Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology for Guodian Skarn Fe Deposit in Qihe–Yucheng District, Luxi Block, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Destruction and Fe Mineralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
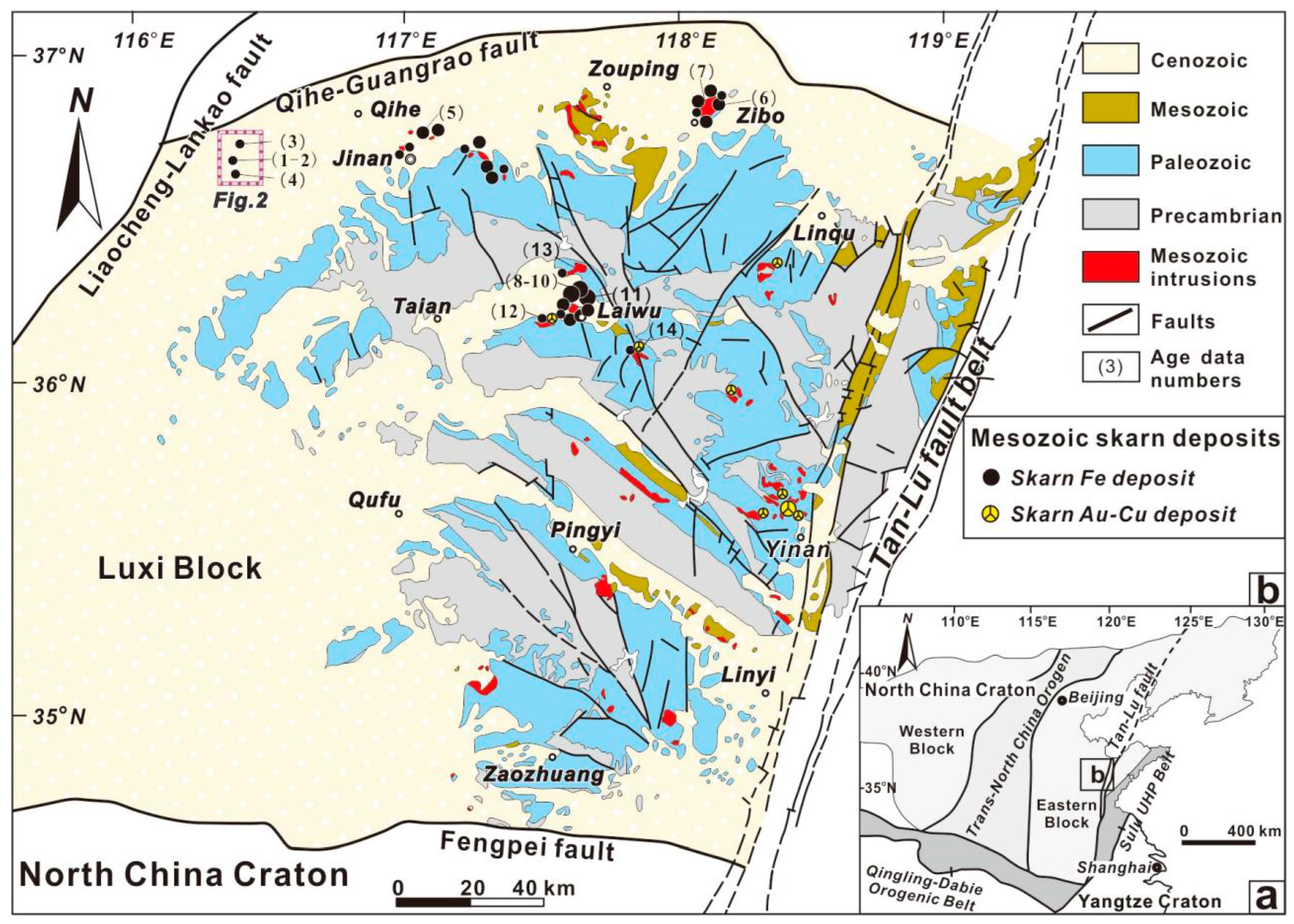
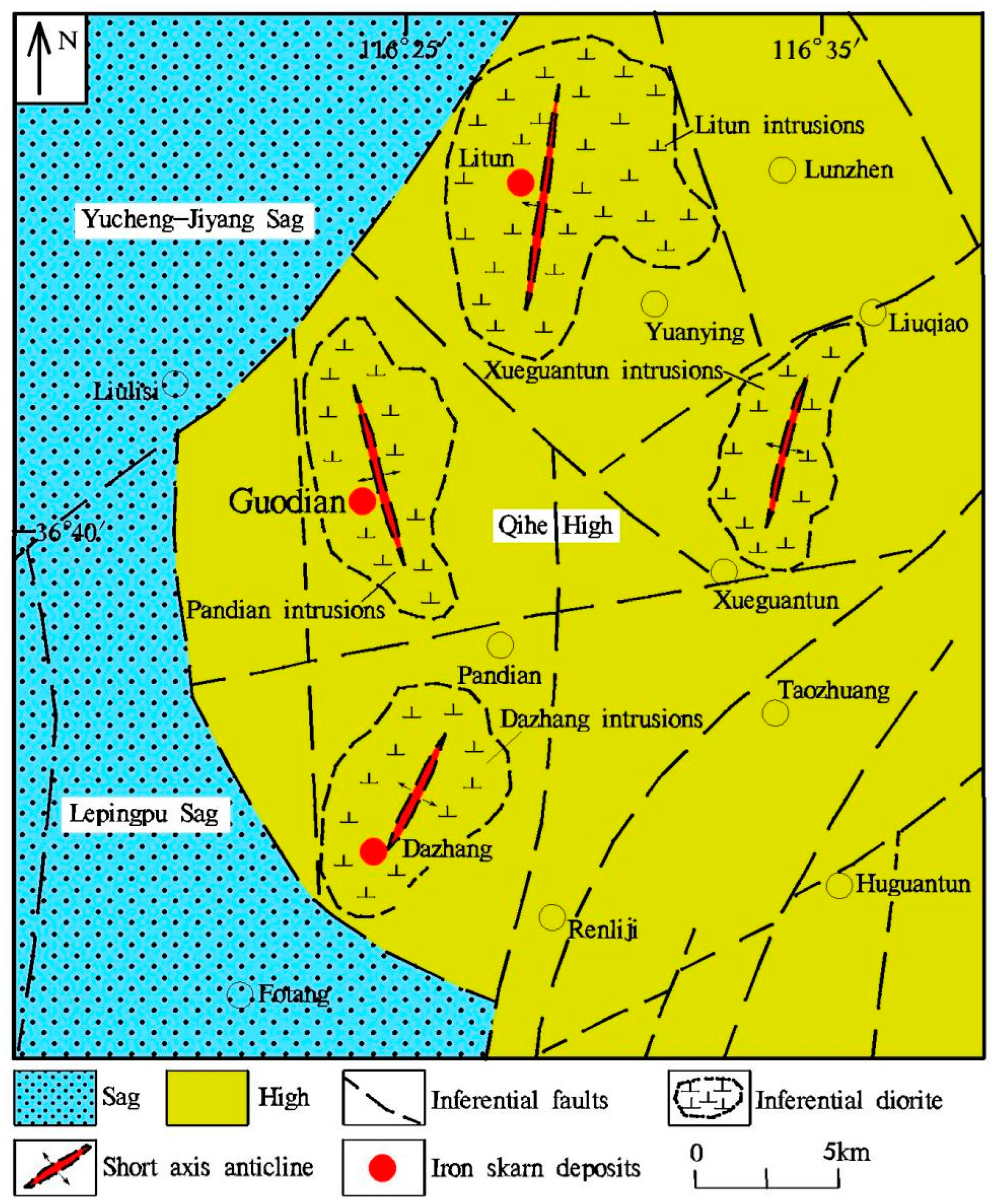
2. Geological Background
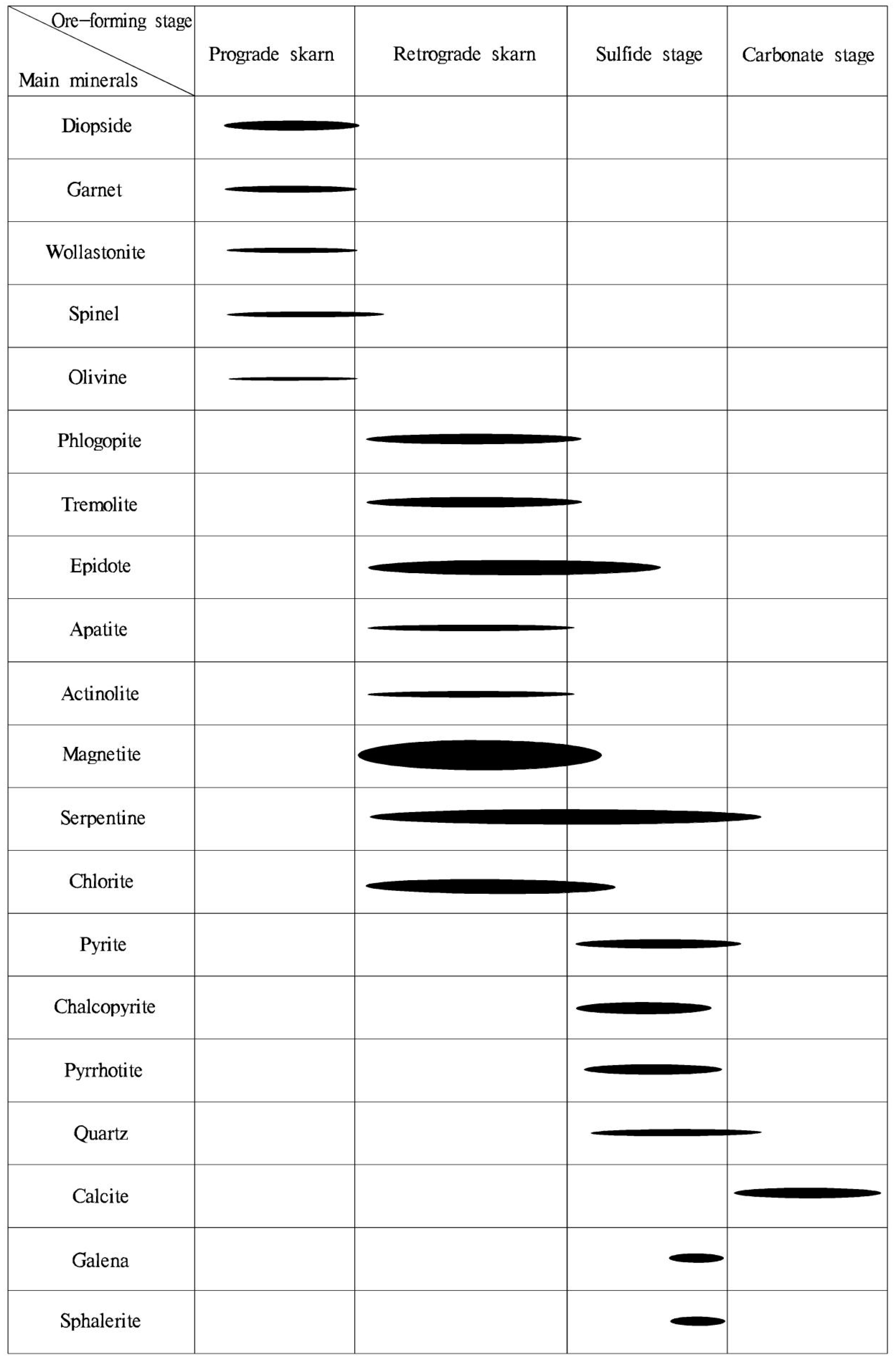
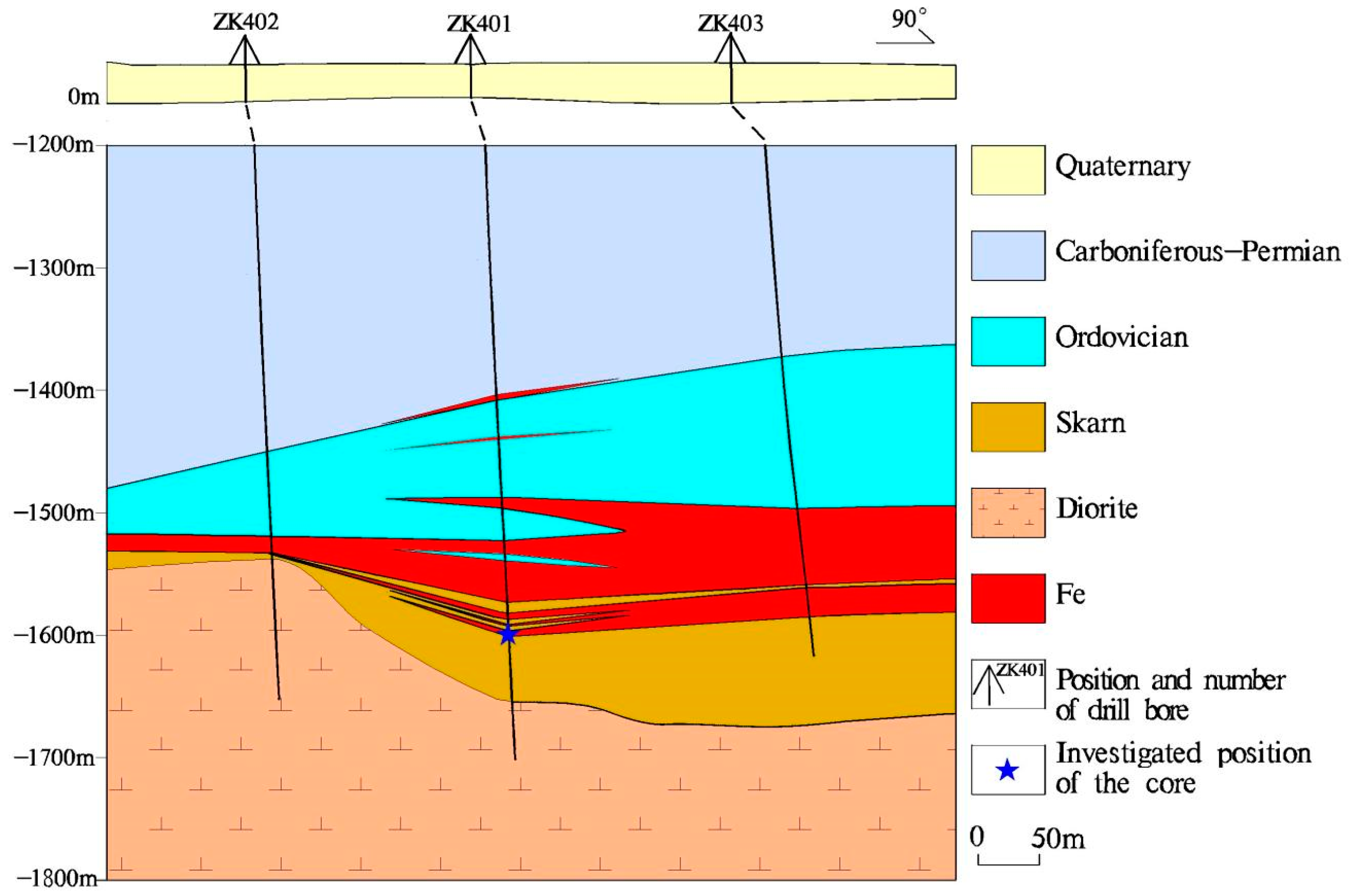
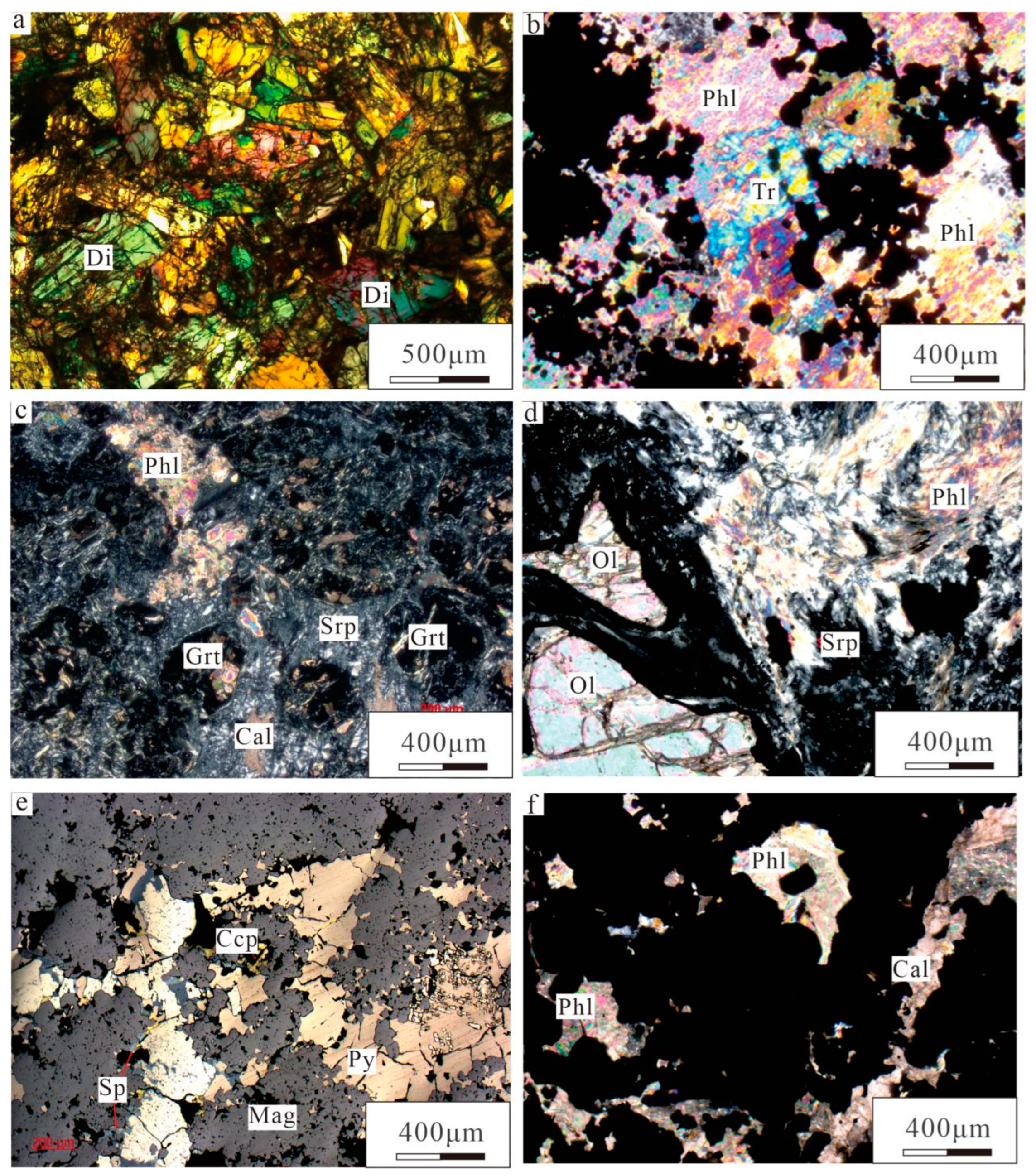
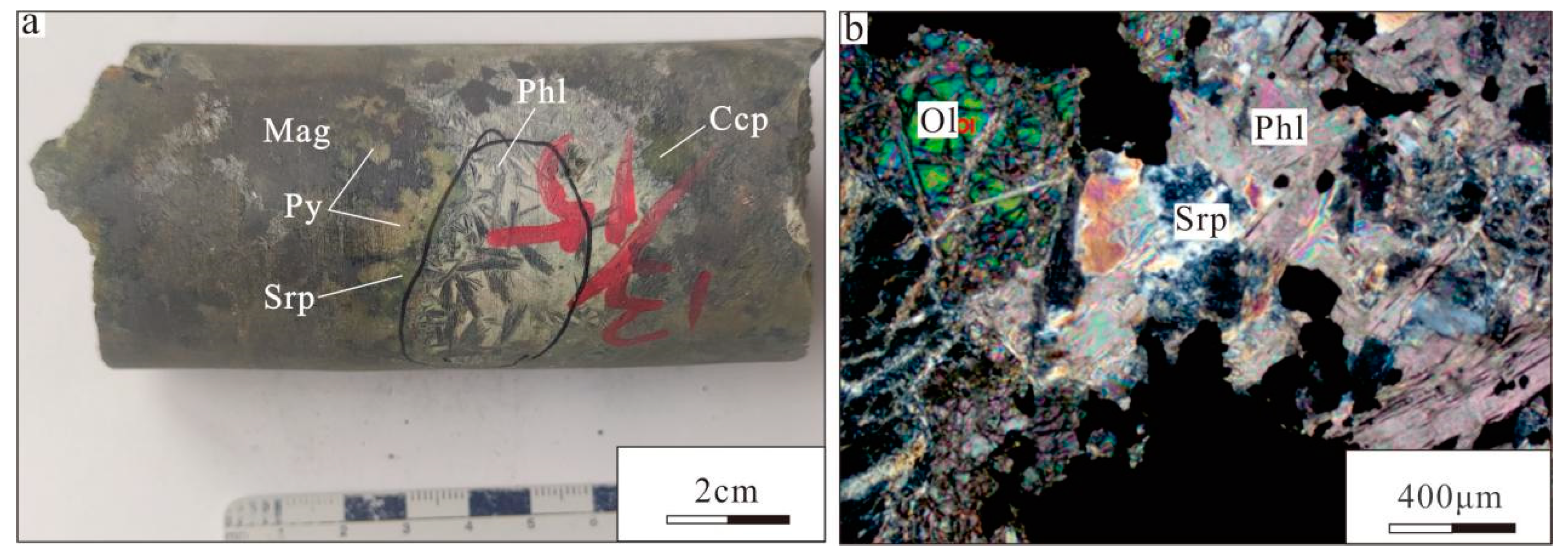
3. Ore Deposit Geology
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
5. Test Results
6. Discussion
6.1. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics
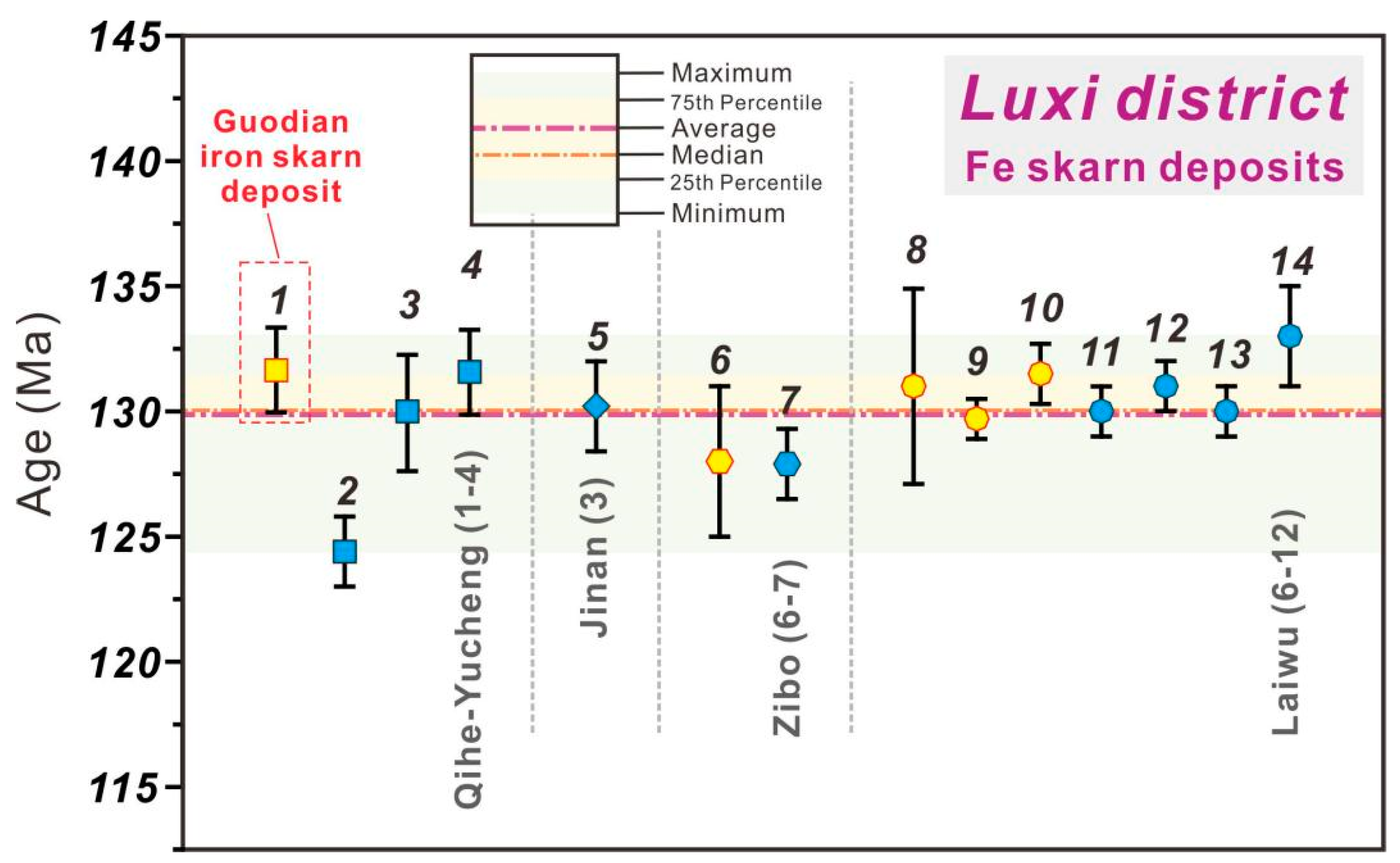
6.2. Age of the Guodian Fe Deposit
6.3. A Causal Link between Iron Skarn Mineralization and Craton Destruction
| Mining Area | Intrusion/Deposit | Number | Sample | Analytical Method | Age (Ma) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qihe-yucheng | Guodian iron deposit | 1 | Phlogopite-bearing iron ores | Phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar Dating | 131.64 ± 1.69 | This study |
| Guodian intrusions | 2 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 124.4 ± 1.4 | [8] | |
| Litun intrusions | 3 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 130 ± 2.3 | [26] | |
| Dazhang intrusions | 4 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 131.6 ± 1.7 | ||
| Ji’nan | Zhangmatun intrusions | 5 | Gabbro | Zircon U-Pb dating | 130.2 ± 1.8 | [57] |
| Zibo | Zhaokou iron deposit | 6 | Garnet skarn | Garnet U-Pb dating | 128 ± 3 | [5] |
| Jinling intrusions | 7 | Biotite diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 127.9 ± 1.4 | [56] | |
| Laiwu | Zhangjiawa iron deposit (I) | 8 | Skarn | Sphene U-Pb dating | 131 ± 3.9 | [4] |
| 9 | Phlogopite-bearing iron ores | Phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar Dating | 129.7 ± 0.8 | [5] | ||
| Zhangjiawa iron deposit (Gangli) | 10 | Phlogopite-bearing iron ores | Phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar Dating | 131.5 ± 1.2 | ||
| Kuangshan intrusions | 11 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 130 ± 1 | [4] | |
| Jiaoyu intrusions | 12 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 131 ± 1 | [55] | |
| Jinniushan intrusions | 13 | Diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 130 ± 1 | ||
| Tietonggou intrusions | 14 | Pyroxene diorite | Zircon U-Pb dating | 133 ± 2 | [56] |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.C.; Li, H.M.; Li, J.W.; Song, X.Y.; Hu, H.; Li, L.F.; Chai, F.M.; Hou, T.; Xu, D.R. Geological settings and metallogenesis of high-grade iron deposits in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 691–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Hou, T.; Li, H.M.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Song, X.Y. Enrichment mechanism of iron in magmatichydrothermal system. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.D.; Li, J.W.; Wen, G. U-Pb Geochronology of Hydrothermal Zircons from the Early Cretaceous Iron Skarn Deposits in the Handan-Xingtai District, North China Craton. