Evolution, Magmatic Source and Metallogenesis of A-Type Granites in the Fanchang Volcanic Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
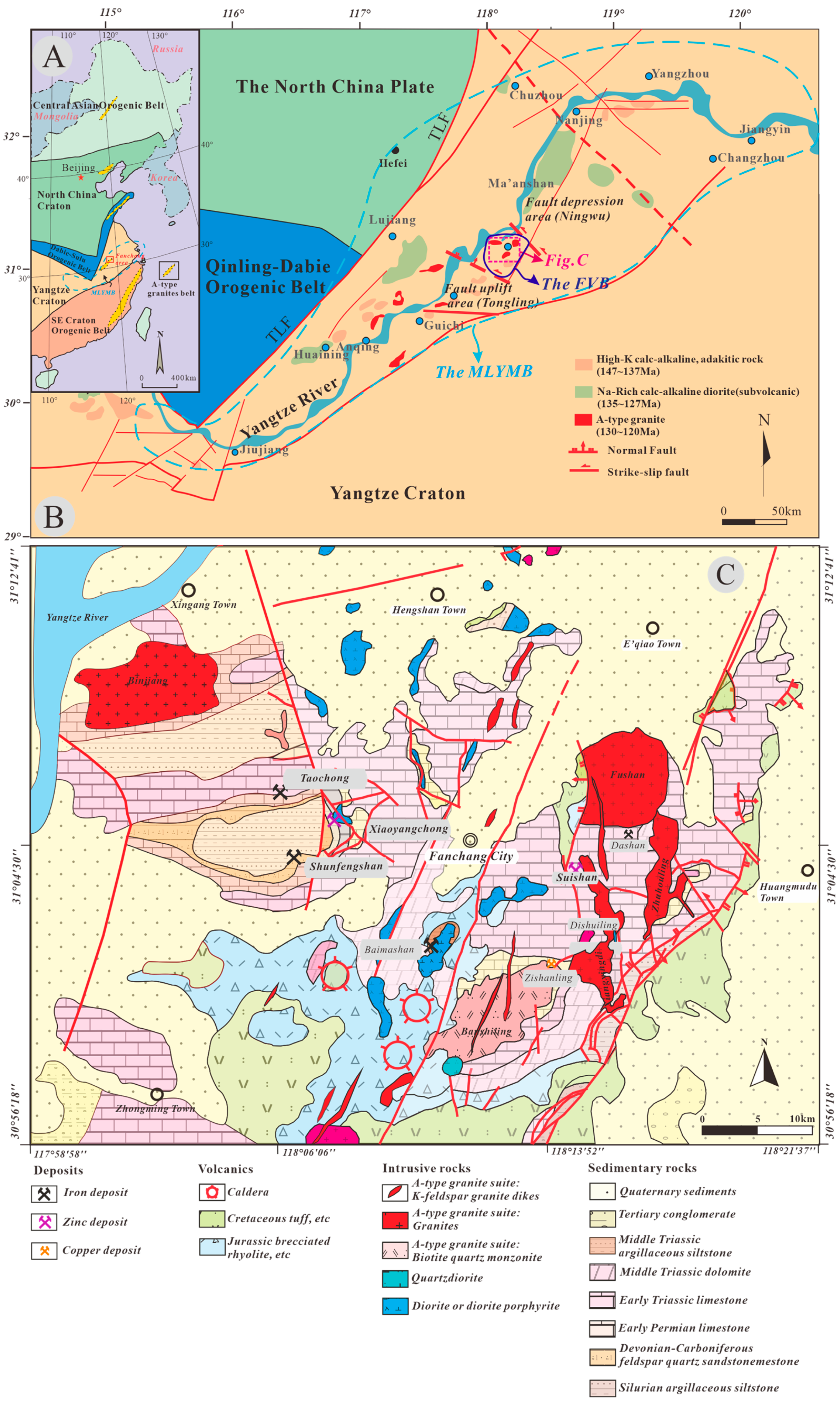
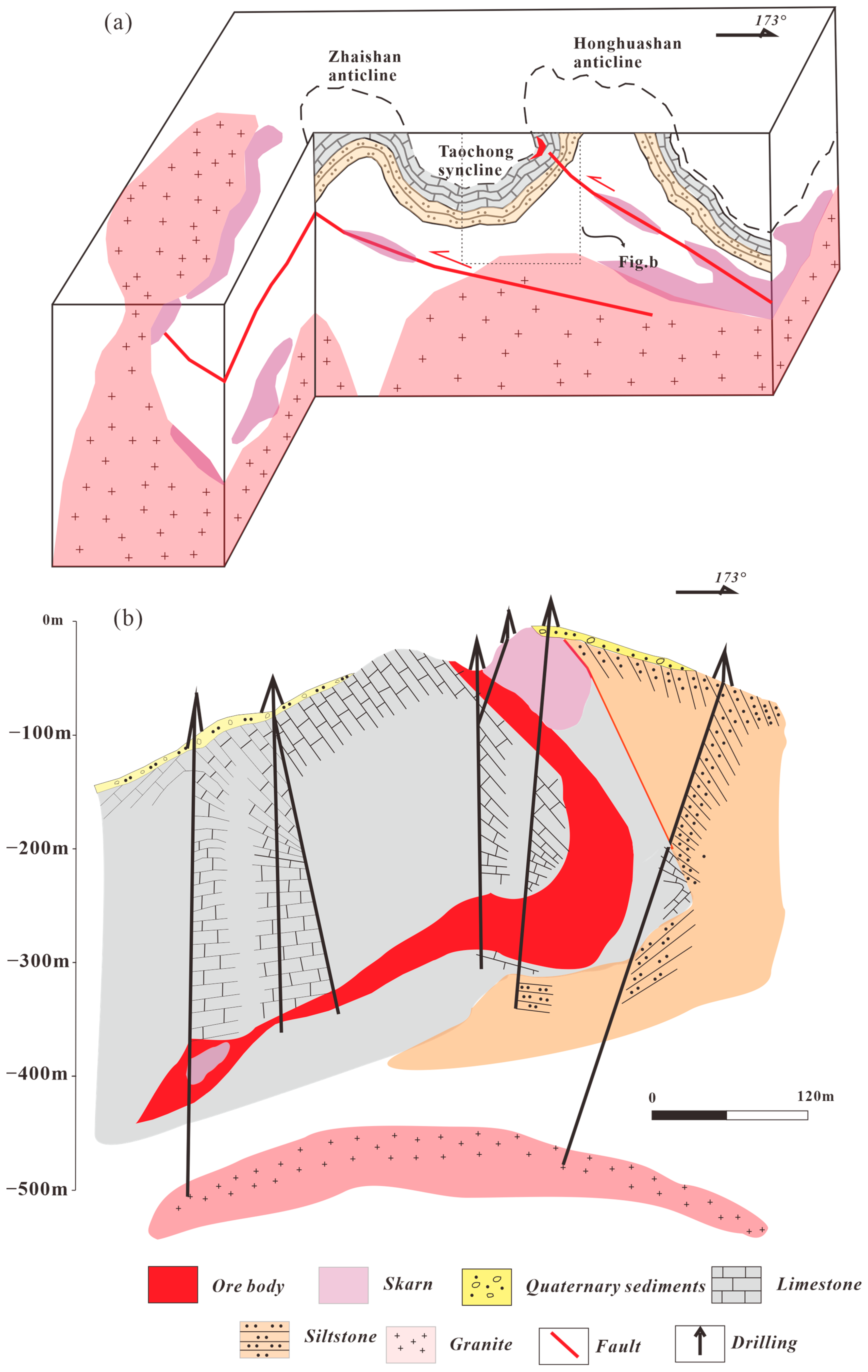
2. Geological Background of the Fanchang Volcanic Basin
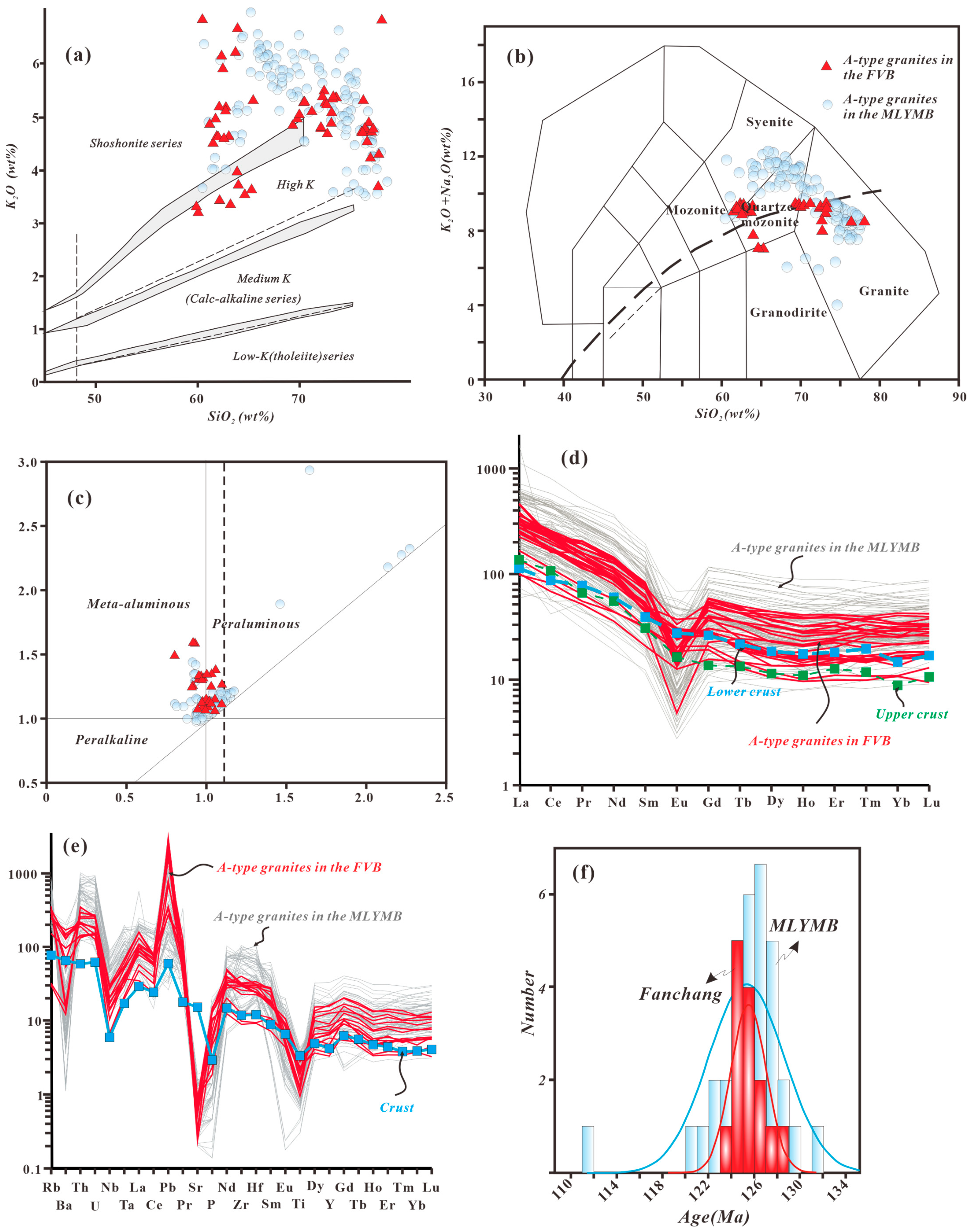
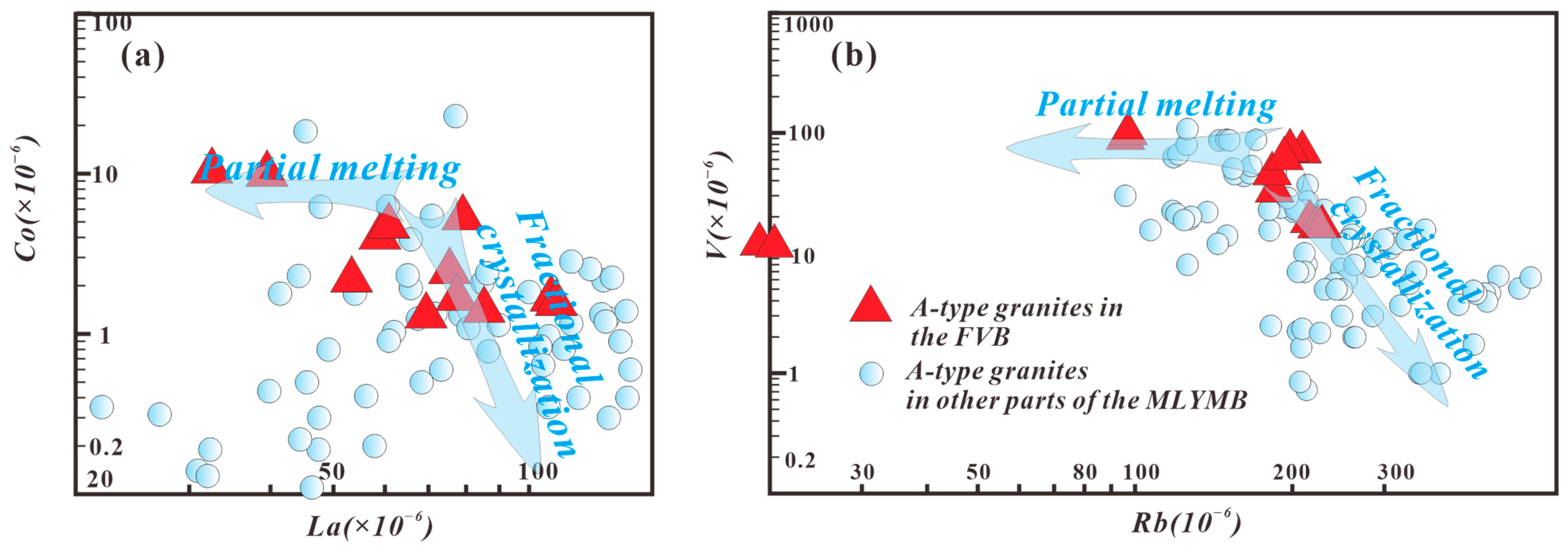
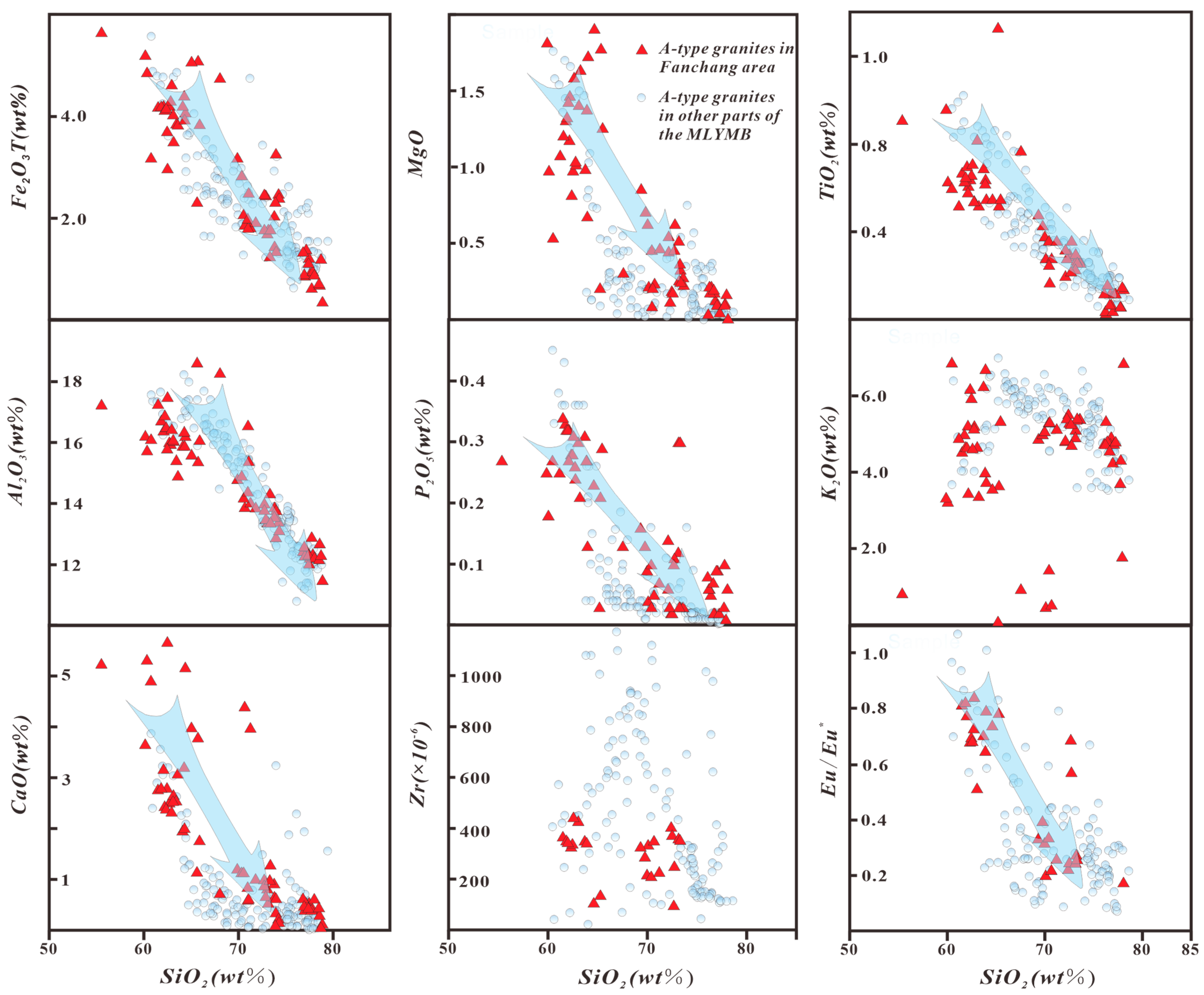
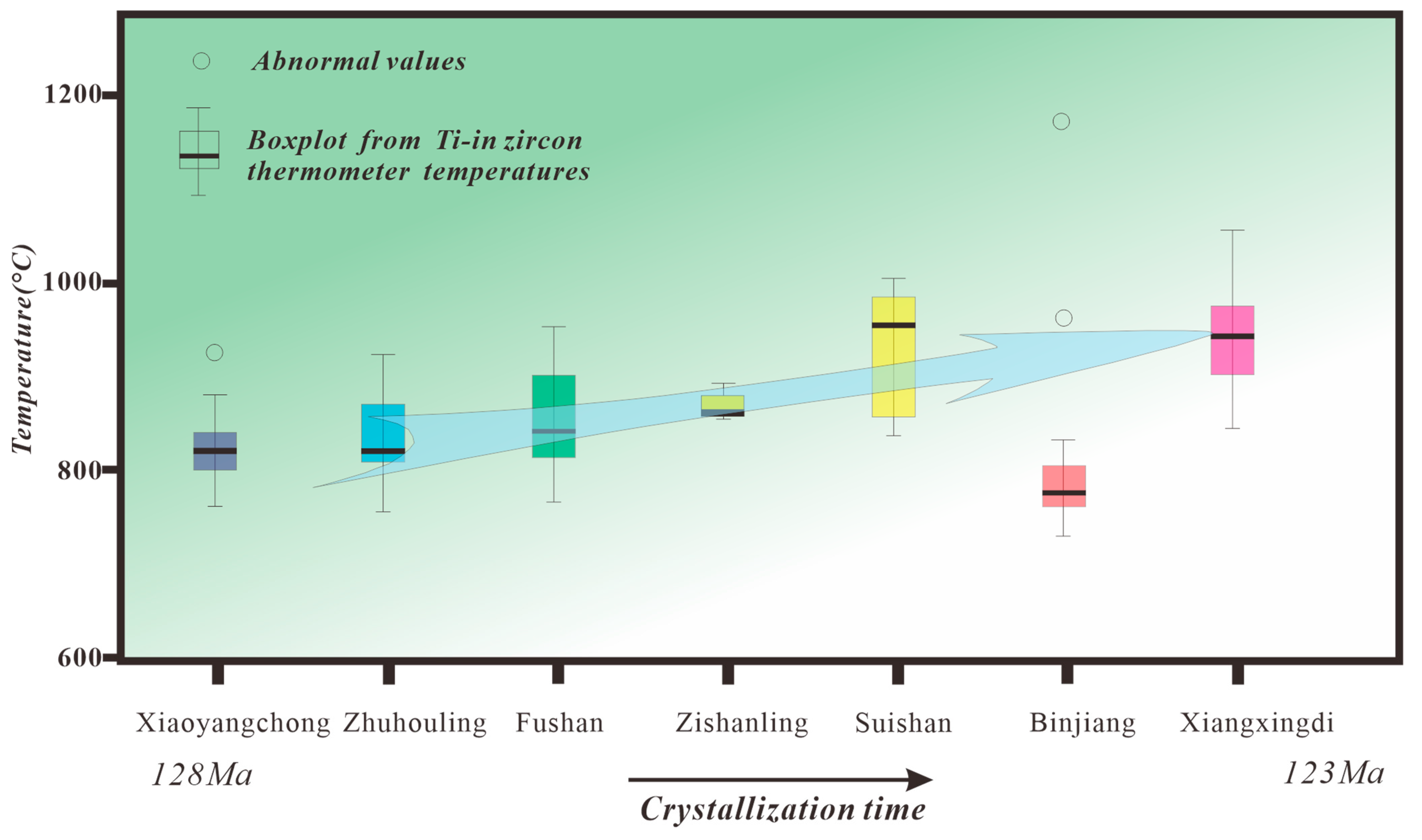
3. Evolution of the A-Type Granites in the FVB
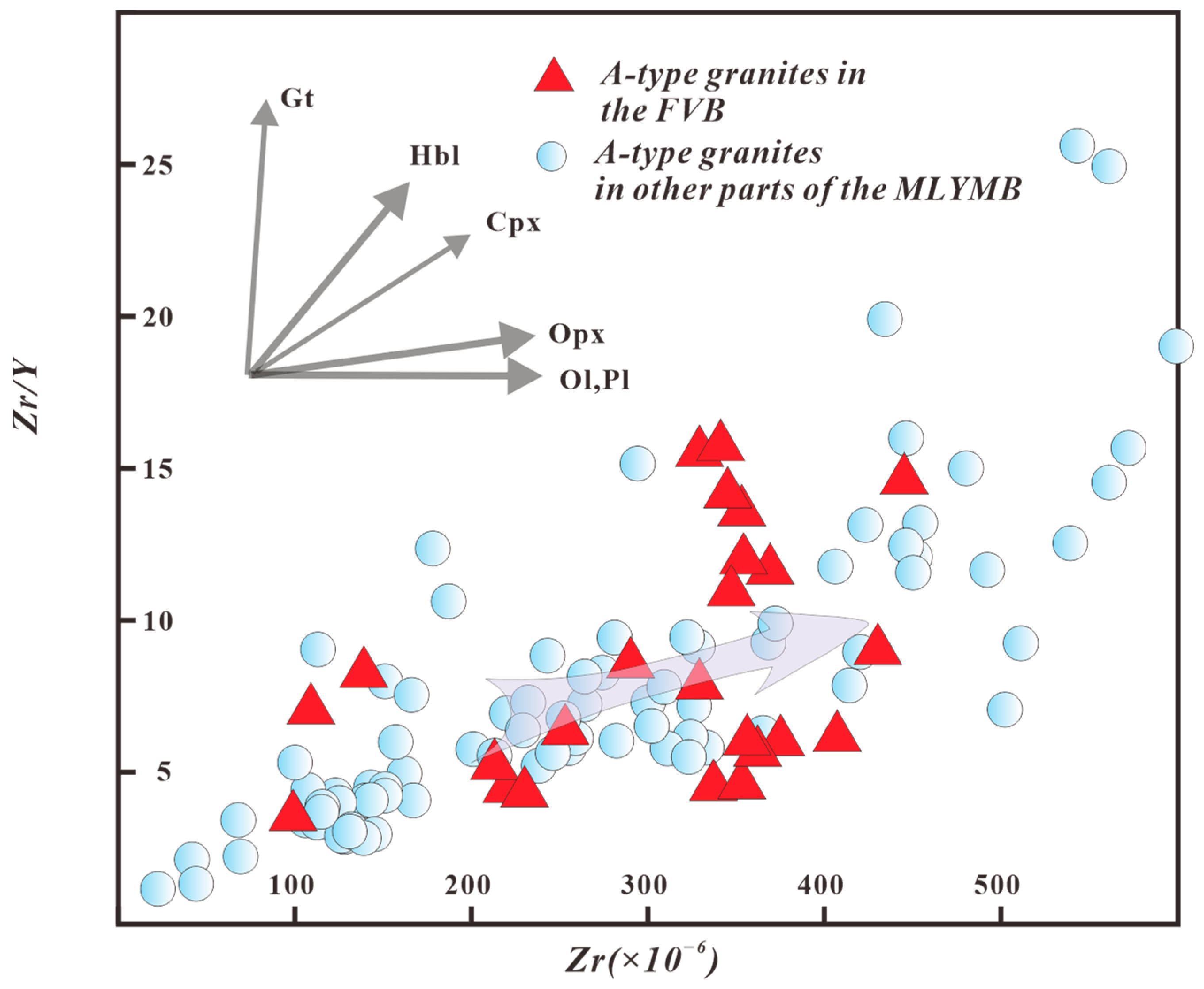
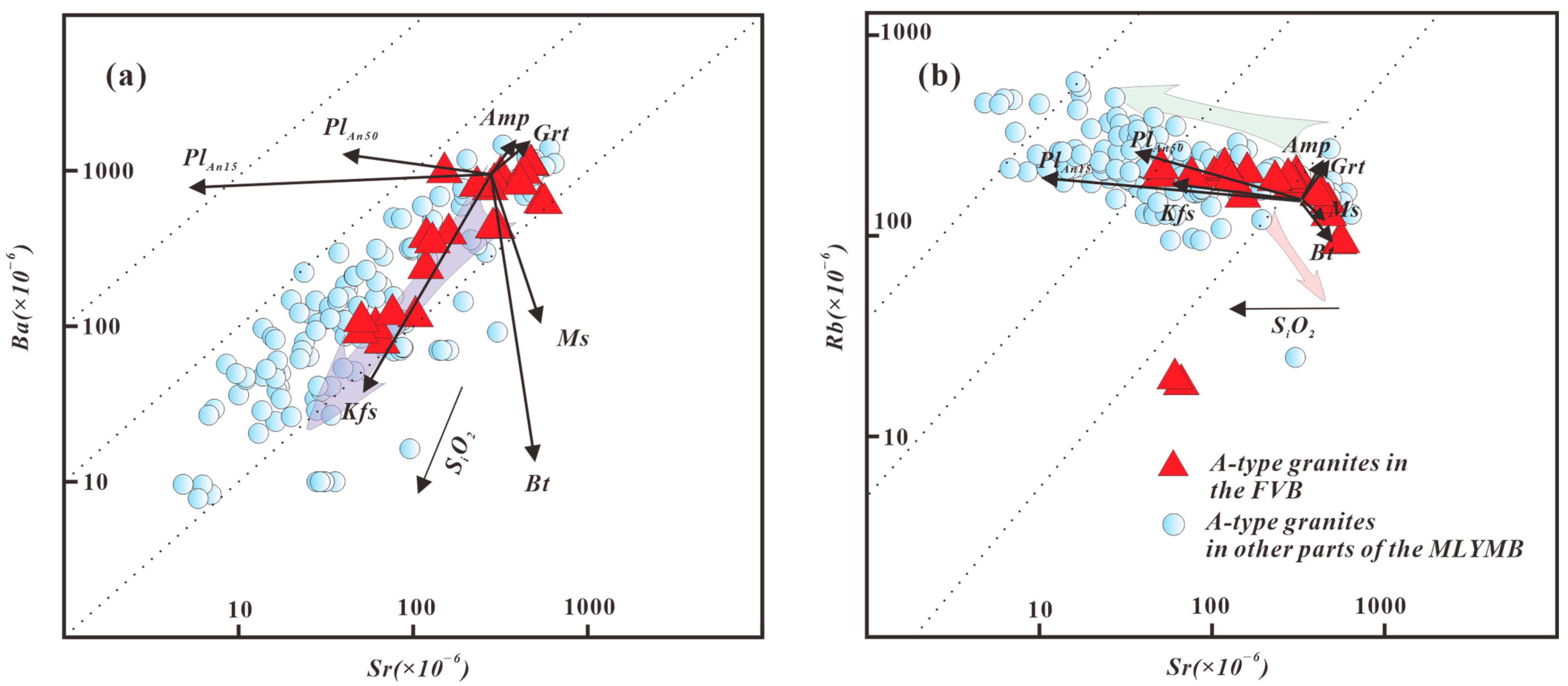
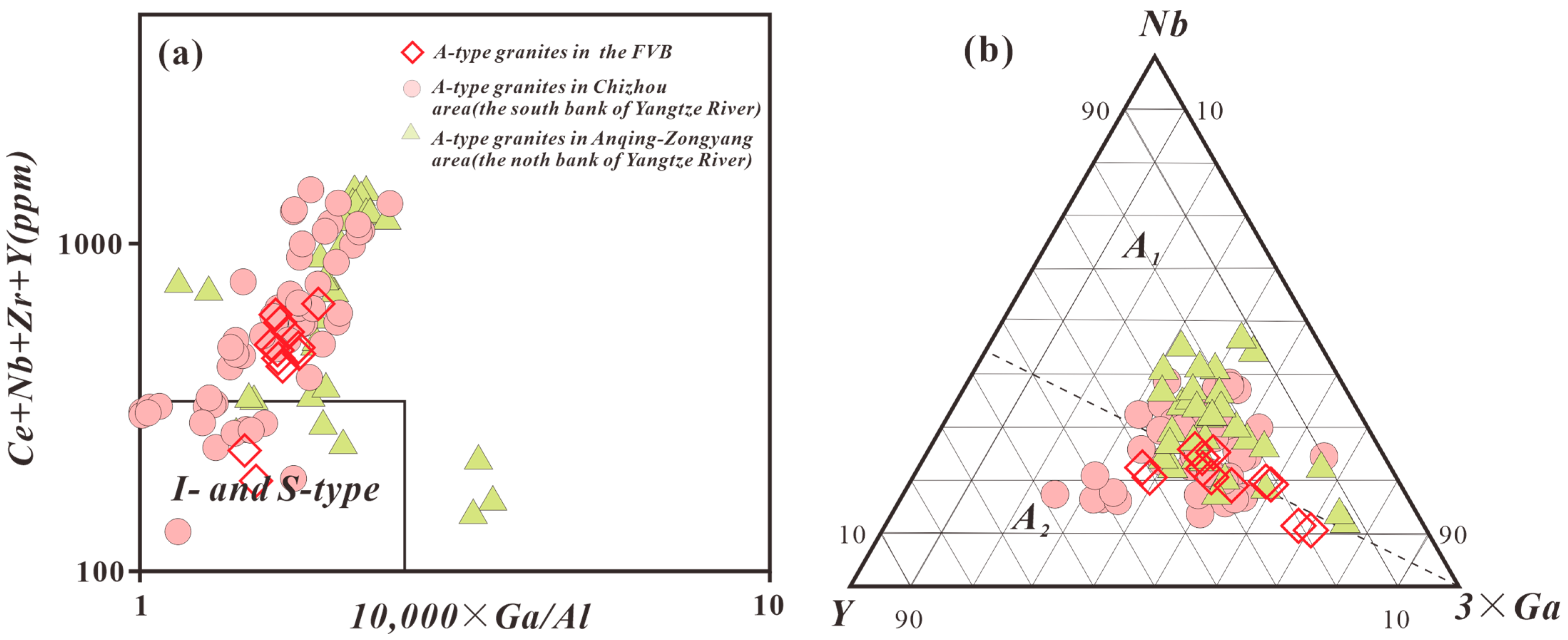
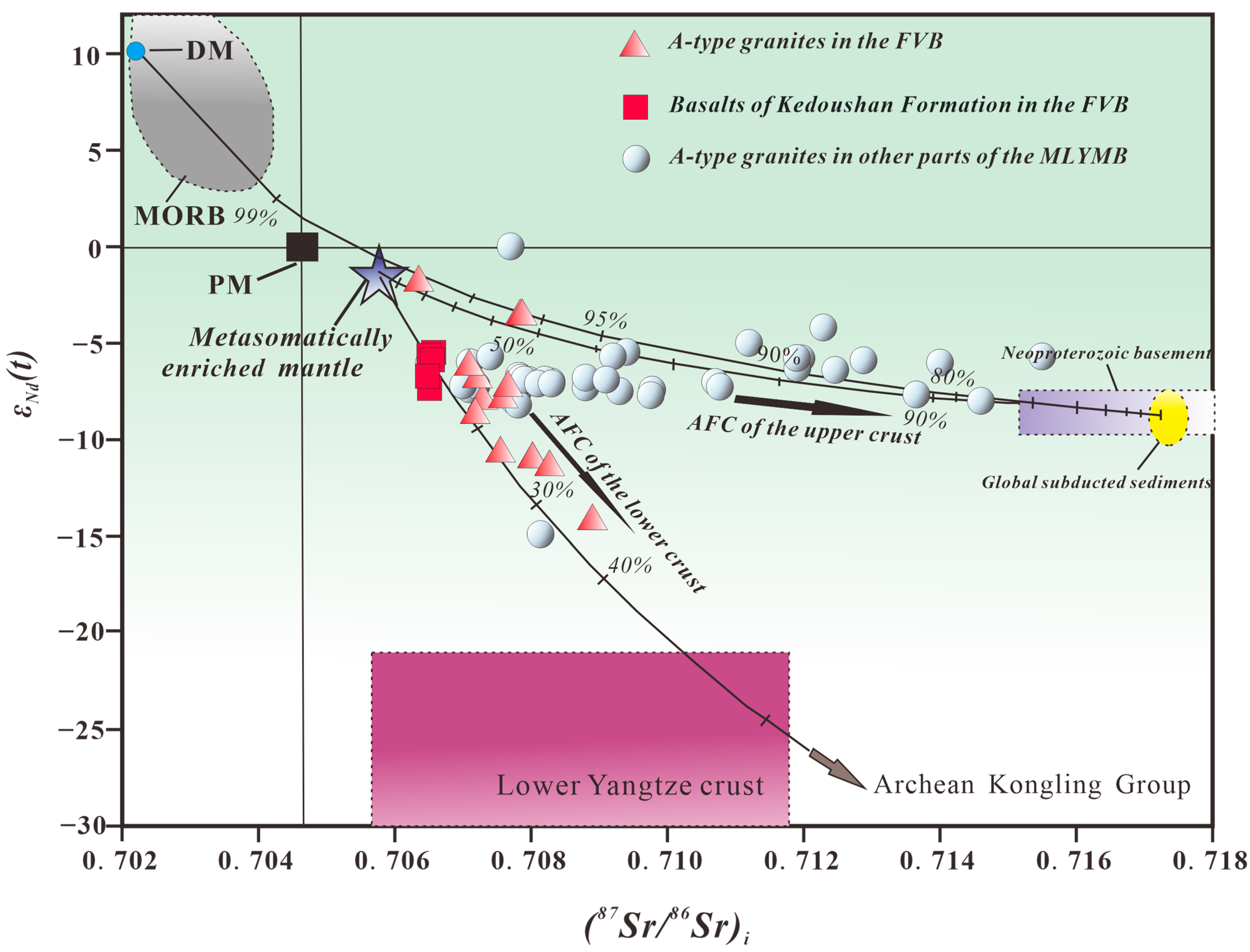
4. Magmatic Source Characteristics of A-Type Granites in the FVB
5. Ore-Controlling Characteristics and Typical Deposits
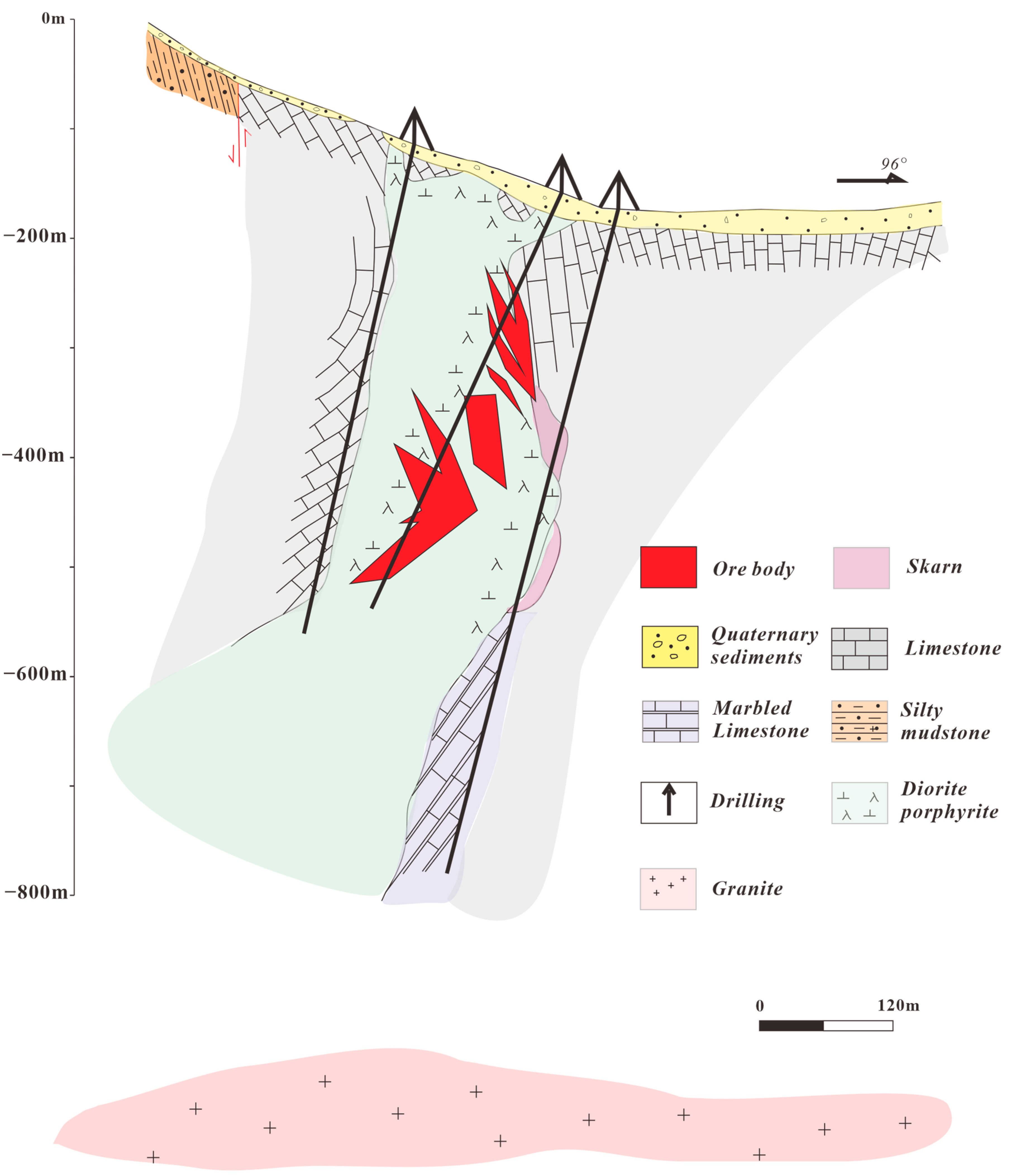
5.1. Taochong Iron Ore Deposit
- (1)
- Geological characteristics
- (2)
- Ore mineral characteristics
5.2. Xiaoyangchong Zinc-Iron Ore
- (1)
- Geological characteristics
- (2)
- Ore mineral characteristics
5.3. Suishan Zinc Ore Deposit
- (1)
- Geological characteristics
- (2)
- Ore mineral characteristics
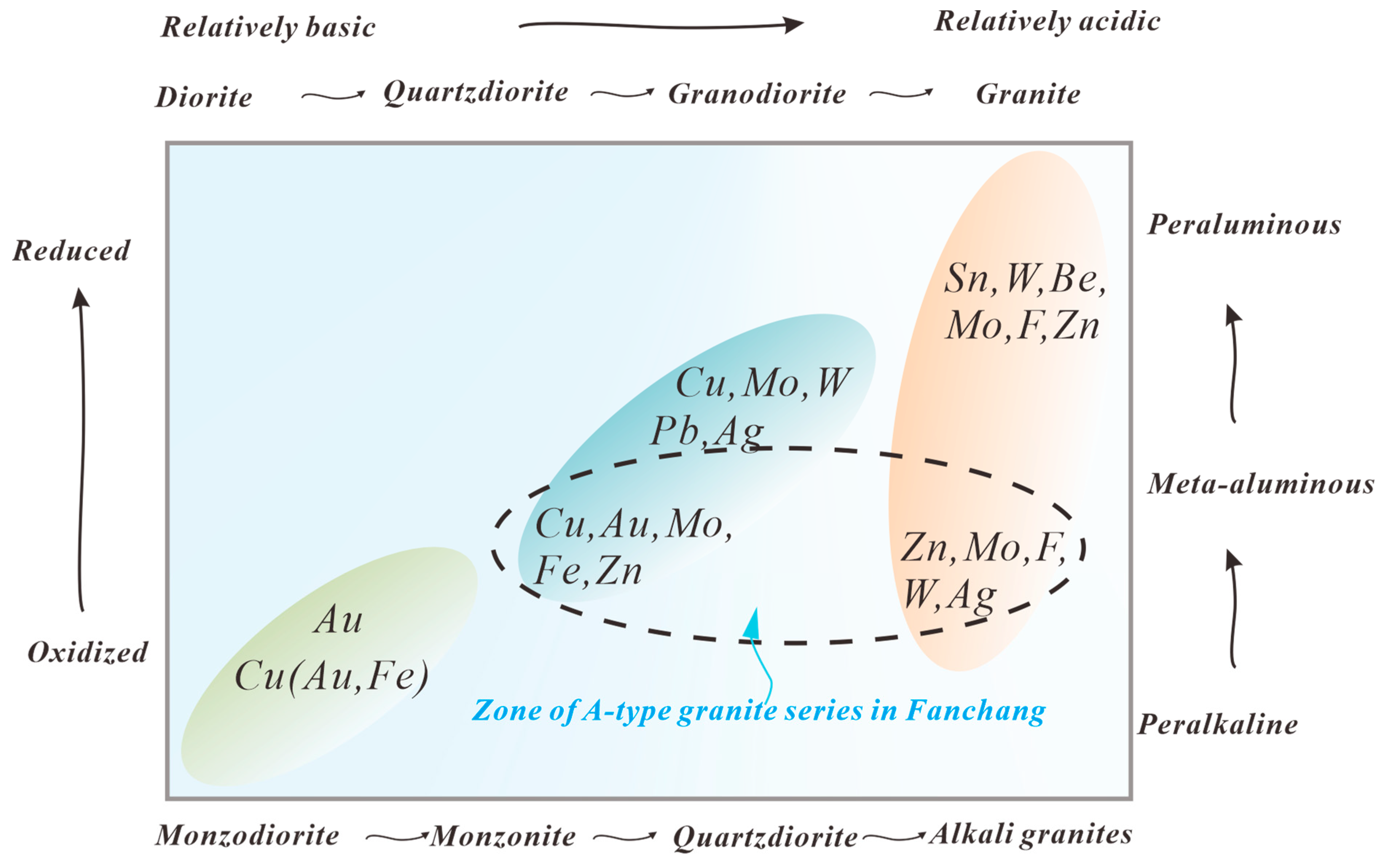
6. Metallogenesis
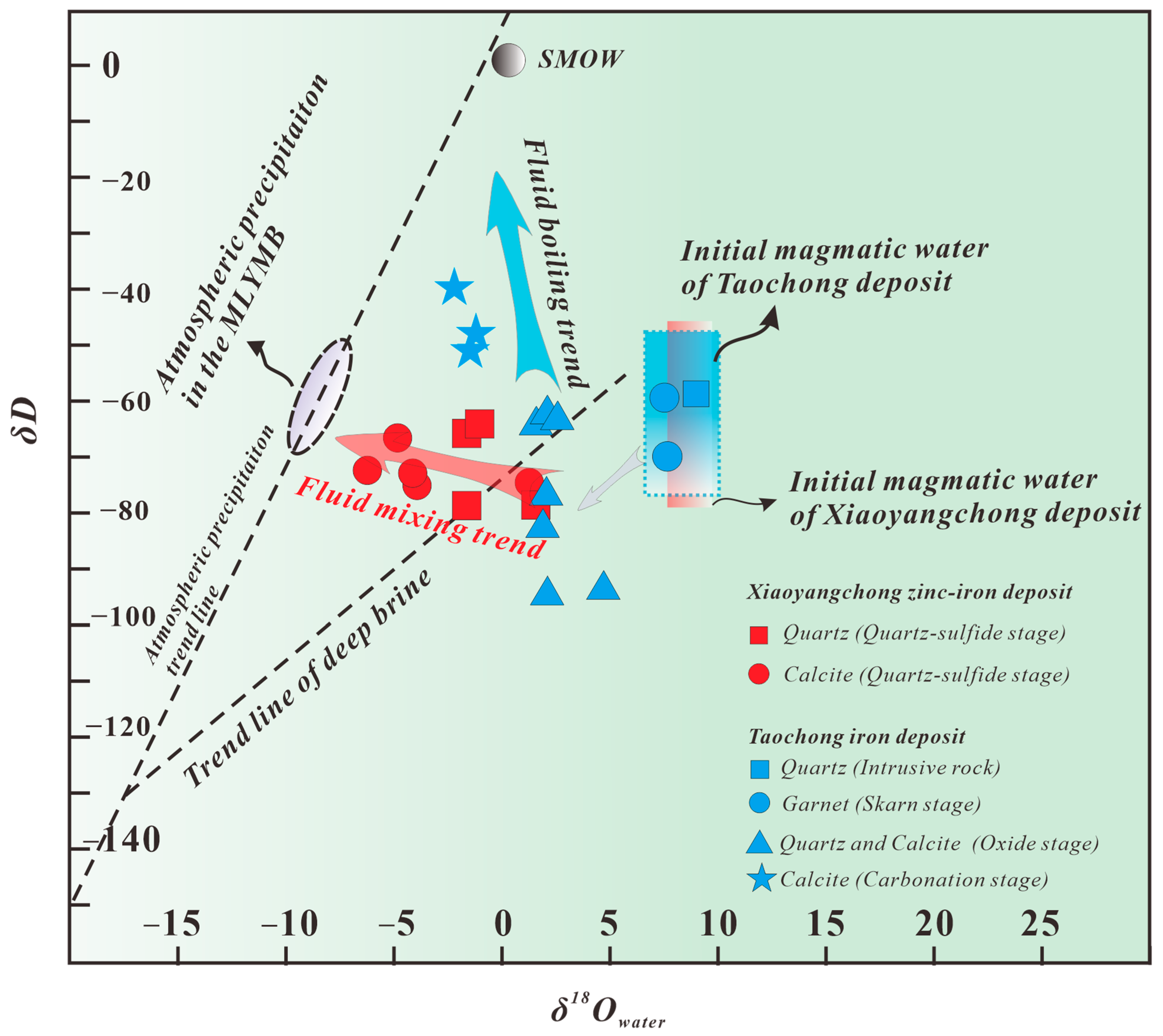
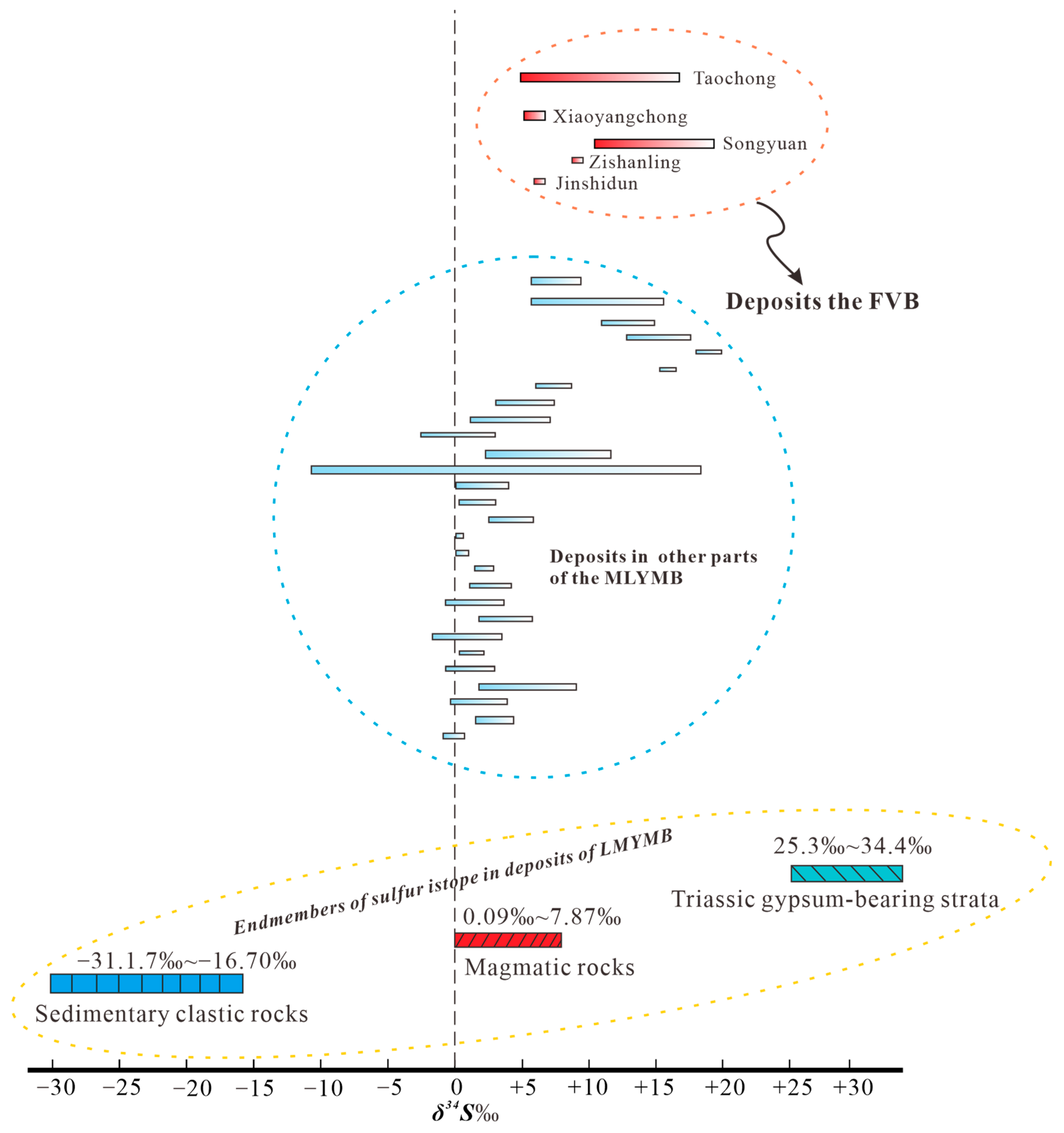
6.1. Genesis of Mineral Deposits
6.2. Metallogenic Potential
6.3. Metallogenetic Mechanism
6.4. Preliminary Analysis of the Metallogenetic Potential of Key Metals
7. Regional Petrogenetic and Metallogenetic Model
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, W.J.; Beams, S.D.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 80, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.D.; Holloway, J.R.; White, A.J.R. Origin of an A-type granite; Experimental constraints. Am. Mineral. 1986, 7, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Miner. Petr. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.J.; Cai, H.L. The nature, genesis and metallogenic relationship of A-type granite in Zhejiang province. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 1987, 6, 234–235, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Eby, G.N.; Woolley, A.R.; Ross, M. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis. Lithos 1990, 26, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.X. Geological features, petrogenesis and metlallogeny of A-type granites. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 1990, 9, 25–31, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Creaser, R.A.; Price, R.C.; Wormald, R.J. A-type granites revisited: Assessment of a residual-source model. Geology 1991, 19, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, G.N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology 1992, 20, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino Douce, A.E.P. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids. Geology 1997, 25, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.L.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W.; Allen, C.M. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type Granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia. J. Petrol. 1997, 38, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.P.; Wang, M.Y.; Qi, K.J. Present situation of researches on A-type granites: A review. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2007, 26, 57–66, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.; Sun, M.; Xing, G.F.; Li, X.H.; Zhao, G.C.; Wong, K.; Yuan, C.; Xia, X.P.; Li, L.M.; Wu, F.Y. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of the Baijuhuajian metaluminous A-type granite: Extension at 125–100 Ma and its tectonic significance for South China. Lithos 2009, 112, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ran, H.; Li, C.D. The criteria and discrimination for A-type granites: A reply to the question put forward by Wang Yang and some other persons for A-type granite: What is the essence? Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2012, 31, 621–626, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Akgul, B. Geochemical associations between fluorite mineralization and A-type shoshonitic magmatism in the Keban-Elazig area, East Anatolia, Turkey. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Qiu, J.S.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.Q. Geochronological, geochemical and Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous A-type granites from the southeastern coast of Fujian Province, South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 338–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, Å. A Tentative Model for the Origin of A-Type Granitoids. Minerals 2023, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, Å.; Waight, T.; Andersen, T.; Simonsen, S.L. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Mesoproterozoic A-type granitoids from the Danish island of Bornholm, southern Fennoscandia. Lithos 2016, 244, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B. Metallogeny of tin; magmatic differentiation versus geochemical heritage. Econ. Geol. 1982, 77, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.L.; Chappell, B.W.; Allen, C.M.; White, A.J.R. Are A-type granites the high temperature felsic granites? Evidence from fractionated granites of the Wangrah Suite. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 48, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevin, P.L. Redox and Compositional Parameters for Interpreting the Granitoid Metallogeny of Eastern Australia: Implications for Gold-rich Ore Systems. Resour. Geol. 2004, 54, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirajno, F. Hydrothermal Process and Mineral System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Pirajno, F.; Mao, J.W.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chai, F.M. The association of mafic-ultramafic intrusions and A-type magmatism in the Tian Shan and Altay orogens, NW China: Implications for geodynamic evolution and potential for the discovery of new ore deposits. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2008, 32, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ye, R.S.; Li, S.Q.; He, J.F.; Siebel, W.; Chen, F.K. Petrology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous A-type granitoids and late Mesozoic mafic dikes and their relationship to adakitic intrusions in the lower Yangtze River belt, Southeast China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2016, 59, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Mao, J.W.; Zhao, H.J.; Zhao, C.S.; Yu, X.F. Two Late Cretaceous A-type granites related to the Yingwuling W-Sn polymetallic mineralization in Guangdong province, South China: Implications for petrogenesis, geodynamic setting, and mineralization. Lithos 2017, 274–275, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Yan, J.M.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.C.; Shen, T.S.; Yang, Y.J. The Wulonggou metaluminous A2-type granites in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Rejuvenation of subduction-related felsic crust and implications for post-collision extension. Lithos 2018, 312–313, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.Y.; Wang, G.C.; Geng, L.; Pang, Z.S.; Jia, H.