Triassic Appinite from the Qinling Orogen (Central China): Hydrous Melting of Depleted Mantle Wedge in Post-Collision Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
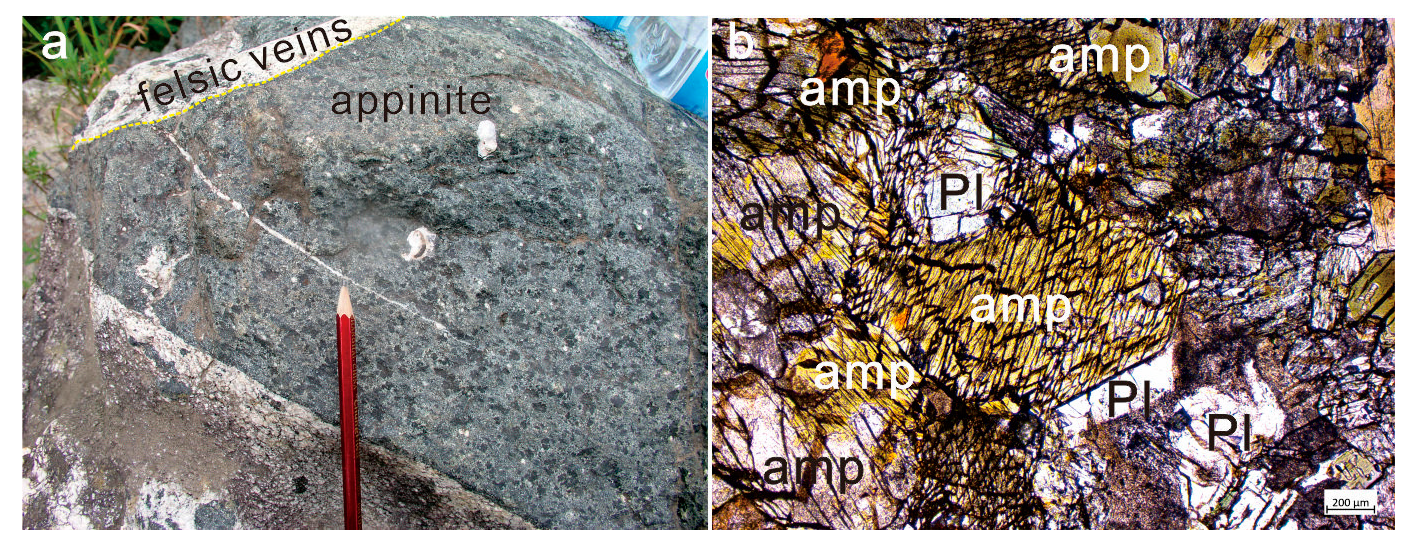
2. Geological Background
3. Analytical Methods
4. Results
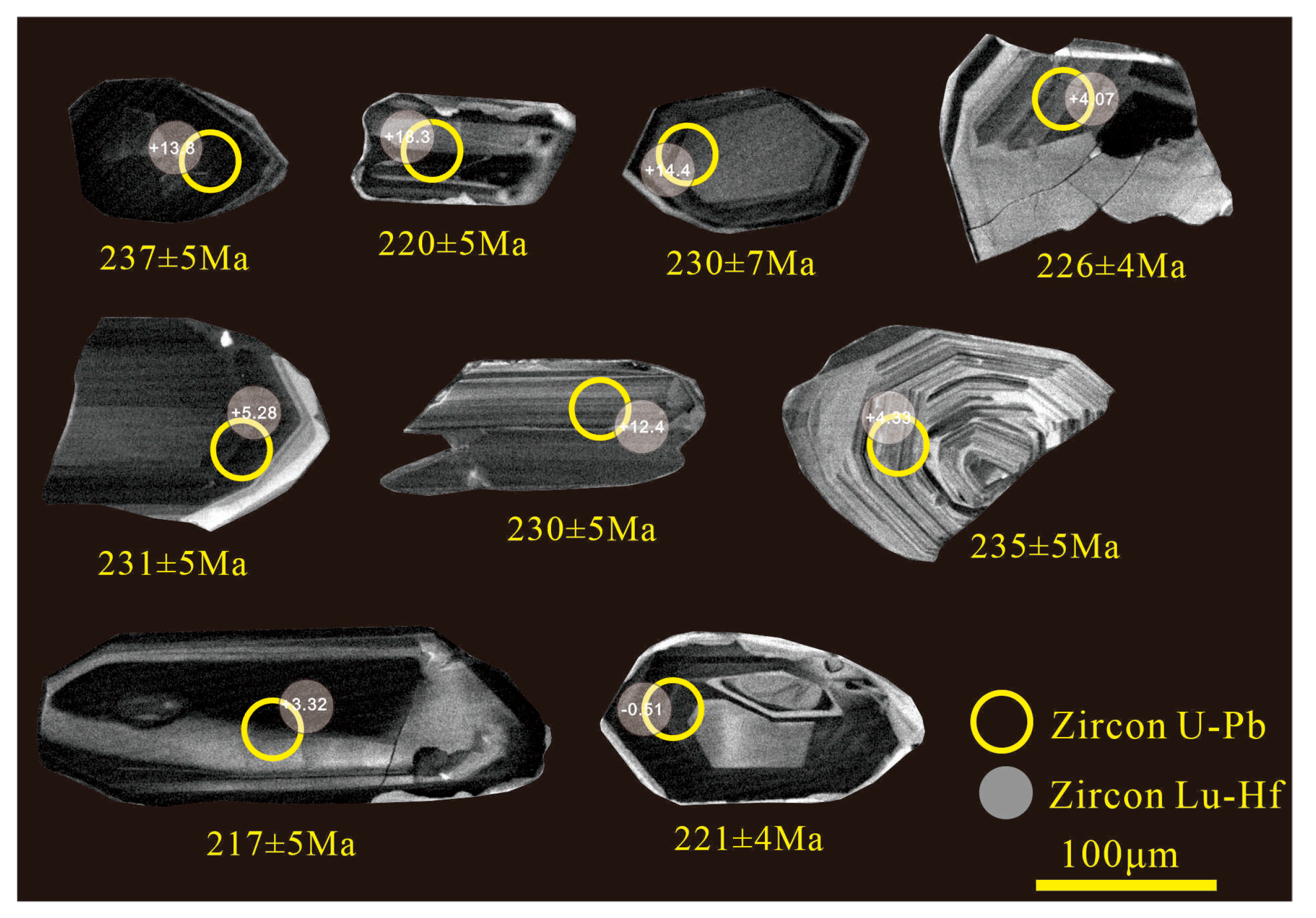
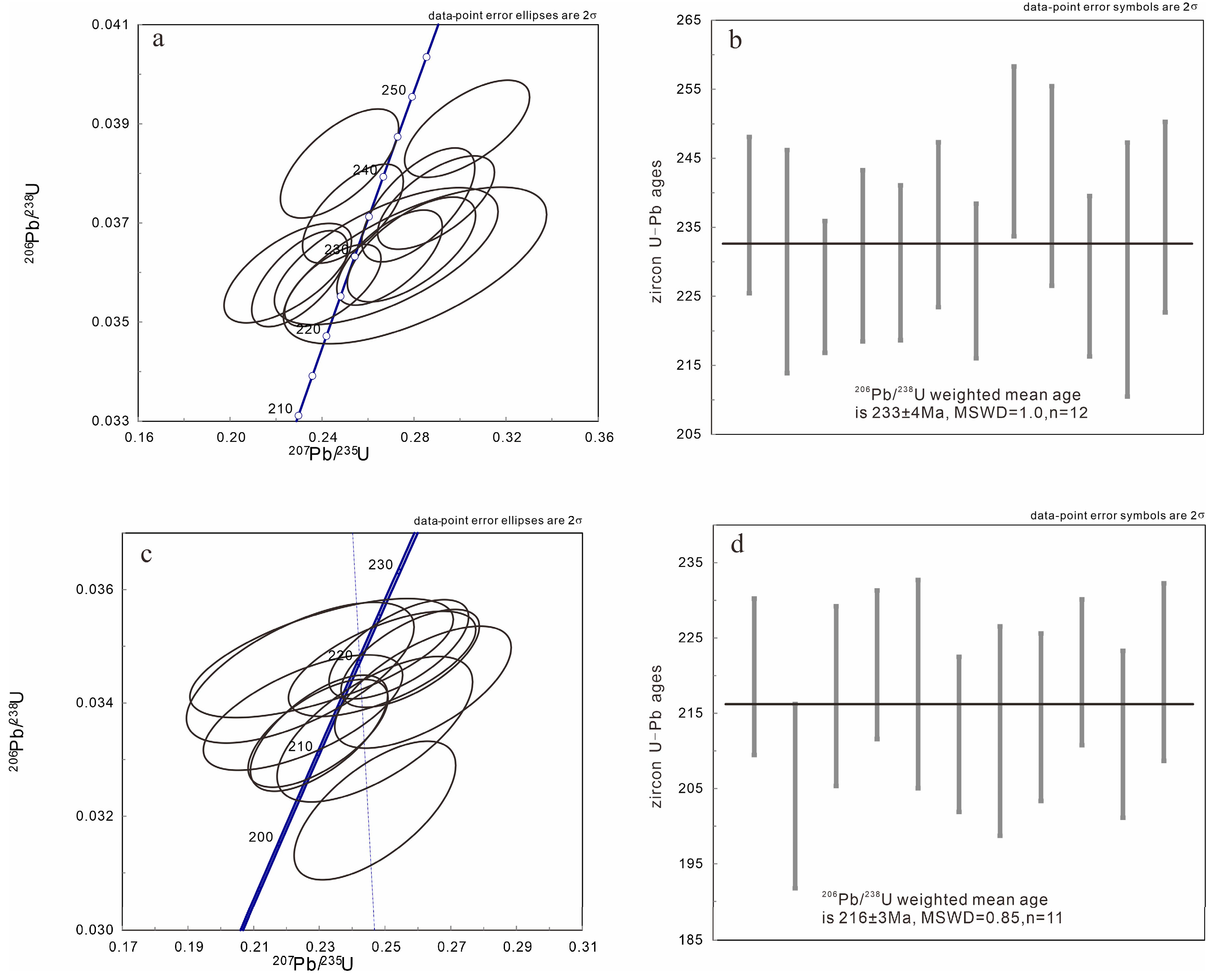
4.1. Zircon LA-ICP MS Dating
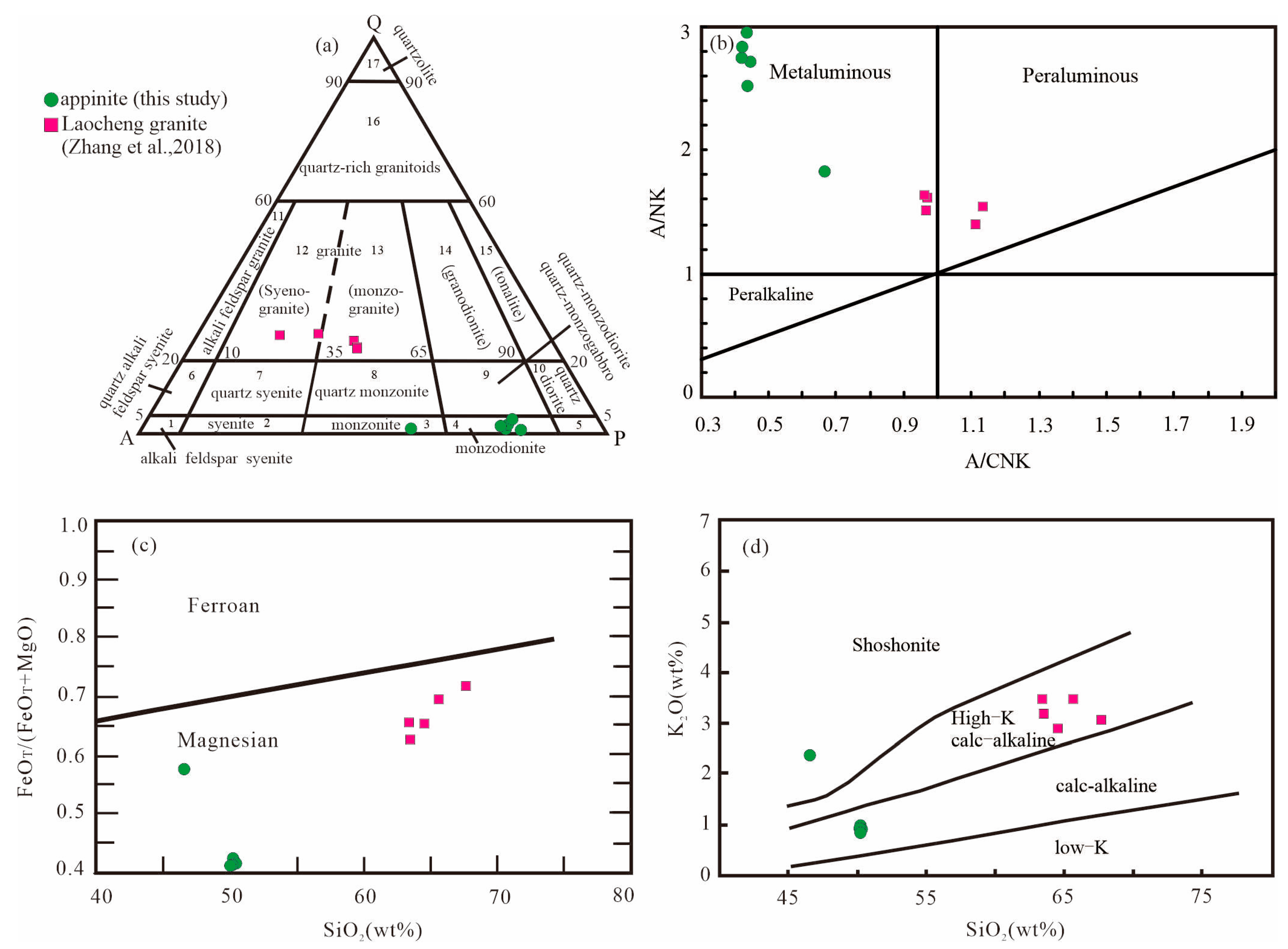
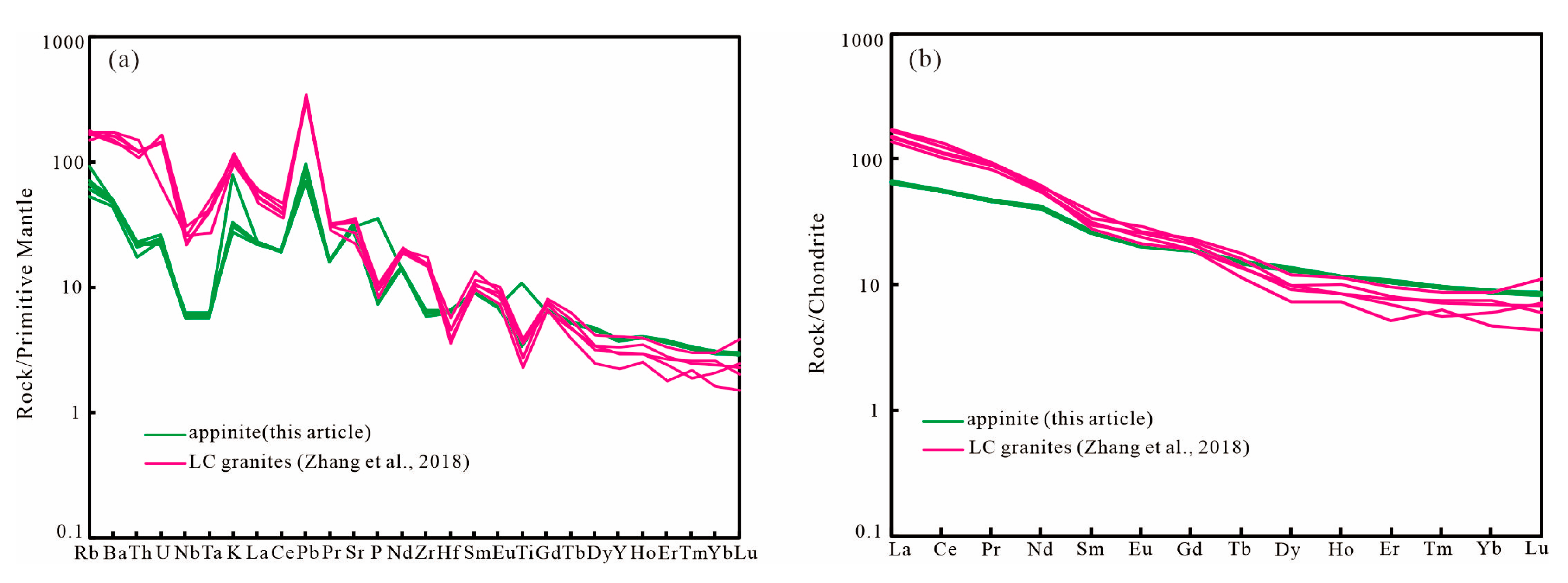
4.2. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry
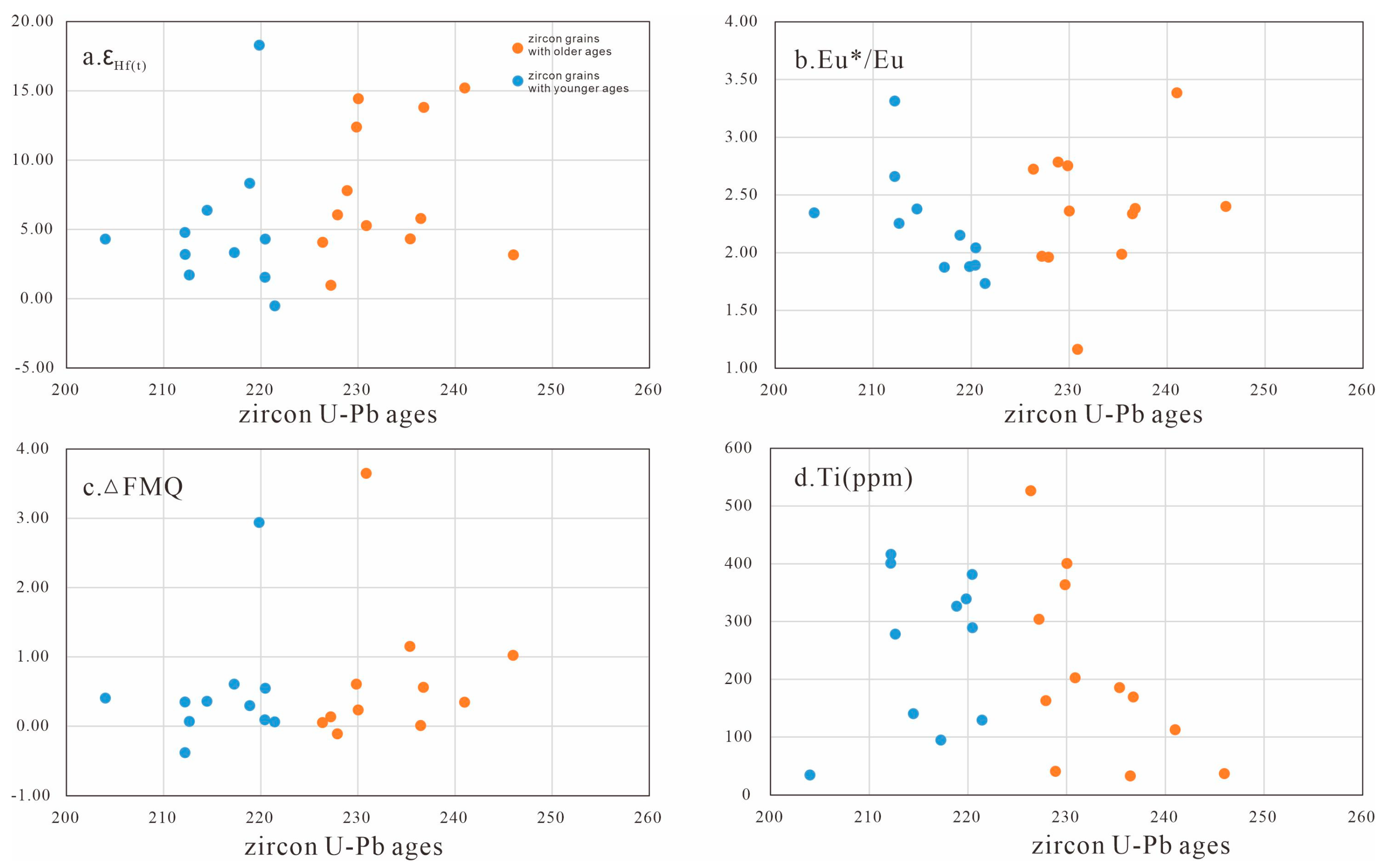
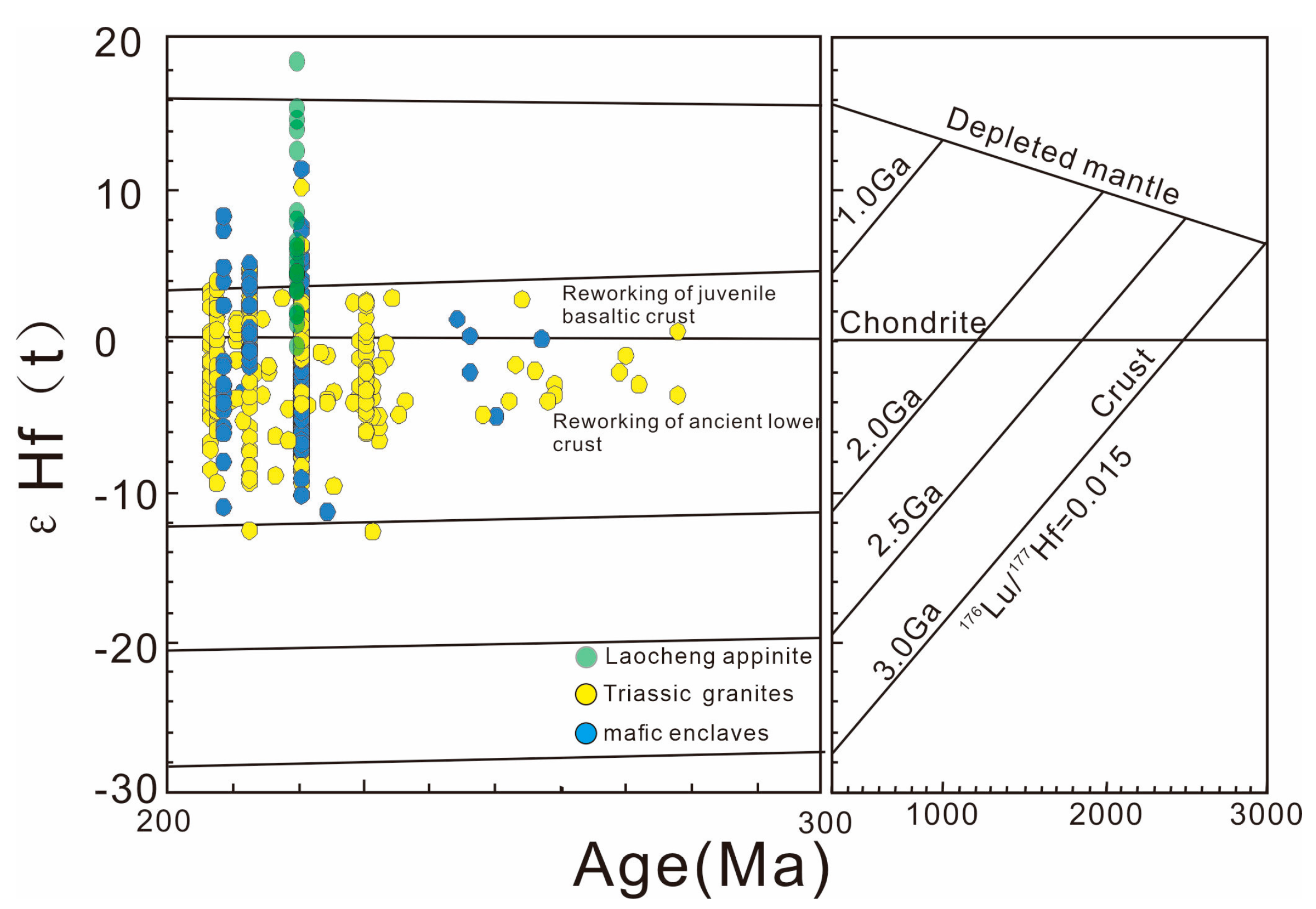
4.3. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotope, Trace Element and Oxygen Fugacity
5. Discussion
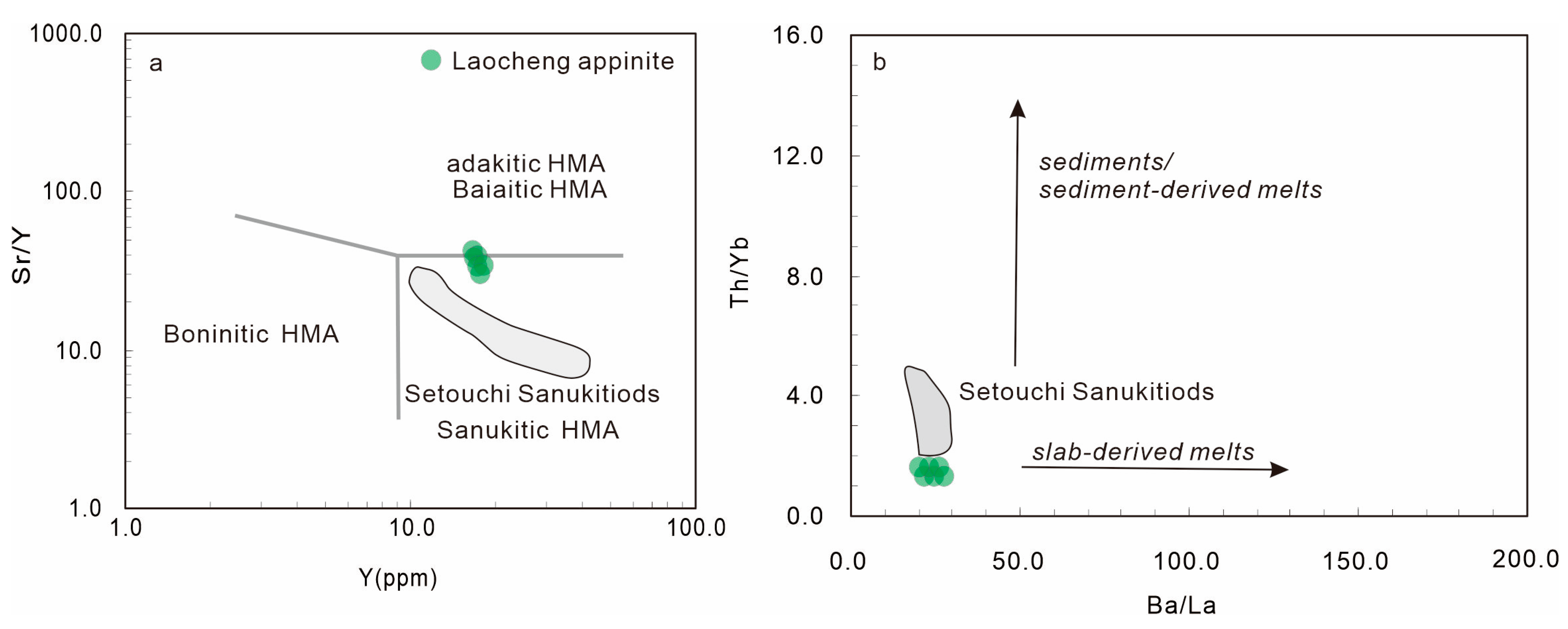
5.1. Hydrous Mafic Melts That Derived from Metasomatized Mantle Wedge
5.2. Crystallization Process and Relative High Oxygen Fugacity
5.3. Significance for the Granitic Magmatism and Magmatic Ore Deposits
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Laocheng appinite has an identical age to the Triassic granites in the Qinling orogenic belt, suggesting coeval mafic magma in the Qinling orogenic belt. Detailed whole-rock geochemistry and zircon chemistry indicate that the Laocheng appinite represent primitive hydrous mafic melts that derived from the melting of the depleted sub-arc mantle wedge.
- (2)
- Zircons from the appinite display depleted Lu-Hf isotopic compositions, suggesting a depleted mantle source. Zircon chemistry also indicates a relative oxidizing condition. The underplating of this oxidizing, hydrous and high-temperature mafic melt beneath the base of the arc crust would induce the extensive melting of the lower crust and lead to the formation of voluminous Triassic granites and associated metal deposits in the Qinling orogenic belt.