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 2159–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Li, J.W. Zircon and titanite U-Pb dating of the Zhangjiawa iron skarn deposit, Luxi district, North China Craton:implications for a craton-wide iron skarn mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 89, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Gao, M.B.; Gao, J.L.; Li, C.J.; Feng, Q.W.; Li, S.Y.; Gao, W.S.; Wang, X.Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Li, J.W. Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Zhangjiawa iron deposit, Laiwu district, Shandong Province: Implications for regional iron skarn mineralization of North China Craton. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.M.; Xie, G.Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, S.M.; Guo, S.F.; Gao, X.; Li, G.D. 40Ar/39Ar dating of phlogopite from the Xishimen skarn deposit in the Handan Xingtai area, southern Hebei, and its implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the basement rocks and dioritic intrusion associated with the Fushan skarn iron deposit, southern Taihang Mountains, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Hao, X.Z. Ore-forming Origin of Rock Mass Zircon U-Pb Chronology and Geochemical Evidence of Pandian Iron Deposit in Luxi Area. Shandong Land. Resour. 2023, 39, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Zhang, A.D.; O’reilly, S.Y.; Ryan, C.G. Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean craton. In Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia, 1st ed.; Flower, M.F.J., Chung, S.L., Lo, C.H., Lee, T.Y., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DA, USA, 1998; Volume 27, pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Baker, J.; Jarvis, K.E.; Mason, P.R.D.; Menzies, M.A. On and off the North China Craton: Where is the Archaean keel? J. Petrol. 2000, 41, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Rudnick, R.L.; Yuan, H.L.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Xu, W.L.; Ling, W.L.; Ayers, J.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, Q.H. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature 2004, 432, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusky, T.M.; Windley, B.F.; Zhai, M.G. Tectonic evolution of the North China Block:from orogen to craton to orogen. Geol. Soc. 2007, 280, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, M.; Xu, Y.G.; Zhang, H.F.; Fan, W.M. Integration of geology, geophysics and geochemistry: A key to understanding the North China Craton. Lithos 2007, 96, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, J.F.; Xu, W.L.; Liu, Y.S. Delamination and destruction of the North China Craton. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, S.A.; Zhou, X.; Nemchin, A.A.; Sun, M. Mesozoic crust-mantle interaction beneath the North China craton: A consequence of the dispersal of Gondwanaland and accretion of Asia. Geology 2003, 31, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Walker, R.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Yuan, H.L.; Yang, J.H. The chemical-temporal evolution of lithospheric mantle underlying the North China Craton. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 5013–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.G.; Bian, A.G.; Zhao, T.P. The amalgamation of the supercontinent of North China Craton at the end of Neo-Archaean and its breakup during late Palaeoproterozoic and Meso-Proterozoic Science in China series D. Earth Sci. 2000, 43, 219–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, J.L. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Pei, F.P.; Lin, J.Q. 40Ar/39Ar dating of hornblende and biotite in Mesozoic intrusive complex from the North China Block: Constraints on the time of lithospheric thinning. Geochimica 2004, 33, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Xu, W.L.; Yang, D.B.; Liu, C.C.; Liu, X.M.; Hu, Z.C. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic High-Mg Diorites in West Shandong: Evidence from Chronology and Petro-geochemistry. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2006, 31, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.X.; Xu, Y.G.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.F.; Xia, Q.K.; Zheng, T.Y. Destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1565–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z. The Mineralization and Mechanism of the Iron Skarn Deposits in Laiwu District, Shandong Province. Doctoral Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.Z.; Zheng, J.M.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.S.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, G.L. Metallogenic Prognosis of Skarn-type Iron Ore Deposits in Qihe–Yucheng Area, Shandong Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Z.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.S.; Li, Y.P.; Zhi, Y.B.; Wang, J.G. Prospecting methods of skarn type iron deposit in Dezhou area, Shandong Province. Miner. Explor. 2020, 11, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.S.; Hao, X.Z.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, H.J.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, H.J.; Yu, L.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Discussion on the boundary of metallogenic geological body of skarn type iron deposits and study on its deep characteristics in Qihe-Yucheng area, Sshandong Province. Prog. Geophys. 2022, 37, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Z.; Guo, Y.M.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, C.C.; Wang, Q.Y.; Liu, B.B.; Zhi, Y.B. Metallogeny of the skarn-type iron deposits in Qihe-Yucheng ore district, Shandong Province. J. Geol. 2019, 43, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, R.Z.; Gao, S.; Feng, C.X.; Qi, L.; Zhong, Z.; Xiao, T.; Qi, Y.Q.; Wang, T.; Coulson, I.M. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and major, traceelemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of mafic dykes inwestern Shandong Province, East China: Constrains on their petro-genesis and geodynamic significance. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S. Age determinations of 40Ar-40K, 40Ar-39Ar and radiogenic 40Ar released characteristics on K-Ar geostandards. Chin. J. Geol. 1983, 4, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Steiger, R.H.; Jager, E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geo-and cosmochronology. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 36, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, A.O. A redetermination of the relative abundances of the isotope of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and potassium. Phys. Rev. 1950, 77, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers, A.A.P. ArArCALC-software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, G.B.; Lanphere, M.A. Potassium-Argon Dating; W. H. Freeman Co.: San Fransisco, CA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Fleck, R.J.; Sutter, J.F.; Elliot, D.H. Interpretation of discordant 40Ar/39Ar age-spectra of Mesozoictholeiites From Antarctica. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1977, 41, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanphere, M.A.; Dalrymple, G.B. The use of 40Ar/39Ar data in evaluation of disturbed K-Ar systems. U. S. Geol. Surv. Open-File Rep. 1978, 701, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Pringle, M.S. Age progressive volcanism in the Musicians Seamounts: A test of the hot spot hypothesis for the late Cretaceous Pacific. In The Mesozoic Pacific: Geology, Tectonics, and Volcanism; Pringle, M.S., Sager, W.W., Sliter, W.V., Stein, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 187–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, G.N.; Smimons, K.P.; Bence, A.E. 40Ar/39Ar spectrumages for biotite, hornblende and muscovite in a contact metamorphic zone. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1975, 39, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.N.; Bai, X.J. Fluid Inclusion 40Ar/39Ar Dating Technique and Its Applications. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.D.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, X.D.; Wu, S.H.; Yuan, Y.B.; Li, X.K.; Wang, T.Z. Geological characteristics and 40Ar-39Argeochronology of the Hongqiling tin deposit in southern Hunan Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3787–3797. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.T.; Zhou, M.F.; Hu, R.Z.; Shen, N.P.; Yuan, S.D.; Bi, X.W.; Du, A.D.; Qu, W.J. Precise molybdenite Re-Os and mica Ar-Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, Central Nanlingdistrict, South China. Miner. Depos. 2006, 41, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World Skarn Deposits: ECONOMIC Geology 100th Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 299–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.T.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Dai, T.M.; Li, Z.L.; Li, X.M.; Shuang, Y.; Yuan, S.D.; Liu, S.R. 40Ar/39Ar isotopic dating of tin mineralization in Furong deposit of Hunan Province and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2007, 26, 237–248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.D.; Peng, J.T.; Shen, N.P.; Hu, R.Z.; Dai, T.M. 40Ar-39Ar isotopic dating of the Xianghualing Sn-polymetallic orefield in southern Hunan, China and its geological implications. Acta Geol. Sinica 2015, 81, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.q.; Mao, J.W.; Zhao, H.J.; Duan, C.; Yao, L. Zircon U-Pb Aad phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Age of the Chengchao and jinshandian skarn Fedposits, southeast Hubei Province, Middle Lower Yangtze River Vallet metallogenicbelt, China. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Vasconcelos, P.M.; Zhou, M.F.; Deng, X.D.; Cohen, B.; Bi, S.J.; Zhao, X.F.; Selby, D. Longevity of magmatic-hydrothermal systems in the Daye Cu-Fe-Au sistrict, eastern China with implications for mineral exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wan, Y.S.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Dai, T.M.; Shi, Z.E.; Sun, J.B. Isotope Geochronology: Technique and Application. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 1917–1947. [Google Scholar]
- Snee, L.W.; Sutter, J.F.; Kelly, W.C. Thermochronology of economic mineral deposits; dating the stages of mineralization at panasqueira, portugal, by high-precision 40/39 Ar age spectrum techniques on muscovite. Econ. Geol. 1988, 83, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.N.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Pang, Z.S.; Shen, L.J.; Guan, J.Y.; Guo, C.F. Enrichment mechanism of iron in Dazhang skarn iron deposit, Shandong Province: Evidence from fluid inclusions and hydrogen-oxygen isotopes. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Lin, W.W.; Bi, C.S.; Li, D.X. Basic Geological Characteristics of skarn deposits of China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. 1986, 8, 59–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, M.H. Closure temperature in cooling geochronological andpetrological systems. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1973, 40, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giletti, B.J.; Tullis, J. Studies in diffusion: Pressure dependence of Ar diffusion in phlogopite mica. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 35, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klötzli, U.; Klötzli, E.; Günes, Z.; Kosler, J. Accuracy of Laser Ablation U-Pb Zircon Dating: Results from a Test Using Five Different Reference Zircons; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Su, L.; Sun, W.D.; Huang, H.Q.; Yi, K. Accuracy of LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb age determination: An inter-laboratory comparison. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Hu, Z.G.; Cao, C.C.; Jiang, X.P.; Mei, Z.H.; Li, Z.P.; Du, L.M.; Hua, B.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S. Iron richpreexploration potential and favorable sites for deep horizon of Jinling maticcomplexdistribution in Zibo, Shandong Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1545–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.L.; Zhao, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.F. Slab mantle interaction in continental subduction channel: Geochemical evidence from Mesozoic gabbroic intrusives in southeastern North China. Lithos 2012, 155, 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.G.