Forced Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness Constrained by Wireline and 3-D Seismic Data Suggest an Elastic Magma-Induced Deformation in Tarim Basin, NW China
Abstract
1. Introduction
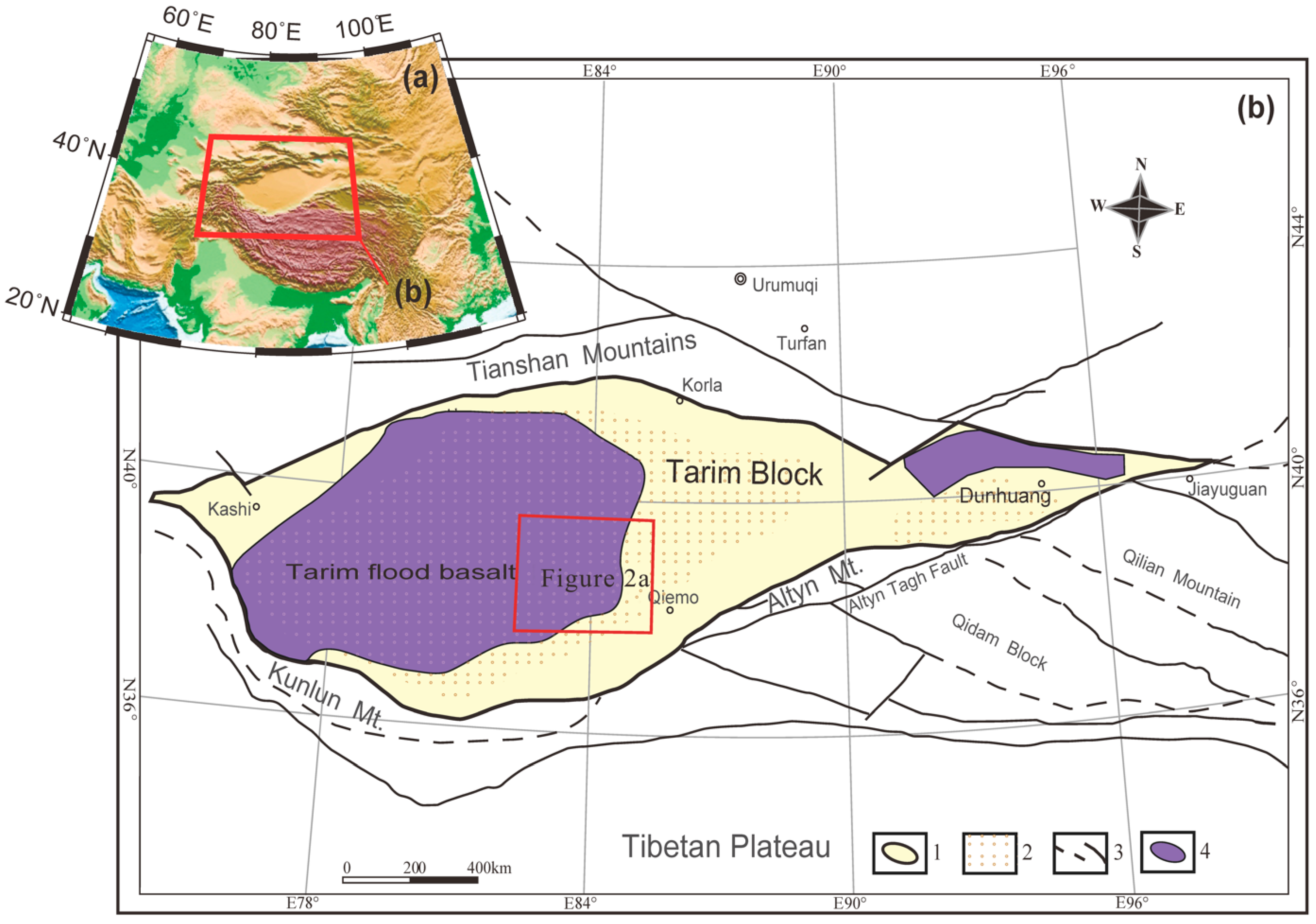
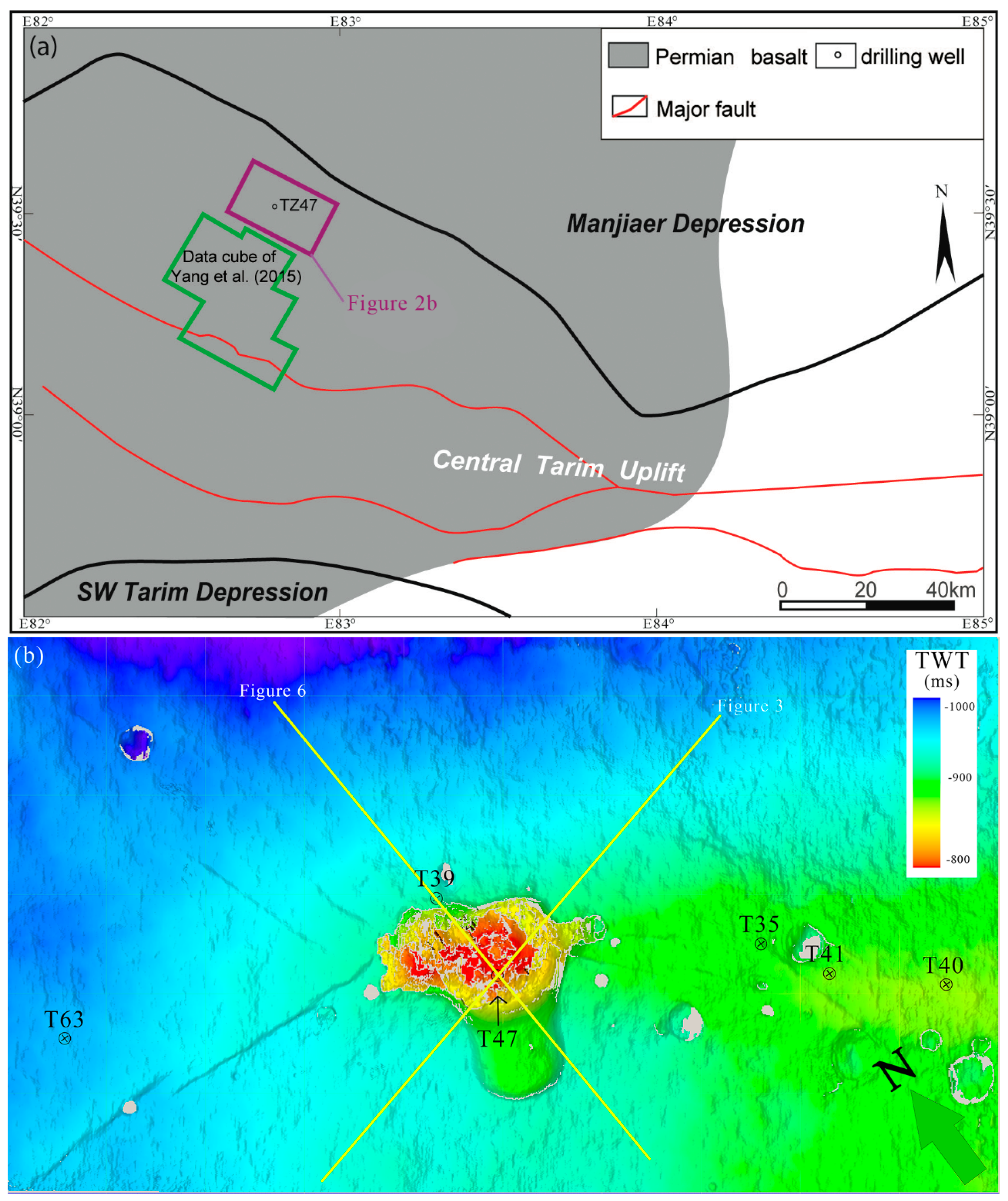
