Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Clay Synthesis
2.2.2. Organophilization
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Clay
3.1.1. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
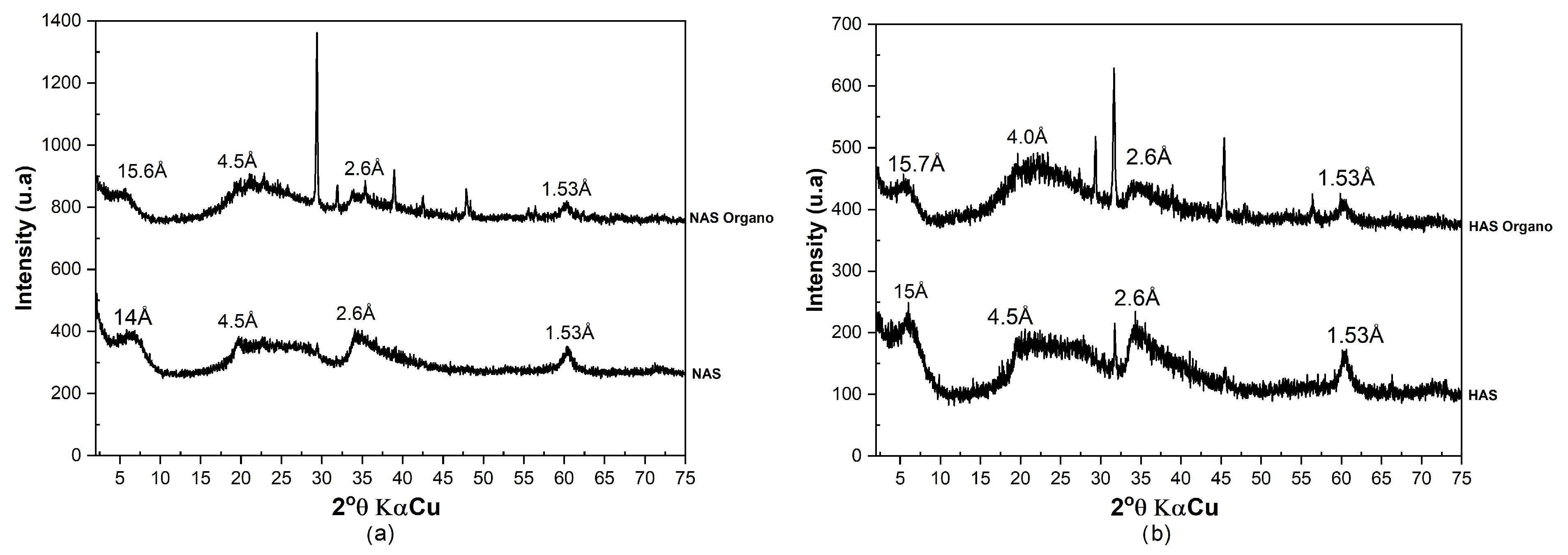
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
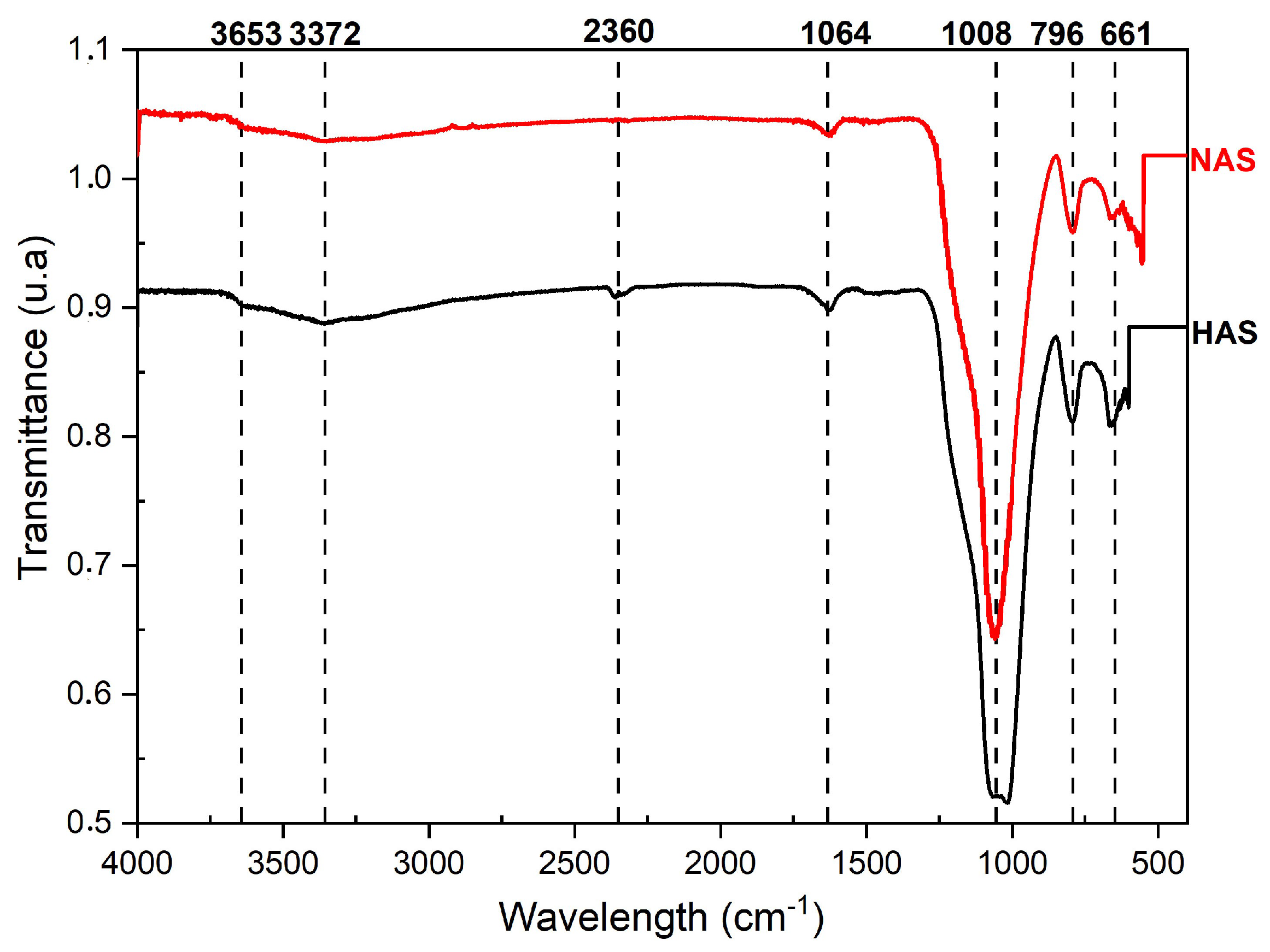
3.1.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
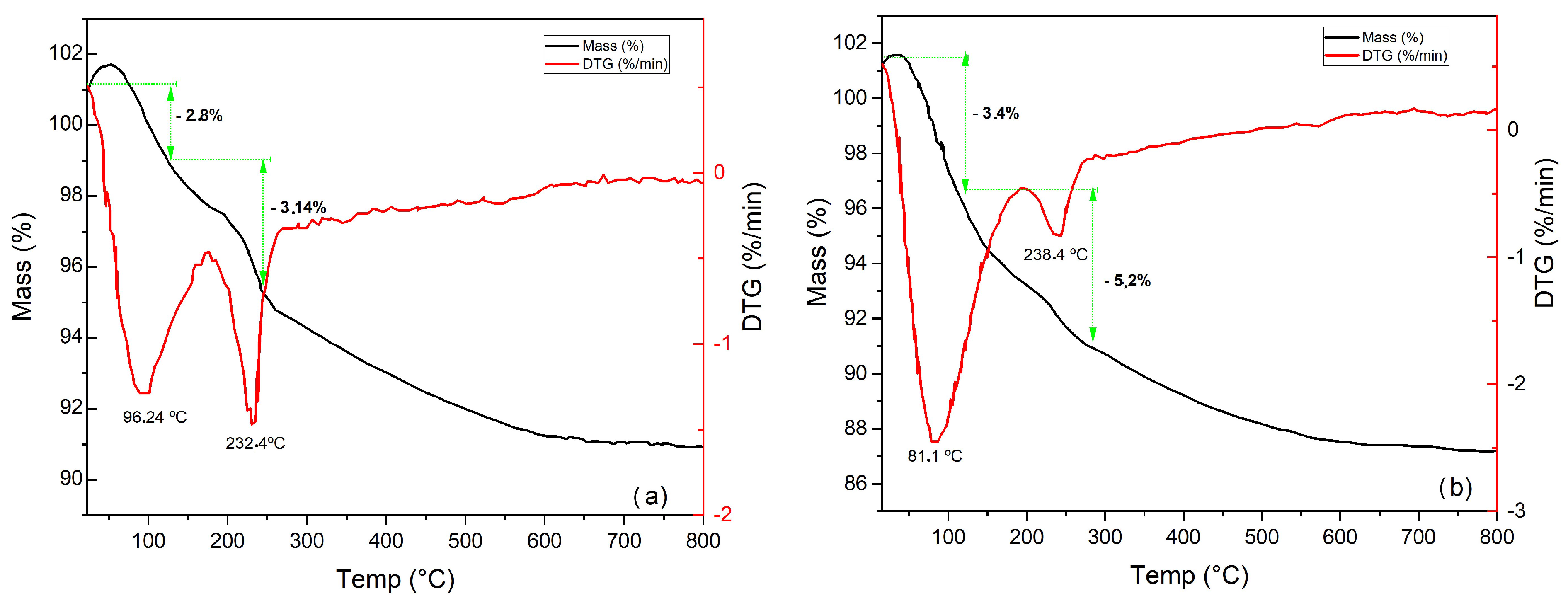
3.1.5. Thermal and Differential Analysis (TG/ DTG)
3.1.6. Nitrogen Adsorption Analysis—BET
3.2. Organophilic Synthetic Clay
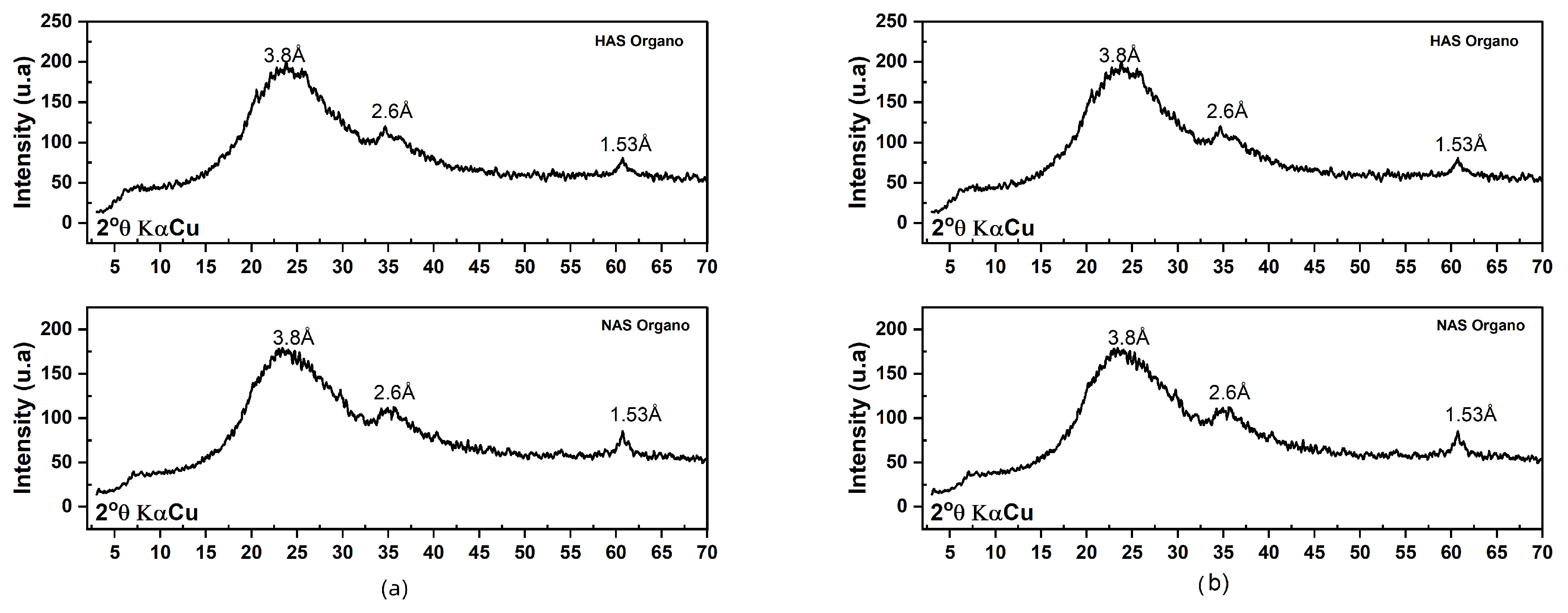
3.2.1. Evaluation of Organophilization by X-ray Diffraction—XRD
3.2.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of Synthetic Clays Organophilized Using the Semi-Dry Method
3.3. Swellability in Water and Organic Liquids of Synthetic and Organophilized Clays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishii, R.; Teshima, N.; Ebina, T.; Mizukami, F. Increasing particle size of a synthetic smectite for polymer nanocomposites using a supercritical hydrothermal treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.E.; Guven, N. Bentonites: Geology, Mineralogy, Properties and Uses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, C.H.; Lin, C.X.; Tong, D.S.; Yu, W.H. Synthesis of clay minerals. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Pozo, M.; Cecilia, J.A.; Benitez-Guerrero, M.; Lorente, M. Effectiveness of microwave assisted acid treatment on dioctahedral and trioctahedral smectites. The influence of octahedral composition. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 120, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari, S.; Komarneni, S.; Mariani, E.; Villa, C. Microwave versus conventional preparation of organoclays from natural and synthetic clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrado, K.A. Synthetic organo-and polymer–clays: Preparation, characterization, and materials applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. General introduction: Clays, clay minerals, and clay science. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.A.M.; Rodriguez, M.A.V.; Reyes-Cruz, V.E. Study of clays electrochemical purification. Chem. Eng. 2014, 41, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, P.G.; Valera, T.S.; Demarquette, N.R. Purification of a brazilian smectite clay. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publ.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 727, pp. 929–934. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadiri, M.; Chrzanowski, W.; Rohanizadeh, R. Biomedical applications of cationic clay minerals. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29467–29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Komarneni, S.; Amonette, J.E. Synthesis of smectite clay minerals: A critical review. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Oya, A. Preparation of a nanocomposite of polypropylene and smectite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1996, 15, 1481–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozsgay, A.; Papp, L.; Fráter, T.; Pukánszky, B. Polypropylene/montmorillonite nanocomposites prepared by the delamination of the filler. In Adsorption and Nanostructure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kumaresan, S.; Pawar, R.R.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Bajaj, H.C. Synthesis of saponite based nanocomposites to improve the controlled oral drug release of model drug quinine hydrochloride dihydrate. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H.; Nakashima, A.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Kurosaka, K. Changes of viscosity in stevensite aqueous dispersions with application of an electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, J.; Berben, P. Preparation and performance of synthetic organoclays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 33, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Forestier, L.; Muller, F.; Villieras, F.; Pelletier, M. Textural and hydration properties of a synthetic montmorillonite compared with a natural Na-exchanged clay analogue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, V.; McHardy, W.; Elsass, F.; Robert, M. hk-ordering in aluminous nontronite and saponite synthesized near 90° C: Effects of synthesis conditions on nontronite composition and ordering. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, R.; Kloprogge, J.; Geus, J. Synthesis and characterization of saponite clays. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Miki, H.; Komarneni, S. Mn-smectites: Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Miki, K.; Komarneni, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of Zn-smectites. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarreau, A. Partitioning of divalent transition elements between octahedral sheets of trioctahedral smectites and water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrado, K.; Decarreau, A.; Petit, S.; Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. Synthetic clay minerals and purification of natural clays. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 115–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrando, E.A.; Silva-Valenzuela, M.; Neves, R.d.F.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F. Síntese e caracterização de argila esmectita Zn-estevensita. Cerâmica 2014, 60, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guggenheim, S.; Pozo, M.; Galán, E. Introduction to Mg-rich clay minerals: Structure and composition. In Magnesian Clays: Characterization, Origin and Applications; Pozo, M., Galán, E., Eds.; Digilabs Pub.: Bari, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela-Díaz, F.R. Preparation of organophilic clays from a Brazilian smectitic clay. Key Eng. Mater. 2001, 189, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.B. Estudo do Potencial de Bentonitas Nacionais e Argentinas na Obtenção de Bentonitas Organofílicas em Dispersão Aquosa e Meio Semi-Sólido Visando à Aplicação em Nanocompósitos Poliméricos. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculdade de Engenharia Química, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, G.E.; Koutsopoulou, E. Thermal behaviour of Stevensite at temperatures up to 800 °C. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2013, 47, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, C.S.; Ohnuma, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Tamura, K.; Yamada, H.; Cuadros, J.; Ye, J. Synthesis of monodisperse Zn-smectite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.D. The relation between composition and swelling in clays. Clays Clay Miner. 1954, 3, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, G.T.; Hathaway, J.C.; Millot, G. A restudy of stevensite and allied minerals. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1959, 44, 342–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sychev, M.; Prihod’ko, R.; Koriabkina, A.; Hensen, E.; Van Veen, J.; Van Santen, R. The application of non-hydrothermally prepared stevensites as support for hydrodesulfurization catalysts. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous Catalysts, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 9 December 2002; Volume 8, pp. 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Azarkan, S.; Peña, A.; Draoui, K.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Adsorption of two fungicides on natural clays of Morocco. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón-Herrero, R.; García-Delgado, C.; Alonso-Izquierdo, M.; García-Rodríguez, G.; Cuevas, J.; Eymar, E. Comparative adsorption of tetracyclines on biochars and stevensite: Looking for the most effective adsorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Ruiz, A.I.; García-Delgado, C.; González-Santamaría, D.E.; Antón-Herrero, R.; Yunta, F.; Poyo, C.; Hernández, A.; Eymar, E.; Cuevas, J. Stevensite-based geofilter for the retention of tetracycline from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussout, H.; Ahlafi, H.; Aazza, M.; Chfaira, R.; Mounir, C. Interfacial electrochemical properties of natural Moroccan Ghassoul (stevensite) clay in aqueous suspension. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhammou, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Nibou, L.; Tanouti, B. Adsorption of metal ions onto Moroccan stevensite: Kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 282, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Fujita, S.; Arai, M. Synthesis and adsorption properties of smectite-like materials prepared using ionic liquids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Righi, D.; Decarreau, A. Transformation of synthetic Zn-stevensite to Zn-talc induced by the Hofmann-Klemen effect. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, G.L.; Sallet, R.G. Caracterição físico-química de argilas do município de ItajÁ-RN para utilização em inústria Câmica vermelha. In Proceedings of the Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia e Ciência dos Materiais—CBECiMat, Natal, Brasil, 9 November 