The Relationship between Natural Pyrite and Impurity Element Semiconductor Properties: A Case Study of Vein Pyrite from the Zaozigou Gold Deposit in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Calculation Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. In Situ Seebeck Coefficient Measurement
2.3. LA-ICP-MS Mapping
2.4. First-Principles Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Pyrite Seebeck Coefficients
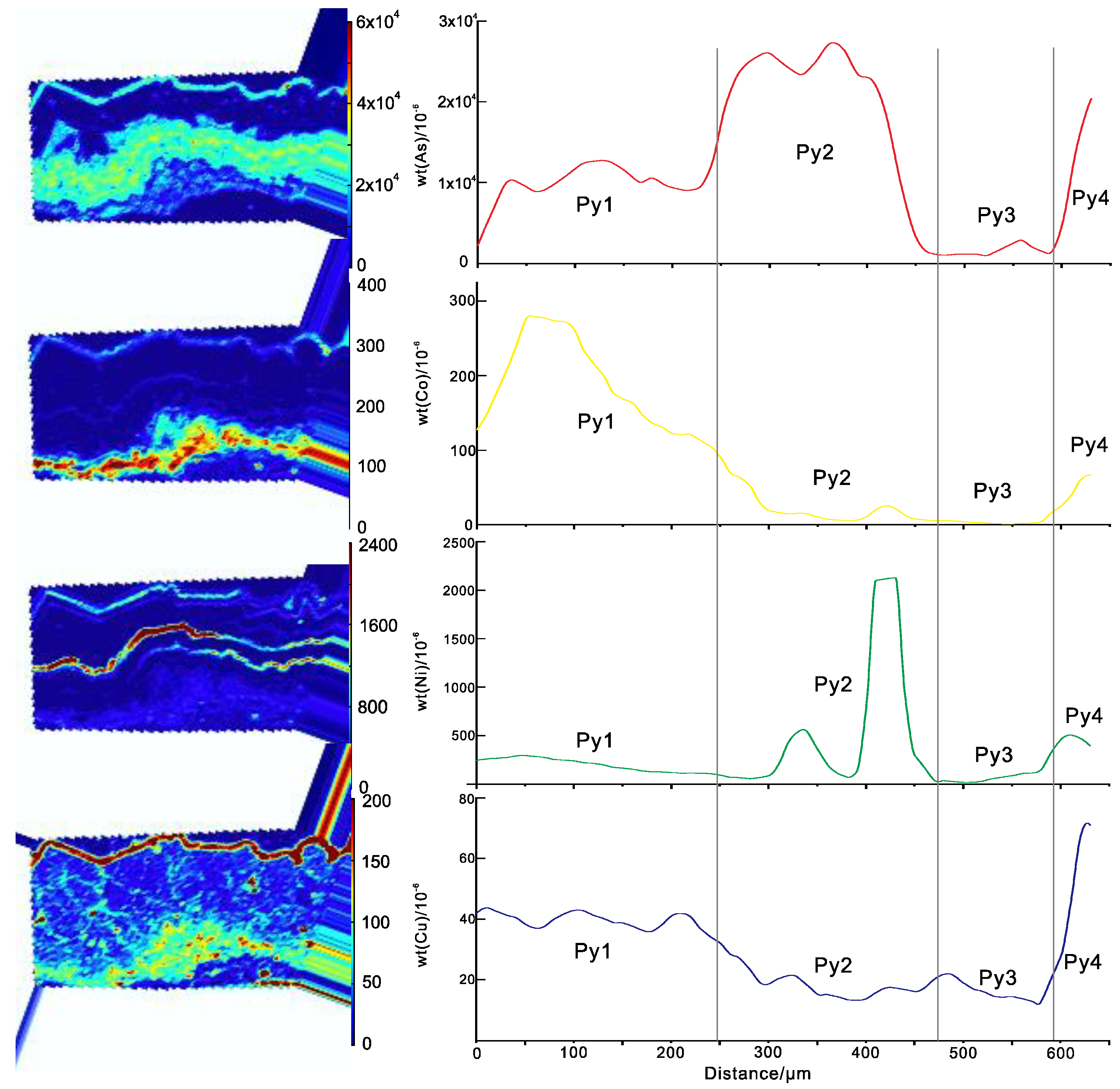
3.2. Impurity Distributions in Pyrite
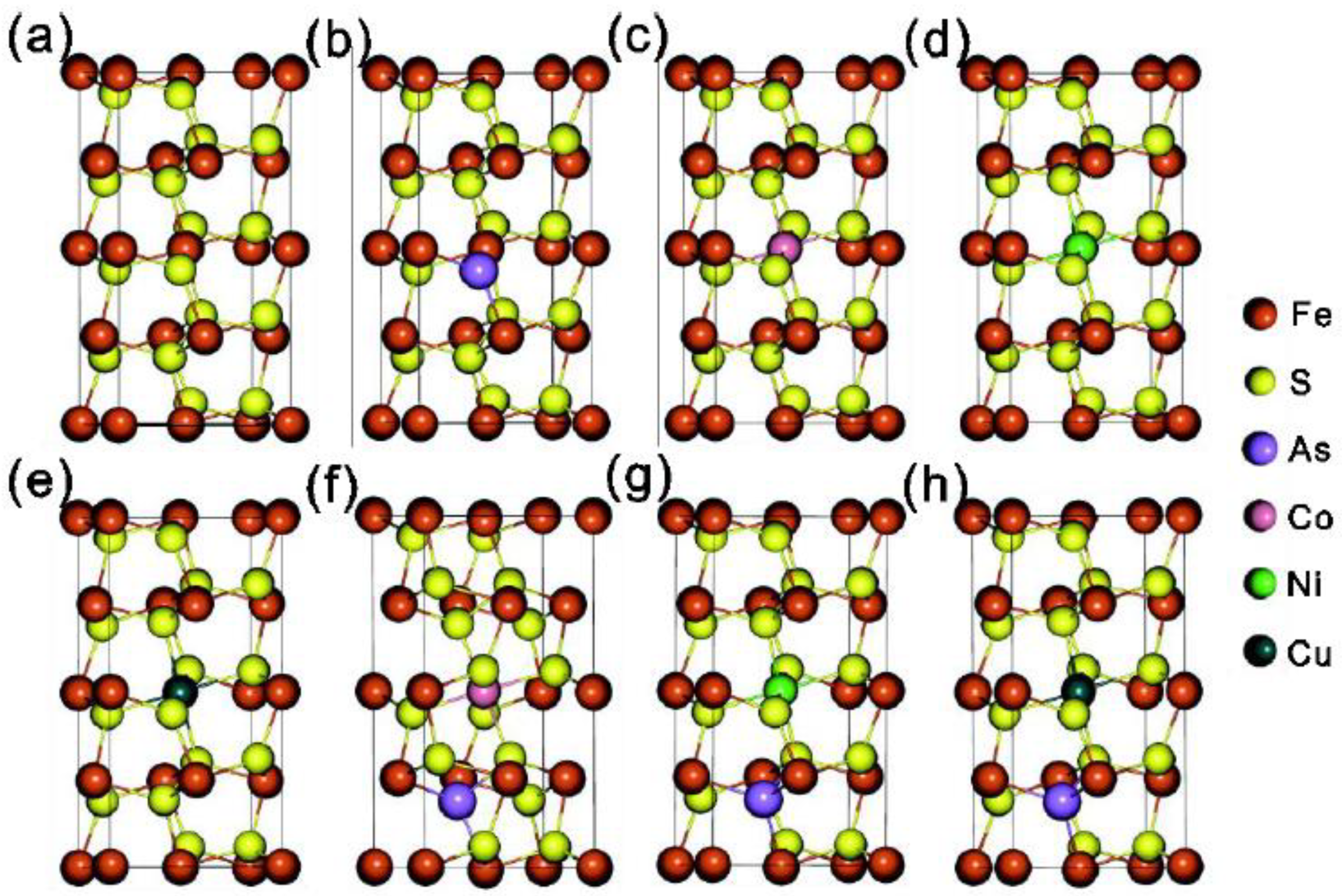
3.3. Calculation of The Crystal Structures and Electronic Structures of Pyrite under Different Doping Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Impurity Elements on the Semiconductor Properties of Pyrite
4.1.1. As
4.1.2. Cu, Co, and Ni
4.1.3. As Mixed with Co, Ni, and Cu
4.2. The Thermoelectric Properties and Formation Temperature of Pyrite
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrie, C.D.; Boyce, A.J.; Boyle, A.P.; Williams, P.J.; Blake, K.; Ogawara, T.; Akai, J.; Prior, D.J. Growth controls in colloform pyrite. Am. Miner. 2009, 94, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, G.; Hofmann, A.; Agangi, A. A revised classification scheme of pyrite in the Witwatersrand Basin and application to placer gold deposits. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.; Smith, D.J.; Jenkin, G.R.; Holwell, D.A.; Dye, M.D. A review of Te and Se systematics in hydrothermal pyrite from precious metal deposits: Insights into ore-forming processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 96, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steadman, J.A.; Large, R.R.; Olin, P.H.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Meffre, S.; Huston, D.; Fabris, A.; Lisitsin, V.; Wells, T. Pyrite trace element behavior in magmatic-hydrothermal environments: An LA-ICPMS imaging study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 128, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Li, S.-R.; Santosh, M.; Shah, A.; Yuan, M.-W.; Khan, H.; Qureshi, J.A.; Zeng, Y.-J. Morphological, thermoelectrical, geochemical and isotopic anatomy of auriferous pyrite from the Bagrote valley placer deposits, North Pakistan: Implications for ore genesis and gold exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Li, L.; Yuan, M.-W.; Alam, M.; Li, S.-R.; Santosh, M.; Deng, C.-Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, G.