Abstract
Dongcao muscovite granite, as the product of the second stage of the magmatic intrusion of the Ganfang composite pluton, is closely related to the mineralization of Li–Nb–Ta rare metals in the Yifeng area. This paper aims to discuss the diagenetic age, evolutionary process, and relationship with the rare metal mineralization of Dongcao muscovite granite by using petrographic, cassiterite U–Pb dating and geochemical analyses. Petrographic analysis shows that the lithology of the Dongcao muscovite granite is medium– to fine–grained muscovite monzogranite. The cassiterite U–Pb dating results show that the diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite is 139.7 ± 6.7 Ma, which is Early Cretaceous. The geochemical analysis indicates that the rock is characterized by high Si, abundant aluminum alkalis, low Ca and Fe, and low Mg, which indicates that this granite is a strongly peraluminous rock. Moreover, the Dongcao muscovite granite is enriched with Rb, U, Ta, Pb, P, and Hf and depleted of Ba, Sr, Ti, and rare earth elements (REEs), with a tetrad effect of REEs. Based on this analysis, the Dongcao muscovite granite is a highly differentiated granite that formed in the tectonic transition from continental collisional to post–collisional settings related to the subduction of the Paleo–Pacific plate. A high degree of crystallization differentiation occurred at the early stage of magmatic evolution, resulting in the initial enrichment of Li–Nb–Ta–Sn. The melt–fluid interaction in the late stage is significant to the high enrichment of Li–Nb–Ta–Sn until the final mineralization.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the new global energy industry, the demand for rare metals, such as lithium, is increasing daily [1]. Major countries and economies have formulated strategic policies and launched a fierce competition for resources [2,3,4]. Major mining companies, geological prospecting units, universities, and scientific research institutes have conducted fundamental investigations and research work. As one of the critical Li–Nb–Ta rare–metal–ore–producing areas in Jiangxi Province, the Yifeng area has attracted much attention. Many Li deposits/Li–bearing porcelain stone deposits have been found in this area, such as the Xikeng (139.09 ± 0.56 Ma) [5], Baishili, Shiziling (141.3 ± 1.5 Ma), Dagang, and Baishuidong (144 ± 5 Ma; 146.3 ± 1.08 Ma) deposits [6,7]. Among them, the Dagang deposit is a super–large Li–bearing porcelain stone deposit with 39.01 million tons of Li2O resources [8]. The ore-bearing rocks in the Yifeng area are mainly altered granite, followed by felsite and aplite, and the ore–bearing mineral is lepidolite, followed by trilithionite [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Previous studies indicate that the formation of these deposits is closely related to the Yanshanian magmatic activity in the area, and the Ganfang composite pluton is a vital ore–forming and ore–hosting pluton [8,9,11,12]. This composite pluton was formed mainly in the early Jurassic and had the characteristics of multi–period magmatic activity [6]. According to the types of magmatic rocks and their relationships, studies have divided them into two stages [12]. Among them, the granitoids that formed in the Early Yanshanian are dominated by altered granite–type and surface–type rare metal mineralization. Deposits related to this kind of mineralization occurred mainly in the Eastern Ganfang composite pluton, such as the Baishuidong deposit (144 ± 5 Ma; 146.3 ± 1.08 Ma) [6,7]. In addition, researchers have also argued that the highly differentiated evolution of granite and the fluid–melt interaction in the late stage are essential metallogenic mechanisms in this region [8]. The granitoids that formed in the late Yanshanian are characterized mainly by pegmatite, aplite, and felsite dikes with Li–bearing porcelain stone lodes [10,12,13]. However, existing studies, including those on the diagenetic and metallogenic ages, tectonic formation setting, and the relationship between diagenesis and rare metal mineralization, are focused on the middle–eastern part of the Ganfang composite pluton. In addition, research on the Dongcao muscovite granite in the middle–western part of the Ganfang composite pluton is still weak.
In this paper, the Dongcao muscovite granite, which is closely related to surface–type rare metal mineralization, was selected as the research object in this work. Based on field geological investigation, systematic petrographic, laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (LA–ICP–MS) cassiterite U–Pb dating, and whole–rock geochemical analyses were carried out. The diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite was determined, its evolutionary process and tectonic setting were analyzed, and the relationship between the Ganfang composite pluton and rare metal mineralization is discussed, which can provide some guidance for rare metal prospecting in the region.
2. Geological Background and Sample Description
2.1. Geological Background
The Yifeng area is one of the most important producing areas of lithium and other rare metals in the northwestern part of Jiangxi Province. This area, which is part of the conjunction zone of the Yangtze Plate and Cathaysia Plate (Figure 1a), is located in the southeastern part of the Jiuling thrust uplift, and the northeastern part of the Pingxiang–Leping depression belt (Figure 1b) [14]. The exposed strata associated with the folded basement are mainly Neoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, which is composed mainly of muscovite quartz schist, two–mica schist, and muscovite schist [7,13]. The fault structures in this region are mainly NE–trending. The convergence of the Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous NE–trending strike–slip faults and nearly EW–trending fault controls the occurrence of the intrusions. Moreover, the NNE–trending faults and nearly EW–trending faults also control the occurrence of ore–bearing dikes [13]. A large area of Mesozoic granitoids is exposed, such as in the case of the Ganfang and Guyangzhai composite plutons [15]. Among them, the Ganfang composite pluton is exposed mainly in the Shangfu–Ganfang–Tangshan area, which is approximately 30 km long from east to west and 16 km wide from north to south, and it covers an area of approximately 400 km2 (Figure 1c) [12].
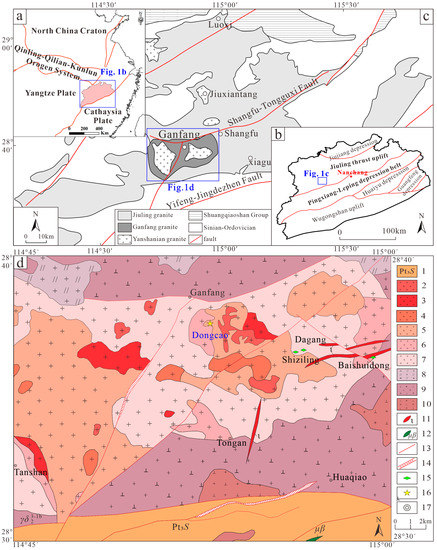
Figure 1.
Geological map of the study area: (a). geotectonic sketch map of Eastern China (modified from [16]); (b). tectonic schematic map of the study area (modified from [17]); (c). structural map of the study area (modified from [9]); (d). geological sketch map of the study area (modified from [12]). (Legend description of (d): 1. Upper Proterozoic Shuangqiaoshan Group; 2. first stage of Late Yanshanian intrusive granite; 3. third intrusive granite in the second stage of the Early Yanshanian; 4. second intrusion of granite in the second stage of the Early Yanshanian; 5. first granite intrusion in the second stage of the Early Yanshanian; 6. second intrusion of granite in the first stage of the Early Yanshanian; 7. first intrusion of granite in the first stage of the Early Yanshanian; 8. first intrusion of monzogranite in the second stage of the Late Jinningian; 9. second intrusion of granodiorite in the first stage of the Late Jinningian; 10. the first intrusion of diorite porphyry in the first stage of the Late Jinningian; 11. aplite/felsite; 12. spilite basalt; 13. crushing zone; 14. fault structure; 15. Li–bearing porcelain ore deposit; 16. sampling location; 17. township).
