Abstract
Amphibole asbestos is related to multiple diseases, mainly those targeting the lungs. Asbestos-related malignancies can also be caused by non-regulated asbestiform minerals and some elongated mineral particles (EMPs). In particular, the role of nano- and micro-sized EMPs internalized by lung epithelial cells must be clarified. This is of major importance when considering that EMPs to which humans are exposed are likely a highly heterogeneous mix of different mineral types, shapes, and sizes. Here, we document that particles smaller than 4.54 µm in length and smaller than 0.89 µm in width (e.g., particles that do not fit the regulatory categories to be identified as asbestos) are easily internalized because of their specific dimensions, surface charge, and shape (mostly dictated by the aspect ratio L/w). Once internalized, these particles can be found in proximity to the cell nucleus, in vesicles, and in the cytoplasm. Examining the localization of particles in cells provides important information, which helps in determining the physicochemical environment found inside the biological compartment, thus allowing for a better comprehension of the mineralogical transformation that might happen after internalization by cells.
1. Introduction
“Asbestos” is intended as an all-inclusive industrial term [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], which groups six minerals together because of their similar function, technological application, and commercial value, but it has a poor and unsatisfactory scientific meaning. The often casual use of the term “asbestos” posed a major problem in the past and continues to do so in the recent literature, with immediate consequences to the regulatory frameworks of many countries around the globe. The relatively new terminology used and proposed by NIOSH [8] represents an important step towards overcoming the limitations of the iconic term “asbestos”.
Asbestosis, pleural abnormalities, bronchogenic carcinoma, and mesothelioma are all potential consequences of human and animal exposure to amphibole asbestos [1,9], similar elongated mineral particles (EMPs), and possibly accompanying (non-regulated) nano- and micro-sized mineral particles [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Specific dimensions were determined by scientists and regulators to categorize and regulate asbestos and other EMPs, which can travel to a certain depth in the lungs. Particles with a specific set of physicochemical characteristics can be less susceptible to lung clearance, and they may trigger phagosome death and, thus, frustrated phagocytosis; therefore, a large body of literature has been dedicated to the investigation of the properties and biological interactions of these arbitrarily categorized particles [19,20].
Surprisingly, the same biochemical and mineralogical studies and dimensional determinations are not commonly performed for non-regulated nano- and micro-sized particles, which are recurrently present in the particle mix, together with regulated fibers, and can be internalized by target cells. Subsequent to uptake by cells, these particles might end up in close contact with the cell nucleus and organelles, possibly generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) in their proximity. The localization of these non-regulated nano- and micro-sized particles is one of the aspects that we have explored in our work. The lack of mineralogical and physicochemical investigations of internalized particles is probably a consequence of the fact that, compared to their asbestos counterparts, amphibole cleavage fragments and short fibers have been poorly examined epidemiologically and toxicologically in relation to the above-mentioned diseases [17,21,22].
Today, however, it is well known that non-regulated asbestiform minerals, and more generally EMPs, can cause malignancies and fibrosis in the same way that asbestos does [8,23].
Most of the asbestos-related literature is rightfully focused on the basic disease-triggering mechanism relying on the so-called frustrated phagocytosis mechanism [24], induced by the presence of asbestos particles. However, there exists only limited research dedicated to the localization, morphology, and dimensional distribution of the particles that are internalized by target cells but cannot be classified as asbestos or EMPs (e.g., those formed by the fragmentation of larger particles).
Studies performed on asbestos cleavage fragments and particles with a length < 5 µm suggest that non-asbestiform amphiboles are less toxic than their asbestiform counterparts [5,8,21,22,24,25,26,27,28]. It is rather difficult, however, to expose lung cells or laboratory animals to a dimensionally homogeneous “asbestos” particle population or to a dimensionally homogeneous EMP population. Commonly, the administered particle populations include a certain percentage of non-asbestiform, non-elongated components and/or cleavage fragments [7]. Consequently, it cannot be ruled out that a synergistic action might exist between certain EMPs and the non-asbestiform, non-elongated components and/or cleavage fragments upon being taken up by target cells. In addition, the related medical and biological studies on the topic only rarely report information on the dimensional distribution of the mineral sample administered to the biological target [18]. This lack of information is also partly a consequence of the limited use of high-end microscopy techniques during studies of histological samples, where the identification, counting, and localization of nano-sized particles are far from being satisfactory or reliable from a mineralogical standpoint.
A large body of literature has revealed that asbestos particles shorter than 5 µm have a lower carcinogenic potential than longer particles [22,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. More recent research by IARC [41] stated that thin and long “fibers” might be more potent in inducing human lung cancer than short and thick “fibers”. The term fiber is given in quotation marks since we believe that its use is inappropriate and outdated for describing short and thick particles.
As mentioned, all these studies have in common a lack of information on the complete particle size distribution [28]. Moreover, simply providing a range of particle dimensions is far from representing the “real” particle size distribution of the sample [18].
Recent studies and reviews in the mineralogical and toxicological literature show that the roles of nano-sized EMPs, cleavage fragments, “fibers” with a length of <5 µm, and particles that originate from the longitudinal splitting of larger particles are still unclear and have been debated over the years [7,15,16,17,18], especially when these particles are mixed with “asbestos”, regulated fibers, or EMPs. There are papers proposing the hypothesis that even “short fibers” might play an important role in triggering mesothelioma [10,11,12,13,14].
Asbestos-related tumors are difficult to diagnose and have long latency periods, and it is not clear whether there is a minimum exposure threshold for carcinogenesis [42]. Thus, the role of each component of the studied system should be investigated and considered in the overall carcinogenic mechanism.
For these reasons, our study focuses on particles that are internalized by alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) and reports on the localization and dimensional distribution of these internalized particles. The present study, in concert with our previous investigation on the transformation of select amphiboles in AECs [7], aims to provide additional information on particles that are not necessarily considered as harmful as long and thin asbestos and/or asbestos-like particles in order to help clarify whether indeed “shorter fibers would have little if any effect” [22] on exposed individuals. In this paper, we focus on amphibole particles within AECs in order to expand the knowledge of the possible cellular internalization mechanism and the dimensional distributions of particles within cells.
Our results suggest a higher uptake intensity of non-asbestiform amphiboles and cleavage fragments when regulated asbestos particles are also present but not internalized by AECs. The mineralogical and structural transformations of these internalized particles have been investigated in a recently published parallel paper [7]. The internalized particles were found inside vesicles, in proximity to the cell nuclei, and adjacent to the cell surface. During our observations, we also detected the presence of possibly newly formed Fe-rich oxides, which were visible in the cells exposed to anthophyllite and grunerite.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Material
The amosite standard from the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) was used here as a reference material. This asbestiform amphibole, referred to hereafter simply as amosite, was selected as a positive control because it is classified as asbestos, is rich in iron, and has been extensively characterized [7,43,44].
The non-asbestiform amphiboles used in this study were anthophyllite from Kongsberg (Norway), labeled MNHN 29_102, and grunerite from Salem (India), labeled MNHN 97_373, both part of the mineralogical collection of the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle in Paris (France).
Cultures of AECs were tested for viability and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), examined using optical microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy, as described in the following section.
The structural localization of the mineral particles within the AECs was performed using TEM after 48 h of interaction.
2.2. Preparation of Minerals for Cell Treatment
The three different amphiboles anthophyllite (Ath), grunerite (Gru), and amosite (Amo) were sterilized in 1.5 mL Safe Lock tubes (Eppendorf, Germany) for 20 min at 121 °C (VX-150, Systec, Germany) before each use with cells to ensure their sterility. The minerals were then suspended in A549 cell growth medium up to the desired maximum concentration (100 µg/mL), with two 5 min sonic bath cycles interspaced with a 2 min vortexing step.
