Diagenetic Facies Controls on Differential Reservoir-Forming Patterns of Mixed Shale Oil Sequences in the Saline Lacustrine Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
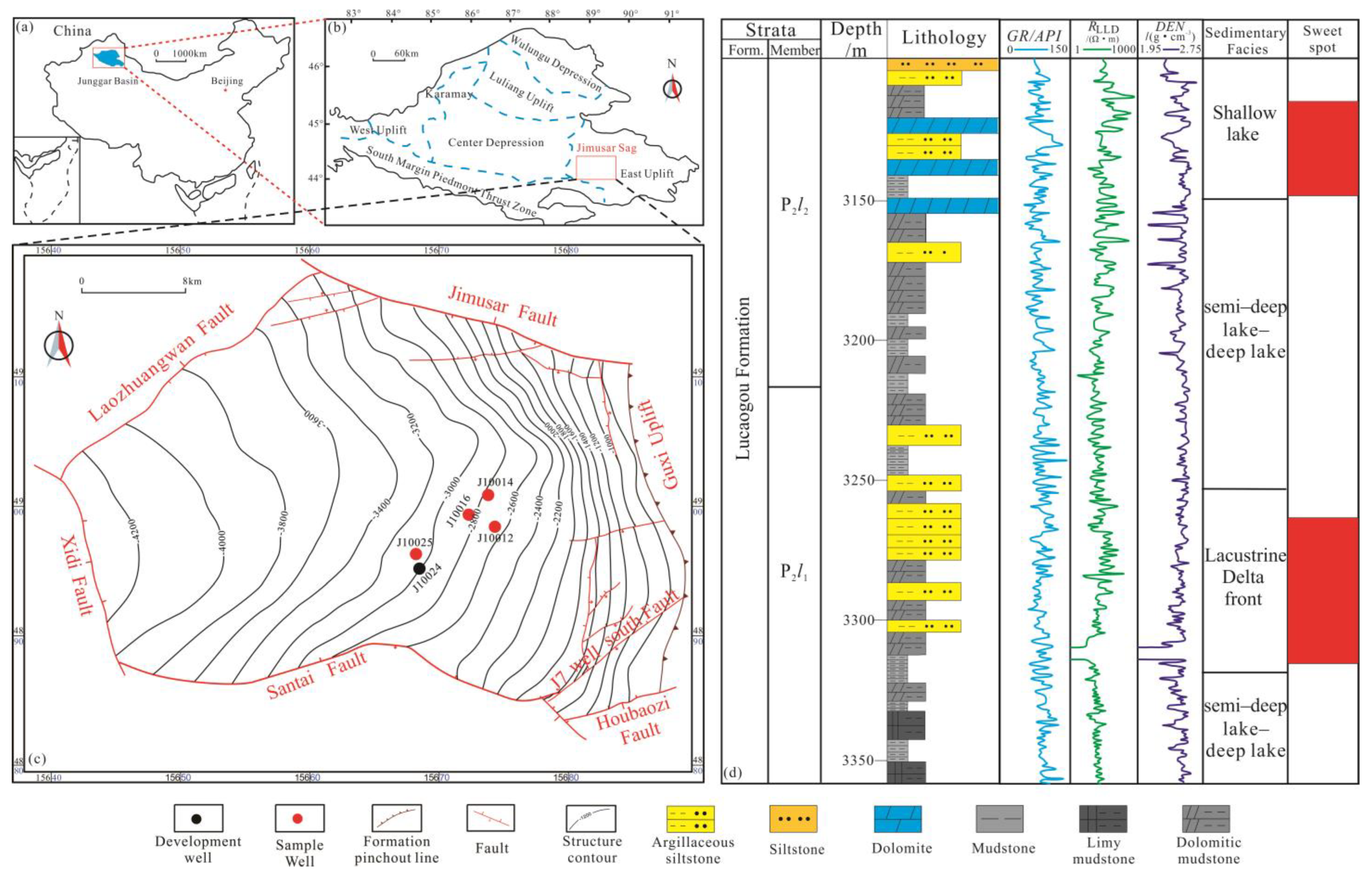
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Experimental Methods and Theories
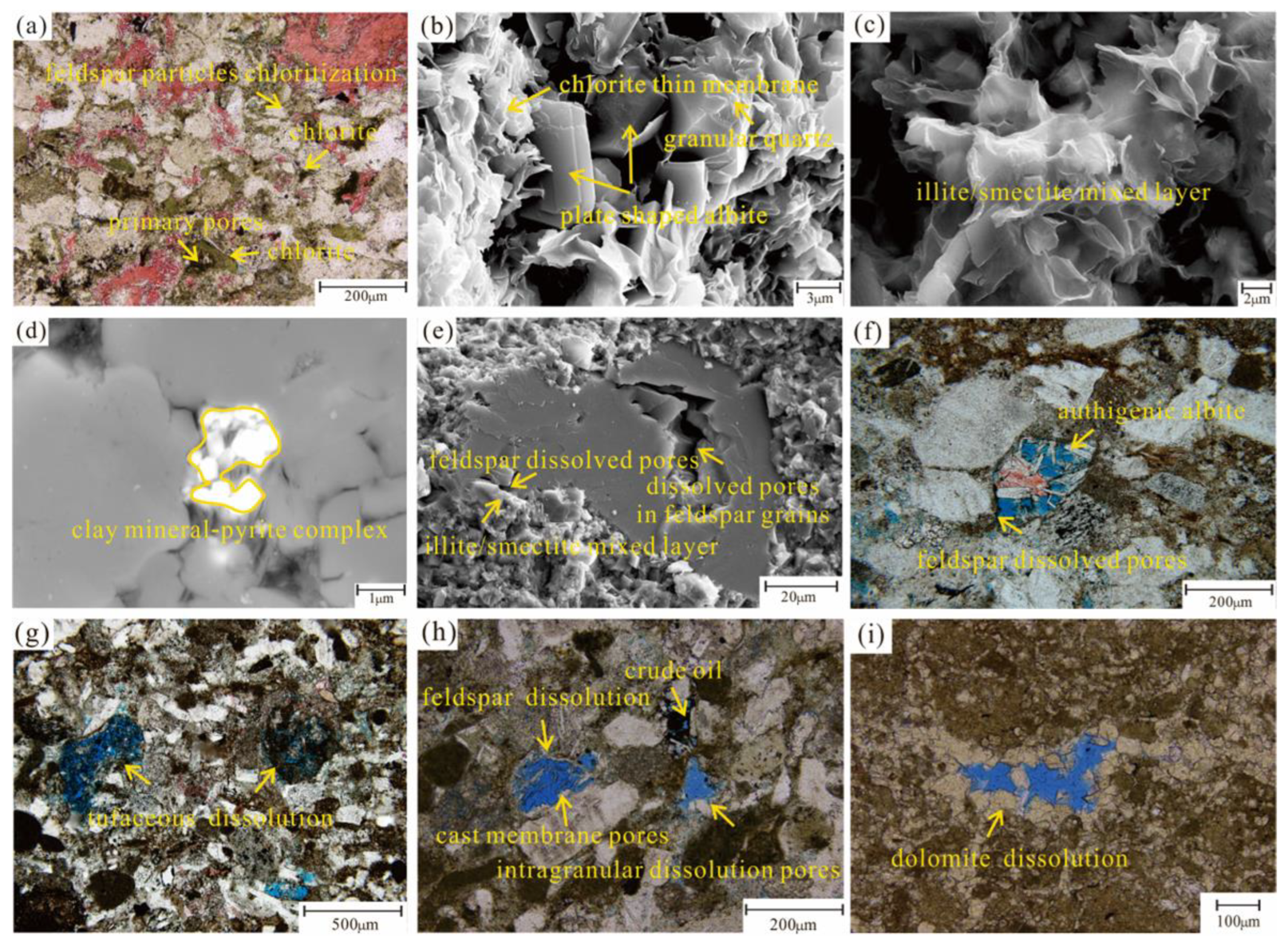
3.2.1. Thin Section Observation
3.2.2. Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
3.2.3. XRD Analysis
3.2.4. Low-Temperature N2 Adsorption
3.2.5. HPMI Analysis
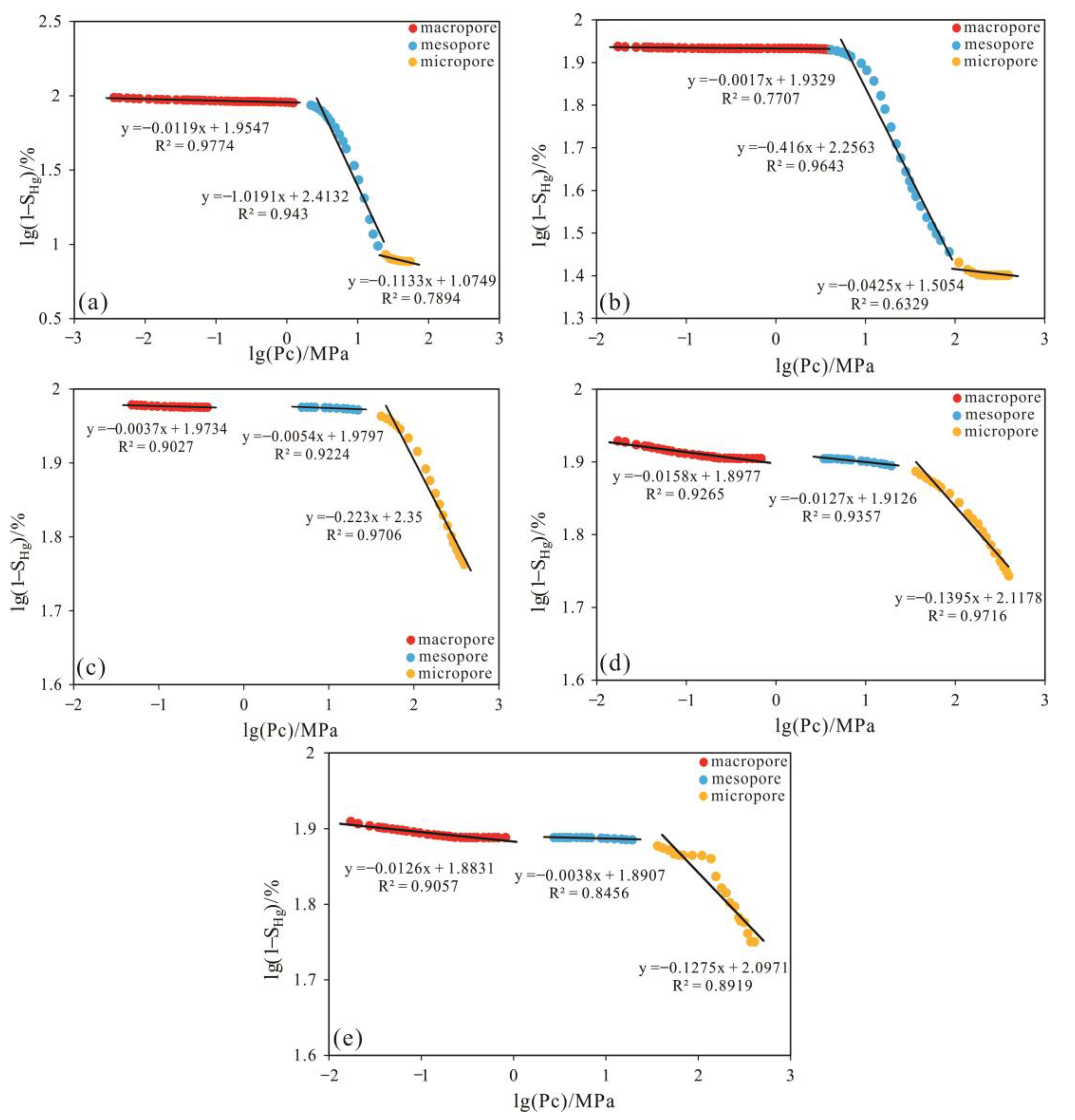
3.2.6. Fractal Theory
4. Results
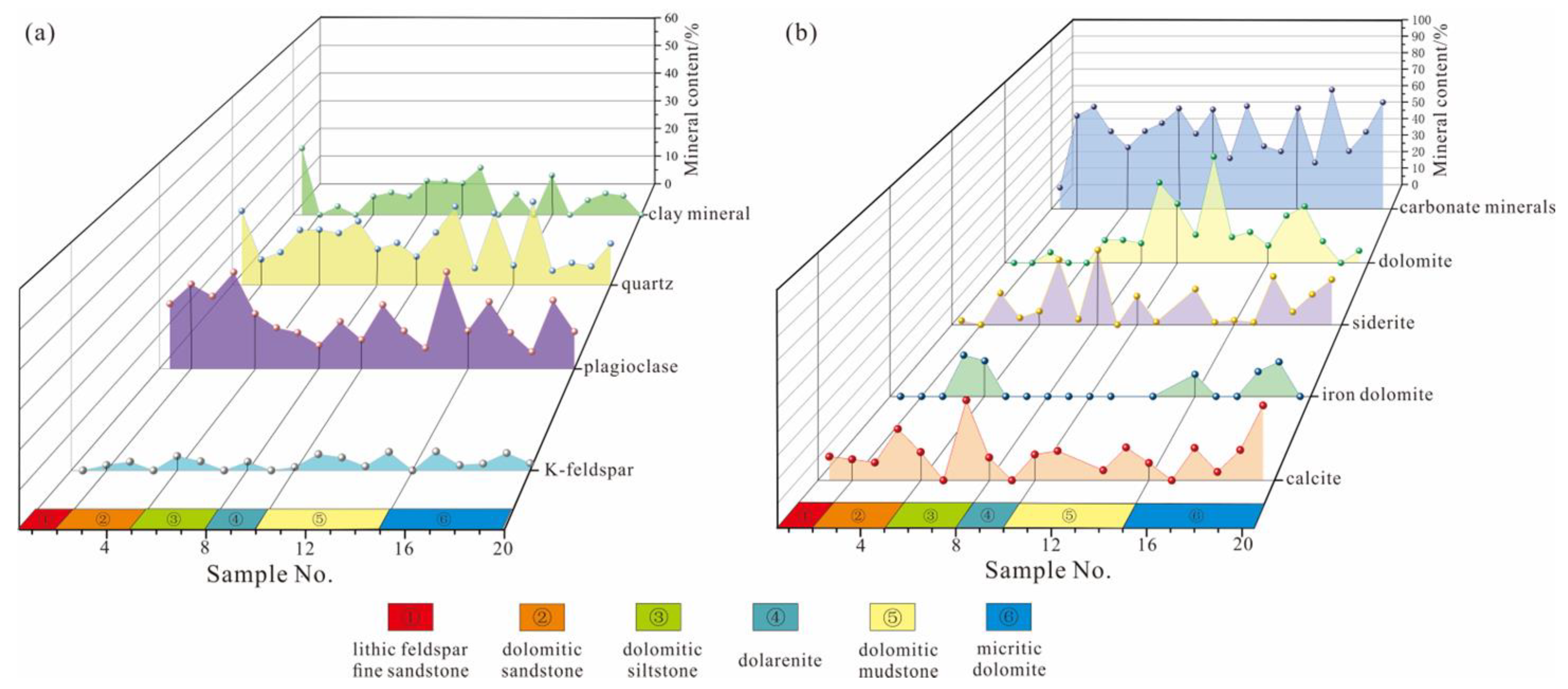
4.1. Petrological Characteristics
4.1.1. Mineral Composition
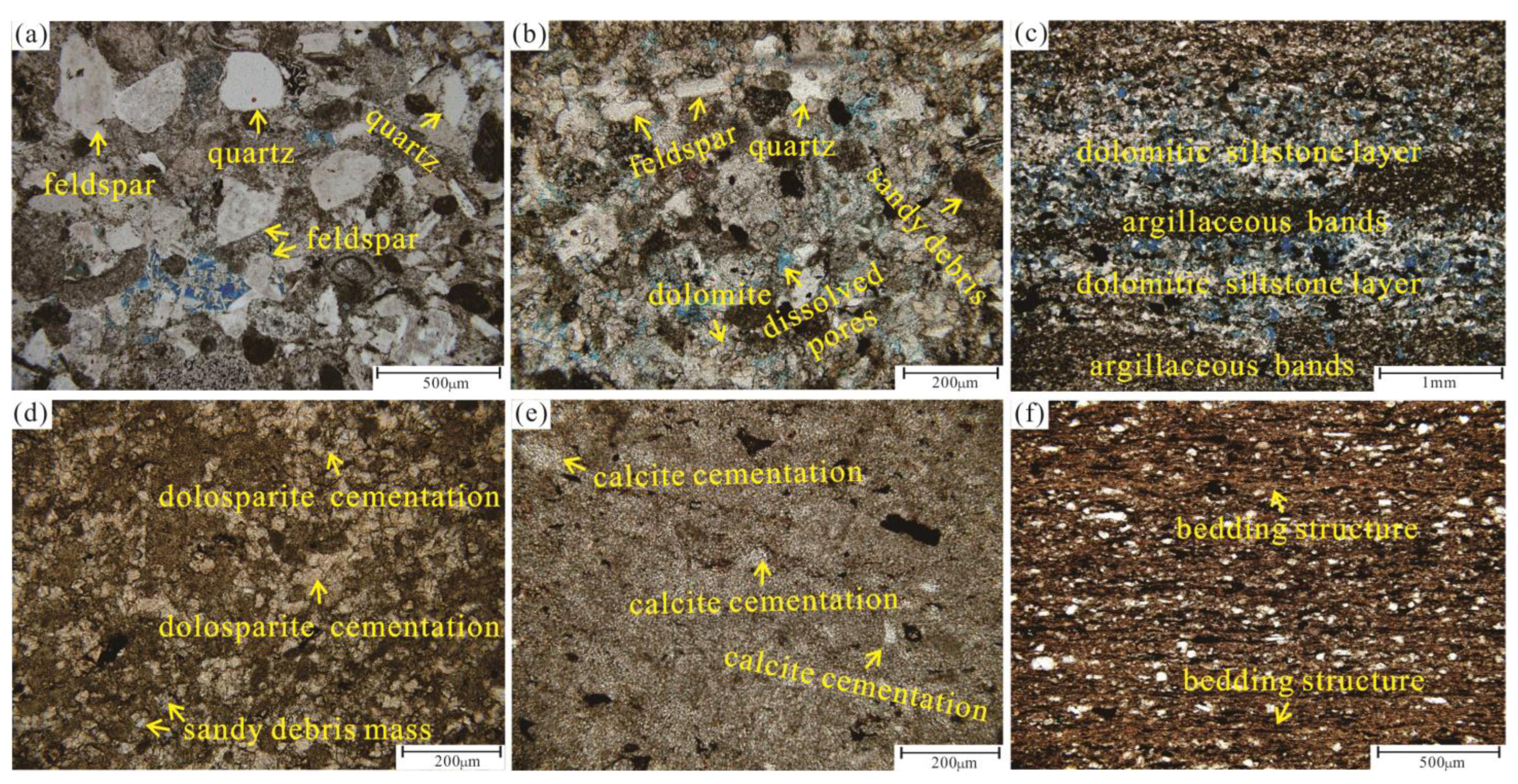
4.1.2. Lithologic Characteristics
4.2. Type of Diagenesis
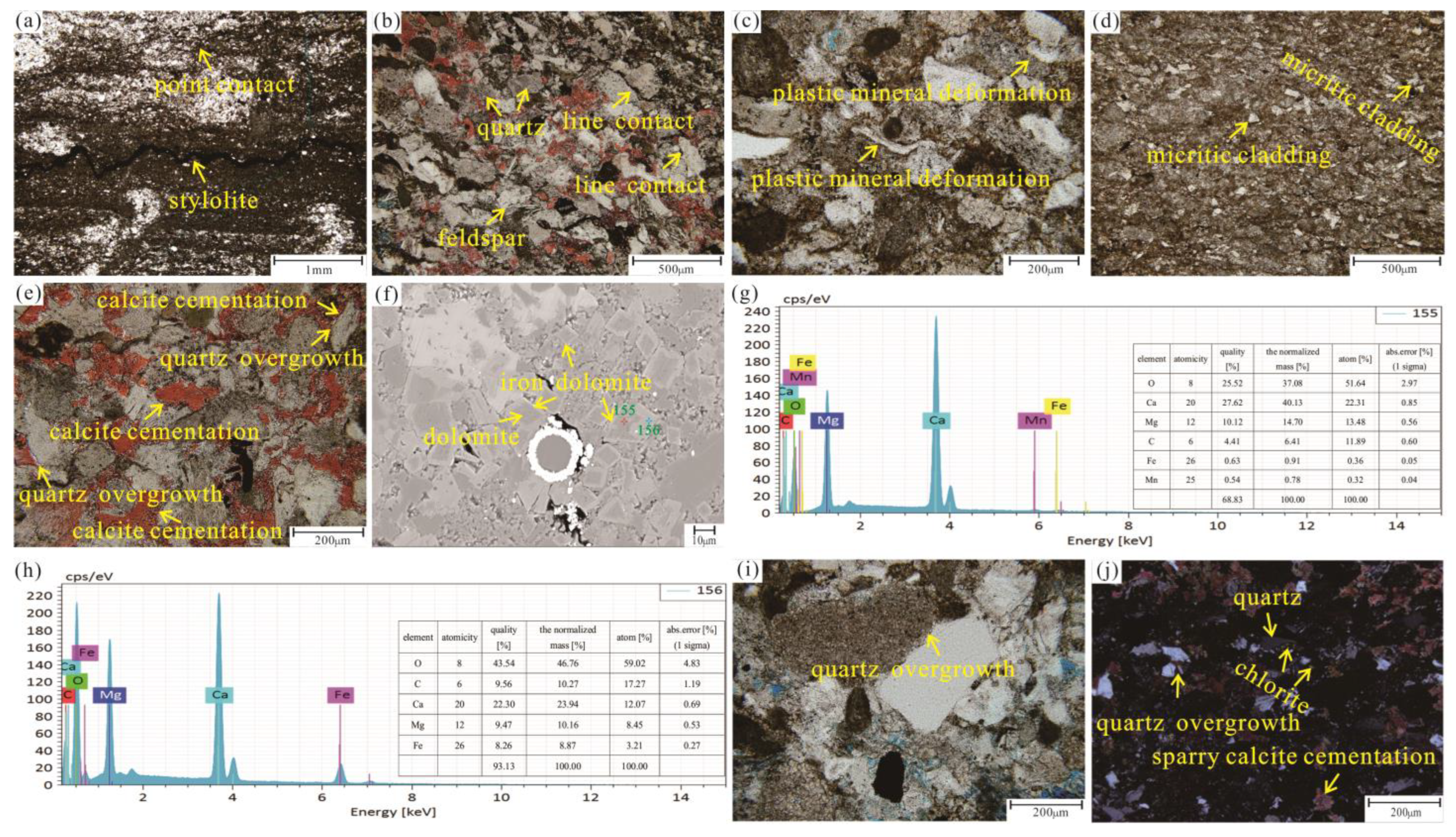
4.2.1. Compaction
4.2.2. Cementation
4.2.3. Dissolution
4.3. Diagenetic Stages and Evolutionary Sequences
4.3.1. Diagenetic Stages
4.3.2. Diagenetic Evolutionary Sequence
4.4. Types and Characteristics of Diagenetic Facies
4.4.1. Tuffaceous-Feldspar Dissolution Facies
4.4.2. Mixed Cementation Dissolution Facies
4.4.3. Chlorite Thin Membrane Facies
4.4.4. Carbonate Cementation Facies
4.4.5. Mixed Cementation Compact Facies