Studies have shown that the Ganfang composite pluton was formed mainly in the Late Jurassic and experienced multi–stage magmatic intrusive activities, which can be roughly divided into two periods and three stages [12]. The long and complicated magmatic intrusive evolutionary process led to the composite and diverse lithology of the Ganfang composite pluton. The lithology of this composite pluton generally presents a transition from medium– to coarse–grained porphyritic biotite granite to medium– to coarse–grained porphyritic two–mica granite to medium– to fine–grained porphyritic two–mica granite to medium– to fine–grained muscovite albite granite. At the same time, in the latest stage of magmatic intrusion, there are more granitic pegmatite, pegmatite, aplite, and felsite dikes in the Ganfang composite pluton (Figure 1d) [11,12]. Most of the lithium deposits in this region occur in the contact zone between the granitoids. In addition, the Ganfang composite pluton has generally undergone auto–metasomatism, and the metamorphic types include mainly potassium feldsparization, albitization, lithiomization, greisenization, and fluoridation. The degree of metamorphism from old to new shows a trend from weak to strong. In other words, the autometamorphism is weak in the first stage of the early Yanshanian and gradually increases in the second stage of the early Yanshanian. It peaked in the late second stage, then dropped sharply, gradually increased to the first stage of the late Yanshanian period, and then formed a peak in the late Yanshanian period [12]. Strong autometamorphism (metasomatism) promoted the enrichment of rare elements, such as Li, Rb, Cs, Nb, and Ta, in the Ganfang composite pluton, forming a large number of rare metal deposits or occurrences, which renders the Yifeng area one of the critical rare metal ore–producing areas in Jiangxi Province, South China [9].
2.2. Sample Description
The Dongcao muscovite granite is exposed mainly in Dongcao village, Southeastern Ganfang town. It is located in the middle–western part of the Ganfang composite pluton, which is part of the product of the second stage of magmatic intrusion in the early Yanshanian. In total, 5 samples of Dongcao muscovite granite (DC1, DC2, DC3, DC4, and DC5) were collected from Ganfang town, which is located 2.5 km northeast of Dongcao village at coordinates 114°53′05′′ E and 28°37′06′′ N (yellow star in Figure 1d). Each sample is approximately 12 cm long, 11 cm wide, and 9 cm thick.
3. Methodology
3.1. Petrographic Identification
Five typical rock samples (i.e., DC1, DC2, DC3, DC4, and DC5) were selected, cut, and ground into 3 mm thick sheets. The preparation of rock samples and petrographic identification were completed in the Mineralogy Laboratory of the China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), and the petrographic identification was completed under a Leica DM4P polarizing microscope.
3.2. Laser Ablation–Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry (LA–ICP–MS) Cassiterite U-Pb Dating
The Dongcao granite sample (DC4) was analyzed. Sample preparation, including crushing, gravity, magnetic separation, cassiterite sample selection, and target preparation, was completed mainly by Guangzhou Tuoyan Testing Technology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). LA–ICP–MS cassiterite U–Pb dating was completed at the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources (GPMR), China University of Geosciences (Wuhan, China). The analytical instruments are the Coherent GeoLas Pro 193 nm laser denudation system and ThermoFisher iCAP RQ inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. The laser ablation spot beam is 50 μm, the laser pulse frequency is 8 Hz, and the energy density is 4 J/cm2. The AY–4 cassiterite standard sample (206Pb/238U age is 158.2 ± 0.4 Ma [18]) that accurately yielded the ID–TIMS U–Pb age was used as the external isotope calibration standard sample. The cassiterite 207Pb/206Pb–238U/206Pb Tera–Wasserburg harmonic diagram was drawn by using Isopolot 3.0 software [19].
3.3. Whole Rock Geochemical Analysis
All the Dongcao granite samples were selected and crushed to less than 200 mesh for whole–rock geochemical analysis. The major, trace, and rare earth element tests of the whole rock were completed at Guangzhou Aoshi Analysis and Testing Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).
The major elements were analyzed by the ME–XRF26F method in a Dutch PANalytical PW2424 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. The specific procedure was as follows: 2 samples were weighed, 1 sample was taken and dried at 105 °C, the required weight was accurately weighed into the platinum crucible, the mixed flux of lithium tetraborate–lithium metaborate–lithium nitrate was added, and it was melted in a high-precision fusion machine at 1050 °C. The molten slurry was poured into the platinum mold and cooled to form a melt sheet, and then the X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (fluorine-containing mode) was used to determine the principal quantity. At the same time, another dry sample was accurately weighed, aerobically burned in a muffle furnace at 1000 °C, and then accurately weighed after cooling. The weight difference between the sample before and after burning is the loss on ignition (LOI), and the sum of LOI and the element content measured by XRF (the total amount is expressed as an oxide) is the “total”. The relative error of the precision control is less than 5%, and the relative error of accuracy control is less than 5%.
The analytical method for trace elements was ME-MS61r, which was tested by the American Agilent 5110 inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and the American Agilent 7900 inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. The sample was weighed in a Teflon test tube and dissolved in perchloric acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and hydrochloric acid, and the volume was determined with dilute hydrochloric acid before being analyzed with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and a plasma mass spectrometer; the final analysis result was obtained after the spectral interference between elements was corrected. The relative error of the precision control is less than 10%, and the relative error of the accuracy control is less than 10%.
The rare earth element (REE) analysis method was ME-MS81, and the test was carried out by an American Agilent 7900 inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. The test steps were as follows: lithium borate (LiBO2/Li2B4O7) flux was added to the sample, mixed evenly, and melted in a furnace at 1025 °C. After cooling, the molten liquid was dissolved with nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and hydrofluoric acid and then analyzed via a plasma mass spectrometer. The relative error of the precision control is less than 10%, and the relative error of the accuracy control is less than 10%.
4. Analytical Results
4.1. Petrographic Characteristics
According to field observations, strong albitization is generally developed in the pluton (Figure 2a,b).
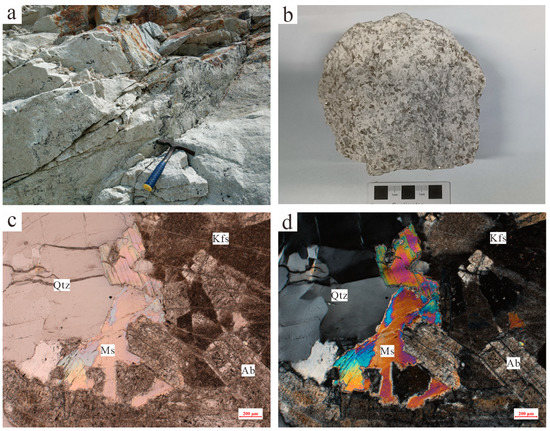
Figure 2.
Field pictures and microphotographs of the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). field outcrops; (b). hand specimens; (c). sample photograph under a single polarizer microscope; and (d). sample photograph under an orthogonal optical microscope. (Legend description: Qtz, Kfs, Ab, and Ms denote quartz, alkali feldspar, albite, and muscovite, respectively).
The fresh surface of the sample is mainly white with a medium- to fine-grained granite texture and a massive structure. The main minerals are quartz (35%), alkali feldspar (30%), plagioclase (25%), and muscovite (10%). Among them, quartz is distributed mainly among other mineral grains in a xenomorphic granular form, with particle sizes ranging from 1 mm to 4 mm; alkaline feldspar is allomorphic granular or subhedral tabular, and its surface is turbid due to kaolinization; plagioclase has a high degree of idiomorphism, is mainly in the shape of idiomorphic–subhedral laths, has apparent lamellar twins, and is composed primarily of albite; mica is typically muscovite, appears mainly in a sheet shape, and has particle sizes ranging from 0.5 mm to 2 mm. At the same time, small amounts of zircon, cassiterite, apatite, and other accessory minerals are visible, and they are distributed mainly among feldspar, quartz, and dolomite parent grains in an euhedral to subhedral granular form (Figure 2c,d).
