Characteristics of Naturally Formed Nanoparticles in Various Media and Their Prospecting Significance in Chaihulanzi Deposit
Abstract
1. Introduction
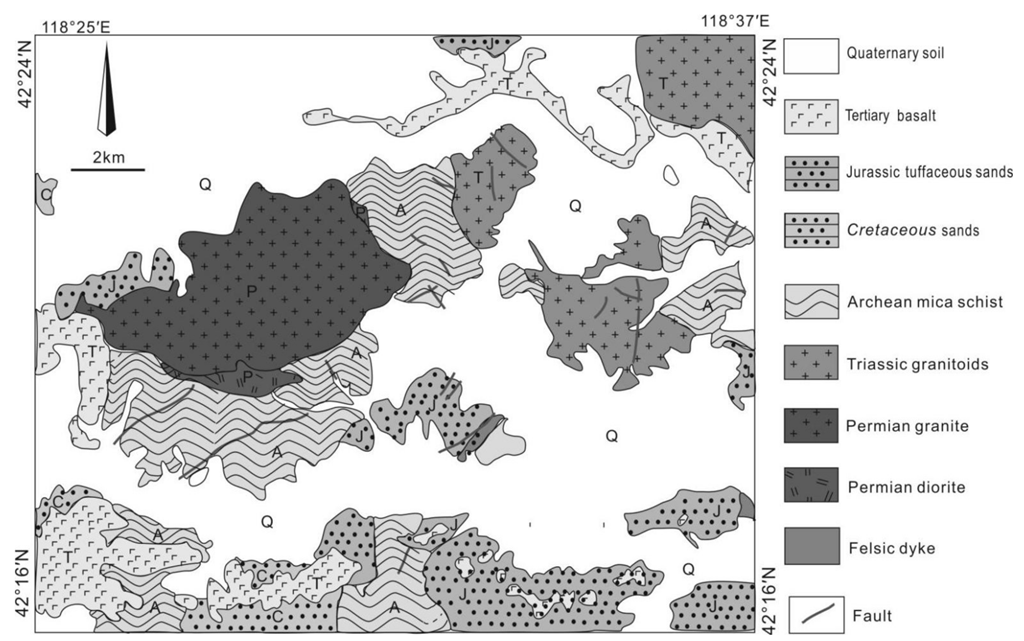
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
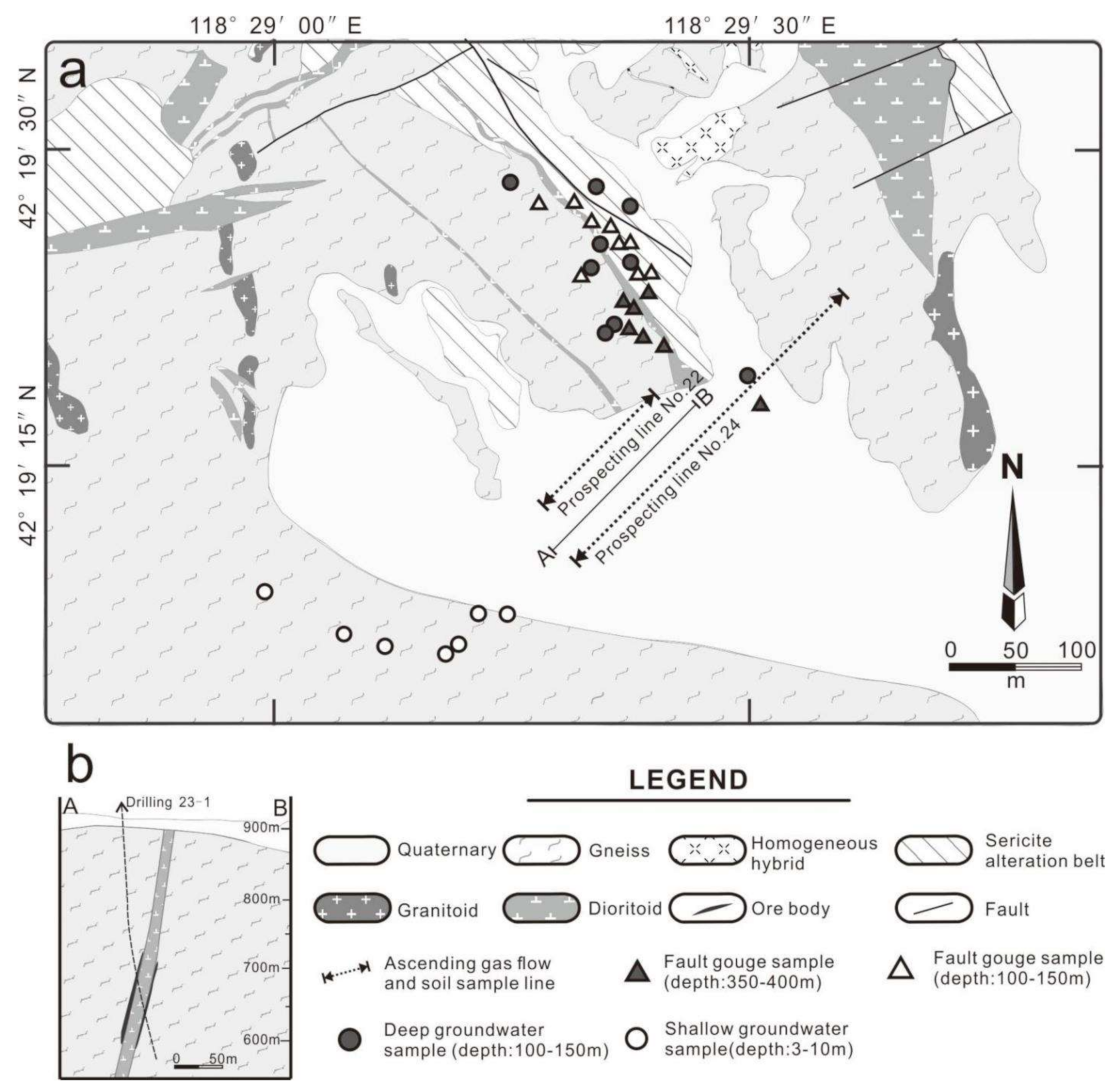
3.1. Deep-Seated Fault Gouge Samples
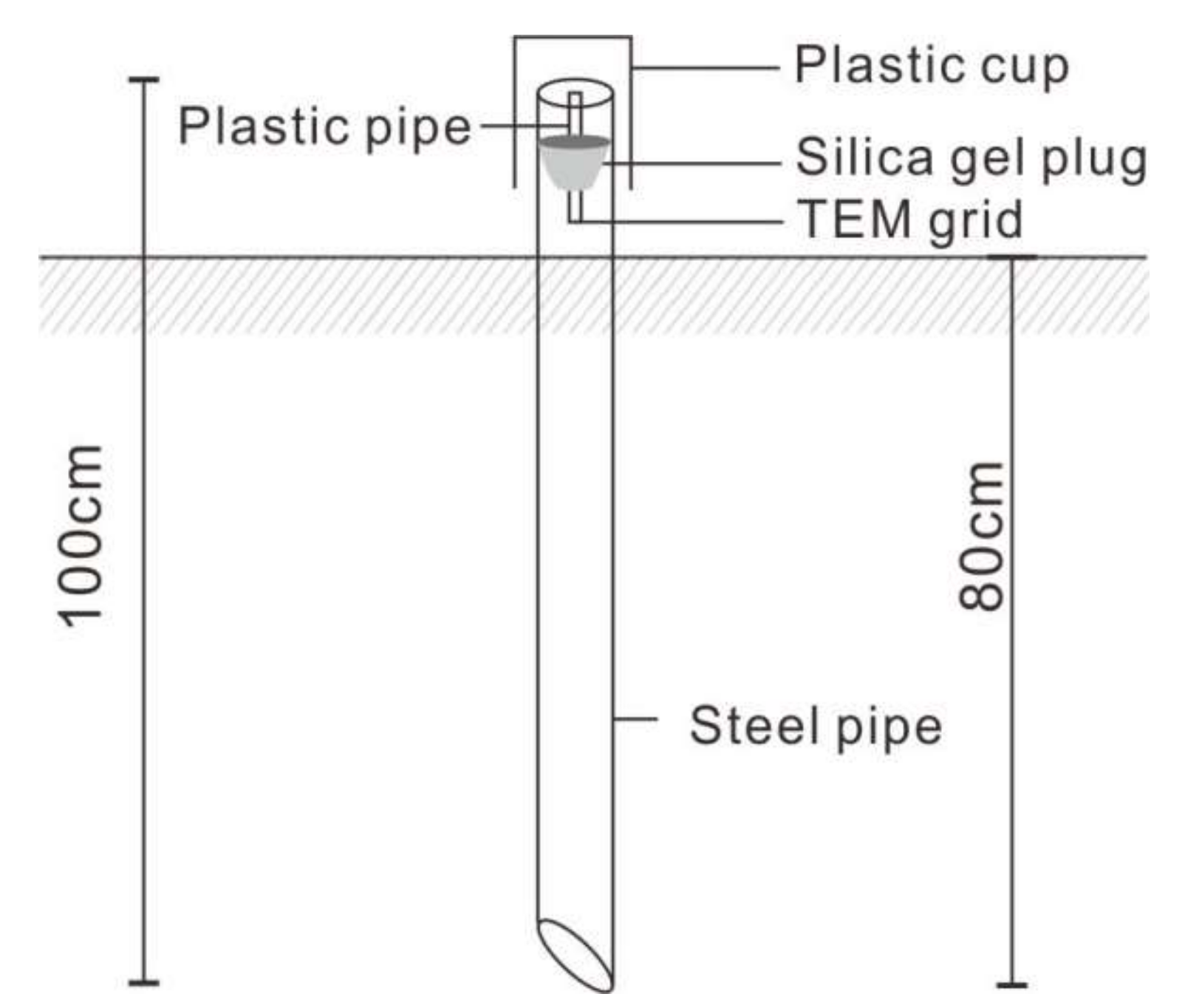
3.2. Ascending Gas Flow and Soil Samples
3.3. Shallow and Deep Groundwater Samples
3.4. TEM Analysis
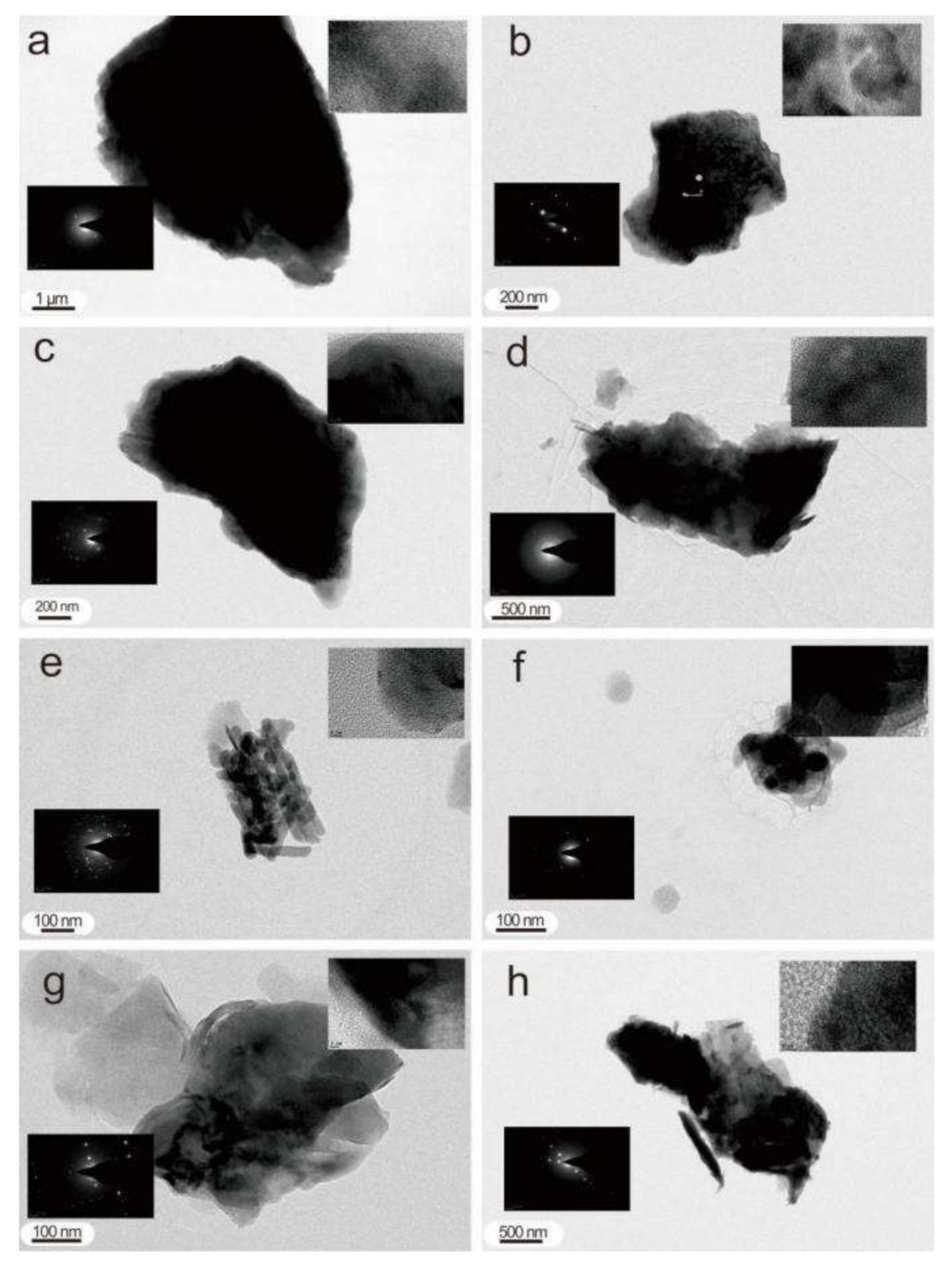
4. Results
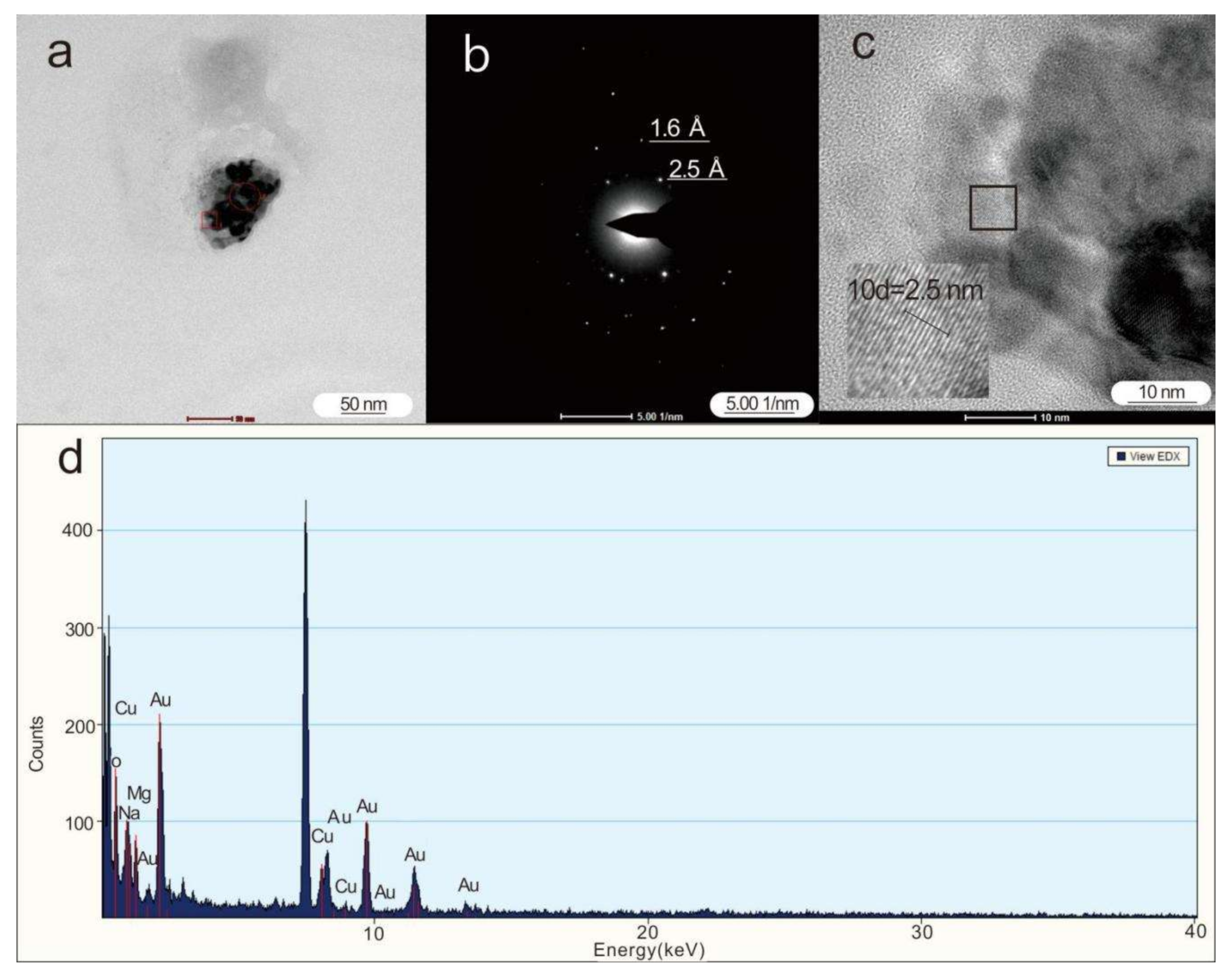
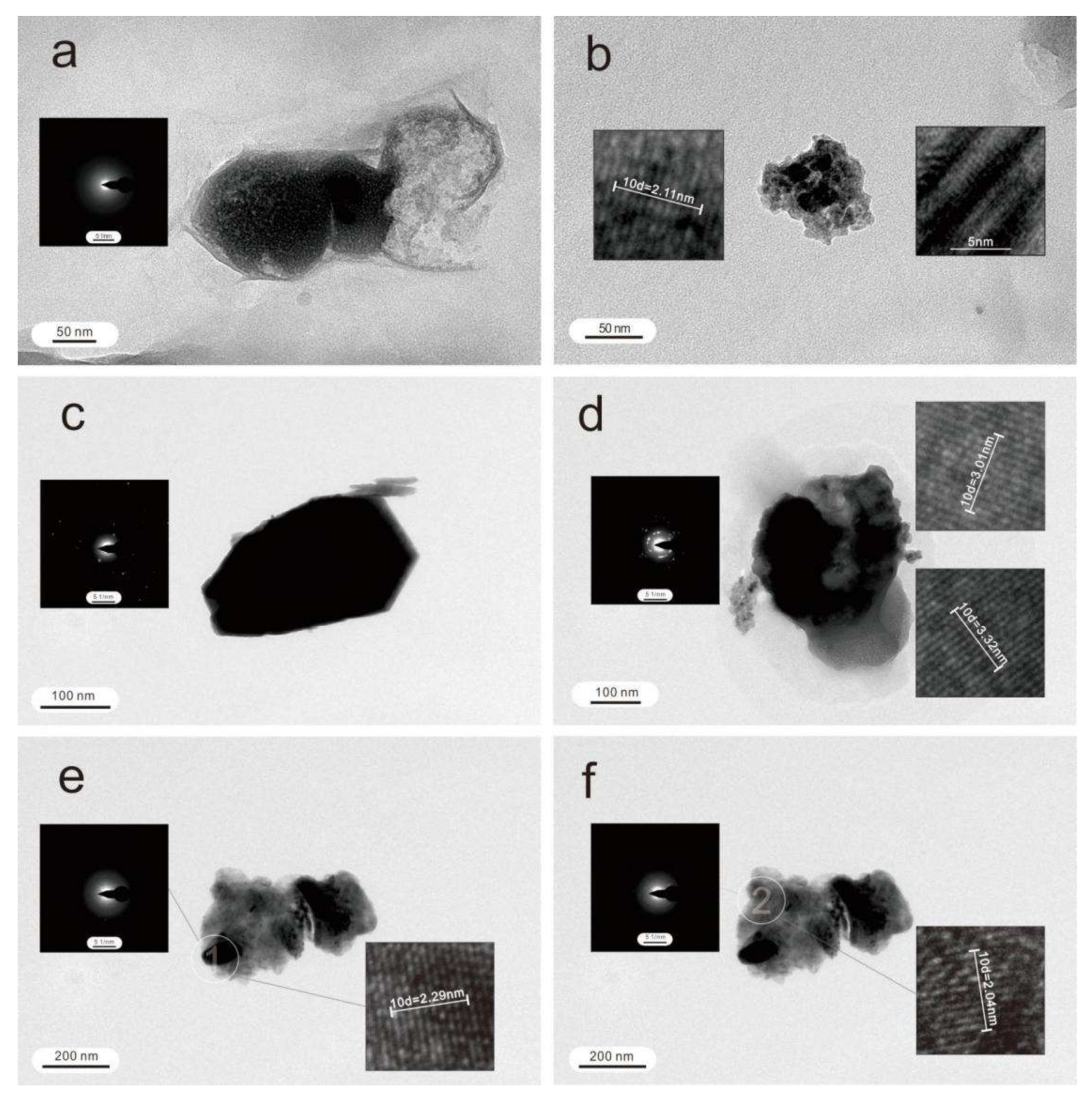
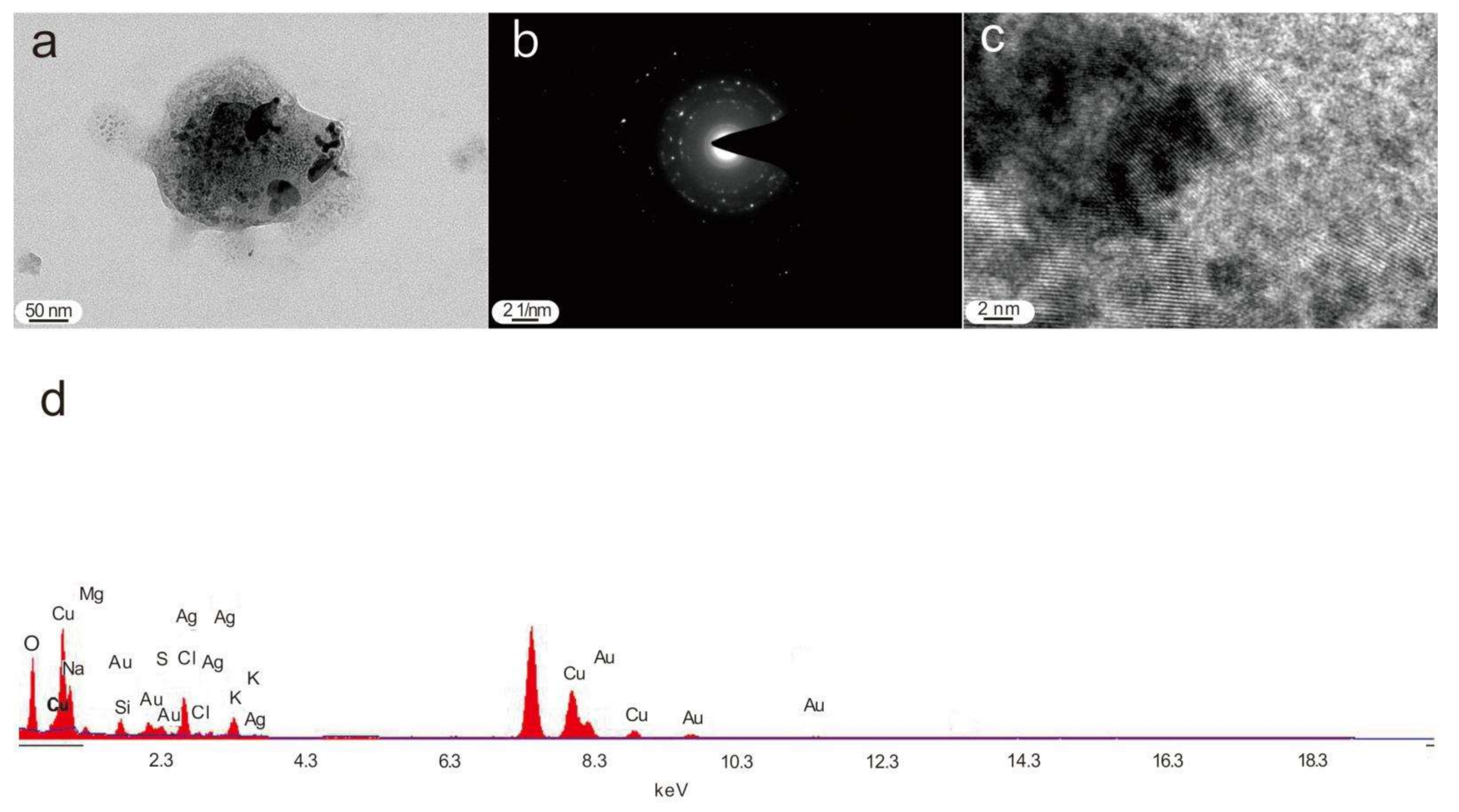
4.1. Nanoparticles in Deep-Seated Fault Gouges
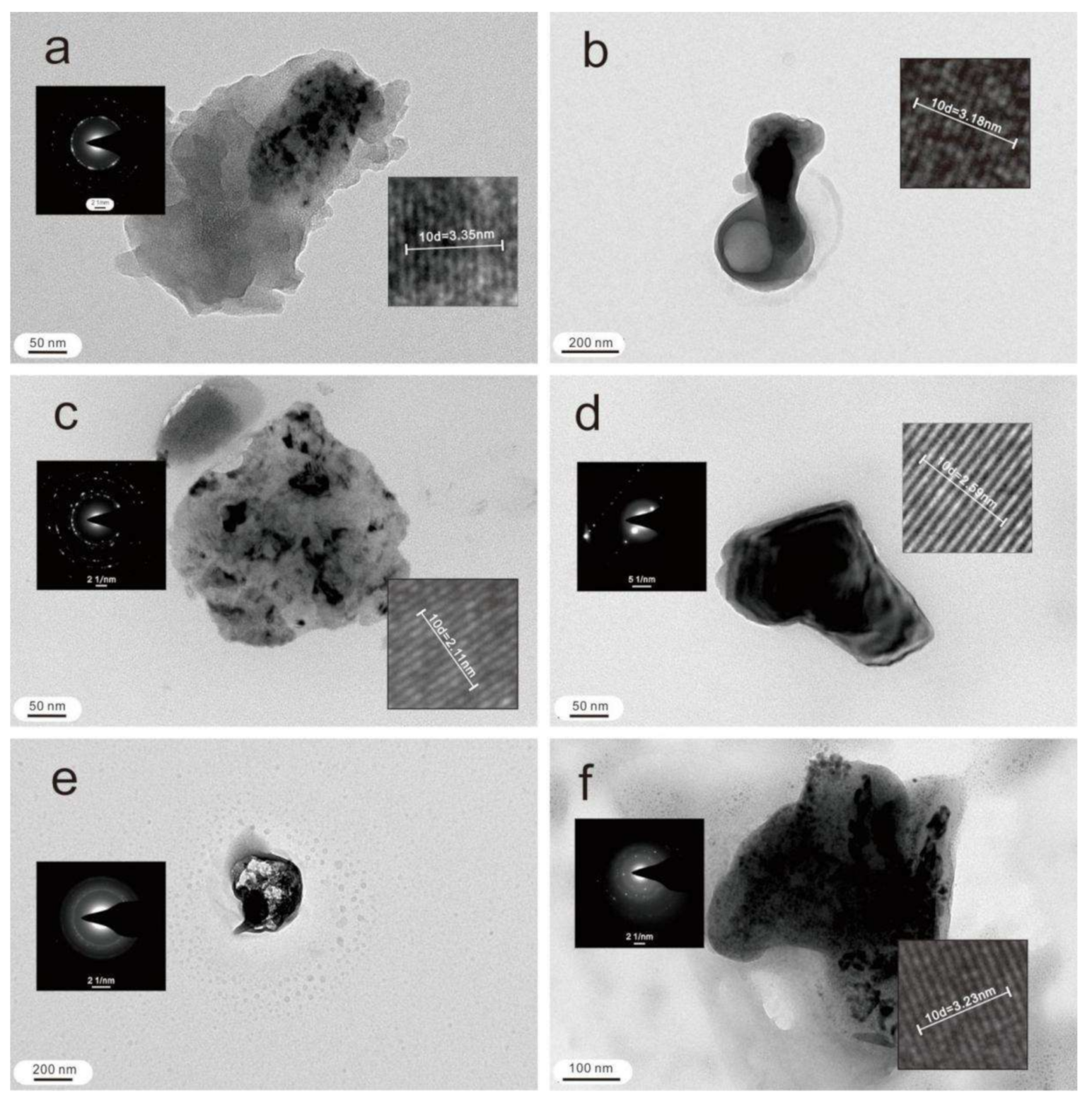
4.2. Nanoparticles in Ascending Gas Flow
4.3. Nanoparticles in Soil
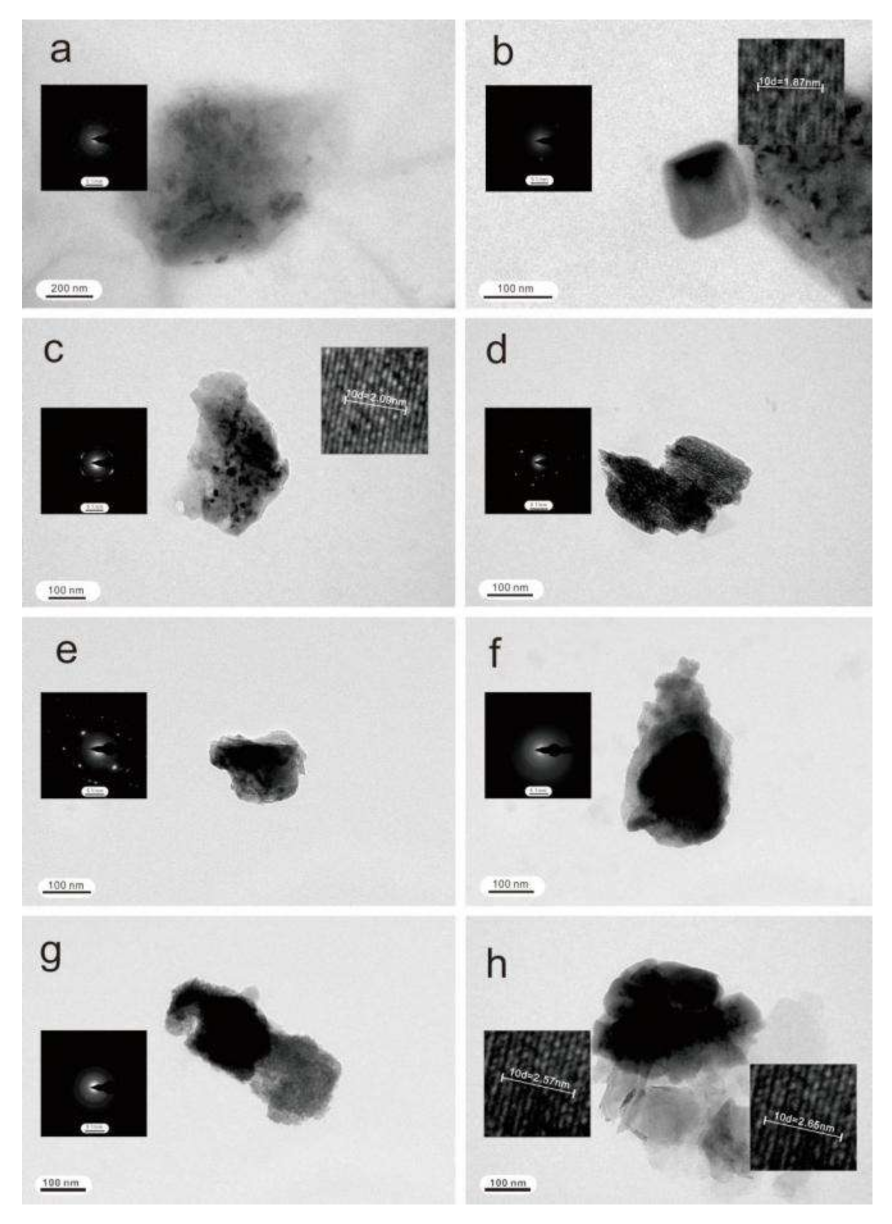
4.4. Nanoparticles in Groundwater
4.4.1. Nanoparticles in Shallow Groundwater
4.4.2. Nanoparticles in Deep Groundwater
4.5. Nanoparticles in Background Area
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of Nanoparticle Characteristics in Different Types of Sample
5.1.1. Nanoparticles in Deep-Seated Fault Gouges
5.1.2. Nanoparticles in Ascending Gas Flow and in Soil
5.1.3. Nanoparticles in Shallow and Deep Groundwater
5.1.4. Summary of Nanoparticle Characteristics in Various Types of Sample
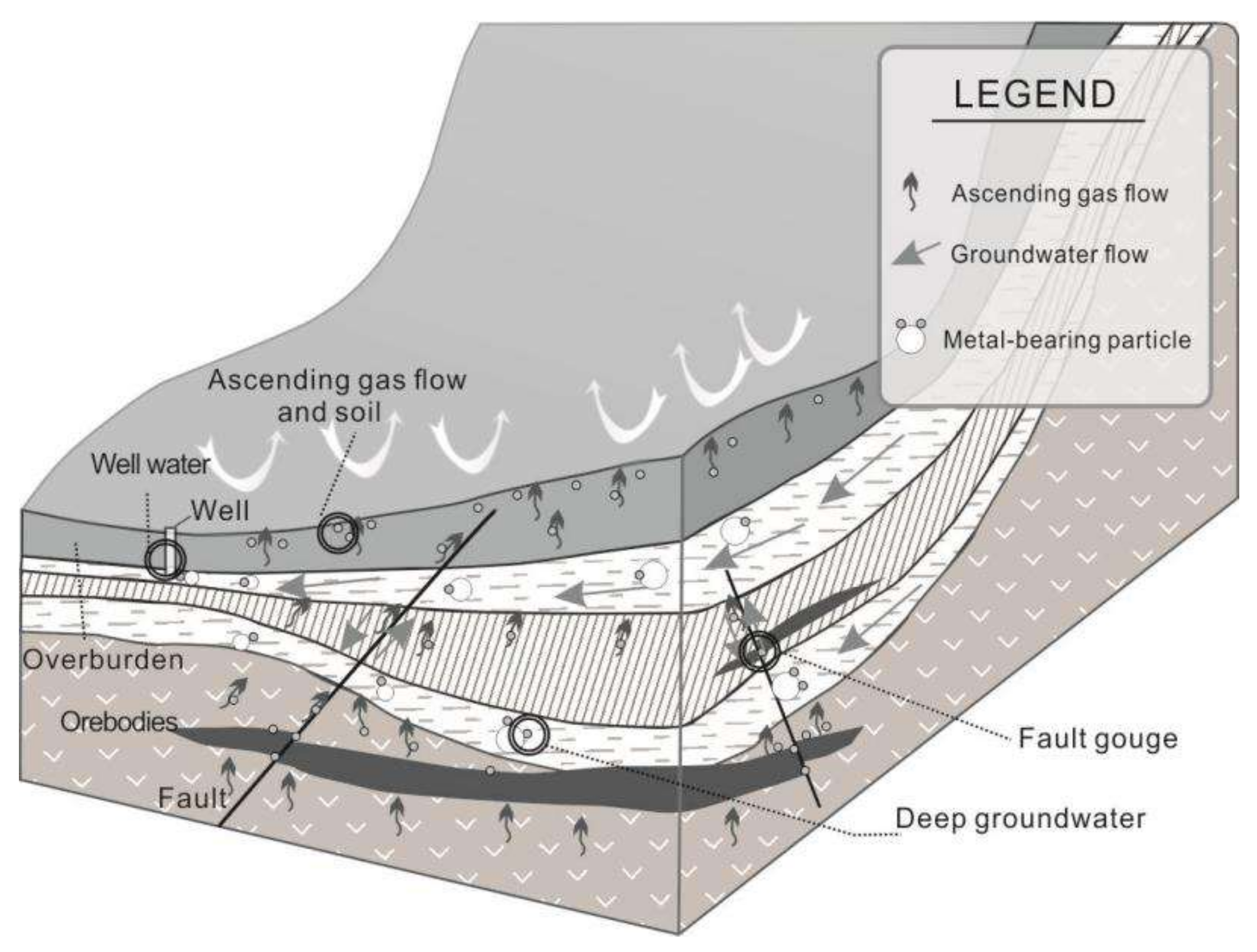
5.2. The Relationship between Shallow and Deep Media and the Orebodies
5.3. Formation of Ore-Bearing Nanoparticles
5.4. Migration Mechanism of the Ore-Bearing Nanoparticles
5.5. The Significance of Ore-Bearing Nanoparticles in Different Media for Prospecting
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kristiansson, K.; Malmqvist, L. Evidence for nondiffusive transport of 86Rn in the ground and a new physical model for the transport. Geophysics 1982, 47, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, K.; Malmqvist, L. Trace elements in the geogas and their relation to bedrock composition. Geoexploration 1987, 24, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Li, J. A new method searching for concealed mineral resources: Geogas prospecting based on nuclear analysis and accumulation sampling. J. China Univ. Geosci. 1999, 10, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.; Jan, B.M.; Tong, C.W.; Berawi, M.A. Advanced nanomaterials in oil and gas industry: Design, application and challenges. Appl. Energy 2017, 191, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arne, D.C.; Stott, J.E.; Waldron, H.M. Biogeochemistry of the Ballarat East Goldfield, Victoria, Australia. J. Geochem. Explor. 1999, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanna, L.; Jorg, E.; Martin, Z. Geogas transport in fractured hard rock—Correlations with mining seismicity at 3.54 km depth, TauTona gold mine, South Africa. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.; Wang, M.; Hu, M.; Gao, Y. Identification of metal sources in Geogas from the Wangjiazhuang copper deposit, Shandong, China: Evidence from lead isotopes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; Meier, A.L.; Riddle, G. Enzyme leaching of surficial geochemical samples for detecting hydromorphic trace-element anomalies associated with precious-metal mineralized bedrock buried beneath glacial overburden in northern Minnesota. In Proceedings of the Gold’90 Symposium-Gold’90, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 26 February–1 March 1990; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.M.; Gunn, A.G. Application of enzyme leach soil analysis for epithermal gold exploration in the Andes of Ecuador. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryss, Y.; Goldberg, I. The partial extraction of metals (CHIM) method inmineral exploration. Method Tech. ONTI VITR Leningr. 1973, 84, 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Antropova, L.V.; Goldberg, I.S.; Voroshilov, N.A.; Ryss, J.S. New methods of regional exploration for blind mineralization: Application in the USSR. J. Geochem. Explor. 