Application and Significance of the Wavelet–Fractal Method on the Data of the Induced Polarization Method in the Graphite Deposits of Datong, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
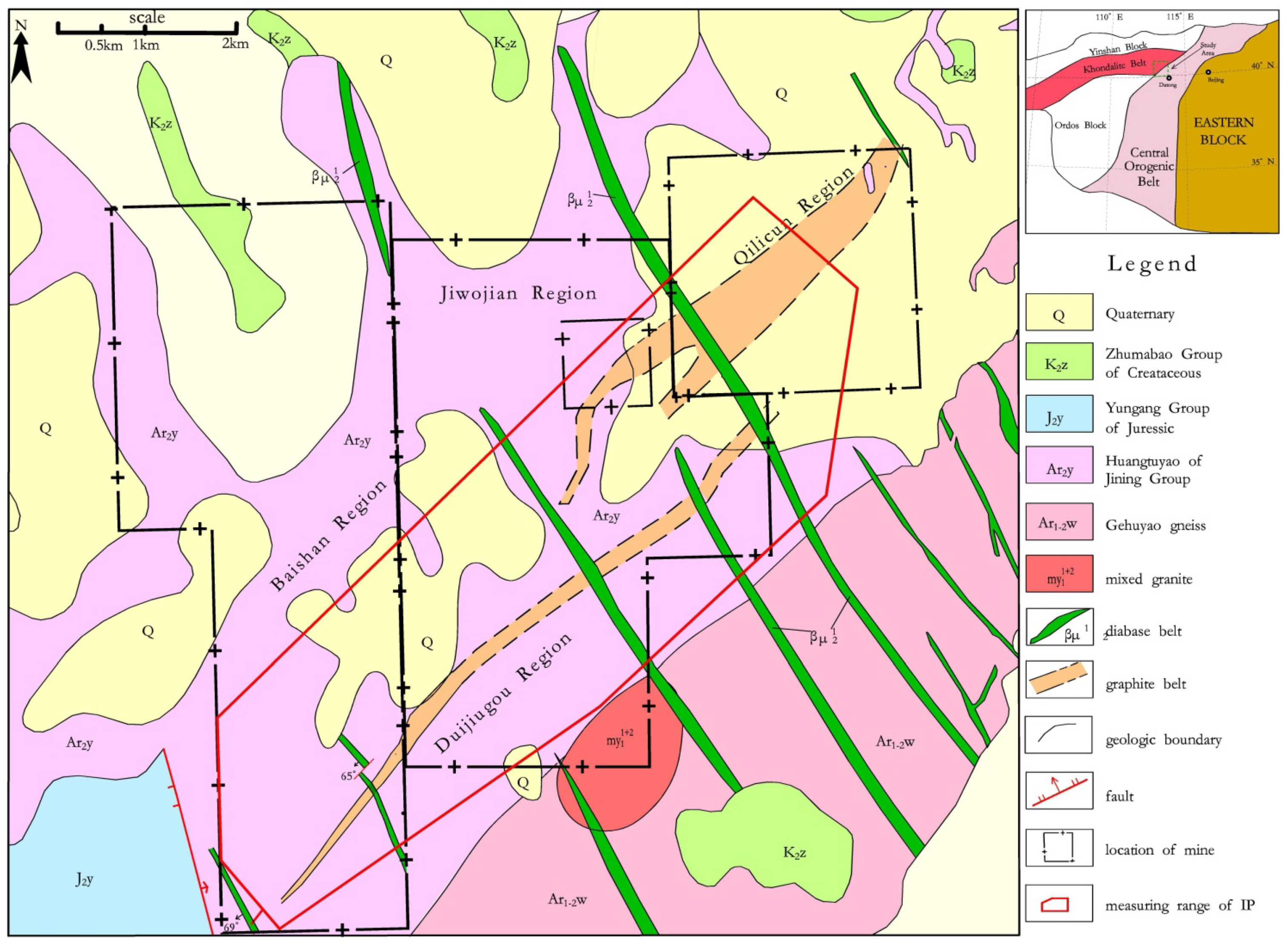
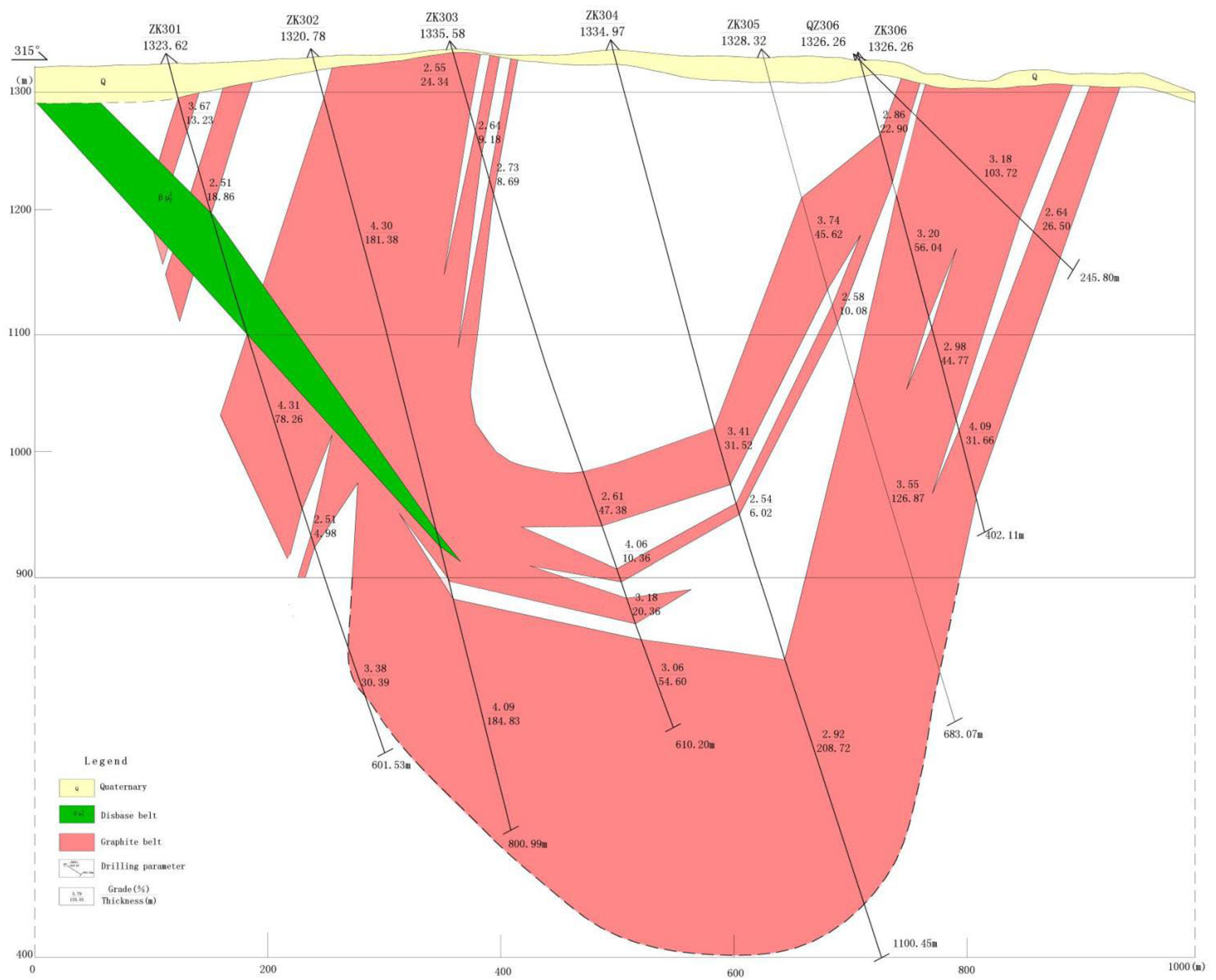
2. Geological Setting
3. Methods
3.1. Wavelet-Number (W-N) Method
3.2. Induced Polarization (IP) Method
3.3. Data Processing
3.3.1. IP Data Set
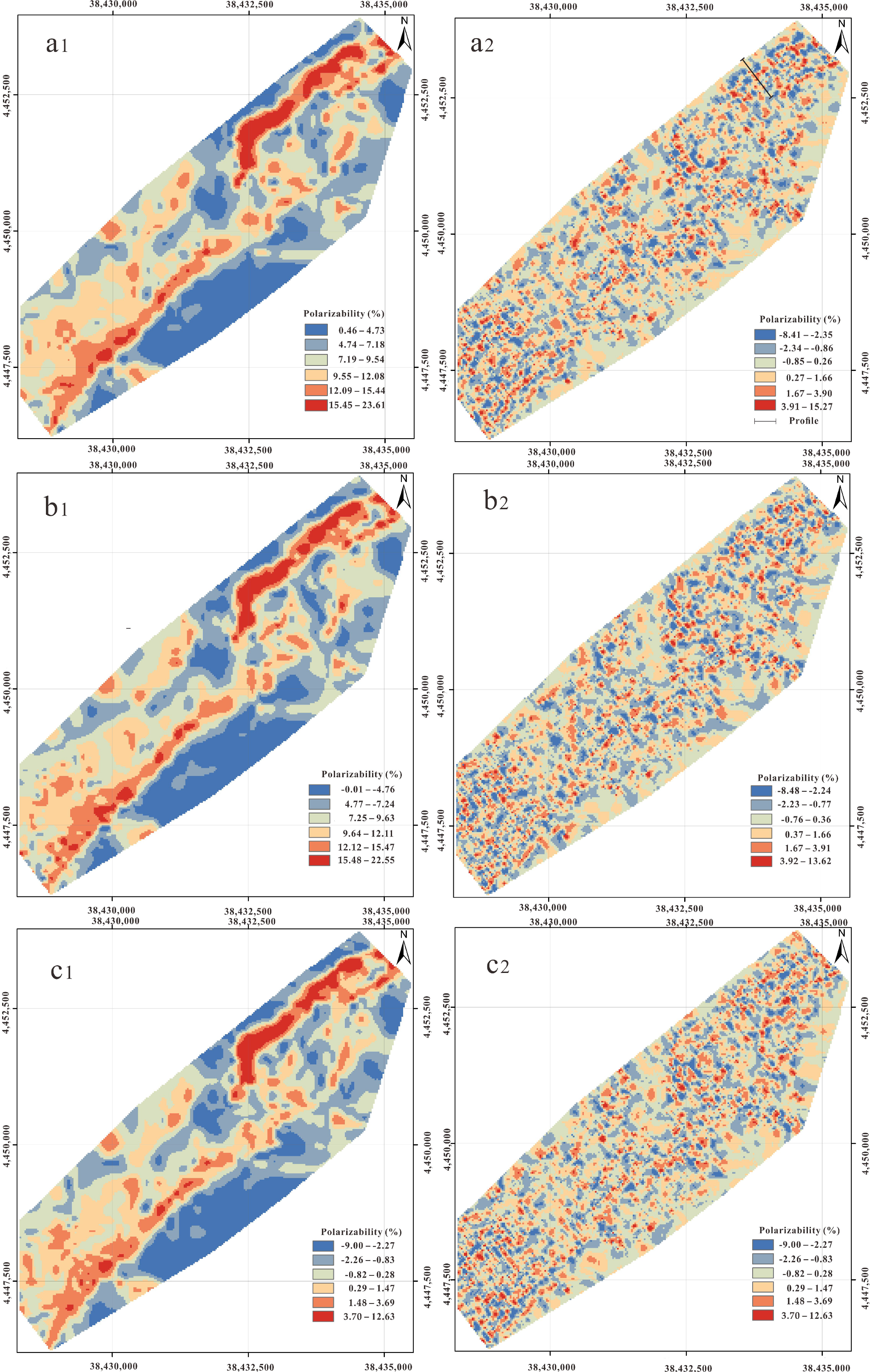
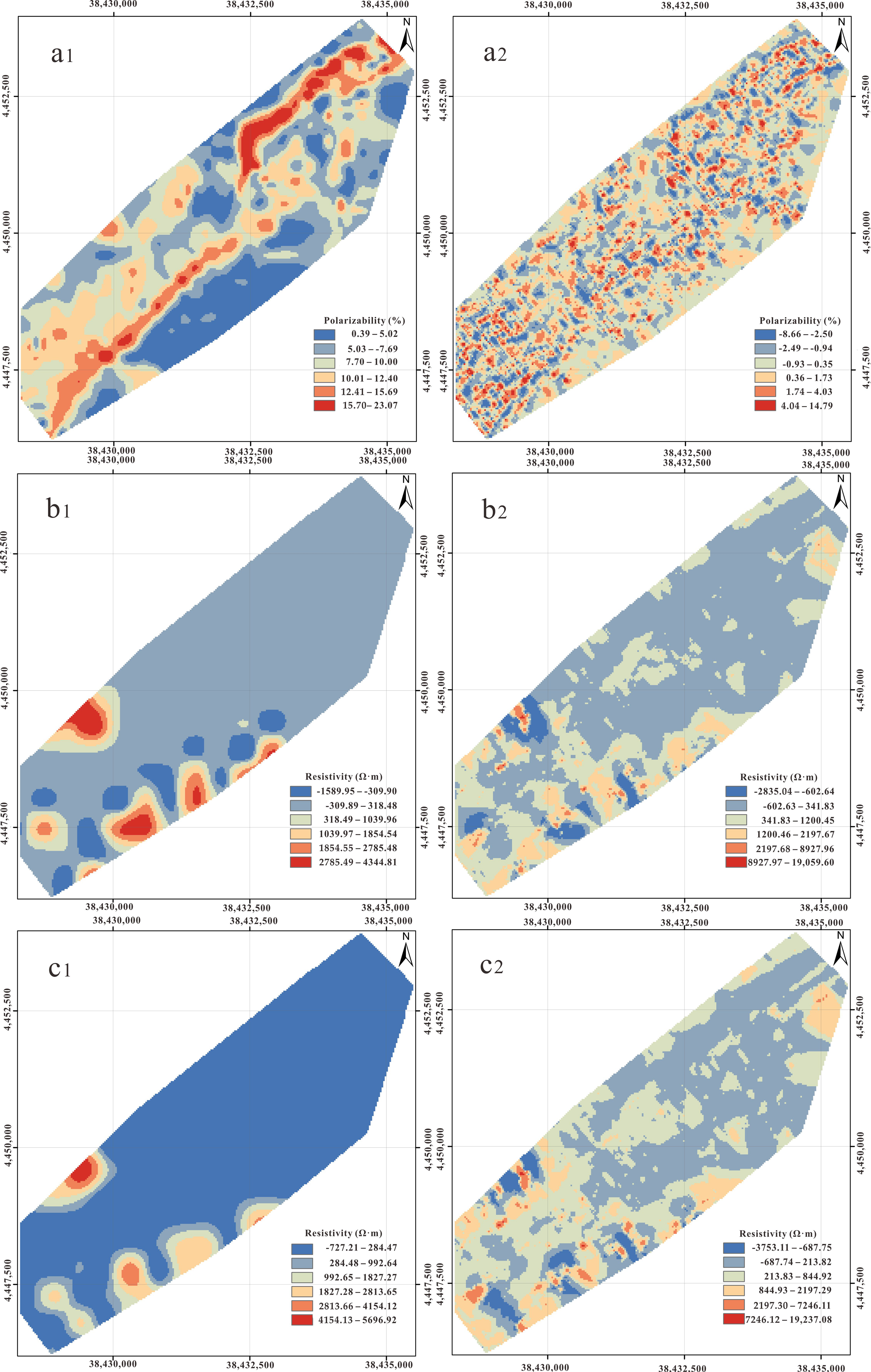
3.3.2. Wavelet Analysis
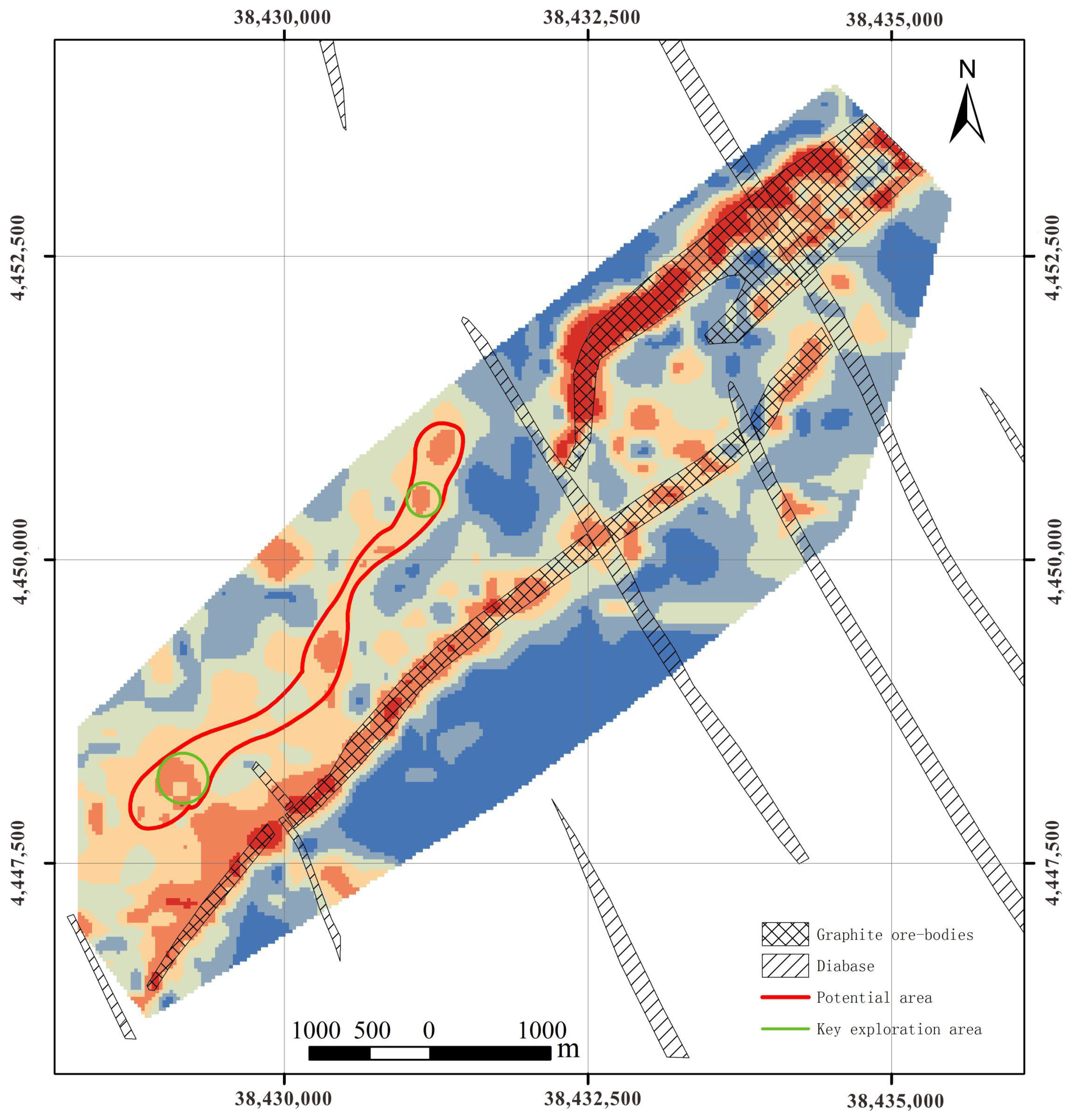
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Background Mode
5.2. Anomaly Mode
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Yuan, D.; Tong, Z. Autonomous pavement distress detection using ground penetrating radar and region-based deep learning. Measurement 2020, 164, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1989, 11, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.Y.; Wai, M.Y.; Chi, H.; Billy, H. Performance of ground penetrating radar in root detection and its application in root diameter estimation under controlled conditions. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gish, T.J.; Dulaney, W.P.; Kung, K.J.S. Evaluating use of ground-penetrating radar for identifying subsurface flow pathways. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zheng, M.; Zuo, W. Multi-stage image denoising with the wavelet transform. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 134, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, H. Wavelet-domain RTM image enhancement using inversion-based imaging condition. Geophysics 2019, 84, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Yu, S. A wavelet coherence approach to detecting ecosystem services trade-off response to land use change. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Cheng, Q.M. Fractal-based wavelet filter for separating geophysical or geochemical anomalies from background. Math. Geosci. 