4.2. Cassiterite U–Pb Dating
The cassiterite in the Dongcao muscovite granite sample (DC4) is distributed mainly among quartz, muscovite, and feldspar grains in the form of semi-euhedral particles, which are grayish white or brownish red, with a particle size range of 100 μm to 200 μm and a length to width ratio of 2:1 to 1:1 (Figure 3a). The reflected light and cathodoluminescence (CL) images show that the structure of the cassiterite mineral is simple, the surface is clean, a small number of cassiterite mineral inclusions are visible, and cracks are not developed (Figure 3b,c), indicating that the cassiterite mineral is an ideal sample for U–Pb dating. According to the shape, structure, and distribution of cassiterite, it can be inferred that it is of magmatic crystallization origin. Moreover, the U–Pb age of cassiterite can approximately represent the diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite.
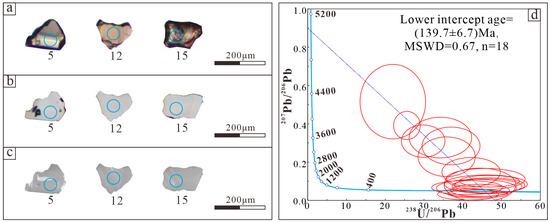
Figure 3.
Cassiterite U–Pb dating results of the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). transmitted image; (b). reflected image; (c). CL image; (d). cassiterite U–Pb Tera–Wasserburg Concordia diagram.
A total of 18 effective testing points of the Dongcao muscovite granite sample (DC4) was obtained (Table 1). The 207Pb/206Pb ratios range from 0.0317 to 0.5157, the 207Pb/235U ratios range from 0.1055 to 3.2386, and the 238U/206Pb ratios range from 21.95 to 46.95. Because the T–W diagram does not need to consider the correction of 206Pb/204Pb or common Pb and has an excellent analytical effect for samples with higher normal Pb, the obtained age value is relatively reliable [20,21]. Therefore, in this paper, a Tera–Wasserburg Concordia diagram is used to invert the age of cassiterite. The result shows that the lower intersection age of the concordance diagram is 139.7 ± 6.7 Ma (mean squared weighted deviation, MSWD = 0.67) (Figure 3d), indicating that the diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite is Early Cretaceous.

Table 1.
LA–ICP–MS U–Pb isotope data of cassiterite from the Dongcao muscovite granite.
4.3. Geochemical Analysis
The main composition of the Dongcao muscovite granite is generally characterized by high contents of Si, Al, and alkali; low contents of Ca and Fe; and low contents of Mg and Ti. Among them, the content ranges (wt.%) of SiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, TFe2O3, CaO, P2O5, MgO, and MnO are 72.57~73.93, 15.08~15.64, 3.43~4.15, 3.35~3.61, 0.90~1.00, 0.36~0.80, 0.36~0.69, 0.01~0.03, and 0.13~0.17, respectively. The content of TiO2 is lower than the detection limit (0.01 wt.%). The total alkali contents (K2O + Na2O) of the Dongcao muscovite granite range from 7.01 to 7.50 wt.%, indicating that the granite is relatively rich in Na (the Na2O/K2O ratios range from 0.95 to 1.24, with an average value of 1.08) (Table 2). According to the total alkali–silica (TAS) diagram [22], all the samples plot in granite areas, showing characteristics of the subalkaline series (Figure 4a). In the K2O vs. SiO2 (wt.%) diagram, all the samples plot in the high–K series area, while in the (K2O + Na2O–CaO) vs. SiO2 (wt.%) diagram, all the samples plot in the calc–alkaline granite area (Figure 4b,c). In addition, the Rittmann index (σ = (Na2O + K2O)2/(SiO2 − 43) (wt.%)) values range from 1.62 to 1.82. These results show that the Dongcao muscovite granite is characteristic of the high–K calc–alkaline series. Additionally, the molar ratio Al2O3/(Na2O + K2O + CaO) or the A/CNK values are relatively high, ranging from 1.34 to 1.44, with an average of 1.39. The molar ratio Al2O3/(Na2O + K2O) or the A/NK values range from 1.47 to 1.64. In the A/NK vs. A/CNK diagram, all the sample plot in the area of peraluminous granite (Figure 4d). Collectively, the Dongcao muscovite granite is a Na–rich, peraluminous, high–K calc–alkaline granite.

Table 2.
Major element (wt.%), trace element (mg/kg), and rare earth element (mg/kg) concentrations of Dongcao muscovite granite.
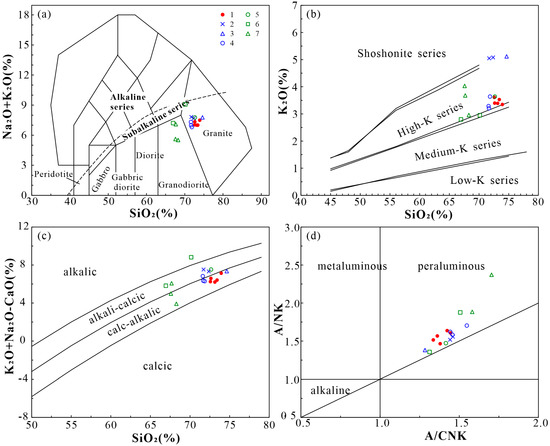
Figure 4.
Major element diagrams of the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). TAS diagram (the base map is derived from [22]); (b). K2O vs. SiO2 diagram (the base map is derived from [23]); (c). (K2O + Na2O + CaO) vs. SiO2 diagram (the base map is derived from [24]); (d). A/NK vs. A/CNK diagram (the base map is derived from [25]). (Legend descriptions: the red dots are data of the Dongcao muscovite granite samples in this paper; the blue crosses are data of the Dagang protolothionite muscovite granite; the blue triangles are data of the Dagang pegmatitic dike; and the blue circles are data of the Dagang lepidolite alkali–feldspar granite [8]; the green circles are data of the Baishuidong Li–rich muscovite granite; the green rectangles are data of the Baishuidong trilithionite granite; and the green triangles are data of the Baishuidong aplite [7].).
The REE contents in the Dongcao muscovite are relatively low; the total rare earth element (ΣREE) contents range from 1.28 mg/kg to 5.64 mg/kg, with an average of 2.86 mg/kg (element contents lower than the detection limit were calculated by using half of the lowest detection limit). The light rare earth element/heavy rare earth element (LREE/HREE) ratios range from 1.25 to 5.64, with an average of 2.65, and the (La/Yb)N ratios vary from 1.30 to 9.22, with an average of 3.70. From the chondrite–normalized REE pattern diagram, it is evident that the samples showed a tetrad effect (e.g., the TE1,3 values range from 1.07 to 1.46, with an average of 1.29) and the content of Eu is relatively depleted (Figure 5a). From the primitive–trace element pattern diagram, it is clear that the Dongcao muscovite granite shows characteristics of enrichment in Rb, U, Ta, Pb, P, and Hf and depletion in Ba, Sr, Ti, REEs, and other elements (Figure 5b).
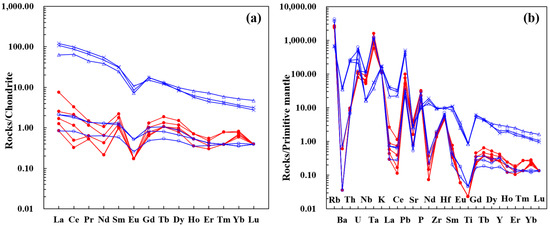
Figure 5.
Distribution patterns of REEs and trace elements in the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). chondrite–normalized REE patterns; (b). primitive mantle–normalized trace element patterns. (Legend description: the red dots are data of the Dongcao muscovite granite samples in this paper; the blue crosses are data of the Dagang protolothionite muscovite granite; the blue triangles are data of the Dagang pegmatitic dike; and the blue circles are data of the Dagang lepidolite alkali–feldspar granite [8]. The standardized data of chondrites and primitive mantle are from [26].).
