Research on Uniaxial Compression Mechanics of Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Realization of Solution Scouring Environment
- (1)
- Measure a quantity of concentrated hydrochloric acid and add distilled water to dilute one 500 mL hydrochloric acid solution.
- (2)
- A total of 0.75 g anhydrous sodium carbonate was weighed as the reference substance and dissolved in 300 mL distilled water, then 5 drops of methyl orange indicator were added.
- (3)
- The sodium carbonate solution in (2) was calibrated with the hydrochloric acid solution configured in (1) until the color turned orange, and the pH value of the solution was determined by the PHS-25 pH meter.
- (4)
- For (3), slowly adding distilled water in the configuration solution to dilute to the required concentration and pH value of Table 3 and adding an appropriate amount of NaCl powder in the dilution process to fully stir until complete dissolution.
2.3. Laboratory Contents and Methods
3. Results
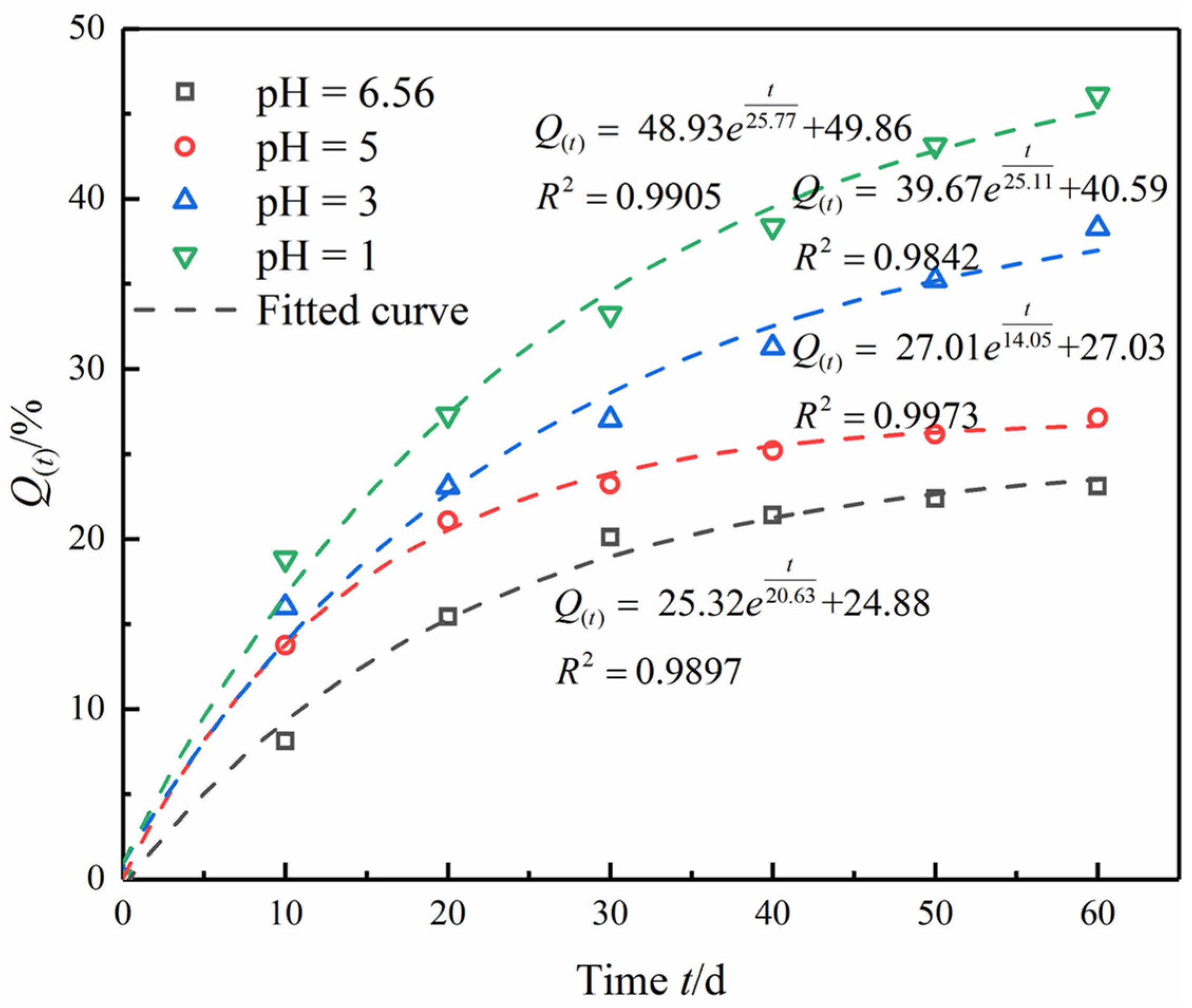
3.1. Effect of Flowing Acid Solution on Elastic Longitudinal Wave of Diorite
- Analysis of variation with pH
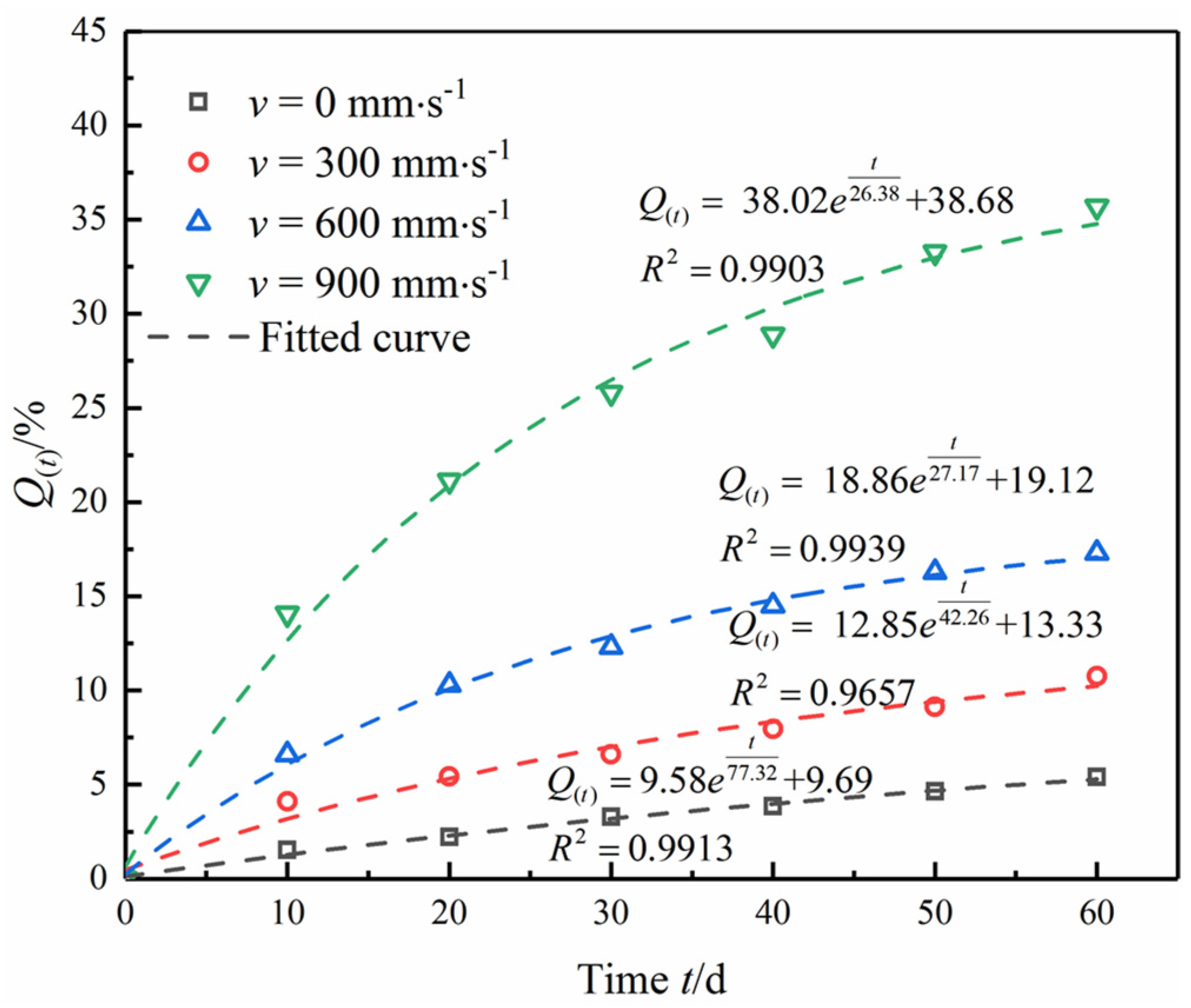
- Analysis of variation with flow velocity
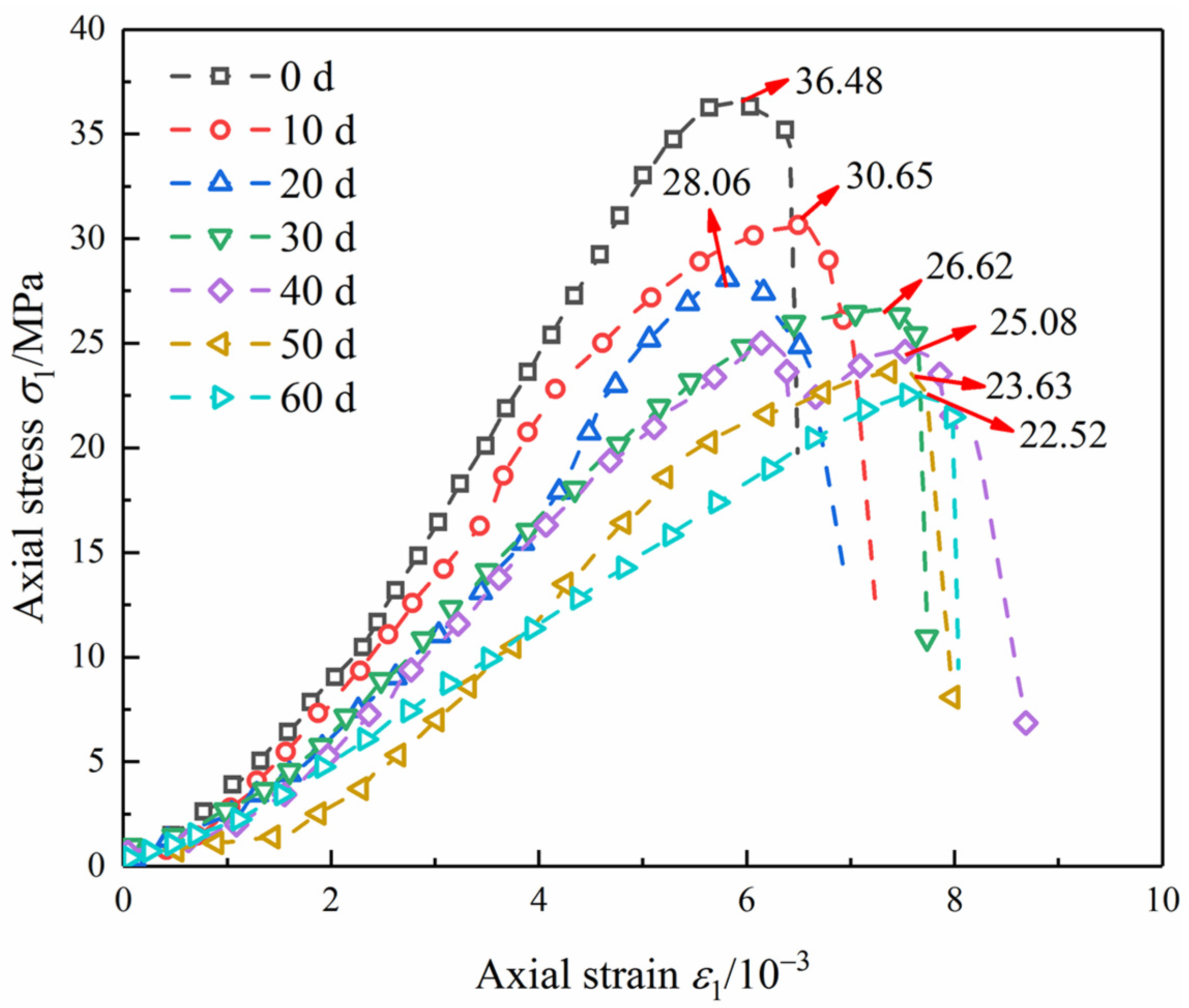
3.2. Analysis of Uniaxial Compression Stress–Strain Curve
3.2.1. Strength and Deformation Characteristics
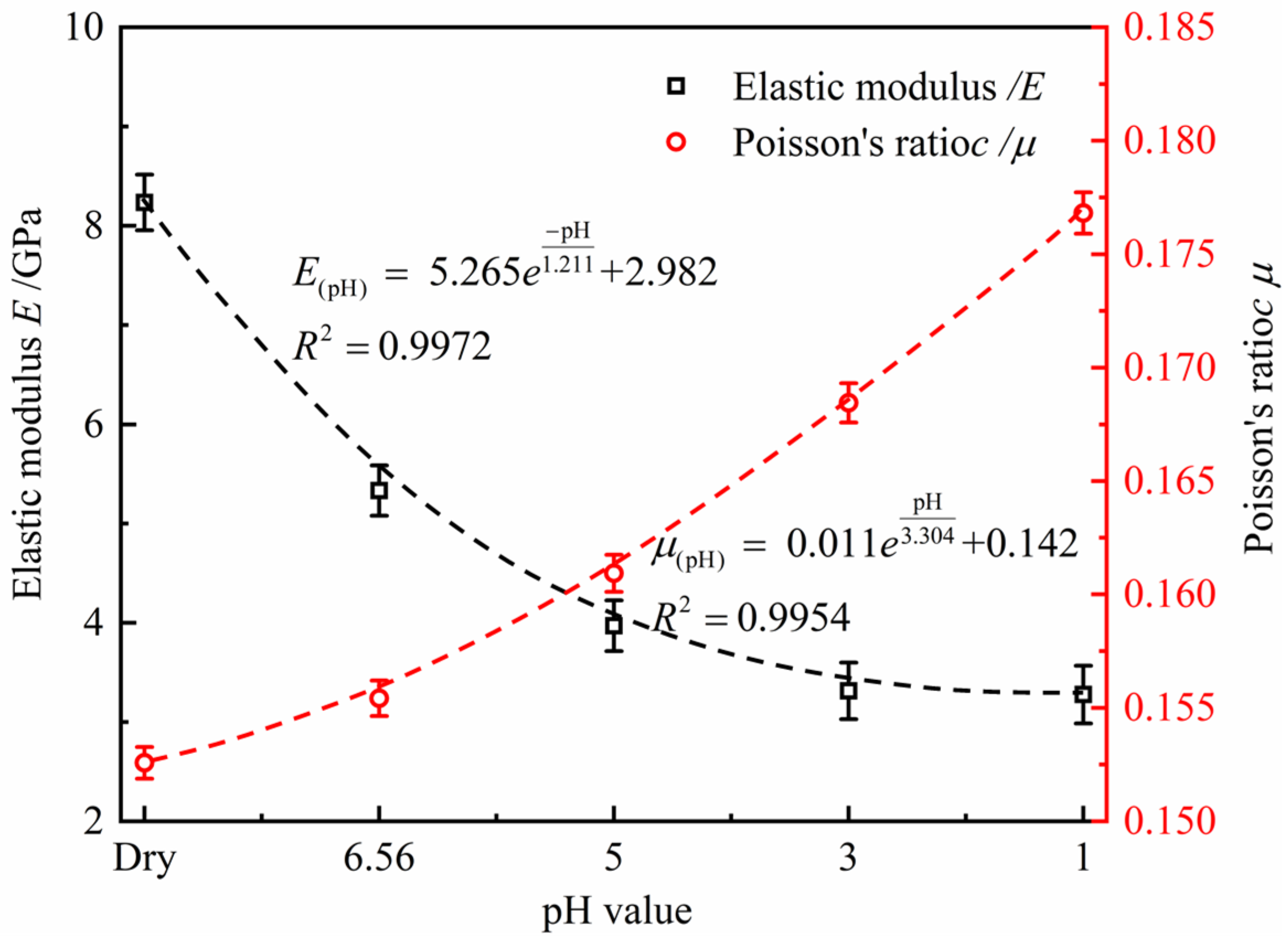
- Effect of pH value on strength and deformation of diorite
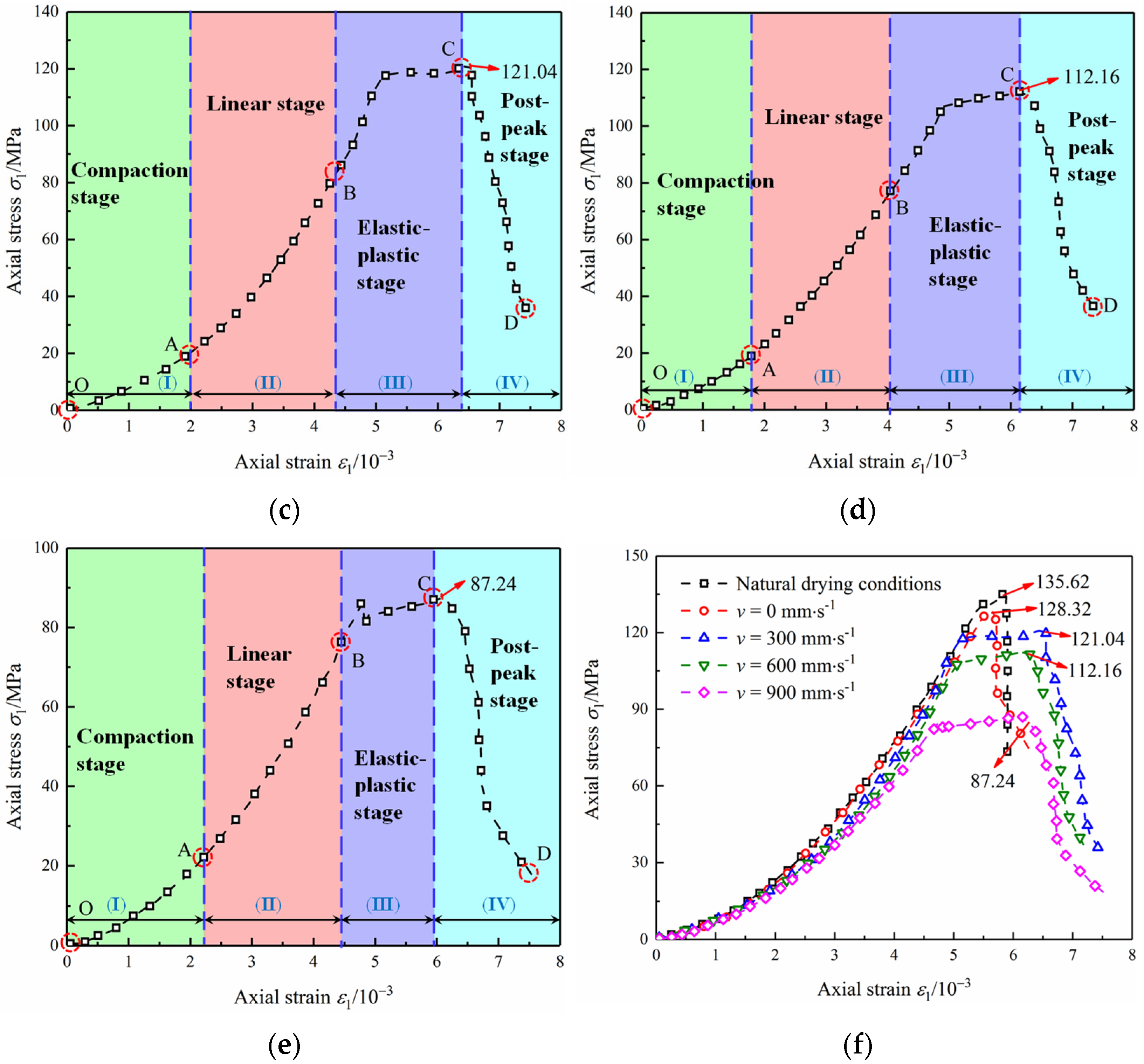
- Effect of flow velocity on strength and deformation of diorite
- (I)
- Initial fracture compacting stage (OA stage): After solution scouring, some specimens show an obvious depression type in this section, especially in the initial stage of the specimen entering the solution environment. It indicates that the erosion and dissolution of the diorite by a solution increase or lengthen its pores and lengthen the initial fracture compaction stage.
- (II)
- Elastic deformation to crack stable expansion stage (AB stage): After different flow rates scouring, the curve slope of the diorite samples at this stage has been reduced in varying degrees. It indicates that the elastic modulus of the diorite decreases after being scoured by the solution, and the elastic modulus of the diorite decreases most obviously after being scoured by v = 900 mm·s−1.
- (III)