2.3. In-Vitro Assays
The biological effects of the selected amphiboles were tested in vitro on the AECs, cell line A549 (American Type Culture Collection, USA, cell number ATCC CCL-185TM). These AECs were grown under standard growth conditions (5% CO2, 37 °C, 90% relative humidity) in F-12K Nut mix medium (21127022 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburg, PA, USA) supplemented with 10% HIFBS (F4135 Burlington, MA, USA), 1% L-glutamine (200 mM, M11-004 Gibco, USA), and 1% antibiotic–antimycotic (100×, 15,240 Gibco, USA). The cells were passaged twice a week using 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (T4049 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburg, PA, USA) for detachment. Amphibole particles were added to cell cultures at various concentrations, ranging from 0.2 µg/mL to 100 µg/mL, and incubated for 8, 24, or 48 h. The main experiments and the TEM observations were conducted on the AECs incubated for 48 h with amphibole particles at a concentration of 50 µg/mL.
2.4. Optical and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
Optical microscopy of the AECs interacting with the asbestos minerals was performed using an inverted microscope (Reichert-Jung, 1820 Biostar, Itasca, IL, USA with an Olympus U-CMAD3 camera, Tokyo, Japan). The cells were seeded on 96-well microtiter plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells per well one day before the experiment. The following day, the three suspensions of Ath, Gru, and Amo in a culture medium were added to a final concentration of 50 µg/mL. At the time of treatment, the cells were at about 70% confluence. Imaging was performed 24 and 48 h after the addition of the minerals.
Confocal laser scanning microscopy was performed after the exposure of the AECs to the amphibole particles to better understand the localization of the particles with respect to the cells. The cells were seeded at a density of 2.1 × 104 cells per well on µ-slides (80826 IBIDI, Gräfelfing, Germany) and treated with the amphibole particles at a final concentration of 50 µg/mL. The cells were incubated with the minerals for 48 h. The plasma membranes were labeled with a Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 (λex = 495 nm/λem = 519 nm, W11261 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburg, PA, USA). The cell nuclei were stained with the fluorescent dye Hoechst 33,342 (λex = 350 nm/λem = 461 nm, H3570 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburg, PA, USA). The cells were imaged using a laser scanning microscope (Leica TCS SP5, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) mounted on an inverted microscope (Leica DMI 6000 CS, Leica Microsystems, Germany). The inverted microscope was equipped with an HCX PL APO 63 × (NA 1.4) oil immersion objective lens. The images were analyzed using Leica Application Suite Advanced Fluorescence Lite (2.5.1 build 6757) software.
2.5. Determination of Cell Viability
The cytotoxicity of the amphiboles on the AECs was evaluated using the cell viability reagent PrestoBlue (A13261 ThermoFischer Scientific, USA). In order to perform a viability assay, the AECs were seeded one day prior to the experiment on 96-well microtiter plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells per well. For the treatment, the initial growth medium was replaced with a growth medium containing serial dilutions of mineral suspensions at concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 100 µg/mL. The microtiter plates were incubated for 48 h under the standard conditions described above. After incubation, the PrestoBlue reagent was added to each well (10% v/v), and the cells were further incubated for 3 h in a cell incubator (Steri-Cult 3307, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburg, PA, USA). The resulting fluorescence (λex = 560 nm/λem = 590 nm) was measured using a FLUOstar Galaxy plate reader (BMG Lab Technologies, Ortenberg, Germany). For the negative control, the cells were grown in a culture medium in the absence of minerals, and their fluorescence values were taken as 100% of cell viability. All tests were performed in triplicate.
2.6. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and H2O2
The formation of ROS and H2O2 in the AECs exposed to the amphiboles was tested using a Fluorometric Intracellular ROS Kit (MAK142, Sigma, USA) and a Fluorometric Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (MAK 165, Sigma, USA), respectively. The AECs were seeded one day prior to the experiment on 96-well microtiter plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells per well. For treatment, the initial growth medium was removed and replaced with a growth medium containing suspended minerals at a concentration of 50 µg/mL. The treated cells were incubated under standard culture conditions for 8, 24, or 48 h. Positive control cells were treated with 20 ng/mL of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), prepared in house, and incubated for 8, 24, or 48 h. The resulting fluorescence for H2O2 (λex = 540 nm/λem = 590 nm) and intracellular ROS (λex = 640 nm/λem = 675 nm) was measured using a Synergy™ Mx Microplate Reader (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Negative control cells were grown in a culture medium in the absence of minerals, and their fluorescence values were taken as the reference values for ROS or H2O2. All tests were performed in triplicate.
2.7. TEM and S/TEM Sample Preparation
The AECs were seeded on 12-well plates at a density of 6.6 × 105 cells per well one day prior to the experiment. The cells were treated with each of the three amphiboles at a final concentration of 50 µg/mL and incubated for 48 h under standard culture conditions. After incubation, the medium was replaced with a fresh one without mineral particles. Subsequently, the cells were detached using a cell scraper.
TEM and acS/TEM investigations were performed after splitting the cell culture into two subsamples, prepared by (1) ultramicrotomy for structural localization (this paper), and (2) chemical digestion to recover the particles for detailed morphometric (this paper), surface, and near-surface analyses [7]. The cells prepared for ultramicrotomy were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M Sörensen’s phosphate buffer (PB), pH 7.2; post-fixed with 1 wt. % OsO4 in 0.1 M PB; and embedded in Agar 100 resin (Agar Scientific, Stansted Essex, United Kingdom). Ultrathin sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. The mineral particles were extracted from the AECs with a chemical digestion procedure using a gentle bleach method [7]: the cells were transferred into a 50 mL tube containing 10 mL of NaClO (14 vol.%), then vortexed, and left to rest for 30 min. The suspension in the tube was then centrifuged at 80,000 RPM, and NaClO was substituted by deionized water. Subsequently, the material was transferred onto lacey carbon copper grids (SPI Supplies, West Chester, PA, USA).
2.8. Structural Localization Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
The ultrathin sections on the lacey carbon copper grids were examined with a CM 100 TEM (Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands), operating at 80 kV, and images were recorded with an Orius SC 200 camera (Gatan Inc., Washington, DC, USA).
2.9. acS/TEM-EDXS
The dimensional investigations of the chemically digested samples were conducted using an atomic-resolution acSTEM (ARM 200 F, JEOL, Akishima, Japan), equipped with a high-brightness Cold Field Emission Gun (CFEG) operating at 80 kV. The microscope was equipped with an EDXS system (Centurio 100 mm2, JEOL, Akishima, Japan), as well as an energy filter (QuantumGIF, Gatan, Pleasanton, CA, USA) for Dual-EELS. The spectroscopes were used to confirm the identity of the particles (see also [7]).
The reduced electron density (Spot size 6) and voltage (80 kV) allowed us to minimize beam damage, dispersion effects, and the evaporation of volatile elements [7,44].