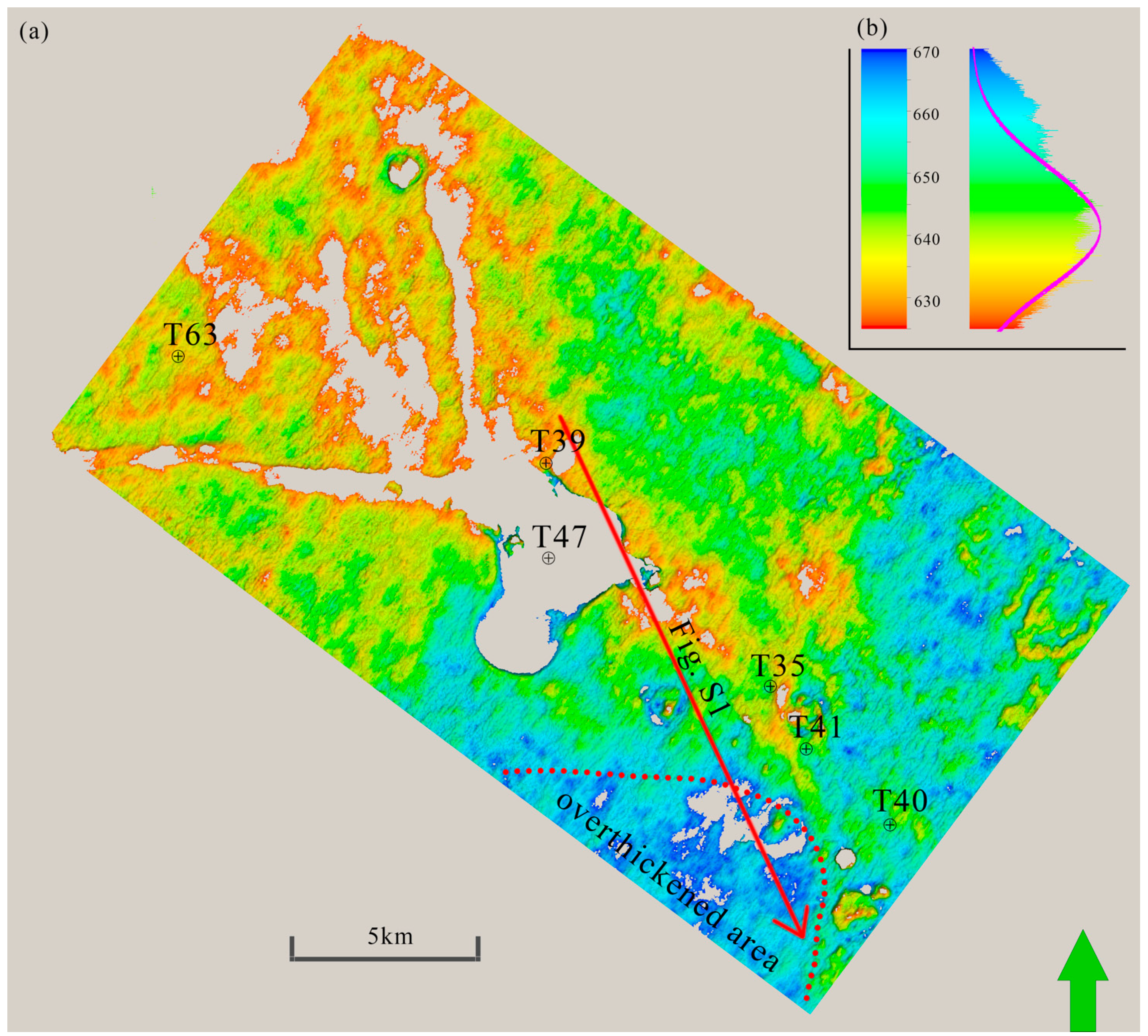
2. Geological Setting and Data Cube Descriptions
3. Data Set and Processing Methods