5. Discussion
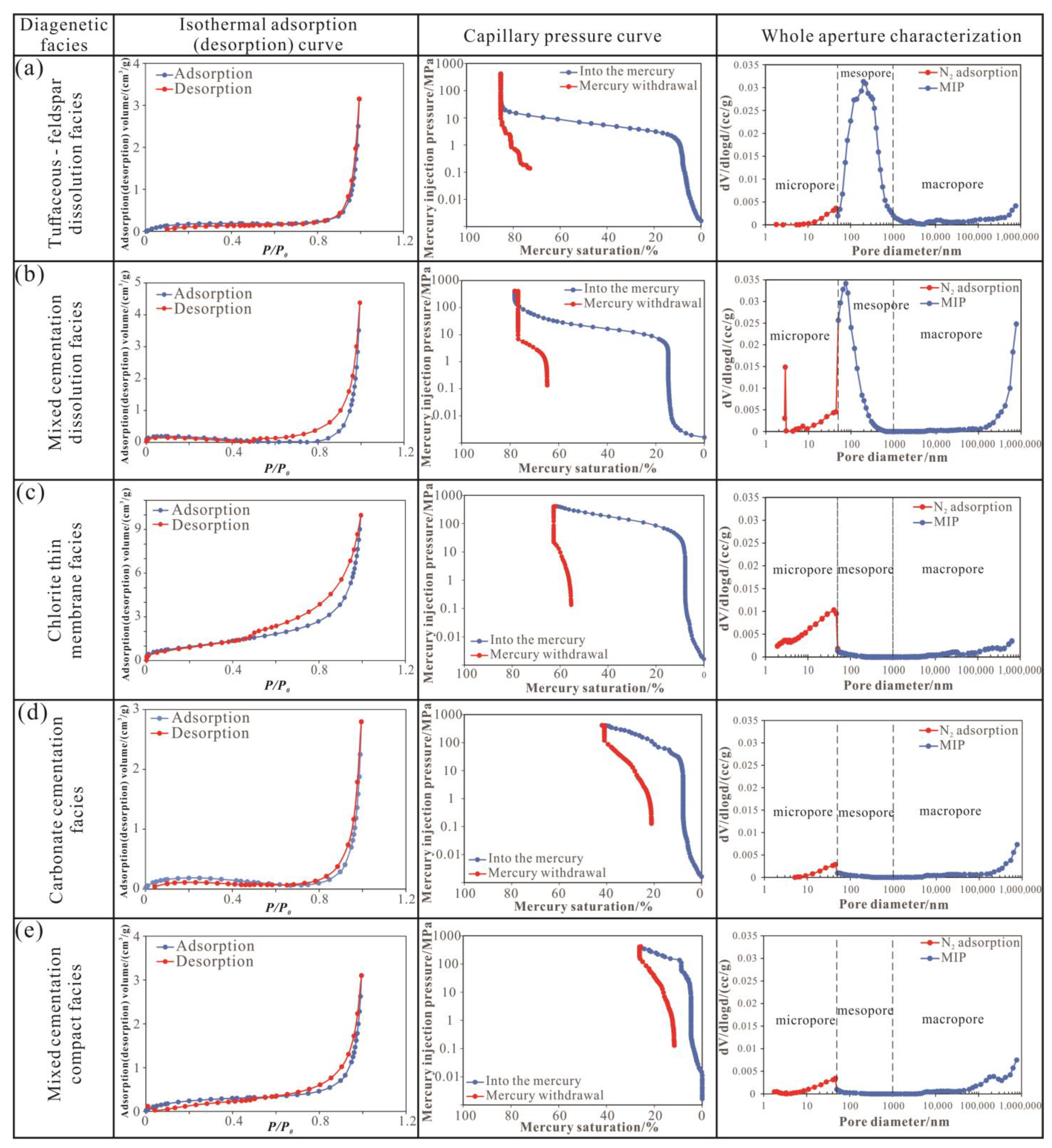
5.1. Micropore Heterogeneity of Shale Oil Reservoirs with Different Diagenetic Facies
5.1.1. Differences in Pore Structure Characteristics
5.1.2. Microscopic Heterogeneity of Reservoir under Differential Diagenesis
5.2. Different Diagenetic Facies Control Reservoir Mechanism
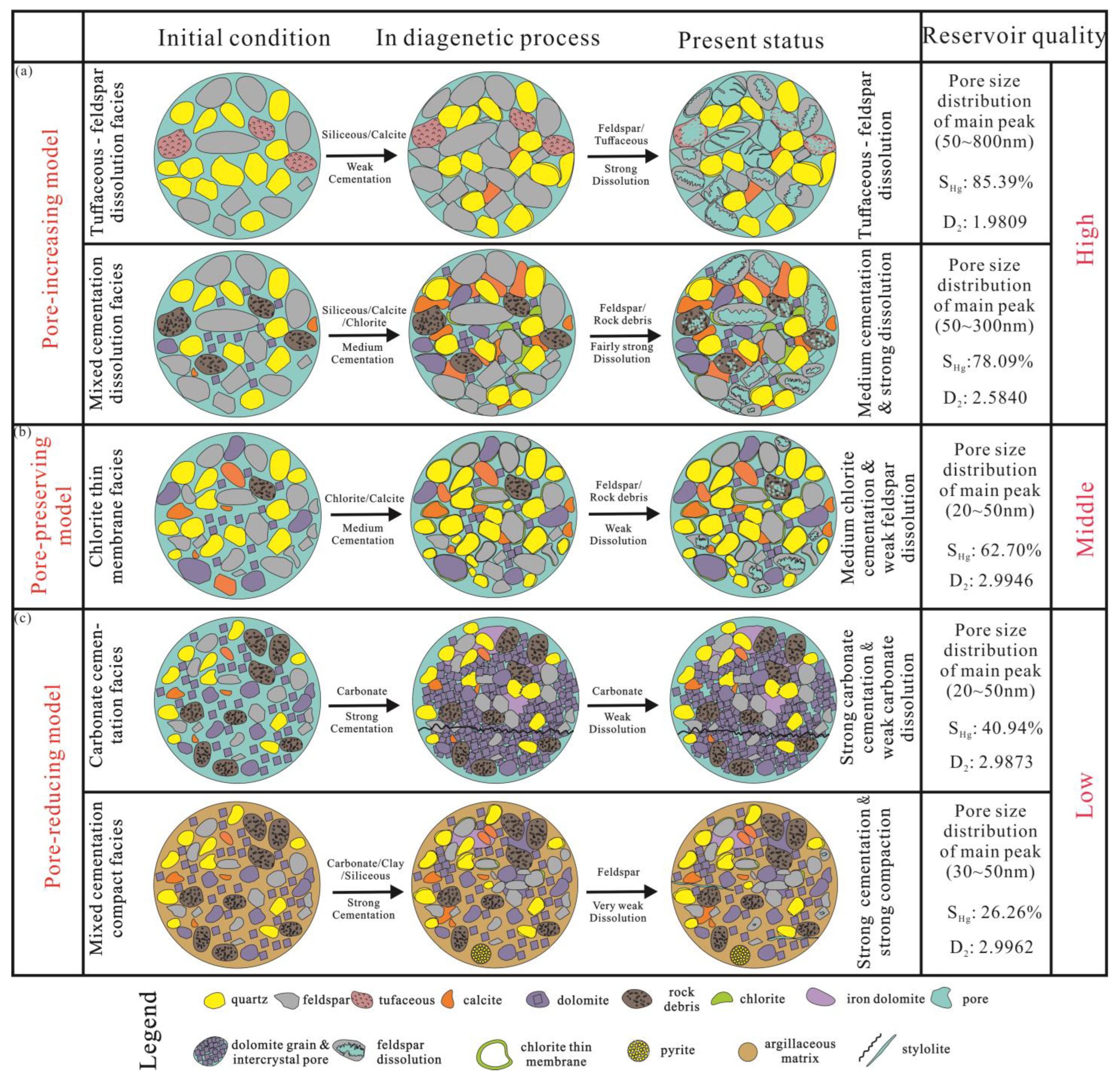
5.3. Different Diagenetic Facies Control Different Reservoir Models
- (1)
- Pore-increasing model: This model is more common in the rock strata where tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies and mixed cementation dissolution facies are developed (Figure 11a). In the tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies and mixed cementation dissolution facies, the dissolution is strong and the cementation is moderate, and the dissolved pores and residual intergranular pores are visible. In this model, the reservoir is of the best quality, usually with large pore volume, mesopore development, and relatively low heterogeneity.
- (2)
- Pore-preserving model: This model is more common in the rock strata where chlorite thin-membrane facies are developed (Figure 11b). The chlorite cementation in the chlorite membrane is moderate, the