2.10. Measurements
For each individual sample, we measured the particle length (L) and width (w), and we calculated the aspect ratio (L/w) before and after interaction with the AECs (see “Results”, Section 3, Table 1 and Figure 1). The length was measured along the amphibole c-axis, while the width was measured perpendicularly to that axis. The field of view was set at 10 × 10 µm (diagonal of square ≈ 14.14 µm), corresponding to a magnification of 2000×, for each randomly selected region, in line with the operational methods proposed by several national and international organizations [18]. Only completely visible particles were measured; particles halfway on the copper grid or undistinguishable aggregated particles were avoided. The percentage of amphibole particles with aspect ratios greater than or equal to 3:1 (EMPs, including the nano-sized component [16,18]) was calculated for each particle population before and after interaction with the AECs. The number of particles measured was set to n = 500 for all starting materials. The number of particles counted in the material after interaction, however, was lower because only the particles that were taken up by the cells were retrieved and, thus, measured (see “Results”, Section 3, Table 2).
Specifically, after the interaction, n was 19, 24, and 59 for Ath, Gru, and Amo, respectively.
3. Results
The starting materials were three comprehensively characterized mineral samples (see Section 2, “Materials and Methods”, for details), namely, two non-asbestiform samples of anthophyllite (Ath) and grunerite (Gru), with comparable dimensions, and the UICC amosite asbestos standard (Amo) [7,43,44].
3.1. Dimensional Characteristics of Amphibole Particles before and after Internalization by AECs
The dimensional parameters L and w, and the aspect ratio L/w (see “Materials and Methods”, Section 2) for each particle population before and after the interaction with the AECs are summarized in Table 1, with the details listed in the dataset.

Table 1.
Summary of the considered dimensional parameters and aspect ratio (L, w, and λ = L/w) for each mineral before and after interaction with AECs. Parameters were determined using acTEM BF (see Table 1). Before interaction, n = 500 for each of the minerals; after interaction, n = 19, 24, and 59 for anthophyllite, grunerite, and amosite, respectively.
Table 1.
Summary of the considered dimensional parameters and aspect ratio (L, w, and λ = L/w) for each mineral before and after interaction with AECs. Parameters were determined using acTEM BF (see Table 1). Before interaction, n = 500 for each of the minerals; after interaction, n = 19, 24, and 59 for anthophyllite, grunerite, and amosite, respectively.
| Anthophyllite | Grunerite | Amosite | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L(µm) | w (µm) | L/w | λ ≥ 3:1 (%) | L (µm) | w (µm) | L/w | λ ≥ 3:1 (%) | L (µm) | w (µm) | L/w | λ ≥ 3:1 (%) | ||
| Before Interaction | Mean | 0.65 | 0.28 | 2.57 | 23.40 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 2.37 | 19.60 | 2.50 | 0.20 | 15.67 | 86.20 |
| σn−1 | 0.92 | 0.38 | 2.02 | 1.02 | 0.50 | 1.46 | 2.62 | 0.17 | 18.51 | ||||
| Max. | 7.00 | 2.94 | 24.98 | 10.22 | 4.70 | 15.42 | 13.43 | 1.29 | 229.24 | ||||
| Min. | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 1.15 | ||||
| After Interaction | Mean | 0.49 | 0.10 | 5.09 | 57.89 | 0.83 | 0.30 | 3.56 | 41.67 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 3.56 | 44.70 |
| σn−1 | 0.61 | 0.09 | 3.87 | 0.59 | 0.19 | 2.61 | 0.77 | 0.13 | 2.83 | ||||
| Max. | 2.16 | 0.31 | 14.27 | 2.50 | 0.89 | 11.53 | 4.54 | 0.81 | 18.65 | ||||
| Min. | 0.06 | 0.02 | 1.55 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 1.16 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.00 | ||||
Based on the particle dimensional distributions, we estimated for each mineral the total particle volume, the average weight of a single particle, and the total number of particles retrieved from the AECs (Table 2 and dataset).

Table 2.
Estimates of the volume, average weight, and number of administered particles for a particle concentration of 50 µg/mL.
Table 2.
Estimates of the volume, average weight, and number of administered particles for a particle concentration of 50 µg/mL.
| Total Particle Volume (µm3) | Average Weight of a Single Particle (µg) | Estimated Total Number of Particles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthophyllite | 250.87 | 1.61 × 10−9 | 3.10 × 1010 |
| Grunerite | 548.82 | 3.79 × 10−9 | 1.32 × 1010 |
| Amosite | 126.49 | 8.73 × 10−10 | 5.73 × 1010 |
For operational reasons, the number of measured administered particles studied (n = 500) is considerably larger than the number that we were able to study after retrieval from the AECs.
Figure 1 shows the difference in the distributions of each particle’s dimensional parameters before and after internalization by the AECs.
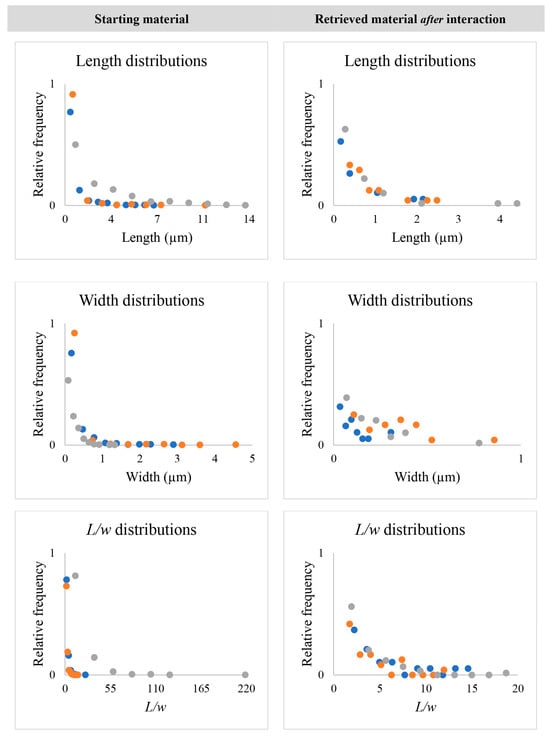
Figure 1.
Dimensional comparison of the starting mineral species and the equivalent material after interaction with the AECs. Anthophyllite is shown in blue, grunerite is in orange, and amosite is in gray.
To compare the actual difference in the size distribution between the materials before and after the interaction, we restricted the dimensional range of interest to that determined for the minerals retrieved from the cells after exposure (more details on this aspect are available in Supplementary Figure S1 and Table S1). The L, w, and L/w distributions of the starting materials differ considerably from those of the particles retrieved from the AECs after interaction (Figure 1). Moreover, the dimensional distribution of the Amo starting material is conspicuously different from that of the other two minerals. The latter are quite similar when comparing the distribution curves and dimensions within the range determined by the minerals retrieved from the cell cultures (See Supplementary Figure S1 and Table S1).
The L, w, and L/w distributions of the overall amphibole particle populations (the Ath, Amo, and Gru particles extracted from different cell cultures were summed together to obtain these distributions) after the interaction with the AECs (Figure 2) and the related dimensional parameters, summarized in Table 3, document a defined dimensional range for the L, w, and calculated ratio L/w of the internalized amphibole particles.