- Unstable rupture development stage (BC stage): Scouring with different flow rates, when the stress reaches a certain value, part of the stress–strain curve for diorite rock samples starts to bend downward. The rock samples after scouring with 300, 600 and 900 mm·s−1 flow rates have an obvious yield platform, and plastic deformation increases, which means that the plasticity of the diorite is enhanced by flow scouring and the peak strength decreases significantly compared with the natural drying state.
- (IV)
- Post rupture stage (CD stage): After scouring by flow rates, specimens still have a relatively large deformation after the peak point, illustrating that the solution scouring increases the ductility of diorite to some extent.
3.2.2. Deterioration Characteristics of Mechanical Parameters
- Effect of pH value on mechanical parameters of diorite
- Effect of flow velocity on mechanical parameters of diorite
4. Analysis of the Damage Mechanism for Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring
4.1. Analysis of Microscopic Change Characteristics
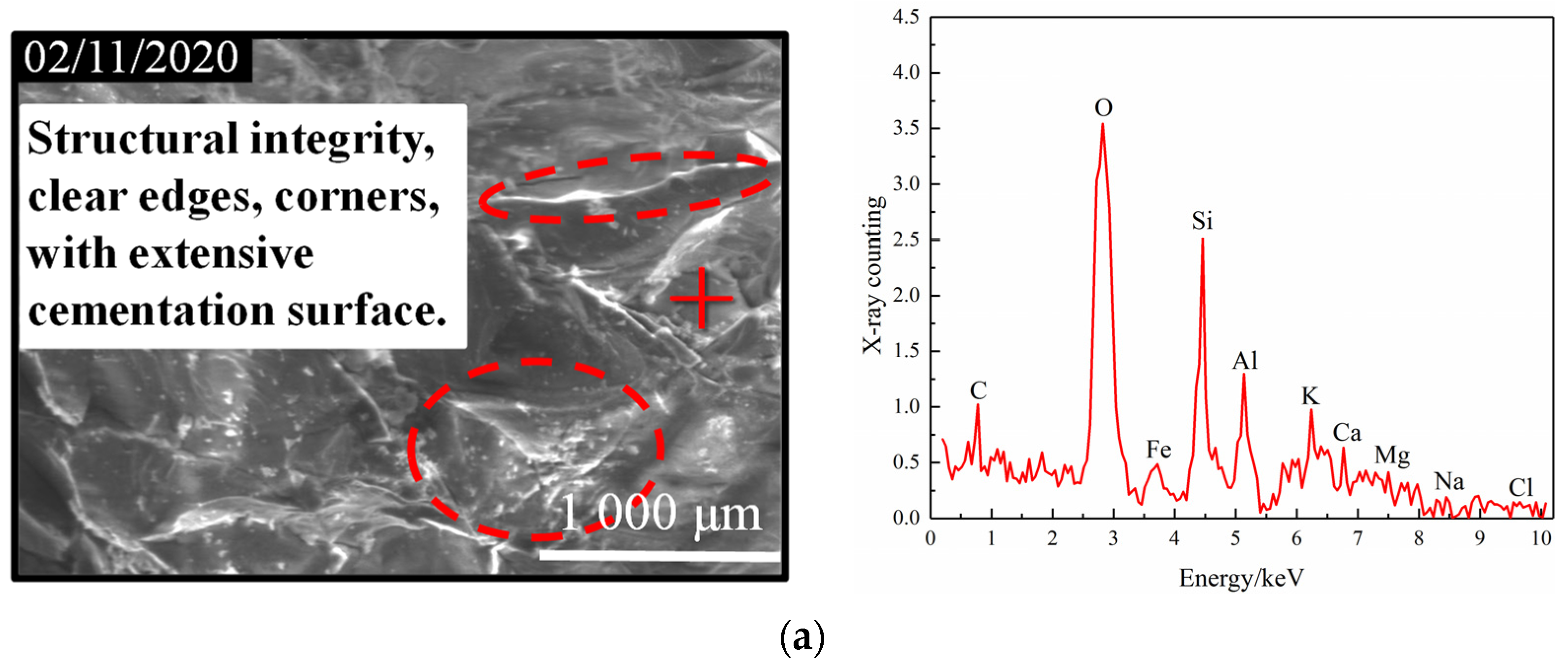
- Analysis of variation with pH
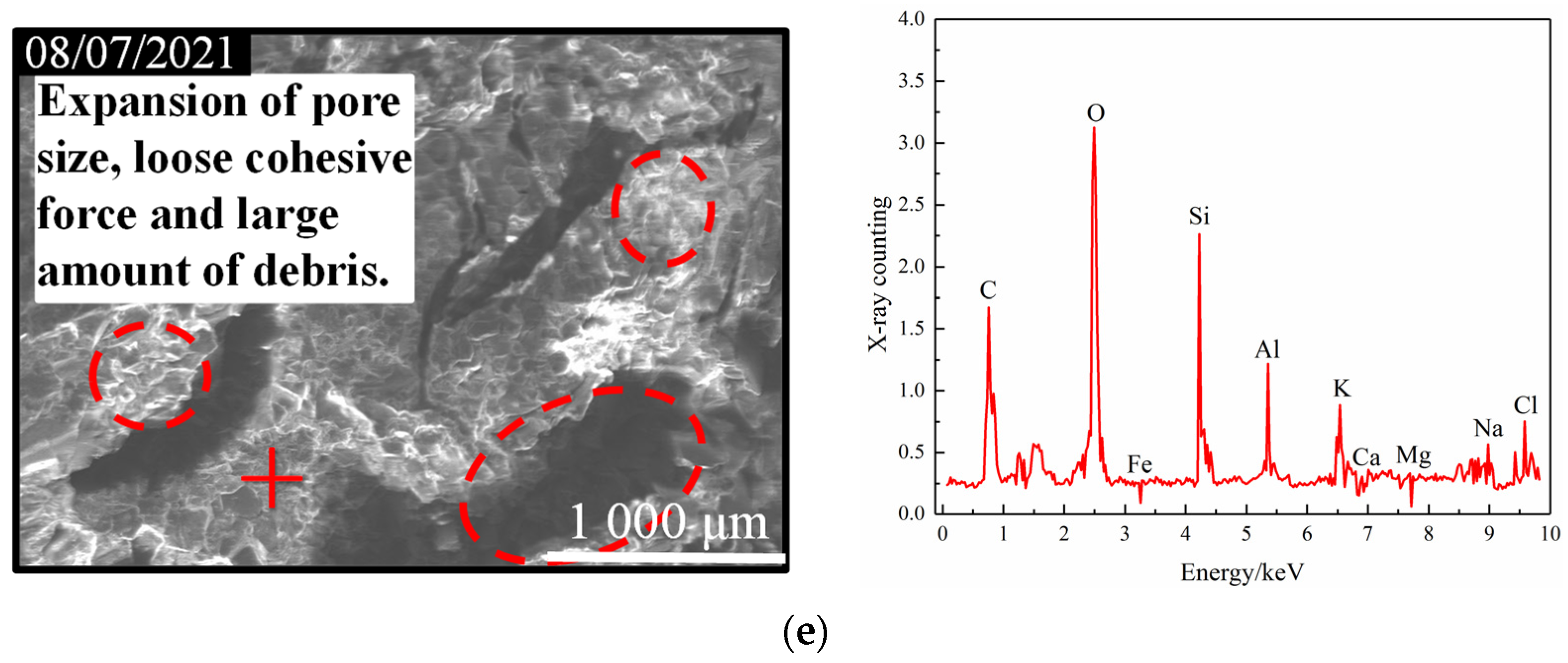
- Analysis of variation with flow velocity
4.2. Analysis of Chemical Damage Mechanism
- Water–rock chemical mechanism
- 2.
- Mechanism of hydration erosion
- 3.
- Physical mechanism of action
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, R.; Cao, J.; Zou, K. Similarity Model Test on the Spatiotemporal Evolution Law of Deformation and Failure of Surrounding Rock-Induced Caving in Multi-Mined-Out Areas. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1224658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, T.; Ning, Z.; Dou, Z.; Dai, F.; Yang, Q. Numerical Modeling of Stability of Fractured Reservoir Bank Slopes Subjected to Water–Rock Interactions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 51, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H. Shear-related roughness classification and strength model of natural rock joint based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 137, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Q.; Jin, Z.-H.; Johnson, S.E. Modelling petroleum migration through microcrack propagation in transversely isotropic source rocks. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 190, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y. Fracture Behavior of Rock with Initial Damage: Theoretical, Experimental, and Numerical Investigations. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 8886843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Weng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Peng, W.; Zhang, S. Deformation and cracking characteristics of ring-shaped granite with inclusion under diametrical compression. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Wu, Q.