Adsorptive Removal Behavior of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment onto Polyaniline-Modified MIL100(Fe)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fabricate of PANI/MIL-100(Fe) Composite
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Removal Experiments
2.4.1. Adsorption Study
2.4.2. Sorption Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies
2.4.3. Reusability
3. Results and Discussions
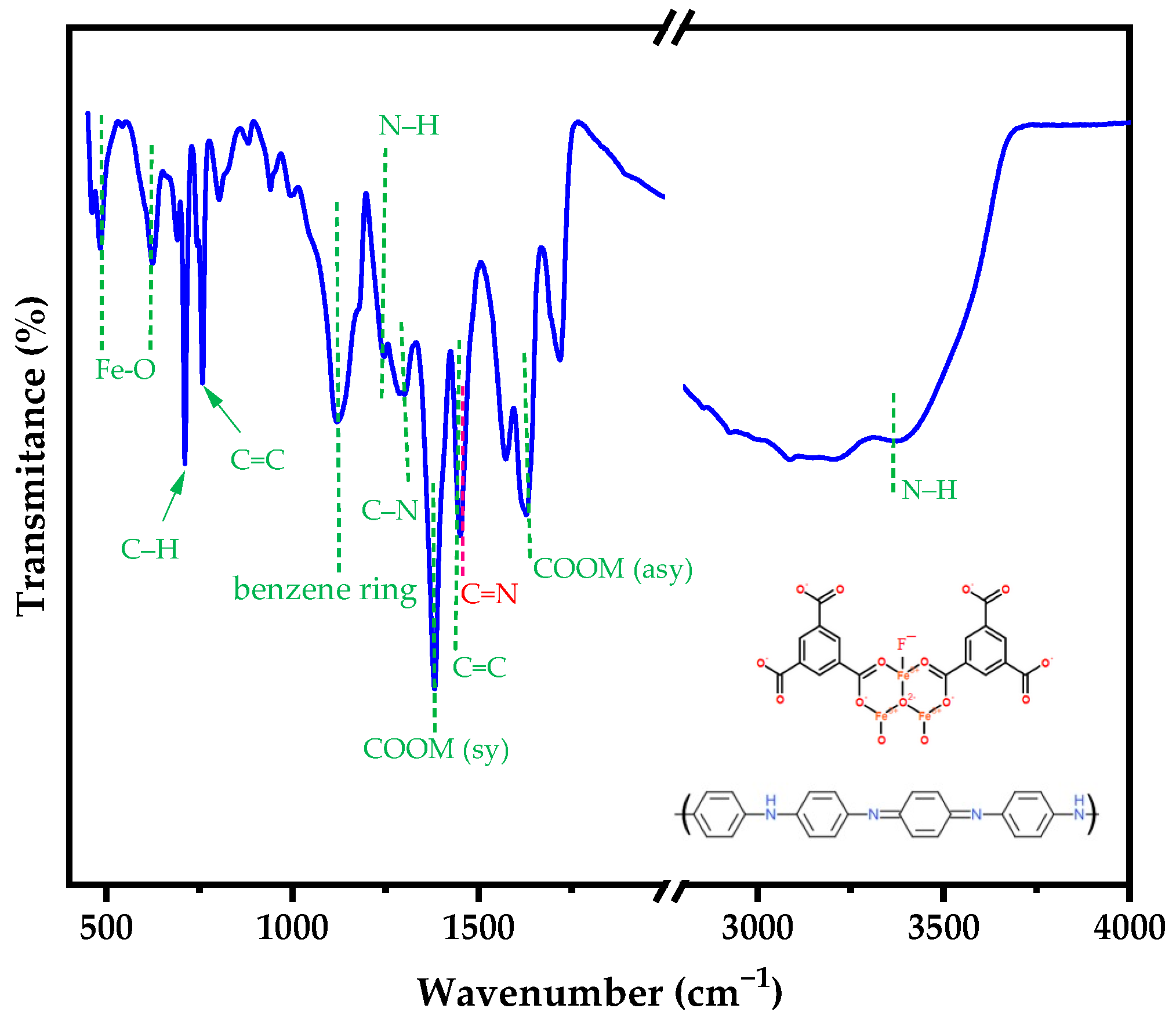
3.1. Characterization
3.2. pH Influences and Adsorption Mechanism
3.3. Study of Kinetic Models
3.4. Experimental Design and Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.6. Reusability of the Adsorbent
3.7. Removal Mechanism of Cr (VI) and Pb (II) on PANI/MIL-100(Fe)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A





References
- Zare, E.N.; Motahari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-L.; Feng, X.-Q.; Han, R.-P.; Zang, S.-Q.; Yang, G. Cr(VI) removal via anion exchange on a silver-triazolate MOF. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, H.; Phuong, T.; Le Hang, P.; Toan, T.; Tuyen, T.; Mau, T.; Khieu, D. Comparative study of Pb (II) adsorption onto MIL–101 and Fe–MIL–101 from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, V.D.; Giang, B.L.; Thu, T.V. Free-standing polypyrrole/polyaniline composite film fabricated by interfacial polymerization at the vapor/liquid interface for enhanced hexavalent chromium adsorption. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5445–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Gao, W.; Jia, G.; Yao, Y. Synergistic effects of iron ion and PANI in biochar material for the efficient removal of Cr(VI). Mater. Lett. 2019, 240, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lv, Z.; Zheng, J.; Hu, J.; Jiang, C.; Ueda, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Positively Charged Nanofiltration Membrane with Dendritic Surface for Toxic Element Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, Y.; Tez, Z. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by sawdust adsorption. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Na, P. Synthesis of magnetic orderly mesoporous α-Fe2O3 nanocluster derived from MIL-100(Fe) for rapid and efficient arsenic (III,V) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheshtzar, I.; Ghorbani, M.; Gatabi, M.; Lashkenari, M. Facile synthesis of smartaminosilane modified-SnO2/porous silica nanocomposite for high efficiency removal of lead ions and bacterial inactivation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rodríguez, A.; Durán-Barrantes, M.; Borja, R.; Sánchez, E.; Colmenarejo, M.; Raposo, F. Heavy metals removal from acid mine drainage water using biogenic hydrogen sulphide and effluent from anaerobic treatment: Effect of pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of a Metal-Organic Framework Containing Large Rectangular Channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10401–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Liu, W.; Kong, Y.; Cheng, R.; Yuan, D. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@MOF-100(Fe) magnetic microspheres for the adsorption of diclofenac sodium in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31705–31717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, N.; Jin, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. A new nFe@ZIF-8 for the removal of Pb (II) from wastewater by selective adsorption and reduction. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wen, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, G. Influence of fulvic acid on Pb(II) removal from water using a post-synthetically modified MIL-100(Fe). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 551, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Navarathna, C.; Warren, S.; Perez, F.; Pittman, C.P., Jr.; Mlsna, T. Iron/titanium oxide-biochar (Fe2TiO5/BC): A versatile adsorbent/photocatalyst for aqueous Cr (VI), Pb2+, F-and methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 614, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Salehi, S.; Anbia, M.; Kazemipour, M. Improving CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/CH4 selectivity with amine functionalization of MIL-100 and MIL-101. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Huang, P.