Movement Laws of the Overlying Strata at the Working Face Ends and Their Effects on the Surface Deformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
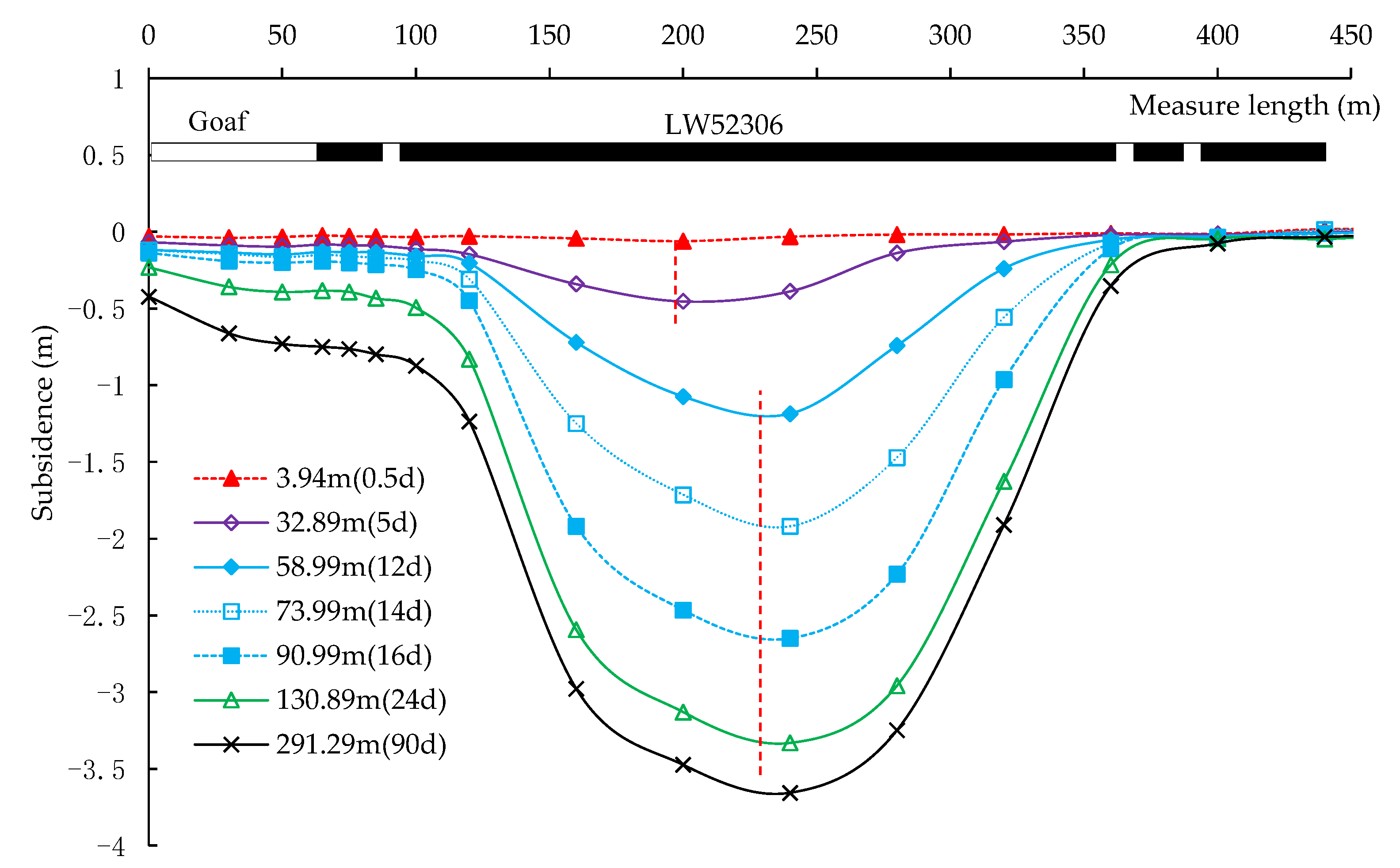
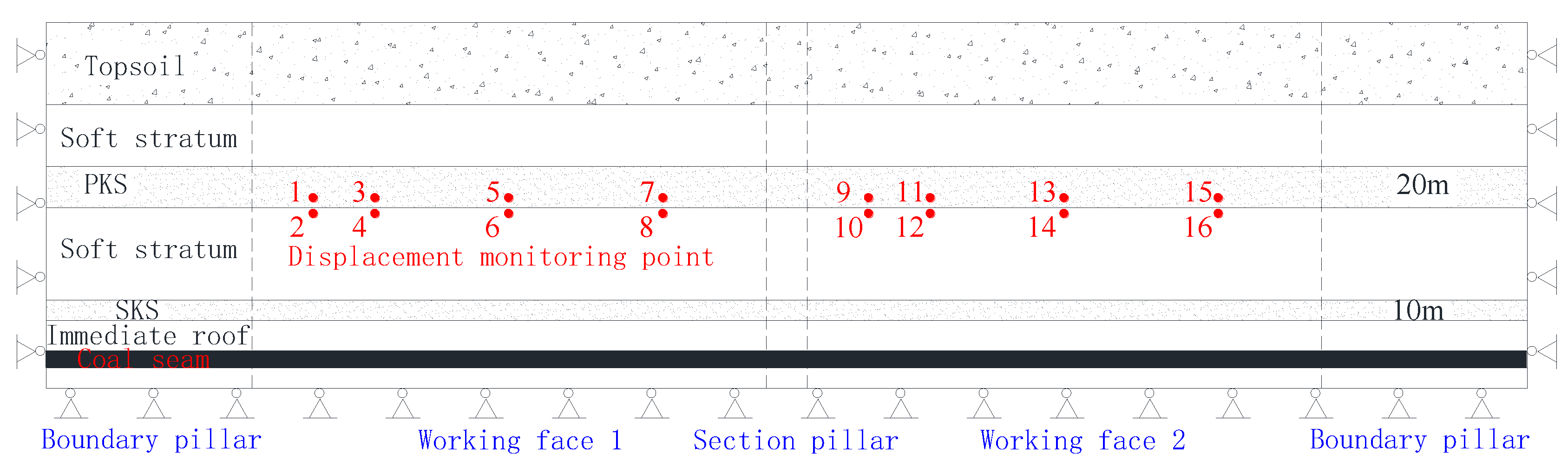
2. Geological Condition and Field Monitoring
3. Physical Model
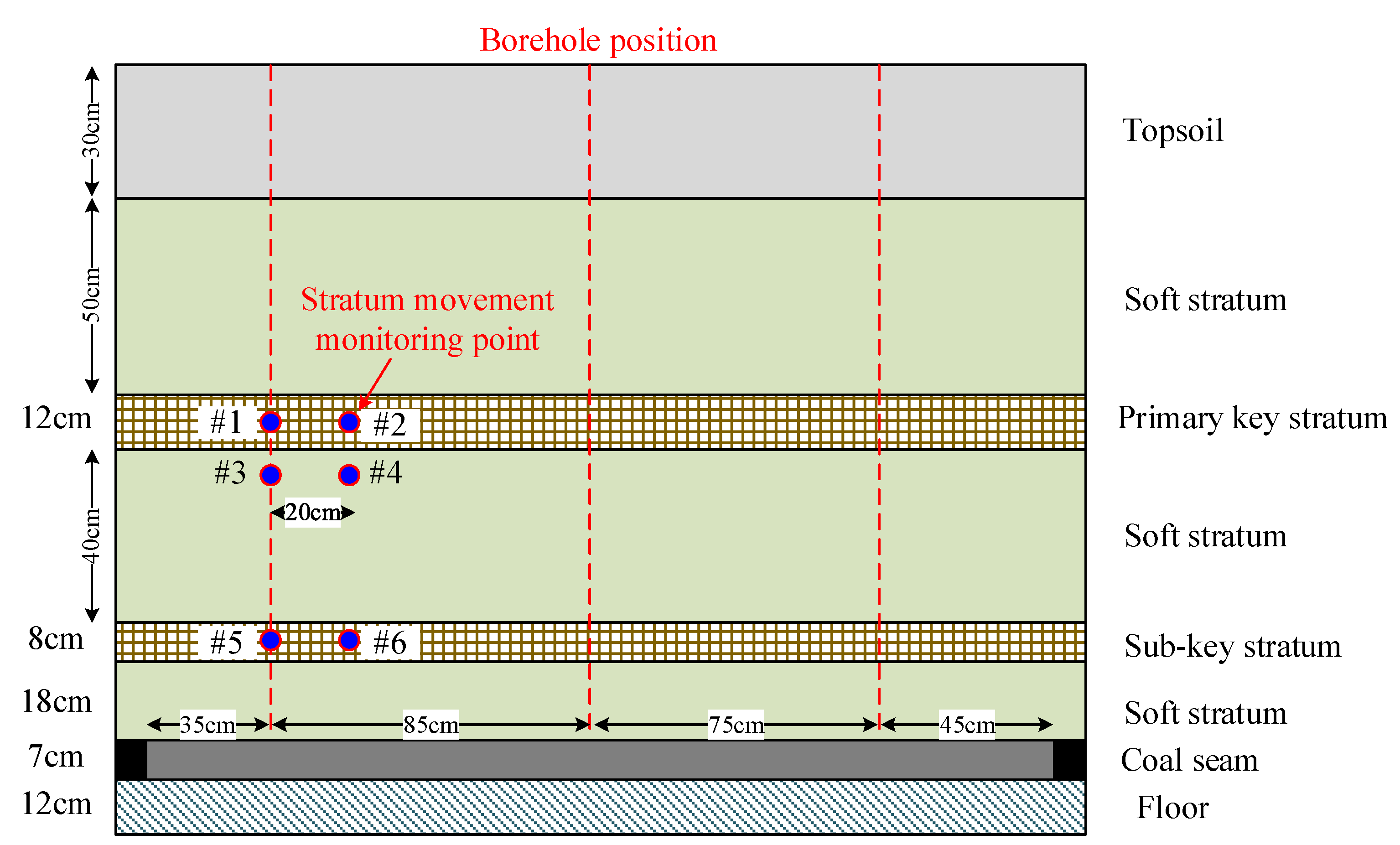
3.1. Model Preparation
3.2. Results
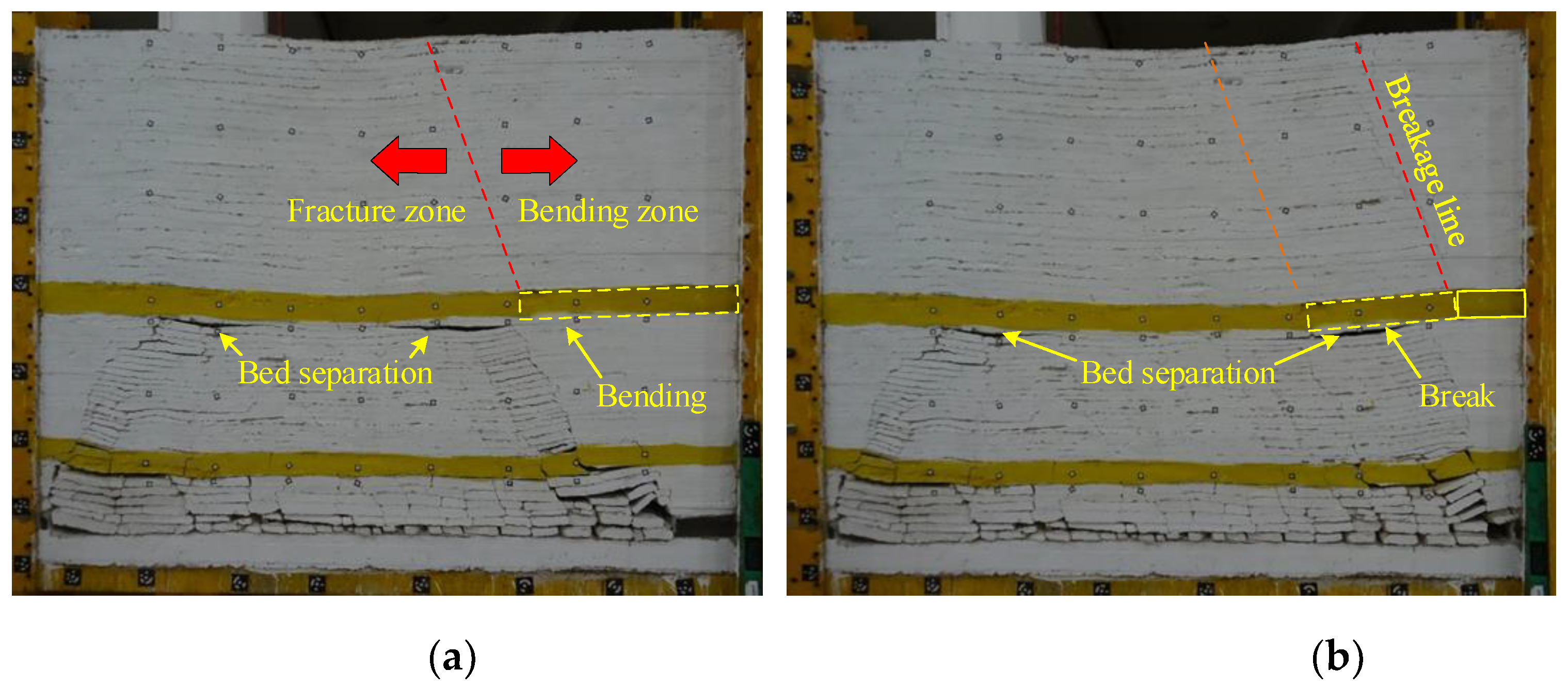
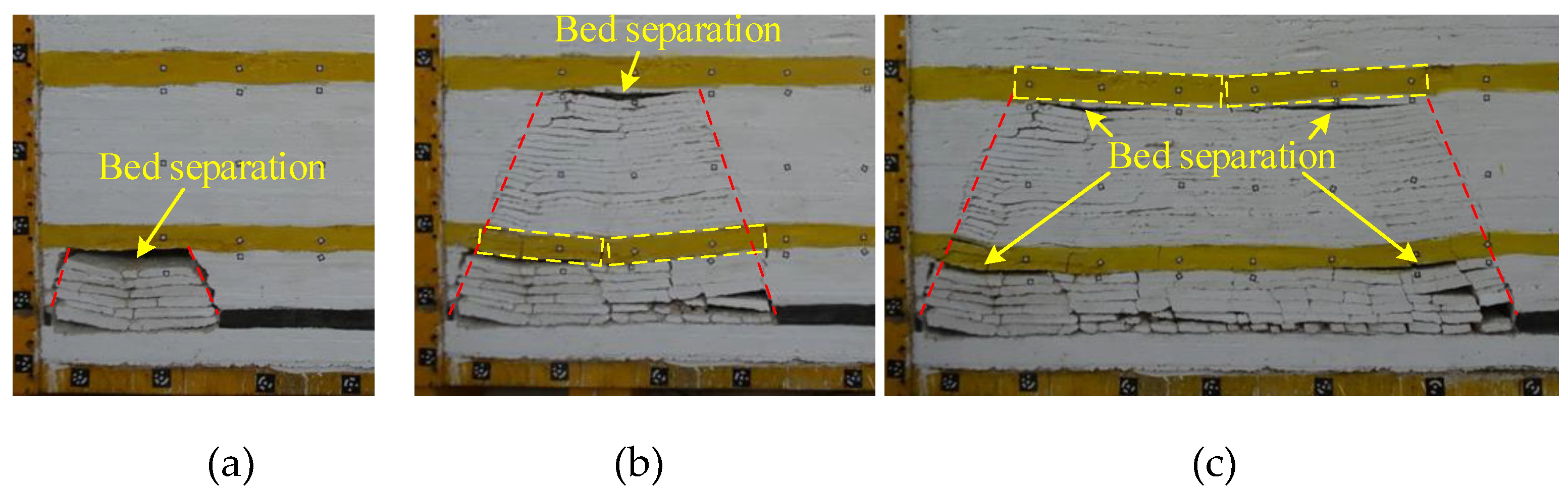
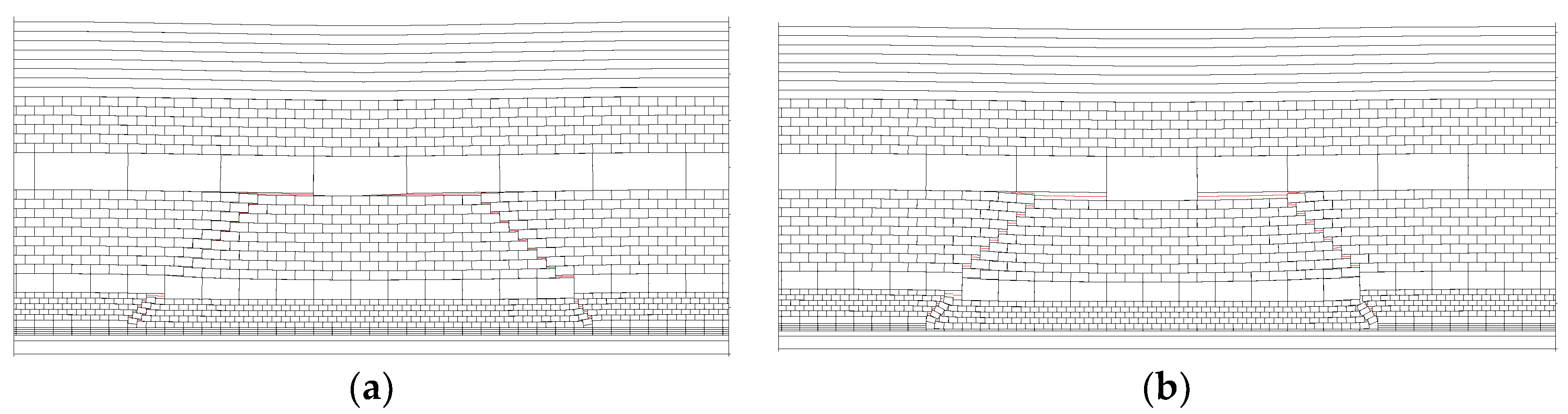
3.2.1. Breakage of the Immediate Roof and SKS
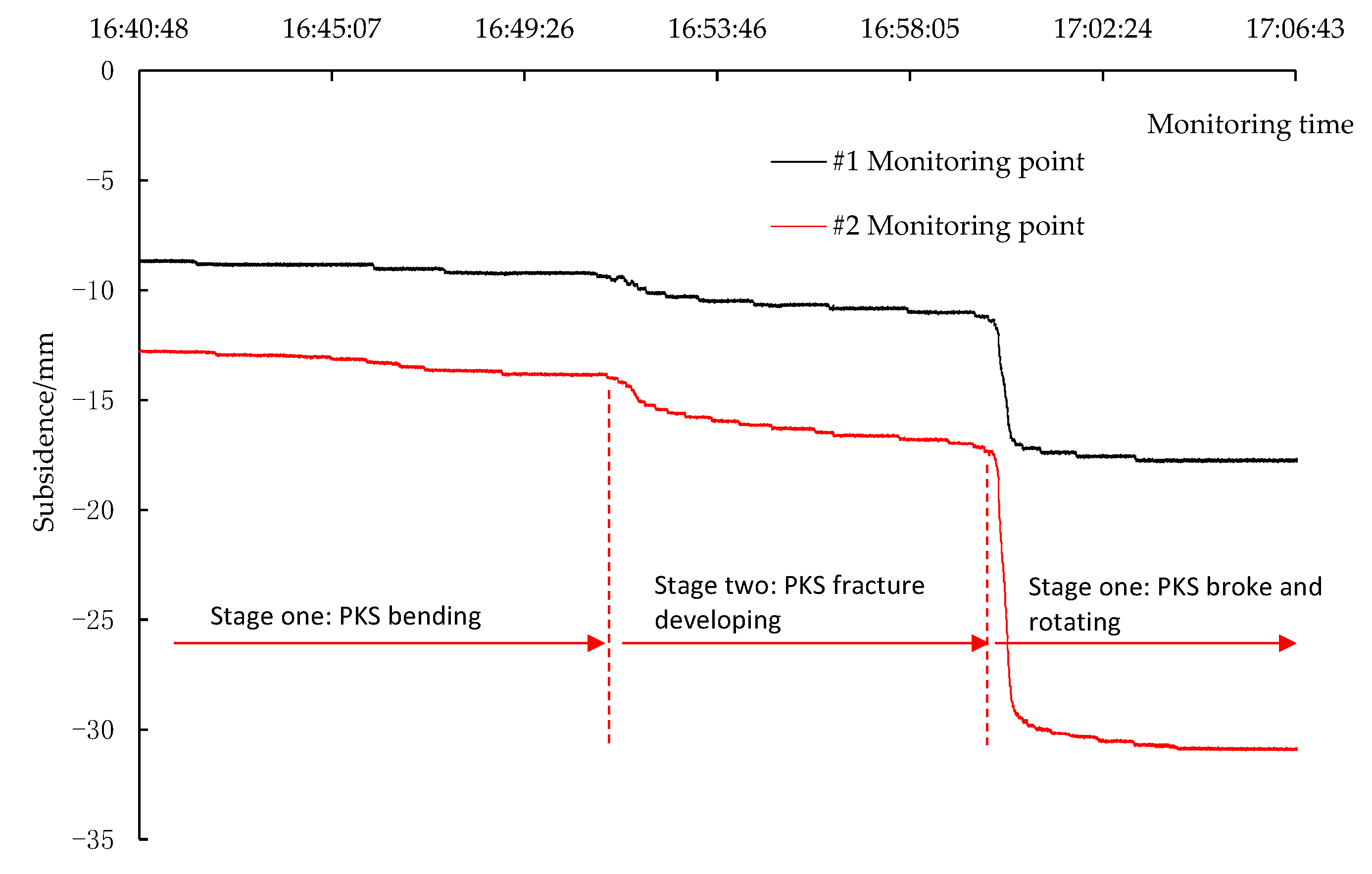
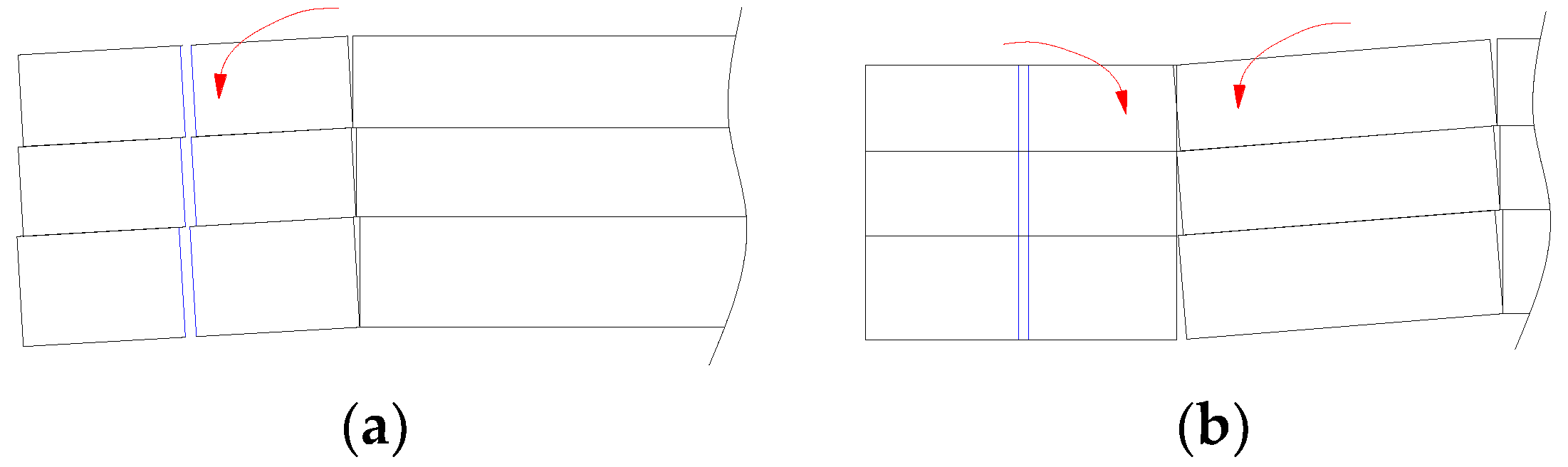
3.2.2. Breakage of the PKS
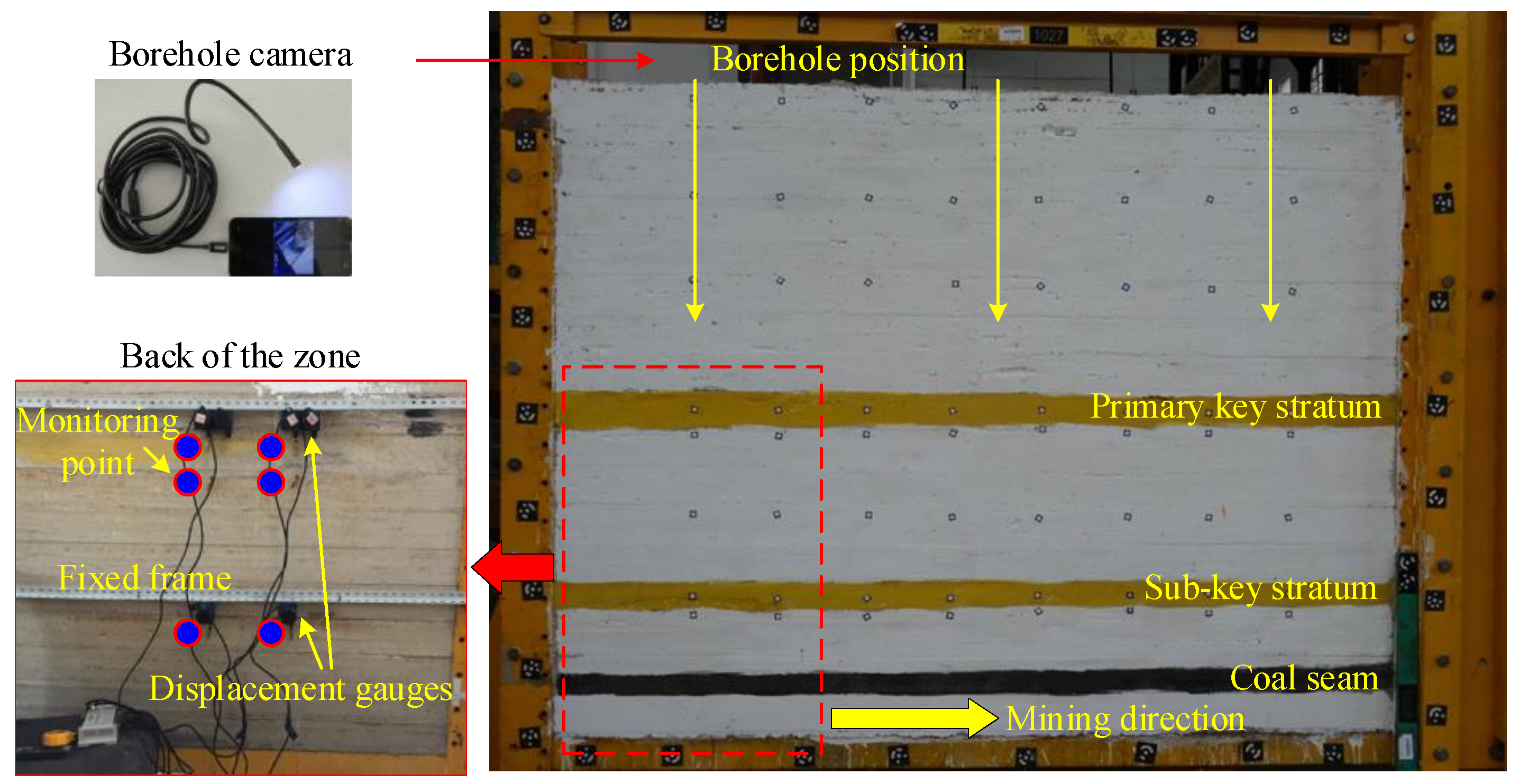
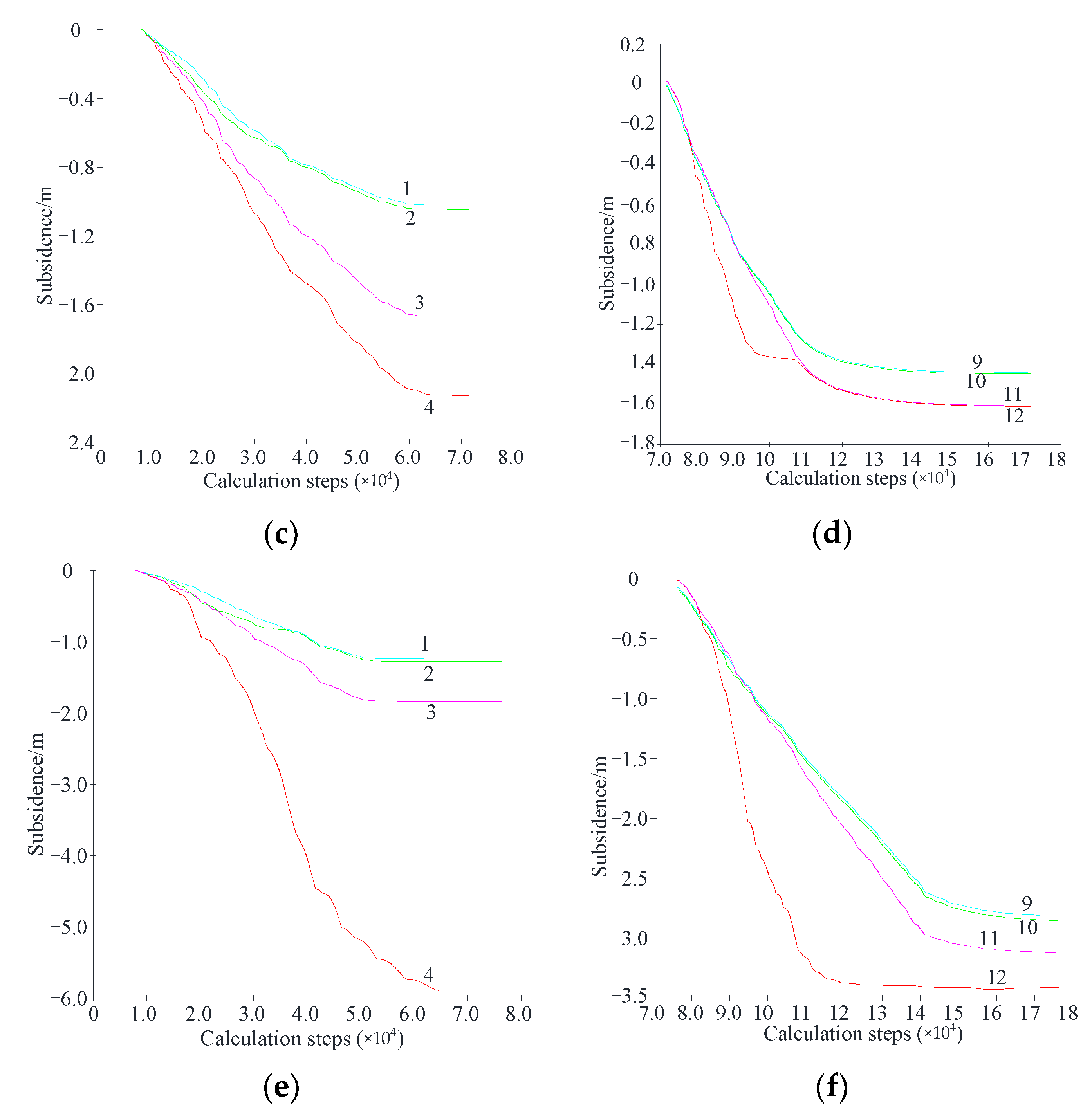
3.2.3. Monitoring Results of the Borehole Cameras
3.2.4. Mining-Induced Fractures and Surface Subsidence
4. Numerical Modelling
4.1. Model Setup and Modelling Plan
4.2. Numerical Model Results
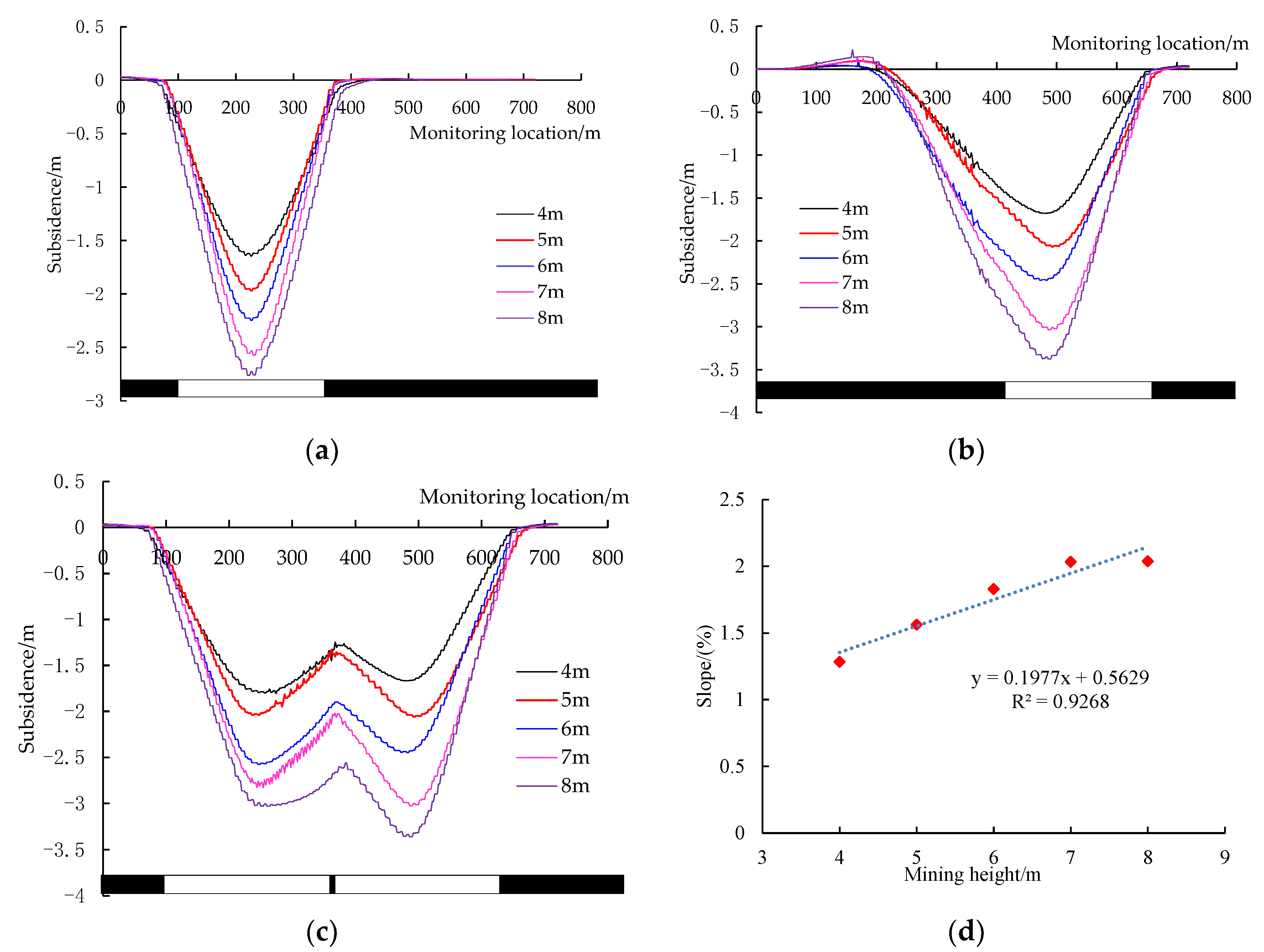
4.2.1. The Effect of Mining Height
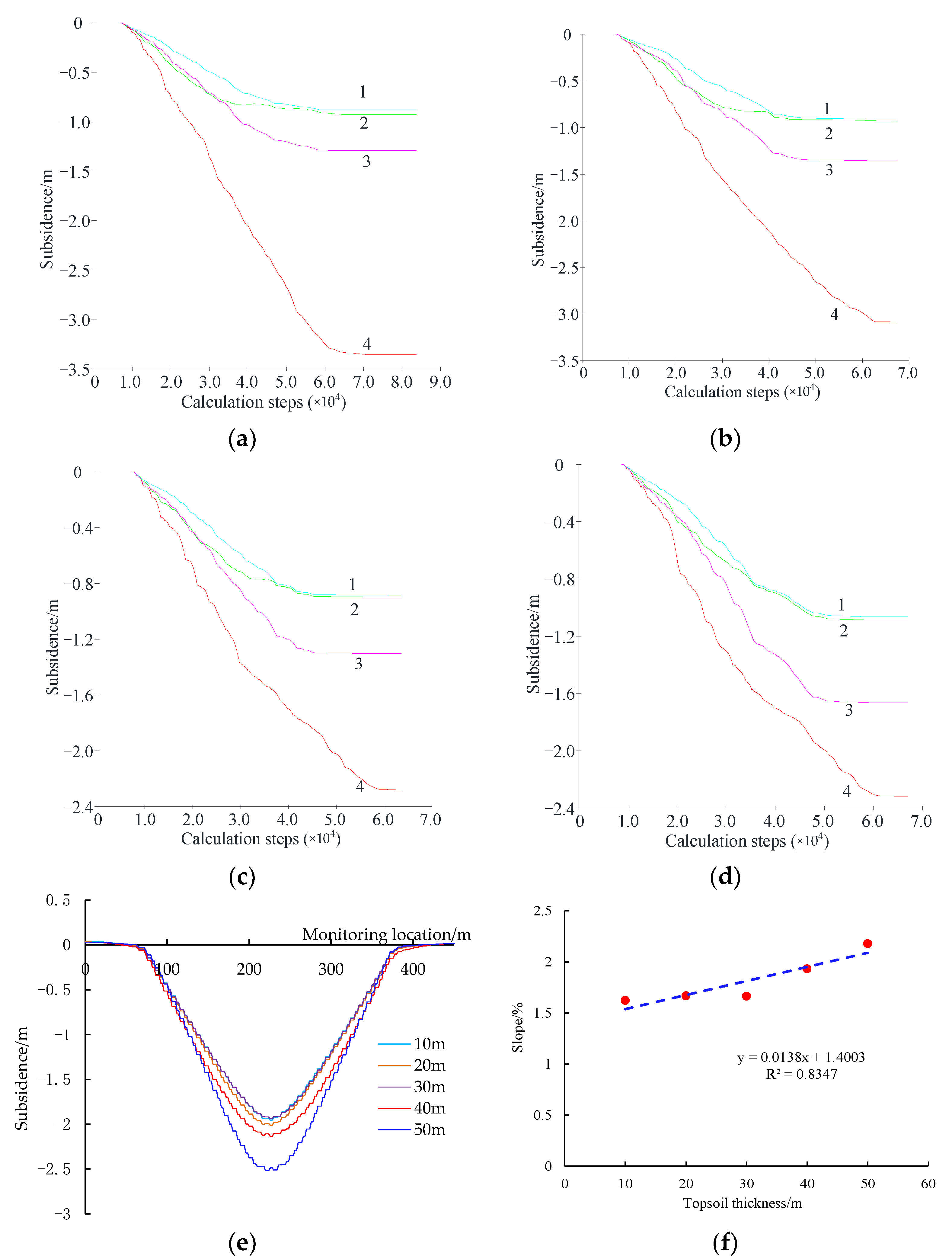
4.2.2. The Effect of the Thickness of Topsoil
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dunrud, C.R. Coal mine subsidence—Western United States. Rev. Eng. Geol. 1984, 1, 151–194. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Xing, Y. Surface Subsidence Prediction Method for Coal Mines with Ultrathick and Hard Stratum. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 3714381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-J.; Lee, S. Integration of ground subsidence hazard maps of abandoned coal mines in Samcheok, Korea. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 86, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, Y. Effects of land subsidence resulted from coal mining on soil nutrient distributions in a loess area of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.G.; Shi, P.W.; Xu, J.L. Mining Pressure and Strata Control; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2003; pp. 188–190. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, W.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. High-intensity longwall mining-induced ground subsidence in Shendong coalfield, China. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 141, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wen, G.; Dai, L.; Sun, H.; Li, X. Ground Subsidence and Surface Cracks Evolution from Shallow-Buried Close-Distance Multi-seam Mining: A Case Study in Bulianta Coal Mine. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 2835–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xia, T.; Nie, J.; Cui, F. The shallow strata structure and soil water content in a coal mining subsidence area detected by GPR and borehole data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Dong, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wong, H. A physical and numerical model-based research on the subsidence features of overlying strata caused by coal mining in Henan, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Huang, Q.; Guo, L. Subsidence prediction of overburden strata and ground surface in shallow coal seam mining. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Yu, S.; Xu, J. Influence of the elastic dilatation of mining-induced unloading rock mass on the development of bed Separation. Energies 2018, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Qin, W.; Xuan, D.Y.; Zhu, W.B. Accumulative effect of overburden strata expansion induced by stress relief. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ghabraie, B.; Ren, G.; Smith, J.V. Characterising the multi-seam subsidence due to varying mining configuration, insights from physical modelling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 93, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabraie, B.; Ren, G.; Zhang, X.; Smith, J. Physical modelling of subsidence from sequential extraction of partially overlapping longwall panels and study of substrata movement characteristics. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 140, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, F.G.; Stacey, T.R.; Genske, D.D. Mining subsidence and its effect on the environment: Some differing examples. Environ. Geol. 2000, 40, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Hu, Z.; Fu, Y. Zoning of land reclamation in coal mining area and new progresses for the past 10 years. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, T.; Takamoto, H.; Shimada, H.; Oya, J.; Hamanaka, A.; Matsui, K. Surface subsidence due to underground mining operation under weak geological condition in Indonesia. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 7, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrožič, T.; Turk, G. Prediction of subsidence due to underground mining by artificial neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, T.; Nordlund, E.; Dahnér-Lindqvist, C. Hangingwall surface subsidence at the Kiirunavaara Mine, Sweden. Eng. Geol. 2011, 121, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.B.; Dhar, B.B. Sinkhole subsidence due to mining. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 1997, 15, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopata, P.; Stoch, T.; Wójcik, A.; Mrocheń, D. Land Surface Subsidence Due to Mining-Induced Tremors in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin (Poland)—Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajduś, K.; Sroka, A.; Misa, R.; Hager, S.; Rusek, J.; Dudek, M.; Wollnik, F. Analysis of Mining-Induced Delayed Surface Subsidence. Minerals 2021, 11, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Li, H. Impact of coal mining subsidence on farmland in eastern China. Int. J. Surf. Min. Reclam. Environ. 1997, 11, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Inyang, H.I.; Daniels, J.L.; Otto, F.; Struthers, S. Environmental issues from coal mining and their solutions. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yi, X.; Liang, Z.; Lou, J.; Zhu, W. Research on Strong Ground Pressure of Multiple-Seam Caused by Remnant Room Pillars Undermining in Shallow Seams. Energies 2021, 14, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, L.; Zhou, D.; Hu, Z. Ground cracks development and characteristics of strata movement under fast excavation: A case study at Bulianta coal mine, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 78, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misa, R.; Sroka, A.; Tajduś, K.; Dudek, M. Analytical design of selected geotechnical solutions which protect civil structures from the effects of underground mining. J. Sustain. Min. 2019, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusek, J.; Tajdus, K.; Firek, K.; Jedrzejczyk, A. Bayesian networks and Support Vector Classifier in damage risk assessment of RC prefabricated building structures in mining areas. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 1–4 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajduś, K.; Misa, R.; Sroka, A. Analysis of the surface horizontal displacement changes due to longwall panel advance. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 104, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardimci, A.G.; Karakus, M. A new protective destressing technique in underground hard coal mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 130, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Jia, J. Dynamic Surface Subsidence Characteristics due to Super-Large Working Face in Fragile-Ecological Mining Areas: A Case Study in Shendong Coalfield, China. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8658753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiránková, E. Utilisation of surface subsidence measurements in assessing failures of rigid strata overlying extracted coal seams. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2012, 53, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, J.; Karakus, M.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Yu, M. A New Theoretical Method to Predict Strata Movement and Surface Subsidence due to Inclined Coal Seam Mining. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 2723–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Guo, G.; Zhang, G.; Guo, K.; Du, Q.; Wang, L. A Vertical Joint Spacing Calculation Method for UDEC Modeling of Large-Scale Strata and Its Influence on Mining-Induced Surface Subsidence. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






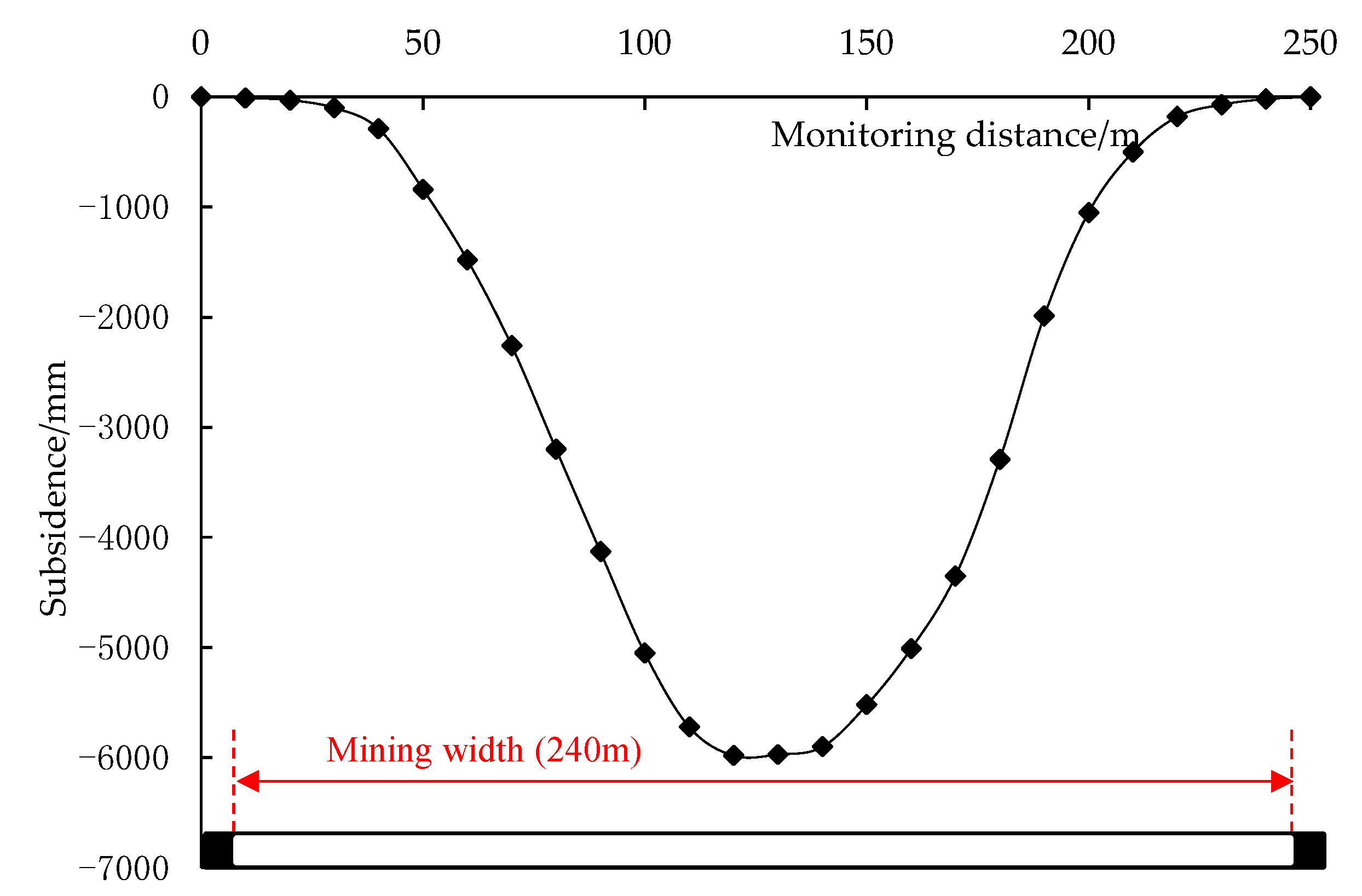

| Distortion Parameter 1 | Slope (%) | Curvature (10−3/m) | Horizontal Disp. (m) | Horizontal Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left side | 3.55 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 1.34 |
| Right side | 4.38 | 1.77 | 1.15 | 1.70 |