-Z. Study on pyrite thermoelectricity, ore-forming fluids and H-O-Rb-Sr isotopes of the Yongxin gold deposit, Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implications for ore genesis and exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 121, 103568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, J.; Ferrer, I.; Cuevas, F.; Sánchez, C.; Ferrer, M.I.J. Growth of pyrite thin-films investigated by thermoelectric measurements. Thin Solid Films 2001, 387, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhuber, F.; Krach, A.; Furtner, A.; Söhnel, T.; Peter, P.; Rothballer, J.; Weihrich, R. Phase stabilities of pyrite-related MTCh compounds (M=Ni, Pd, Pt; T=Si, Ge, Sn, Pb; Ch=S, Se, Te): A systematic DFT study. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 226, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridmore, D.F.; Shuey, R.T. The electrical resistivity of galena, pyrite, and chalcopyrite. Am. Min. 1976, 61, 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, F.M.; Mirza, A.H. Electrochemical oxidation of pyrite samples with known composition and electrical properties. Electrochem. Proc. 1996, 96, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Schieck, R.; Hartmann, A.; Fiechter, S.; Knenkamp, R.; Wetzel, H. Electrical properties of natural and synthetic pyrite (FeS2) crystals. J. Mat. Res. 1990, 5, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favorov, V.A.; Krasnikov, V.J.; Sychugov, V.S. Variations in semiconductor properties of pyrite and arsenopyrite and their determinants. Int. Geol. Rev. 1974, 16, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraitis, P.K.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Vaughan, D.J. Variations in the compositional, textural and electrical properties of natural pyrite: A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Li, S.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of the genetic mineralogy of pyrite and its significance for prospecting in the Denggezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, Y.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Kong, L.; Jia, W.; et al. Typomorphic characteristics of pyrite: Criteria for 3D exploration targeting in the xishan gold deposit, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 164, 136–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, H. Typomorphic characteristics of pyrite from the Linglong gold deposit: Its vertical variation and prospecting significance. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 55–75. [Google Scholar]