2018, 50, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.L.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.Q. Surface wave attenuation based polarization attributes in time-frequency domain for multicomponent seismic data. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 15, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.; Norden, B.; Ivanova, A. Wavelet transform-based seismic facies classification and modelling: Application to a geothermal target horizon in the NE German Basin. Geophys. Prospect. 2019, 68, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, H.; Lopes, D.; Cruz, O. Crustal thermal structure of the brazilian equatorial margin using fourier and continuous wavelet transforms: A comparative analysis based on different magnetic datasets. Surv. Geophys. Int. Rev. J. Geophys. Planet. Sci. 2022, 43, 883–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xue, G.; Xiao, P.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Fang, G. The removal of the high-frequency motion-induced noise in helicopter-borne transient electromagnetic data based on wavelet neural networks. Geophysics 2018, 84, 1JF-Z5. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qadi, I.L.; Shan, Z.; Shangguan, P. Railway ballast fouling detection using GPR data: Introducing a combined time–frequency and discrete wavelet techniques. Near Surf. Geophys. 2016, 14, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J. Application of local mean decomposition in marine gravity anomaly data processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Computer Science, Qingdao, China, 26–27 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bolzan, M.; Echer, E.; Franco, A. Identification of the planetary magnetosphere boundaries with the wavelet multi-resolution analysis. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2022, 230, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Liang, W.; Jiao, L.; Yan, J.W.; Zhang, W.B.; Wang, F.J.; Gou, F.; Wang, C.X.; Cheng, X.; Shao, Q.Q. Identification of dominant climate variables on spatiotemporal variation in reference evapotranspiration on the loess plateau, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 620–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, Y. Object detection in large-scale remote-sensing images based on time-frequency analysis and feature optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 1200–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coifman, R.R.; Donoho, D.L. Translation-Invariant De-Noising Wavelets and Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, A.G.; Gao, H.Y. WaveShrink: Shrinkage functions and thresholds. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1995, 2569, 270–281. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.Y.; Qin, H.F.; Yu, C.B. Research of signal denoising method based on an improved wavelet threasholding. Piezoel Ectectrics Acoustooptics 2008, 30, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.Z.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yang, L.Z. An improved wavelet threshold denoising algorithm. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2019, 42, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kumlu, D.; Erer, I. The multiscale directional neighborhood filter and its application to clutter removal in GPR data. Signal Image Video Process. 2018, 12, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Baan, M. Strong random noise attenuation by shearlet transform and time-frequency peak filtering. Geophysics 2019, 84, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pourgholam, M.M.; Afzal, P.; Yasrebi, A.B. Detection of geochemical anomalies using a fractal-wavelet model in ipack area, central Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. J. Assoc. Explor. Geochem. 2021, 220, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torshizian, H.; Afzal, P.; Rahbar, K. Application of modified wavelet and fractal modeling for detection of geochemical anomaly. Chem. Der Erde Geochem. 2021, 4, 125800. [Google Scholar]
