Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Clay Synthesis
2.2.2. Organophilization
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Clay
3.1.1. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
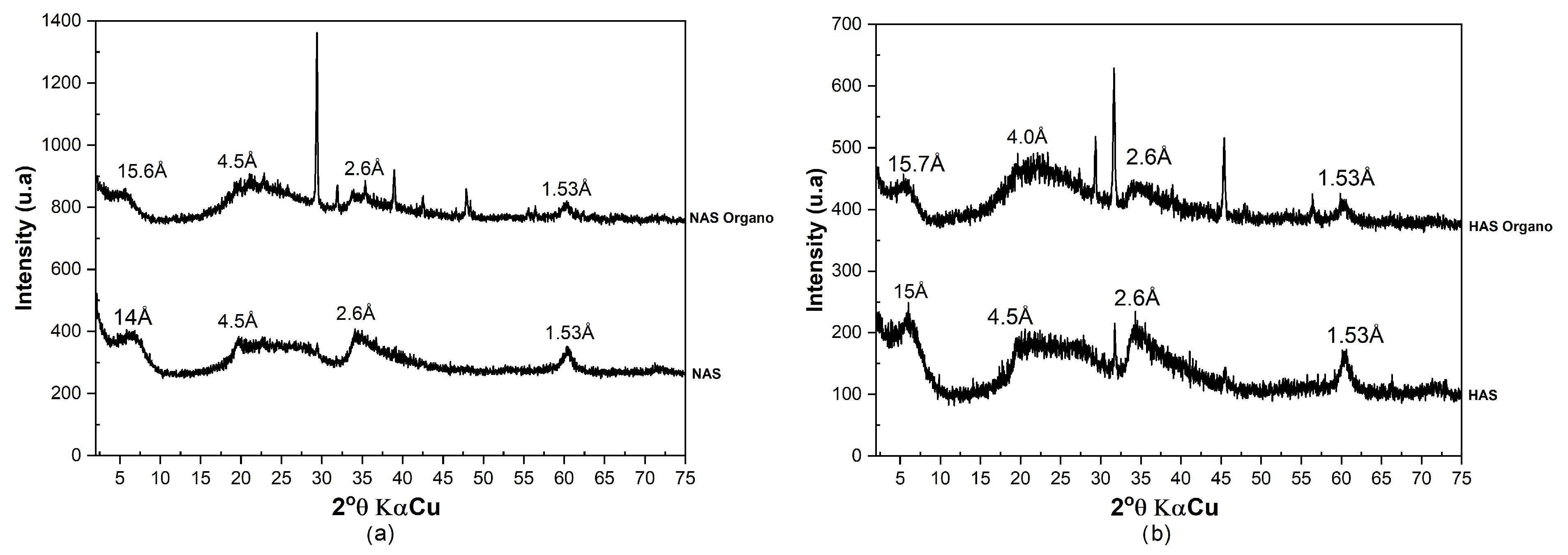
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
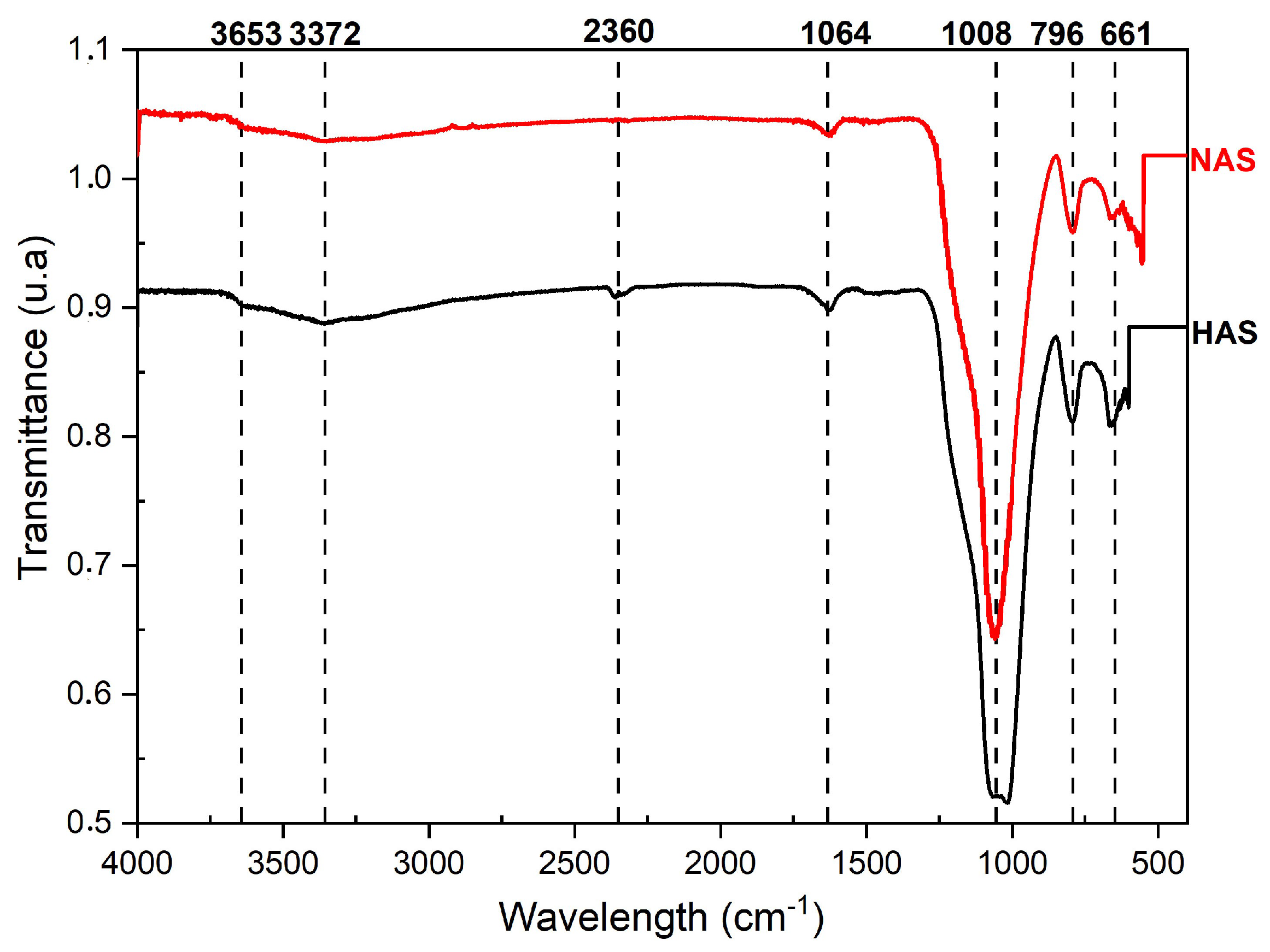
3.1.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
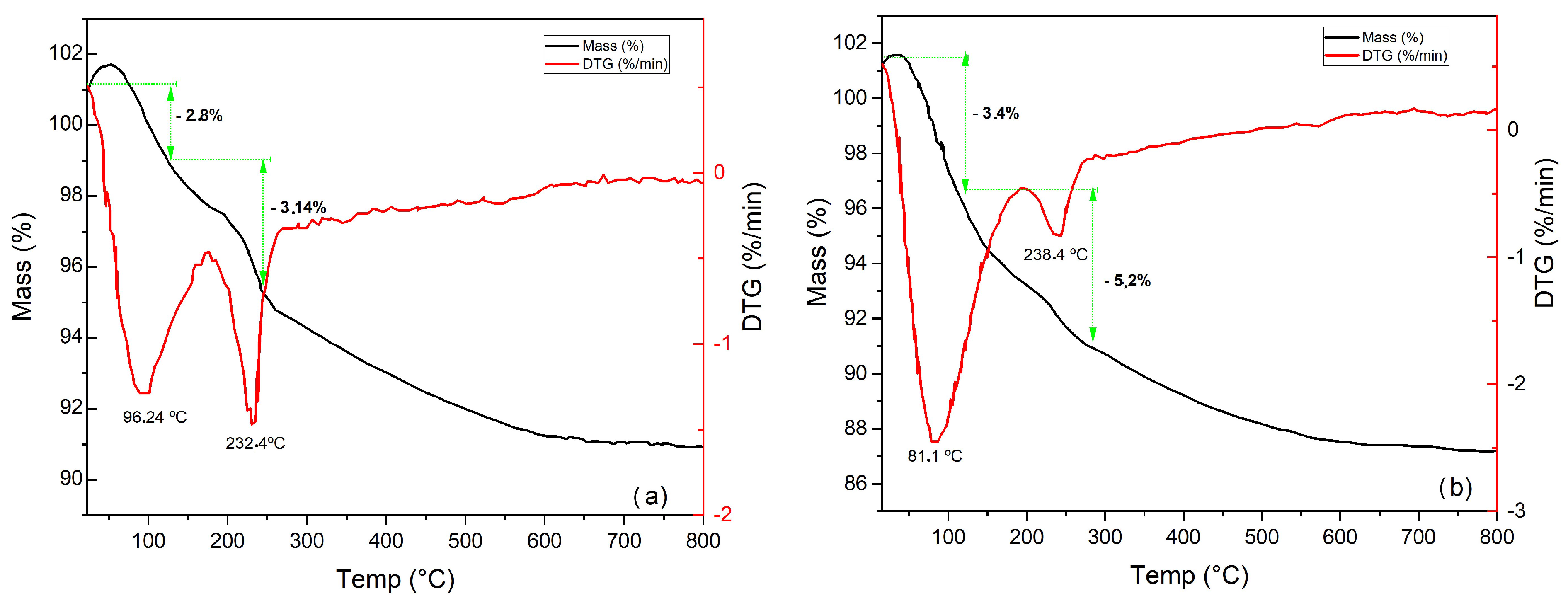
3.1.5. Thermal and Differential Analysis (TG/ DTG)
3.1.6. Nitrogen Adsorption Analysis—BET
3.2. Organophilic Synthetic Clay
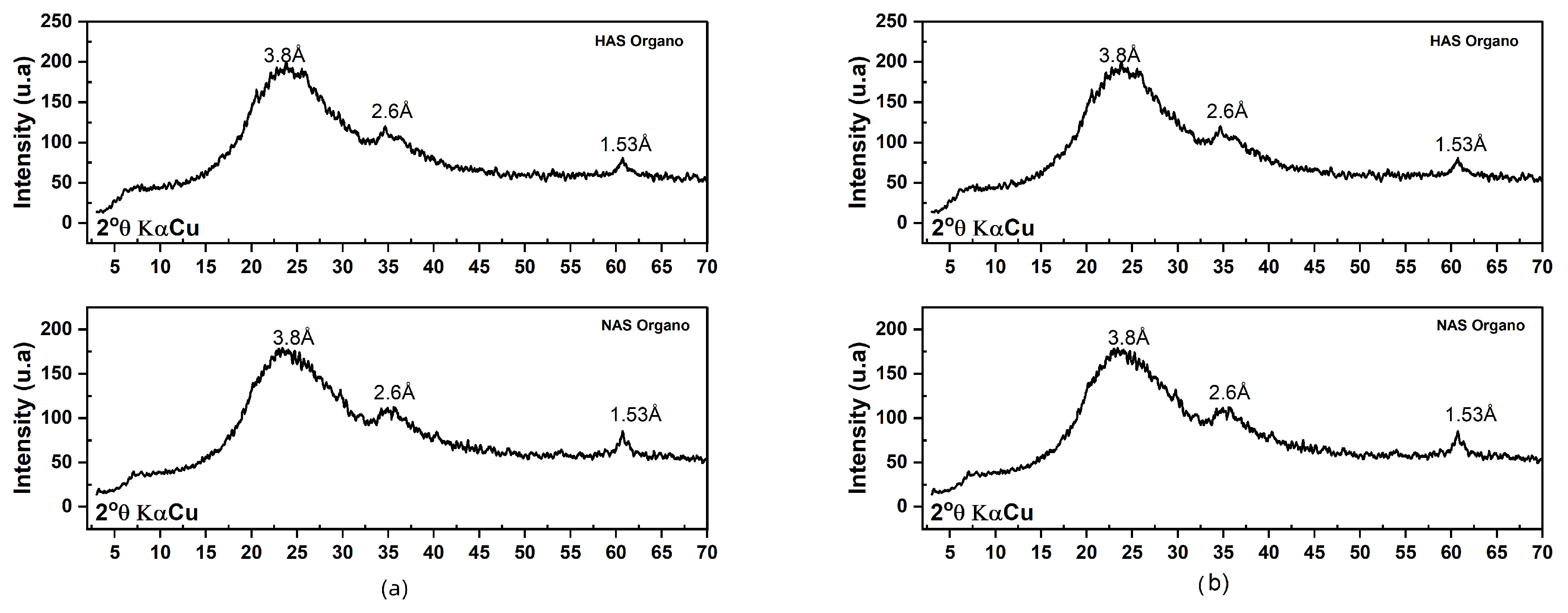
3.2.1. Evaluation of Organophilization by X-ray Diffraction—XRD
3.2.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of Synthetic Clays Organophilized Using the Semi-Dry Method
3.3. Swellability in Water and Organic Liquids of Synthetic and Organophilized Clays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishii, R.; Teshima, N.; Ebina, T.; Mizukami, F. Increasing particle size of a synthetic smectite for polymer nanocomposites using a supercritical hydrothermal treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.E.; Guven, N. Bentonites: Geology, Mineralogy, Properties and Uses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, C.H.; Lin, C.X.; Tong, D.S.; Yu, W.H. Synthesis of clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Pozo, M.; Cecilia, J.A.; Benitez-Guerrero, M.; Lorente, M. Effectiveness of microwave assisted acid treatment on dioctahedral and trioctahedral smectites. The influence of octahedral composition. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 120, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari, S.; Komarneni, S.; Mariani, E.; Villa, C. Microwave versus conventional preparation of organoclays from natural and synthetic clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrado, K.A. Synthetic organo-and polymer–clays: Preparation, characterization, and materials applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. General introduction: Clays, clay minerals, and clay science. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.A.M.; Rodriguez, M.A.V.; Reyes-Cruz, V.E. Study of clays electrochemical purification. Chem. Eng. 2014, 41, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, P.G.; Valera, T.