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ducea, M.N.; Saleeby, J.B.; Bergantz, G. The Architecture, Chemistry, and Evolution of Continental Magmatic Arcs. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 43, 299–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Y.; Tang, G.; et al. Adakitic rocks at convergent plate boundaries: Compositions and petrogenesis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 1992–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Murphy, J.B.; Johnson, T.E.; Huang, H.-Q. Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.B. Appinite suites and their genetic relationship with coeval voluminous granitoid batholiths. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 62, 683–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.B. Appinite suites: A record of the role of water in the genesis, transport, emplacement and crystallization of magma. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 119, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A. Tonalite–granodiorite suites as cotectic systems: A review of experimental studies with applications to granitoid petrogenesis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 124, 68–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, F.; Yuan, L.; Ma, Y.; Wilde, S.A. Late Permian appinite–granite complex from northwestern Liaoning, North China Craton: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Lithos 2012, 155, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qin, K.-Z.; Song, G.-X.; Li, G.-M.; Mao, J.-W. The Triassic Duobaoshan appinite-granite suite, NE China: Implications for a water-fluxed lithospheric mantle and an extensional setting related to the subduction of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean. Lithos 2021, 394–395, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Timing of synorogenic granitoids in the South Qinling, central China: Constraints on the evolution of the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt. J. Geol. 2002, 110, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-F.; Lai, S.