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Tiantangshan A-Type Granite, Cathaysia Block, SE China: Implication for the Tin Mineralization. Minerals 2019, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Chaudhri, N.; Eliyas, N. Chlorine-rich amphibole and biotite in the A-type granites, Rajasthan, NW India: Potential indicators of subsolidus fluid-rock interaction and metallogeny. Geol. J. 2019, 54, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Lü, X.; Chen, C. Geochemical Characteristics of A-Type Granite near the Hongyan Cu-Polymetallic Deposit in the Eastern Hegenshan-Heihe Suture Zone, NE China: Implications for Petrogenesis, Mineralization and Tectonic Setting. Minerals 2019, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyukova, O.; Williams, J.A. Partial melting, fractional crystallisation, liquid immiscibility and hydrothermal mobilization—A ‘recipe’ for the formation of economic A-type granite-hosted HFSE deposits. Lithos 2020, 356–357, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonopartis, L.C.; Kinnaird, J.A.; Nex, P.A.M.; Robb, L.J. African A-Type granites: A geochemical review on metallogenic potential. Lithos 2021, 396–397, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A. Two contrasting granite types. Pac. Geol. 1974, 8, 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- Maaloe, S.; Wyllie, P.J. Water content of a granite magma deduced from the sequence of crystallization determined experimentally with water undersaturated conditions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1975, 52, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiselle, M.C.; Wones, D.R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites. Geol. Soc. Am. Abst. Prog. 1979, 11, 468. [Google Scholar]
- Barbarin, B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environment. Lithos 1999, 46, 605–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 48, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R.; Barnes, C.G.; Collins, W.J.; Arculus, R.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Frost, C.D. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yang, J.H.; Zheng, Y.F. Discussions on petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1217–1238, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Ultrametamorphism and granitoid genesis. Tectonophysics 1977, 43, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, L.; Bonin, B. Post-orogenic and non-orogenic alkaline granite associations: The Sibro intrusive suite, southern Brazil: A case study. Chem. Geol. 1991, 92, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Hildebrand, R.S. Trace element discrimination of arc, slab failure, and A-type granitic rocks. Lithos 2019, 348–349, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.P.; Foden, J.D.; Morrison, R.S. Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma: An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia. Lithos 1992, 28, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Li, H.M.; Jahn, B.M.; Wilde, S. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis. Chem. Geol. 2002, 187, 143–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. A-type granites of crustal origin ultimately result from open-system fenitization-type reactions in an extensional environment. Lithos 2006, 91, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Chu, M.F. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, northeast China: Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos 2006, 89, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos 2007, 97, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ling, M.X.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Yang, X.Y.; Fan, W.M.; Li, Y.L.; Sun, W.D. A-type granite belts of two chemical subgroups in central eastern China: Indication of ridge subduction. Lithos 2012, 150, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Mao, J.W.; Santosh, M.; Bao, Z.A.; Zeng, X.J.; Jia, L.H. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous A-type granite from the Feie’shan W-Sn deposit in the eastern Guangdong Province, SE China: Implications for W-Sn mineralization and geodynamic setting. Lithos 2018, 300–301, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wei, J.H.; Tan, J.; Fu, L.B.; Li, H.; Ke, K.J. Albian Cenomanian A-type granite-related Ag-Pb-Zn veins in the central Yidun Terrane, SW China: Constraints from the Xiasai deposit. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 1047–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.W.; Wang, S.G.; Han, B.F.; Jin, M.Y. Classification of tectonic environment of alkaline granites and their identification criteria. Sci. China Ser. B 1995, 4, 418–426, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, P.R.; Wang, R.C.; Hu, H. Subdivision, discrimination and genesis for A-type rock suite. Geol. J. China Univ. 2003, 9, 573–591, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.L.; Liu, L.; Che, Z.C.; Luo, J.H.; Zhang, Y.X. Determination and preliminary study of Indosinian aluminous A-type granites in the Qimantag area, southeastern Xinjiang. Geochimica 2001, 30, 540–546, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.M.; Ma, C.Q.; Xie, C.F.; Zhang, Y.M.; Peng, S.B. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of Xishan aluminous A-type granitic volcanic-intrusive complex Southern Hunan. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2004, 26, 15–23, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Chen, X.M.; Wang, R.C.; Zhang, W.L.; Hu, H. Isotopic dating and origin of complexly zoned micas for A-type Nankunshan aluminous granite. Geol. Rev. 2005, 51, 193–200+227, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, C.W.; Ohmoto, H. Late-stage processes of felsic magmatism. Geol. Spec. Issue 1980, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, S. The granitoid series and mineralization. Econ. Geol. 1981, 75, 458–484. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, S.; Izawa, E.; Shimazaki, H. Granitoid series and mineralization in the Circum-Pacific Phanerozoic granitic belts. Resour. Geol. 2010, 48, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S. Granitoid Series and REE-Y-Zr-Ta-Nb Mineralization. Mater. Sci. Forum 1991, 70–72, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevin, P.L.; Chappell, B.W. The role of magma sources, oxidation states and fractionation in determining the granite metallogeny of eastern Australia. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1992, 83, 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.F.H.; Sillitoe, R.H.; Baker, T.; Lang, J.R.; Mortensen, J.K. Intrusion-related gold deposits associated with tungsten-tin provinces. Miner. Depos. 1999, 34, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, D.L.; Mernagh, T.P.; Hagemann, S.G.; Doublier, M.P.; Fiorentini, M.; Champion, D.C.; Jaques, A.L.; Czarnota, K.; Cayley, R.; Skirrow, R.; et al. Tectono-metallogenic systems-The place of mineral systems within tectonic evolution, with an emphasis on Australian examples. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 76, 168–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevin, P.L.; Chappell, B.W.; Allen, C.M. Intrusive metallogenic provinces in eastern Australia based on granite source and composition. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. Earth Sci. 1996, 87, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, D.H.; Shi, C.L.; Zhang, R.Z. Rethinking of the metallogenic specialization and ore bearing potential of redox related granitoid. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2014, 33, 955–964, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.C.; Santosh, M.; Zhang, D.Y. Geochronology, geochemistry and metallogenic implications of the Boziguo’er rare metal-bearing peralkaline granitic intrusion in South Tianshan, NW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 61, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Zhao, C.H.; Zhu, J.J.; Wang, X.S.; Cui, T. He, Ar, and S isotopic constraints on the relationship between A-type granites and tin mineralization: A case study of tin deposits in the Tengchong-Lianghe tin belt, southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Zhao, S.H.; Liu, W.C. The relationship between gold mineralization, high K calc-alkaline to alkaline volcanic rocks, and A-type granite: Formation of the Daxiyingzi gold deposit in northern North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Liu, W.H.; Lentz, D.R.; Wu, Z.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Yang, S.L. Tin enrichment in a highly fractionated A-type granite: Origin and mineralization potential of the Dayishan granite batholith in the Shi-Hang magmatic zone, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, Y.C. The Copper-Ion Belt of the Lower and Middle Districts of the Yangtze River; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 1–379. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.S.; Yao, S.Z.; Lin, X.D. Metallogenic regularity of iron and copper deposits in the middle and lower valley of the Yangtze River. Miner. Depos. 1992, 11, 1–12, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F. Advances on petrogenesis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1665–1678, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.B.; Yang, M.; Cong, G.X. Study on A-type granitoids in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. South. Met. 2015, 15–21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Zhou, T.F.; Xie, G.Q.; Yuan, F.; Duan, C. Metallogeny in Middle-Lower Yangtze River Ore Belt: Advances and problems remained. Miner. Depos. 2020, 39, 547–558, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, S. Critical metal resources in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt. Sci. China Press 2020, 65, 3665–3677, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.M.; Fu, P.R.; Chen, W.L.; Liu, X.D.; Lu, J.J.; Lin, J.F.; Yao, J.M.; Qi, H.W.; Zhang, Z.S.; Gu, S.Y. Mesozoic and Cenozoic metallogenic systems related to granitoids in south China. Sci. China Ser. D 2003, 33, 335–343, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.Z. The study of granitic rocks in south China: Looking back and forward. Geol. J. China Univ. 2004, 10, 305–314, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.M.; Xu, X. Two A-type granite belts from Anhui. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1994, 13, 357–369, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis on the metallogenic characteristics of rich iron ore in Fanchang area. Express Inf. Min. Ind 2007, 75–77, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.G.; Lu, S.M.; Wu, L.B. Mineral Geology of China: Volume of Anhui Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 1–541. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.Z.; Zhao, G.T.; Qiu, J.S. The tectonic constraint on the Late Mesozonic A-type granitoids in eastern China. Geol. J. Univ. 1995, 1, 13–21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.S.; Chen, S.X. Geological characteristics and prospecting signs of Changlongshan iron deposit in Fanchang County, Anhui Province. Mordenmining 2010, 26, 64–67, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Du, Y.S.; Gao, F.P.; Hu, L.F.; Xin, F.P.; Pang, Z.S. Origin and evolution of hydrothermal fluids in the Taochong iron deposit, Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley, Eastern China: Evidence from microthermometric and stable isotope analyses of fluid inclusions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, W.; Wang, K.Y.; Han, Z.S.; Yang, Y.L. Study of ore-forming fluid and ore-forming age of skarn-type iron ore in Fanchang area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 1297–1320, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.E. Characteristics and Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in Fanchang, Anhui Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–103, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.E.; Du, Y.S. Characteristics and zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in Fanchang, Anhui province. Ceochemica 2006, 35, 359–366, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Ji, W.Q.; Sun, D.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Li, X.H. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesozoic granites in southern Anhui Province, China. Lithos 2012, 150, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Peng, G.; Liu, J.M.; Li, Q.Z.; Chen, Z.H.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, Z.Z. Petrogenesis of granites from Fanchang district, the lower Yangtze region: Zircon geochrology and Hf-isotopes constrains. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3209–3227, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, J.M.; Li, Q.Z.; Xing, G.F.; Liu, X.Q.; Xie, J.C.; Chu, X.Q.; Chen, Z.H. In situ zircon Hf-O isotopic analyses of late Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, central eastern China: Implications for petrogenesis and geodynamic evolution. Lithos 2015, 227, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Duan, C.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, C. Metallogeny and corresponding mineral deposit model of the Cretaceous terrestrial volcanic-intrusive rocks-related polymetallic iron deposits in Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 1–14, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.S.; Gao, F.P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dong, Q.; Lin, L.J. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Fushan moyite in the Fanchang area, Anhui Province-Evidence from zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Hf isotopes. Geol. Bull. China 2017, 36, 402–417, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.S.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Han, C.S.; Yang, Y.L. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the origin of the Mesozoic granitoids in the Fanchang volcanic basin, the Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt. Solid Earth Sci. 2021, 6, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, J.; Song, C.Z.; Li, Q.Z.; Peng, G.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.Q. Geochronology and geochemistry of the volcanic rocks from Fanchang basin in the middle-lower Yangtze River: Petrogenesis and geological significances. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3228–3240, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G. Petrogenesis and Deep Processes of Late Mesozoic A-Type Granite in the Lower Yangtze Region. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2012; pp. 1–83, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.A.; Gu, H.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Yan, Z.Z.; Sun, W.D. Chronology and Hf isotopic study of igneous rocks in the Liwan Cu-polymetal deposit in Guichi along the Middle-Lower Yangtze River. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 1943–1961, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Z. Geochemical Studies of Copper Related adakitic Rocks and the Magmatic Rocks of Post-Mineralization in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Belt. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 1–219, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.L. The Yanshanian Magmatism and Its Relations to the Cu (Mo)-Au Mineralization in Guichi District, Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of Chin, Hefei, China, 2017; pp. 1–212, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Ling, M.X.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Z.K.; Sun, W.D.; Sui, Q.L.; Xia, X.P. Insights into the origin of coexisting A1- and A2-type granites: Implications from zircon Hf-O isotopes of the Huayuangong intrusion in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China. Lithos 2018, 318–319, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.N.; Song, S.M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, J.M. Petrogenesis of the late Mesozoic Bashan complex in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China: Implications for the definition and significance of A-type granite. Lithos 2021, 392–393, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Du, Y.S.; Cai, C.L.; Qin, X.L.; Li, S.T.; Xiang, W.S. Mesozoic A-type Granitoids and xenoliths in the Lujiang-Zongyang area, Anhui province: Significance in post-collisional magmatic evolution. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 565–576, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Zhou, T.F.; Yuan, F. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of the A-type granites in the Lu-zong (Lujiang-Zongyang) area and their geological significances. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1715–1724, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Ling, M.X.; Wang, F.Y.; Ding, X.; Zhou, J.B.; Yang, X.Y.; Tu, X.L.; Sun, W.D. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb study of the Huangmeijian A-type granite: Implications for geological evolution of the Lower Yangtze River belt. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 499–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Niu, M.L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, T.; Fei, L.L. Zircon U-Pb age, petrogenesis of the Changgang A-type granites in the Lujiang segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone and their implication. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 1031–1048, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, X. Discussion on Genesis of A-Type Granite in Southern Luzong Basin. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2018; pp. 1–75, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.K. Characteristics and Petrogenesis of the Dalongshan Granitoids in Anqing Area. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–51, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.W. Whole-Rock Element and Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotope Study of Dalongshan and Huangmeijian Granitoids in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Region and Their Geological Significances. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, China, 2019; pp. 1–72, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.M. The Diagenesis of Fanchang Basin and Ore Mineralization of Taochong. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2010; pp. 1–84, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.Z.; Jiang, Q.S.; Li, J.H.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Han, Z.S.; Huang, W.P.; Yu, G. Relationship between structures and their controls to ores in the southern margin of Fanchang Basin in Anhui Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3197–3208, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.B.; Lu, J.H. Geological characteristics and genesis of Xiaozi mountain lead-zinc deposit in Fanchang county, Anhui Province. Geol. Prospect. 2018, 194–195, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Chuan, C.Z.; Zhang, L.J.; Qian, C.C.; Lu, S.M.; David, R.C. Temporal-spatial framework of magmatic intrusions in Luzong volcanic basin in east China and their constrain to mineralizations. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 2694–2714, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Ma, C.Q.; Lu, Z.Y.; Huang, W.P. Zircon U-Pb age, element and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Guichi metallogenic district in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Region. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3287–3305, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Lu, B.; Shi, L.S.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. Geochronology of Huangmeijian composite pluton in Middle-lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt, China: Implications on the petrogenesis and metallogeny. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2022, 44, 220–242, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y. Studies on Mesozoic A-Type Granitoids and Their Rock Xenoliths in Lujiang-Zongyang Area. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–68, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. The Yanshannian Intrusive Rocks and Their Relationship with Metallogenesis in the Chizhou Area, Lower Yangtze River Belt. Ph.D. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei China, 2021; pp. 1–278, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.W.; Wang, A.D.; Lai, D.R.; Li, Q.Z.; Wan, J.J.; Li, X.C. Zircon U-Pb Chronology and Hf Isotope of Dalongshan and Huangmeijian A-type Granites in Anhui Province. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2018, 18, 1–15, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Anhui Province. Regional Geological Survey Report: 1/50000 Hengshanqiao, Wuhu, Fanchang and Huangmu Duzhang; Printing Factory of Surveying and Mapping Team of Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources: Hefei, China, 1989; pp. 1–249, (In Chinese with English abstract).