- Shuey, R.T. Semiconducting Ore Minerals. In Developments in Economic Geology; Shuey, R.T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 4, pp. 304–318. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, M.I.J.; De La Heras, C.; Sanchez, C. The effect of Ni impurities on some structural properties of pyrite thin films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 7, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, S.; Savage, K.; Ayers, J. Vapor growth and characterization of pyrite (FeS2) doped with Co, Ni, and As: Variations in semiconducting properties. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 286, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.S.; Stefan, D.; Lehner, S.W. Impurities and heterogeneity in pyrite: Influences on electrical properties and oxidation products. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, C.; Guenes, E.; Schulze, A.S.; Elm, M.T.; Klar, P.J.; Schlecht, S. Nanoscale FeS2 (Pyrite) as a Sustainable Thermoelectric Material. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J. Density functional theory study of influence of impurity on electronic properties and reactivity of pyrite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Shen, J.; Santosh, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K. Textural, compositional and isotopic characteristics of pyrite from the Zaozigou gold deposit in West Qinling, China: Implications for gold metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 130, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzek, D.; Karpinski, G.; Stiewe, C.; Ziolkowski, P.; Drasar, C.; Müller, E. Potential-Seebeck-microprobe (PSM): Measuring the spatial resolution of the Seebeck coefficient and the electric potential. In Proceedings of the ICT 2005, 24th International Conference on Thermoelectrics, Clemson, SC, USA, 19–23 June 2005; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nieroda, P.; Leszczyński, J.; Mikuła, A.; Mars, K.; Kruszewski, M.J.; Koleżyński, A. Thermoelectric properties of Cu2S obtained by high temperature synthesis and sintered by IHP method. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 25460–25466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayachi, S.; Hernandez, G.C.; Pham, N.H.; Farahi, N.; Müller, E.; De Boor, J. Developing Contacting Solutions for Mg2Si1–xSnx-Based Thermoelectric Generators: Cu and Ni45Cu55 as Potential Contacting Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 40769–40780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, G.; Ning, S.; Nie, L.; Zhong, G.; White, N.C. A new approach to LA-ICP-MS mapping and application in geology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3422–3436. [Google Scholar]