-C.; Grapes, R.; Diwu, C.-r.; Ju, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-F. Origin of LateTriassic high-Mg adakitic granitoid rocks from the Dongjiangkou area, Qinling orogen, central China: Implications for subduction of continental crust. Lithos 2010, 120, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-F.; Lai, S.-C.; Li, Y.-F. Multi-stage granitic magmatism during exhumation of subducted continental lithosphere: Evidence from the Wulong pluton, South Qinling. Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 1108–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-F.; Lai, S.-C.; Long, X.-P.; Li, Y.-F.; Ju, Y.-J.; Zhao, S.-W.; Zhu, R.Z.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, Z.Z. Hydrous melting of metasomatized mantle wedge and crustal growth in the post-collisional stage: Evidence from Late Triassic monzodiorite and its mafic enclaves in the south Qinling (central China). Lithosphere 2019, 11, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Liu, S.; Ducea, M.N.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Z. The geochemical evolution of the granitoid rocks in the South Qinling Belt: Insights from the Dongjiangkou and Zhashui intrusions, central China. Lithos 2017, 278–281, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, S.; Santosh, M.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; He, D.; Shi, X.; Hui, B.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, G. Central China Orogenic Belt and amalgamation of East Asian continents. Gondwana Res. 2021, 100, 131–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Lai, S.; Li, Y. Slab Breakoff Model for the Triassic Post-Collisional Adakitic Granitoids in the Qinling