| Stratum | Thickness (cm) | Sand (kg) | CaCO3 (kg) | Gypsum (kg) | Water (L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | 30 | 346.5 | 34.7 | 14.9 | 44.0 |
| Soft rock layer | 50 | 550.0 | 77.0 | 33.0 | 73.3 |
| Primary key stratum | 12 | 118.8 | 11.9 | 27.7 | 17.6 |
| Soft rock layer | 40 | 440.0 | 61.6 | 26.4 | 58.7 |
| Sub-key stratum | 8 | 79.2 | 7.9 | 18.5 | 11.7 |
| Soft rock layer | 18 | 198.0 | 27.7 | 11.9 | 26.4 |
| Coal seam | 7 | 69.3 | 6.9 | 16.2 | 10.3 |
| Floor | 12 | 132.0 | 7.9 | 18.5 | 176 |
| / | Total sub./mm | Bending | Fracturing | Rotating | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub./mm | Ratio | Sub./mm | Ratio | Sub./mm | Ratio | ||
| #1 | 9.22 | 0.96 | 10.4% | 1.56 | 16.9% | 6.71 | 72.8% |
| #2 | 18.47 | 1.81 | 9.8% | 2.88 | 15.6 | 13.78 | 74.6% |
| No. | Mining Height/m | Topsoil Thickness/m | Cover Depth/m | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 40 | 160 | Study the mining height effect |
| 2 | 5 | 40 | 160 | |
| 3 | 6 | 40 | 160 | |
| 4 | 7 | 40 | 160 | |
| 5 | 8 | 40 | 160 | |
| 6 | 7 | 10 | 130 | Study the effect of topsoil thickness (along with test No. 4) |
| 7 | 7 | 20 | 140 | |
| 8 | 7 | 30 | 150 | |
| 9 | 7 | 50 | 170 |
| Lithology | Thickness (m) | Unit Weight (kN m−3) | Material Parameters | Joint Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohesion (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | Normal Stiffness (GPa/m) | Shear Stiffness (GPa/m) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | |||