4. Results
4.1. Pre-Deformation Thickness of the Host Strata
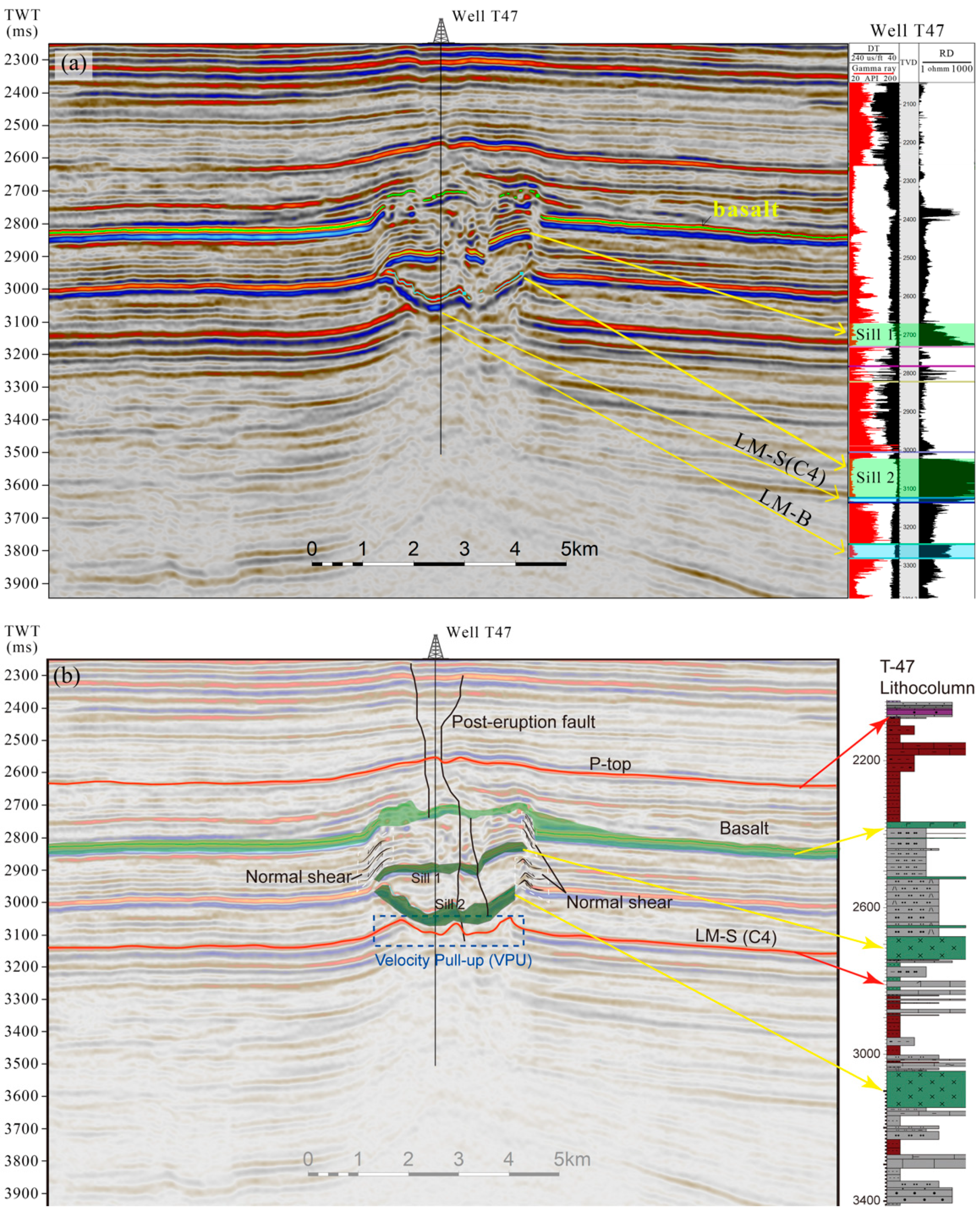