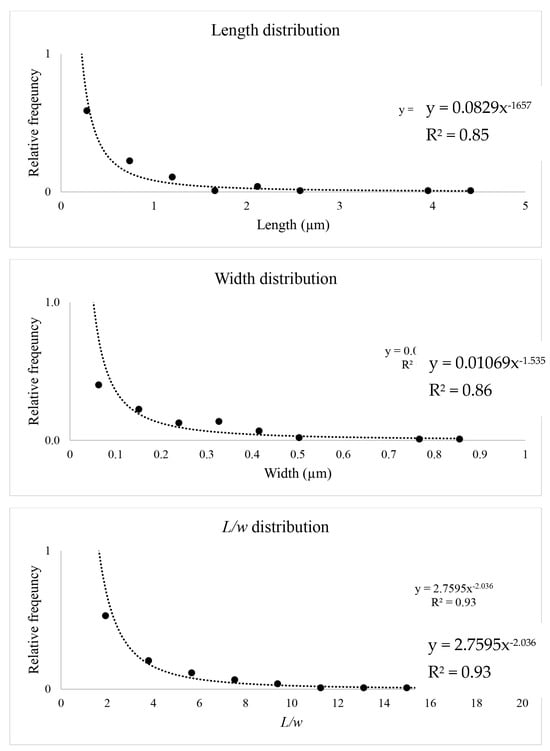
Figure 2.
Dimensional parameters of the overall particle population taken up by the AECs. This overall dataset results from the combination of the dimensional parameters of all internalized anthophyllite, grunerite, and amosite particles (n = 102; distributed over 10 bins). The dotted line represents the power law fit, with the equation and R2 given in each chart.

Table 3.
Dimensional parameters of the overall amphibole particles taken up by the AECs. This overall dataset results from the combination of the dimensional parameters of all internalized anthophyllite, grunerite, and amosite particles (n = 102).
3.2. Localization of Particles with Respect to AECs: Preliminary Observations
While the goal of this paper was to determine the dimensional parameters of the particles retrieved from the AECs, we made some preliminary observations on where the amphibole particles were located in relation to individual AECs in the cell cultures. Through preliminary optical microscopy, we documented that AECs tend to gather and proliferate on and around elongated particle bundles with high aspect ratios, e.g., Amo (Figure 3).
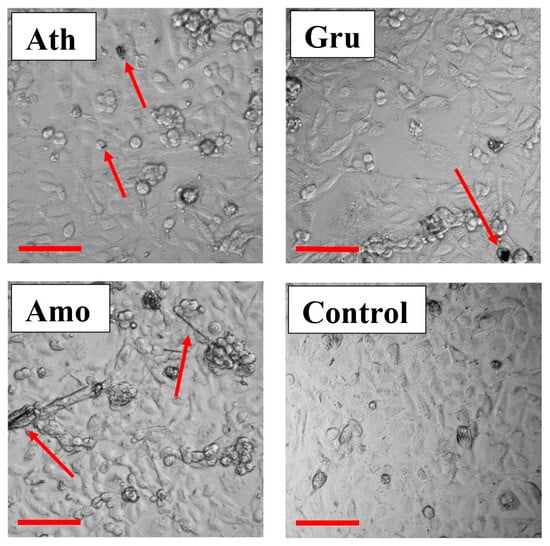
Figure 3.
Optical microscopy image of A549 cells 48 h after treatment with the three amphiboles anthophyllite (Ath), grunerite (Gru), and amosite (Amo) at an administered concentration of 50 µg/mL. “Control” = A549 cells only, without exposure to minerals. Scale bars represent 100 µm. The red arrows point to the amphibole particles or bundles.
Preliminary confocal microscopy observations suggest that both large non-asbestiform particles (e.g., Figure 4a) and elongated asbestos particles (e.g., Figure 4b) were in contact with, but not internalized by, the AECs.
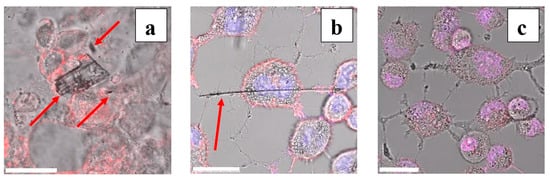
Figure 4.
Confocal microscopy images of A549 cells 48 h after treatment with 50 µg/mL of (a) grunerite (non-elongated mineral particles); (b) amosite (elongated mineral particles); and (c) control (no mineral particles). Scale bars represent 25 µm. The cell membrane was labeled with Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488, shown in red, whereas the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342, shown in blue. The colors are unsaturated because of the superimposition of the optical image recorded in the same region of interest (in grayscale). The red arrows point to the amphibole minerals.
This was also manually verified by continuously changing the focus of the observed image, which revealed that the cells and the particles were never in focus at the same time.
3.3. Localization of Amphibole Particles Internalized by AECs
After internalization by the AECs, the particles of all tested minerals studied here were located in similar regions (Figure 5 and Supplementary Figures S2 and S3). The particles taken up were mostly contained in vesicles or surrounded by a (possibly lipid) bilayer (Figure 5b and Supplementary Figure S3), whereas some particles were in proximity to the nucleus (Figure 5a,c and Supplementary Figure S3) or adjacent to the cell surface (Figure 5d).
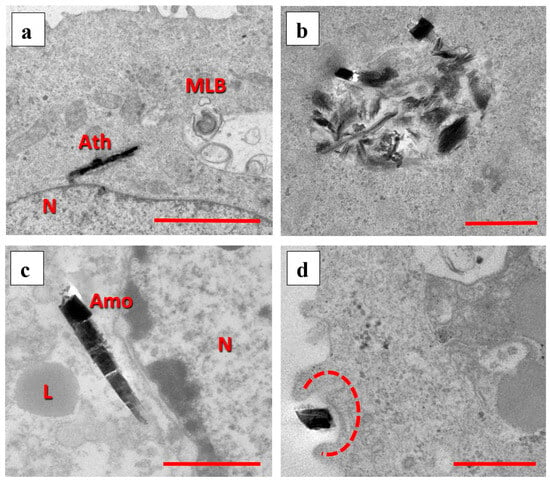
Figure 5.
TEM images of amphiboles within the AECs or in contact with the cell surface. (a) High-aspect-ratio anthophyllite particle within the AEC cytoplasm; scale bar 2 µm. (b) Various grunerite particles and other material contained in a vesicle; scale bar 1 µm. (c) Amosite particle in proximity to the AEC nucleus; scale bar 1 µm. (d) Grunerite particle in contact with the cell surface and partially surrounded by protrusions (dashed red line); scale bar 0.5 µm. Abbreviations: N = nucleus; L = lipid droplet; Ath = anthophyllite; Amo = amosite; MLB = multilamellar body.
3.4. Cell Viability and ROS Production
We observed an apparent, i.e., statistically non-significant, increase in viability with a higher mineral concentration (Supplementary Figure S4). Moreover, 8 h after treatment with grunerite, we observed a very small decrease in ROS production (Supplementary Figure S5).
4. Discussion
4.1. Dimensional Characteristics of Amphibole Particles before and after Internalization by AECs
The difference in the dimensional range between the starting materials and the materials retrieved from the AECs suggests that the cells selectively internalized particles in a certain dimensional range (Figure 1; see also Supplementary Figure S1 and Table S1), which underlines the similarities among the particles before and after the interaction within the same range. However, the aspect ratio (L/w) after the interaction is very similar among all three mineral species, suggesting that the aspect ratio, together with the overall particle shape, controls the likelihood of a certain particle to be internalized by the AECs. Since the number of particles retrieved from the AECs is extremely low (namely, n = 19 for Ath; n = 24 for Gru; n = 59 for Amo) compared to the number of measured particles in the starting material (n = 500 for each amphibole species), one should naturally be very careful with the reliability of, and the conclusion drawn from, the results. This discrepancy in the number of analyzed particles is a consequence of the fact that the number of particles retrieved from within the cells depends on several factors, which cannot be controlled directly, including the dynamics of biological uptake and the orientation of every single cell relative to the ultramicrotomy blade while cutting the sample slices. However, since the dimensions and the dimensional range of the retrieved particles within the cells are similar and coherent among the different amphibole particles administered to the cells, we think that our results can still be very valuable as a starting point for future investigations.