2002; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, N.I.A.; Rocha, M.C.G.; Bertolino, L.C. Determinação da área superficial específica e da porosidade de duas amostras de argilas provenientes da bacia de Taubaté-São Paulo. Braz. Appl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 5, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouna, L.; Rhouta, B.; Amjoud, M.; Jada, A.; Maury, F.; Daoudi, L.; Senocq, F. Correlation between eletrokinetic mobility and ionic dyes adsorption of Moroccan stevensite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.E. Modern concepts of clay materials. J. Geol. 1942, 50, 225–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Oxides (%) | MgO | Cl | CaO | ZnO | LOI * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAS | 1.2 | - | 0.1 | 59.1 | - | - | - | - | - | 27.8 | 11.9 |
| HAS | 1.3 | - | 0.1 | 61.1 | - | 0.8 | - | - | - | 25.6 | 11.1 |
| Data | NAS | HAS |
|---|---|---|
| BET area (m/g) | 163.16 | 197.41 |
| Pore volume (cm/g) | 0.93 | 1.09 |
| External surface area (m/g) | 189.60 | 213.29 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 196.82 | 205.48 |
| Mean diameter of nanopores (Å) | 367.73 | 303.93 |
| Samples | Swelling (mL/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Ethyl Alcohol | Methyl Alcohol | Isopropyl Alcohol | Toluene | Xylol | Kerosene | |
| NAS Organo | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.5 |
| HAS Organo | 2.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2,0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, T.; Neves, R.; Hildebrando, E.; de Paiva, L.B.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F.R. Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals 2022, 12, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
Carvalho T, Neves R, Hildebrando E, de Paiva LB, Valenzuela-Diaz FR. Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Thamyres, Roberto Neves, Edemarino Hildebrando, Lucilene Betega de Paiva, and Francisco R. Valenzuela-Diaz. 2022. "Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568
APA StyleCarvalho, T., Neves, R., Hildebrando, E., de Paiva, L. B., & Valenzuela-Diaz, F. R. (2022). Organophilic Synthetic Stevensite-Zn: Synthesis and Characterization, an Alternative Simple Method. Minerals, 12(12), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121568






