Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials and Their Performance for Iodide Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Hal Support and Hal/Ag2O Nanomaterials
3.2. Performance of the Hal/Ag2O Nanomaterial for I− Adsorption
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Fan, Q.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Chi, F.; Xie, Y.; Yu, S.; Xiao, C.; et al. Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 933–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Um, W. Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni. Minerals 2021, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.I.; Serne, R.J.; Parker, K.E.; Kutnyakov, I.V. Iodide Sorption to Subsurface Sediments and Illitic Minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, R.; Johnson, C.C. Iodine and human health, the role of environmental geochemistry and diet, a review. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Roden, E.E.; Wan, Q. Efficient adsorption of iodide from water by chrysotile bundles with wedge-shaped nanopores. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, S.; Kim, M.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, M.G.; Um, W. Effects of Radiation and Temperature on Iodide Sorption by Surfactant-Modified Bentonite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9684–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiss, F.L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Iodide removal using LDH technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Takahashi, Y. Selective immobilization of iodide onto a novel bismuth-impregnated layered mixed metal oxide: Batch and EXAFS studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Muramatsu, Y.; Uchida, S. Studies on the sorption of I− (iodide) and IO3− (iodate) onto Andosols. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1992, 63, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.H.; Huang, Y.Z.; Wang, R.Q.; Zhu, Y.G. Adsorption and desorption of iodine by various Chinese soils: II. Iodide and iodate. Geoderma 2009, 153, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.Z. Adsorption behaviors of iodide anion on silver loaded macroporous silicas. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2015, 26, 30301. [Google Scholar]