The relevance of our data on particle uptake by the AECs deserves special consideration. All cell cultures were exposed to the same particle weight (50 µg), but the collected dimensional information enabled us to estimate the average number of particles in the administered dose for each mineral. The number of particles calculated for 50 µg of starting material, based on the dimensional distribution obtained for 500 particles in each sample, was 3.10 × 1010 for Ath, 1.32 × 1010 for Gru, and 5.73 × 1010 for Amo (Table 2). The number of particles for each mineral population was thus of the same order of magnitude, but the Amo particles were clearly present in higher numbers. Moreover, we were able to retrieve more Amo particles from the cells (n = 59) than Ath (n = 19) and Gru (n = 24) particles, suggesting that Amo was also taken up the most intensively (see Table 1 caption and supplementary Table S1). However, even though the calculated number of Ath particles in the administered 50 µg was more than twice that of Gru (Table 2), Ath uptake appeared to be the lowest (Table 1). Therefore, there was no clear relationship between the number of particles available to the AECs and the extent of internalization. The higher internalization rate of Amo could be a consequence of (i) a higher number of particles with certain dimensions; (ii) a particle shape that is more easily internalized by the cells; and (iii) the co-presence of elongated particles, which cannot be internalized (because they are too large) but may stimulate the uptake activity of the cells for the observed smaller particles via other pathways. When considering all our dimensional and shape-related particle data, we conclude that the “asbestos dose” that is administered during toxicological investigations cannot be expressed only in terms of weight or density (even if the surface area is included in the information) but rather must be fully characterized and reported by specifying the distributions for L, w, and L/w, as well as the estimated number of particles per weight unit.
Since the L/w value and the L and w distributions of the internalized particles of all three minerals (Ath, Gru, and Amo) are more similar to each other and have a more similar dimensional range than the distributions observed in the starting material (Figure 1), we postulate that there exists a preferential uptake of amphibole particles with certain dimensions and, possibly, a certain morphology. Therefore, we combined the dimensional parameters of all three types of internalized amphibole particles into a unique dataset, without making a distinction between the mineral species (Table 3). This combined dataset of all internalized amphibole particles (resulting in a number of particles of n = 102, i.e., the sum of the 19 Ath, 24 Gru, and 59 Amo particles) revealed that the population of particles targeted by the cells can be described, with a good approximation, by the use of a power law for each considered parameter (Figure 2).
Even though the dimensional parameters (L and w) and the aspect ratio (L/w) have a larger and more variable range in the starting material (i.e., before internalization by the AECs), they are limited to a certain dimensional range after internalization (Table 3, Figure 1, and supplementary Figure S1 and Table S1). In particular, and in accordance with He and Park [45], we observed an increase in the population with an aspect ratio (L/w) ≥ 3 for both the Ath (from 23.40% to 57.89%) and the Gru (from 19.60% to 41.67%) particles internalized by the AECs. Conversely, the decrease in the number of particles with L/w ≥ 3 in the Amo sample (from 86.20% to 44.70%) is probably due to the fact that the Amo particle population tends to be extremely long (i.e., larger than the cell diameter); high-L/w particles with L and w above a certain range (see Figure 1, Table 1, and the above Section 3.2) are not internalized by the AECs.
In conclusion, the amphibole particles (when all three tested minerals are considered together) retrieved from the AECs are smaller (L: 0.05–4.54 µm; w: 0.02–0.89 µm; L/w: 1.00–18.65) than those that generate asbestos bodies (L typically > 10 µm; w < 0.5 µm as in [29], or diameter < 1 µm e.g., [46,47]).
The observed poor uptake of Ath (n = 19) and Gru (n = 24) is, in our opinion, consistent with the epidemiological evidence suggesting that non-asbestiform amphiboles alone cannot induce an increase in mesothelioma and lung cancer occurrences [21]. However, this does not represent a sufficient piece of evidence to rule out a possible role of cleavage fragments and non-asbestiform particles in the co-induction of carcinogenesis when present together with asbestiform particles in the same biological environment. This hypothesis is based on the fact that the AECs exposed to Amo showed an increased uptake of small particles (n = 59), which can be related to the co-presence of elongated, non-internalized asbestiform particles in the administered particle populations (Figure 1, Figure 3, and Figure 4, and Supplementary Figure S1 and Table S1). Therefore, we conclude that elongated (higher L/w and L) particles that are not internalized by AECs in a cell culture experiment are able to promote the uptake of smaller, non-asbestiform particles, in addition to all their other well-known effects when interacting with cells and tissues (e.g., inducing frustrated phagocytosis, inducing ROS production, and triggering an inflammatory cascade). This is an important factor to account for, since cleavage fragments and non-asbestiform amphiboles inside AECs are often close to the cell nuclei, one of the possible major targets of ROS.
This inferred promotion of smaller particle (in the range shown in Figure 2 and Table 3) uptake by particles that appear too large for internalization could be a consequence of two or more factors, with one being related to the physical characteristics of amphibole particles and the other to cell activity. The main properties of the nano-sized portion of the amphibole-particle population that influence its uptake by cells are the sign and magnitude of the surface charge, as well as the dimension, shape, and aspect ratio [9,45,48,49]. These properties are also likely to determine the uptake of the micro-sized portion of the amphibole particle population, albeit to a different extent. In amphiboles, the crystallographic planes that intersect the particle elongation axis (c) and are exposed at the ends of a particle are theoretically positively charged [50,51], whereas the other planes, i.e., those parallel to c, are negatively charged. This feature should result in a “more positive” overall charge for non-elongated particles (Ath and Gru in our case) and a “more negative” overall charge for elongated particles (Amo). Similarly, particle uptake can be influenced by shape. It has been demonstrated, for example, that different cell lines show a preferential uptake of spherical or rod-shaped nano-sized particles [49], and, therefore, shape-controlled internalization might also be cell-line-dependent. Our study suggests that the preferential uptake of rod-shaped particles should also apply to micro-sized particles, since we observed an increase in the percentage of particles with λ ≥ 3:1 for Ath and Gru but not for Amo for the reason that we explained previously. Furthermore, particle uptake can also be influenced by cell surface properties and the type of endocytosis mechanism [48,52]. Particle uptake is a relatively rapid process, taking place within a few hours after administration [9].
Based on our own observations (considering all three tested minerals together, as in Table 3 and Figure 2), we conclude that smaller amphibole particles (in our specific case, 0.05 µm < L < 4.54 µm; 0.02 µm < w < 0.89 µm) with an overall negative surface charge and with an L/w value between 1.00 and 18.65 are taken up by AECs more easily than particles outside these dimensional ranges. A similar conclusion on small particles was also reached by Yao et al. [53] by using 3D Raman imaging on lung cells exposed to different asbestos minerals. At this stage and under the used experimental conditions, it is not possible to assess to which magnitude each characteristic (i.e., surface charge, dimensional parameters, and shape factors) determines the extent of uptake or to establish an accurate dimensional limit for particles to be internalized. A future study should be dedicated to refining this dimensional range of “optimal uptake dimensions of amphibole” for AECs, using a larger number of particles. Clearly, the determination of an “optimal uptake dimension of amphibole” would be applicable to cell cultures, but the result would not necessarily be valid for more complex systems, such as lungs and other target organs. In these systems, sampling yields would be extremely low and may not be completely representative of the internalization mechanism for either the entire target organ or the involved cells, which both may react differently when exposed to the same exogenous agent.