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.W.; Liu, L. Generation of high Mgdiorites and associated iron mineralization within an intracontinental setting: Insights from ore-barren and oer-bearing intrusions in the eastern North China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2019, 72, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.L.; Zhang, Z.C.; Hou, T.; Santosh, M.; Han, L. Geneticrelationship of high-Mg diorotic pluton to iron mineralization: A case study from the Jinling skarn type iron deposit in the North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.C.; Hou, T.; Santosh, M.; Jin, Z.L.; Han, L.; Cheng, Z.G. Petrogenesis of the Zhangmatun gabbro in the Ji’nan Comples, North China Craton: Implications for skarn-type iron mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 1197–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.M.; Menzies, M.A. Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and accretion of asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China. Geotecton. Et Metallog. 1992, 16, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, M.A.; Fan, W.M.; Zhang, M. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. Geol. Soc. 1993, 76, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.F.; Mo, X.X.; Zhang, H.L.; Luo, Z.H.; Du, Y.S. Lithosphere root/de-rooting and activation of the east China continent. Geoscience 1994, 8, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, M.A.; Xu, Y.G. Geodynamics of the North China Craton. In Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asiain, 1st ed.; Flower, M.F.J., Chung, S.L., Lo, C.H., Lee, T.Y., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DA, USA, 1998; Volume 27, pp. 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Wilde, S.A. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: An association with lithospheric thinning. Ore Geol. Rev. 2003, 23, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.H. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Ji, L.; Ni, J.L.; Chen, X.Y. Dynamics of the Early Cretaceous lithospheric thinning and destruction of the North China craton as the consequence of Paleo-Pacific type active continental margin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3360–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.D.; Gao, M.B.; Gao, J.L.; Li, S.Y.; Feng, Q.W.; Li, J.; Cui, T.; Liu, Y.K. Geochronological, Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of pyroxene diorites in the Sanchahe iron-gold deposit, Western Shandong. Minerals 2022, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.J.; Sun, F.Y.; Liu, F.L.; Liu, J.H.; Peng, Q.M.; Ji, P.; Li, B.L.; Zhang, P.J. Mesozoic geodynamic evolution and metallogenic series of major metal deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 3045–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Duan, Z.; Gao, J.L.; Hu, H.; Wen, G.; Li, J.W. Controls on metal fertility of dioritic intrusions in the Laiwu district, North China craton: Insights from wholerock geochemistry and mineral compositions. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2023, 136, 1287–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