dissolution is weak, and residual intergranular pores are visible. The reservoirs formed in this model are of medium quality, usually with micropore development and the weakest heterogeneity.
- (3)
- Pore-reducing model: This model is more common in the rock strata where carbonate cementation facies and mixed cementation compact facies are developed (Figure 11c). The carbonate cementation facies and mixed cementation compact facies have strong compaction, moderate cementation, almost no dissolution, and undeveloped nano-pores under the microscope. The reservoirs formed in this model are of poor quality, usually with small pore volume, poor pore throat connectivity, and strong heterogeneity.
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The diagenetic stage of the Lucaogou Formation shale oil reservoir in Jimusar Sag is in the middle diagenetic stage A, and the diagenetic evolution sequence of the reservoir is compaction—chlorite cementation—silica cementation—first-stage carbonate cementation—first-stage dissolution of authentic albite—illite/smectite mixed layer cementation—second-stage carbonate cementation—second-stage dissolution. The diagenetic facies of the shale oil reservoir in the Lucaogou Formation in the study area can be divided into five categories.
- (2)
- The characteristics of pore type, pore size distribution, and pore structure heterogeneity of the different diagenetic facies are obviously different. The tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies is dominated by the dissolved pores, with the widest pore size distribution range, and the main peaks are concentrated in 50~800 nm. The mesopores are the main reservoir space, and the maximum mercury saturation reaches 85.39%, reflecting good pore connectivity, as well as the lowest D2 value of 1.9809, making it the optimal diagenetic facies for the target layer. The mixed cementation dissolution facies developed dissolved pores and residual intergranular pores, and the main peaks are concentrated in 50~300 nm. Compared with the tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies, the maximum mercury saturation reaches 78.09% and the D2 value is slightly higher at 2.5840, which make it a better diagenetic facies for the target layer. The chlorite thin membrane facies is mainly composed of residual intergranular pores with small pore size, with relatively developed micropores and the lowest D1 value of 2.7770, which make it a favorable diagenetic facies for the target layer. The carbonate cementation facies and mixed cementation compact facies have poor pore development, and their main peak pore size is concentrated in 30~50 nm, with lower mercury saturation and higher D2 value, which make them usually not studied as favorable diagenetic facies.
- (3)
- According to the diagenetic facies differential control mechanism, the reservoir can be divided into three types. The high-quality reservoir consists of rocks developed by the tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies and mixed cementation dissolution facies, mainly developing dissolved pores and residual intergranular pores, with large pore volume, good pore connectivity, weak pore structure heterogeneity, and good reservoir capacity. The medium reservoir consists of rocks developed by the chlorite thin-membrane facies, mainly developing chlorite residual intergranular pores, with large pore volume, good pore connectivity, weak pore structure heterogeneity, and medium reservoir capacity. The poor reservoir consists of rocks developed by the carbonate cementation facies and mixed cementation compact facies, with undeveloped pores, poor pore connectivity, strong pore structure heterogeneity, and poor reservoir capacity.