-H.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-M. Dynamic response and failure of rock in initial gradient stress field under stress wave loading. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Yu, J.; Fu, G.F.; Li, H. Experimental investigation on the relevance of mechanical properties and porosity of sandstone after hydrochemical erosion. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 2053–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.; Wang, S.; Ji, Y.; Wang, F.; Ren, F.; Nguyen, V.-T. The effects of dry and wet rock surfaces on shear behavior of the interface between rock and cemented paste backfill. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L. Influence of Water-rock Chemical Erosion on the Shear Strength of Coastal Buildings. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Dou, Z.; Yang, Q. Shear behaviors of granite fractures immersed in chemical solutions. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Rock slope stability analysis considering the effect of locked section. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 7241–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H. Editorial: Hydro-Mechanical Coupling and Creep Behaviors of Geomaterials. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. Coupled seepage-damage effect in fractured rock masses: Model development and a case study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 144, 104822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, S.; Jiao, B.; Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Lian, S. Aging features and strength model of diorite’s damage considering acidization. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, E.; Jiang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Feng, D.; Deng, H. Study on the Creep Constitutive Model of a Sandstone Rock under the Water-Rock Interaction. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6648421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T. Mesoscopic Weakening Feature of Marble during Water Rock Interaction. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wan, W.; Feng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, S. Mechanical characteristics of skarns from Chuanyandong orefield of Wengfu phosphate mine under various humidity ratios and stress states. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2021, 40, 2510–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Cai, M.; Guo, Q.; Wang, P.; Liang, M. Damage effects and mechanisms in granite treated with acidic chemical solutions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 88, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.; Chang, L. Crack coalescence patterns and local strain behaviors near flaw tip for rock-like material containing two flaws subjected to biaxial compression. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L. Theoretical and numerical models of rock wing crack subjected to hydraulic pressure and far-field stresses. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-H.; Weng, L.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Feng, F. Influence of infilling stiffness on mechanical and fracturing responses of hollow cylindrical sandstone under uniaxial compression tests. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wan, W.; Zhao, Y.; He, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, S. Mechanical damage evolution and mechanism of sandstone with prefabricated parallel double fissures under high-humidity condition. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.; Reis, E.; Santos, P.P. Exploring spatial relationships between stream channel features, water depths and flow velocities during flash floods using HEC-GeoRAS and Geographic Information Systems. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fan, L.; Wu, Z. Effects of Microfracture on Wave Propagation through Rock Mass. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04017072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Davoodi, P.K.; Najmoddini, I. Studying the correlation of rock properties with P-wave velocity index in dry and saturated conditions. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 169, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Weng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, B.; Luo, T. On the tensile mechanical characteristics of fine-grained granite after heating/cooling treatments with different cooling rates. Eng. Geol. 2019, 253, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Sun, Q.; Li, G. Inconsistency of changes in uniaxial compressive strength and P-wave velocity of sandstone after temperature treatments. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.; Maji, V.B.; Boominathan, A. Influence of rock joints on longitudinal wave velocity using experimental and numerical techniques. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 141, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Eichhubl, P.; Newell, P. Basement Fault Reactivation by Fluid Injection into Sedimentary Reservoirs: Poroelastic Effects. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 7354–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motra, H.B.; Mager, J.; Ismail, A.; Wuttke, F.; Rabbel, W.; Köhn, D.; Thorwart, M.; Simonetta, C.; Costantino, N. Determining the influence of pressure and temperature on the elastic constants of anisotropic rock samples using ultrasonic wave techniques. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 159, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lei, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Deterioration of non-persistent rock joints: A focus on impact of freeze–thaw cycles. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 135, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Lin, H.; Cao, P. Strength and failure characteristics of brittle jointed rock-like specimens under uniaxial compression: Digital speckle technology and a particle mechanics approach. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ren, F.; Cai, M. Effect of Joint Density on Rockburst Proneness of the Elastic-Brittle-Plastic Rock Mass. Shock. Vib. 2021, 2021, 5574325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-Q.; Tian, W.-L.; Zeng, W.; Yu, L.-Y. An experimental study on fracture mechanical behavior of rock-like materials containing two unparallel fissures under uniaxial compression. Acta Mech. Sin. 2016, 32, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Weng, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, R. Experimental investigation of the dynamic response of prestressed rockbolt by using an SHPB-based rockbolt test system. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 93, 103088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Shen, B.; Dlamini, B.; Zhu, Y. Experimental Investigation on Rockbolt Performance under the Tension Load. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 4605–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Luo, S. Numerical Analysis of the Mud Inflow Model of Fractured Rock Mass Based on Particle Flow. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 5599748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L. The compressive-shear fracture strength of rock containing water based on Druker-Prager failure criterion. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Pu, C.; Wan, W.; Tang, J. Cracking and Stress–Strain Behavior of Rock-Like Material Containing Two Flaws under Uniaxial Compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 2665–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, J.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical properties, damage evolution, and constitutive model of rock-encased backfill under uniaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yong, W.; Gao, F. Influence of wing crack propagation on the failure process and strength of fractured specimens. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wan, W.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y. Creep Behavior of Intact and Cracked Limestone under Multi-Level Loading and Unloading Cycles. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Chan, A. Damage constitutive model of single flaw sandstone under freeze-thaw and load. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 159, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Luxbacher, K.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Yan, Z.; Wei, M.; Yu, L. Micro-structural evolution and their effects on physical properties in different types of tectonically deformed coals. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
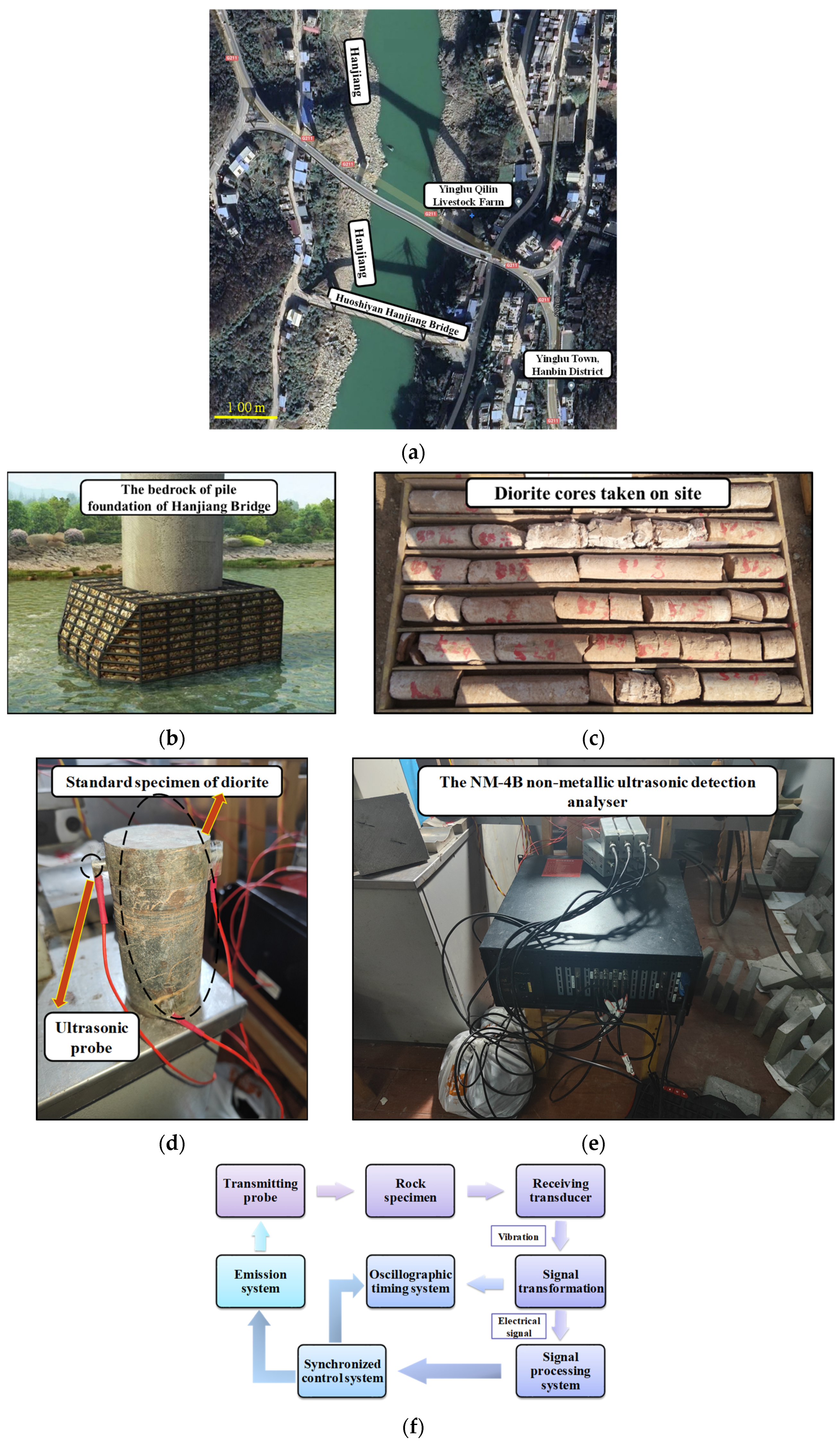











| Minerals | Plagioclase | Dark Minerals | Quartz | Ore Minerals | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Potassium feldspar Albite Anorthite etc. | FeO Fe2O3 MgO Mica etc. | — | CaOAl2O3 Na2O K2O etc. | — |
| Mass percentage | 51–57% | 21–32% | 17–20% | 3–5% | 1–2% |
| Sample Number | Height /mm | Diameter /mm | Mass /g | Volume /cm3 | Porosity /% | Bulk Density g/cm3 | Longitudinal Wave Velocity /m s−1 | Natural Water Content/% | Saturated Moisture Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | 100.02 | 50.01 | 534.18 | 188.91 | 5.27 | 2.86 | 4693 | 0.92 | 3.36 |
| S-2 | 100.02 | 50.02 | 538.07 | 189.12 | 5.35 | 2.79 | 4310 | 0.89 | 3.19 |
| S-3 | 100.04 | 49.84 | 536.32 | 189.07 | 5.24 | 2.81 | 4135 | 0.91 | 3.25 |
| S-4 | 100.01 | 49.93 | 535.78 | 188.87 | 5.20 | 2.85 | 4001 | 0.93 | 3.37 |
| S-5 | 100.03 | 50.05 | 538.03 | 189.23 | 4.98 | 2.82 | 4736 | 0.88 | 3.37 |
| S-6 | 100.05 | 50.03 | 536.51 | 189.33 | 4.97 | 2.84 | 4342 | 0.86 | 3.29 |
| S-7 | 100.02 | 49.79 | 538.03 | 188.64 | 5.19 | 2.80 | 4878 | 0.79 | 3.30 |
| S-8 | 100.03 | 49.97 | 532.35 | 189.05 | 5.22 | 2.81 | 4833 | 0.87 | 3.24 |
| S-9 | 100.04 | 50.04 | 537.14 | 189.15 | 5.25 | 2.85 | 4407 | 0.93 | 3.36 |
| S-10 | 99.98 | 50.06 | 535.68 | 188.97 | 5.17 | 2.81 | 4092 | 0.92 | 3.38 |
| S-11 | 99.97 | 49.86 | 537.91 | 188.82 | 4.96 | 2.76 | 4137 | 0.91 | 3.27 |
| S-12 | 100.02 | 49.92 | 529.68 | 189.07 | 4.78 | 2.78 | 4286 | 0.87 | 3.31 |
| S-13 | 100.04 | 49.76 | 532.26 | 188.56 | 5.15 | 2.83 | 4025 | 0.86 | 3.34 |
| S-14 | 100.01 | 50.02 | 530.85 | 189.31 | 5.23 | 2.84 | 4012 | 0.91 | 3.28 |
| S-15 | 99.97 | 50.04 | 534.43 | 188.79 | 5.26 | 2.79 | 4225 | 0.88 | 3.31 |
| S-16 | 99.96 | 50.03 | 530.28 | 189.23 | 5.19 | 2.82 | 4532 | 0.77 | 3.32 |
