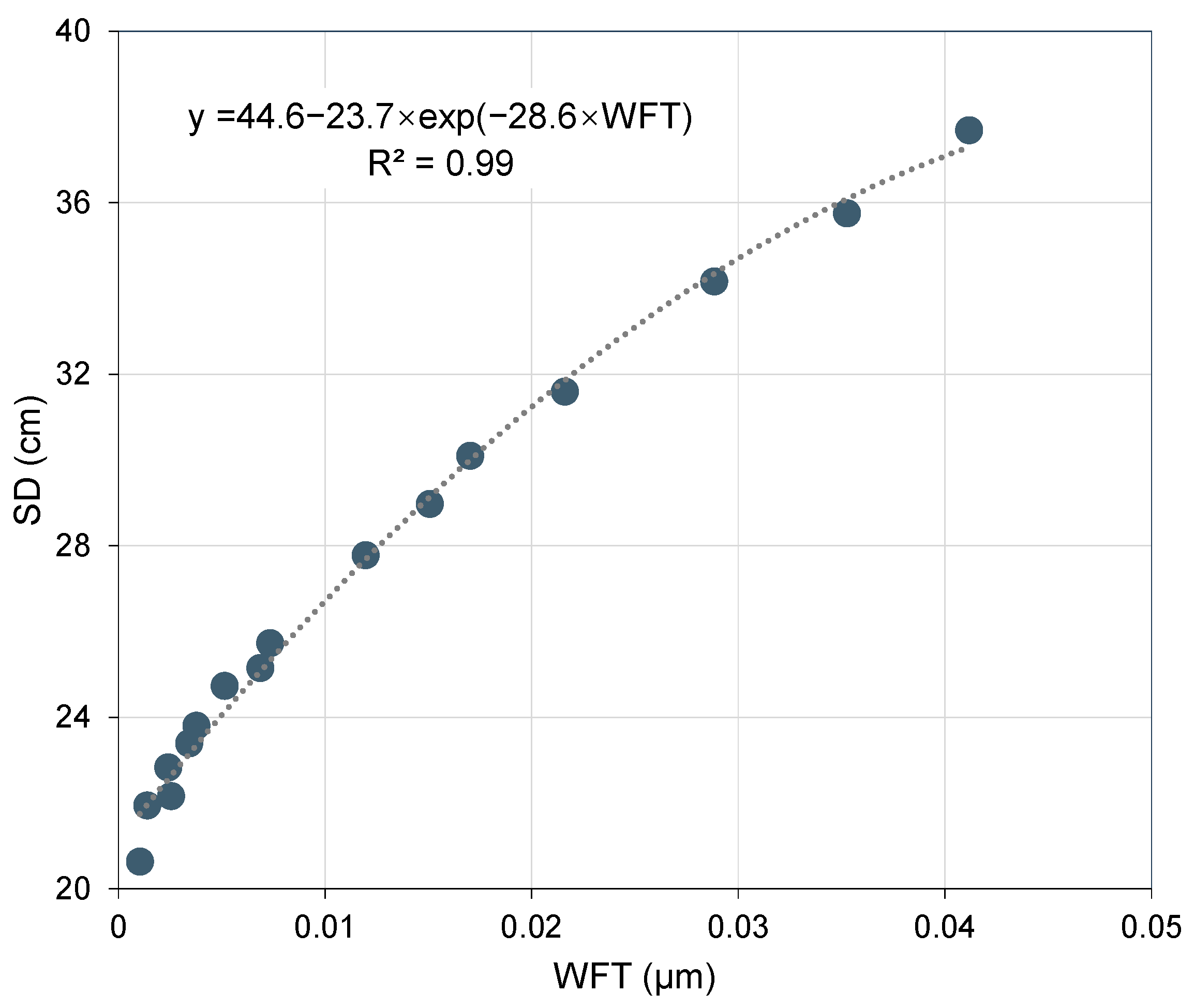
4.1.3. Relationship Between WFT and Fluidity of STCPB
4.2. UCS Characteristics of STCPB
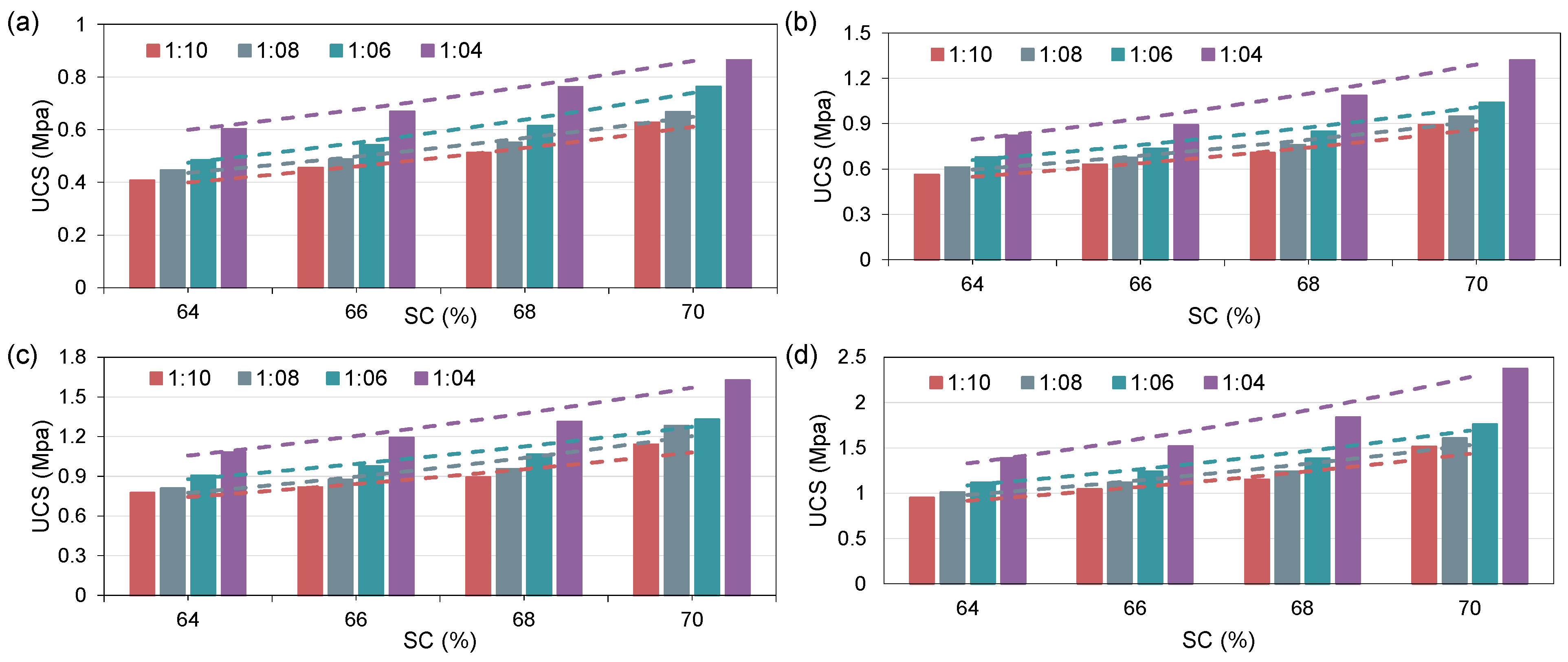
4.2.1. Effect of CTR
4.2.2. Effect of SC
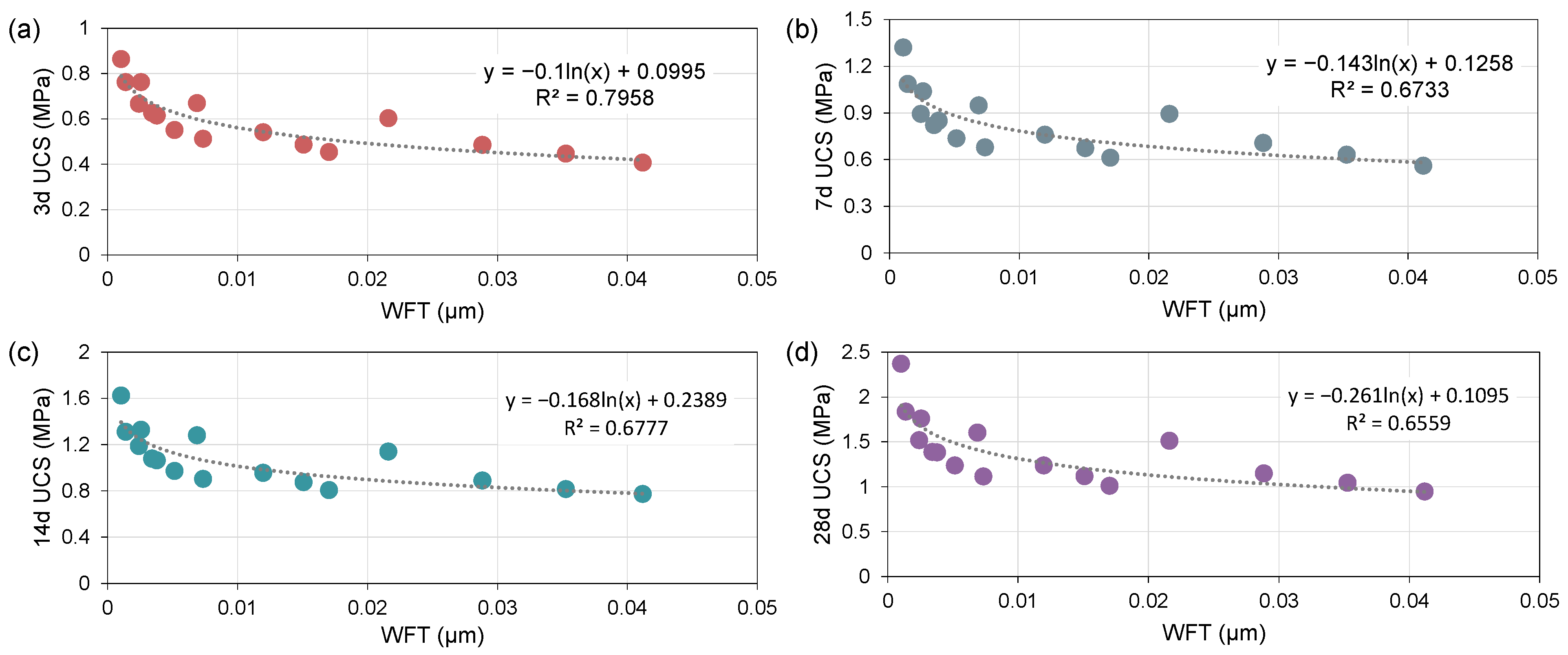
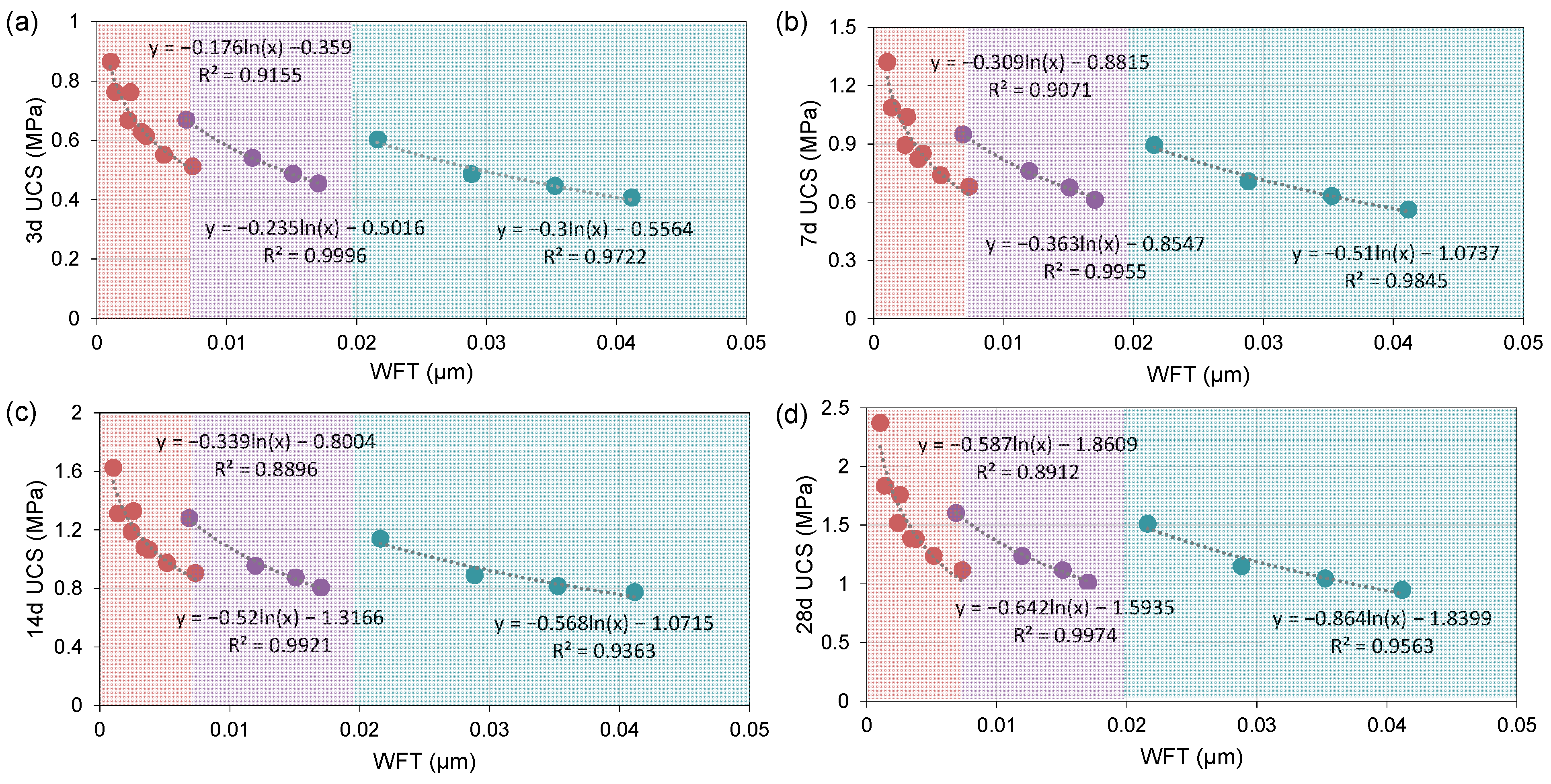
4.2.3. Relationship Between WFT and UCS of STCPB
4.3. Pore Structure Characteristics of STCPB
4.4. Interaction of STCPB with Reinforcements: Challenges and Characteristics
5. Conclusions
- The cement–tailings ratio (CTR) and solid content (SC) exhibit distinct linear and logarithmic relationships, respectively, with the spread diameter (SD) of STCPB. Furthermore, WFT demonstrates a significant exponential correlation with SD, where an increase in WFT reduces inter-particle friction, thereby enhancing fluidity;
- The CTR and SC demonstrate exponential relationships with the UCS of STCPB, with higher values enhancing strength due to increased hydration products and reduced porosity;
- The effect of WFT on the UCS of STCPB is complex and varies across low, moderate, and high ranges. At low WFT (0 μm < WFT < 0.0071 μm), cement hydration and particle bonding are enhanced, resulting in higher strength. In the moderate WFT range (0.0071 μm < WFT < 0.0193 μm), a balance between hydration and flowability is achieved. However, at high WFT (WFT > 0.0193 μm), hydration efficiency and bonding decrease, leading to a reduction in STCPB strength;
- The introduction of superfine cement significantly improves the pore structure of STCPB, reducing porosity and the proportion of macropores. These structural refinements enhance the overall mechanical performance compared to conventional cement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, G.; Dai, K.; Hu, Q.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, K.; et al. Study on the Rheological and Thixotropic Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Cemented Paste Backfill Containing Blast Furnace Slag. Minerals 2024, 14, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Pel, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Kwek, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Qu, Z. A Contribution to Understanding the Rheological Measurement, Yielding Mechanism and Structural Evolution of Fresh Cemented Paste Backfill. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 143, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moselly, Z.; Fall, M. Multiphysical Testing of Strength Development of Cemented Paste Backfill Containing Superplasticizer. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 105772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, H.; Wu, A.; Jiao, H.; Chen, X.; Kou, Y.; Dong, M. Particle Aggregation and Breakage Kinetics in Cemented Paste Backfill. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagade, A.; Fall, M. Study of Fresh Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill Material with Ternary Cement Blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupouli, N.J.F.; Belem, T.; Rivard, P.; Effenguet, H. Direct Shear Tests on Cemented Paste Backfill–Rock Wall and Cemented Paste Backfill–Backfill Interfaces. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solismaa, S.; Torppa, A.; Kuva, J.; Heikkilä, P.; Hyvönen, S.; Juntunen, P.; Benzaazoua, M.; Kauppila, T. Substitution of Cement with Granulated Blast Furnace Slag in Cemented Paste Backfill: Evaluation of Technical and Chemical Properties. Minerals 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhers, S.; Guggenberger, R.; Freimut, D.; Fataei, S.; Schwesig, P.; Martic, Z. Impact of Admixtures on Environmental Footprint, Rheological and Mechanical Properties of LC3 Cemented Paste Backfill Systems. Minerals 2023, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E. Structural Characteristics of Cement-Based Tail Fill with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate, Azodicarbonamide, and Dodecyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide. Powder Technol. 2024, 452, 120507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E. Characterizing Mechanical and Multiscale Porosity Features of Cementitious High Sulfur Tailings Backfill Using CT Technology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 194, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M. A Comparative Study on the Workability, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cemented Fine Tailings Backfill with Different Binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, L.; Ngo, I.; Yu, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, J.; Gao, Q.; Peng, C.; Wang, D.; Alarifi, S.S.; et al. Experimental Investigation on Hydrophobic Alteration of Mining Solid Waste Backfill Material. Minerals 2024, 14, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Key Theory and Technology of Cemented Paste Backfill for Green Mining of Metal Mines. Green Smart Min. Eng. 2024, 1, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Tailings Fineness on Flow, Strength, Ultrasonic and Microstructure Characteristics of Cemented Paste Backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, B.; Han, B. Development of Cemented Paste Backfill with Superfine Tailings: Fluidity, Mechanical Properties, and Microstructure Characteristics. Materials 2023, 16, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, P.; Guo, N. Analysis of the Sedimentation Characteristics of Ultrafine Tailings Based on an Orthogonal Experiment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5137092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, H. Improving the Performance of Superfine-Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill with a New Blended Binder. Powder Technol. 2021, 394, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gan, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J. Additivity Effect on Properties of Cemented Ultra-Fine Tailings Backfill Containing Sodium Silicate and Calcium Chloride. Minerals 2024, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, K.; Cai, R.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Han, B. Properties of Modified Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill: Effects of Mixing Time and Al2O3 Dosage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, B.; Han, B. Effect of Nano-SiO2 on Mechanical Properties, Fluidity, and Microstructure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Exploring the Influence Factors of Early Hydration of Ultrafine Cement. Materials 2021, 14, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Kwan, A.K.H. Superfine Cement for Improving Packing Density, Rheology and Strength of Cement Paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, Z.; Zou, Y.; Xie, H.; Guan, R. Study on the Strength and Micro Characteristics of Grouted Specimens with Different Superfine Cement Contents. Materials 2021, 14, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Mollamahmutoğlu, M. UCS Properties of Superfine Cement–Grouted Sand. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 6016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; She, W.; Sun, W. Reducing Environmental Impacts and Carbon Emissions: Study of Effects of Superfine Cement Particles on Blended Cement Containing High Volume Mineral Admixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Packing Density and Water Film Thickness on the Fluidity Behaviour of Cemented Paste Backfill. Powder Technol. 