5. Discussion
5.1. Diagenetic and Metallogenic Age
Zircon is rich in Th and U, with a low content of ordinary Pb and a high closure temperature of the U–Th–Pb system, making it an ideal isotope dating mineral, especially for magmatic rocks [27]. However, high U contents and detrital zircons commonly occur in highly differentiated granites that are associated with the mineralization of rare metals [28]. When these zircons are dated via LA–ICP–MS, the “high U matrix effect” in the calibration of U/Pb fractionation results in unreliable ages [29,30]. The Yanshanian granites of the Ganfang composite pluton are highly differentiated peraluminous granites. The zircons in these granites are high–uranium zircons, making it difficult to date the granites in this area. Cassiterite minerals with a high content of U are also commonly developed in these granites but are not prone to deviation. Therefore, it is necessary and feasible to date the highly differentiated peraluminous granites with U–Pb isotopes via cassiterite minerals [31].
The Dongcao muscovite granite is distributed in the Dongcao village area in the middle of the Ganfang composite pluton. It is the product of the second stage of the early Yanshanian magmatic intrusion and is closely related to the mineralization of altered granite–type rare metals in the area. According to Section 4.2, the concordant age of the Dongcao muscovite granite is 139.7 ± 6.7 Ma (MSWD = 0.67), indicating that the Dongcao muscovite granite was formed in the Early Cretaceous. U–Pb dating of columbite in the Baishuidong lepidolite granite in the Eastern Ganfang composite pluton was carried out by using LA–ICP–MS, and concordant ages were obtained, namely, 144 ± 5 Ma [7]. At the same time, the zircon U–Pb age of the Shiziling muscovite granite with rare metal mineralization in the middle of the Ganfang composite pluton is 141.3 ± 1.5 Ma [11]. The U–Pb ages of cassiterite in the Dongcao muscovite granite that were obtained in this paper are consistent with these two ages in the error range, which clearly indicates that the mineralization of rare metals in the altered granite type in the Ganfang area may have occurred mainly in the Early Cretaceous (~140 Ma).
5.2. Genesis and Evolution Processes
Different genetic types of granites usually have different magmatic origins, formations, and evolutionary processes. The Dongcao muscovite granite has a high Ga/Al ratio (ranging from 4.01 to 4.29, with an average of 4.14) and is enriched with Rb, U, Ta, Pb, P, and Hf and depleted of Ba, Sr, Zr, Ti, REEs, and other elements, showing characteristics of A-type granites [32,33,34,35,36]. However, many scholars have found that the I-type and S-type granites with excessive differentiation also have a relatively high Ga/Al ratio (e.g., higher than 2.6) and are enriched with high field strength elements (HFSEs), which are similar to A-type granites [37,38,39]. The Dongcao muscovite granite has a high differentiation index (the sum of normative percentages of quartz, orthoclase, albite, nepeline, leucite, and kalsilite) [40] values (varying from 89.97 to 92.34, with an average of 90.95), Rb values (ranging from 1490 mg/kg to 1695 mg/kg, with an average of 1602 mg/kg), and Cs values (ranging from 210 mg/kg to 247 mg/kg, with an average of 229 mg/kg); low K/Rb ratios (ranging from 17.95 to 19.46, with an average of 18.59); low Nb/Ta ratios (ranging from 0.97 to 1.55, with an average of 1.27); and low Zr/Hf ratios (ranging from 10.71 to 12.86, with an average of 11.62), indicating that it has experienced high crystallization differentiation and is a highly differentiated granite [39,41,42,43]. In the Zr vs.10,000 Ga/Al and the (K2O + Na2O)/CaO vs. Nb + Zr + Ce + Y diagrams, the sample points also plot in the highly differentiated granite area (Figure 6a,b), indicating that it is a highly differentiated I-type or S-type granite. In addition, cordierite is not found in the rock. At the same time, a large amount of muscovite is developed, so the high Al2O3 contents (ranging from 15.08 wt.% to 15.64 wt.%, with an average of 15.36 wt.%) and A/CNK values (ranging from 1.34 to 1.44, with an average of 1.39) may be caused by the high content of aluminum-rich muscovite that is formed by the highly differentiated evolution of magma. At the same time, although the sample has a high P2O5 range (0.36 wt.%~0.69 wt.%), it shows a significant downward trend, with an increasing SiO2 content (Figure 6d), which is contrary to the positive correlation or the inconspicuously changed correlation of differentiated S-type granite but is consistent with the differentiated I-type granites [37,44,45]. In the Na2O vs. K2O discrimination diagram, the sample points plot mostly in the area of I-type granites (Figure 6c). In conclusion, the Dongcao muscovite granite is a highly differentiated I-type granite. However, this conclusion still needs to be supported by other evidence, such as a Sr-Nd isotope.
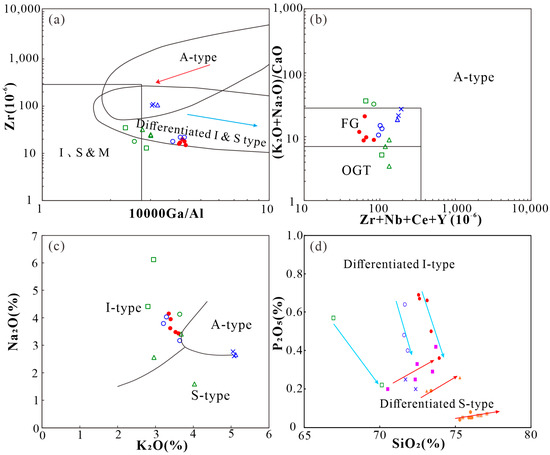
Figure 6.
Discrimination diagrams of the petrogenesis type for the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). Zr vs. Ga/Al discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [39]); (b). (K2O + Na2O)/CaO vs. (Nb + Zr + Ce + Y) discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [46]); (c). Na2O vs. K2O discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [47]); (d). P2O5 vs. SiO2 discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [48]). (Legend description: the red dots are data of the Dongcao muscovite granite samples in this paper; the blue crosses are data of the Dagang protolothionite muscovite granite; the blue triangles are data of the Dagang pegmatitic dike; and the blue circles are data of the Dagang lepidolite alkali–feldspar granite [8]; the green circles are data of the Baishuidong Li–rich muscovite granite; the green rectangles are data of the Baishuidong trilithionite granite; and the green triangles are data of the Baishuidong aplite [7]; the purple rectangles are data of differentiated S–type granite [44]; the orange circles are data of Tieshanlong porphyroid biotite granite; the orange rectangles are data of Tieshanlong two–mica granite; and the orange triangles are data of Tieshanlong granite porphyry [45].).
Studies show that Sr tends to enter plagioclase during the evolution of magmatic crystallization differentiation, and the fractional crystallization of plagioclase leads to a decrease in the Sr content and an increase in the Ba/Sr ratio in residual magma. While Ba tends to enter potassium feldspar, the fractional crystallization of potassium feldspar usually leads to a decrease in the Ba content and Ba/Sr ratio in residual magma [37,49]. The Dongcao muscovite granite has noticeable depletions in Ba and Sr, and the lack of Ba is severe. The Ba content in most samples is lower than the detection limit, indicating that they have experienced vital feldspar mineral fractional crystallization in the evolutionary process and mainly potassium feldspar fractional crystallization, which is more consistent with the discrimination results of sample points in the Ba vs. Rb and Rb/Sr vs. Sr discrimination diagrams (Figure 7a,b). There is an apparent negative Ti anomaly in the rocks, which is generally believed to be caused by the fractional crystallization of Ti–rich minerals, such as rutile, ilmenite, and sphene. These minerals are also the main host minerals of Nb and Ta. If apparent fractional crystallization occurs, the Nb and Ta contents in the residual magma are also reduced, contrary to the relative enrichment of Nb and Ta in the Dongcao muscovite granite. Stepanove et al. proposed that the fractional crystallization of biotite, a Ti–rich silicate mineral, consumes the Ti in the magma and promotes the continuous enrichment of Nb and Ta and the reduction in the Nb/Ta ratio in the residual magma [50]. Therefore, the Nb, Ta, and Ti anomalies in the Dongcao muscovite granite may be caused by the fractional crystallization of biotite, which is different from Ta/Nb. The distribution characteristics of sample points in the Ta/Nb vs. Ta discrimination diagrams are relatively consistent (Figure 7c). In the (La/Yb)N vs. La discrimination diagram, the distribution of sample points is fairly consistent with the changing trend of elements under the separate crystallization of monazite, epidote, and other minerals (Figure 7d), indicating that the different crystallization of monazite, epidote, and other abundant and rare earth minerals may cause a substantial loss of rare earth elements in the rock. According to the comprehensive petro–geochemical characteristics and discrimination results, the Dongcao muscovite granite experienced a high degree of differentiation and evolution during its formation. It may have undergone intense fractional crystallization of potassium feldspar, biotite, monazite, allanite, and other minerals.