- George, L.L.; Biagioni, C.; D’Orazio, M.; Cook, N.J. Textural and trace element evolution of pyrite during greenschist facies metamorphic recrystallization in the southern Apuan Alps (Tuscany, Italy): Influence on the formation of Tl-rich sulfosalt melt. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 59–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agangi, A.; Hofmann, A.; Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C. Pyrite Zoning as a Record of Mineralization in the Ventersdorp Contact Reef, Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 1243–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Ciobanu, C.; George, L.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Wade, B.; Ehrig, K. Trace Element Analysis of Minerals in Magmatic-Hydrothermal Ores by Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: Approaches and Opportunities. Minerals 2016, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paton, C.; Hellstrom, J.; Paul, B.; Woodhead, J.; Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Ridley, W.I.; Koenig, A.E. Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y. First-principles study of sulfur isotope fractionation in pyrite-type disulfides. Am. Miner. 2014, 100, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Chevary, J.A.; Vosko, S.H.; Jackson, K.A.; Pederson, M.R.; Singh, D.J.; Fiolhais, C. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 6671–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Hu, C.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, K. Strain Effects to Optimize Thermoelectric Properties of Doped Bi2O2Se via Tran–Blaha Modified Becke–Johnson Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 21597–21602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Ewing, R.C.; Hough, R.; Walshe, J. Trace metal nanoparticles in pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, M.E.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Davidson, R.; Weisener, C.G.; Maclean, P.J. Arsenian pyrite from gold deposits: Au and As distribution investigated by SIMS and EMP, and color staining and surface oxidation by XPS and LIMS. Can. Mineral. 1993, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, D.L.; Sie, S.H.; Suter, G.F.; Cooke, D.R.; Both, R.A. Trace elements in sulfide minerals from eastern Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits, Part II.Selenium levels in pyrite: Comparison with d34S values and implications for the source of sulfur in volcanogenic hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 1167–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L. Detecting magmatic-derived fluids using pyrite chemistry: Example of the Chibougamau area, Abitibi Subprovince, Québec. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Simon, A.C.; Deditius, A.; Barra, F.; Chryssoulis, S.; Lagas, G.; Tardani, D.; Knipping, J.; Bilenker, L.; Sánchez-Alfaro, P.; et al. Trace element signature of pyrite from the los colorados iron oxide-apatite (IOA) Deposit, Chile: A missing link between andean ioa and iron oxide copper-gold systems? Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steadman, J.A.; Large, R.R.; Meffre, S.; Olin, P.H.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Gregory, D.D.; Belousov, I.; Lounejeva, E.; Ireland, T.R.; Holden, P. Synsedimentary to Early Diagenetic Gold in Black Shale-Hosted Pyrite Nodules at the Golden Mile Deposit, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1157–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, S.; Cooke, D.R.; Meffre, S.; Stephanov, A.S.; Gardner, K.; Scott, R.; Selley, D.; Harris, A.C. Evolution of Pyrite Trace Element Compositions from Porphyry-Style and Epithermal Conditions at the Lihir Gold Deposit: Implications for Ore Genesis and Mineral Processing. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Biagioni, C.; Dini, A.; Vezzoni, S. Thallium-rich pyrite ores from the Apuan Alps, Tuscany, Italy:constraints for their origin and environmental concerns. Miner. Deposita 2017, 52, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, M.E.; MacLean, P.J.; Barbier, J. Oscillatory-zoned As-bearing pyrite from strata-bound and stratiform gold deposits: An indicator of ore fluid evolution. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 1989, 6, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Large, R.; Danyushevsky, L.V. Study of Trace Element Zonation in Vent Chimneys from the Silurian Yaman-Kasy Volcanic-Hosted Massive Sulfide Deposit (Southern Urals, Russia) Using Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 1111–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Deditius, A.; Chryssoulis, S.; Li, J.-W.; Ma, C.-Q.; Parada, M.A.; Barra, F.; Mittermayr, F. Pyrite as a record of hydrothermal fluid evolution in a porphyry copper system: A SIMS/EMPA trace element study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 104, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
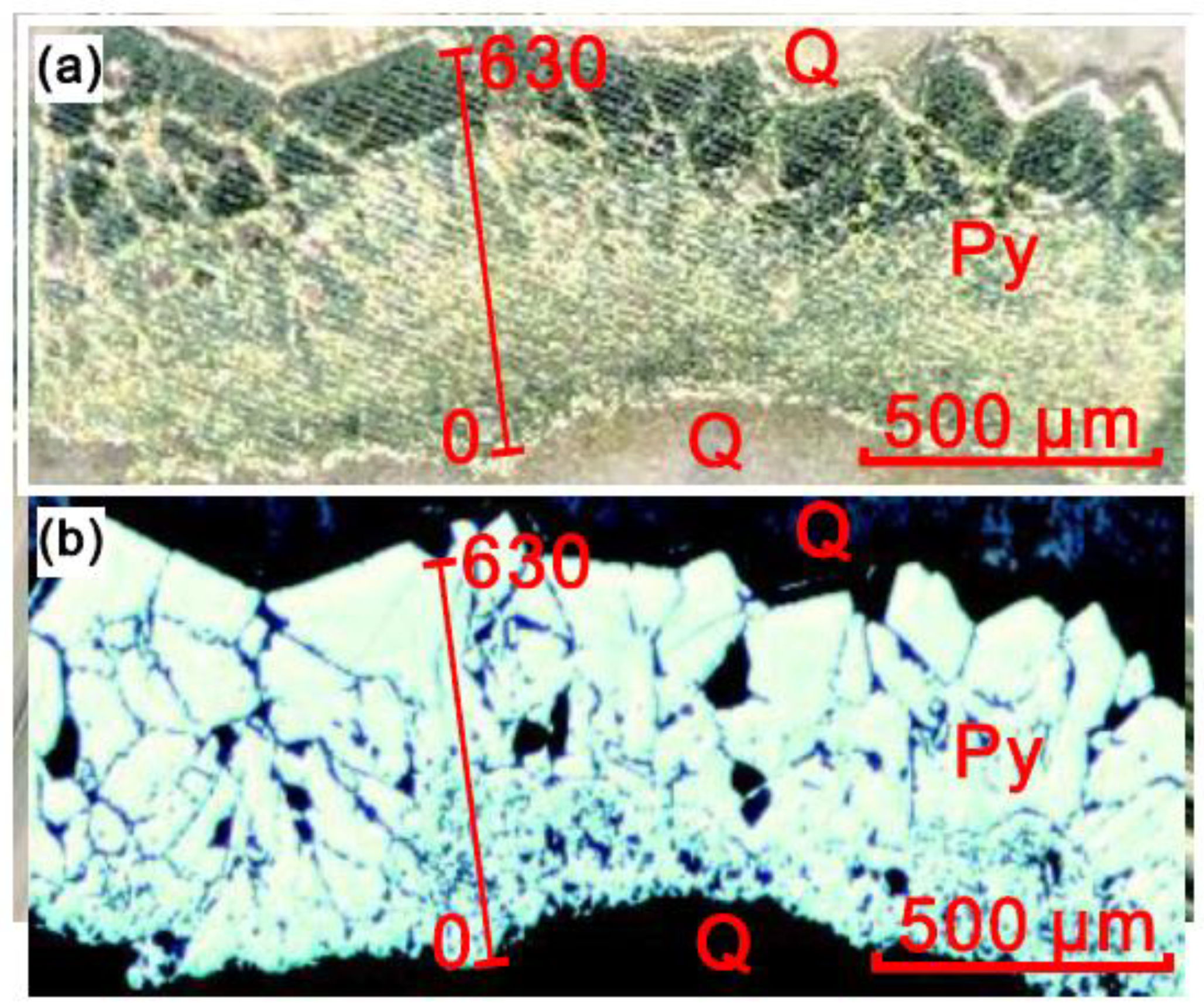