2020, 359, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.A.; Tawfik, T.A.; Abd El-razik, M.M.; Faried, A.S. Mechanical and Acoustic Absorption Properties of Lightweight Fly Ash/Slag-Based Geopolymer Concrete with Various Aggregates. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 21142–21154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.H.C.; Kwan, A.K.H. Packing Density of Cementitious Materials: Part 1—Measurement Using a Wet Packing Method. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2008, 41, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Fung, W.W.S.; Wong, H.H.C. Water Film Thickness, Flowability and Rheology of Cement–Sand Mortar. Adv. Cem. Res. 2010, 22, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Xing, J.; Li, S. Strength Characteristics and Failure Mechanism of Cemented Super-Fine Unclassified Tailings Backfill. Minerals 2017, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W. Evaluation of Viscosity, Strength and Microstructural Properties of Cemented Tailings Backfill. Minerals 2018, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Kirichek, A.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, L. Recycling Waste Tyre Polymer for Production of Fibre Reinforced Cemented Tailings Backfill in Green Mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, K.; Kirichek, A.; Liu, C.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, Z. Rheology of Flexible Fiber-Reinforced Cement Pastes: Maximum Packing Fraction Determination and Structural Build-up Analysis. Compos. Struct. 2025, 352, 118662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Long, J.; Lu, G.; Lei, H. Investigation on Roles of Packing Density and Water Film Thickness in Synergistic Effects of Slag and Silica Fume. Materials 2022, 15, 8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, H.; Xing, J.; Sun, X.; Ma, Z. Flowability of Ultrafine-Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill Incorporating Superplasticizer: Insight from Water Film Thickness Theory. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.K.H.; Fung, W.W.S. Roles of Water Film Thickness and SP Dosage in Rheology and Cohesiveness of Mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, W.; Yilmaz, E.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, J. A Combined Experimental and Numerical Study on the Triaxial and Dynamic Compression Behavior of Cemented Tailings Backfill. Eng. Struct. 