- Chen, X.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Lu, Q.L.; Yuan, F.; Ren, Z.; Fan, Y. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological characteristics of the granite porphyry beneath Guilinzheng Mo deposit, Chizhou, southern Anhui. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3200–3216, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.P.; Xu, G.P.; Zhang, B.T.; Hu, K. Comagmatic characteristics of the Luzong Volcanic Rocks and subalkaline quartz syenite rock-belt and their genesis. Geol. Rev. 1999, 45, 707–711, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Xiao, J.G.; Cao, D.W. Geological characteristics, genesis and metallogenic model of Xuncun uranium deposit in the northern margin of Huangmeijian intrusive body, Anhui Province. East China Geol. 2021, 42, 318–329, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Yue, S.C.; Yuan, F.; Liu, X.D.; Zhao, Y. Isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur and lead in two series of copper and gold deposits and their ore-forming fluid system in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Sci. China Ser. D 2000, 30, 122–128, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y. Polygenetic compound mineralization and tectonic evolution: Study in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3067–3075, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Gu, H.L.; Yan, Z.Z.; Lu, Q.L.; Duan, L.; Deng, J.H.; Zhu, Y.S.; Wang, M.S.; Zhao, D.K. Metallogenic relationship between Yanshanian magmatic rocks and Cu-Au-Mo deposits in Guichi area of Anhui: Evidence from geological-geochemical-geophysical characteristics. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2016, 38, 444–463, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.C.; An, Y.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Fu, Z.Y. Ziron U-Pb ages and element geochemistry characteristics of magmatic rocks in Nanling-Xuancheng area of Anhui, China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2020, 42, 15–35, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.M.; Xu, X. High-potassium calc-alkaline intrusive rocks in Tongling area, Anhui province. Geochimica 1996, 25, 29–38, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.S.; Qin, X.L.; Li, X.J. Mesozoic mantle-derived magma underplating in Tongling, Anhui Province from megacrysts and Xenoliths. Acta Petrol. Min. 2004, 23, 109–116, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.S.; Li, S.T.; Cao, Y.; Qin, X.L.; Lou, Y.E. UAFC-related origin of the late Jurassic to early Cretaceous intrusions in the Tongguanshan ore field, Tongling, Anhui province, east China. Geoscience 2007, 21, 71–77, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.C.; Bai, R.Y.; Xie, Q.Q.; Lou, J.W.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liu, Q.N.; Chen, L.W. Re-understanding of the geological and geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks from Tongling area of Anhui Province, and discussions on their genesis. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3139–3169, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Duan, D.F.; Xu, Y.M.; SAMAKE, B.; Li, Z.H. Geological characteristic and discrimination criteria of the ore related granitoids from the E’dong and Juirui districts in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3609–3628, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Duan, C.; Pirajno, F.; Ishiyama, D.; Chen, Y.C. A tectono-genetic model for porphyry-skarn-strata bound Cu-Au-Mo-Fe and magnetite-apatite deposits along the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China (EI). Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 294–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xie, G.Q.; Zhang, C.S.; Liu, J.L.; Yang, H.B.; Zheng, X.W.; Liu, X.F. Mineral characteristics of skarns in the Chengchao large-scale Fe deposit of southeastern Hubei Province and their geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 133–146, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.J.; Xie, G.Q.; Wei, K.T.; Ke, Y.F. Mineral compositions and fluid evolution of the Tonglushan skarn Cu-Fe deposit, SE Hubei, east-central China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 54, 737–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.H.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.J. Geochemical constraints on Cu-Fe and Fe skarn deposits in the E’dong district, Middle-Lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningwu Research Project’s Writing Group. Porphyrite Iron Ore in Ningwu Area; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1978; pp. 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Jian, P.; Liu, D.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Qian, Q. Zircon SHRIMP dating of Ningwu volcanic rocks and its significance. Sci. China Ser. D 2003, 33, 309–314, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Huang, D.Z.; Zhou, W.J.; Teng, X.; Liang, E.Y.; Dai, T.G. Genesis of Early Cretaceous porphyrite-type iron deposits and related sub-volcanic rocks in the Ningwu Volcanic Basin, Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, Southeast China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 1507–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geology and Mineral Resources Bureau of Anhui Province. Regional Geology of Anhui Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1987; pp. 1–723. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.M.; Yan, J.; Chen, D.D.; Li, Q.Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Yao, H.Z.; Shi, L.; Chen, Z.H. Petrogenesis of the volcanic rocks in Fanchang basin, the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt: Zircon Hf-O isotopic constraints. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 289–302, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, H.Q.; Song, C.Z.; Xu, X.S.; An, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Dai, L.Q. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the volcanic rocks from Fanchang-Ningwu volcanic basins in the Lower Yangtze region and its geological implications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G. Infrastructure of Mesozoic magmatic rocks and copper-iron metallogenic belt in the middle and lower Yangtze river reaches. Geol. Anhui 2001, 11, 118–122, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Li, R.L.; Cao, J.J. Discussion on some problems of Mesozoic and Cenozoic geodynamics of southeastern China. Geol. Rev. 2005, 51, 613–620, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Chen, J.F.; Xie, Z.; Yang, G.; Yu, G.; Qian, H. Geochemistry of late Mesozoic from Kedoushan in the middle and lower Yangtze regions: Constrains on characteristics and evolution of the lithospheric mantle. Geochimica 2005, 34, 455–469, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Lu, S.M.; Qian, C.C.; Zhang, L.J.; Duan, C.; Tang, M.H. Source, evolution and tectonic setting of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Luzong basin, Anhui province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1691–1702, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.C.; Xu, X.Y.; Xie, Q.Q.; Fu, Z.Y.; Qian, S.L.; Xie, Z.J. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Chating copper-gold deposit in Xuancheng City. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3659–3676, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.F.; Ceng, L.P.; Liao, W.; Li, W.T.; Hu, H.; Li, J.W. An overview of recent advances in porphyrite iron (iron oxide-apatite, IOA) deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt and its implication for ore genesis. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 197–217, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.Y.; Ren, Q.J.; Xu, Z.W.; Sun, Y.D.; Guo, G.Z. The magma source of Bajiatan volcanic-intrusive complex in the Lujiang-Zongyang area, Anhui province. Geochimica 1993, 22, 197–206, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Xing, F.M.; Zhu, C.M.; Zhao, J.S.; Cai, E.Z.; Xu, X. Study on genesis of magma forming intermediate and intermediate-acid magmatic rocks from middle-lower reaches of Changjiang river and copper mineralization. Geochimica 1996, 25, 387–400, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.M.; Zhao, B.