| Topsoil | 40 | 21.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 15 | 1.59 | 1 | 3 |
| Soft stratum | 30 | 22.5 | 3 | 1.3 | 25 | 8 | 4.5 | 15 |
| PKS | 20 | 27.2 | 20 | 4.0 | 35 | 20 | 16 | 20 |
| Soft stratum | 45 | 22 | 4 | 1.3 | 28 | 8 | 4.5 | 15 |
| SKS | 10 | 26 | 8 | 3.0 | 30 | 18 | 13 | 18 |
| Immediate roof | 15 | 22 | 1 | 1.3 | 28 | 8 | 4.5 | 15 |
| Coal seam | 7 | 17 | 2 | 1.0 | 25 | 5 | 3 | 6 |
| Floor | 11 | 26 | 8 | 4.0 | 30 | 20 | 16 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Juan, P.; Zhu, W. Movement Laws of the Overlying Strata at the Working Face Ends and Their Effects on the Surface Deformation. Minerals 2022, 12, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121485
Xu J, Juan P, Zhu W. Movement Laws of the Overlying Strata at the Working Face Ends and Their Effects on the Surface Deformation. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121485
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jingmin, Ping Juan, and Weibing Zhu. 2022. "Movement Laws of the Overlying Strata at the Working Face Ends and Their Effects on the Surface Deformation" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121485
APA StyleXu, J., Juan, P., & Zhu, W. (2022). Movement Laws of the Overlying Strata at the Working Face Ends and Their Effects on the Surface Deformation. Minerals, 12(12), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121485