1992, 43, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hou, B.; Wen, M.; Zeng, N.; John, K.; Roger, F.; Adrian, F. CHIM-geoelectrochemical method in search of concealed mineralisation in China and Australia. Chin. J. Geochem. 2008, 27, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, H. Preliminary studies on deep-penetrating geochemical methods in exploration for concealed volcanic-type uranium deposit. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 569, 012103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Birrell, R.; Humphreys, D.; Perdrix, J. Application of the mobile metal ion technique to routine geochemical exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 1998, 61, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Mills, D.; Fedikow, M.; Prince, P. The evaluation of geological exploration samples using multi-element mobile metal ion (MMI-M) selective weak extraction and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Geochem. Case Hist. Geochem. Explor. Methods. 2007, 7, 793–977. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, X.; Nakagoshi, N. Geoelectrochemical-extraction measurement method to look for hidden lead-zinc ore deposit and prospecting effect. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 734, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liang, B.; Geng, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q. Extraction of soils above concealed lithium deposits for rare metal exploration in Jiajika area: A pilot study. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 107, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, L.; Kristiansson, K. Experimental evidence for an ascending microflow of geogas in the ground. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 70, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, K.; Malmqvist, L.; Persson, W. Geogas prospecting: A new tool in the search for concealed mineralizations. Endeavour 1990, 14, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, T.; Soter, S. The deep earth-gas hypothesis. Sci. Am. 1980, 242, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morner, N.; Etiope, G. Carbon degassing from the lithosphere. Glob. Planet. Change 2002, 33, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziatellis, A.; Ciotoli, G.; Lombardia, S.; Nolasco, F. Short- and long-term gas hazard: The release of toxic gases in the Alban Hills volcanic area (central Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 77, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C.E.; Kremer, Y.; Johnson, G.; Hicks, N.; Lister, R.; Jones, D.J.; Haszeldine, S.; Saunders, I.; Gilfillan, S.M.V.; Shipton, Z.K.; et al. The physical characteristics of a CO2 seeping fault: The implications of fracture permeability for carbon capture and storage integrity. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 61, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, S.M.V.; Györe, D.; Flude, S.; Bond, C.E.; Hicks, N.; Lister, R.; Jones, D.G.; Kremer, R.S.H.; Stuart, F.M. Noble gases confirm plume-related mantle degassing beneath Southern Africa. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Li, J.; Ge, L.; Yang, F. Experimental observation of the nano-scale particles in geogas matters and its geological significance. China. Sci. China Ser. D 1998, 41, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Hu, R.; Liang, Z.; Peng, Z. TEM observation of geogas-carried particles from the Changkeng concealed gold deposit, Guangdong Province, South China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 101, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, C. Method for Prospecting with Geo-Gas Particles. CN Patent Application 2010101544226, 14 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Method for Predicting Concealed Deposits using Chemical Composition Data from Single Nanoparticles. CN Patent Application 2020101001628, 18 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Hopke, P.; Holub, R.; Jiang, T. The discovery of the metallic particles of groundwater from the Dongshengmiao polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia, and their prospecting significance. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 161, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, G.; Yi, Z. TEM observations of particles in groundwater and their prospecting significance in the Bofang copper deposit, Hunan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 95, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, G.; Wang, G. A study of metal-bearing nanoparticles from the Kangjiawan Pb-Zn deposit and their prospecting significance. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 105, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Dang, W.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, J. Nanoparticles in groundwater of the Qujia deposit, eastern China: Prospecting significance for deep-seated ore resources. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 120, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Cao, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z. Characterization of metal-bearing particles in groundwater from the Weilasituo Zn-Cu-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for mineral exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 117, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Cao, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. Nanoparticles in various media on surfaces of ore deposits: Study of the more than 1000 m deep concealed Shaling gold deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis on Fault Gouges from the Depths of the Bairendaba Polymetallic Deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 6549–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Dai, D. TEM analysis of nano-or near-nanoparticles in fault gouge from the Kaxiutata iron deposit (CHN) and the implications for ore body exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Characteristics, formation and migration of the particles carried by ascending gas flow from the concealed metal deposits. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 113–119, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J.; Hopke, P.; Holub, F. Study of carbon-bearing particles in ascending geogas flows in the Dongshengmiao polymetallic pyrite deposit, inner Mongolia China. Resour. Geol. 2015, 65, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Qiu, J.; Liu, X. Ore-forming elements and their distribution of nanoparticles in the updraft from the Sanshandao concealed deposit, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Cao, J.; Yan, H.; Yi, J. TEM observations of particles based on sampling in gas and soil at the Dongshengmiao polymetallic pyrite deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 158, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Z. A TEM study of particles carried by ascending gas flows from the Bairendaba lead-zinc deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 105, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yi, Z. Prospecting Application of Nanoparticles and Nearly Nanoscale Particles Within Plant Tissues. Resour. Geol. 2017, 67, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J.; Jiang, T. Discovery and prospecting significance of metal-bearing nanoparticles within natural invertebrate tissues. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 99, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cao, J. Discovery of nano-sized gold particles in natural plant tissues. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.; Xu, G.; Zhou, R. The tectonic and magmatic activities in early Mesozoic and their controlling on gold mineralization in Honghuagou gold field, Inner Mongolia. China Geosci. 