Abstract
The influence of the paleo-Tethys or paleo-Pacific oceanic plate subduction on Early Triassic South China has long been debated. We have studied the zircon U-Th-Hf isotopes, trace elements, and whole-rock geochemistry of Early Triassic peraluminous granitoids in the Qinzhou Bay area, South China Block. LA–ICP–MS zircon U–Pb dating has revealed the Jiuzhou granodiorites and Dasi-Taima granite porphyries formed between 248.32 ± 0.98 and 246.6 ± 1.1 Ma. These rocks are characterized by high K2O and Al2O3, and low MgO, CaO, and P2O5 contents with A/CNK = 1.06–1.17, showing high-K calc-alkaline S-type affinities. The Early Triassic intrusive rocks and adjacent silicic volcanic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area were found to be comagmatic and derived from a common magma pool, detached in an undifferentiated melt instead of indicating remarkable crystal—melt separation. Although the analyzed granitoids have highly enriched zircon Hf isotopic compositions (εHf(t) = −23.9 to −7.8), they cannot originate solely from metasedimentary protoliths. Source discrimination indicators have revealed enriched lithospheric mantle-derived magma was also an endmember component of the S-type silicic magma, which provided a heat source for the crustal anatectic melting as well. We inferred the studied Early Triassic granitoids formed under the paleo-Tethys tectonic regime before the collision of South China and Indochina blocks, as the oceanic plate subduction would have created an extensional setting which further caused the mantle-derived upwelling and volcanic eruption.
1. Introduction
The Triassic tectonic evolution of the Asian continent is important and puzzling, performed by the successive amalgamation of continental blocks such as Siberia, North China, South China, Indochina, and India [1,2,3]. The tectonic development during this period involved large-scale intracontinental deformation and associated magmatism, especially in the South China Block [4]. However, the tectonic setting of the Triassic South China Block is a point of debate, for which two main models are proposed: (i) the Andean-type subduction of the paleo-Tethys oceanic plate followed by continent—continent collision [4,5], and (ii) the flat-slab subduction of the paleo-Pacific oceanic plate followed by slab foundering and retreat [6,7]. In addition, a few studies have considered the Emeishan plume as a possible heat source for the high- or ultrahigh-temperature magmatism and coeval metamorphism that characterized this period [8,9].
The voluminous Jurassic–Cretaceous granitoids and silicic volcanic rocks found in coastal South China reflect the history of the paleo-Pacific oceanic plate subduction [10,11]. By contrast, the Triassic igneous rocks in South China are dispersed and occur mainly in the inland region, comprising mainly of granitic intrusions with much rarer volcanic rocks [4]. The older Triassic igneous rocks were emplaced mainly at the southern and southwestern margins of the block, such as Hainan Island and the Qinzhou Bay area, adjacent to the northeastern part of the Indochina Block [12]. Here, we present a study of the geochronology and geochemistry of Early Triassic S-type granitoids from the Qinzhou Bay area, to place constraints on their petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Our new zircon U–Pb–Hf isotopic and whole-rock geochemical compositions allow us to constrain the timing and origin of the silicic magmatism. Based on these results, we examine the nature of Triassic tectono-magmatic activity in South China.
2. Geological Background and Sampling
Formed through the collision of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks at ca. 880 Ma [2], the South China Block is separated from the Indochina Block by the Ailaoshan-Song Ma suture zone in the southwest, from the North China Block by the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt in the north, and from Tibet by the Longmenshan Fault in the west [2] (Figure 1a). It is also bounded by the Pacific oceanic plate in the east. Silicic magmatism occurred primarily within the Cathaysia Block, and formed granitoids covering ca. 30% of the area in multiple periods from early Paleozoic (ca. 450–420 Ma) to Permian–Triassic (ca. 280–205 Ma), and Jurassic–Cretaceous (ca. 195–70 Ma) [4,5,11,13,14,15].
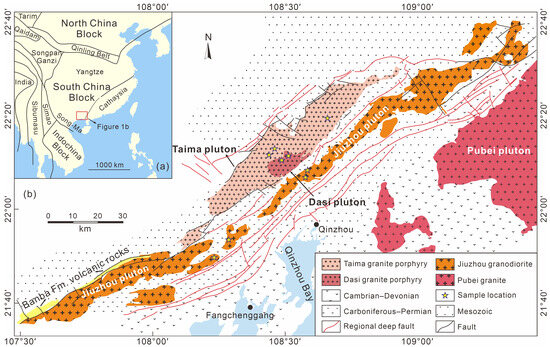
Figure 1.
(a) Tectonic schematic map of South China and its surrounding blocks, including North China Block in the north and Indochina Block in the southwest, as well as Tibet in the west, which is subdivided into several smaller terranes; (b) geological map of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex [16] with sample locations.
The late Permian to Triassic magmatic rocks in South China primarily developed within the interior of the block [5,6,13], with the older segments emerging along the southern and southwestern margins, notably in regions such as Hainan Island, the Qinzhou Bay area, the Ailaoshan, and the southern Lancangjiang zones [4,12,17,18]. These rocks are predominantly granites, accompanied by minor syenites, diabase, gabbros, and infrequent mafic enclaves [15]. Among them, the prevailing types are biotite granites, two-mica granites, and muscovite granites [5,13]. Geochemically, the granitoids are mainly high in potassium, calc-alkalic, weakly to strongly peraluminous, and are predominantly categorized as S-type and I-type or, more rarely, A-type granitoids [15].
The Qinzhou Bay area hosts the Late Permian to Triassic granitoids, forming the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex, known for their typical S-type composition containing cordierite [16]. The granitic complex strikes northeast parallel to the regional deep faults and is approximately 400 km in length and 20–75 km in width, potentially extending further into Vietnam, with a total outcrop area exceeding 10,000 km2 (Figure 1). The magmatic rocks intruded into Cambrian–Permian sediments, and the country rocks are mainly flysch formations with locally distributed molasse and carbonate rock formations [18]. This granitic complex comprises over 40 plutons of different sizes, including the plutonic Darongshan biotite granite suite, plutonic and hypabyssal Jiuzhou granodiorite suite, and superhypabyssal-subvolcanic Taima granite porphyry suite, stretching from northeast to southwest [18]. Enclaves, primarily metapelitic granulite, along with quartzo-feldspathic gneiss, schist, arkose quartzite, hornfels, and sporadic mafic microgranular enclaves, can be found dispersed within the granitoids, some reaching decimeter sizes [19]. Additionally, this region exhibits the only known occurrence of Early Mesozoic silicic volcanic rocks within the South China Block [20,21].
In total, nine granitic samples were collected from different granite quarries (Figure 1b). The Jiuzhou granodiorite exhibits a medium- to coarse-grained equigranular texture (Figure 2a,b), composed of plagioclase (30–50 vol.%), quartz (25–35 vol.%), alkali feldspar (10–30 vol.%), biotite (8 vol.%), orthopyroxene (5 vol.%), and less than 1 vol.% cordierite. It also contains accessory minerals such as zircon, monazite, apatite, and ilmenite. The rocks of the Taima pluton are porphyritic, characterized by a phenocryst content of up to 40–50 vol.% (Figure 2c). These phenocrysts consist of plagioclase (35–40 vol.%), quartz (25–30 vol.%), alkali feldspar (25–30 vol.%), minor orthopyroxene, biotite, and cordierite (<3 vol.%). They are embedded in a matrix composed of plagioclase, alkali feldspar, quartz, and biotite, along with accessory minerals such as zircon, monazite, apatite, and ilmenite. The rocks of Dasi pluton display an even higher phenocryst content (up to 50–60 vol.%) compared to the Taima granite porphyries. The mineral textures and compositions of the crystal clusters in the Dasi pluton resemble those found in the Taima pluton (Figure 2d).
