Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Significance of the Demingding Mo-Cu Porphyry Deposit in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang: Insights from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Geochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
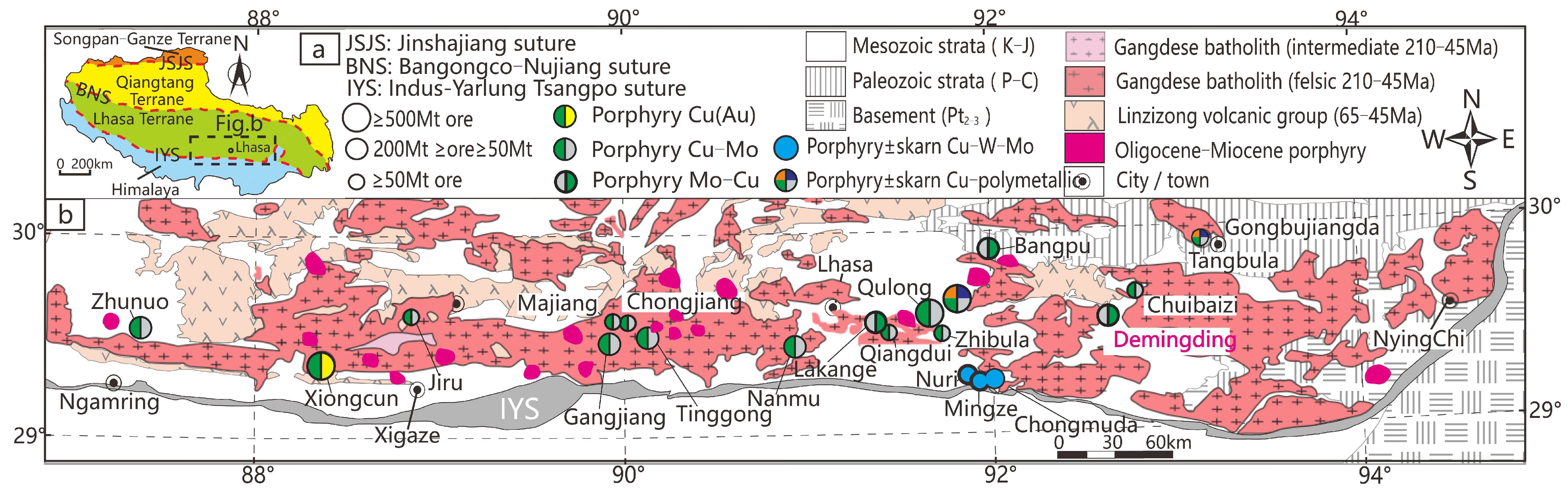
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
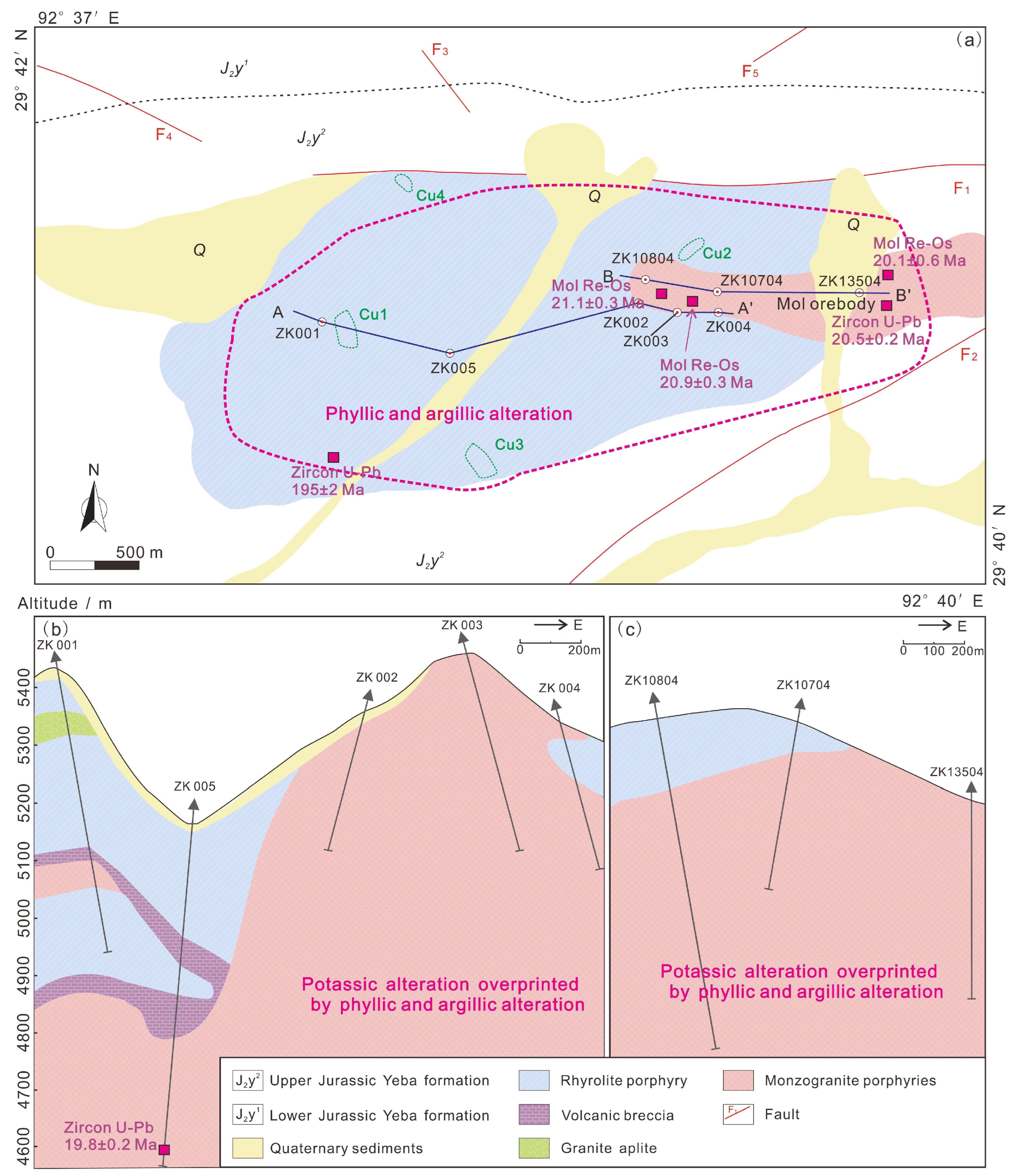
3.1. Sampling
3.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements Analyses
3.3. LA–ICP–MS Zircon U–Pb Isotope Analyses
3.4. Molybdenite Re–Os Isotope Analyses
4. Results
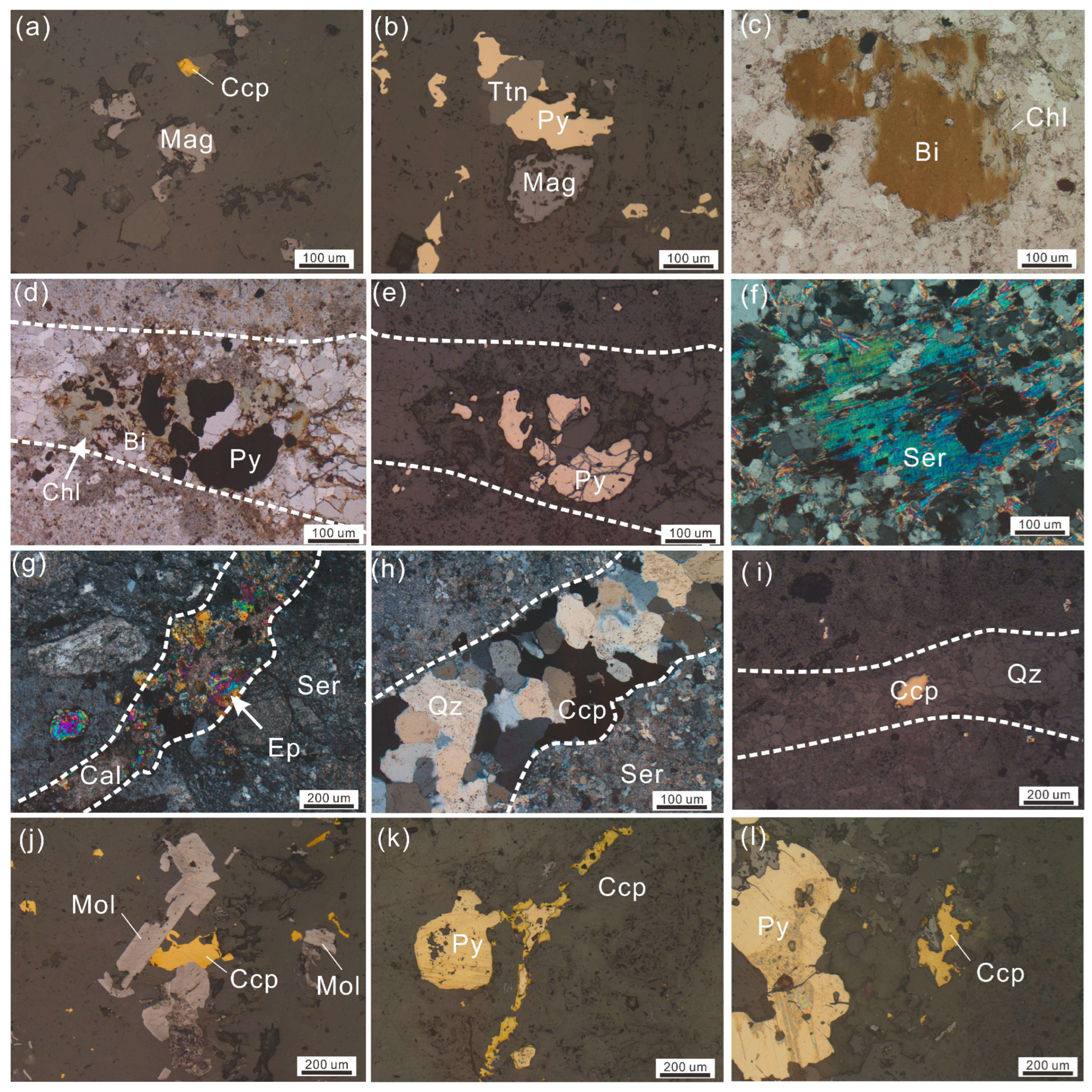
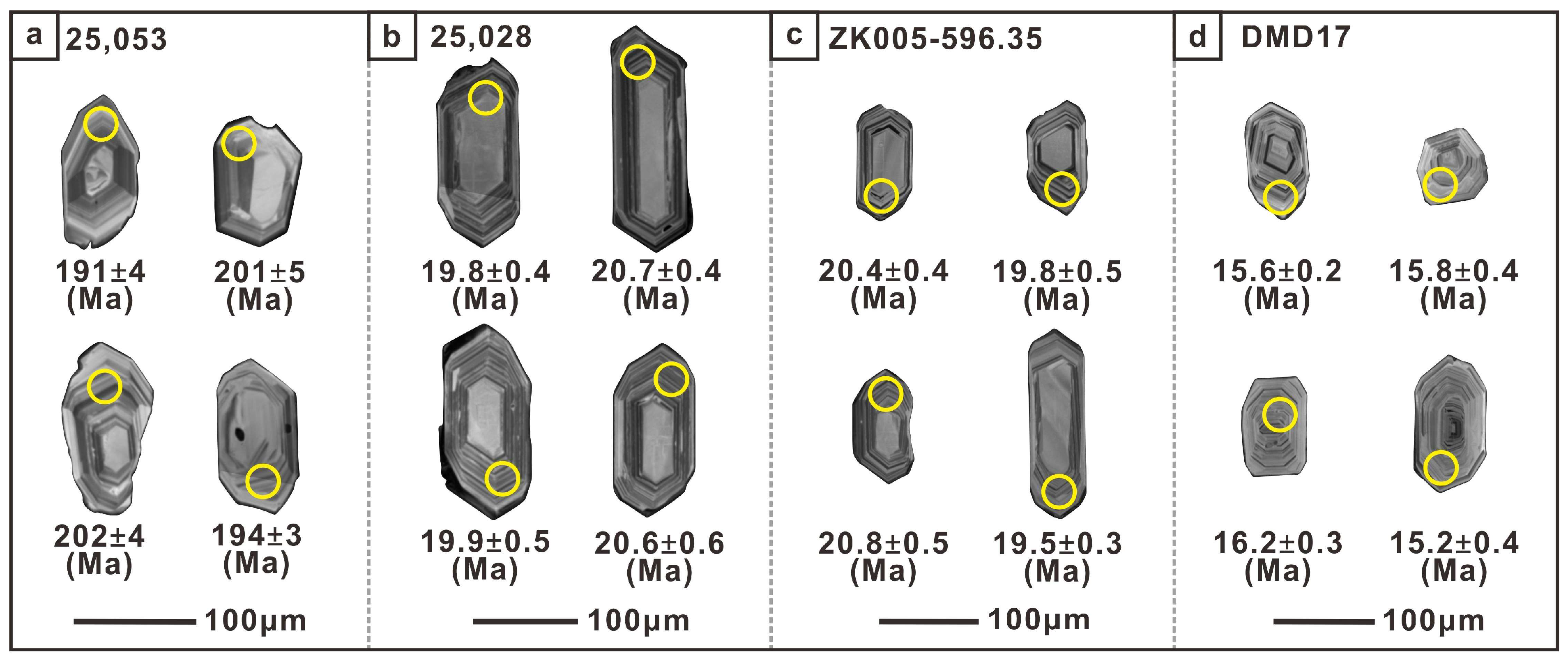
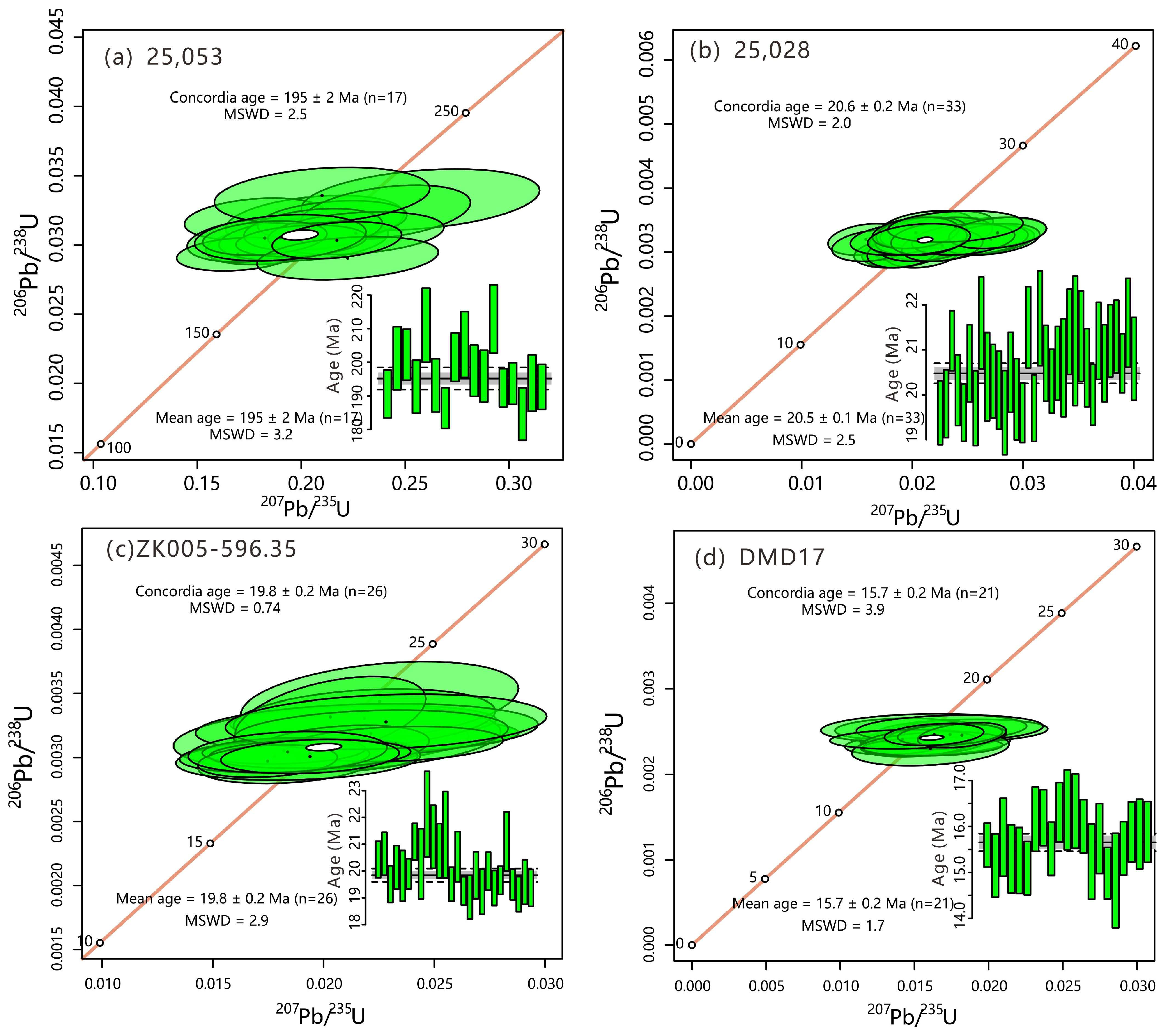
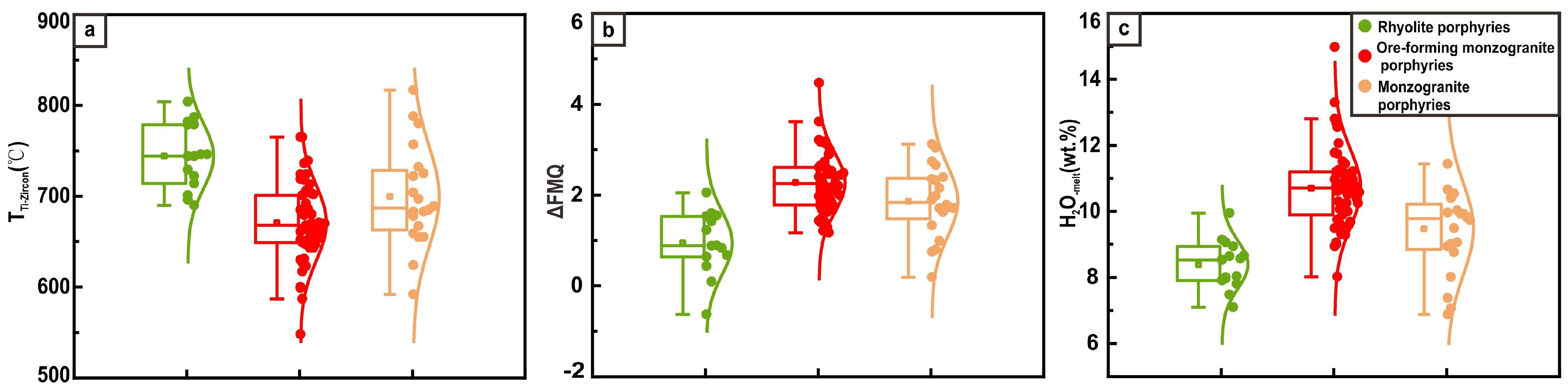
4.1. Zircon Morphology, U-Pb Age, Oxygen Fugacity, and H2O Content
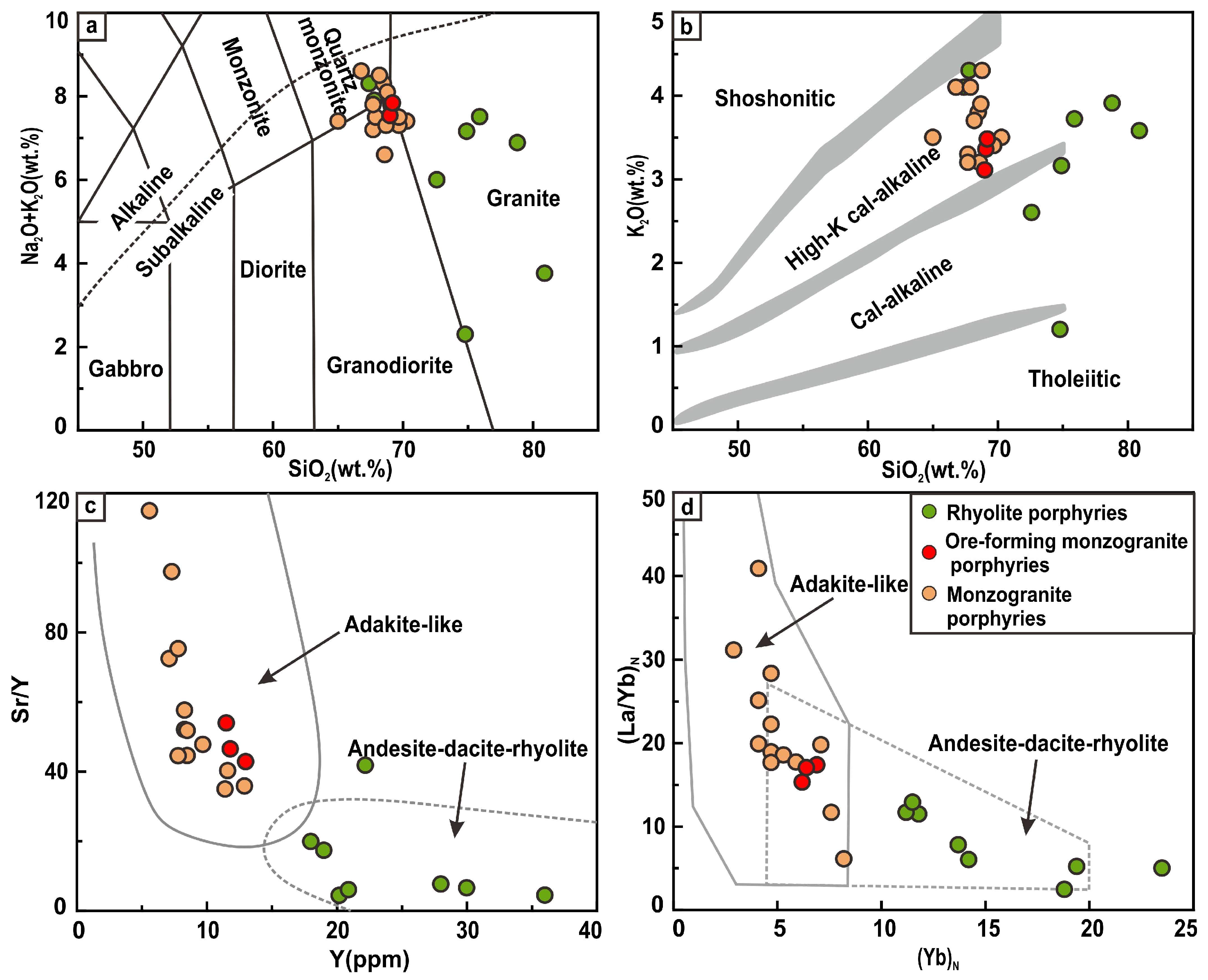
4.2. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Element Compositions
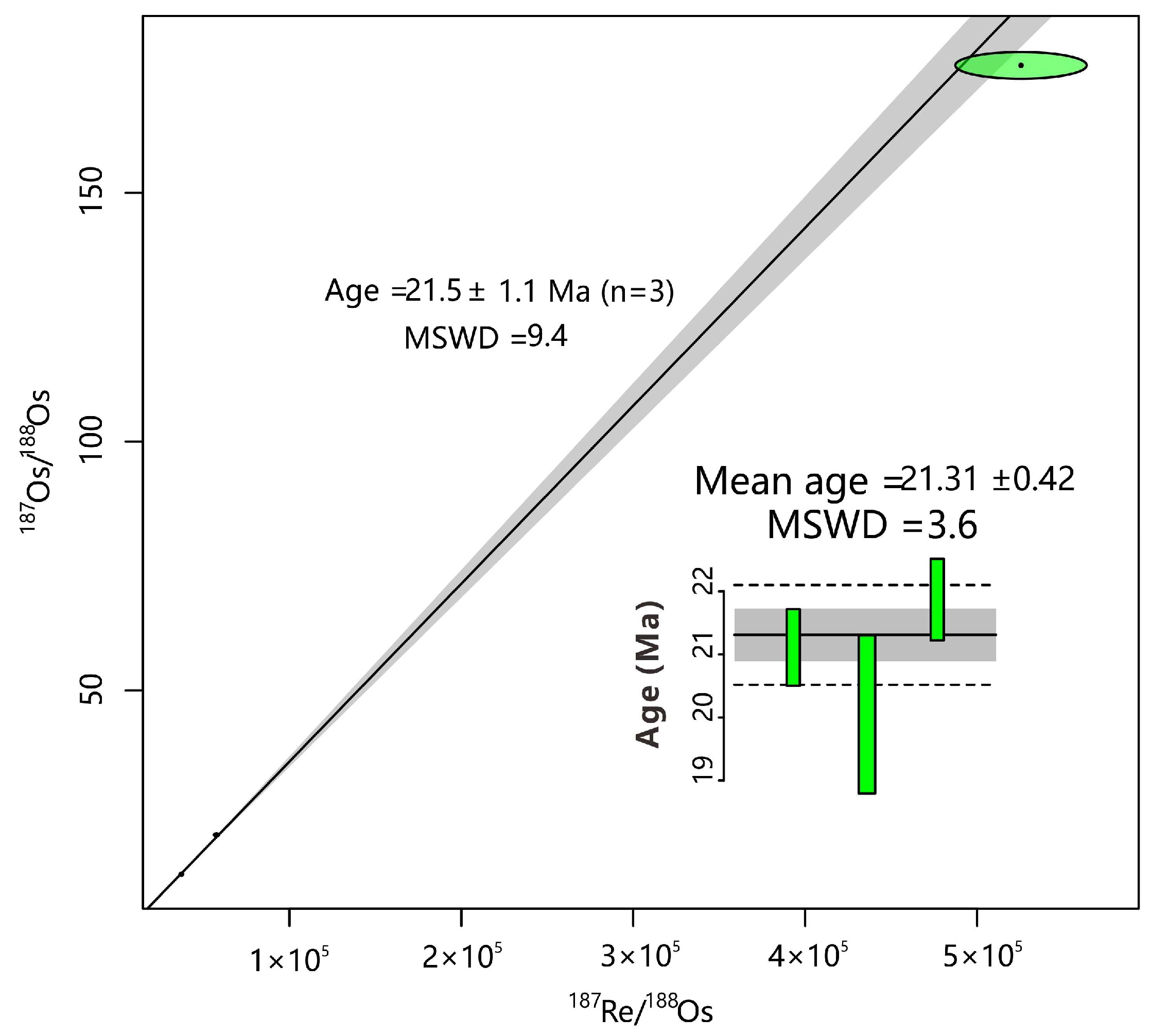
4.3. Molybdenite Re–Os Age
5. Discussion
5.1. Age of Magmatism and Mineralization
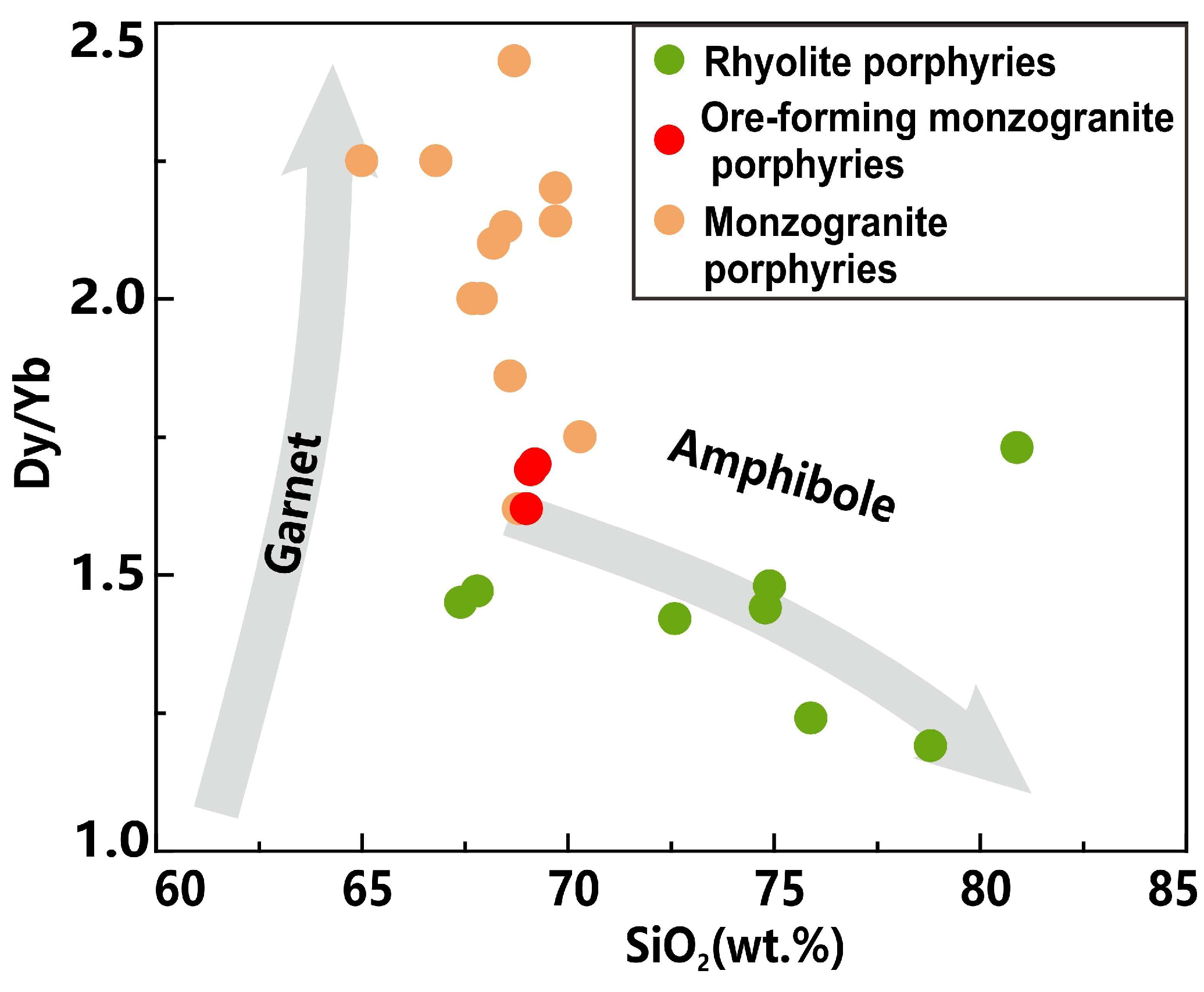
5.2. Petrogenesis of Ore-Forming Porphyries
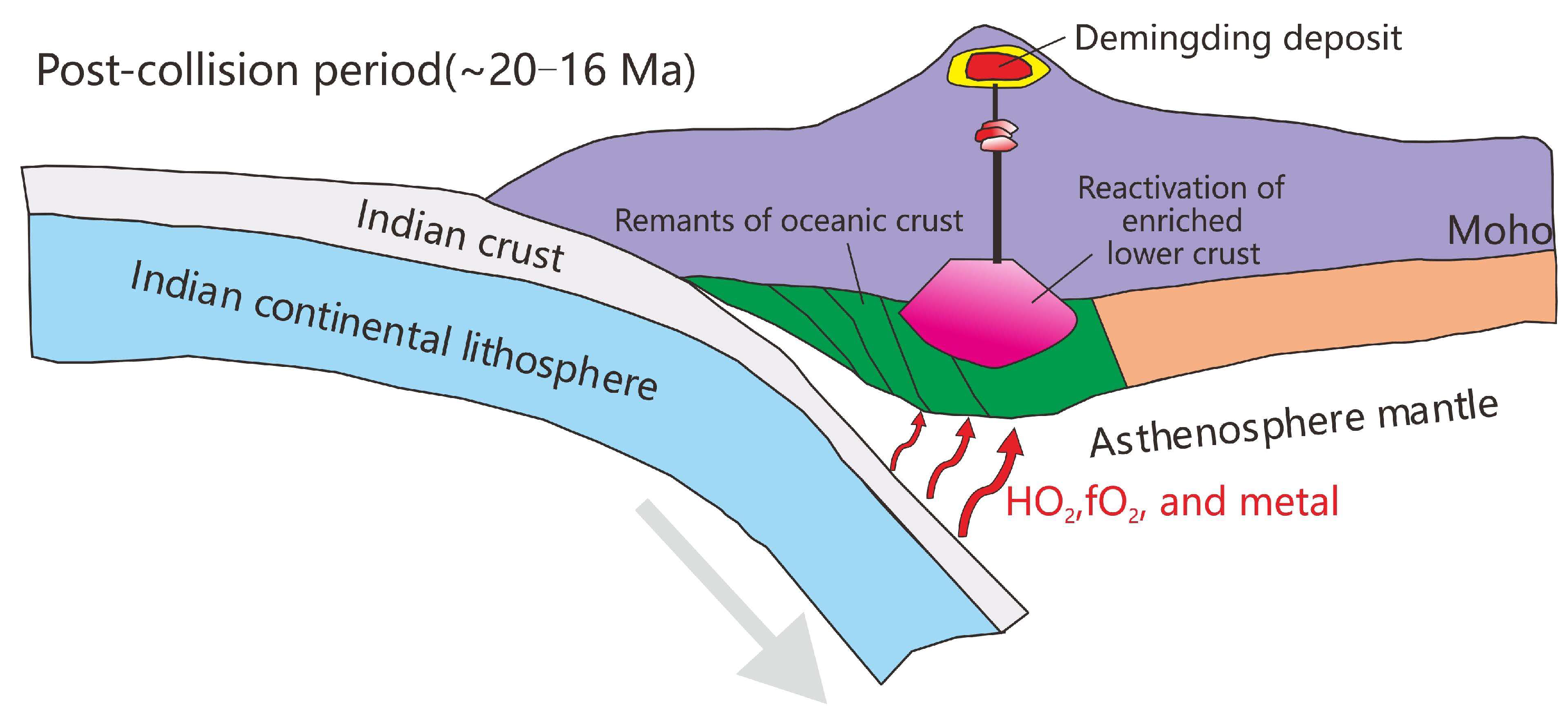
5.3. Implication for Mineralization Model
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Demingding deposit exemplifies a Mo-dominated porphyry system, characterized by distinct alteration zoning that transitions from inner potassic to outer propylitic zones, significantly overprinted by phyllic alteration associated with Mo and Cu mineralization.
- (2)
- Zircon U-Pb dating of the ore-forming porphyries indicates crystallization ages of 19–21 Ma, which closely align with the mean Re-Os age of 21.3 ± 0.4 Ma for Mo veins and veinlets, suggesting a late Miocene magmatic event marked by Mo-dominated mineralization coinciding with the post-collision period of the Indian and Asian continents.
- (3)
- The ore-forming porphyries, ranging from granodiorite to monzogranite, are classified as high-K calc-alkaline with adakite-like features, primarily resulting from the partial melting of thickened mafic lower crust.
- (4)
- These porphyries exhibit higher fO2 and H2O levels compared to barren porphyries and 190 Ma arc magma formed in a subduction environment, underscoring the critical role of hydrous and oxidized fluids from their source in the Mo-Cu mineralization process.
- (5)
- Regional data indicate that the Gangdese porphyry metallogenic belt experienced concentrated Cu-Mo mineralization between 17 and 13 Ma. The formation of Mo-dominated deposits such as Demingding and Tangbula in the eastern segment of the belt, with slightly older ages around 20 Ma, underscores the presence of a significant porphyry Mo metallogenic event during this critical post-collision mineralization period.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry copper systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, S.; Dilles, J.H.; Tosdal, R.M. Footprints: Hydrothermal Alteration and Geochemical Dispersion Around Porphyry Copper Deposits. SEG Discov. 