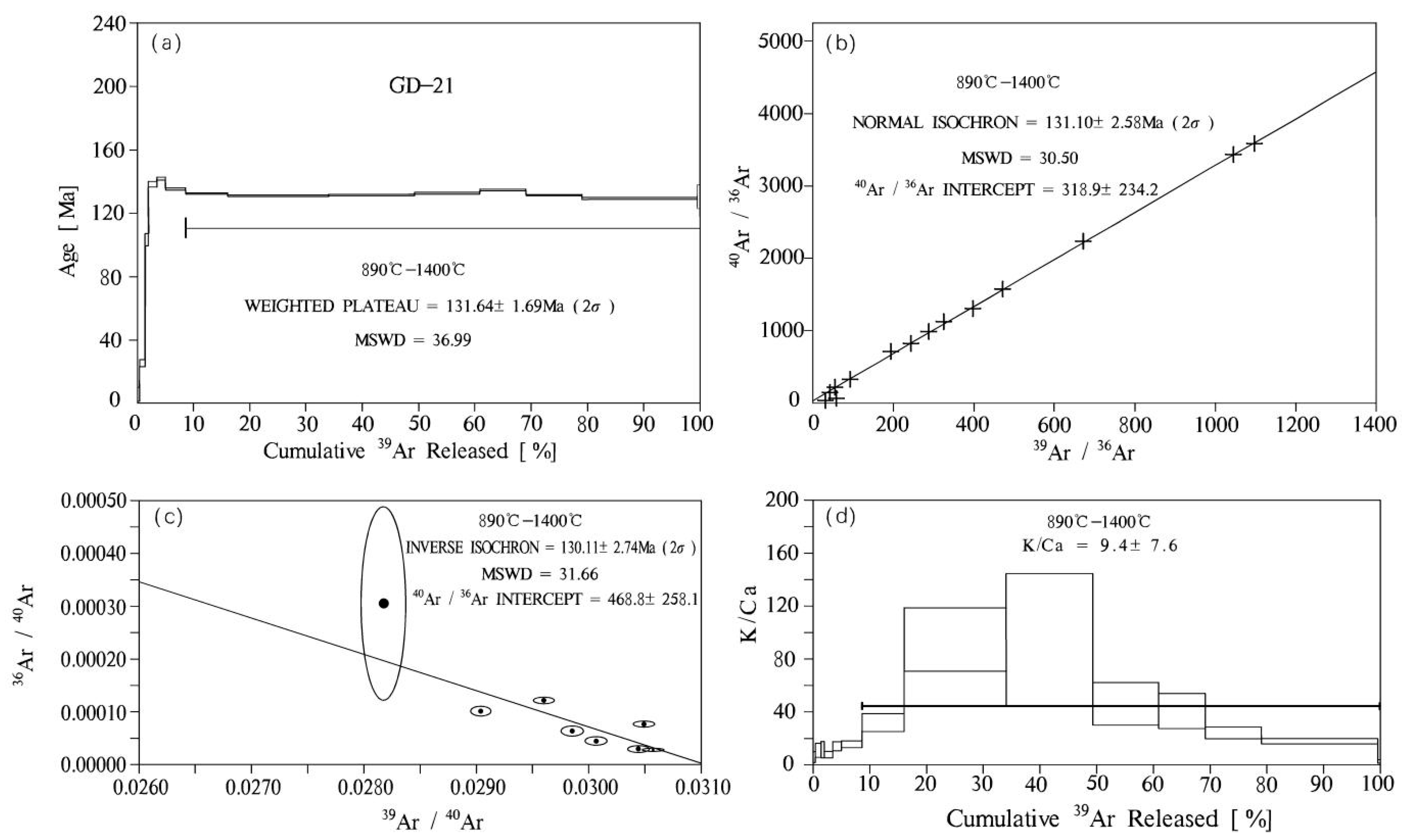
| Stage | Temperature (°C) | 36Ar [V] | 37Ar [V] | 38Ar [V] | 39Ar [V] | 40Ar [V] | 40(r)/39(k) | ±2σ | Age | ±2σ (Ma) |
| 1 | 650 | 0.0006111 | 0.0014474 | 0.0006399 | 0.0194853 | 0.20707 | 1.35719 | ±1.07573 | 5.67 | ±4.49 |
| 2 | 700 | 0.0008191 | 0.0018672 | 0.0014131 | 0.0479480 | 0.53465 | 6.09557 | ±0.51705 | 25.34 | ±2.13 |
| 3 | 740 | 0.0006790 | 0.0010850 | 0.0007522 | 0.0289415 | 0.93576 | 25.39494 | ±1.01684 | 103.31 | ±4.02 |
| 4 | 780 | 0.0012697 | 0.0038268 | 0.0019475 | 0.0698092 | 2.77303 | 34.34818 | ±0.47695 | 138.37 | ±1.85 |
| 5 | 820 | 0.0003878 | 0.0022915 | 0.0018773 | 0.0747677 | 2.74966 | 35.23811 | ±0.23765 | 141.82 | ±0.92 |
| 6 | 860 | 0.0005383 | 0.0048232 | 0.0042820 | 0.1746391 | 6.01760 | 33.54046 | ±0.18276 | 135.23 | ±0.71 |
| 7 | 890 | 0.0005312 | 0.0047771 | 0.0087042 | 0.3552671 | 11.82105 | 32.82266 | ±0.13381 | 132.44 | ±0.52 |
| 8 | 920 | 0.0007925 | 0.0039318 | 0.0208988 | 0.8652336 | 28.31166 | 32.43965 | ±0.10900 | 130.95 | ±0.42 |
| 9 | 950 | 0.0007064 | 0.0033577 | 0.0176964 | 0.7348026 | 24.14709 | 32.56683 | ±0.12146 | 131.45 | ±0.47 |
| 10 | 990 | 0.0011850 | 0.0051861 | 0.0137757 | 0.5563839 | 18.64310 | 32.86823 | ±0.14694 | 132.62 | ± 0.57 |
| 11 | 1030 | 0.0013723 | 0.0041595 | 0.0097853 | 0.3940666 | 13.57517 | 33.41007 | ±0.13906 | 134.73 | ± 0.54 |
| 12 | 1080 | 0.0019651 | 0.0084992 | 0.0119605 | 0.4784379 | 16.16810 | 32.57155 | ±0.12096 | 131.47 | ± 0.47 |
| 13 | 1200 | 0.0024833 | 0.0236282 | 0.0241768 | 0.9832604 | 32.25763 | 32.05353 | ±0.11515 | 129.45 | ± 0.45 |
| 14 | 1400 | 0.0002591 | 0.0039277 | 0.0006847 | 0.0238091 | 0.84498 | 32.29633 | ±1.94521 | 130.39 | ± 7.58 |
| Stage | Temperature (°C) | Time (days) | 40Ar(r) (%) | 39Ar(k) (%) | K/Ca | ±2σ | 40Ar/39Ar | 37Ar/39Ar | 36Ar/39Ar | 40Ar(moles) (×10−11) |
| 1 | 650 | 120.604 | 12.77 | 0.41 | 5.8 | ±4.2 | 10.6272 | 0.0743 | 0.0314 | 408.14 |
| 2 | 700 | 120.604 | 54.66 | 1.00 | 11.0 | ±5.3 | 11.1506 | 0.0389 | 0.0171 | 10.54 |
| 3 | 740 | 120.604 | 78.53 | 0.60 | 11.5 | ±6.2 | 32.3328 | 0.0375 | 0.0235 | 18.44 |
| 4 | 780 | 120.604 | 86.45 | 1.45 | 7.8 | ±2.4 | 39.7230 | 0.0548 | 0.0182 | 54.66 |
| 5 | 820 | 120.604 | 95.81 | 1.56 | 14.0 | ±3.4 | 36.7761 | 0.0306 | 0.0052 | 54.20 |
| 6 | 860 | 120.604 | 97.33 | 3.63 | 15.6 | ±2.5 | 34.4573 | 0.0276 | 0.0031 | 1.19 |
| 7 | 890 | 121.604 | 98.64 | 7.39 | 32.0 | ±6.8 | 33.2737 | 0.0134 | 0.0015 | 2.33 |
| 8 | 920 | 121.604 | 99.14 | 18.00 | 94.6 | ±23.9 | 32.7214 | 0.0045 | 0.0009 | 5.58 |
| 9 | 950 | 121.604 | 99.10 | 15.29 | 94.1 | ±50.0 | 32.8620 | 0.0046 | 0.0010 | 4.76 |
| 10 | 990 | 121.604 | 98.09 | 11.58 | 46.1 | ±16.1 | 33.5076 | 0.0093 | 0.0021 | 3.68 |
| 11 | 1030 | 121.604 | 96.98 | 8.20 | 40.7 | ±13.3 | 34.4489 | 0.0106 | 0.0035 | 2.68 |
| 12 | 1080 | 121.604 | 96.38 | 9.95 | 24.2 | ±4.5 | 33.7935 | 0.0178 | 0.0041 | 3.19 |
| 13 | 1200 | 121.604 | 97.70 | 20.45 | 17.9 | ±1.9 | 32.8068 | 0.0240 | 0.0025 | 6.36 |
| 14 | 1400 | 121.604 | 90.96 | 0.50 | 2.6 | ±1.3 | 35.4896 | 0.1650 | 0.0109 | 1.67 |