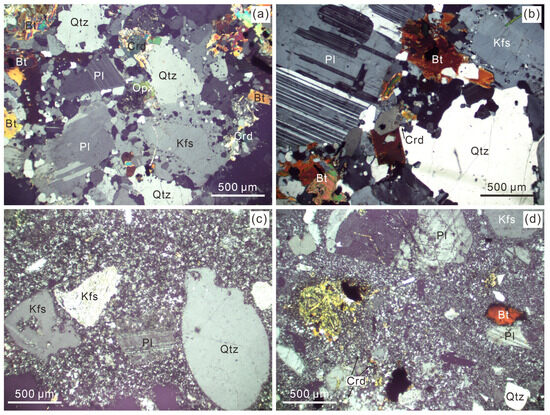
Figure 2.
Representative photomicrographs of (a,b) the Jiuzhou granodiorites, (c) Taima granite porphyry, and (d) Dasi granite porphyry, respectively. Notes: Pl, plagioclase; Kfs, K-feldspar; Qtz, quartz; Bt, biotite; Opx, orthopyroxene; Crd, cordierite.
3. Analytical Methods
All analyses were carried out at the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Hidden Metallic Ore Deposits Exploration, Guilin University of Technology, China.
Zircon grains were randomly extracted and mounted in a 2.5 cm diameter epoxy disk, and then polished to expose the central parts of the grains. Photomicrographs and cathodoluminescence (CL) images were obtained to characterize the internal structures of the grains and to select appropriate analysis sites excluding small crystal and melt inclusions.
Zircon U–Pb dating was carried out using an Agilent 7500 ICP–MS equipped with a GeoLas HD laser sampler. Elements such as Si, Ti, Y, and rare earth elements (REEs) were simultaneously analyzed together with U–Th–Pb isotopic compositions. The standard zircon GJ-1 was analyzed frequently to monitor the reproducibility and the stability of the instrument. The analyses were conducted with a beam diameter of 32 μm, 6 Hz repetition rate, and energy of 10 J/cm2. For the instrument settings, analytical procedures, and data processing, we followed Liu et al. (2010) [22].
The Lu–Hf analysis spot was placed in a similar domain of a previous U–Pb spot within the same zircon, based on the photomicrograph and CL image (Figure 3). In situ zircon Hf isotope analyses were performed using a GeoLas HD laser ablation system with a Neptune Plus MC–ICPMS, with a beam diameter of 44 μm, 6 Hz repetition rate, and energy of 10 J/cm2. Zircon GJ-1 was used as the reference standard during the analyses. The analytical details were similar to Liu et al. (2016) [11]. The initial 176Hf/177Hf ratios were calculated using 176Lu decay constant of 1.867 × 10−11 yr−1 [23]. The chondritic values of 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282785 and 176Lu/177Hf = 0.0336 [24] were used to calculate εHf values. The depleted mantle Hf model ages (TDM) were calculated using the depleted mantle reservoir present 176Hf/177Hf ratio of 0.28325 and 176Lu/177Hf ratio of 0.0384 [25]. A two-stage model age (TDM2) was also calculated by assuming the parental magma was produced from a Depleted Mantle-derived average continental crust (176Lu/177Hf = 0.015) [26].
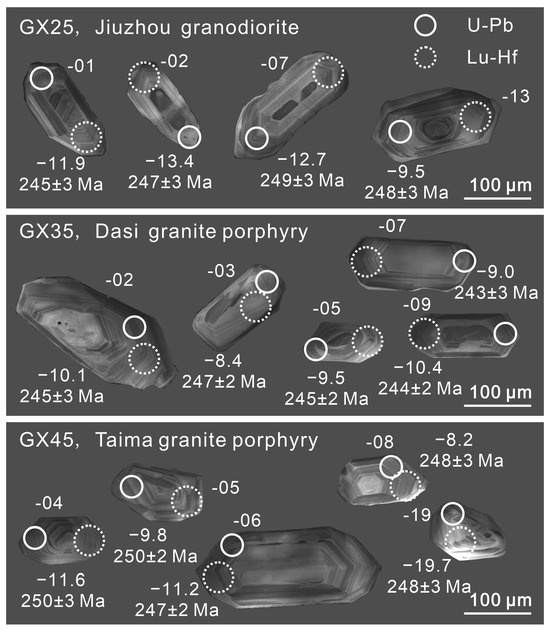

Figure 3.
Cathodoluminescence images of representative zircons from granitic rocks of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex.
Whole-rock major element analyses were conducted using the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) method, whereas the loss-on-ignition (LOI) values of each sample were measured after heating to 1000 °C. Trace element analyses were undertaken with an Agilent 7900CX ICP–MS instrument after the acid dissolution of the samples in a mixture of HNO3, HCl, and HF. The U.S. Geological Survey standards BHVO, AGV, W-2, and G-2 and Chinese national rock standards (GSR-1, GSR-2, and GSR-3) were used to monitor analytical quality. The analytical precision was better than ±5% for major elements and better than ±2%–5% for most trace elements.
4. Results
4.1. Zircon U–Pb Geochronology and Trace Elements
The analyzed zircons, typically colorless or light yellow and transparent, exhibit a primarily prismatic shape with lengths ranging between 100–300 μm and aspect ratios of 1:1 to 3:1. Within some zircon grains, there are small crystal and melt inclusions alongside ellipsoidal inherited zircon cores shown in the CL images (Figure 3). These zircons demonstrate a magmatic origin, evident through distinct oscillatory zoning and high Th/U ratios [27] (Table S1). In addition, they display depletion in light REEs with strong negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* ≤ 0.06) and positive Ce anomalies (Ce/Ce* ≥ 1.53; Table S2), further confirming their igneous origin.
One sample from each of the studied granitic bodies was selected for zircon U–Pb dating (Table S1). The results of the analyses were all concordant or nearly concordant (Figure 4), yielding weighted mean 206Pb/208U ages of 247.4 ± 1.0 Ma (2σ; MSWD = 0.66; n = 22) for Jiuzhou granodiorite, 246.6 ± 1.1 Ma (2σ; MSWD = 0.47; n = 20) for Dasi granite porphyry, and 248.32 ± 0.98 Ma (2σ; MSWD = 0.27; n = 23) for Taima granite porphyry, being identical within error with each other. Moreover, one zircon grain from the Jiuzhou granodiorite exhibits an older 206Pb/208U age of 357 ± 5 Ma, as is also the case for three zircons (694 ± 4 Ma, 536 ± 10 Ma, 451 ± 11 Ma, respectively) from the Dasi granite porphyry, implying these are inherited zircons.
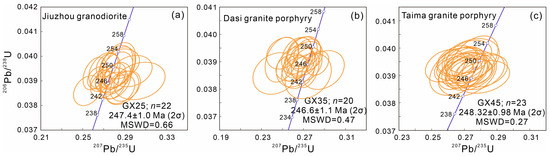
Figure 4.
Zircon U–Pb dating results for samples of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex.