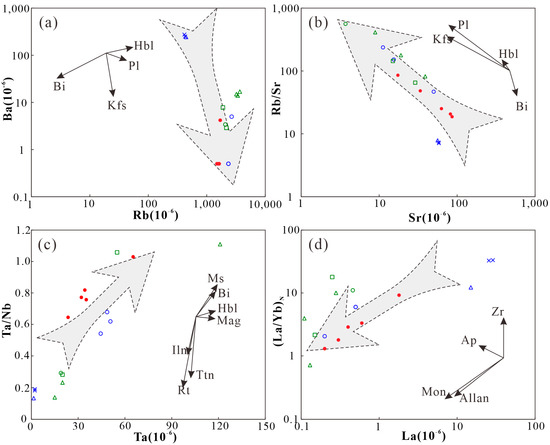
Figure 7.
Discrimination diagrams of the fractional crystallization processes of the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). Ba vs. Rb discrimination diagram; (b). Rb/Sr vs. Sr discrimination diagram; (c). Ta/Nb vs. Ta discrimination diagram; (d). (La/Yb)N vs. La discrimination diagram. (Legend description: Pl: plagioclase; Kfs: potassium feldspar; Bi: biotite; MS: muscovite; Hbl: hornblende; Mag: magnetite; Ilm: ilmenite; Rt: rutile; Ttn: sphene; Zr: zircon; Ap: apatite; Mon: monazite; Allan: epidote. The red dots are data of the Dongcao muscovite granite samples in this paper; the blue crosses are data of the Dagang protolothionite muscovite granite; the blue triangles are data of the Dagang pegmatitic dike; and the blue circles are data of the Dagang lepidolite alkali–feldspar granite [8]; the green circles are data of the Baishuidong Li–rich muscovite granite; the green rectangles are data of the Baishuidong trilithionite granite; and the green triangles are data of the Baishuidong aplite [7]).
Studies have noted that rare metal mineralization in South China is often closely related to fluorine–rich felsic rocks. The fluorine–rich felsic system in South China is further divided into high–phosphorus subtypes (P2O5 > 0.4 wt.%) and low–phosphorus subtypes (P2O5 < 0.1 wt.%), according to the P2O5 content in the rocks. Among them, the high–phosphorus subtypes are characterized by low Si (<73 wt.%), high Al (>14 wt.%), and low REE contents and generally have experienced two stages of formation and evolution, namely, early magmatic crystallization differentiation and late melt–fluid interaction [48,51,52,53,54,55,56]. The Dongcao muscovite granite has high F (ranging from 0.6 wt.% to 0.7 wt.%), P2O5 (ranging from 0.36 wt.% to 0.69 wt.%, with an average of 0.58 wt.%), and Al2O3 (ranging from 15.08 wt.% to 15.64 wt.%) contents; medium–high SiO2 contents (ranging from 72.57 wt.% to 73.93 wt.%, with an average of 73.14 wt.%); and meager total rare earth element contents (ΣREE = 1.28~5.64 mg/kg). These values are more consistent with the high–phosphorus and fluorine–rich felsic system, indicating that it may also have undergone two stages of formation and evolution; that is, the Dongcao muscovite granite may have also experienced melt–fluid interaction in its late evolution, in addition to the early high degree of crystallization differentiation. Ballouard et al. proposed that peraluminous granites can be divided into typical crystallization differentiation origins and magma hydrothermal interaction origins by Nb/Ta = 5 [43]. Bau also proposed Zr/Hf = 26 as the magmatic–hydrothermal boundary of the granite system [57]. At the same time, with the proposal of the tetrad effect of rare earth elements in rocks and the deepening of research, many scholars also regard it as an important symbol of melt–fluid interaction in late magmatic evolution [58,59]. The Dongcao muscovite granite shows low Nb/Ta (0.97~1.55) and Zr/Hf (10.71~12.86) ratios, and it also shows a significant tetrad effect in terms of rare earth elements (TE1,3 = 1.07~1.46, average of 1.29), indicating that it experienced strong melt–fluid interaction in the late evolution.
In summary, the Dongcao muscovite granite is a highly differentiated I-type granite, which experienced a high degree of crystallization differentiation evolution in the early stage and melt–fluid interaction in the late stage.
5.3. Tectonic Setting
The Lower and Middle Jurassic strata are present in the Jiangnan Orogen, while the Upper Jurassic strata are absent. The lithology is dominated by fluvial and lacustrine sedimentary facies [15,60]. The overlying Cretaceous strata have complex and diverse rock types, including eruptive volcanic rocks and clastic sedimentary rocks. The composition of clastic rocks is complex, with various sedimentary modes, which are the products of a typical extension environment. The unconformity between the Jurassic and Cretaceous strata indicates that this region may undergo a crustal uplift process during this period, resulting in discontinuous sedimentation. In addition, regarding the regional structure, fold deformation generally occurred in the Carboniferous–Middle Jurassic strata, while it only partially occurred in the Cretaceous strata. At the same time, in the Middle and Late Jurassic, the tectonic activity in the region was intense, and many thrust faults were formed. In the Cretaceous, the tectonic activity became weaker. The faults were mainly normal faults [60]. The above evidence indicates that the region may have experienced a compressional–collisional orogeny in the Middle–Late Jurassic. In the Cretaceous, the area was affected mainly by the subduction of the ancient Pacific plate, and the tectonic environment gradually changed to a post–collisional extensional environment.
Researchers have also shown that under the influence of the closure of the northern Paleo–Tethyan Ocean and the northwestward subduction of the Paleo–Pacific plate, a large-scale hedged thrust occurred in this region during the Indosinian–Yanshanian stage. Influenced by the collision of the North China block and the South China block along the Dabie Mountain, the Northern Jiuling mountain system thrust southward along the Yifeng–Jingdezhen fault zone, while the southern Wugongshan mountain system thrust southward along the Pingxiang–Guangfeng fault zone. Together, they constitute the “hedged” thrust nappe [61,62]. Later, with the complete subduction of the Paleo–Tethyan Ocean, the region transitioned from the Paleo–Tethyan tectonic domain to the Paleo–Pacific tectonic environment. At the same time, due to the weakening of Paleo–Pacific subduction and the withdrawal of the subduction plate, the region gradually transitioned from an earlier compressional environment to an extensional environment in the early stage of the late Yanshanian period (Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous). Regional extension triggered large–scale magmatism and led to Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous mineralization in the Qinhang Junction zone and its adjacent areas, forming many Li–Nb–Ta–W–Sn deposits that are closely related to magmatism. These deposits include the Zhuxi W–Cu deposit, the Dahutang tungsten deposit, the Yichun 414 Nb–Ta deposit, and the Baishitong Li–bearing porcelain ore deposit [7,41,63,64,65,66]. Cassiterite U–Pb dating results show that the diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite is 139.7 ± 6.7 Ma, which is Early Cretaceous and roughly in the transition period from regional extrusion to extension and stretching.