Orogen, Central China: Zircon U-Pb Ages, Geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Constraints. Int. Geol. Rev. 2008, 50, 1080–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattauer, M.; Matte, P.; Malavieille, J.; Tapponnier, P.; Maluski, H.; Qin, X.Z.; Lun, L.Y.; Qin, T.Y. Tectonics of the Qinling Belt: Build-up and evolution of eastern Asia. Nature 1985, 317, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Qin, J.; Chen, L.; Grapes, R. Geochemistry of ophiolites from the Mian-Lue suture zone: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen, central China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2008, 50, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Diwu, C.; Yuan, H.; Gao, S. Evaluation of accuracy and long-term stability of determination of 37 trace elements in geological samples by ICP-MS. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.-L.; Gao, S.; Dai, M.-N.; Zong, C.-L.; Günther, D.; Fontaine, G.H.; Liu, X.M.; Diwu, C. Simultaneous determinations of U–Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, D.; Hattendorf, B. Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goolaerts, A.; Mattielli, N.; de Jong, J.; Weis, D.; Scoates, J.S. Hf and Lu isotopic reference values for the zircon standard 91500 by MC-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-H.; Zhao, Z.-F.; Zheng, Y.-F. Geochemical constraints on the source nature and melting conditions of Triassic granites from South Qinling in central China. Lithos 2016, 264, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Shimizu, N.; Norman, M.D.; Applegate, G.S. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa. Chem. Geol. 1999, 160, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawabata, H.; Sato, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Chang, Q.; Takahashi, T.; Tani, K.; Shibata, T.; Yoshikawa, M. The Petrology and Geochemistry of Oto-Zan Composite Lava Flow on Shodo-Shima Island, SW Japan: Remelting of a Solidified High-Mg Andesite Magma. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 595–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Yang, Z.-M.; Hou, Z.-Q. Fluid flux melting generated post-collisional high Sr/Y copper ore–forming water-rich magmas in Tibet. Geology 2015, 43, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, H.; Jin, L. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of Indosinian granitoids from the Bikou block, northwest of the Yangtze plate: Constraints on petrogenesis, nature of deep crust and geodynamics. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyen, J.-F.; Martin, H. Forty years of TTG research. Lithos 2012, 148, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Smithies, R.H.; Rapp, R.; Moyen, J.F.; Champion, D. An overview of adakite, tonalite–trondhjemite–granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos 2005, 79, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromet, P.; Silver, L.T. REE Variations Across the Peninsular Ranges Batholith: Implications for Batholithic Petrogenesis and Crustal Growth in Magmatic Arcs. J. Petrol. 1987, 28, 75–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Henríquez, G.J. New Magmatic Oxybarometer Using Trace Elements in Zircon. J. Petrol. 2020, 61, egaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, I.J.; Arculus, R.J. The redox state of subduction zones: Insights from arc-peridotites. Chem. Geol. 1999, 160, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe-Piper, G.; Piper, D.J. The Jeffers Brook diorite–granodiorite pluton: Style of emplacement and role of volatiles at various crustal levels in Avalonian appinites, Canadian Appalachians. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Santosh, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, G.; Liu, F. Late Triassic crustal growth in southern Tibet: Evidence from the Gangdese magmatic belt. Gondwana Res. 2016, 37, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseeva, E.S.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Yaxley, G.M.; Shee, S.R. Mantle melting versus mantle metasomatism–“The chicken or the egg” dilemma. Chem. Geol. 2017, 455, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.V.; Edmonds, M. Mafic glass compositions: A record of magma storage conditions, mixing and ascent. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 377, 20180004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandler, B.E.; Grove, T.L. Controls on the stability and composition of amphibole in the Earth’s mantle. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 171, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Ji, W.-Q.; Chu, X.; Wu, A.; Chen, C. Reconstructing crustal thickness evolution from europium anomalies in detrital zircons. Geology 2020, 49, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Castro, A.; Pedreira, R.; Lu, X.; Xiao, Q. Triassic granitoids of the Qinling orogen, central China: Genetic relationship of enclaves and rapakivi-textured rocks. Lithos 2011, 126, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, X.-X.; Lo, C.-H.; Wu, F.-Y.; He, H.-Y.; Yang, L.-K.; Zhu, R.X. Post-collisional, potassic monzonite–minette complex (Shahewan) in the Qinling Mountains (central China): 40Ar/39Ar thermochronology, petrogenesis, and implications for the dynamic setting of the Qinling orogen. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2007, 31, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | LC-01 | LC-02 | LC-03 | LC-06 | LC-07 | LC-08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 46.55 | 50.16 | 50.24 | 50.21 | 50.38 | 50.44 |