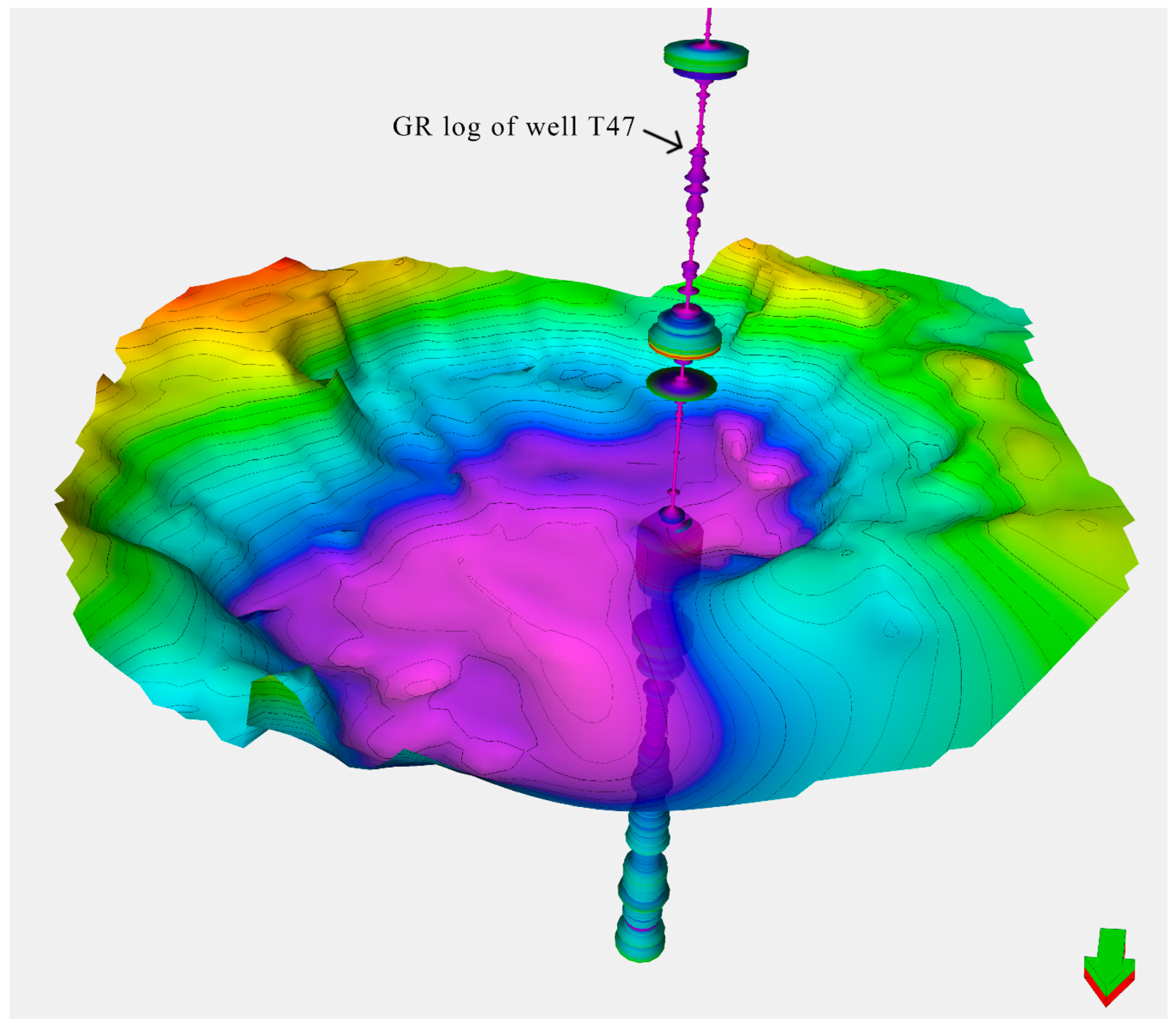
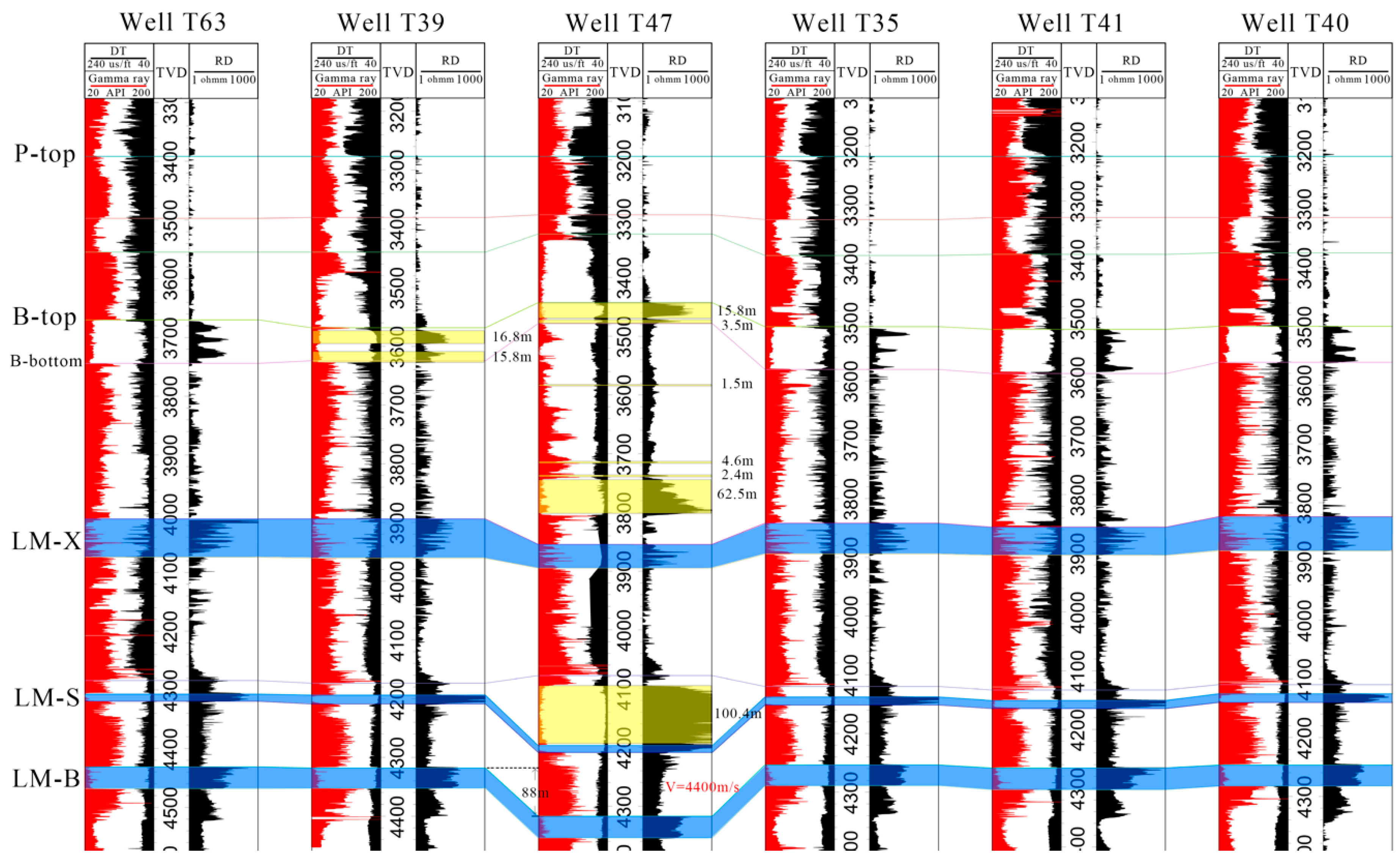
4.2. Saucer-Shaped