2020, 219, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barralet, J.E.; Gaunt, T.; Wright, A.J.; Gibson, I.R.; Knowles, J.C. Effect of Porosity Reduction by Compaction on Compressive Strength and Microstructure of Calcium Phosphate Cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2002, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Nie, S.; Skibsted, J.; Ye, G. Structural Evolution of Calcium Sodium Aluminosilicate Hydrate (C-(N-) ASH) Gels Induced by Water Exposure: The Impact of Na Leaching. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 178, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Hydration Kinetics, Strength, Autogenous Shrinkage, and Sustainability of Cement Pastes Incorporating Ultrafine Limestone Powder. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xing, M.; Yang, X.; Jiao, H.; Yang, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Study on the Long-Term Durability and Leaching Characteristics of Low-Consumption Cement Backfill under Different Environmental Conditions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Hwang, Y.-C. Numerical Analysis on Effect of Permeability and Reinforcement Length (Drainage Path) in Reinforced Soil. J. Korean GEO Environ. Soc. 2007, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, A.; Room, S.; Iqbal, S.; Mahmood, K.; Iqbal, Q. An Experimental Study of Bond Behavior of Micro Steel Fibers Added Self-Compacting Concrete with Steel Reinforcement. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2020, 64, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshan, K.; Sampath, K. Impact of Particle Morphology on the Shear Behavior of Quarry Dust/Sea Sand+ Concrete Interface in Geotechnical Structures. In Proceedings of the 2024 Moratuwa Engineering Research Conference (MERCon), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 8–10 August 2024; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Leklou, N.; Casari, P.; de Barros, S. Fiber-Matrix Bond Strength by Pull-out Tests on Slag-Based Geopolymer with Embedded Glass and Carbon Fibers. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SC (%) | CTR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:10 | 1:8 | 1:6 | 1:4 | |
| 64 | 37.68 | 35.74 | 34.16 | 31.59 |
| 66 | 30.08 | 28.96 | 27.77 | 25.14 |
| 68 | 25.73 | 24.73 | 23.80 | 22.16 |
| 70 | 23.39 | 22.82 | 21.94 | 20.63 |
| Fitting Type | SC (%) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 66 | 68 | 70 | ||