| TiO2 | 2.33 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.73 |
| Al2O3 | 15.59 | 11.91 | 12.61 | 11.74 | 11.99 | 12.18 |
| Fe2O3T | 11.48 | 8.19 | 8.27 | 8.39 | 8.21 | 8.31 |
| MnO | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| MgO | 7.62 | 10.56 | 10.09 | 10.76 | 10.47 | 10.58 |
| CaO | 8.16 | 13.29 | 13.03 | 13.11 | 12.52 | 13.15 |
| Na2O | 3.61 | 1.93 | 2.27 | 1.94 | 2.28 | 1.89 |
| K2O | 2.37 | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.91 |
| P2O5 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.17 |
| LOI | 1.73 | 1.56 | 1.13 | 1.58 | 1.68 | 1.58 |
| TOTAL | 100.35 | 99.57 | 99.5 | 99.78 | 99.51 | 100.07 |
| Li | 47.5 | 38.4 | 43.2 | 47 | 40.5 | 42.9 |
| Be | 0.78 | 0.7 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.74 |
| Sc | 30.1 | 30.5 | 33.5 | 31.6 | 30.7 | 33.6 |
| V | 193 | 190 | 184 | 191 | 186 | 194 |
| Cr | 650 | 672 | 599 | 680 | 623 | 677 |
| Co | 52.2 | 51.3 | 52.4 | 52.4 | 50.1 | 52.7 |
| Ni | 127 | 129 | 121 | 127 | 130 | 125 |
| Cu | 70.7 | 66.2 | 81.5 | 65.7 | 67.8 | 67.8 |
| Zn | 61.4 | 159 | 56.9 | 63.1 | 123 | 56.7 |
| Ga | 13.7 | 13.5 | 14.1 | 13.5 | 13.3 | 13.6 |
| Ge | 1.46 | 1.46 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.37 | 1.48 |
| Rb | 58.6 | 42.6 | 33.6 | 45.5 | 41.9 | 38.7 |
| Sr | 635 | 625 | 651 | 614 | 676 | 596 |
| Y | 17.1 | 17 | 17.4 | 17.3 | 16.7 | 17.5 |
| Zr | 72.2 | 69.7 | 64.9 | 70.3 | 69.2 | 69.1 |
| Nb | 4.17 | 4.03 | 4.41 | 4.1 | 3.99 | 4.21 |
| Cs | 2.98 | 2.72 | 2.4 | 3.06 | 2.19 | 2.58 |
| Ba | 347 | 340 | 311 | 350 | 334 | 332 |
| La | 15.6 | 15.5 | 15 | 15.7 | 15.4 | 15.6 |
| Ce | 34 | 34.3 | 34 | 34.4 | 33.8 | 34.3 |
| Pr | 4.4 | 4.41 | 4.45 | 4.47 | 4.34 | 4.48 |
| Nd | 18.9 | 19 | 19.1 | 19.4 | 18.8 | 19.5 |
| Sm | 3.95 | 4.01 | 4.03 | 4.04 | 3.93 | 4.09 |
| Eu | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.18 | 1.15 | 1.19 |
| Gd | 3.8 | 3.83 | 3.85 | 3.89 | 3.79 | 3.93 |