2015, 100, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.R.; Hollings, P.; Walsh, J.L. Giant porphyry deposits: Characteristics, distribution, and tectonic controls. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, B.; Haschke, M.; Shahabpour, J. Recycling of orogenic arc crust triggers porphyry Cu mineralization in Kerman Cenozoic arc rocks, southeastern Iran. Miner. Depos. 2009, 44, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P.; Spell, T.; Rameh, E.; Razique, A.; Fletcher, T. High Sr/Y Magmas Reflect Arc Maturity, High Magmatic Water Content, and Porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au Potential: Examples from the Tethyan Arcs of Central and Eastern Iran and Western Pakistan. Econ. Geol. 2012, 107, 295–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Pan, X.; Yang, Z. Porphyry Cu (-Mo-Au) deposits related to melting of thickened mafic lower crust: Examples from the eastern Tethyan metallogenic domain. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-M.; Goldfarb, R.; Chang, Z.-S. Generation of Postcollisional Porphyry Copper Deposits in Southern Tibet Triggered by Subduction of the Indian Continental Plate. In Tectonics and Metallogeny of the Tethyan Orogenic Belt; Richards, J.P., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016; Volume 19, pp. 279–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Weinberg, R.F.; Collins, W.J.; Richards, J.P.; Zhu, D.-C. Origin of postcollisional magmas and formation of porphyry Cu deposits in southern Tibet. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 181, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Mo, X. Porphyry mineralization in the Tethyan orogen. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 2042–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Luo, C.-H.; Xia, W.-J.; He, W.-Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, M.-L.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Zhu, D.-C. Role of Alkaline Magmatism in Formation of Porphyry Deposits in Nonarc Settings: Gangdese and Sanjiang Metallogenic Belts. In Tectonomagmatic Influences on Metallogeny and Hydrothermal Ore Deposits: A Tribute to Jeremy P. Richards (Volume II); Sholeh, A., Wang, R., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.-H.; Wang, R.; Weinberg, R.F.; Hou, Z. Isotopic spatial-temporal evolution of magmatic rocks in the Gangdese belt: Implications for the origin of Miocene post-collisional giant porphyry deposits in southern Tibet. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2022, 134, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, S.; Ci, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Gao, S.; Lin, H. A modified genetic model for multiple pulsed mineralized processes at the giant Qulong porphyry Cu-Mo mineralization system. Am. Mineral. 2024, 109, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Palmer, M.R.; Zhao, K.; Hernandez-Uribe, D.; Gao, S.; Wu, S. Magma mixing and magmatic-to-hydrothermal fluid evolution revealed by chemical and boron isotopic signatures in tourmaline from the Zhunuo-Beimulang porphyry Cu-Mo deposits. Miner. Depos. 