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.M.; Zhao, J.S.; Cai, E.Z. Experiment study on the genesis of intrusive rocks in the Tongling area, Anhui. Reginal Geol. China 1997, 16, 267–274, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Geochemical characteristics of volcanic rocks from Ningwu area, and its significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2001, 17, 565–575, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.L. Studies on Sulfide-Metal Oxide Inclusions from Mesozoic Intrusions and Their Rock Xenoliths. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–158, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.J.; Mao, J.W.; Zhang, C.Q. Evidence of mantle participation in the mineralization of Ningwu porphyrite-like rocks in Ningwu basin-from C and Sr isotope. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2007, 17, 1216–1221, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A. Trace Element Characteristics of Lavas from Destructive Plate Boundaries; Chichester: Wiley, UK, 1982; pp. 525–547. [Google Scholar]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Janoušek, V.; Finger, F.; Roberts, M.; Fryda, J.; Pin, C.; Dolejš, D. Deciphering the petrogenesis of deeply buried granites: Whole-rock geochemical constraints on the origin of largely undepleted felsic granulites from the Moldanubian Zone of the Bohemian Massif. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2004, 95, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.H. Subduction and Cu-Au Mineralization: Comparing Studies of the Early Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks and Adakitic Rocks in Luzong Basin, LYRB and Central Philippines. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2015; pp. 1–172, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.F.; Gao, S.; Wu, F.Y. Zircon isotope evidence for ≥3.5Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of China. Precambrian Res. 2006, 146, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.F.; Gao, S.; Wu, F.Y. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotope evidence for Paleoproterozoic metamorphic event in South China. Precambrian Res. 2006, 151, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.F.; Gao, S.; Wu, F.Y. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope evidence for 3.8 Ga crustal remnant and episodic reworking of Archean crust in South China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 252, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.L.; Huang, G.C.; Ding, L.X.; Wu, C.X.; Zhu, J.M.; Jin, S.G. Paleoproterozoic-Archean basement beneath southeast Hubei Province: Evidence from U-Pb-Hf isotopes in zircons from the Tonggushan pluton. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 691–701, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A.W. Sampling Mantle Heterogeneity through Oceanic Basalts: Isotopes and Trace Elements. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 2, 568. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, T.; Langmuir, C.H.; Albarede, F.; Blicherttoft, J.; Staudigel, H.; White, W.M. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chem. Geol. 1998, 145, 325–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Yan, J.; Xie, Z.; Xu, X.; Xing, F. Nd and Sr isotopic compositions of igneous rocks from the Lower Yangtze region in eastern China: Constraints on sources. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.M.; Wu, F.Y.; Lo, C.H.; Tsai, C.H. Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collision mafic-ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chem. Geol. 1999, 157, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.X.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wu, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.F.; Zhang, S.B.; Liu, X.M.; Wu, F.Y. Reworking of juvenile crust: Element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambrian Res. 2006, 146, 179–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhou, J.C.; Wan, Y.S.; Kitajima, K.; Wang, D.; Bonamici, C.; Qiu, J.S.; Sun, T. Magmatic evolution and crustal recycling for Neoproterozoic strongly peraluminous granitoids from southern China: Hf and O isotopes in zircon. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 366, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.J.; Lin, X.D. An investigation into the genesis of the Changlongshan skarn-magma type of iron deposit, Anhui province. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 1990, 15, 649–656+722, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.F.; Huang, C.Y. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Taochong iron deposit in Fanchang District, Anhui Province, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 82–95, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.H. Summary Report of Geological Survey of Suishan Zinc Mine, Fanchang County, Anhui Province; Team of Geological Bureau: Fanchang, China, 1960; pp. 1–200.
- Lin, S.Z. A contribution to the chemistry, origin and evolution of magnetite. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1982, 3, 166–174, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.G. Application of Stable Isotopes in Geology; Science and Technology Press of Shaanxi: Xi’an, China, 1985; pp. 1–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Yue, S.C. Isotope geochemistry of copper mineralization in Yueshan, Anhui. Miner. Depos. 1996, 15, 54–63, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shmulovich, K.I.; Landwehr, D.; Simon, K.; Heinrich, W. Stable isotope fractionation between liquid and vapor in water-salt systems up to 600 °C. Chem. Geol. 1999, 157, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, R.O.; Ohmoto, H. Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: A review. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.S.; Yao, S.Z.; Cai, K.Q. Mineralogy; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.L.; Wang, Y. Relationship between the hard-soft acid-base properties of magmatic hydrothermal and the metal metallogenic specificity. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2014, 36, 83–93, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, J.M.; Li, Q.Z. Characteristics of oxygen fugacity of the late Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the middle-lower Yangtze River Belt and its significance. Chin. J. Geol. 2016, 51, 1163–1180, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Wang, B.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhong, G.X. Apatite-actinolite-magnetite deposit related to A-type granite in Luzong basin: Evidence from Makou iron deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3087–3098, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.H. Study on geological characteristics of uranium mineralization and control factors in Huangmeijian area, Anhui Province. J. East China Inst. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2014, 37, 150–157, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.D.; Zhao, W.G.; Wei, G.H. The mineralization related with the syenite in Luzong Basin, Anhui Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 519–531, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.R. A brief analysis of geological features of the Dalongshan uranium ore deposit. Geol. Anhui 2017, 27, 95–98, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Meng, X.; Ren, K.D.; Chen, X.F.; Ye, L.X.; Xiong, Z.Y. Mineralogy, temporal and spatial distribution of Mo mineralization in Guilinzheng Mo-W deposit, Jiangnan W mineralization belt and its significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2821–2842, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Wang, H.N.; Wang, M.Y. Coordination and its Application in Geology; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1987; pp. 1–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.M.; Yang, N.Q.; Li, K.Q.; Ding, G.X. The metallogenesis and magmatic differentiation of Suzhou A-type granite. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1993, 9, 33–43, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Aylett, B.J. Group IIB. In Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 1–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.O. Cadmium in Zinc Deposits: Economic Geology of a Polluting Element. Int. Geol. Rev. 2000, 42, 445–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Pan, Z.P.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, T.G.; Xia, B. The present situation and prospects of geochemical researches on cadmium. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2005, 24, 339–348, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.X.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhou, G.F.; Li, X.B.; Ding, W.; Bao, G.P. Trace elements and rare earth elements of sulfide minerals in the Tianqiao Pb-Zn ore deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2011, 85, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fontboté, L.; Kouzmanov, K.; Chiaradia, M.; Pokrovski, G.S. Sulfide Minerals in Hydrothermal Deposits. Elements 2017, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.K.; Li, B.; Shen, P.; Zha, Z.H.; Lei, Z.; Wang, X.F.; Tao, S.Y.; Hu, Q. Trace elements in sulfide minerals from the Huangshaping copper-polymetallic deposit, Hunan, China: Ore genesis and element occurrence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Isozaki, Y.; Kimura, G.; Terabayashi, M. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present. Isl. Arc 1997, 6, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, J.F.; Ji, G.Y. A perspective on the geotectonic setting of early Cretaceous adakite-like rocks in the Lower Reaches of Yangtze River and its significance for copper-gold mineralization. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 297–314, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.D.; Ding, X.; Hu, Y.H.; Li, X.H. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2007, 262, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.D.; Ling, M.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Fan, W.M.; Ding, X.; Liang, H.Y. Oceanic ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization. Sci. China Ser. D 2010, 40, 127–137, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.J. The relationship of gypsum salt beds with endogenic copper and iron ores in the middle-lower Yangtze Valley. Geochimica 1980, 9, 193–199, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, D.X.; Lou, W.; Hu, Z.Q.; Liu, J.B. In situ LA-ICP-MS determination of trace elements in magnetite from a gypsum-salt bearing iron deposit and geochemical characteristics. Rock Miner. Anal. 2022, 41, 564–574. [Google Scholar]





| No. | Area | Rock Massif | Location (Approximate Center) | Outcrop Area (km2) | Lithology | Minerals | Sr-Nd | Hf-O | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ages (Ma) | (87Sr/86Sr) | εNd (t) | εHf (t) | δ18O‰ | |||||||||
| 1 | Fanchang | Banshiling | 30°59′59″ N | 118°11′06″ E | 16.29 | Biotite quartz monzonite | Kfs (45%) + Pl (35%) + Qtz (10%) + Bt (6%) | 125.3 ± 1.4 | - | - | - | - | [46] |
| 124.9 ± 1. 7 | 0.7072 | −6.8 | −2.7~−6.3 | 6.7~7.4 | [85,86] | ||||||||
| 125.3 ± 2.9 | - | - | - | - | [83] | ||||||||
| 125.4 ± 1.6 | 0.70827 | −11.2 | - | - | [89] | ||||||||
| 2 | Fanchang | Fushan | 31°09′05″ N | 118°03′08″ E | 15.25 | Syenogranite | Kfs (55%) + Qtz (30%) + Pl (5%) + Bt (5%) | 124.9 ± 2.0 | - | - | −5.8~−10.0 | - | [88] |
| 126.8 | - | - | −7.52 | - | [84] | ||||||||
| 126.4 ± 1.7 | 0.7076 | −7.7 | −1.6~7.9 | 7.1~9.1 | [85,86] | ||||||||
| 3 | Fanchang | Binjiang | 31°09′05″ N | 118°03′08″ E | 12 | Granitic porphyry | Kfs (60%) + Pl (20%) + Qz (15%) +Bt (5%) | 124.3 ± 2.5 | - | - | - | - | [83] |
| 124.6 ± 4.7 (coarse-grained granite) | 0.7078 | −3.4 | 0~−6.6 | 8.0~10.3 | [85,86] | ||||||||
| 123.0 ± 1.8 (granite porphyry) | |||||||||||||
| 4 | Fanchang | Xiangxingdi | 31°02′00″ N | 118°15′30″ E | 6 | Granitic porphyry | Qtz(25%) + Pl(70%) + Hb(2%) | 124.3 ± 1.2 | - | - | - | - | [89] |
| 5 | Fanchang | Suishan | 31°05′00″ N | 118°12′00″ E | - | Granite | Qtz(22%) +Pl(20%) + Kfs(53%) + Bt(4%) | 124.3 ± 1.2 | 0.70755 | −10.5 | - | - | [89] |
| 6 | Fanchang | Zhuhouling | 31°05′00″ N | 118°16′00″ E | 4.85 | Granitic porphyry | Kfs(70~80%) + Qtz(<5%) + Pl(10~15%) | 127.6 ± 1.8 | 0.70827 | −11.2 | - | - | [89] |
| 7 | Fanchang | Xiaoyang- chong | 31°05′30″ N | 118°07′00″ E | 0.13 | Quartz diorite and granodiorite | Kfs(15%) + Qtz(18~20%) + Pl(50~60%) + Bt(5~10%) | 126~128 | - | - | - | - | [113] |
| 8 | Chizhou | Huayuan- gong | 117°36′00″ N | 30°37′00″ E | 220 | Quartz syenite | Kfs(70~80%) + Qtz(<5%) + Pl(10%) | 126.2 ± 1.2 | 0.7081 | −6.7 | −7.4 | - | [93] |
| Syenogranite | Kfs(64~67%) + Qtz(25~33%) + Pl(2.5~3.0%) + Bt(1.0%) | 125.3 ± 1.2 [47] | -- | - | −7.3, −7.89 [42] | - | [42,46] | ||||||
| Quartz monzonite | Kfs(30~35%) + Qtz(5~10%) + Pl(45~55%) + Bt(3~6%) + Hb(2~4%) | 127 ± 1 | 0.709776 | −7.42 | - | - | [108] | ||||||
| Quartz syenite | Kfs(65~75%) + Qtz(5~10%) + Pl(7~9%) + Bt(1~3%) + Hb(1~4%) | 127 | 0.713653 | −7.67 | - | - | [108] | ||||||
| Syenogranite | Kfs(55~65%) + Qtz(5~10%) + Pl(2~5%) + Bt(1~2%) | 127 | 0.740000 | −7.97 | - | - | [108] | ||||||
| Syenogranite | 122.6 ± 1.3 | - | - | −4.7 | - | [92] | |||||||
| Syenogranite | 122.6 ± 1.3 | - | - | −6.7~−2.1 | - | [94] | |||||||
| 9 | Chizhou | Bashan | 117°38′00″ N | 30°35′00″ E | 40 | Syenogranite | Kfs(66%) + Qtz(25%) + Pl(2%) + Ab(5%) | 121.6 ± 2.8 | 0.7082~0.7091 | −7.2~−7.5 | - | - | [111] |
| 10 | Chizhou | Guilinzheng | 117°40′00″ N | 30°25′00″ E | - | Granitic porphyry | Kfs(40~60%) + Qtz(35~45%) + Pl(5~10%) + Bt(<5%) | 127.0 ± 0.5 [94]; 127.6 ± 1.5 [114] | - | - | −2.9~5.9 | - | [94,114] |
| 11 | Chizhou | Yangshan | 117°50′00″N | 30°30′00″ E | 30 | Syenitic porphyry | Kfs(40~45%) + Qtz(5~10%) + Pl(40~50%) | 127.0 ± 0.6 | 0.7107~0.7140 | −7.02~−5.78 | −5.5~−3.7 | - | [94] |
| Syenogranitic porphyry | Kfs(30~35%) + Qtz(55~65%) | 126.0 ± 1.0 | 0.7094~0.7065 | −6.03~−5.47 | −6.4~−4.4 | - | [94] | ||||||
| Syenogranite | - | 127.6 ± 0.6 | - | - | −7.5~−2.3 | - | [94] | ||||||
| 12 | Chizhou | Maotan | 117°47′00″ N | 30°42′00″ E | 25 | Syenite | Kfs(55~65%) + Qtz(30%) + Pl(10%) + Bt(2~5%) | 127.7 ± 1.8 | 0.70076 | −7.03 | - | - | [91] |