- Rakoto, H.A.; Riva, R.; Ralay, R.; Boni, R. Evaluation of flake graphite ore using self-potential (SP), electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and induced polarization (IP) methods in east coast of Madagascar. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 169, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.L.; Zhang, S.G.; Liu, J.X.; Hi, H.J.; Zhang, W.S. Integrated interpretation of dual frequency induced polarization measurement based on wavelet analysis and metal factor methods. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, P.; Ahmadi, K.; Rahbar, K. Application of fractal-wavelet analysis for separation of geochemical anomalies. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 128, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; He, Z.B.; Wu, X.M. Stratigraphic Interfaces Identification based on the wavelet transform of geophysical logging data. Uranium Geol. 2021, 37, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Tiwari, V.M. Application of the continuous wavelet transform of gravity and magnetic data to estimate sub-basalt sediment thickness. Geophys. Prospect. 2014, 62, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.H.; Yang, H.Y. Optimistic wavelet basis selection in seismic signal noise elimination. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2011, 46, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.J.; Fan, Y.R.; Deng, S.G.; Li, X. Selection of optimum wavelet base of multiscale analysis in well loggong. Coal Geol. Explor. 2006, 34, 71–74, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Darowicki, K.; ZieliSki, A. Optmal wavelet choice in electrochemical experiments. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2006, 6, L215–L225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.J.; Li, J.R.; Dong, Y. Influence of wavelet base and threshold parameters on denoising effect of transient electromagnetic signal. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 682–690. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.C.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.L. Research on geochemistry characteristics and genesis of the graphite deposit in Xinrong district of Datong city, Shanxi province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 827–834. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Xia, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Geochemical characteristics and indication of graphite deposits in Xinrong Region, Shanxi, China. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2022, 22, geochem2021-086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.K. Detailed Investigation Report of Graphite Mine in Qilicun-Duijiugou of Xinrong District, Datong, Shanxi; Government of Shanxi Province: Datong, China, 2021; (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Moulin, P. Information-theoretic analysis of interscale and intrascale dependencies between image wavelet coefficients. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Pelton, W.H.; Ward, S.H.; Hallof, P.G.; Sill, W.R.; Nelson, P.H. Mineral discrimination and removal of inductive coupling with multifrequency IP. Geophysics 1978, 43, 588–609. [Google Scholar]
- Seigel, H.; Nabighian, M.; Parasnis, D.S.; Vozoff, K. The early history of the induced polarization method. Lead. Edge 2007, 3, 312–321. [Google Scholar]
- Gianluca, F.; James, R.; Andrew, B.; Andrew, B.; Aurelie, G.; Anders, V.C.; Esben, A. Resolving spectral information from time domain induced polarization data through 2-D inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 2, 631–646. [Google Scholar]
- Well, A.; Slater, L.; Nordsiek, S. On the relationship between induced polarization and surface conductivity: Implications for petrophysical interpretation of electrical measurements. Geophys. J. Soc. Explor. Geophys. 2013, 78, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, A.; Camerlynck, C.; Florsch, N.; Cosenza, P.; Revil, A. Bayesian inference of the Cole-Cole parameters from time and frequency-domain induced polarization. Geophys. Prospect. 2007, 55, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seigel, H. Mathematical formulation and type curves for induced polarization. Geophysics 1959, 24, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.J.; Madden, T.R. Induced polarization: A study of its causes. Geophysics 1959, 24, 790–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurin, G.; Titov, K.; Ilyin, Y.; Tarasov, A. Induced polarization of disseminated electronically conductive minerals: A semi-empirical model. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 200, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.B.; Biswas, D.; Kar, G.; Ghosh, H. Geoelectric exploration for graphite in the Balangir district, Orissa, India. Geoexploration 1984, 22, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, G.; Cosenza, P.; Ghorbani, A.; Camerlynck, C.; Cabrera, N.F.; Revil, A. Localization and characterization of cracks in clay-rocks using frequency and time-domain induced polarization. Geophys. Prospect. 2013, 61, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Titov, K. Relaxation time distribution from time domain induced polarization measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Li, Y.G. Inversion of induced polarization data. Geophysics 1994, 59, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.K. Detailed Investigation Report of Graphite Mine in Baishancun of Xinrong District, Datong, Shanxi; Government of Shanxi Province: Datong, China, 2021; (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, G.C. General Survey Report of Graphite Mine in Liumudi of Xinrong District, Datong, Shanxi; Government of Shanxi Province: Datong, China, 2019; (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Cheng, Q.M. Non-Linear theory and Power-Law models for information integration and mineral resources quantitative assessments. Math. Geosci. 2008, 40, 503–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name of Rock | Number of Specimens | Induced Polarization (%) | Electrical Resistivity(Ω·m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | Range | Mean | ||