2000, 14, 408–416, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- She, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Feng, C.; Li, D. The mafic granulite xenoliths and its implications to mineralization in chaihulanzi gold deposit, inner mongolian, China. Acta Geol. Sini. 2006, 80, 863–875, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; She, H.; Xu, G.; Zheng, D.; Fu, D.; Cui, C. Yanshanian magmatic rocks and gold deposits of Chaihulanzi gold field, inner mongolia. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1999, 15, 475–483. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Wilde, S. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China craton: An association with lithospheric thinning. Ore Geol. Rev. 2003, 23, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, C.; Ye, J.; Zeng, Q. Integrated geological and geophysical exploration for concealed ores beneath cover in the chaihulanzi goldfield, northern China. Geophys. Prospect. 2006, 54, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Methane-rich Fluid of Chaihulanzi Gold Deposit. Acta Geol. Sini. (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 88, 1214–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Chong, S. Characteristic and essence of rubefication in wall rock alteration of Anjiayingzi gold deposit in Harqin banner, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 576–588. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Qiu, K.; Deng, J. Orogenic gold deposits of China. Soc. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2019, 22, 263–324. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Ma, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, H. Geological, fluid inclusion, and O-C-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Honghuagou lode gold deposit, northern North China Craton. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Y.; Gao, J.; Xiao, R. Sources of metals and fluids for the Taijiying gold deposit on the northern margin of the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, K.; Ulrich, T.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, R. Early Permian lode gold mineralization in the northern North China Craton: Constraints from S-Pb isotope geochemistry and pyrite Re-Os geochronology of the Chaihulanzi deposit. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 218, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.; Xia, J.; Xu, D.; Li, X. Geology, geochronology and tectonic setting of the Chaihulanzi gold deposit in Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cao, J.; Holub, R.F.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhao, S.J. TEM study of geogas-transported nanoparticles from the Fankou lead-zinc deposit, Guangdong Province, South China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 128, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Z. Characteristics of soil particles in the Xiaohulishan deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, Z.; She, H.; Liu, D. The discovery of Phanerozoic granulite in Chifeng area of North Craton and its implication. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 188–198, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y. Zircon U-Pb ages of mesozoic volcanic rocks in Chifeng. Area J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2012, 42, 257–267, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cline, J.S. Timing of gold and arsenic sulfide mineral deposition at the Getchell Carlin-type gold deposit, North-Central Nevada. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, A.; Tomkins, A.; Bierlin, F.; Wienberg, R.; Davidson, G. Bimodal distribution of gold in pyrite and arsenopyrite: Examples from the Archean Boorara and Bardoc shear systems, Yilgarn craton, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Ewing, R.C.; Hough, R.; Walshe, J. Trace metal nanoparticles in pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Cao, M.; Hollings, P.; Watanabe, Y. The metallogenic system deep structure and formation process for the northeastern china compound orogenic belt: Introduction. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 146, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W.; Weiss, D.; Kramers, J.D.; Frei, R.