- (4)
- The reservoir control model under differential compaction, differential cementation and differential dissolution of shale oil reservoirs is summarized, that is, dissolution increases pores, chlorite cementation preserves pores, and compaction cementation reduces pores. This model can provide reference value for the evaluation of saline lake mixed shale oil reservoir classification.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, Z.J.; Zhu, R.K.; Liang, X.P.; Shen, Y.Q. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Ma, F.; Pan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Fu, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z. Formation and distribution potential of global shale oil and the developments of continental shale oil theory and technology in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2023, 30, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.K.; Zhang, P.X.; Bian, R.K.; Wu, X.L.; Zhai, C.B. Oil accumulation characteristics of China continental shale. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.G.; Liu, D.R.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y.F. Current status and prospects of China’s continental shale oil exploration and development. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2022, 42, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.G.; He, W.J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.T.; Feng, Y.L.; Jia, X.Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, L. Evaluation and application of key technologies of “sweet area” of shale oil in Junggar Basin: Case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Depression. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Ma, R.; Li, J.B.; Lu, S.F.; Li, C.M.; Guo, Z.L.; Li, Z. Occurrence mechanism of lacustrine shale oil in the Paleogene Shahejie Formation of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, X.W.; Niu, X.B.; Feng, S.B.; You, Y. Geological conditions for continental tight oil formation and the main controlling factors for the enrichment: A case of Chang 7 Member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.S. Effective reservoir spaces of Paleogene shale oil in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2018, 40, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.S.; Ye, Y.P.; Qin, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Xiao, D.S. Microscopic pore structure characterization and oil-bearing property evaluation of lacustrine shale reservoir: A case study of the Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.G.; Du, M.; Chen, C.; Qin, M.; Jia, N.H.; Lv, W.F.; Ding, Z.H.; Xiang, Y. Quantitative characterization of pore structure of shale reservoirs of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag. Lithol. Reserv. 2022, 34, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.Y.; Zhong, D.K.; Niu, S.L.; Sun, H.T.; Cao, X.; Wang, F. Alkaline Diagenesis and Porosity Evolution of Zhuhai Formation Reservoirs in Eastern Huizhou Sag. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2020, 38, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.Z. Acid-base alternation diagenesis and its influence on shale reservoirs in the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, J.W.; Worley, W.G.; Robinson, B.A.; Grigsby, C.O.; Feerer, J.L. Correlating quartz dissolution kinetics in pure water from 25 to 625 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Qiu, R.; Chen, W.; Tu, Y. Alkaline diagenesis and its influence on a reservoir in the Biyang depression. Sci. Sin. (Terrae) 2002, 45, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.Q.; Zhu, Y.M.; Chen, S.B. Diagenesis controlling mechanism of pore characteristics in the Qiongzhusi Formation Shale, East Yunnan. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.F.; Luo, X.R.; Zhang, L.K.; Sui, F.G.; Lin, H.X.; Lei, Y.H. Diagenetic evolution of deep sandstones and multiple-stage oil entrapment: A case study from the Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation in the Fukang Sag, central Junggar Basin (NW China). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 152, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.T.; Zhang, L.K.; Ye, M.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Xiu, J.L.; Ping, Z.Z.; Cao, B.F.; Li, C.; Lei, Y.H.; Cheng, M.; et al. Different diagenesis of deep sandstone reservoir and its relationship with reservoir property: Case study of Jurassic in Zhengshacun area, central Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Q.; Xu, S.M.; Ren, X.C.; Chi, X.Q.; Shu, P.C.; Liu, X.; Kong, J.H. Diageneses and controlling factors of Jurassic Sangonghe Formation reservoirs on the west side of the hinterland of Junggar Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 319. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.Y.; Huang, C.G.; Xia, Q.S.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, F.; Wan, C.; Pan, X. The characteristics of carbonate reservoir, and formation mechanism of pores in the saline lacustrine basin: A case study of the lower Eocene Ganchaigou formation in western Qaidam Basin. Geol. Rev. 2016, 62, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fresca, B.; Pinkston, D.; Loucks, R.G.; LeFever, R. The three Forks playa lake depositional model: Implications for characterization and development of an unconventional carbonate play. AAPG Bull. 2018, 102, 1455–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, S.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Long, G.H.; Gong, Q.S.; Tian, M.Z.; Wu, J. Genetic mechanism and development model of lacustrine hybrid carbonate reservoirs in the western Yingxiongling structural belt, Qaidam Basin. J. China Univ. Pet. Ed. Nat. Sci. 2022, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.X.; Yao, S.P.; Lu, X.C.; Wu, H.G.; Sun, F.N.; Jin, J. Effects of organic matter evolution on oil reservoir property during diagenesis of typical continental shale sequences. Oil Gas Geol. 2019, 40, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.L.; Wu, S.T.; Liu, J.D.; Yuan, Y.J.; Cui, J.G.; Su, L.; Jiang, X.H.; Wang, J. New insights into controlling factors of pore evolution in organic-rich shale. Energy Fuels. 2021, 35, 4858–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.B.; Liu, H.M.; Qiu, L.W.; Zhang, S.P.; Fang, Z.W.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Miao, Z.W. Characteristics and influencing factors of shale oil reservoir space in Paleogene shale of Dongying Sag. Earth Sci. 2022; 1–21, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.D.; Wang, K.Z.; Juan, D.F.; Liu, F. Diagenetic facies types of tight reservoir and its effects on productivity: A case of Chang 8 reservoir in Jiangjiachuan area, Ordos Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2018, 30, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.L.; Lu, F.Y.; Dan, W.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Cui, G.X.; Wang, S. Classification of diagenetic facies in tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Chang 33 reservoir in the west of Huanxian, Ordos Basin. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2020, 27, 591–596. [Google Scholar]
- Grigsby, J.D.; Langford, R.P. Effects of diagenesis on enhanced-resolution bulk density logs in Tertiary Gulf Coast sandstones: An example from the lower Vicksburg Formation, McAllen Ranch field, south Texas. AAPG Bull. 1996, 80, 1801–1819. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.B.; Ying, F.X.; Zheng, J.M.; Guo, H.L.; Zhu, R.K. Numerical simulation of clastic diagenesis and its application. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2004, 31, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Xin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, C.; Han, C.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Q. Diagenetic facies analysis of tight sandstone gas reservoir of Bashijiqike Formation in Kuqa Depression. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2014, 25, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, J.F. Diagenetic facies and its porosity evolution of ultra-low permeability reservoir in Putaohua Reservoir in Da’an Oilfield in Songliao Basin. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing, 2022; 1–12, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Ji, Y.L.; Yang, K.M. Diagenetic facies and reservoir evaluation in sequence framework of Upper Shaximiao Formation in middle area of western Sichuan Depression. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2019, 26, 550–554. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.H.; Tan, C.Q.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J. Different influence of diagenesis on micro pore-throat characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs: Case study of the Triassic Chang 7 member in Jiyuan and Zhenbei areas, Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 826–835. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B.; Ma, L.; Liu, R.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, G.; Wang, W. Diagenesis of Permian volcanic rocks and its influence on reservoir performance in Jianyang area, Sichuan, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Tech. (Sci. Tech. Ed.) 2020, 47, 711–723. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Ran, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, Y. Impact of diagenesis on the reservoir quality of tight oil sandstones: The case of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 7 oil layers in Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 145, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.Q.; Chen, S.M.; Yan, W.L.; Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, J. Pore structure evaluation of low permeability clastic reservoirs based on sedimentation diagenesis: A case study of the Chang 8 reservoirs in the Zhenbei region, Ordos Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.C.