| Mixed granite | 35 | 0.93–4.24 | 2.05 | 12.4–884.2 | 546 |
| Garnet gneiss | 28 | 0.68–5.11 | 2.24 | 5.3–1085 | 186 |
| Graphite gneiss | 40 | 1.10–41.5 | 13.34 | 3.5–918 | 36.1 |
| Diabase | 12 | 0.49–6.92 | 3.62 | 15.5–671.2 | 282.2 |
| Wavelet Type | Proportion of Ore Bodies to Abnormal Area (%) | Background | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anomalies | |||||
| Low | Middle | High | Sum | ||
| Sym5 | 22.74 | 37.68 | 26.83 | 87.25 | 12.75 |
| Sym6 | 22.89 | 36.82 | 26.56 | 86.27 | 13.73 |
| Sym7 | 25.55 | 36.28 | 25.12 | 86.95 | 13.05 |
| Sym8 | 24.46 | 37.1 | 22.81 | 84.37 | 15.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, M.; Bi, R.; Liu, J. Application and Significance of the Wavelet–Fractal Method on the Data of the Induced Polarization Method in the Graphite Deposits of Datong, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060760
Liang Y, Xia Q, Zhao M, Bi R, Liu J. Application and Significance of the Wavelet–Fractal Method on the Data of the Induced Polarization Method in the Graphite Deposits of Datong, China. Minerals. 2023; 13(6):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yuqi, Qinglin Xia, Mengyu Zhao, Rui Bi, and Jiankang Liu. 2023. "Application and Significance of the Wavelet–Fractal Method on the Data of the Induced Polarization Method in the Graphite Deposits of Datong, China" Minerals 13, no. 6: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060760
APA StyleLiang, Y., Xia, Q., Zhao, M., Bi, R., & Liu, J. (2023). Application and Significance of the Wavelet–Fractal Method on the Data of the Induced Polarization Method in the Graphite Deposits of Datong, China. Minerals, 13(6), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060760