The Dongcao muscovite granite is a highly differentiated I–type granite. Many studies have shown that highly differentiated I-type granite was primarily formed in an island arc environment under subduction or in an intracontinental collision environment caused by oceanic subduction. At the same time, they were mainly formed with the contribution of mantle-derived materials, either providing materials for crust–mantle mixing or providing heat to induce crustal re-melting [67,68,69,70,71]. In the Nb vs. Y diagram, the sample points plot in the region of volcanic arc and syn-collisional granite (Figure 8a). In the Rb vs. Y + Nb chart, the sample points plot in the syn-collisional granite region (Figure 8b), which reflects the affinity with the syn-collisional granite. In the R2 vs. R1 diagram, the sample sites are located in the area between the syn-collisional and post-orogenic granites (Figure 8c), while in the log[CaO/(Na2O + K2O)] vs. SiO2 tectonic environment discrimination diagram, the sample sites are located in the transition region between the extrusion and extensional types (Figure 8d). The synthesis suggests that it may have been formed during the transition period between the collision and post-collision stage.
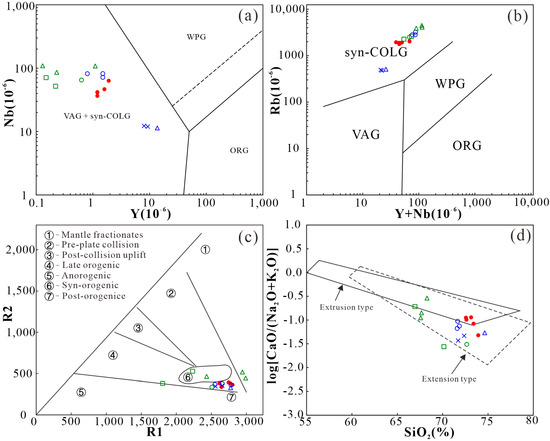
Figure 8.
The tectonic discrimination diagrams of the Dongcao muscovite granite: (a). Nb vs. Y discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [72]); (b). Rb vs. (Y + Nb) discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [72]); (c). R2 vs. R1 discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [73]); (d). log[CaO/(Na2O + K2O)] vs. SiO2 discrimination diagram (the base map is derived from [74]). (Legend description: ORG: ocean ridge granites; WPG: granites within the plate; VAG: volcanic arc granites; Syn–COLG: syn–collisional granites. The red dots are data of the Dongcao muscovite granite samples in this paper; the blue crosses are data of the Dagang protolothionite muscovite granite; the blue triangles are data of the Dagang pegmatitic dike; and the blue circles are data of the Dagang lepidolite alkali–feldspar granite [8]; the green circles are data of the Baishuidong Li–rich muscovite granite; the green rectangles are data of the Baishuidong trilithionite granite; and the green triangles are data of the Baishuidong aplite [7].).
Based on the age of rock mass formation, petro-geochemical characteristics, and the results of the geochemical discrimination diagrams, this work suggests that the Dongcao muscovite granite may have been formed in the tectonic environment of the intercontinental syn-collisional to post-collisional transition under the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate. The dynamic background of regional compressional to extensional tension caused by the transition from syn-collision to post-collision was very conducive to the upsurge of asthenospheric material, which induced crustal re-melting, and molten magma was quickly emplaced along the earlier Yifeng–Jingdezhen deep thrust nappe fault zone. At the same time, due to the continuous supply of deep heat, sufficient crystallization differentiation occurred in the magma melt during the ascent process, and rare metal elements, such as Li, Nb, and Ta, were preliminarily enriched with the residual melt. In the late period of magma evolution, many dissolved hydrothermal fluids interacted with the residual melt, further enriching the rare metal content in the residual melt. In the end, late muscovite granites, lepidolite granite, and aplite dikes rich in Li, Nb, Ta, and other rare metals were formed.
5.4. Constraints on Rare Metal Mineralization
Studies have suggested that the high differentiation evolution of magma and the melt–fluid interaction in the late evolution period are the main mechanisms of granite–type rare metal mineralization in South China [9,55,58,59,61,75,76,77]. With the continuous process of magmatic differentiation, many characteristic minerals, such as lepidolite, spodumene, petalite, fluorite, topaz, tourmaline, and apatite, gradually formed. With the evolution of magma, the evolution trend of mica is as follows: magnesia biotite, iron biotite, muscovite, Li–bearing muscovite, and lepidolite [39,41,78]. Regional geological surveys show that the rock types in the Ganfang composite pluton from old to new generally show a transition trend: biotite granite, two–mica granite, muscovite granite, (containing) lepidolite granite, and aplite [12]. This order shows the increasing degree of differentiation and evolution. Statistical analysis of different types of granites in the Ganfang composite pluton was conducted in this work (Table 3 and Figure 9). It was found that with the continuous differentiation and evolution of magma, rare metal elements, such as Li, Nb, Ta, W, and Sn, in the rock generally showed an increasing trend, revealing an apparent positive correlation between the element content and degree of differentiation. The results show that the high degree of crystallization differentiation and evolution of magma can enrich Li, Nb, Ta, W, Sn, and other elements in the residual magma, which lays a specific foundation for the late mineralization of rare metal elements.

Table 3.
Comparison of characteristics of different types of granite in the Ganfang area.
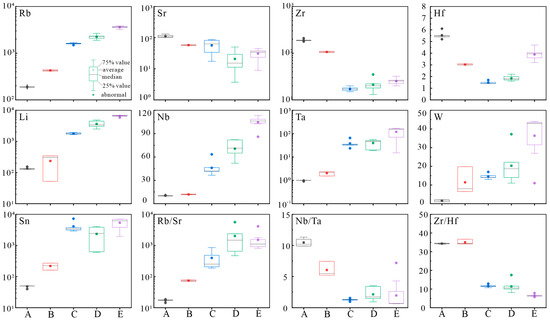
Figure 9.
Statistical map of the trace element contents of different types of rocks in the Ganfang composite pluton. (Legend description: A denotes biotite granite, and the data are from unpublished data of our project team; B denotes protolothionite muscovite granite, and the data are derived from [8]; C denotes muscovite granite; D denotes lepidolite granite, and the data are from [7,8]; E denotes aplite, and the data are from unpublished data of the project team and [7]).
In addition, previous studies have suggested that differentiated magmatic rocks can be divided into typical crystallization differentiation origins and magma hydrothermal interaction origins, with Zr/Hf = 26 and Nb/Ta = 5 as boundaries [43,57]. On this basis, the five types of granites mentioned above can be roughly divided into two categories. One type is biotite granite and two–mica granite, which are formed via normal crystalline differentiation diagenesis, mainly due to the evolution of a high degree of crystalline differentiation. The second type is upper muscovite granite, (containing) lepidolite granite, and aplite, which has an origin of high crystallization differentiation and melt–fluid interaction. The formation and evolutionary process experienced both an early high degree of crystallization differentiation evolution and a later stage of melt–fluid interaction. By comparing the changes in the element contents in the two types of rocks, it is not difficult to find that the range of rare metal elements, such as Li, Nb, Ta, and Sn, in the rocks not only increase with the increase in magmatic differentiation and evolution but also increase exponentially after experiencing late melt–fluid interaction (Figure 9); this finding indicates that the high degree of magmatic differentiation and evolution affect the contents of Li, Nb, Ta, and other rare metal elements, with particular enrichment, but the melt–fluid interaction in the late magmatic evolution may be the key to the high enrichment of rare metal elements and the final mineralization. This conclusion is consistent with the results obtained when Xu et al. studied the Yichun–Yashan Nb–Ta deposit [79]. By comparing the changing trend of the W content in the two types of rocks, it is found that the rate of increase in the content is basically unchanged or relatively stable, which may indicate that the late melt–fluid interaction has not significantly enriched W in the residual melt; that is, the enrichment W may be restricted mainly by the degree of magmatic crystallization differentiation.