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Gloor, M.S. Geochemistry of the peat bog at Etang de la Gruère, Jura Mountains, Switzerland, and its record of atmospheric Pb and lithogenic trace metals (Sc, Ti, Y, Zr, and REE) since 12,370 14C yr BP. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2001, 65, 2337–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.; Santosh, M.; Dotto, G.; Silva, L.F.O.; Hochella, M.F. A review on Pb-bearing nanoparticles, particulate matter and colloids released from mining and smelting activities. Gondwana Res. 2022, 110, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.; Kamber, B.S. High-resolution lake sediment reconstruction of industrial impact in a world-class mining and smelting center, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, J.R.; Wilson, A.I.; Stohl, A.; Steffensen, J.P. Lead pollution recorded in Greenland ice indicates European emissions tracked plagues, wars, and imperial expansion during antiquity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5726–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenik, C.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.; Wang, L.; Ewing, R. “Invisible” gold revealed: Direct imaging of gold nanoparticles in a Carlin-type deposit. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.C.G.; Kontak, D.J.; Lafrance, B. Gold remobilization: Insights from gold deposits in the Archean Swayze greenstone belt, Abitibi Subprovince, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, X.; Cook, N.; Lin, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Brugger, J. Nano- to micron-scale particulate gold hosted by magnetite: A product of gold scavenging by bismuth melts. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.M.; Noble, R.R.P.; Hitchen, G.J.; Hart, R.; Reddy, S.M.; Saunders, M.; Clode, P.; Vaughan, D.; Lowe, J.; Gray, D.J.; et al. Naturally occurring gold nanoparticles and nanoplates. Geology 2008, 36, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J. Metal-containing nanoparticles derived from concealed metal deposits: An important source of toxic nanoparticles in aquatic environments. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 726–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J. Migration mechanisms of gold nanoparticles explored in geogas of the Hetai ore district, southern China. Geochem. J. 2011, 45, e9–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, J.; Baubron, J. Gas geochemistry and seismotectonics: A review. Tectonophysics 1999, 304, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Martinelli, G. Migration of carrier and trace gases in the geosphere: An overview. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2002, 129, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, L.; Kristiansson, K.; Kristiansson, P. Geogas prospecting—An ideal industrial application of PIXE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1999, 150, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Qin, T. Particles carried by ascending gas flow at the Tongchanghe copper mine, Guizhou Province. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Zou, X. Simulation of adsorption of gold nanoparticles carried by gas ascending from the Earth’s interior in alluvial cover of the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Geofluids 2010, 10, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Cao, J.; Lai, P.; Wu, Z. TEM study on particles transported by ascending gas flowin the Kaxiutata iron deposit, Inner Mongolia, North China. Geochem. Explor. Env. 2015, 15, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Hu, R.; Liu, S.; Xie, G. Simulation test on migration of geogas-carrying gold nanoparticles in slope sediments. In Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 897–900. [Google Scholar]