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Purification of a brazilian smectite clay. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publ.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 727, pp. 929–934. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadiri, M.; Chrzanowski, W.; Rohanizadeh, R. Biomedical applications of cationic clay minerals. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29467–29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Komarneni, S.; Amonette, J.E. Synthesis of smectite clay minerals: A critical review. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Oya, A. Preparation of a nanocomposite of polypropylene and smectite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1996, 15, 1481–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozsgay, A.; Papp, L.; Fráter, T.; Pukánszky, B. Polypropylene/montmorillonite nanocomposites prepared by the delamination of the filler. In Adsorption and Nanostructure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaresan, S.; Pawar, R.R.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Bajaj, H.C. Synthesis of saponite based nanocomposites to improve the controlled oral drug release of model drug quinine hydrochloride dihydrate. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H.; Nakashima, A.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Kurosaka, K. Changes of viscosity in stevensite aqueous dispersions with application of an electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, J.; Berben, P. Preparation and performance of synthetic organoclays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 33, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Forestier, L.; Muller, F.; Villieras, F.; Pelletier, M. Textural and hydration properties of a synthetic montmorillonite compared with a natural Na-exchanged clay analogue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, V.; McHardy, W.; Elsass, F.; Robert, M. hk-ordering in aluminous nontronite and saponite synthesized near 90° C: Effects of synthesis conditions on nontronite composition and ordering. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, R.; Kloprogge, J.; Geus, J. Synthesis and characterization of saponite clays. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Miki, H.; Komarneni, S. Mn-smectites: Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashi, S.; Miki, K.; Komarneni, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of Zn-smectites. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarreau, A. Partitioning of divalent transition elements between octahedral sheets of trioctahedral smectites and water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrado, K.; Decarreau, A.; Petit, S.; Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. Synthetic clay minerals and purification of natural clays. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 115–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrando, E.A.; Silva-Valenzuela, M.; Neves, R.d.F.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F. Síntese e caracterização de argila esmectita Zn-estevensita. Cerâmica 2014, 60, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guggenheim, S.; Pozo, M.; Galán, E. Introduction to Mg-rich clay minerals: Structure and composition. In Magnesian Clays: Characterization, Origin and Applications; Pozo, M., Galán, E., Eds.; Digilabs Pub.: Bari, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela-Díaz, F.R. Preparation of organophilic clays from a Brazilian smectitic clay. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 189, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.B. Estudo do Potencial de Bentonitas Nacionais e Argentinas na Obtenção de Bentonitas Organofílicas em Dispersão Aquosa e Meio Semi-Sólido Visando à Aplicação em Nanocompósitos Poliméricos. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia Química, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, G.E.; Koutsopoulou, E. Thermal behaviour of Stevensite at temperatures up to 800 °C. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2013, 47, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, C.S.; Ohnuma, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Tamura, K.; Yamada, H.; Cuadros, J.; Ye, J. Synthesis of monodisperse Zn-smectite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.D. The relation between composition and swelling in clays. Clays Clay Miner. 1954, 3, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, G.T.; Hathaway, J.C.; Millot, G. A restudy of stevensite and allied minerals. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1959, 44, 342–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sychev, M.; Prihod’ko, R.; Koriabkina, A.; Hensen, E.; Van Veen, J.; Van Santen, R. The application of non-hydrothermally prepared stevensites as support for hydrodesulfurization catalysts. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous Catalysts, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 9 December 2002; Volume 8, pp. 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Azarkan, S.; Peña, A.; Draoui, K.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Adsorption of two fungicides on natural clays of Morocco. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón-Herrero, R.; García-Delgado, C.; Alonso-Izquierdo, M.; García-Rodríguez, G.; Cuevas, J.; Eymar, E. Comparative adsorption of tetracyclines on biochars and stevensite: Looking for the most effective adsorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Ruiz, A.I.; García-Delgado, C.; González-Santamaría, D.E.; Antón-Herrero, R.; Yunta, F.; Poyo, C.; Hernández, A.; Eymar, E.; Cuevas, J. Stevensite-based geofilter for the retention of tetracycline from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussout, H.; Ahlafi, H.; Aazza, M.; Chfaira, R.; Mounir, C. Interfacial electrochemical properties of natural Moroccan Ghassoul (stevensite) clay in aqueous suspension. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhammou, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Nibou, L.; Tanouti, B. Adsorption of metal ions onto Moroccan stevensite: Kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 282, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Fujita, S.; Arai, M. Synthesis and adsorption properties of smectite-like materials prepared using ionic liquids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Righi, D.; Decarreau, A. Transformation of synthetic Zn-stevensite to Zn-talc induced by the Hofmann-Klemen effect. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, G.L.; Sallet, R.G. Caracterição físico-química de argilas do município de ItajÁ-RN para utilização em inústria Câmica vermelha. In Proceedings of the Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia e Ciência dos Materiais—CBECiMat, Natal, Brasil, 9 November 2002; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, N.I.A.; Rocha, M.C.G.; Bertolino, L.C. Determinação da área superficial específica e da porosidade de duas amostras de argilas provenientes da bacia de Taubaté-São Paulo. Braz. Appl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 5, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouna, L.; Rhouta, B.; Amjoud, M.; Jada, A.; Maury, F.; Daoudi, L.; Senocq, F. Correlation between eletrokinetic mobility and ionic dyes adsorption of Moroccan stevensite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.E. Modern concepts of clay materials. J. Geol. 1942, 50, 225–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Oxides (%) | MgO | Cl | CaO | ZnO | LOI * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAS | 1.2 | - | 0.1 | 59.1 | - | - | - | - | - | 27.8 | 11.9 |
| HAS | 1.3 | - | 0.1 | 61.1 | - | 0.8 | - | - | - | 25.6 | 11.1 |
| Data | NAS | HAS |
|---|---|---|
| BET area (m/g) | 163.16 | 197.41 |
| Pore volume (cm/g) | 0.93 | 1.09 |
| External surface area (m/g) | 189.60 | 213.29 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 196.82 | 205.48 |
| Mean diameter of nanopores (Å) | 367.73 | 303.93 |
| Samples | Swelling (mL/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Ethyl Alcohol | Methyl Alcohol | Isopropyl Alcohol | Toluene | Xylol | Kerosene | |
| NAS Organo | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.5 |
| HAS Organo | 2.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2,0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, T.; Neves, R.; Hildebrando, E.; de Paiva, L.B.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F.R. Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals 2022, 12, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
Carvalho T, Neves R, Hildebrando E, de Paiva LB, Valenzuela-Diaz FR. Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Thamyres, Roberto Neves, Edemarino Hildebrando, Lucilene Betega de Paiva, and Francisco R. Valenzuela-Diaz. 2022. "Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
APA StyleCarvalho, T., Neves, R., Hildebrando, E., de Paiva, L. B., & Valenzuela-Diaz, F. R. (2022). Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals, 12(12), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568