The trace elements of zircons in the analyzed samples largely overlap with each other (Figure 5; Table S2). Most zircons, which we inferred to be magmatic, displayed notably low concentrations of La (<1 ppm), except for two grains (La = 1.38 and 2.65 ppm), which may contain micro-inclusions and were thus excluded from subsequent statistical analysis [28]. These zircons have regular contents of Th (39.7–201 ppm), U (162–604 ppm), and Ti (3.08–17.9 ppm) but much higher Hf (9820–12496 ppm) and Y (1223–2658 ppm) contents. Estimations of the crystallization temperatures for these magmatic zircon grains, using Ti-in-zircon thermometry [29], yielded values of 702–882 °C (Table S2), with average temperatures of 811 °C, 805 °C, and 808 °C for the Jiuzhou granodiorite and the Dasi-Taima granite porphyries, respectively. Notably, the magmatic temperatures of the Jiuzhou granodiorite are slightly higher than those of the Dasi-Taima granite porphyries (Figure 5a). Additionally, the Hf contents display an increase with decreasing Ti, i.e., with lower temperature. The Y/Dy values slightly increase with decreasing Th/U (Figure 5b), comparable to those values of coeval silicic volcanic rocks [21]. The calculated ΔFMQ values of these samples are highly similar, with averages of −4.8, −4.8, and −4.6 for the Jiuzhou granodiorite and the Dasi and Taima granite porphyries, respectively. It suggests a comparable oxidation state of the magma, as the state can be determined based on the magnitude of zircon Ce anomalies [30].
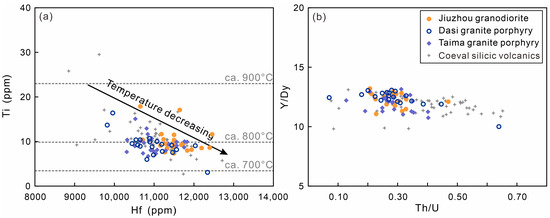
Figure 5.
(a) Ti vs. Hf and (b) Y/Dy vs. Th/U variations in zircons from granitic rocks of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex. Previously published data for the coeval silicic volcanic rocks are from [21].
4.2. Zircon Hf Isotopes
The εHf(t) values of the analyzed zircons span a wide range from −23.9 to −7.8 (Figure 6; Table S3). Although each sample has one or two zircons reflecting a highly enriched Hf isotopic composition (εHf(t) < −18.5), most of the zircons show unimodal distributions ranging within 5–6 units. Excluding several outliers, the weighted mean εHf(t) values are −10.5 ± 0.6, −9.8 ± 0.6, and −9.8 ± 0.5, corresponding to two-stage model ages (TDM2) of 1.76–2.10 Ga, 1.74–2.07 Ga, and 1.77–2.03 Ga for the Jiuzhou granodiorite and Dasi and Taima granite porphyries, respectively. As for the highly enriched members, the two-stage model ages range from 2.20 to 2.75 Ga.
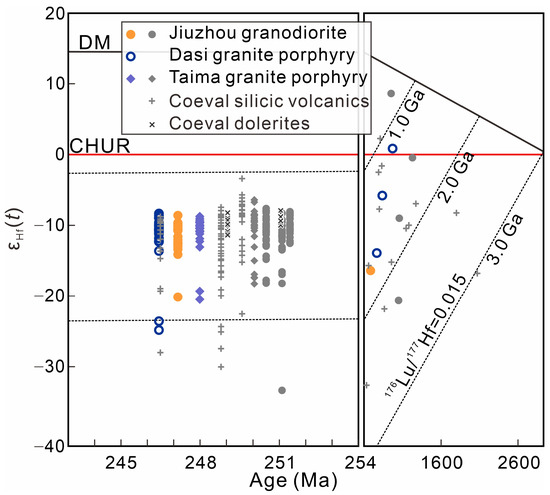
Figure 6.
Zircon εHf(t) vs. U–Pb age diagram for rocks of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex. The previously published data for the granitoids and coeval silicic volcanic rocks are from [18,21,31] and those for the coeval dolerites are from [32].
4.3. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements
The whole-rock major and trace element compositions of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex are given in Table 1. The granitic samples span a range of SiO2 contents from 64.02 wt.% to 72.54 wt.%, and the total alkali (K2O + Na2O) contents range from 5.22 wt.% to 7.41 wt.%, showing geochemical features typical of high-K calc-alkaline granites and granodiorites (Figure 7a,c). Moreover, the magmatic rocks exhibit relatively low contents of TiO2 (0.37–1.12 wt.%), MgO (0.60–2.15 wt.%), CaO (1.61–3.51 wt.%), and P2O5 (0.12–0.16 wt.%) but high Fe2O3T (2.35–7.28 wt.%) and Al2O3 (13.90–14.42 wt.%). Therefore, these samples are peraluminous with A/CNK values ranging from 1.06 to 1.17 (Figure 7b), showing S-type affinities (Figure 7d).
The studied granitic rocks have REE contents of 187–327 ppm, with relative light over heavy REE enrichment {(La/Yb)N = 6.16–13.03} and negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu⁎ = 0.47–0.56) (Figure 8a). All samples exhibit similar trace elemental patterns, with significant depletion of high-field-strength elements (e.g., Nb, Ta, and Ti) and enrichment of large-ion-lithophile elements (e.g., Rb and K) (Figure 8b).

Table 1.
Analytical results of whole-rock major (wt.%) and trace elements (ppm) for granitic rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex.
Table 1.
Analytical results of whole-rock major (wt.%) and trace elements (ppm) for granitic rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex.