| Syenogranite | Kfs(76~79%) + Qtz(7~22%) + Pl(1~4%) + Bt(0.5~3%) | 125.4 ± 2.2 | - | - | - | - | [46] | ||||||
| 13 | Chizhou | Xiangshui- jian | 118°14′00″N | 31°02′00″ E | 20 | Syenogranite | Kfs(64~67%) + Qtz(22~28%) + Pl(2~3%) + Bt(5~8%) | 125.4 ± 1.4 | - | - | - | - | [46] |
| 14 | Anqing-Guichi | Dalongshan | 117°04′00″ N | 30°36′00″ E | 90 | Quartz syenite | Kfs(60~70%) + Qtz(10~15%) + Pl(10~15%) + Bt(<5%) | 125.8 ± 1.6, 126.4 ± 3.5 [112]; 123.8.4 ± 2.1 [84] | 0.706444 [115] | −6.8~−7.7 [115] | −4~+1.1,−7.8~−3.6 [112]; −3.41 [84] | - | [84,112,115] |
| 15 | Anqing-Guichi | Huashan | 117°09′00″ N | 30°42′00″ E | 21 | Syenogranite | Kfs(70%) + Qtz(20%) + Pl(10%) + Bt(<5%) | 126.2 ± 0.8; 124.4 ± 2.2 | - | - | −3.51 | - | [84] |
| 16 | Anqing-Guichi | Zongyang | 117°14′00″ N | 30°43′00″ E | 10 | Syenogranite | Kfs(70%) + Qtz(20%) + Pl(12%) + Bt(<1%) | 124.8 ± 2.2 [98]; 125.4 ± 1.5 [84] | - | - | −3.57 [84] | - | [84,98] |
| 17 | Anqing-Guichi | Chengshan | 117°14′00″ N | 30°46′00″ E | 19 | Syenogranite | Kfs(70%) + Qtz(20%) + Pl(8%) + Aegirine(a small amount) | 126.5 ± 2.1 [98] 125.0 ± 1.7 [84] | 0.7076 [115]; 0.70695~0.70742 [101] | −5.0, −6.3~−4.2 [101] | −4.72 [84] | - | [84,98,101,115] |
| 18 | Anqing-Guichi | Hejiaao | 117°13′00″N | 30°43′00″ E | 5 | Syenogranite | Kfs(75%) + Qtz(20%) + Pl(8%) + Ae(a small amount) | 128 ± 1 | 0.70795~0.70931 | −6.4~−5.8 | - | - | [101] |
| 19 | Anqing-Guichi | Meilin | 117°12′30″ N | 30°43′00″ E | 7 | Syenogranite | Kfs(75%) + Qtz(20%) + Pl(5%) + Ae(a small amount) | 128 ± 2 | 0.7364~0.7659 | −5.2, −6.0, −5.4 | - | - | [101] |
| 20 | Anqing-Guichi | Huangmeijian | 117°34′00″ N | 30°55′30″ E | 120 | Quartz syenite | Kfs(86%) + Qtz(12%) + Pl(<2%) | 127.6 ± 2.1; 127.2 ± 2.1 [112] | 0.7078 [115]; 0.7089 [110] | −7.7 [115]; −2.5 [110] | −3.3~+2.1 [112]; −3.8~−0.1 [112]; −3.38 [84] | - | [84,110,112,115,116] |
| 21 | Anqing-Guichi | Changgang | 117°12′00″ N | 31°20′00″ E | 0.5 | Syenogranitic porphyry | Kfs(45~55%) + Qtz(15~20%) + Pl(20~30%) + Bt(a small amount) | 120 ± 2 | 0.7082 | −14.9 | −18.3 | 5.99 | [100] |
| No. | Location | Related Intrusive Rock Type | Deposit | Ore Type | Amount | Grade | Type of Ore | Alteration | Ore Minerals | Metallogenic Age | Metallogenic Type | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Method | Age | ||||||||||||
| 1 | Fanchang | Banshiling, biotite quartz monzonite | Zishanling | Cu | No data | 0.35% | Copper-bearing limonite ore and copper-bearing marble ore | Marbleization, skarnization, silicification, and chloritization | Chalcopyrite, bornite, and limonite | - | - | - | Hydrothermal-type | [113] |
| 2 | Fanchang | Binjiang, granitic porphyry | Taochong | Fe, Zn | 34.71 Mt | 44.29% | Skarn-type iron ore | Skarnization, breccification, marblelization, and silicification | Magnetite, hematite, and specularite | - | - | - | Layered skarn-type | [164] |
| 3 | Fanchang | Suishan, granite | Suishan | Zn | 7331 t | 10% | Massive zinc ore, zinc-bearing skarn ore, zinc-bearing marble ore | Skarnization, dolomitization, carbonation, chloritization, silicification, etc. | Mainly sphalerite, pyrite, and cobaltite | - | - | - | Skarn-type | [77] |
| 4 | Fanchang | Suishan, granite | Songyuan | S(Fe) | No data | 28.35% | Pyrite ore | Garnet skarnization, carbonation, and silicification | Pyrite and specularite | - | - | - | Skarn-type | [77] |
| 5 | Fanchang | Xiaoyangchong, granodiorite | Xiaoyangchong | Zn (Fe) | Zn: 91,962 t; Fe: 2898 t | Zn: 6.7%; Fe: 37.97% | Massive zinc-iron ore, disseminated magnetite ore | Marbleization and skarnization | Sphalerite, magnetite, and hematite | Pyrite | Re-Os | 125.7 Ma | Skarn-type | [77] |
| 6 | Chizhou | Huayuangong, Syenogranite | Liwan | Cu | 40,000 t | 0.62% | Copper-bearing pyrite, copper-bearing sulfur skarn, lead-zinc skarn | Marbleization and skarnization | Chalcopyrite, bornite, sphalerite, pyrite, and molybdenite | - | - | - | Skarn-type | [92] |
| 7 | Chizhou | Guilinzheng, granitic porphyry | Guilinzheng | Mo (W) | 0.15 Mt | 0.13% | Disseminated ore and banded ore | Silicification, sericitization, skarnization, and serpentinization | Molybdenite, sphalerite, molybdenum-rich scheelite, magnetite, and galena | - | - | - | Skarn-type | [114,179] |
| 8 | Anqing-Zongyang | Dalongshan, quartz syenite | Dalongshan | U | Small deposit | 0.81% | Sandstone type ore and quartz syenite type ore | Hydromica, albitization, hematite, carbonation, silicification, pyritization, and chloritization | Pitchblende, microcrystalline quartz, hematite, and pyrite | Pitchblende | U-Pb isochron method | 130.0 Ma and 111.7 Ma | Hydrothermal-type | [178] |
| 9 | Anqing-Zongyang | Huangmeijian, quartz syenite | Dingjiashan | U | No data | 0.1~0.2% | Sandstone type ore and quartz syenite type ore | Silicification, carbonation, chloritization, discoloration, pyritization, brass mineralization, and kaolinization | Pitchblende and uranium | Pitchblende | U-Pb isochron method | 108.7 Ma | Hydrothermal-type | [176] |
| 10 | Anqing-Zongyang | Huangmeijian, quartz syenite | Xucun | U | No data | 0.28% | Felsic sandstone type and quartz syenite type | Silicitization, pyritization, carbonatization, greenization, and hydromicatization | Pitchblende and uranium | Single mineral zircon in pitchblende | U-Pb | 108 ± 1.5 Ma and 71.3 ± 1.0 Ma | Hydrothermal-type | [116] |
| 11 | Anqing-Zongyang | Huangmeijian, quartz syenite | Makou | Fe | 0.08 Mt | No data | Reticulated and massive magnetite ore | Potassic mineralization | Magnetite, apatite, pyrite, and sphalerite | Phlogopite | 40Ar-39Ar | 127.3 ± 0.8 Ma | Hydrothermal-type | [175] |
| Name of Mine | Exploration Stage | Ore Type | Associated Key Metal and Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xiaoyangchong zinc-iron mine | Mining | Massive sphalerite and magnetite ores | Cd: 100–900 ppm |
| Suishan zinc mine | Mineral prospecting | Sphalerite ore and pyrite ore | Cd: 1111 ppm Se: 25–60 ppm |
| Shunfengshan iron mine | Detailed mineral prospecting | Magnetite ore | Ga: 21 ppm |
| Fuchengdun copper mine | Mineral prospecting | Chalcopyrite ore | Cd: 100 ppm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, L. Evolution, Magmatic Source and Metallogenesis of A-Type Granites in the Fanchang Volcanic Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: A Review. Minerals 2023, 13, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040571
Zhang S, Yang X, Liu L. Evolution, Magmatic Source and Metallogenesis of A-Type Granites in the Fanchang Volcanic Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: A Review. Minerals. 2023; 13(4):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040571
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Songsong, Xiaoyong Yang, and Lei Liu. 2023. "Evolution, Magmatic Source and Metallogenesis of A-Type Granites in the Fanchang Volcanic Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: A Review" Minerals 13, no. 4: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040571
APA StyleZhang, S., Yang, X., & Liu, L. (2023). Evolution, Magmatic Source and Metallogenesis of A-Type Granites in the Fanchang Volcanic Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: A Review. Minerals, 13(4), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040571