| Mine | Typical Deposit | Ore-Forming Intrusions | Ore-Controlling Strata | Ore-Controlling Structure | Orebody Space Occurrence | Wall Rock Alteration and Metamorphism | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intrusions | Lithology | ||||||
| Qihe–Yucheng | Guodian | Pandian intrusion | Pyroxene diorite, diorite, | Ordovician dolomitic limestone, dolomite, Carboniferous–Permian sandstone and mudstone | The intersection of fault structures or the intersection of fault structures and the core of brachy anticline | Contact zone occurrence, interlayer filling, xenolith structure, fracture penetration | Skarnization, phlogopitization, serpentinization, sodium alteration, marblezation, keratinization |
| Litun | Litun intrusion | Pyroxene diorite, hornblende diorite, quartz diorite | Carboniferous–Permian Sand–mudstone | ||||
| Dazhang | Dazhang intrusion | Dioritic | Ordovician dolomitic limestone and limestone | ||||
| Zibo | Wang Wangzhuang | Jinling complex | Monzodiorite, hornblende diorite | Ordovician limestone and dolomitic limestone | Jinling brachy anticline | Contact zone occurrence | Potassic, sodium alteration, marblezation,skarnization |
| Laiwu | Zhang Jiawa | Kuangshan pluton | Pyroxene diorite, diorite, monzonite, monzodiorite | Ordovician dolomite and dolomitic limestone | Mine anticline and its secondary folds | Contact zone occurrence, interlayer filling, xenolith structure, fracture penetration | Skarnization, phlogopitization, serpentinization, chloritization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Q.; Gao, M.; Fu, C.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, B.; et al. Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology for Guodian Skarn Fe Deposit in Qihe–Yucheng District, Luxi Block, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Destruction and Fe Mineralization. Minerals 2024, 14, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070690
Feng Q, Gao M, Fu C, Li S, Li Y, Gao J, Ma M, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Wu B, et al. Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology for Guodian Skarn Fe Deposit in Qihe–Yucheng District, Luxi Block, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Destruction and Fe Mineralization. Minerals. 2024; 14(7):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070690
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Qiwei, Mingbo Gao, Chao Fu, Siyuan Li, Yadong Li, Jilei Gao, Ming Ma, Zhaozhong Wang, Yidan Zhu, Binglu Wu, and et al. 2024. "Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology for Guodian Skarn Fe Deposit in Qihe–Yucheng District, Luxi Block, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Destruction and Fe Mineralization" Minerals 14, no. 7: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070690
APA StyleFeng, Q., Gao, M., Fu, C., Li, S., Li, Y., Gao, J., Ma, M., Wang, Z., Zhu, Y., Wu, B., Duan, Z., & Dang, Z. (2024). Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology for Guodian Skarn Fe Deposit in Qihe–Yucheng District, Luxi Block, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Destruction and Fe Mineralization. Minerals, 14(7), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070690