- Bichsel, Y.; von Gunten, U. Oxidation of Iodide and Hypoiodous Acid in the Disinfection of Natural Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Na, P. Efficient removal of radioactive iodide ions from water by three-dimensional Ag2O–Ag/TiO2 composites under visible light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, K.; Liao, X.; Kurosawa, F. Electrolysis of ammonium iodide solution in a Na2CO3 I2 hybrid cycle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 1986, 11, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wan, Q.; Tan, D.; Yang, S.; Qin, Z.; Nie, X. Removal of iodide from water using halloysite/Ag2O composites as efficient adsorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 213, 106241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talan, D.; Huang, Q. Separation of Radionuclides from a Rare Earth-Containing Solution by Zeolite Adsorption. Minerals 2021, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, J.S.; Karanfil, T.; Serkiz, S.M. Removal and Sequestration of Iodide Using Silver-Impregnated Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; Kruichak, J.; Mills, M.; Wang, Y. Iodide uptake by negatively charged clay interlayers? J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 147, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mao, P.; Qi, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; et al. AgII doped MIL-101 and its adsorption of iodine with high speed in solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 237, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, P.; Jia, L.; Zhang, G. An investigation into the use of cuprous chloride for the removal of radioactive iodide from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, A.; Sarina, S.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, H. Removal of radioactive iodine from water using Ag2O grafted titanate nanolamina as efficient adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Sarina, S.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, M.; Smith, S.V.; Komarneni, S. Capture of radioactive cesium and iodide ions from water by using titanate nanofibers and nanotubes. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10782–10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals–a review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of halloysite clay nanotubes by grafting with γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: Recent research advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112–113, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Halloysite as support matrices: A review. Emerging Mater. Res. 2012, 1, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Jin, B.; Wei, C.; Guo, R.; Miao, S. Selective decorating Ag and MnOx nanoparticles on halloysite and used as micromotor for bacterial killing. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 216, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Guo, B.B.; Fu, L.J.; Yang, H.M.; Hu, Y.H.; Tang, A.D.; Long, H.M.; Jin, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J.L. Radical guided selective loading of silver nanoparticles at interior lumen and out surface of halloysite nanotubes. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Niedenthal, W.; Smarsly, B.M.; Natile, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Carraro, M. Au nanoparticles supported on piranha etched halloysite nanotubes for highly efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 546, 149100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, D.; Komarneni, S.; Panagiotaras, D.; Stathatos, E.; Toli, D.; Christoforidis, K.C.; Fernández-García, M.; Li, H.; Yin, S.; Sato, T.; et al. Halloysite–TiO2 nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 132-133, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Tan, D.; Fang, Y.; Roden, E.E.; Wan, Q. Adsorption of iodate on nanosized tubular halloysite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 184, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikari, M.; Matsui, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Shirasaki, N. Removal of iodide from water by chlorination and subsequent adsorption on powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2015, 68, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.Y.; Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Yu, H.G.; Liu, D.; Liu, H.M.; He, H.P. Natural halloysite nanotubes as mesoporous carriers for the loading of ibuprofen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton-Holzer, J.; McCarthy, G.; Grier, D. Grant-in-Aid, I. North Dakota State University; ICDD Grant-in-Aid: Fargo, ND, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, J.; Mu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Mineralogy and Physico-Chemical Data of Two Newly Discovered Halloysite in China and Their Contrasts with Some Typical Minerals. Minerals 2018, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choung, S.; Um, W.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.G. Uptake Mechanism for Iodine Species to Black Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10349–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Warner, J.A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Casey, W.H. Reactivity of iodide in volcanic soils and noncrystalline soil constituents. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, G.; Walcarius, A.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; Bessière, J. Sorption of Iodide on Cuprite (Cu2O). Langmuir 2000, 16, 4519–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, L. Adsorption behavior of calcined layered double hydroxides towards removal of iodide contaminants. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2007, 273, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
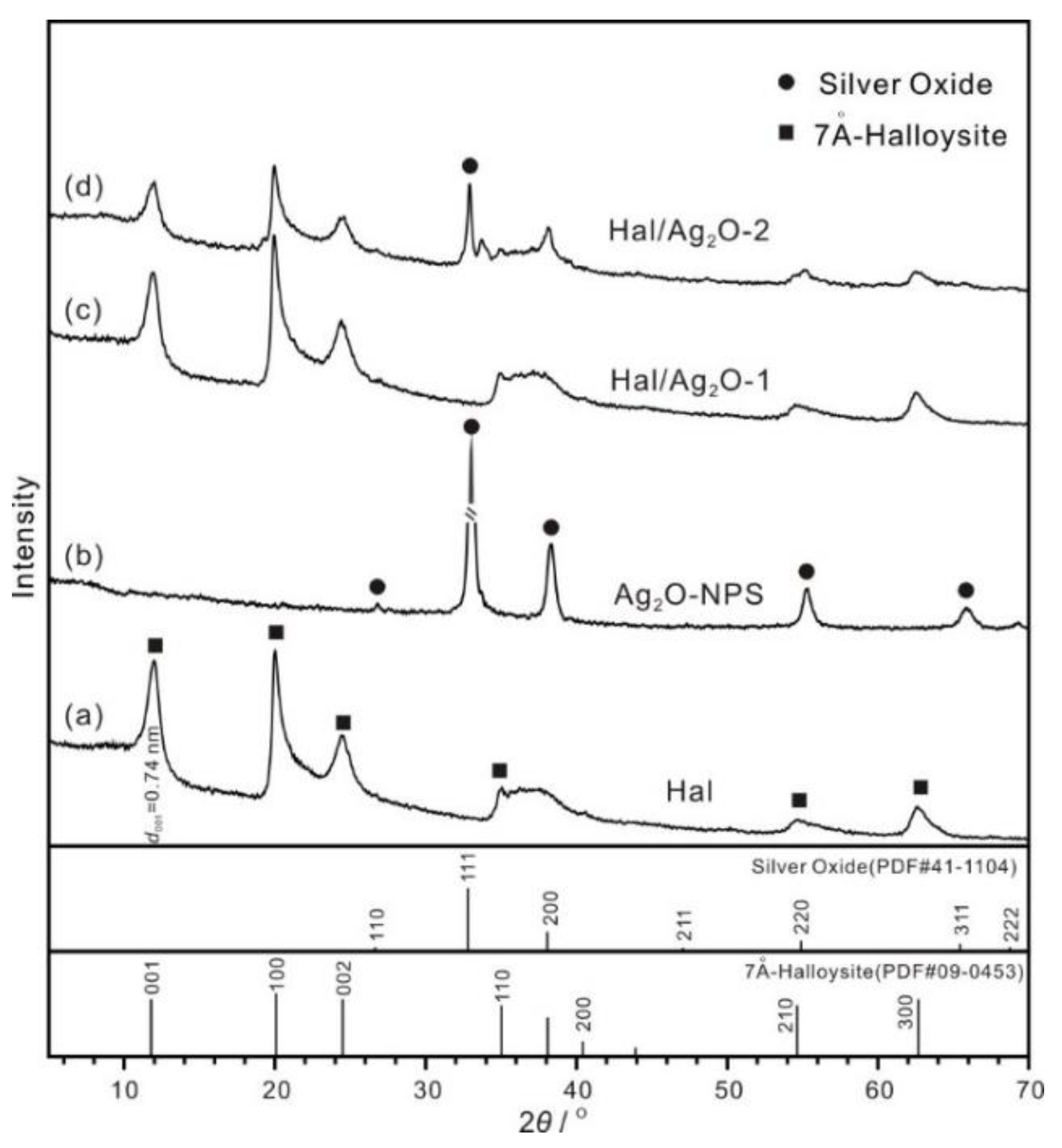

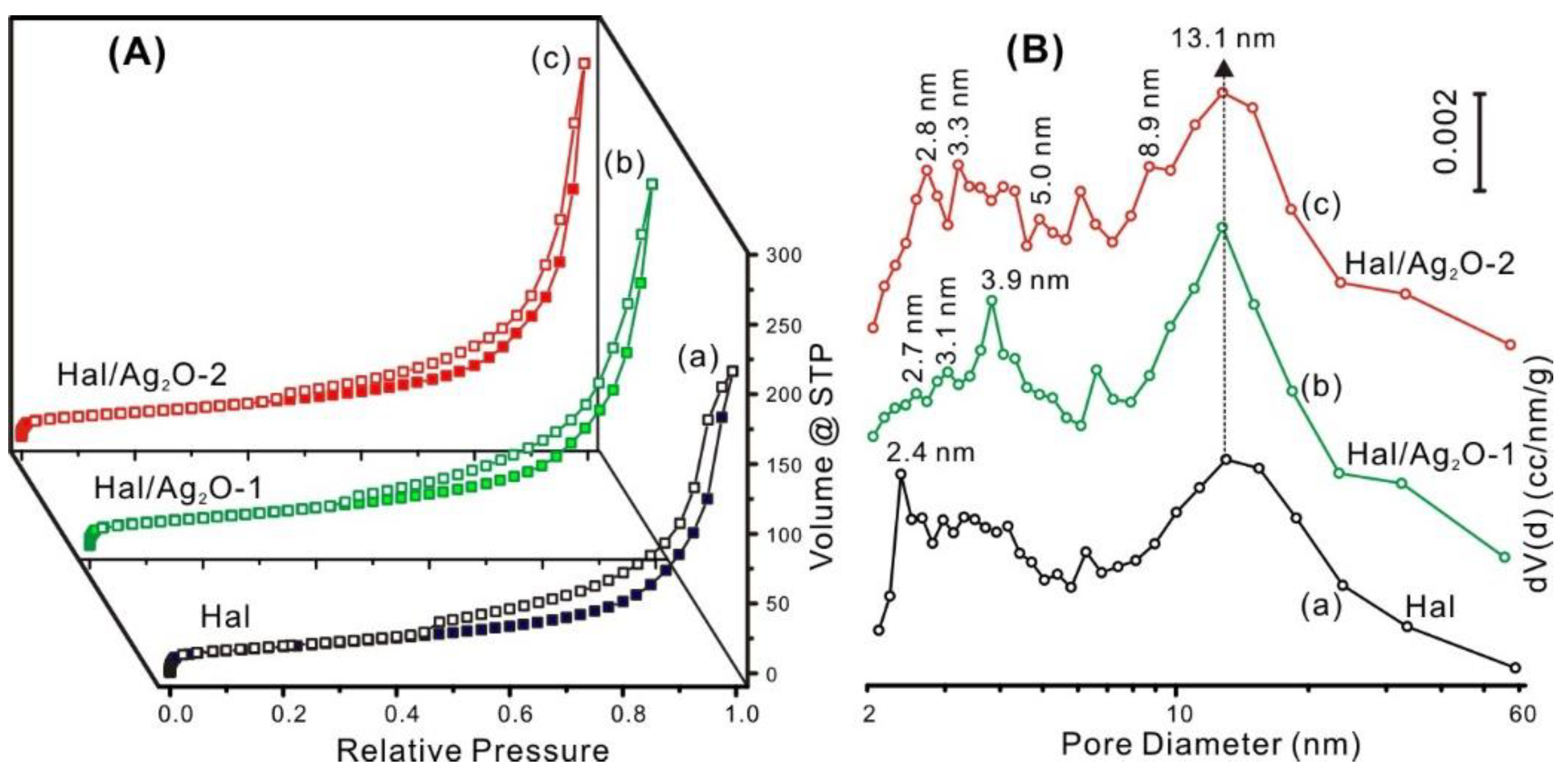

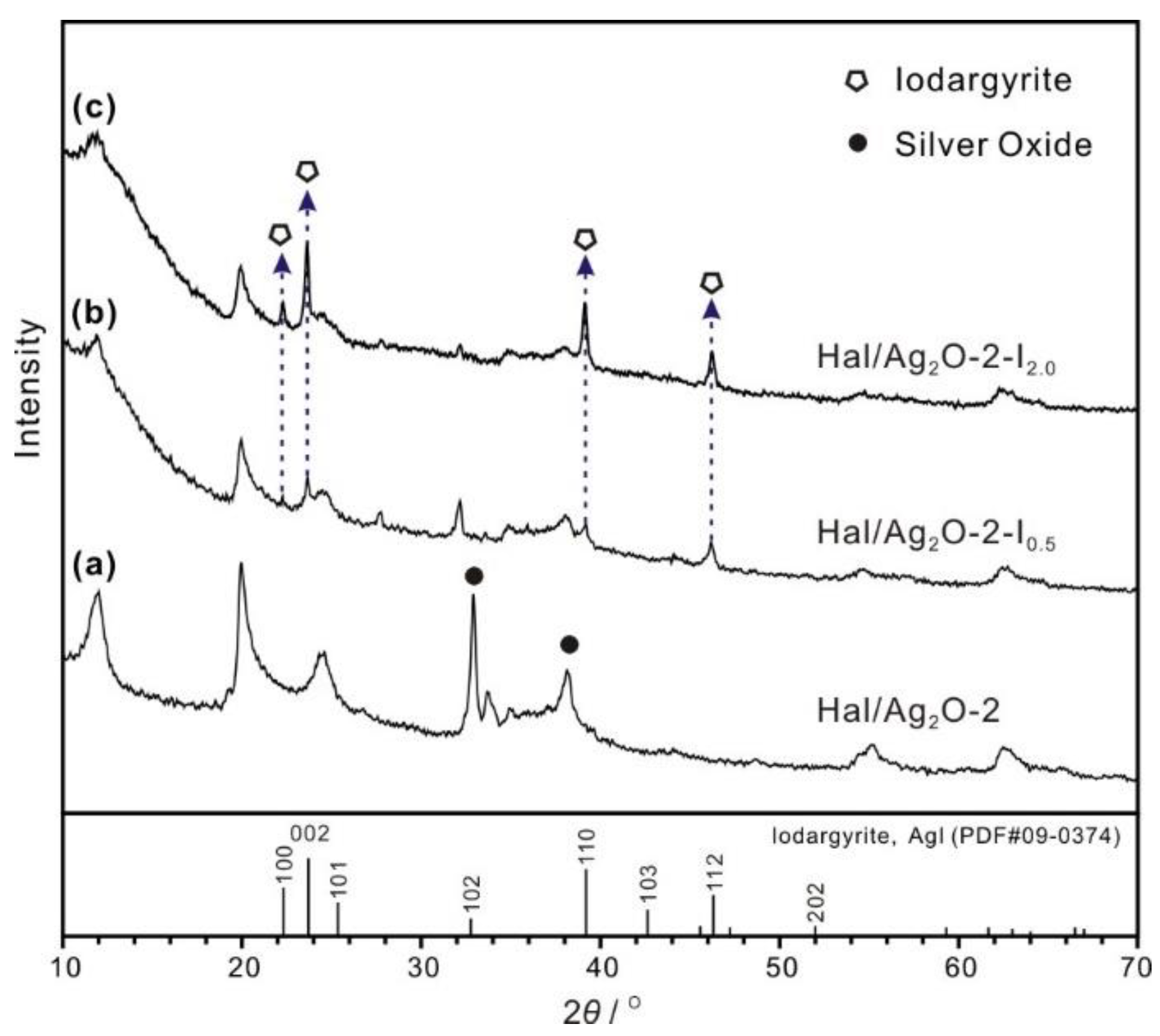
| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (mL/g) | WAg (wt%) 1 | W Ag2O (wt%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hal | 67.7 | 0.3344 | -- | -- |
| Hal/Ag2O-1 | 73.8 | 0.4003 | 0.64 | 0.69 |
| Hal/Ag2O-2 | 65.2 | 0.4146 | 5.92 | 6.36 |
| Adsorbents | I– Adsorption Capacities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hal/Ag2O-2 | 57.7 mg/g | This work |
| Black carbon | ~2 mg/g | [39] |
| Activated carbon | ~12.7 mg/g | [17] |
| Chrysotile bundles | 4.13 mg/g | [5] |
| Ferrihydrite | <0.127 mg/g | [40] |
| LDH | 5.8 mg/g | [42] |
| Calcined LDH | 96.1 mg/g | [42] |
| Cuprite (Cu2O) | ~0.15 mg/g | [41] |
| Ag2O-grafted titanate nanolamina | 431.8 mg/g | [21] |
| Ag2O-grafted titanate nanofibers | 381 mg/g | [22] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Dong, Q.; Yu, W.; Qin, Z.; Nie, X.; Wan, Q.; Chen, X. Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials and Their Performance for Iodide Adsorption. Minerals 2022, 12, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12030304
Yu W, Dong Q, Yu W, Qin Z, Nie X, Wan Q, Chen X. Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials and Their Performance for Iodide Adsorption. Minerals. 2022; 12(3):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12030304
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wenlin, Qinpeng Dong, Wenbin Yu, Zonghua Qin, Xin Nie, Quan Wan, and Xiuli Chen. 2022. "Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials and Their Performance for Iodide Adsorption" Minerals 12, no. 3: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12030304
APA StyleYu, W., Dong, Q., Yu, W., Qin, Z., Nie, X., Wan, Q., & Chen, X. (2022). Preparation of Halloysite/Ag2O Nanomaterials and Their Performance for Iodide Adsorption. Minerals, 12(3), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12030304