| Solution Fraction | Concentration/(mol·L−1) | pH Value |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 0.01 | 1, 3, 5 |
| On-site groundwater solution | — | 6.56 |
| pH | Elastic Longitudinal Wave Velocity at Each Time Point/(m·s−1) | Dp/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| 6.56 | 4693 | 4708 | 4732 | 4793 | 4880 | 4680 | 4585 | 2.30 |
| 5 | 4342 | 4368 | 4382 | 4481 | 4594 | 4385 | 4104 | 5.48 |
| 3 | 4137 | 4154 | 4196 | 4286 | 4384 | 4084 | 3794 | 8.29 |
| 1 | 4025 | 4039 | 4075 | 4142 | 4213 | 3867 | 3477 | 13.61 |
| Sample Number | Flow Rate v/(mm·s−1) | vsp/(m·s−1) | vfp/(m·s−1) | Dp/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | 0 | 4455 | 4301 | 3.46 |
| S-2 | 4310 | 4178 | 3.06 | |
| S-3 | 4135 | 4105 | 0.73 | |
| S-4 | 4001 | 3969 | 0.80 | |
| S-5 | 300 | 4737 | 4366 | 7.83 |
| S-6 | 4660 | 4416 | 5.24 | |
| S-7 | 4879 | 4493 | 7.91 | |
| S-8 | 4834 | 4598 | 4.88 | |
| S-9 | 600 | 4408 | 4119 | 6.56 |
| S-10 | 4092 | 3640 | 11.05 | |
| S-11 | 4178 | 3744 | 10.39 | |
| S-12 | 4286 | 3902 | 8.96 | |
| S-13 | 900 | 3891 | 3308 | 14.98 |
| S-14 | 3998 | 3450 | 13.71 | |
| S-15 | 4225 | 3557 | 15.81 | |
| S-16 | 4533 | 3686 | 18.69 |
| Rock Sample State | Natural Drying State | pH = 6.56 | pH = 5 | pH = 3 | pH = 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average elastic modulus/GPa | 8.23571 | 5.33329 | 3.97002 | 3.31398 | 3.27747 |
| Average Poisson’s ratio | 0.15258 | 0.15542 | 0.16093 | 0.16845 | 0.17682 |
| Rock Sample State | Natural Drying State | v = 0 mm·s−1 | v = 300 mm·s−1 | v = 600 mm·s−1 | v = 900 mm·s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average elastic modulus/GPa | 30.88272 | 29.08670 | 26.79987 | 25.77859 | 24.29699 |
| Average Poisson’s ratio | 0.37652 | 0.43542 | 0.54885 | 0.66345 | 0.81369 |
| Parameter | C | O | Si | Al | K | Ca | Fe | Mg | Na | Cl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass content/% | Dry state | 9.22 | 31.69 | 22.51 | 11.63 | 8.76 | 5.66 | 4.36 | 3.68 | 1.65 | 0.86 |
| pH = 6.56 | 12.26 | 29.92 | 20.35 | 9.54 | 11.32 | 6.12 | 3.68 | 2.82 | 2.36 | 1.63 | |
| pH = 5 | 10.66 | 32.08 | 24.53 | 8.43 | 8.63 | 5.06 | 3.15 | 2.04 | 2.99 | 2.43 | |
| pH = 3 | 8.71 | 34.38 | 21.65 | 11.57 | 6.03 | 4.12 | 2.56 | 1.74 | 5.35 | 3.89 | |
| pH = 1 | 11.56 | 30.85 | 26.34 | 7.69 | 5.28 | 3.86 | 2.02 | 1.56 | 5.94 | 4.90 | |
| Atomic number content/% | Dry state | 15.68 | 40.46 | 16.37 | 8.80 | 4.57 | 2.88 | 1.56 | 3.07 | 1.46 | 0.50 |
| pH = 6.56 | 20.85 | 38.20 | 14.80 | 7.22 | 5.91 | 3.11 | 1.31 | 2.35 | 2.09 | 0.95 | |
| pH = 5 | 18.13 | 40.95 | 17.84 | 6.38 | 4.50 | 2.57 | 1.13 | 1.70 | 2.65 | 1.41 | |