| Plutons | Jiuzhou Granodiorite | Dasi Granite Porphyry | Taima Granite Porphyry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | GX18 | GX19 | GX25 | GX44 | GX35 | GX36 | GX39 | GX41 | GX45 |
| SiO2 | 66.67 | 67.24 | 64.02 | 67.50 | 68.99 | 69.24 | 72.54 | 72.26 | 72.26 |
| TiO2 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 1.12 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.39 |
| Al2O3 | 13.95 | 14.18 | 14.01 | 14.13 | 14.03 | 14.14 | 13.90 | 14.42 | 14.18 |
| Fe2O3T | 5.76 | 6.04 | 7.28 | 5.77 | 4.89 | 4.63 | 2.68 | 2.35 | 2.68 |
| MnO | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| MgO | 1.86 | 1.84 | 2.15 | 1.81 | 1.44 | 1.34 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.64 |
| CaO | 2.77 | 3.11 | 3.51 | 3.25 | 2.91 | 2.81 | 1.93 | 2.33 | 1.61 |
| Na2O | 1.73 | 1.84 | 1.90 | 1.61 | 2.15 | 1.96 | 2.18 | 2.21 | 1.98 |
| K2O | 3.79 | 3.82 | 3.32 | 3.99 | 4.05 | 4.23 | 4.91 | 4.91 | 5.43 |
| P2O5 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| LOI | 1.36 | 0.77 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.16 |
| Total | 98.94 | 99.95 | 98.51 | 99.11 | 99.72 | 99.85 | 99.72 | 99.71 | 99.49 |
| A/NK | 2.01 | 1.98 | 2.09 | 2.02 | 1.77 | 1.81 | 1.56 | 1.61 | 1.55 |
| A/CNK | 1.16 | 1.11 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 1.09 | 1.12 | 1.09 | 1.17 |
| V | 92.5 | 94.2 | 68.3 | 100 | 68.9 | 61.8 | 24.5 | 23.6 | 26.9 |
| Co | 32.0 | 52.4 | 62.0 | 45.9 | 22.9 | 33.5 | 15.6 | 19.3 | 29.8 |
| Ni | 32.8 | 40.3 | 30.1 | 66.2 | 16.6 | 21.2 | 4.97 | 6.24 | 102 |
| Ga | 27.2 | 33.4 | 28.7 | 41.3 | 31.1 | 31.1 | 28.4 | 31.2 | 32.4 |
| Rb | 184 | 171 | 189 | 160 | 190 | 174 | 181 | 195 | 225 |
| Sr | 127 | 156 | 138 | 153 | 121 | 117 | 100 | 124 | 90.6 |
| Y | 39.1 | 40.0 | 37.9 | 36.3 | 41.2 | 36.9 | 36.6 | 36.7 | 43.5 |
| Zr | 284 | 272 | 218 | 429 | 305 | 268 | 204 | 200 | 214 |
| Nb | 16.2 | 16.0 | 14.4 | 19.8 | 15.8 | 14.0 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 11.9 |
| Cs | 13.7 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 9.49 | 7.67 | 8.36 | 11.4 | 10.8 | 15.1 |
| Ba | 590 | 788 | 670 | 1039 | 734 | 739 | 686 | 762 | 747 |
| La | 54.8 | 56.7 | 41.2 | 70.0 | 55.7 | 52.9 | 40.1 | 44.8 | 38.5 |
| Ce | 99.0 | 102 | 74.5 | 137 | 101 | 93.9 | 72.0 | 79.5 | 72.5 |
| Pr | 12.3 | 12.6 | 9.35 | 17.0 | 12.4 | 11.8 | 9.21 | 10.1 | 10.1 |
| Nd | 45.4 | 46.1 | 34.9 | 62.9 | 45.8 | 43.8 | 33.9 | 37.3 | 37.3 |
| Sm | 8.95 | 8.92 | 7.23 | 11.0 | 9.02 | 8.56 | 6.94 | 7.44 | 7.99 |
| Eu | 1.33 | 1.57 | 1.30 | 1.84 | 1.37 | 1.38 | 1.13 | 1.25 | 1.26 |
| Gd | 8.21 | 8.29 | 7.01 | 9.66 | 8.37 | 7.80 | 6.71 | 7.19 | 8.06 |
| Tb | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.07 | 1.25 | 1.24 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 1.12 | 1.32 |
| Dy | 6.87 | 7.04 | 6.56 | 6.64 | 7.29 | 6.76 | 6.46 | 6.65 | 8.21 |
| Ho | 1.36 | 1.41 | 1.31 | 1.29 | 1.47 | 1.33 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 1.68 |
| Er | 3.85 | 3.88 | 3.66 | 3.68 | 4.08 | 3.70 | 3.63 | 3.71 | 4.78 |
| Tm | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.70 |
| Yb | 3.73 | 3.87 | 3.54 | 3.72 | 3.79 | 3.47 | 3.31 | 3.36 | 4.33 |
| Lu | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.60 |
| Hf | 7.68 | 7.31 | 6.05 | 11.5 | 8.21 | 7.36 | 5.67 | 5.60 | 6.17 |
| Ta | 1.27 | 1.41 | 1.46 | 1.48 | 1.21 | 1.34 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 1.31 |
| Pb | 30.0 | 31.6 | 35.0 | 28.7 | 31.6 | 29.7 | 30.5 | 32.7 | 30.4 |
| Th | 25.8 | 25.9 | 18.1 | 36.0 | 25.3 | 25.9 | 22.3 | 25.0 | 24.4 |
| U | 4.41 | 4.08 | 4.86 | 3.58 | 4.48 | 4.01 | 4.09 | 4.59 | 4.95 |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.47 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.48 |
| ΣREE | 248 | 254 | 193 | 327 | 253 | 238 | 187 | 205 | 197 |
Note: Eu/Eu* = EuN/(SmN × GdN)0.5, where N are normalization values after [33]. “T” means “in total”, assuming that total Fe in rocks appear as Fe2O3.
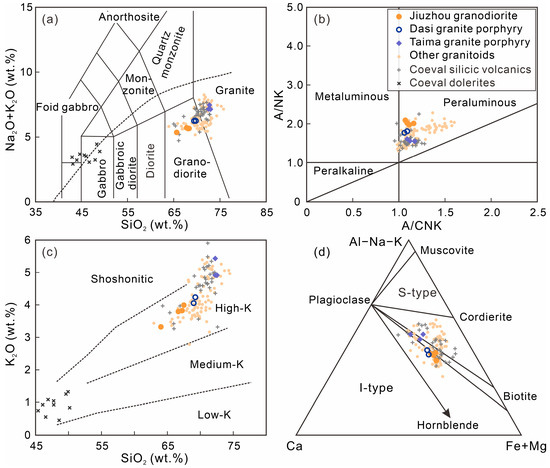
Figure 7.
(a) Total alkali vs. silica [34], (b) A/NK vs. A/CNK, (c) K2O vs. SiO2 [35], and (d) ACF [36] diagrams for rocks of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex. Previously published data for granitoids and coeval silicic volcanic rocks are from [16,19,20,21,37,38,39], and for coeval dolerites are from [32].
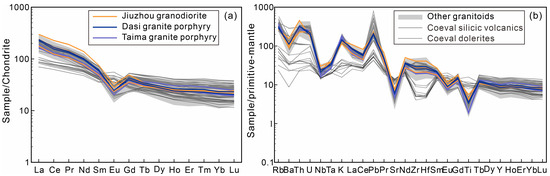
Figure 8.
(a) Chondrite-normalized REE patterns [33] and (b) primitive-mantle-normalized trace element variation diagram [40]. Data sources are the same as for Figure 7.
5. Discussion
5.1. Genetic Relationship with the Coeval Silicic Volcanic Rocks
One striking feature of the Qinzhou Bay area is that it hosts the only occurrence of Early Triassic silicic volcanic rocks within the South China Block [20,21]. Closely associated with the Jiuzhou pluton, the Triassic Banba Fm. volcanic rocks primarily comprise of rhyolites interlayered with perlites, tuff lavas, agglomerate lavas, and rhyolitic tuffs. Meanwhile, the lower Triassic Beisi Fm. volcanic rocks exhibit a volcanic succession characterized by alternating dacitic-rhyolitic lavas interlayered with pyroclastic rocks. These distinct volcanic formations, the Banba and Beisi Fms., are situated on the southeast and northwest side, respectively, of the Shiwandashan Mesozoic–Cenozoic Basin. These silicic volcanic rocks not only have comparable whole-rock geochemical and almost identical isotopic compositions (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8) but also formed coevally with the coexisting granites, with zircon U–Pb dating results ranging from 248.8 ± 1.6 to 246.5 ± 1.3 Ma [21].
The genetic relationship between silicic plutonic and volcanic rocks has long been a subject of debate, holding key significance in comprehending the geochemical evolution of silicic magma systems [41]. Scholars have presented conflicting perspectives on this matter. Some have argued the plutonic and volcanic rocks formed independently via different processes. According to this view, large caldera-forming eruptions resulted from rapid magmatic input, whereas the large plutons evolved incrementally over millions of years, influenced by a lower thermal flux [41,42,43]. By contrast, an alternative theory suggests a crystal—melt separation model that volcanic rocks arise from the extraction of a fractionated melt from crystal mushes, while plutons are considered the residual crystal cumulates left behind after the eruption of volcanic magma [44,45,46].