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zou, Y.; Chu, H.; Yan, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; et al. A pyridine vapor sensor based on metal-organic framework-modified quartz crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, C.A.; Liu, D.; Meyer, T.J.; Lin, W. Amplified Luminescence Quenching of Phosphorescent Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3991–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehrmansouri, H.; Zarei, M.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Moosavi-Zare, A.R.; Rostamnia, S.; Moradi, S. Multilinker phosphorous acid anchored En/MIL-100(Cr) as a novel nanoporous catalyst for the synthesis of new N-heterocyclic pyrimido [4,5-b] quinolines. Mol. Catal. 2020, 481, 110303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzempek, W.; Menaszek, E.; Gil, B. Fe-MIL-100 as drug delivery system for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatment and diagnosis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 280, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, P.-P.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, J. Mechanism study about the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) with iron-trimesic metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, E.; Mohaghegh, N. Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from Sungun Acid Rock Drainage Using Mordenite Zeolite, Graphene Nanosheets, and a Novel Metal-Organic Framework. Mine Water Environ. 2016, 35, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Yoo, D.K.; Jhung, S.H. Polyaniline-Encapsulated Metal-Organic Framework MIL-101: Adsorbent with Record-High Adsorption Capacity for the Removal of Both Basic Quinoline and Neutral Indole from Liquid Fuel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35639–35646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakouraj, M.; Zare, E.; Moghadam, P. Synthesis of novel conductive poly (p-phenylenediamine)/Fe3O4 nanocomposite via emulsion polymerization and investigation of antioxidant activity. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2014, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution using polyaniline grafted chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, Q. Polyaniline-based adsorbents for removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution: A mini review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6158–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushra, R.; Shahadat, M.; Raeisssi, A.; Nabi, S.A. Development of nano-composite adsorbent for removal of heavy metals from industrial effluent and synthetic mixtures; its conducting behavior. Desalination 2012, 289, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, M.; Azizi, A.; Livani, M.; Kafshgari, L. Adsorption of lead (II) and chromium (VI) from aqueous environment onto metal-organic framework MIL-100(Fe): Synthesis, kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 291, 121636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-D.; Yi, X.-H.; Zhao, C.; Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.-C. Polyaniline modified MIL-100(Fe) for enhanced photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction and tetracycline degradation under white light. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Awasthi, G.P.; Kim, H.J. Novel insight into the adsorption of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions by MOF derived Co-Al layered double hydroxide @hematite nanorods on 3D porous carbon nanofiber network. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, S.M.; Soleimani, M.; Jokar, M.; Richards, T.; Pettersson, A.; Mirghaffari, N. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic waste as a precursor for synthesis of high porous activated carbon and its application for Pb (II) and Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zeng, G.; Jia, F.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H. Effect of mineralizing agents on the adsorption performance of metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe) towards chromium (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K.; Beram, S.M.; Siadatnasab, F.; Bayat, P.; Ramezanpour, A. An investigation on MIL-101 Fe/PANI/Pd nanohybrid as a novel photocatalyst based on MIL-101(Fe) metal–organic frameworks removing methylene blue dye. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1231, 130007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiang, G.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Yuan, S. Core–shell structured magnetic γ-Fe2O3@ PANI nanocomposites for enhanced As (V) adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7554–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-K.; Chitale, S.K.; Lee, U.-H.; Patil, P.; Chang, J.-S.; Hwang, Y.K. Formation of Polyaniline-MOF Nanocomposites Using Nano-Sized Fe(III)-MOF for Humidity Sensing Application. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 8157–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, G.; He, J.; Feng, H. Electrochemically-deposited PANI on iron mesh-based metal-organic framework with enhanced visible-light response towards elimination of thiamphenicol and E. coli. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Honda, R.; Kumagai, S.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ by tripolyphosphate-crosslinked chitosan-modified montmorillonite. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 277, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafshgari, L.; Ghorbani, M.; Azizi, A. Fabrication and investigation of MnFe2O4/MWCNTs nanocomposite by hydrothermal technique and adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Yadav, A.; Verma, N. Carbon gel-supported Fe-graphene disks: Synthesis, adsorption of aqueous Cr (VI) and Pb (II) and the removal mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-H. Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of paclitaxel onto Sylopute. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 130, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumar, H.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Shanmugam, K.; Kushwaha, O.S. Growth of MWCNTs from Azadirachta indica oil for optimization of chromium(VI) removal efficiency using machine learning approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 34841–34860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touihri, M.; Guesmi, F.; Hannachi, C.; Hamrouni, B.; Sellaoui, L.; Badawi, M.; Poch, J.; Fiol, N. Single and simultaneous adsorption of Cr (VI) and Cu (II) on a novel Fe3O4/pine cones gel beads nanocomposite: Experiments, characterization and isotherms modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, R.; Zhu, X.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y. Sorption of tetrabromobisphenol A onto microplastics: Behavior, mechanisms, and the effects of sorbent and environmental factors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babapour, M.; Dehghani, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Arjmand, M.; Salari, M.; Rasuli, L.; Mubarak, N.; Khan, N. Adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution using mesoporous metal-organic framework-5 functionalized with the amino acids: Characterization, optimization, linear and nonlinear kinetic models. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, P.; Wu, P.; Fang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, S. UiO-66 derived N-doped carbon nanoparticles coated by PANI for simultaneous adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium from waste water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) by magnetic activated carbon and its mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikuku, V.O.; Zanella, R.; Kowenje, C.O.; Donato, F.F.; Bandeira, N.M.G.; Prestes, O.D. Single and binary adsorption of sulfonamide antibiotics onto iron-modified clay: Linear and nonlinear isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanistic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Adenosine-functionalized UiO-66-NH2 to efficiently remove Pb (II) and Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Thermodynamics, kinetics and isothermal adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Model/Equation | Parameter | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | qt (mg/mL): amount of adsorbate adsorbed at time t qe (mg/g): equilibrium sorption capacity K1 (1/min): pseudo-first-order equilibrium rate constant | [37] |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | K2 (g/mg min): pseudo-second-order equilibrium rate constant | [38] |
| Intraparticle diffusion | Kid (mg/g min1/2): intraparticle diffusion rate constant C: boundary layer obtained by extrapolation of the linear portion of the plot of qt versus t0.5 | [37] |