In summary, we believe that the high degree of differentiation and evolution of magma and the melted fluid interaction in the late evolution are significant constraints for the enrichment and mineralization of rare metal elements, such as granite–type Li, Nb, Ta, and Sn. Among them, the high degree of differentiation and evolution of magma is mainly for the initial enrichment of ore–forming elements. The melt–fluid interaction in the late evolution is critical for its high concentration and final mineralization.
6. Conclusions
According to this paper, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
- Cassiterite U–Pb dating results show that the diagenetic age of the Dongcao muscovite granite is 139.7 ± 6.7 Ma (MSWD = 0.67), which is Early Cretaceous.
- (2)
- The Dongcao muscovite granite is characterized by high Si, is rich in alumina and alkali, is low in Ca and Fe, and is poor in Mg and Ti. The Na2O/K2O ratios range from 0.95 to 1.24, with an average of 1.08, and the A/CNK values vary from 1.34 to 1.44, with an average of 1.39, indicating a strong peraluminous environment that is enriched with sodium. The trace elements of Dongcao muscovite granite are enriched with Rb, U, Ta, Pb, P, and Hf and depleted of Ba, Sr, Ti, REEs, etc. The total rare earth element (ΣREE) content is relatively low, and the negative Eu anomaly and tetrad effect are apparent.
- (3)
- Evidence from petrographic, cassiterite U–Pb dating and petro–geochemical data indicate that the Dongcao muscovite granite is a highly differentiated granite, which was formed in the tectonic environment of the intracontinental collision to post–collisional transition under the subduction of the Paleo–Pacific plate. In the formation process, it experienced a high degree of crystallization differentiation evolution in the early stage and melt–fluid interaction in the late stage of evolution.
- (4)
- The highly differentiated evolution of magma and the melt–fluid interaction in the late stage of magmatic evolution are significant constraints for forming granite–type Li–Nb–Ta–Sn rare metal deposits in the Ganfang area. The former causes the initial enrichment of ore–forming elements, while the latter causes ore–forming elements to be highly concentrated and finally mineralized.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Y.O.; methodology, R.Z.; investigation, D.M.; writing—review and editing, T.L.; visualization, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Technical Due Diligence Assessment of the Lithium Ore Deposit Project in Yifeng County, Jiangxi Province funded by AnShan Heavy Duty Mining Machinery Co., Ltd. (No. AZGF-912-202103-001).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editors and other anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mao, J.W.; Yuan, S.D.; Xie, G.Q.; Song, S.W.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.B.; Liu, X.; Fu, X.F.; Cao, J.; Zeng, Z.L.; et al. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century. Miner. Depos. 2019, 38, 935–969. [Google Scholar]
- Bobba, S.; Carrara, S.; Huisman, J.; Mathieux, F.; Pavel, C. Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU—A Foresight Study; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on Critical Mineral Impacts of the U.S. Economy; Committee on Earth Resources; National Research Council. Minerals, Critical Minerals, and the US Economy; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mudd, G.M.; Werner, T.T.; Weng, Z.H.; Yellishetty, M.; Yuan, Y.; McAlpine, S.R.B.; Skirrow, R.; Czarnota, K. Critical Minerals in Australia: A Review of Opportunities and Research Needs; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.L.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, S.; Xu, L. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Xikeng lithium deposit and the 40Ar/39Ar chronology of lepidolite of the deposit in Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2022, 42, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.L.; Zhao, J.; Lin, M.H.; Zhang, L. Zircon U–Pb age of ore–forming magmatic rocks in Baishuidong Li–Nb–Ta deposit, Yifeng County, Jiangxi Province and its significance. World Nonferrous Met. 2022, 19, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.C.; Hu, H.; Che, X.D.; Xiang, L. Li–Nb–Ta mineralization in the Jurassic Yifeng granite–aplite intrusion within the Neoproterozoic Jiuling batholith, south China: A fluid–rich and quenching ore–forming process. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 185, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Z.; Zhou, Z.B.; Peng, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.B.; Yu, H.Q.; Wan, J.J.; Yang, S. A discussion on geological characteristics and genetic mechanism of Dagang superlarge lithium–bearing porcelain stone deposit in Yifeng County, Jiangxi Province. Miner. Depos. 2020, 39, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.B.; Chen, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.H.; Cao, S.H.; Fan, X.J. Progress of research on the Shilizing rare meatals mineralization from Jiuling–type rock and its significance for prospecting. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, S.L.; Xing, X.L.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, Y. Distribution, types and prospecting potential of Lithium deposits in Jiangxi Province. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2019, 33, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C. Preliminary Study of Mineralization Potentiality of Shiziling Muscovite Granite, Jiangxi Province; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.T.; Wang, G.B.; He, S.F.; Fan, A.C. Diagenesis and mineralization of Ganfang rock in Yifeng, Jiangxi province. J. East China Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 34, 345–358. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Wu, Z.H.; Ding, L.; Long, X.Y. Study on the characteristics and metallogenic regularity of Lithium deposits in Yifeng–Fengxin area, Jiangxi Province. China Met. Bull. 2020, 1012, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.M.; Zhou, M.J.; Luo, X.C.; Zhou, J.T. The metallogenic conditions and prospecting potential of lithium andrare metals in northwestern Jiangxi. East China Geol. 2016, 37, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.J.; Liu, J.W.; Zeng, Q.Y.; Pan, S.Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Peng, S.T.; Lu, S.Y. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the proclain stone (lithium–bearing) in Yifeng area, Jiangxi province. Nonferrous Met. (Min. Sect.) 2022, 74, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Hao, J.; Xiao, L. Tectonic research of China: Review and prospect. Geol. Rev. 2002, 48, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Z. The evolution chracteristics and the basic laws of geotechonics in Jiangxi province. J. East China Coll. Geol. 1987, 10, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.D.; Peng, J.T.; Hao, S.; Li, H.M.; Geng, J.Z.; Zhang, D.L. In situ LA–MC–ICP–MS and ID–TIMS U–Pb geochronology of cassiterite in the giant Furong tin deposit, Hunan Province, South China: New constraints on the timing of tin–polymetallic mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. Isoplot 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol. Cent. Spec. Publ. 2003, 4, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Ding, X.; Ling, M.X.; Fan, W.M.; Sun, W.D. Dating cassiterite using laser ablation ICP–MS. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, D.M.; Petrus, J.A.; Kamber, B.S. U–Pb LA–ICPMS dating using accessory minerals with variable common Pb. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth–Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of eocene calc–alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R.; Barnes, C.G.; Collins, W.J.; Arculus, R.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Frost, C.D. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniar, P.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.D.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Li, X.H.; Lan, Z.W.; Guo, C.L.; Yang, Y.N.; Liu, Y.; Tang, G.Q. Monazite and xenotime U–Th–Pb geochronology by ion microprobe: Dating highly fractionated granites at Xihuashan tungsten mine, SE China. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 166, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, N.M.; Ntaflos, T.; Pease, V.; Sami, M.; Slobodník, M.; Steet, A.A.A.; Abdelfadil, K.M.; Fathy, D. Combined zircon U–Pb dating and chemical Th–U–total Pb chronology of monazite and thorite, Abu Diab A–type granite, Central Eastern Desert of Egypt: Constraints on the timing and magmatic–hydrothermal evolution of rare metal granitic magmatism in the Arabian Nubian Shield. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125669. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.L.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, G.Q.; Yang, J.H.; Zhu, W.G. Precise U–Pb and Pb–Pb dating of Phanerozoic baddeleyite by SIMS with oxygen flooding technique. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.T.; Ireland, T.R. High–uranium matrix effect in zircon and its implications for SHRIMP U–Pb age determinations. Chem. Geol. 2012, 306–307, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.; Zoheir, B.A.; Neymark, L.A.; Zeh, A.; Moscati, R.J. Monazite and cassiterite Usingle bond Pb dating of the Abu Dabbab rare–metal granite, Egypt: Late Cryogenian metalliferous granite magmatism in the Arabian–Nubian Shield. Gondwana Res. 2020, 84, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.P.; Tang, H.F. Trace element geochemistry of A–type granite. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2005, 24, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.P.; Wang, Y.M.; Qi, K.J. Present situation of researches on A–type granites: A review. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2007, 26, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.G. A–type granites: Research progress and implications. Geotecton. Metallog. 2009, 33, 465–480. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.W.; Mo, X.X.; Zhao, Z.D.; Zhu, D.C. A discussion on how to discriminate A–type granite. Geol. Bull. China 2010, 29, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Sami, M.; Monsef, M.A.E.; Abart, R.; Toksoy–Köksal, F.; Abdelfadil, K.M. Unraveling the genesis of highly fractionated rare–metal granites in the Nubian Shield via the rare–earth elements tetrad effect, Sr–Nd isotope systematics, and mineral chemistry. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 2368–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, G.J.; Qi, C.S. U–Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I– and A–type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat–slab? Lithos 2007, 96, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Zheng, Y.F. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Ji, W.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, L. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C.P.; Tuttle, O.F. Chemistry of igneous rocks--[Part] 1, differentiation index. Am. J. Sci. 1960, 258, 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.L. Mechanism of Ta–Nb enrichment and magmatic evolution in the Yashan granites, Jiangxi Province, South China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 4311–4322. [Google Scholar]