- Dilinas, J.; Jurevicius, A.; Karveliene, D. Migration forms of main chemical elements in the groundwater of the Quaternary deposits of Lithuania. Baltica 2009, 22, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Barnesa, M.C.; Jeon, I.D.; Kimb, D.Y.; Huang, N.M. Generation of charged clusters during thermal evaporation of gold. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 242, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Cao, J. Natural uranium-bearing nanoparticles in surface media. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Nie, X.; Yang, M.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, P.; Wan, Q. Sorption of differently charged gold nanoparticles on synthetic pyrite. Minerals 2018, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Type | Sample Quantity | Number of Observed Particles | Particle ID | pH | Depth (m) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep-seated fault gouge | 17 | 49 | 1–7 | - | 100–150 and 350–400 m | Deep-seated mine (Chaihulanzi deposit) |
| Ascending gas flow | 36 | 147 | 8–13 | - | Surface | Prospecting lines 22 and 24 (Chaihulanzi deposit) |
| Soil | 36 | 133 | 14–19 | - | 0.8 | Prospecting lines 22 and 24 (Chaihulanzi deposit) |
| Shallow groundwater | 7 | 26 | 20–23 | 7.73–8.36 | 3–10 | Water wells in southwest of the deposit |
| Deep groundwater | 9 | 28 | 24–27 | 7.76–8.26 | 100–150 | Deep-seated mine (Chaihulanzi deposit) |
| Background ascending gas flow | 5 | 13 | B1–B4 | - | Surface | Yangbadi village |
| Background soil | 5 | 40 | B5–B8 | - | 0.8 | Yangbadi village |
| Particle ID | Elements (%) | Au | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | Cl | K | Ca | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zn | Mo | Sn | Pt | Pb | Bi | As | F | Size/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | wt% | 74.0 | 12.5 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 7.6 | 150 × 80 | |||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 24.6 | 51.15 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 7.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | wt% | 47.0 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 31.0 | 7.8 | 2.7 | 150 × 100 | ||||||||||||||
| at% | 74.3 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 3.8 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 14.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 | wt% | 17.4 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 3.7 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 63.7 | 3.6 | 70 × 50 | ||||||||||||||
| at% | 40.2 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 37.0 | 7.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4 | wt% | 11.8 | 19.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 68.0 | 200 × 350 | |||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 28.1 | 31.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 39.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | wt% | 9.5 | 5.5 | 1.4 | 6.3 | 9.2 | 3.8 | 54.1 | 10.2 | 300 × 350 | ||||||||||||||||
| at% | 41.3 | 10.7 | 1.8 | 6.9 | 9.7 | 2.2 | 18.1 | 9.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | wt% | 19.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 9.1 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 37.2 | 28.0 | 1.5 | 250 × 350 | ||||||||||||||
| at% | 50.0 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 11.6 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 23.9 | 5.5 | 3.2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 7 | wt% | 61.0 | 5.0 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 6.7 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 250 × 350 | ||||||||||||
| at% | 77.7 | 4.5 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 4.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 2.2 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||