| Linear | 0.991 | 0.951 | 0.981 | 0.967 | 0.973 |
| Exponential | 0.986 | 0.940 | 0.975 | 0.961 | 0.966 |
| Logarithmic | 0.930 | 0.844 | 0.902 | 0.864 | 0.885 |
| Fitting Type | CTR | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:4 | 1:6 | 1:8 | 1:10 | ||
| Linear | 0.912 | 0.942 | 0.940 | 0.941 | 0.934 |
| Exponential | 0.943 | 0.969 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.962 |
| Logarithmic | 0.990 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.995 |
| CTR | Curing Time (d) | SC (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 66 | 68 | 70 | ||
| 1:4 | 3 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.86 |
| 7 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 1.09 | 1.32 | |
| 14 | 1.08 | 1.19 | 1.31 | 1.62 | |
| 28 | 1.39 | 1.52 | 1.84 | 2.37 | |
| 1:6 | 3 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.76 |
| 7 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.85 | 1.04 | |
| 14 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 1.06 | 1.33 | |
| 28 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.38 | 1.76 | |
| 1:8 | 3 | 0.45 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.67 |
| 7 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.95 | |
| 14 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 1.28 | |
| 28 | 1.01 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.61 | |
| 1:10 | 3 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.63 |
| 7 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 0.89 | |
| 14 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 1.14 | |
| 28 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 1.15 | 1.51 | |
| Curing Time (d) | Fitting Type | SC (%) | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 66 | 68 | 70 | |||
| 3 | Linear | 0.914 | 0.909 | 0.913 | 0.968 | 0.926 |
| Exponential | 0.940 | 0.938 | 0.942 | 0.981 | 0.951 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.791 | 0.775 | 0.780 | 0.863 | 0.802 | |
| 7 | Linear | 0.938 | 0.914 | 0.892 | 0.870 | 0.903 |
| Exponential | 0.961 | 0.939 | 0.926 | 0.904 | 0.933 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.820 | 0.783 | 0.752 | 0.724 | 0.770 | |
| 14 | Linear | 0.910 | 0.919 | 0.915 | 0.905 | 0.912 |
| Exponential | 0.936 | 0.946 | 0.943 | 0.924 | 0.937 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.769 | 0.789 | 0.783 | 0.806 | 0.787 | |
| 28 | Linear | 0.898 | 0.912 | 0.870 | 0.833 | 0.878 |