- Dostal, J.; Kontak, D.J.; Gerel, O.; Shellnutt, J.G.; Fayek, M. Cretaceous ongonites (topaz–bearing albite–rich microleucogranites) from Ongon Khairkhan, Central Mongolia: Products of extreme magmatic fractionation and pervasive metasomatic fluid: Rock interaction. Lithos 2015, 236–237, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballouard, C.; Branquet, Y.; Tartese, R.; Poujol, M.; Boulvais, P.; Vigneresse, J.L. Nb–Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites: A marker of the magmatic hydrothermal transition: REPLY. Geology 2016, 44, e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W. Aluminium saturation in I– and S–type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos 1999, 46, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L. The Evolution of Yanshanian Granite and Tungsten Mineralization in Southern Jiangxi Province and Adjacent Region; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A–type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Beams, S.D.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Nature and origin of A–type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 80, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. Phosphorus in S–type magmas: The P2O5 content of feldspars from peraluminous granites, pegmatites, and rhyolites. Am. Mineral. 1992, 77, 126–145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, Z.X. On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling Range, South China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, A.; Mavrogenes, J.A.; Meffre, S.; Davidson, P. The key role of mica during igneous concentration of tantalum. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 167, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.P. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of the Pleasant Ridge zinnwaldite–topaz granite, southern New Brunswick, and comparisons with other topaz–bearing felsic rocks. Can. Mineral. 1992, 30, 895–921. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.L.; Wang, R.C.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, P.R.; Liu, C.S. Contrast between the high–P subtype and low–P subtype of F–rich granites in South China. Geol. Rev. 1998, 44, 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.C.; Zhu, J.C.; Jin, Z.D. Genetic interpretation of Li–F–rich rare metal–bearing granites in South China. Miner. Depos. 2000, 19, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.L.; Wang, R.C.; Chen, X.M.; Liu, C.S. Phosphate minerals from the Yashan F– and P– rich granite in Yichun, Jiangxi Province: Genetic implications. Geol. Rev. 2001, 47, 542–550. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Mineralogical Constraints on Magmatic and Hydrothermal Evolutions of the Mesozoic Rare–Metal Granites in South China; The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Guangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.C.; Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Che, X.D.; Xiang, L.; Liu, C. Global tempo–spatial distribution of rare–metal mineralization and continential evolution. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Masuda, A.; Shabani, M.B. Tetrad effects of rare–earth elements in rare metal granites. Geochemica 1992, 3, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Xiong, X.L.; Han, X.D. Discussion on the formation mechanism of tetrad effect of rare earth elements in granites: Taking Qianlishan and Baerzhe granites as examples. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1999, 29, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangxi Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration. Regional Geological Records of China: Jiangxi Records; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.S. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block. Geol. Bull. China 2012, 31, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, J.; Wu, C.J. Tectonic–sedimentary characteristics of Ping (Pingxiang)–Le(Leping) depression in Jiangxi Province and its implications on coal mineral resource prospecting. Geotecton. Et Metallog. 2011, 35, 513–524. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.L.; Qiu, J.S.; Xing, G.F.; Yu, M.G.; Zhao, J.L. Petrogenesis and magmatic evolution of the Yashan granite pluton in Yichun, Jiangxi Province, and their constraints on mineralization. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 850–868. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, P.P.; Niu, J.; Liang, J. Plate tectonism of Qinzhou Bay–Hangzhou Bay juncture orogenic belt (South China) before Mesozoic tectonic transition event. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Peng, N.J.; Huang, L.C.; Xu, Y.M.; Zhan, G.L.; Dan, X.H. Geological characteristic and ore genesis of the giant tungsten deposits from the Dahutang ore–concentrated district in northern Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 639–655. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.L.; Zhang, D.; Wu, G.G.; Di, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, F.; Hu, B.J.; Huo, H.L.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Control of interaction between stress and fluid in tectonic transition background on metallogenesis of giant Zhuxi W–Cu deposit, South China. Miner. Depos. 2021, 40, 1135–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, B.; Sun, K.K. Petrogenesis of the Maogongdong highly differentiated granite in the Dahutang tungsten ore field, Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.S.; Xiao, E.; Hu, J.; Xu, X.S.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, Z. Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I–type granites in the coastal area of northeastern Fujian Province: Constrains from zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Nd–Hf isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 2468–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, X.H.; Cen, T. Petrogenesis of early Yanshanian highly evolved granites in the Longyuanba area, southern Jiangxi Province: Evidence from zircon U–Pb dating, Hf–O isotope and whole–rock geochemistry. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 43, 922–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Z.; Wei, J.H.; Shi, W.J.; Zhang, S.T.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Shen, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Zeng, R.L. Late Triassic post–collision extension at Elashan magmatic belt, East Kunlun orogenic belt: Insights from Suolagou highly fractionated I–type granite. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 150–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.C.; Mo, X.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.N.; Zhou, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H. Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I–type granites in the Chayu area of eastern Gangdese, Tibet: Constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2009, 39, 833–848. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, R.A.; Bowden, P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chem. Geol. 1985, 48, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.C.; Thorpe, R.S.; Webb, P.C. The geochemical characteristics of granitoids in contrasting arcs and comments on magma sources. J. Geol. Soc. 1984, 141, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H. Ore–Forming Mechanisms and Prospecting Models of Typical Granite Type Rare Metal Deposits in South China; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.H.; Zhang, J.T. Some problems on the genesis of rare elements mineralized granite in the South of China. J. Earth Sci. 1982, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.B.; Shan, Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Luo, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Li, N.B.; Niu, H.C. Petrogenic and metallogenic action of the alkaline granitoids in Baerzhe Area: A comparison between mineralized and barren plutons. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2011, 41, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.C.; Rao, B.; Xiong, X.L.; Li, F.C.; Zhang, P.H. Comparison and genetic interpretation of Li–F rich, rare–metal bearing granitic rocks. Geochemica 2002, 31, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, D.W.; Wu, Z.C.; Fu, H.M.; Liu, Q.H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.S. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Yashan Niobium–Tantalum deposit at Yichun, Jiangxi Province. J. East China Univ. Technol. 2018, 41, 364–378. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).