| 8 | wt% | 54.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 43.1 | 30 × 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 80.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 18.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | wt% | 20.8 | 0.4 | 61.1 | 17.7 | 60 × 70 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 55.2 | 0.3 | 40.7 | 3.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | wt% | 22.3 | 2.60 | 65.9 | 9.2 | 100 × 200 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 53.6 | 3.60 | 39.8 | 3.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | wt% | 67.2 | 5.50 | 19.0 | 8.3 | 50 × 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 88.8 | 4.20 | 6.2 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | wt% | 20.0 | 11.2 | 1.5 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 7.80 | 4.9 | 0.8 | 14.2 | 1.8 | 30.7 | 50 × 250 | |||||||||||||
| at% | 46.4 | 18.2 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 7.20 | 3.6 | 0.5 | 8.3 | 1.0 | 5.5 | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | wt% | 57.3 | 1.4 | 28.2 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 5.4 | 100 × 200 | ||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 77.0 | 1.2 | 17.1 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Particle ID | Elements (%) | Au | Ag | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | Cl | Ar | K | Ca | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zn | As | Mo | Sn | Pb | Size/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | wt% | 3.9 | 2.1 | 30.4 | 11.6 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 2.3 | 39.9 | 250 × 300 | |||||||||||||
| at% | 0.6 | 0.6 | 55.1 | 14.6 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 1.0 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 18.2 | |||||||||||||||
| 15 | wt% | 62.8 | 9.5 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 18.5 | 0.8 | 100 × 350 | |||||||||||||||||
| at% | 82.4 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 6.9 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | wt% | 47.1 | 3.5 | 5.7 | 43.7 | 200 × 400 | |||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 74.8 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 17.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | wt% | 61.4 | 9.9 | 17.6 | 11.2 | 200 × 230 | |||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 84.4 | 7.7 | 6.1 | 2.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | wt% | 52.2 | 47.8 | 100 × 150 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 81.7 | 18.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | wt% | 78.2 | 8.8 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 200 × 210 | ||||||||||||||||
| at% | 86.6 | 6.8 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | wt% | 51.6 | 30.4 | 8.8 | 2.3 | 3.6 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 290 × 300 | |||||||||||||||
| at% | 62.4 | 25.6 | 7.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 21 | wt% | 59.5 | 0.2 | 8.2 | 5.6 | 1.5 | 8.8 | 1.0 | 13.3 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 300 × 300 | |||||||||||||
| at% | 77.9 | 0.2 | 6.3 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 4.5 | 0.4 | 5.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||
| 22 | wt% | 12.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 76.8 | 6.5 | 80 × 80 | |||||||||||||
| at% | 36.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 56.0 | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||
| 23 | wt% | 13.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 14.4 | 2.3 | 58.6 | 8.2 | 2.0 | 150 × 250 | ||||||||||||||
| at% | 34.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 11.6 | 1.8 | 44.2 | 5.4 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 24 | wt% | 31.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 56.9 | 6.7 | 100 × 200 | |||||||||||||||
| at% | 60.7 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 31.4 | 3.5 | |||||||||||||||||
| 25 | wt% | 9.3 | 19.4 | 1.4 | 14.5 | 14.2 | 41.3 | 100 × 100 | |||||||||||||||||
| at% | 22.5 | 32.6 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 9.3 | 24.5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | wt% | 9.8 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 34.1 | 3.5 | 46.2 | 200 × 300 | ||||||||||||||