| Exponential | 0.928 | 0.939 | 0.910 | 0.876 | 0.913 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.760 | 0.778 | 0.724 | 0.679 | 0.735 | |
| Curing Time (d) | Fitting Type | CTR | Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:10 | 1:8 | 1:6 | 1:4 | |||
| 3 | Linear | 0.953 | 0.946 | 0.946 | 0.991 | 0.959 |
| Exponential | 0.975 | 0.970 | 0.971 | 0.998 | 0.979 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.845 | 0.829 | 0.832 | 0.916 | 0.856 | |
| 7 | Linear | 0.935 | 0.934 | 0.943 | 0.954 | 0.942 |
| Exponential | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.969 | 0.978 | 0.968 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.820 | 0.814 | 0.821 | 0.836 | 0.823 | |
| 14 | Linear | 0.853 | 0.855 | 0.897 | 0.928 | 0.883 |
| Exponential | 0.889 | 0.895 | 0.926 | 0.954 | 0.916 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.703 | 0.710 | 0.762 | 0.809 | 0.746 | |
| 28 | Linear | 0.886 | 0.901 | 0.922 | 0.930 | 0.910 |
| Exponential | 0.922 | 0.935 | 0.951 | 0.965 | 0.943 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.752 | 0.771 | 0.798 | 0.799 | 0.780 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, K.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Luo, G.; Dai, K.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Effects of Superfine Cement on Fluidity, Strength, and Pore Structure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill. Minerals 2025, 15, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010024
Zhu K, Wang H, Zhao X, Luo G, Dai K, Hu Q, Liu Y, Liu B, Miao Y, Liu J, et al. Effects of Superfine Cement on Fluidity, Strength, and Pore Structure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill. Minerals. 2025; 15(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Kunlei, Haijun Wang, Xulin Zhao, Guanghua Luo, Kewei Dai, Qinghua Hu, Yang Liu, Baowen Liu, Yonggang Miao, Jianbo Liu, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Superfine Cement on Fluidity, Strength, and Pore Structure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill" Minerals 15, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010024
APA StyleZhu, K., Wang, H., Zhao, X., Luo, G., Dai, K., Hu, Q., Liu, Y., Liu, B., Miao, Y., Liu, J., & Lv, D. (2025). Effects of Superfine Cement on Fluidity, Strength, and Pore Structure of Superfine Tailings Cemented Paste Backfill. Minerals, 15(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010024