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g): maximum sorption capacity KL (L/mg): Langmuir sorption équation constant Ce (mg/L): equilibrium adsorbate concentration in solution C0 (mg/L): initial adsorbate concentration in solution RL: separation factor | [42] |
| Freundlich | KF (L/mg)1/n(mg/g): Freundlich parameter 1/nf: constant corresponded to adsorption intensity | [42] |
| Temkin | KT (L/mg): Temkin adsorption potential BT (KJ/mol): heat of sorption | [42] |
| Sips | Ks (L/mg): Sips model constant 1/ns: Sips model exponent | [25] |
| Kc: distribution coefficient Cs (mg/g): amount of ion adsorbent ΔG° (kJ/mol): change in standard free energy ΔS° (kJ/mol): standard entropy ΔH° (kJ/mol): standard enthalpy R (8.314 J/mol K): universal gas constant | [42] | |
| Modified Arrhenius | Ea: activation energy S*: sticking probability θ: surface coverage | [35] |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | Pb (II) | Cr (VI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 50 | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 (1/min) | 0.8425 | 0.3420 |
| qe (mg/g) | 34.072 | 17.570 | |
| R2 | 0.9390 | 0.8812 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K2 (1/min) | 0.0453 | 0.0246 |
| qe (mg/g) | 35.408 | 19.000 | |
| R2 | 0.9648 | 0.9575 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | Kid,1 (mg/g min1/2) | 1.4887 | 1.7300 |
| C1 (mg/g) | 26.809 | 8.8330 | |
| R2 | 0.9796 | 0.9040 | |
| Kid,2 (mg/g min1/2) | 0.9563 | 0.6715 | |
| C2 (mg/g) | 28.921 | 13.690 | |
| R2 | 0.9274 | 0.8264 | |
| Kid,3 (mg/g min1/2) | 1.5188 | 0.2072 | |
| C3 (mg/g) | 24.936 | 17.780 | |
| R2 | 0.9110 | 0.7231 |
| Isotherm Parameters | Temperature (K) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (II) | Cr (VI) | |||||
| 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | |
| Langmuir | ||||||
| qmax (mg/g) | 67.787 | 69.103 | 71.426 | 39.450 | 39.515 | 39.995 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.3747 | 0.5088 | 0.7185 | 6.1265 | 8.8427 | 12.233 |
| RL | 0.0326 | 0.0242 | 0.0173 | 0.0046 | 0.0032 | 0.0023 |
| R2 | 0.9552 | 0.9563 | 0.9541 | 0.8437 | 0.8555 | 0.9489 |
| Freundlich | ||||||
| KF (L/mg)1/n(mg/g) | 28.113 | 30.982 | 33.725 | 29.325 | 30.732 | 32.124 |
| nf | 4.6339 | 4.9407 | 5.0787 | 5.7175 | 6.2932 | 7.4515 |
| R2 | 0.8878 | 0.8860 | 0.9070 | 0.9904 | 0.9794 | 0.9091 |
| Temkin | ||||||
| BT (kJ/mol) | 10.591 | 10.305 | 10.332 | 5.325 | 4.950 | 4.411 |
| KT (L/mg) | 9.9494 | 15.632 | 22.894 | 301.37 | 616.43 | 1803.79 |
| R2 | 0.9699 | 0.9719 | 0.9835 | 0.9981 | 0.9979 | 0.9583 |
| Sips | ||||||
| qmax (mg/g) | 76.934 | 77.909 | 81.760 | 72.370 | 58.554 | 43.865 |
| KS (L/mg) | 0.4079 | 0.5116 | 0.6183 | 0.7101 | 1.203 | 4.079 |
| ns | 1.4799 | 1.5069 | 1.6017 | 3.2154 | 2.8224 | 1.6795 |
| R2 | 0.9879 | 0.9947 | 0.9953 | 0.9965 | 0.9939 | 0.9903 |
| Heavy Metal Ions | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol·K) | Ea (kJ/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 °K | 308 °K | 313 °K | 318 °K | 323 °K | ||||
| Pb (II) | −4.77167 | −5.68388 | −6.33805 | −7.13721 | −8.17302 | +32.9148 | +126.012 | +30.3047 |
| Cr (VI) | −5.85144 | −6.40522 | −6.81851 | −7.27772 | −7.79501 | +17.1887 | +76.9815 | +16.0097 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, A.; Forghani, M.; Kafshgari, L.A.; Hassanzadeh, A. Adsorptive Removal Behavior of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment onto Polyaniline-Modified MIL100(Fe). Minerals 2023, 13, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030299
Azizi A, Forghani M, Kafshgari LA, Hassanzadeh A. Adsorptive Removal Behavior of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment onto Polyaniline-Modified MIL100(Fe). Minerals. 2023; 13(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Asghar, Mojtaba Forghani, Leila Asadi Kafshgari, and Ahmad Hassanzadeh. 2023. "Adsorptive Removal Behavior of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment onto Polyaniline-Modified MIL100(Fe)" Minerals 13, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030299
APA StyleAzizi, A., Forghani, M., Kafshgari, L. A., & Hassanzadeh, A. (2023). Adsorptive Removal Behavior of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment onto Polyaniline-Modified MIL100(Fe). Minerals, 13(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030299