4.2. Localization of Amphibole Particles within AECs
Consistent with the quantitative observations documenting the number of particles that we were able to retrieve and count after the NaClO digestion of the cells (Section 4.1), the qualitative TEM observations suggest that the uptake of Amo particles by the AECs was the most intense (Supplementary Figure S2).
Transcellular transport and epithelial cell engulfment are the most likely uptake pathways for “insoluble particles”, including asbestos. When focusing on the activity of a single cell, particle endocytosis (possible phagocytosis) or engulfment by epithelial cells has been proposed [54,55,56]. In our experiments, we observed cell protrusions around particles and the invagination of AEC membranes (e.g., Figure 5d). Moreover, Jablonski et al. [9] showed that smaller amphibole particles are usually retained to a greater extent and cleared more slowly. Indeed, we observed a similar phenomenon for the amphiboles internalized by the AECs: the dimensional ranges (max and min) of all three amphiboles tested were smaller for the particles retrieved from within the cells than for the particles present in the respective starting materials before the interaction (Table 1 and Figure 1). However, the dimensional distribution of the particles within the same range (before and after the interaction) had a similar trend and shape. In addition, as shown in the previous sections, we retrieved fewer Ath (n = 19) and Gru particles (n = 24) than Amo particles (n = 59), suggesting that the presence of elongated particles, which cannot be internalized, and a higher number of particles may promote the uptake of smaller non-asbestiform particles belonging to the same particle population.
The amphibole particles internalized by the cells were in many cases near or in direct contact with the cell nuclei and organelles (Figure 5a,c and Supplementary Figures S2 and S3), with the possibility of generating ROS from within the cell at an extremely short distance from the target molecules. This latter observation is extremely important because the •OH radical acts at a short spatial and temporal distance from its generation point [57], and, therefore, the proximity of the particles to the nuclei or organelles can play a major role in the continuous damaging of the cells over time. Of course, this mechanism is not antagonistic to the frustrated phagocytosis mechanism, but it may operate independently of, and contemporaneously with, the frustrated phagocytosis mechanism. In our experiments, however, both the viability and the ROS tests showed no statistically significant change at any dose for any of the three amphibole types (Supplementary Figures S4–S6). The apparent (statistically not significant) increase in viability with a higher mineral concentration (Supplementary Figure S4) may be a consequence of particle agglomeration [53] and may also be influenced by the additional surface area that long particle bundles or particle agglomerates can provide to cells, thus inducing cell growth. The lack of ROS production is consistent with our previous experimental findings [7], showing that amphiboles become progressively covered by Fe3+-rich material, which represents a poorly reactive particle “entombment” [58] that reduces further interactions between the mineral particles and the surrounding biological environment. The weak cellular response in terms of ROS and viability is also in line with the recent literature review published by Bernstein [22].
In conclusion, a consequence of our dimensional observations described above is that, even if Cullen’s [59] amphibole hypothesis—questioned since its publication and still debated today (e.g., Finkelstein [60])—would have been correct, chrysotile or any other EMP not directly internalized by AECs may be a small-particle uptake promoter (SPUP). Instead, chrysotile or any other EMP (particularly amphibole EMPs, as in our case, Amo) may contribute to toxicity not only via the induction of frustrated phagocytosis by macrophages (if the particles are biodurable and less likely to go through lung clearance) but also via the promotion of the uptake and the deposition of potentially ROS-inducing smaller particles in proximity to the cell nuclei and organelles. Of course, one should be careful with these conclusions since an in-vitro study can lead to results that are different to those of in-vivo experiments and epidemiological evidence [22].
Moreover, when viewing our results in the light of Bernstein’s publication [1], we could infer that chrysotile might act as an SPUP for a shorter period of time than amphibole EMPs because it is more readily and easily removed from organisms [1], and, thus, the overall toxicity would be lower.
Nevertheless, more research needs to be conducted on the internalization and interaction of particle populations, i.e., those with varying dimensional parameters, shapes, and aspect ratios, and chemical compositions, since different particles may play a role in different locations (i.e., inside cells, in contact with cells, or dispersed in body fluids), which, in turn, could lead to important hard-to-detect synergistic effects on toxicity and disease development. Additionally, our results are representative when considering a cell culture system, but they might be not representative in a real human body or animal system.
Another important implication of our study is that the asbestos doses (or the doses of other EMPs) administered during toxicological investigations cannot be expressed solely in terms of weight or density (even when the specific surface area is considered in the data). Rather, the administered particles must be fully characterized, and a complete dataset for the distributions for L, w, and L/w, as well as the estimated number of particles per weight unit, must be reported. This approach will lead to a more impactful assessment of potential or suspected correlations between the mineralogical population characteristics and the changes induced in the target biological systems and vice versa.
In summary, larger EMPs are not taken up but rather seem to promote cell proliferation and activity, including SPUP, whereas smaller particles are easily internalized because of their specific dimensions, surface charge, and shape. Our microscopic observations further suggest that AECs tend to gather and proliferate in contact with elongated amosite particles or bundles (Figure 3), which is consistent with the evidence of the enhanced proliferation of cells exposed to different types of asbestos in vivo, as reported by, e.g., Shukla et al. [61] and Haegens et al. [62].
Without neglecting the fundamental importance of the frustrated phagocytosis mechanism and the role of amphibole asbestos bodies in the human body’s inflammatory response, we believe that the proximity of amphibole particles to the cell nuclei, as shown here for AECs, should be included, or at least further mechanistically investigated, as a possible synergistic factor in the list of triggers of lung injury and related cyto- and genotoxic models. Since amphiboles that are classified as asbestos (or recognized as carcinogenic agents) are always accompanied by a certain percentage of smaller particles (e.g., nano-EMPs), it is thus likely that, for any given “amphibole asbestos” detected within mammal tissues and described in the literature, there is an “n” number of undetected non-regulated EMPs inside the cells forming that given tissue. A synergistic effect of extra-cellular and nuclei-proximal amphibole particles (NPAPs) could have been overlooked since most of the literature rightfully observes the larger “fibers” using a certain technique that has statistical and clinical solidity but clear limits in terms of spatial resolution and the simultaneous observation of very large versus extremely small particles. The inclusion of NPAPs in the disease model proposed by the medical and biological community does not contradict the confirmed mechanism of cyto-/genotoxicity and pathogenesis but rather allows for a better understanding of the fundamental mechanisms that can cause damage to molecules within AECs and possibly other similar target cells. Furthermore, the dimensional distribution and localization of internalized amphibole nanoparticles suggest that micro- and nano-sized EMPs should be regulated, and particle (i.e., EMP) counting protocols should consider the not strictly asbestiform component of the studied mineral particle population.
As stated previously, our study focused on the interaction between amphiboles and AECs in cell cultures; since this is not a real system (compared to, e.g., lungs), it was not possible to reliably calculate the carcinogenic potency of EMPs [63]. A future line of research could replicate our experiment at a larger scale and adapt the methodology applied to the estimation of carcinogenic potency (usually derived from lung burden data [63,64]) for cell cultures.