2024, 59, 1133–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.T.; Mo, X.X.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, G.M.; Zhao, Z.D.; Geng, Q.R.; Liao, Z.L. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Duan, L.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Pei, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Lithospheric Architecture of the Lhasa Terrane and Its Control on Ore Deposits in the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1541–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Chung, S.-L.; Cawood, P.A.; Niu, Y.; Liu, S.-A.; Wu, F.-Y.; Mo, X.-X. Magmatic record of India-Asia collision. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedorff, E.; Dilles, J.H.; Proffett, J.M.; Einaudi, M.T.; Barton, M. Porphyry Deposits Characteristics and Origin of Hypogene Features. Econ. Geol. Ann. 2005, 100, 251–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Luo, M.; Xie, G.; Liu, J.; Wu, S. Basic Characteristics and New Advances in Research and Exploration on Porphyry Copper Deposits. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 2153–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cooke, D.R. Chapter 5 Porphyry Copper Deposits in China. In Mineral Deposits China; Chang, Z., Goldfarb, R.J., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2019; Volume 22, pp. 133–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, X.; Schertl, H.-P.; Palmer, M.R.; Zheng, Y.; Su, H.; Gao, S.; Ci, Q.; Jiang, J. Mobilization and fractionation of Ti-Nb-Ta at the giant Qulong porphyry Cu-Mo mineralization system, Xizang. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 172, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Pan, G.-T.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kang, Z.-Q.; Liao, Z.-L.; Wang, L.-Q.; Li, G.-M.; Dong, G.-C.; Liu, B. Early cretaceous subduction-related adakite-like rocks of the Gangdese Belt, southern Tibet: Products of slab melting and subsequent melt-peridotite interaction? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Niu, Y.; Dilek, Y.; Mo, X.-X. Lhasa terrane in southern Tibet came from Australia. Geology 2011, 39, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Li, S.-M.; Cawood, P.A.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Liu, S.-A.; Wang, L.-Q. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction. Lithos 2016, 245, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Kemp, A.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z.; Duan, L. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones. Geology 2015, 43, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, R.; Cai, P.; Lu, L.; Hou, W.