As mentioned above, the comparable whole-rock geochemical compositions of the coexisting plutonic and volcanic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area indicate they are comagmatic rather than independent in terms of magmatic origin. On the other hand, the crystal—melt separation model assumes silicic volcanic rocks undergo more extensive crystal fractionation than their plutonic equivalents. In their case study, Medlin et al. (2015) [47] investigated the intra-caldera Kathleen ignimbrite and Rowland Suite intrusions in West Musgrave Province, Australia, and suggested the crystal-rich, porphyritic Rowland Suite rhyolite intrusions represented a primitive cumulate endmember, whereas the Kathleen ignimbrite eruption sequence represented the evolved and highly fractionated endmember of the magmatic system. Yan et al. (2016) [48] also interpreted rhyolitic extrusives in the Yandangshan caldera, SE China, as a highly fractionated endmember, whereas the subvolcanic intrusions of porphyritic quartz syenites could be residual crystal mushes. However, the Early Triassic granitic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area have a total SiO2 range of 62.95–74.47 wt.%, encompassing their volcanic equivalents (SiO2 = 64.32–72.65 wt.%; Figure 9). There exists no complementary geochemical relationship between the silicic volcanic rocks and granitic intrusions.
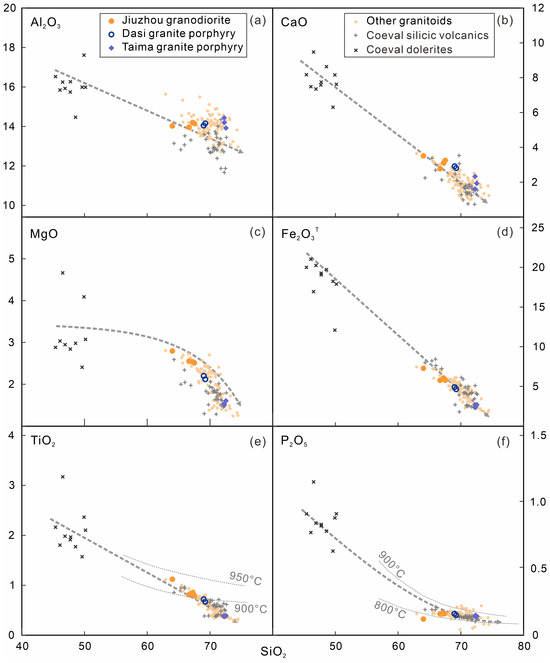
Figure 9.
SiO2 vs. Al2O3 (a), CaO (b), MgO (c), Fe2O3T (d), TiO2 (e), and P2O5 (f) diagrams (in wt.%) of rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex. Temperature estimate lines in (e) are after [49] and those in (f) are after [50]. Symbols and data sources are the same as in Figure 7.
Trace elements in igneous zircon crystals offer valuable insights into the conditions of crystallization as a record of various magmatic processes, including magma rejuvenation, magma mixing, and fractional crystallization [27,51,52]. For example, variations in elements such as Hf and Th/U ratios in zircon can signify changes in melt composition and temperature during crystallization. Notably, Hf in zircon typically increases, while Th/U ratios decrease, with decreasing temperature [53]. Zircon trace elements of the Qinzhou Bay volcanic and plutonic rocks also display almost identical compositional variations, with no complementary signatures (Figure 5). Hence, it is impossible that the granitic rocks are cumulates left behind after volcanic melt extraction.
In addition, a typical volcanic-intrusive complex would form in a ring structure, with voluminous volcanics on the outside and subsequent intrusives at the center. The volcanic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area, on the contrary, are located in the distant corner of the entire volcanic-intrusive sequence, with a negligible mass compared to the granitoids. The characteristics of the silicic volcanics and adjacent Jiuzhou pluton are clearly controlled by the regional deep fault (Figure 1). Therefore, we believe the Early Triassic volcanic and intrusive rocks are comagmatic and derived from a common magma pool, detached in an undifferentiated melt instead of indicating remarkable crystal—melt separation.
In fact, we consider fractional crystallization played a less important role during the silicic magmatic evolution of the Early Triassic Qinzhou Bay area. Another reason for this is the rather homogeneous whole-rock geochemical composition observed within a single granitoid body. The Jiuzhou pluton has a narrow SiO2 range of 64–68 wt.% in the case of our sample and one of 64–70 wt.% based on the combined data from the references. The same is true for the Dasi and Taima granite porphyries, with SiO2 ranges of 68–70 wt.% and 70–73 wt.%, respectively. The narrow and uncoincidental compositional variation within a voluminous granitoid body requires a magmatic mechanism other than fractional crystallization.
5.2. Petrogenesis of the Granitoids and Mantle-Derived Contribution
The granitoids in the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex have long been demonstrated as unambiguous S-type granitoids, by their high Al2O3 contents, highly enriched radiogenic Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic compositions, low oxygen fugacity, and, especially, the common presence of conspicuous cordierite in these granitoids [18,19,31,32,54,55]. The studied Jiuzhou granodiorites and Dasi-Taima granite porphyries are characterized by a high silica content (mostly SiO2 > 66 wt.%), peraluminous composition (A/CNK = 1.06–1.17), and low Sr abundance (90.6–170 ppm). These attributes suggest the magma most likely originate from Al-rich metasedimentary protoliths [56]. Their low zircon εHf(t) (−23.9 to −7.8), low whole-rock εNd(t) (−11.6 to −11.2), and high initial 87Sr/86Sr (0.71874 to 0.72157) [16] reveal a crustal source with an average crustal resident age exceeding 1.8 Ga. This is consistent with the low zircon oxygen fugacity (ΔFMQ < 0), as magmas derived from the melting of metasedimentary rocks commonly exhibit similarly low fO2 [57]. We should note the widespread occurrence of metapelitic granulite enclaved in the Jiuzhou granodiorites [19], supporting the idea that the granitic complex is predominantly derived from the melting of ancient metasedimentary rocks [18,19]. These granulite enclaves are considered residual material from the host granitoids, supported by systematic elemental variation trends and similar Sr–Nd isotope compositions between them [16,19].
Zhao et al. (2012) [19] conducted a subdivision of the granulite enclaves based on their different initial 87Sr/86Sr values. According to their estimations, approximately 10%–40% low-87Sr/86Sr(i) and 60%–90% high-87Sr/86Sr(i) granulites were constrained as the magma source for the host granitoids. Nonetheless, the granulite endmembers used for this estimation have εNd(t) values at 253 Ma of −13.30 and −12.84, lower than the εNd(t) of the host granitoids (−11.6 to −11.2) [16]. Thus, an extra high-εNd(t) endmember should be included in the estimation of the magma source.
Combined with the coeval silicic volcanic rocks and granitoids reported in the literature, our data show the content of SiO2 correlated negatively with Fe2O3T, Al2O3, MgO, CaO, TiO2, P2O5, and MnO (Figure 9) and positively with K2O and Na2O + K2O (Figure 7a,c). Several processes could potentially account for the modification of granitic magma compositions, including fractional crystallization and cumulate formation, the entrainment of restitic material, and/or magma mixing with mantle-derived melts. Above, we have argued fractional crystallization might have played a less important role during the magmatic evolution, because of the narrow geochemical variation within a single granitoid body and the lack of a fractional signature in the cogenetic silicic volcanic rocks. Although restitic material was notably found within the Jiuzhou granodiorites, occurring both in centimeter-size enclaves and micro-restite [16], the whole-rock geochemical trends could not be explained by restite entrainment as plagioclases in the restite were insufficient in content to replicate the observed compositional variations [58].