| pH = 3 | 14.81 | 43.89 | 15.74 | 8.76 | 3.15 | 2.10 | 0.91 | 1.45 | 4.74 | 2.26 | |
| pH = 1 | 19.66 | 39.38 | 19.15 | 5.82 | 2.76 | 1.96 | 0.72 | 1.30 | 5.27 | 2.85 | |
| Parameter | C | O | Si | Al | K | Ca | Fe | Mg | Na | Cl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass content/% | Dry state | 10.15 | 29.36 | 23.41 | 12.07 | 9.16 | 5.33 | 4.46 | 3.72 | 1.43 | 0.91 |
| v = 0 mm·s−1 | 13.20 | 27.51 | 21.68 | 10.87 | 10.56 | 5.08 | 3.32 | 3.06 | 2.79 | 1.93 | |
| v = 300 mm·s−1 | 11.71 | 28.64 | 22.68 | 9.26 | 11.46 | 4.73 | 3.01 | 2.32 | 3.54 | 2.65 | |
| v = 600 mm·s−1 | 12.84 | 27.84 | 20.94 | 11.73 | 9.65 | 4.03 | 1.98 | 1.66 | 5.08 | 4.25 | |
| v = 900 mm·s−1 | 15.05 | 28.12 | 20.35 | 10.95 | 7.94 | 1.67 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 7.74 | 6.78 | |
| Atomic number content/% | Dry state | 17.26 | 37.48 | 17.02 | 9.13 | 4.78 | 2.71 | 1.59 | 3.10 | 1.27 | 0.53 |
| v = 0 mm·s−1 | 22.45 | 35.12 | 15.76 | 8.23 | 5.51 | 2.58 | 1.19 | 2.55 | 2.47 | 1.12 | |
| v = 300 mm·s−1 | 19.92 | 36.56 | 16.49 | 7.01 | 5.98 | 2.41 | 1.08 | 1.93 | 3.14 | 1.54 | |
| v = 600 mm·s−1 | 21.84 | 35.54 | 15.23 | 8.88 | 5.04 | 2.05 | 0.71 | 1.38 | 4.50 | 2.47 | |
| v = 900 mm·s−1 | 25.60 | 35.90 | 14.80 | 8.29 | 4.14 | 0.85 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 6.86 | 3.94 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Wu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Wan, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Peng, W.; Zeng, X.; Ren, Z.; Xie, S.; et al. Research on Uniaxial Compression Mechanics of Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring. Minerals 2022, 12, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060770
Chen W, Wu L, Zeng Z, Wan W, Liu J, Wu X, Peng W, Zeng X, Ren Z, Xie S, et al. Research on Uniaxial Compression Mechanics of Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060770
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei, Li Wu, Zhi Zeng, Wen Wan, Jie Liu, Xiaofan Wu, Wenqing Peng, Xiantao Zeng, Zhenhua Ren, Senlin Xie, and et al. 2022. "Research on Uniaxial Compression Mechanics of Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring" Minerals 12, no. 6: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060770
APA StyleChen, W., Wu, L., Zeng, Z., Wan, W., Liu, J., Wu, X., Peng, W., Zeng, X., Ren, Z., Xie, S., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Research on Uniaxial Compression Mechanics of Diorite under Flowing Acidic Solution Scouring. Minerals, 12(6), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060770