| Distance (μm) | Seebeck Coefficients (μV/K) | Distance (μm) | Seebeck Coefficients (μV/K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −0.60 | 320 | −6.25 |
| 10 | 0.38 | 330 | −47.45 |
| 20 | 0.82 | 340 | 46.22 |
| 30 | 1.94 | 350 | 127.78 |
| 40 | 5.55 | 360 | −11.17 |
| 50 | 0.65 | 370 | −8.00 |
| 60 | −1.55 | 380 | 141.19 |
| 70 | 2.18 | 390 | −30.63 |
| 80 | 4.34 | 400 | 151.39 |
| 90 | 4.52 | 410 | 26.91 |
| 100 | 3.63 | 420 | 18.32 |
| 110 | 2.73 | 430 | 19.92 |
| 120 | 1.39 | 440 | 15.30 |
| 130 | 2.22 | 450 | 17.56 |
| 140 | 11.61 | 460 | −10.13 |
| 150 | 0.79 | 470 | −10.52 |
| 160 | 2.59 | 480 | −10.21 |
| 170 | 5.41 | 490 | −4.37 |
| 180 | 7.60 | 500 | −8.67 |
| 190 | 11.28 | 510 | −7.82 |
| 200 | 3.26 | 520 | −6.98 |
| 210 | −4.77 | 530 | -4.19 |
| 220 | 12.39 | 540 | −5.47 |
| 230 | −2.10 | 550 | −4.68 |
| 240 | −16.58 | 560 | −4.05 |
| 250 | −5.41 | 570 | −4.06 |
| 260 | −10.28 | 580 | 13.03 |
| 270 | 142.12 | 590 | 66.87 |
| 280 | −7.40 | 600 | 28.00 |
| 290 | −26.12 | 610 | 29.08 |
| 300 | −23.14 | 620 | 27.25 |
| 310 | −12.26 | 630 | 25.42 |
| Species | Fe8S16 | Fe7Co1S16 | Fe7Co1S15As1 | Fe7Ni1S16 | Fe8S15As1 | Fe7Ni1S15As1 | Fe7Cu1S16 | Fe7Cu1S15As1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume/Å3 | 316.12 | 316.82 | 321.13 | 321.21 | 321.86 | 324.57 | 324.84 | 328.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Du, B.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. The Relationship between Natural Pyrite and Impurity Element Semiconductor Properties: A Case Study of Vein Pyrite from the Zaozigou Gold Deposit in China. Minerals 2021, 11, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060596
Wang S, Shen J, Du B, Xu K, Zhang Z, Liu C. The Relationship between Natural Pyrite and Impurity Element Semiconductor Properties: A Case Study of Vein Pyrite from the Zaozigou Gold Deposit in China. Minerals. 2021; 11(6):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060596
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuhao, Junfeng Shen, Baisong Du, Kexin Xu, Zhengshuai Zhang, and Chengyu Liu. 2021. "The Relationship between Natural Pyrite and Impurity Element Semiconductor Properties: A Case Study of Vein Pyrite from the Zaozigou Gold Deposit in China" Minerals 11, no. 6: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060596
APA StyleWang, S., Shen, J., Du, B., Xu, K., Zhang, Z., & Liu, C. (2021). The Relationship between Natural Pyrite and Impurity Element Semiconductor Properties: A Case Study of Vein Pyrite from the Zaozigou Gold Deposit in China. Minerals, 11(6), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060596