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y. Tracking the timing and nature of protolith, metamorphism, and partial melting of tourmaline-bearing migmatites by zircon U–Pb and Hf isotopic compositions in the Yuka terrane, North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt. Geol. J. 2018, 54, 1013–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X. Syn-collisional magmatism at the Longgen Pb–Zn deposit, western Nyainqentanglha belt, Tibet: Petrogenesis and implications for regional polymetallic metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Long, T.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X. Timing and genetic link of porphyry Mo and skarn Pb-Zn mineralization in the Chagele deposit, Western Nyainqentanglha belt, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 129, 103929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, S.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, J.; Cai, P.; Lin, C. Ages and petrogenesis of the late Triassic andesitic rocks at the Luerma porphyry Cu deposit, western Gangdese, and implications for regional metallogeny. Gondwana Res. 2020, 85, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafti, R.; Lang, J.R.; Mortensen, J.K.; Oliver, J.L.; Rebagliati, C.M. Geology and Geochronology of the Xietongmen (Xiongcun) Cu-Au Porphyry District, Southern Tibet, China. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 1967–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Sun, X.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; You, Z.; Li, J. Multiple mineralization events at the Jiru porphyry copper deposit, southern Tibet: Implications for Eocene and Miocene magma sources and resource potential. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; You, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, T.; Dong, J. Mineralization age and petrogenesis of associated intrusions in the Mingze-Chengba porphyry-skarn Mo-Cu deposit, Gangdese. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, R.; Gao, S.; Pang, Y.; Cao, L.; Du, A.; Shi, Y. Geochronologic constraints on magmatic intrusions and mineralization of the Zhunuo porphyry copper deposit in Gangdese, Tibet. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-X.; Wang, D.-H.; Wang, X.-W.; Zhong, K.-H.; Ying, L.-J.; Zheng, W.-B.; Li, F.-J.; Guo, N.; Qin, Z.-P.; Yao, X.-F.; et al. Geological Features and Metallogenic Model of the Jiama Copper-Polymetallic Deposit in Tibet. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2010, 31, 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Sun, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Metallogenesis and the minerogenetic series in the Gangdese polymetallic copper belt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, K.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z. Origin and Geodynamic Mechanism of the Tibetan Demingding Porphyry Mo (Cu) Deposit from Oceanic Subduction to Continental Collision. Minerals 2022, 12, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Zuo, L.; Chen, L.; Gao, F.; Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Shu, D.; et al. Short-wavelength infrared characteristics and composition of white mica in the Demingding porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Gangdese