These findings and proposals do not neglect the fact that it is the longer, thinner amphibole “fibers” that have the greatest potency for causing lung cancer [1] but rather raise the question as to whether the simultaneous presence of extra-cellular amphibole asbestos and NPAPs is determinant and a necessary condition for the development of lung cancer.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min14010101/s1, Figure S1: Dimensional distributions of the particles in the starting material considering the range determined by the maximum and minimum dimensions of the retrieved particles (after the interaction). Anthophyllite is in blue, grunerite is in orange, and amosite is in gray. Figure S2: Low-magnification TEM images of AECs containing (a) anthophyllite (Ath); (b) grunerite (Gru); and (c) amosite (Amo) after 48 h of exposure. N: cell nucleus. Figure S3: Low-magnification TEM images of AECs: (a) and (b) control cells with irregularly shaped nuclei (N) and many mitochondria (M); (c) multilamellar bodies (MLBs) in control cells; (d) anthophyllite particle (Ath) in proximity to the nuclear membrane; (e) several grunerite particles (Gru) contained in a lysosome (L); (f) amosite particle (Amo) near the nucleus. Figure S4: Cell viability (% of control) for different concentrations of amphiboles. The red line represents the untreated (negative) control (100%). Figure S5: ROS (Sigma MAK142) measurements conducted using a concentration of 50 µg/mL of each mineral and the related TNF (positive) control. The results are expressed as % of the negative control. The red line/bar represents the untreated (negative) control (100%). Figure S6: H2O2 (Sigma MAK 165) test conducted using a concentration of 50 µg/mL of each mineral and the related TNF (positive) control. The results are expressed as % of the negative control. The red line/bar represents the untreated (negative) control (100%). Table S1: Dimensional parameters and aspect ratios of particle populations before interaction with the AECs. Here, we considered the range determined by the maximum and minimum dimensions of the retrieved particles (after the interaction).
Author Contributions
R.V.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project Administration, Funding Acquisition; M.J.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization; G.D.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project Administration, Funding Acquisition; M.P.: Methodology, Validation, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project Administration, Funding Acquisition; M.T.Ž.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Funding Acquisition; G.D.V.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Review and Editing, Visualization, Funding Acquisition; G.J.R.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Review and Editing; N.Ž.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Review and Editing, Visualization; S.C.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision; R.G.: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Funding Acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a Rotary Global Grant (GG1640842) awarded to Dr. Ruggero Vigliaturo, from the Rotary Foundation; grant P2-0393 from Slovenian Research Agency awarded to Dr. Prof. Goran Dražić; and grant P1-01840391 awarded to the University of Ljubljana and grant P4-0165 awarded to the National Institute of Biology (Prof. Gregor Anderluh), both from Slovenian Research Agency. This study was further supported in part by grants P30-ES013508 and P42-ES023720 awarded by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). The findings are not the official opinions of NIEHS or NIH. Giancarlo Della Ventura was supported by a grant awarded to the Department of Science, Roma Tre University (MIUR-Italy Dipartimenti di Eccellenza, ARTICOLO 1, COMMI 314—337 LEGGE 232/2016).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the “Mendeley Data” repository, Vigliaturo, Ruggero (2022), “Dimensional distribution and localization of amphiboles within human AECs”, Mendeley Data, V1, https://doi.org/10.17632/prnhy5zt8m.1. (accessed 15 January 2024). The dataset is also available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Marcello Serracino (CNR-IGAG, Rome) for helping with the collection of EPMA data and Federico Galdenzi (University Roma of Tre) for helping with Raman spectroscopy. Cristiano Ferraris (Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris) allowed us to select the studied samples from the museum collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bernstein, D.M.; Dunnigan, J.; Hesterberg, T.; Brown, R.; Velasco, J.A.L.; Barrera, R.; Hoskins, J.; Gibbs, A. Health risk of chrysotile revisited. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 154–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Labor. Occupational exposure to asbestos. Fed. Regul. 1975, 40, 47652–47665. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, W.J.; Blake, R.L.; Brown, L.L.; Cather, E.E.; Sjoberg, J.J. Selected Silicate Minerals and Their Asbestiform Varieties: Mineralogical Definitions and Identification-Characterization; Bureau of Mines Information Circular IC-8751; Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1977.
- Case, B.W.; Abraham, J.L.; Meeker, G.; Pooley, F.D.; Pinkerton, K.E. Applying definitions of “asbestos” to environmental and “low dose” exposure levels and health effects, particularly malignant mesothelioma. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2011, 14, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Dell, L.; Adams, R.; Rose, T.; Van Orden, D. State-of-the-science assessment of non-asbestos amphibole exposure: Is there a cancer risk? Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Ventura, G.; Vigliaturo, R.; Gieré, R.; Pollastri, S.; Gualtieri, A.F.; Iezzi, G. Infra Red spectroscopy of the regulated asbestos amphiboles. Minerals 2018, 8, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliaturo, R.; Jamnik, M.; Dražić, G.; Podobnik, M.; Tušek Žnidarič, M.; Della Ventura, G.; Redhammer, G.J.; Žnidaršič, N.; Caserman, S.; Gieré, R. Nanoscale transformations of amphiboles within human alveolar epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, R.P.; Kim, S.J.; Cheresh, P.; Kamp, D.W. Insights into mineral fibre-induced lung epithelial cell toxicity and pulmonary fibrosis. EMU Notes Mineral. 2017, 14, 447–500. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, R.F.; Atkinson, M.A.; Levin, J.L. Asbestos fiber length as related to potential pathogenicity: A critical review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2003, 44, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yuen, S.R.; Ashley, R. Short, thin asbestos fibers contribute to the development of human malignant mesothelioma: Pathological evidence. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemen, R.A. Epidemiology of asbestos-related diseases and the knowledge that led to what is known today. In Asbestos, Risk Assessment, Epidemiology, and Health Effects; Dodson, R.F., Hamnar, S.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 201–308. [Google Scholar]
- Adib, G.; Labreche, F.; De Guire, L.; Dion, C.; Dufresne, A. Short, fine and WHO fibers in the lungs of Quebec workers with an asbestos-related disease. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2013, 56, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggli, V.L. The so-called short-fiber controversy literature review and critical analysis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, M.E. Elongate mineral particles in the natural environment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 361, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Graham, U. Predicting EMP hazard: Lessons from studies with inhaled fibrous and non-fibrous nano- and micro-particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 361, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germine, M.; Puffer, J.H. Analytical transmission electron microscopy of amosite asbestos from South Africa. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2019, 75, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliaturo, R.; Elkassas, S.M.; Della Ventura, G.; Redhammer, G.J.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; O’Shea, M.J.; Dražić, G.; Gieré, R. Multi-scale characterization of glaucophane from Chiavolino (Biella, Italy): Implications for international regulations on elongate mineral particles. Eur. J. Mineral. 2021, 33, 77–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluso, E.; Cavallo, A.; Halterman, D. Crystal habit of mineral fibres. EMU Notes Miner. 2017, 18, 65–109. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, T.A.; Belluso, E.; Vigliaturo, R.; Gieré, R.; Emmett, E.A.; Testa, J.R.; Steinhorn, G.; Wallis, S.L. Asbestos and Other Hazardous Fibrous Minerals: Potential Exposure Pathways and Associated Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, J.F.; Gibbs, G.W. An evaluation of the risks of lung cancer and mesothelioma from exposure to amphibole cleavage fragments. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52 (Suppl. S1), S154–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.M. The health effects of short fiber chrysotile and amphibole asbestoss. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2022, 52, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Asbestos Fibers and Other Elongate Mineral Particles: State of the Science and Roadmap for Research. Revised Edn. Department of Health and Human Services, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2011–159. Curr. Intell. Bull. 2011, 62, 1–159. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2011-159/default.html (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Baumann, F.; Ambrosi, J.P.; Carbone, M. Asbestos is not just asbestos: An unrecognized health hazard. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 576–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaton, A.; Tran, L.; Aitken, R.; Donaldson, K. Nanoparticles, human health hazard and regulation. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S119–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgren, E.B. The biology of cleavage fragments: A brief synthesis and analysis of current knowledge. Indoor Built. Environ. 2004, 13, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, J.; McConnell, E.E. A review of carcinogenicity studies of asbestos and non-asbestos tremolite and other amphiboles. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52 (Suppl. S1), S187–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossman, B.T. Assessment of the pathogenic potential of asbestiform vs. nonasbestiform particulates (cleavage fragments) in in vitro (cell or organ culture) models and bioassays. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, S200–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turci, F.; Tomatis, M.; Pacella, A. Surface and bulk properties of mineral fibres relevant to toxicity. In Mineral Fibres: Crystal Chemistry, Chemical–Physical Properties, Biological Interaction and Toxicity; Gualtieri, A.F., Ed.; European Mineralogical Union: London, UK, 2017; pp. 171–214. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, M.F.; Layard, M.; Tegeris, M.A.; Miller, E.; May, M.; Morgan, E.; Smith, A. Relation of particle dimension to carcinogenicity in amphibole asbestoses and other fibrous minerals. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1981, 67, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Platek, S.F.; Groth, D.H.; Ulrich, C.E.; Stettler, L.E.; Finnell, M.S.; Stoll, M. Chronic inhalation of short asbestos fibers. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1985, 5, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.C.; Skidmore, J.W.; Hill, R.J.; Griffiths, D.M. Erionite exposure and mesotheliomas in rats. Br. J. Cancer 1985, 51, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Addison, J.; Bolton, R.E.; Donaldson, K.; Jones, A.D.; Miller, B.G. Inhalation studies on the effects of tremolite and brucite dust in rats. Carcinogenesis 1985, 6, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Addison, J.; Bolton, R.E.; Donaldson, K.; Jones, A.D.; Smith, T. The pathogenicity of long versus short fibre samples of amosite asbestos administered to rats by inhalation and intraperitoneal injection. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1986, 67, 415–430. [Google Scholar]
- Muhle, H.; Pott, F.; Bellman, B.; Takenaka, S.; Ziem, U. Inhalation and injection experiments in rats to test the carcinogenicity of MMMF. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1987, 31, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.C. Significance of the fibre size of erionite. In Proceedings of the VIIth International Pneumoconiosis Conferences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 23 August 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.M.; Jones, A.D. Comparison of the pathogenicity of long and short fibres of chrysotile asbestos in rats. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1988, 69, 717–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Man-Made Mineral Fibres and Radon, Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 1988; Volume 43, p. 300.
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Silica, Some Silicates, Coal Dust and Para-Aramid Fibrils; World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 1997; Volume 68, p. 521.
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Man-Made Mineral Fibres; World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 81, p. 381.
- Stettler, L.E.; Sharpnack, D.D.; Krieg, E.F. Chronic inhalation of short asbestos: Lung fiber burdens and histopathology for monkeys maintained for 11.5 years after exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Arsenic, Metals, Fibres, and Dusts, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Volume 100C; World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 2012; pp. 11–465.
- U.S. National Research Council. Asbestiform Fibres: Nonoccupational Health Risks; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pollastri, S.; Gualtieri, A.F.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M.; Hanuskova, M.; Cavallo, A.; Gaudino, G. The zeta potential of mineral fibres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigliaturo, R.; Pollastri, S.; Gieré, R.; Gualtieri, A.F.; Dražić, G. Experimental quantification of the Fe-valence state at amosite-asbestos boundaries using acSTEM dual-electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2019, 104, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Park, K. Effects of the Microparticle Shape on Cellular Uptake. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella, S.; Belluso, E.; Bursi Gandolfi, N.; Tibaldi, E.; Mandrioli, D.; Belpoggi, F. In vivo biological activity of mineral fibres. In Mineral Fibres: Crystal Chemistry, Chemical-Physical Properties, Biological Interaction and Toxicity; Gualtieri, A.F., Ed.; European Mineralogical Union: London, UK, 2017; pp. 307–346. [Google Scholar]
- Bursi Gandolfi, N.; Gualtieri, A.F.; Pollastri, S.; Tibaldi, E.; Belpoggi, F. Assessment of asbestos body formation by high resolution FEG-SEM after exposure of Sprague-Dawley rats to chrysotile, crocidolite, or erionite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 306, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Wong, S.; Lu, M.; Xiao, P.; Stenzel, M.H. Influence of nanoparticle shapes on cellular uptake of paclitaxel loaded nanoparticles in 2D and 3D cancer models. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3317–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, J.E.; Payne, S.L.; Khalafalla, S.E. Surface charge heterogeneity in amphibole cleavage fragments and asbestos fibers. Science 1980, 209, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veblen, D.R.; Wylie, A.G. Chapter 3. Mineralogy of amphiboles and 1:1 layer silicates. In Health Effects of Mineral Dusts; Guthrie, G.D., Mossman, B.T., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 61–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, C.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Johnston AP, R.; Scott, A.M.; Nice, E.C.; Heath, J.K.; Caruso, F. Influence of Size, Surface, Cell Line, and Kinetic Properties on the Specific Binding of A33 Antigen-Targeted Multilayered Particles and Capsules to Colorectal Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Iezzi, G.; Della Ventura, G.; Bellatreccia, F.; Petibois, C.; Marcelli, A.; Nazzari, M.; Lazzarin, F.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Petrarca, C. Mineralogy and textures of riebeckite asbestos (crocidolite): The role of single versus agglomerated fibres in toxicological experiments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.Y.; Brain, J.D. Uptake of iron oxide aerosols by mouse airway epithelium. Lab. Investig. 1979, 40, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mossman, B.T.; Kessler, J.B.; Ley, B.W.; Craighead, J.E. Interaction of crocidolite asbestos with hamster respiratory mucosa in organ culture. Lab. Investig. 1977, 36, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mossman, B.T.; Adler, K.B.; Craighead, J.E. Interaction of carbon particles with tracheal epithelium in organ culture. Environ. Res. 1978, 16, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, W.A. Oxy-radicals and related species: Their formation, lifetimes, and reactions. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1986, 48, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantauzzi, M.; Pacella, A.; Atzei, D.; Gianfagna, A.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Rossi, A. Combined use of X-ray photoelectron and Mössbauer spectroscopic techniques in the analytical characterization of iron oxidation state in amphibole asbestos. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, M.R. The amphibole hypothesis of asbestos-related cance—Gone but not forgotten. Am. J. Public Health 1996, 86, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finkelstein, M.M. Letter to the Editor re Bernstein et al: Health risk of chrysotile revisited. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 154–183. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Gulumian, M.; Hei, T.K.; Kamp, D.; Rahaman, Q.; Mossman, B.T. Multiple roles of oxidants in the pathogenesis of asbestos-induced diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegens, A.; van der Vliet, A.; Butnor, K.J.; Heintz, N.; Taatjes, D.; Hemenway, D.; Vacek, P.; Freeman, B.A.; Hazen, S.L.; Brennan, M.L.; et al. Asbestos-induced lung inflammation and epithelial cell proliferation are altered in myeloperoxidase-null mice. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9670–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, A.G.; Korchevskiy, A.A. Dimensions of elongate mineral particles and cancer: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 230, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchevskiy, A.A.; Wylie, A.G. Asbestos exposure, lung fiber burden, and mesothelioma rates: Mechanistic modelling for risk assessment. Comput. Toxicol. 2022, 24, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).