| Tb | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.57 |
| Dy | 3.28 | 3.32 | 3.31 | 3.41 | 3.28 | 3.45 |
| Ho | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.66 |
| Er | 1.72 | 1.73 | 1.76 | 1.76 | 1.72 | 1.79 |
| Tm | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Yb | 1.47 | 1.46 | 1.48 | 1.51 | 1.45 | 1.51 |
| Lu | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
| Hf | 2 | 1.97 | 1.93 | 1.98 | 1.94 | 1.99 |
| Ta | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Pb | 4.9 | 5.97 | 6.83 | 4.97 | 6.19 | 4.94 |
| Th | 1.92 | 1.83 | 1.46 | 1.94 | 1.76 | 1.8 |
| U | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.49 |
| Mg# | 61 | 75 | 74 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| ΣREE | 90 | 90 | 90 | 91 | 89 | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, B. Triassic Appinite from the Qinling Orogen (Central China): Hydrous Melting of Depleted Mantle Wedge in Post-Collision Stage. Minerals 2023, 13, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030441
Liu H, Gong H, Luo F, Zhang Y, Dang B. Triassic Appinite from the Qinling Orogen (Central China): Hydrous Melting of Depleted Mantle Wedge in Post-Collision Stage. Minerals. 2023; 13(3):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030441
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hang, Hujun Gong, Fenhong Luo, Yaqin Zhang, and Ben Dang. 2023. "Triassic Appinite from the Qinling Orogen (Central China): Hydrous Melting of Depleted Mantle Wedge in Post-Collision Stage" Minerals 13, no. 3: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030441
APA StyleLiu, H., Gong, H., Luo, F., Zhang, Y., & Dang, B. (2023). Triassic Appinite from the Qinling Orogen (Central China): Hydrous Melting of Depleted Mantle Wedge in Post-Collision Stage. Minerals, 13(3), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030441