belt, Tibet: Implications for mineral exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 164, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Shan, G.; Ling, W.L.; Liu, Y.S.; McDonough, W.F. Petrology and geochemistry of spinel peridotite xenoliths from Hannuoba and Qixia, North China craton. Lithos 2004, 77, 609–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Guenther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schertl, H.-P.; Hart, E.; Majka, J.; Cambeses, A.; Hernández-Uribe, D.; Zheng, Y. Mobilization and fractionation of Ti-Nb-Ta during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 319, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schertl, H.-P.; Cambeses, A.; Hart, E.; Lin, C.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Y. Cyclicity of multistage anatexis of deeply subducted continental crust during the North Qaidam orogeny: Tracing the source, timescale, and evolution of pulsed melts. Am. J. Sci. 2022, 322, 225–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P. IsoplotR: A free and open toolbox for geochronology. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Henriquez, G.J. New Magmatic Oxybarometer Using Trace Elements in Zircon. J. Petrol. 2020, 61, egaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.-F.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhu, W.-B.; Wang, X.-L. Earth’s early continental crust formed from wet and oxidizing arc magmas. Nature 2023, 623, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, A.D.; Wu, S.Q.; Sun, D.Z.; Wang, S.X.; Qu, W.J.; Markey, R.; Stain, H.; Morgan, J.; Malinovskiy, D. Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials: Molybdenites HLP and JDC. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2004, 28, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Li, W.-X.; Li, Z.-X.; Lo, C.-H.; Wang, J.; Ye, M.-F.; Yang, Y.-H. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks. Precambrian Res. 2009, 174, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1554–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.; Mccuaig, T.C.; Evans, N.J.; Yang, Z.-M.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Kirkland, C.L.; Parra-avila, L.A.; Kobussen, A. Zircon compositions as a pathfinder for porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au mineral deposits. In Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication No. 19 on Tethyan Tectonics and Metallogeny; Richards, J., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma, igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.P.; Clemens, J.D. Origin of high-potassium, calc-alkaline, I-type granitoids. Geology 1993, 21, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ding, F.; Yang, H.; Xie, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y. U-Pb and Re-Os geochronological evidence for the Jurassic porphyry metallogenic event of the Xiongcun district in the Gangdese porphyry copper belt, southern Tibet, PRC. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhai, M.; Santosh, M.; Ma, X.; Shan, H.; Cui, X. Paleoproterozoic tectonic transition from collision to extension in the eastern Cathaysia Block, South China: Evidence from geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Nd-Hf isotopes of a granite-charnockite suite in southwestern Zhejiang. Lithos 2014, 184, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, R. Shallow subduction of Indian slab and tectono-magmatic control on post-collisional porphyry mineralization in southeastern Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 155, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Selby, D.; Condon, D.; Tapster, S. Cyclic Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution in Porphyry Systems: High-Precision U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology Constraints on the Tibetan Qulong Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposit. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1419–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Tang, J.X.; Tang, P.; Zheng, W.B.; Song, Y.; Li, F.Q.; Leng, Q.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Qi, J.; Sun, M.; et al. Geology, geochronology, and exploration of the Jiama giant porphyry copper deposit (11 Mt), Tibet, China: A review. China Geol. 2023, 6, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Hoare, L.; Schertl, H.-P.; Palmer, M.R.; Zhang, W.; Cai, P.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, S. Substantial in situ Ti isotope variations in rutile record source and fluid evolution of porphyry copper mineralization systems. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2024, 1–14, Early Publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Brzozowski, M.J.; Zou, S.; Qi, L.; Li, K.; Leng, C.-B. Platinum-Group Element Geochemistry of Igneous Rocks in the Chongjiang Cu–Mo–Au Deposit, Southern Tibet: Implications for the Formation of Post-Collisional Porphyry Cu Deposits. J. Petrol. 2024, 65, egae025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, Y.-J.; McCuaig, T.C.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Chang, H.-F.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.-J. Miocene Ultrapotassic, High-Mg Dioritic, and Adakite-like Rocks from Zhunuo in Southern Tibet: Implications for Mantle Metasomatism and Porphyry Copper Mineralization in Collisional Orogens. J. Petrol. 2018, 59, 341–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. Cenozoic eastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau controlled by tearing of the Indian slab. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Smithies, R.H.; Rapp, R.; Moyen, J.F.; Champion, D. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos 2005, 79, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.G.; Dreher, S.T.; Thirlwall, M.F. Adakites without slab melting: High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 243, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, M.P.; Petford, N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust. Nature 1993, 362, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.L.; Liu, D.Y.; Ji, J.Q.; Chu, M.F.; Lee, H.Y.; Wen, D.J.; Lo, C.H.; Lee, T.Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q. Adakites from continental collision zones: Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet. Geology 2003, 31, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.L.; Li, X.H.; Xu, J.F.; Li, W.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.M. Extremely high-Na adakite-like magmas derived from alkali-rich basaltic underplate: The Late Cretaceous Zhantang andesites in the Huichang Basin, SE China. Geochem. J. 2003, 37, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Gao, Y.F.; Qu, X.M.; Rui, Z.Y.; Mo, X.X. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene east-west extension in southern Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-L.; Chu, M.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Lo, C.-H.; Lee, T.-Y.; Lan, C.-Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 68, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; McDermott, F.; Xu, J.F.; Bellon, H.; Zhu, Y.T. Cenozoic K-rich adakitic volcanic rocks in the Hohxil area, northern Tibet: Lower-crustal melting in an intracontinental setting. Geology 2005, 33, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilhol, P.; Jagoutz, O.; Hanchar, J.M.; Dudas, F.O. Dating the India-Eurasia collision through arc magmatic records. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 366, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Garzanti, E.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; An, W.; Webb, A. The timing of India-Asia collision onset–Facts, theories, controversies. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 160, 264–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Cawood, P.A.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Mo, X.-X. Raising the Gangdese Mountains in southern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res-Sol. Earth 2017, 122, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Li, Q.L.; Griffin, W.L.; Stern, R.J.; Ishizuka, O.; Henry, H.; Lucci, F.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Ghorbani, G. Repeated magmatic buildup and deep “hot zones” in continental evolution: The Cadomian crust of Iran. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 531, 115989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.L.; Adam, J.; Green, T.H. Rutile stability and rutile/melt HFSE partitioning during partial melting of hydrous basalt: Implications for TTG genesis. Chem. Geol. 2005, 218, 339–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, L.; Ducea, M.N.; Chapman, J.B.; Paterson, S.R.; Gonzales, S.M.H.; Kirsch, M.; Petrescu, L.; DeCelles, P.G. Quantifying crustal thickness over time in magmatic arcs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, J.; Pirajno, F.; Ishiyama, D.; Su, H.; Guo, C.; Chen, Y. Porphyry Cu-Au-Mo-epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn-distal hydrothermal Au deposits in the Dexing area, Jiangxi province, East China-A linked ore system. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhou, J.C.; Qiu, J.S.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, G.L. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution. Precambrian Res. 2006, 145, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Liang, C.; Li, W. Petrogenesis of episodic volcanic-intrusive rocks in SE China: Crystal-melt segregation and magma mixing. Chem. Geol. 2024, 670, 122457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-D.; Huang, R.-F.; Liang, H.-Y.; Ling, M.-X.; Li, C.-Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Ireland, T.; Fan, W.-M. Magnetite-hematite, oxygen fugacity, adakite and porphyry copper deposits: Reply to Richards. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 126, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-M.; Lu, Y.-J.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Chang, Z.-S. High-Mg Diorite from Qulong in Southern Tibet: Implications for the Genesis of Adakite-like Intrusions and Associated Porphyry Cu Deposits in Collisional Orogens. J. Petrol. 2015, 56, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Baker, M.J.; Han, J.; Xiao, B.; Yang, J.; Jourdan, F. Multiple mineralization events of the Paleozoic Tuwu porphyry copper deposit, Eastern Tianshan: Evidence from geology, fluid inclusions, sulfur isotopes, and geochronology. Miner. Depos. 2019, 54, 1053–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, S.; Ren, H.; Jiang, X. Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Significance of the Demingding Mo-Cu Porphyry Deposit in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang: Insights from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Geochemistry. Minerals 2024, 14, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14121232
Shi S, Chen S, Luo S, Ren H, Jiang X. Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Significance of the Demingding Mo-Cu Porphyry Deposit in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang: Insights from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Geochemistry. Minerals. 2024; 14(12):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14121232
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Sudong, Shuyuan Chen, Sangjiancuo Luo, Huan Ren, and Xiaojia Jiang. 2024. "Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Significance of the Demingding Mo-Cu Porphyry Deposit in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang: Insights from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Geochemistry" Minerals 14, no. 12: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14121232
APA StyleShi, S., Chen, S., Luo, S., Ren, H., & Jiang, X. (2024). Petrogenesis and Metallogenic Significance of the Demingding Mo-Cu Porphyry Deposit in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang: Insights from U-Pb and Re-Os Geochronology and Geochemistry. Minerals, 14(12), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14121232