| at% | 33.5 | 0.4 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 29.4 | 3.0 | 26.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 27 | wt% | 18.9 | 3.5 | 21.1 | 9.7 | 46.8 | 100 × 300 | ||||||||||||||||||
| at% | 53.8 | 3.9 | 17.3 | 7.0 | 18.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | wt% | 15.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 12.8 | 0.3 | 68.7 | 1.6 | 180 × 250 | |||||||||||||||
| at% | 36.3 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 15.0 | 0.3 | 46.3 | 0.3 |
| Particle ID | Elements (%) | O | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe | Size/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | wt% | 59.3 | 19.4 | 21.4 | 4000 × 6000 | |||||
| at% | 70.4 | 15.4 | 14.5 | |||||||
| B2 | wt% | 74.0 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 13.3 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 300 × 500 | |
| at% | 83.2 | 1.7 | 5.7 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | |||
| B3 | wt% | 91.2 | 1.9 | 6.9 | 400 × 700 | |||||
| at% | 96.0 | 1.2 | 2.9 | |||||||
| B4 | wt% | 64.4 | 2.0 | 11.1 | 20.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 600 × 900 | |
| at% | 76.0 | 1.5 | 7.8 | 14.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||
| B5 | wt% | 78.7 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 16.0 | 1.1 | 150 × 200 | ||
| at% | 89.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1.7 | 7.2 | 0.4 | ||||
| B6 | wt% | 87.2 | 7.6 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 100 × 150 | ||||
| at% | 93.0 | 4.6 | 2.0 | 0.5 | ||||||
| B7 | wt% | 67.5 | 3.1 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 21.2 | 400 × 500 | |||
| at% | 84.9 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 1.8 | 7.7 | |||||
| B8 | wt% | 91.7 | 8.3 | 500 × 900 | ||||||
| at% | 96.5 | 3.5 |
| Sample Type | Characteristics of the Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Element Association | Sharp | |
| Fault gouge sample | Fe oxide; Pb2O3; As oxide; Cu2O; ZnO; Bi oxide; CuSO4; Mo oxide | Fe-Pb-As-Mn; Fe-Cu-Mn; Zn-Fe-Co; Pb-Zn-Fe-Cu-Sn; Cu-Bi-Fe; Cu-Fe-Mo | Irregular shape, hexagon; some of them with twisted crystal lattices, always with sharp and clearly edges |
| Ascending gas flow sample | Fe oxide; CuO; Pb oxide; Zn oxide; Mo oxide | Fe-Mn-Cr; Cu-Pt; Cu-Sn; Pb-Zn; Fe-Cu-Zn-Bi; Zn-Mo | Subcircular, trigonal, strip or unregular shape; always with smooth edges |
| Soil sample | Cu oxide; Fe oxide; CuSO4; Sn oxide; ZnO; Pb oxide | Fe-Mn-Cr-Cu; Fe-Cu; Cu-SnPb-Zn; Cu-Zn-Mo-Bi | Irregular shape, spherical, hexagon; always in the form of aggregation |
| Well (shallow) water sample | Fe oxide; Zn oxide; As oxide; CuO; Cu-Sn alloy; Mo oxide | Fe-Zn-As; Cu-Sn; Fe-Mn-Cr-Cu-Mn; Fe-Mn-Co | Irregular shape, rhomboid, always with smooth edges |
| Deep groundwater sample | Fe oxide; Zn oxide; Cu oxide; Mo oxide; Sn oxide; Fe2(SO4)3 | Fe-Co-Zn-V; Cu-Mo-Zn; Fe-Cu-Sn; Fe-Pb | Irregular shape, some of them with sharp edges |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G. Characteristics of Naturally Formed Nanoparticles in Various Media and Their Prospecting Significance in Chaihulanzi Deposit. Minerals 2022, 12, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101289
Lu M, Cao J, Wang Z, Wang G. Characteristics of Naturally Formed Nanoparticles in Various Media and Their Prospecting Significance in Chaihulanzi Deposit. Minerals. 2022; 12(10):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Meiqu, Jianjin Cao, Zhengyang Wang, and Guoqiang Wang. 2022. "Characteristics of Naturally Formed Nanoparticles in Various Media and Their Prospecting Significance in Chaihulanzi Deposit" Minerals 12, no. 10: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101289
APA StyleLu, M., Cao, J., Wang, Z., & Wang, G. (2022). Characteristics of Naturally Formed Nanoparticles in Various Media and Their Prospecting Significance in Chaihulanzi Deposit. Minerals, 12(10), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12101289