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, S.M.; Xi, K.L.; Xue, X.J. Diagenesis and reserving space characteristics of tight oil reservoirs of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Sag of Junggar Basin. China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2019, 41, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Peng, S.C.; Gao, Q.H.; Li, C.L.; Lin, Y.S. Diagenesis and pore structure characteristics of carbonate component of lacustrine mixed rocks: A case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Sag, Xinjiang. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2020, 27, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Shar, A.M.; Mahesar, A.A.; Abbasi, G.R.; Narejo, A.A.; Hakro, A.A.A.D. Influence of diagenetic features on petrophysical properties of fine-grained rocks of Oligocene strata in the Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.X.; Han, C.Y.; Kang, J.L.; Li, B.; Wu, J.P.; Jiang, T.; Fan, J.; Ye, D.S. New genesis model of the shale oil sweet-spot reservoir: Case study of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2022, 33, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Chang, Q.S.; Qian, Y.X.; Liu, G.L.; Wan, M.; Huang, L.L. Reservoir characteristics and genesis of shale oil "sweet spots" in Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 42, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, X.J.; Lai, F.Q.; Gao, X.B.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.C.; Luo, X.; et al. Characteristics and genetic mechanism of pore throat structure of shale oil reservoir in saline lake—A case study of shale oil of the Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Energies 2021, 14, 8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.C.; Liu, K.Y.; Gao, Y.; Qin, Z.J. Fractal characteristics of the pore structures of fine-grained, mixed sedimentary rocks from the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin: Implications for lacustrine tight oil accumulations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 182, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.J.; Wang, G.W.; Kuang, L.C.; Li, H.B.; Zhao, Y.D.; Li, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.T.; Feng, Z.; Lai, J. Insights into the pore structure and oil mobility in fine-grained sedimentary rocks: The Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 137, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.S.; Qiu, L.W.; Cao, Y.C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, K.H.; Wan, M.; Du, L. Organic petrology characteristics and occurrence of source rocks in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar sag. J. China Univ. Pet., Ed. Nat. Sci. 2017, 41, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.H.; Jia, C.Z.; Guo, Z.J.; Song, Y.; Xu, H.M.; Liu, L.J. New view on the Permian evolution of the Junggar Basin and its implications for tectonic evolution. Earth Sci. Front. 2006, 13, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhi, D.M.; Xiang, B.L.; Li, E.T. Enrichment law of shale oil of Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar sag, Junggar Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2022, 43, 1253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, S.Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Characteristics of the high-resolution sequence stratigraphy and the distribution of tight oil reservoirs in the salt lake: A case from the a region of Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag. Geoscience 2016, 30, 1096–1104, 1114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, E.T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, B.Z. Genesis and pore development characteristics of Permian Lucaogou migmatites, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Exp. Pet. Geol. 2022, 44, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Tian, J.J.; Han, C.C.; Zhang, W.W.; Deng, S.W.; Sun, G.X. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Jungger Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2021, 33, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.W.; Han, C.C.; Tian, J.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.Q. Sequence stratigraphy division and evolutionary features of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag. Lithol. Reserv. 2021, 33, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zeng, Z.P.; Tian, J.J.; Li, Y.L.; Li, W.A.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, Z.H. Genesis and distribution prediction of sweet spots of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag. Lithol. Reserv. 2022, 34, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Anovitz, L.M.; Cole, D.R. Characterization and analysis of porosity and pore structures. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2015, 80, 61–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.F.; Hu, C.P.; Wang, B.; Peng, K.; Liu, H.Q. Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 301. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, X.; Xie, Z. Controlling effect of fine-grained sedimentary microfacies upon the microstructure of shale oil reservoirs in the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2016, 37, 923–934. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.W.; Li, P.C.; Sun, Z.Y.; Lu, Z.W.; Du, Z.H.; Liang, H.B.; Lu, D.T. A new method for analysis of dual pore size distributions in shale using nitrogen adsorption measurements. Fuel 2017, 210, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Z.; Liu, G.D.; Yang, W.W.; Zou, H.Y.; Sun, M.L.; Wang, X.L. Multi-fractal distribution analysis for pore structure characterization of tight sandstone—A case study of the Upper Paleozoic tight formations in the Longdong District, Ordos Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 92, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.J.; Wan, H.F. Study of pore structure of tight sandstone reservoir based on fractal theory: A case study from Chang 7 tight sandstone of Yanchang formation in Qingcheng area, Ordos Basin. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2022, 51, 941–955. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Zhong, F.X.; He, C.Z.; Feng, W.G. Fractal texture research on the pores in reservoir rocks and its application. Nat. Gas Ind. 2000, 20, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.D.; Liu, C.L.; Zang, Q.B.; Wu, Y.P.; Yang, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Zeng, X.X.; Li, W.D. Application of high pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance in analysis of the pore structure of dense sandstone: A case study of the Heshui area, Ordos Basin. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.Z.; Zhu, H.H. Micro-pore structure and fractal characteristics of the Xiashihezi Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in Sulige Area, Ordos Basin. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L.; Meng, Q.X.; Liu, Z.L.; Yang, W.; Jin, H.; Shen, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, S.B. Physical property and heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case of the Upper Triassic 6th member of Xujiahe Formation, Guang’an, central Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 597–609. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, M.; Su, Y.; Gao, C.H.; Qu, X.; Wang, X.; Ding, X. Tight reservoir space characteristics and controlling factors: An example from Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag, Junggar basin, northwest China. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 88–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.M. Diagenesis and Genetic Mechanism of Tight Oil Reservoir of the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar Sag, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Dongying, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M.; Ma, K.; Hou, J.G.; Yan, L.; Chen, F.L. Diagenetic controls on the quality of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation tight reservoir, southeastern Junggar Basin, northwestern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 178, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Qiu, L.W.; Cao, Y.C.; Chen, C.; Lei, D.W.; Wan, M. Reservoir quality and diagenesis of the Permian Lucaogou Formation tight carbonates in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, West China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K. Genesis of Mixed Sedimentation and Densification Mechanism of Tight Reservoir in Terrestrial Lacustrine Basin—A Case Study of Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Commission, S.E.T. SY/T 5477—2003; The division of diageneticstages in clastic rocks. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Wei, Z.Z.; Zhu, S.Y.; Wang, X.W. Reservoir characteristics of Chang 8 Oil-bearing Formation and quantitative analysis of diagenetic facies in Longdong Area of Ordos Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 12519–12528. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.Q. Micro-Characteristics and Controlling Factors on Physical Properties of Tight Mixed Dolomitic-Clastic Rocks Reservoirs of Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag, NW China. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Dongying, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.H.; Zhong, D.K.; Yao, J.L.; Sun, H.T.; Niu, X.B.; Liang, X.W.; You, Y.; Li, X. Alkaline diagenesis and its effects on reservoir porosity: A case study of Upper Triassic Chang 7 tight sandstones in Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2015, 42, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.Z.; Sun, W.; Wei, H.; Qu, X.F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Diagenetic facies of Chang 81 sandstone reservoir in Huaqing Oilfield. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 33, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.P.; Sun, W.; Ouyang, S.Q. Diagenetic facies micro- pore structure characteristics and production dynamics of Chang 81 reservoir in Banqiao-Heshui Area. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 37, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.F.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Xue, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Classification of microscopic pore-throats and the grading evaluation on shale oil reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, D.; Zuo, R.; Gu, X.M.; Zhang, F. Pore characteristic responses to categories of depositional microfacies of delta-lacustrine tight reservoirs in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 118, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.M.; Song, Y.; Jiang, Z.X.; Chen, L.; Wang, P.F.; Liu, Q.X.; Gao, F.L.; Yang, X. Micro-nano pore structure characteristics and its control factors of shale in Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 37, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Tiang, X.L.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.X.; Yang, P.P.; Yang, X.; Li, W.B.; Hao, J. The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.J.; Cheng, B.Y.; Meng, F.L.; Xu, H.M. Effects of microscopic pore structure heterogeneity on the distribution and morphology of remaining oil. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xiao, D.S.; Peng, S.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, F. Heterogeneity of microscopic pores in shale oil reservoir and its controlling factors: Taking the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Sag as an example. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2021, 40, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dutton, S.P.; Loucks, R.G.; Day-Stirrat, R.J. Impact of regional variation in detrital mineral composition on reservoir quality in deep to ultradeep lower Miocene sandstones, western Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 35, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, B.; Fan, X.J.; Wu, Y.J. Characteristics of micro-pore structure and differential analysis of logging identification for different diagenetic facies in low permeability reservoir:A case study on Chang 61 reservoir in Wangpanshan area of Jiyuan Oilfield. Geoscience 2018, 32, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Hou, J.G.; Yan, L.; Chen, F.L. Pore-throat structures and their control of terrestrial lacustrine tight reservoir quality: The Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag, northwestern China. Interpretation 2018, 6, T889–T906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zha, M.; Ding, X.J.; Qu, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, C.; Stefan, I. Pore type and pore size distribution of tight reservoirs in the Permian Lucaogou Formation of the Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 89, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.G.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, X.L.; Liao, Z.W. A unique lacustrine mixed dolomitic-clastic sequence for tight oil reservoir within the middle Permian Lucaogou Formation of the Junggar Basin, NW China: Reservoir characteristics and origin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 76, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.G.; Hu, W.X.; Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Kang, X. The impact of organic fluids on the carbon isotopic compositions of carbonate-rich reservoirs: Case study of the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 85, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Liu, B.; Song, X.M.; Li, L.K.; Xu, J.Z.; Su, J.; Wu, K.L.; Chen, Z.X. Fractal characteristics of lacustrine tight carbonate nanoscale reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.R.; Xi, K.L.; Cao, Y.C.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, K. Petrographic features and diagenetic alteration in the shale strata of the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar sag, Junggar Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.F.; Huang, J.H.; Li, J.; Gao, H.C.; Kuang, H.; Jiang, W. Origin of carbonate cements and the transformation of the reservoir in sandstone under the deep burial condition: A case study on Eocene Kongdian Formation in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Geol. Rev. 2015, 61, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C. Characteristics and significance of carbonate cements in member 3 of Shahejie Formation in the Northern Subsag of Laizhouwan Sag. Geol. J. China Univ. 2021, 27, 526–535. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.H.; Cao, Y.C.; Jia, Z.Z.; Glugas, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xi, K.L. Selective dissolution of feldspars in the presence of carbonates: The way to generate secondary pores in buried sandstones by organic CO2. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 60, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Fu, L.; Gao, J.R.; Song, W.; Chen, X.J. Interstitial matter and its impact on reservoir development in Chang 6 deepwater tight sandstone in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, D.K.; Zhu, H.H.; Sun, H.T.; Cai, C.; Yao, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Deng, X.Q.; Luo, A.X. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of sandstones in Longdong Area, Ordos Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Pang, X.Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zheng, X.W.; Ding, X.G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, C.X.; Li, H. Oil content evaluation of lacustrine organic-rich shale with strong heterogeneity: A case study of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Fuel 2018, 221, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Diagenetic Facies Type | Tuffaceous-Feldspar Dissolution Facies | Mixed Cementation Dissolution Facies | Chlorite Thin Membrane Facies | Carbonate Cementation Facies | Mixed Cementation Compact Facies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original lithologies | Lithic feldspar silty sandstones Dolomitic siltstones Dolomitic sandstones | Lithic feldspar silty sandstones Dolomitic siltstones Dolomitic sandstones Dolarenites | Dolomitic siltstones Dolomitic sandstones | Dolarenites Micrite dolomites | Dolomitic siltstones Dolomitic sandstones Dolomitic mudstones |
| Major diagenesis | Compaction Feldspar dissolution Tuffaceous dissolution | Compaction Feldspar dissolution Calcite cementation Chlorite cementation | Compaction Chlorite cementation | Compaction Calcite cementation Dolomite cementation Iron dolomite cementation | Compaction Illite/smectite mixed layer Quartz overgrowth Calcite cementation |
| Secondary diagenesis | Quartz overgrowth Calcite cementation Authigenic albite Illite/smectite mixed layer | Quartz overgrowth Authigenic albite Dolomite cementation Iron dolomite cementation Illite/smectite mixed layer | Quartz overgrowth Illite/smectite mixed layer Feldspar dissolution | Illite/smectite mixed layer Pyrite Carbonate dissolution | Dolomite cementation Pyrite |
| Particle contact relationship | Line contact | Line contact | Line contact | Concavo–convex contact | Concavo–convex contact |
| Diagenetic Facies | Representative Samples ID | Displacement Pressure/MPa | The Maximum Pore Throat Radius/nm | The Maximum Mercury Inlet Saturation/% | Total Pore Volume/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies | J25-13 | 2.9 | 25.3 | 85.39 | 0.0265 |
| Mixed cementation dissolution facies | J25-16 | 3.0 | 24.5 | 78.09 | 0.0288 |
| Chlorite thin-membrane facies | J14-2 | 30 | 2.5 | 62.70 | 0.0185 |
| Carbonate cementation facies | J25-4 | 25 | 2.9 | 40.94 | 0.0065 |
| Mixed cementation compact facies | J12-2 | 68 | 1.1 | 26.26 | 0.0082 |
| Diagenetic Facies | Representative Samples ID | Micropores | Mesopores | Macropores | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | R2 | D2 | R2 | D3 | R2 | ||
| Tuffaceous–feldspar dissolution facies | J25-13 | 2.8867 | 0.7894 | 1.9809 | 0.943 | 2.9881 | 0.9774 |
| Mixed cementation dissolution facies | J25-16 | 2.9575 | 0.6359 | 2.5840 | 0.9643 | 2.9983 | 0.7707 |
| Chlorite thin-membrane facies | J14-2 | 2.7770 | 0.9706 | 2.9946 | 0.9224 | 2.9963 | 0.9027 |
| Carbonate cementation facies | J25-4 | 2.8605 | 0.9716 | 2.9873 | 0.9357 | 2.9842 | 0.9265 |
| Mixed cementation compact facies | J12-2 | 2.8725 | 0.8919 | 2.9962 | 0.8456 | 2.9874 | 0.9507 |
| Average value | - | 2.8708 | - | 2.7086 | - | 2.9909 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, M.; Yang, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Hou, H.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Diagenetic Facies Controls on Differential Reservoir-Forming Patterns of Mixed Shale Oil Sequences in the Saline Lacustrine Basin. Minerals 2023, 13, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020143
Xie M, Yang W, Zhao M, Li Y, Deng Y, Gao Y, Xu C, Hou H, Yao L, Zhang Z, et al. Diagenetic Facies Controls on Differential Reservoir-Forming Patterns of Mixed Shale Oil Sequences in the Saline Lacustrine Basin. Minerals. 2023; 13(2):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020143
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Ming, Wei Yang, Mingzhu Zhao, Yingyan Li, Yuan Deng, Yang Gao, Changfu Xu, Haodong Hou, Linjie Yao, Zilong Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Diagenetic Facies Controls on Differential Reservoir-Forming Patterns of Mixed Shale Oil Sequences in the Saline Lacustrine Basin" Minerals 13, no. 2: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020143
APA StyleXie, M., Yang, W., Zhao, M., Li, Y., Deng, Y., Gao, Y., Xu, C., Hou, H., Yao, L., Zhang, Z., & Lu, J. (2023). Diagenetic Facies Controls on Differential Reservoir-Forming Patterns of Mixed Shale Oil Sequences in the Saline Lacustrine Basin. Minerals, 13(2), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020143