The granitoids in the Qinzhou Bay area, together with the cogenetic volcanic rocks, exhibited lower molar Al2O3/(MgO + FeOT), (Na2O + K2O)/(FeO + MgO + TiO2), Al2O3/TiO2, Rb/Sr, and Rb/Ba ratios but a higher CaO/Na2O ratio compared to the typical metapelite-derived melt (Figure 10), which was discussed above as the major magma source. Thus, these compositional distinctions suggested magmas of such compositions could not solely originate from metapelitic sources. Instead, an evident transitional trend between metapelite- and basalt-derived melts reveals the input of mantle-derived materials or juvenile crust cannot be precluded in the genesis of the granitoids.
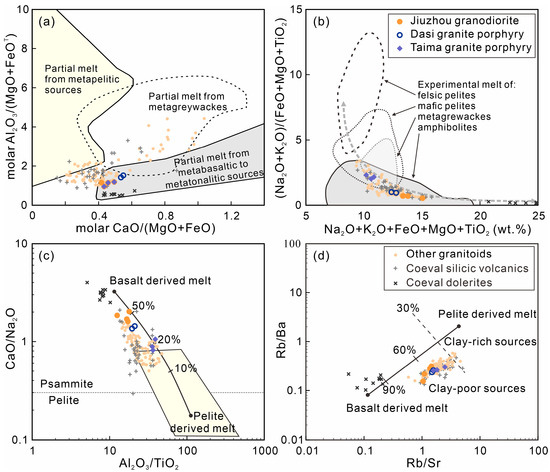
Figure 10.
Source discrimination diagrams for rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex: (a) after [59]; (b) after [60]; and (c,d) after [56]. Symbols and data sources are the same as in Figure 7.
The zircon saturation temperature estimation using the Watson and Harrison (1983) [61] model reveals a narrow temperature range from 848 °C to 868 °C, although zircon inheritance might partly contribute to the whole-rock Zr contents [62]. The calculated Ti-in-zircon temperatures also imply magmatic activity mostly (for more than 95% of the zircon grains) at 780–882 °C (Figure 5a), whereas major element contents of whole-rocks, such as TiO2 and P2O5, yield temperatures higher than 800 °C or even 900 °C (Figure 9e,f). Therefore, the granitoids were generated at a temperature even higher than that of the coeval I- and S-type granites in the interior South China Block [18].
The high-temperature magmatism and coeval metamorphism [16,18,19] require an intense heat source. Previous studies have often ruled out the possibility of mantle-derived material input in the granitic magma, mainly because of the enriched Sr–Nd of whole-rocks and Hf isotopic compositions of their zircons [18,20,31]. However, Xu et al. (2018) [32] recently presented a case study of contemporary dolerites and basalts between the Jiuzhou and Darongshan plutons in the Qinzhou Bay area, which were inferred to originate from an enriched lithospheric mantle source with minor contamination. These mafic rocks display comparable zircon Hf isotopic compositions (εHf(t) = −10.9 to −7.6, for t = ca. 250 Ma) but higher whole-rock εNd(t) values (−10.4 to −6.7) than the granitoids [32]. Apparently, the input of such mantle-derived materials into granitic magma would match the isotopic characteristics of the studied granitoids.
Therefore, we suggest the mantle-derived mafic magma played an important role in the generation of the granitic and volcanic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area, not only as a heat source for anatectic melting but may also as a component endmember. The compositional variation of the peraluminous rocks was at least partly, if not purely, due to varying degrees of mixing between crust- and mantle-derived magmas. Considering the lower SiO2 content and the presence of microgranular enclaves in the Jiuzhou granodiorites, as well as the slightly higher estimated zircon saturation and Ti-in-zircon temperatures, the contribution of the mafic endmember in the Jiuzhou granodiorites might be higher than that in the Dasi and Taima granite porphyries, which formed in succession.
5.3. Implications for Paleo-Tethys Geodynamic Evolution
Several geodynamic evolution models have emerged to explain the Early Triassic tectono-magmatism in the Qinzhou Bay area, including subduction of the oceanic plate [5,6,18,20,55] or disturbance caused by the Emeishan mantle plume [9,63]. Some studies have entertained the idea of Emeishan plume as a possible heat source for the high-temperature/ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism [8,9,63,64]. However, precise geochronological studies have indicated the Emeishan mantle plume ceased at ca. 259.1 ± 0.5 Ma [65], nearly 10 Ma before the onset of the magmatism and metamorphism in the Qinzhou Bay area. Additionally, the Qinzhou Bay area sits approximately 900 km distant from the Emeishan mantle plume center [66]. Moreover, mafic flows and dikes in western Guangxi induced by the Emeishan plume typically exhibit markedly elevated Ti/Y ratios with a limited εNd(t) range from +0.41 to +1.81 [67]. These characteristics stand in clear contrast to the mafic volcanic rocks found in the Qinzhou Bay area [32].
The studied granitic rocks exhibit obvious light REEs enrichment relative to heavy REEs and are significantly depleted in high-field-strength elements (e.g., Nb, Ta, and Ti) and enriched in large-ion-lithophile elements (e.g., Rb, and K). These geochemical traits showcase signatures typical of arc-related origins [20]. The genesis of the Late Permian to Early Triassic igneous rocks in the Qinzhou Bay and neighboring regions has been associated with either paleo-Tethys subduction [4,5,55,58,68] or paleo-Pacific subduction [6,12,18,32]. This study confirms a subduction setting, wherein intense mantle-derived upwelling is postulated to have functioned not only as a heat source but also as a direct contributor to the formation of the granitoids and related silicic volcanic rocks in the Qinzhou Bay area. Nevertheless, the debate persists regarding whether the regional tectono-magmatism was controlled by paleo-Tethys or paleo-Pacific plate subduction.
Currently, it is widely accepted the substantial Late Mesozoic silicic magmatism in SE China stemmed from the paleo-Pacific subduction during 204–88 Ma [4,5,6,13,14]. The Early Triassic granitoids and silicic volcanic rocks display no close spatial—temporal association with the Late Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in SE China, since there is a significant time gap of over 40 Ma and a spatial separation of over 700 km between them. Underplating of mantle-derived magma, the heat source accounting for the Late Permian–Triassic magmatism and metamorphism in the study area, has been proposed to result from slab roll-back and/or tearing of the oceanic plate [18,32]. Some argued the stretching direction in NE of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex coincided better with a NW-ward paleo-Pacific subduction model rather than a NE-ward paleo-Tethys subduction model [12,18,32]. It is worth noting the stretching shapes of Jiuzhou, Dasi, and Taima plutons are obviously controlled by the regional deep faults, while the Pubei pluton to the east of the faults displays in a much round shape. Thus, in our opinion, the silicic magmas rose and intruded primarily along the pre-existing faults which have plausibly been activated by the oceanic plate subduction (Figure 11).
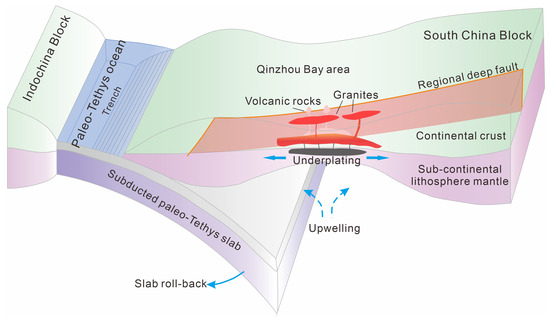
Figure 11.
Schematic geodynamical model of Early Triassic tectono-magmatism in the Qinzhou Bay area, South China (modified after [68]). A sequence of Permian–Triassic arc igneous rocks, along with high-pressure, low-temperature metamorphic rocks, and notably ophiolites, are observed across the Ailaoshan-Song Ma suture zone, stretching towards Hainan Island [55,68] (and references therein). It is also essential to highlight the higher temperatures necessary for the formation of the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex compared to those of the coeval I- and S-type granites in the interior South China Block. Our preference leans toward the model that asserts the Late Permian–Triassic tectono-magmatism in the South China Block was influenced by paleo-Tethys subduction.
The S-type Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex is considered to originate from various degrees of melting of the similar protolith at different crustal levels [54]. Zhao et al. (2017) [16] put forth the notion of rapid migration of a magma source, indicating an early (255–249 Ma) melting event at ~950 ± 30 °C and ~500 ± 80 MPa, followed by a later (245–246 Ma) melting event at ~905 ± 15 °C and ~675 ± 25 MPa. It was inferred the crustal magma source had rapidly migrated from a depth of ~18 to ~25 km within 3–10 Ma [16], implying distinct crustal thickening. On one hand, this contradicts the theory of the paleo-Pacific subduction model, which involves no crustal thickening event. On the other hand, the rapid crustal thickening indicates a switch in the geodynamic regime from subduction to continent–continent collision between the South China and Indochina blocks, because the volcanic rocks and mantle-derived underplating should have formed in an extensional setting due to subduction. In this case, it is plausible the Early Triassic granitic rocks formed in the latest stage of subduction, just before the closure of the eastern paleo-Tethys [55] (Figure 11).
6. Conclusions
The Jiuzhou granodiorites and Dasi-Taima granite porphyries in the Qinzhou Bay area, South China, formed between 248.32 ± 0.98 and 246.6 ± 1.1 Ma, coeval to the adjacent silicic volcanic rocks. The granitoids also show whole-rock geochemical features very similar to those of the volcanic rocks; thus, we inferred they were comagmatic and derived from a common magma pool. Although fractional crystallization might have played a less important role during the magmatic evolution, it was more likely the silicic magma was detached in an undifferentiated melt instead of evolving due to remarkable crystal—melt separation. Moreover, the source discrimination indicators and high calculated Ti-in-zircon temperatures (702–882 °C) reveal magma derived from the enriched lithospheric mantle not only provided a heat source for the anatectic melting of the metasedimentary protoliths but was also an endmember component of the S-type silicic magma. We inferred the studied Early Triassic granitoids formed immediately before the closure of the paleo-Tethys Ocean, as the subduction associated with this event would have generated an extensional setting in which the mantle-derived upwelling and volcanic activity occurred.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min14010022/s1, Table S1: LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results for rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex; Table S2: LA-ICP-MS zircon trace element concentrations (ppm) of rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex; Table S3: Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of rocks from the Qinzhou Bay Granitic Complex.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L. and W.X.; methodology, L.L.; formal analysis, W.X., X.L., L.L. and Z.Z.; investigation, L.L., Z.Z. and Y.W.; data curation, L.L., W.X., X.L. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, W.X. and X.L.; supervision, W.X. and X.L.; project administration, W.X.; funding acquisition, W.X. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Program (2021GXNSFAA220077, 2021GXNSFBA220063) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (42073031, 92055208). This is a contribution to “Xinjiang Tianchi Distinguished Expert” to Liu Xijun and Guangxi Key Mineral Resources Deep Exploration Talent Highland.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Zhenglin Li and Hongxia Yu for their technical support for sample analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Metcalfe, I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 66, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Li, W.-X.; Li, Z.-X.; Lo, C.-H.; Wang, J.; Ye, M.-F.; Yang, Y.-H. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China: Constraints from SHRIMP U–Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd–Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks. Precambrian Res. 2009, 174, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Lin, W.; Chu, Y.; Lepvrier, C. Triassic tectonics of the southern margin of the South China Block. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2016, 348, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.-L.; Du, D.-H.; Xing, G.-F.; Fu, J.-M.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.-M. Refining the spatio-temporal distributions of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in SE China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 201, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, T.; Shen, W.; Shu, L.; Niu, Y. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in south China: A response to tectonic evolution. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2006, 29, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-X.; Li, X.-H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model. Geology 2007, 35, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-Y.; Li, Z.-X.; Xu, X.-S.; Wilde, S.A.; Chen, H.-L. Early Mesozoic ferroan (A-type) and magnesian granitoids in eastern South China: Tracing the influence of flat-slab subduction at the western Pacific margin. Lithos 2016, 240–243, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Qin, X.; Li, H. Crustal evolution of the Shiwandashan area in South China: Zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic records from granulite enclaves in Indo-Sinian granites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Hsieh, P.-S.; Lee, C.-Y.; Zhou, H.-W. Two episodes of the Indosinian thermal event on the South China Block: Constraints from LA-ICPMS U–Pb zircon and electron microprobe monazite ages of the Darongshan S-type granitic suite. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Multi-stage crust–mantle interaction in SE China: Temporal, thermal and compositional constraints from the Mesozoic felsic volcanic rocks in eastern Guangdong–Fujian provinces. Lithos 2012, 150, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Yang, J.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, F.-Y.; Wilde, S.A. Genesis of late Early Cretaceous high-silica rhyolites in eastern Zhejiang Province, southeast China: A crystal mush origin with mantle input. Lithos 2018, 296–299, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yu, J.-H.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Griffin, W.L.; Zhou, X. Subduction-related middle Permian to early Triassic magmatism in central Hainan Island, South China. Lithos 2018, 318–319, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhang, Y.H. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and controversies. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1273–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-Y.; Li, X.-H. In situ zircon U–Pb and Hf–O isotopic results for ca. 73 Ma granite in Hainan Island: Implications for the termination of an Andean-type active continental margin in southeast China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 82, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Zhao, Z.-F. Triassic granites in South China: A geochemical perspective on their characteristics, petrogenesis, and tectonic significance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 266–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xu, X.; Erdmann, S.; Liu, L.; Xia, Y. Rapid migration of a magma source from mid- to deep-crustal levels: Insights from restitic granulite enclaves and anatectic granite. GSA Bull. 2017, 129, 1708–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, A.M.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhang, Y.Z. Permian arc–back-arc basin development along the Ailaoshan tectonic zone: Geochemical, isotopic and geochronological evidence from the Mojiang volcanic rocks, Southwest China. Lithos 2010, 119, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.-J.; Li, X.-H.; Huang, H.-Q.; Deng, X.-G. Metasedimentary melting in the formation of charnockite: Petrological and zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotope evidence from the Darongshan S-type granitic complex in southern China. Lithos 2015, 239, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Qin, X.; Li, H. Origin of the granulite enclaves in Indo-Sinian peraluminous granites, South China and its implication for crustal anatexis. Lithos 2012, 150, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, L.Z.; Hu, G.A.; Zhou, F.S. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Mesozoic acid volcanic rocks from Southwest Guangxi: Constraints on tectonic evolution of the southwestern segment of Qinzhou-Hangzhou joint belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 794–808, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, W. Early Triassic silicic volcanic rocks of South China: Petrogenesis and constraints on the geodynamic evolution of the paleo-Tethys Ocean region. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zong, K.; Wang, D. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-induced Melt–Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U–Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, U.; Patchett, P.J.; Vervoort, J.D.; Isachsen, C.E. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu–Hf and U–Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 219, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, A.; Vervoort, J.D.; Patchett, P.J. The Lu–Hf and Sm–Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 273, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Pearson, N.J.; Belousova, E.; Jackson, S.E.; van Achterbergh, E.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Shee, S.R. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Wang, X.; Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos 2002, 61, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Schaltegger, U. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Jiang, J.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, X. Progress in the principle and application of zircon trace element. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 985–999, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Bruce Watson, E.; Tailby, N.D. Ce and Eu anomalies in zircon as proxies for the oxidation state of magmas. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.S.; Deng, X.; Li, X.H.; Li, W.-X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L. Origin of the Darongshan-Shiwandashan S-type granitoid belt from southeastern Guangxi: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 403–412, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.-C.; Luo, B.-J.; Xu, Y.-J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q. Geochronology, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of late Permian to early Triassic mafic rocks from Darongshan, South China: Implications for ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism and S-type granite generation. Lithos 2018, 308–309, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, E.; Grevesse, N. Abundances of the elements: Meteoritic and solar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Ultrametamorphism and granitoid genesis. Tectonophys 1977, 43, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xin, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, Y. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and geochemical analysis of the Darongshan–Shiwandashan granitoids in southwestern South China and their geological implications. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2018, 39, 179–188, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiao, W.; Bao, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Liao, S.; Qin, X. Geochronology, geochemistry and Hf isotopes of volcanic rocks in Pingxiang area, southwest Guangxi: Implications for the latest stage of paleo-Tethyan ocean northward subduction. J. Geomech. 2019, 25, 932–946, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, D. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Early Mesozoic Rhyolite in Southwestern Guangxi and Its Geological Significance. Geosci. 2021, 35, 981–996, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, W.F.; Sun, S.S. The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazner, A.F.; Coleman, D.S.; Mills, R.D. The Volcanic-Plutonic Connection. In Physical Geology of Shallow Magmatic Systems: Dykes, Sills and Laccoliths; Breitkreuz, C., Rocchi, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 61–82. [Google Scholar]
- de Silva, S.L.; Gosnold, W.D. Episodic construction of batholiths: Insights from the spatiotemporal development of an ignimbrite flare-up. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2007, 167, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, C. From plutons to magma chambers: Thermal constraints on the accumulation of eruptible silicic magma in the upper crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O.; Bergantz, G.W. On the Origin of Crystal-poor Rhyolites: Extracted from Batholithic Crystal Mushes. J. Petrol. 2004, 45, 1565–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelberger, J.C.; Izbekov, P.E.; Browne, B.L. Bulk chemical trends at arc volcanoes are not liquid lines of descent. Lithos 2006, 87, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O.; Miller, C.F.; de Silva, S.L. The volcanic–plutonic connection as a stage for understanding crustal magmatism. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2007, 167, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlin, C.C.; Jowitt, S.M.; Cas, R.A.F.; Smithies, R.H.; Kirkland, C.L.; Maas, R.A.; Raveggi, M.; Howard, H.M.; Wingate, M.T.D. Petrogenesis of the A-type, Mesoproterozoic Intra-caldera Rheomorphic Kathleen Ignimbrite and Comagmatic Rowland Suite Intrusions, West Musgrave Province, Central Australia: Products of Extreme Fractional Crystallization in a Failed Rift Setting. J. Petrol. 2015, 56, 493–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-L.; He, Z.-Y.; Jahn, B.-M.; Zhao, Z.-D. Formation of the Yandangshan volcanic–plutonic complex (SE China) by melt extraction and crystal accumulation. Lithos 2016, 266–267, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.H.; Pearson, N.J. Ti-rich accessory phase saturation in hydrous mafic-felsic compositions at high P,T. Chem. Geol. 1986, 54, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.M.; Watson, E.B. The behavior of apatite during crustal anatexis: Equilibrium and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Zircon Crystal Morphology, Trace Element Signatures and Hf Isotope Composition as a Tool for Petrogenetic Modelling: Examples from Eastern Australian Granitoids. J. Petrol. 2005, 47, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-L.; He, Z.-Y.; Beier, C.; Klemd, R. Zircon trace element constrains on the link between volcanism and plutonism in SE China. Lithos 2018, 320–321, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.R.; Vazquez, J.A.; Schmitt, A.K. Zircon-scale insights into the history of a Supervolcano, Bishop Tuff, Long Valley, California, with implications for the Ti-in-zircon geothermometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 161, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoy, B.; Barbey, P. Ferromagnesian silicate association in S-type granites: The Darongshan granitic complex (Guangxi, South China). Bull. Société Géologique Fr. 2008, 179, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wei, J.H.; Santosh, M.; Tan, J.; Fu, L.B.; Zhao, S.Q. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Middle Permian S-type granitoid in southeastern Guangxi Province, South China: Implications for closure of the eastern Paleo-Tethys. Tectonophysics 2016, 682, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 1998, 45, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, R.H.; Shaw, S.E. A cordierite-bearing granite suite from the New England Batholith, N.S.W., Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1975, 52, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xu, X.; Erdmann, S. Thermodynamic modeling for an incrementally fractionated granite magma system: Implications for the origin of igneous charnockite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 499, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, R.; Siebel, W. I-type plutonism in a continental back-arc setting: Miocene granitoids and monzonites from the central Aegean Sea, Greece. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 143, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño Douce, A.E.; Castro, A.; Fernández, C.; Vigneresse, J.L. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas? In Understanding Granites: Integrating New and Classical Techniques; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 1999; Volume 168, pp. 55–75. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, E.B.; Harrison, T.M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1983, 64, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R.; Williams, I.S.; Wyborn, D.; Ishihara, S.; Stephens, W.E.; Harley, S.L.; Arima, M.; Nakajima, T. Low- and high-temperature granites. In The Fifth Hutton Symposium on the Origin of Granites and Related Rocks; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004; Volume 389, pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Guo, J.H.; Peng, S. Petrogenesis of garnet in the Darongshan-Shiwandashan granitic suite of the South China Block and the metamorphism of the granulite enclave. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1740–1758, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.; Li, C.; Qin, X.; Li, H. Late Paleozoic ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in South China: A case study of granulite enclaves in the Shiwandashan granites. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 1707–1720, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shellnutt, J.G.; Zhou, M.-F.; Yan, D.-P.; Wang, Y.J. Longevity of the Permian Emeishan mantle plume (SW China): 1 Ma, 8 Ma or 18 Ma? Geol. Mag. 2008, 145, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ernst, R.; Lü, L.; Santosh, M.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, Z. Giant radiating mafic dyke swarm of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province: Identifying the mantle plume centre. Terra Nova 2015, 27, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Yan, Q.; Xia, L.; Xia, W.; White, J.D.L. Petrogenesis of the Early-Middle Triassic high-Mg andesitic rocks in the southern margin of the South China Block: Implications for the convergence between the South China and Indochina Blocks. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 232, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhu, D.-C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.Q.; Mo, X.X.; Wei, J.C. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic Yeba Formation volcanic rocks in southern Tibet: Initiation of back-arc rifting and crustal accretion in the southern Lhasa Terrane. Lithos 2017, 278–281, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).