Sills Measured by Combination of Wireline and Seismic Data
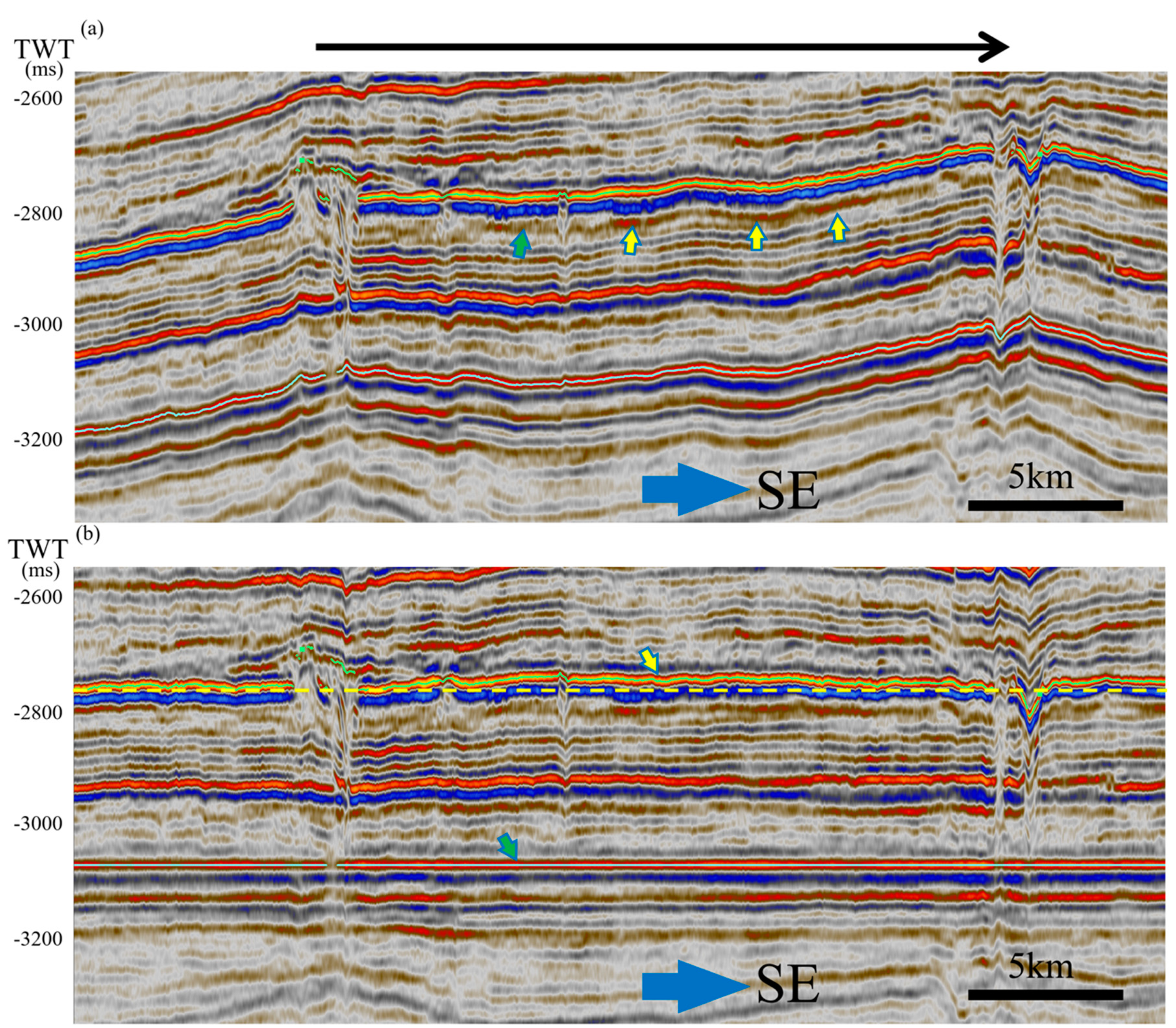
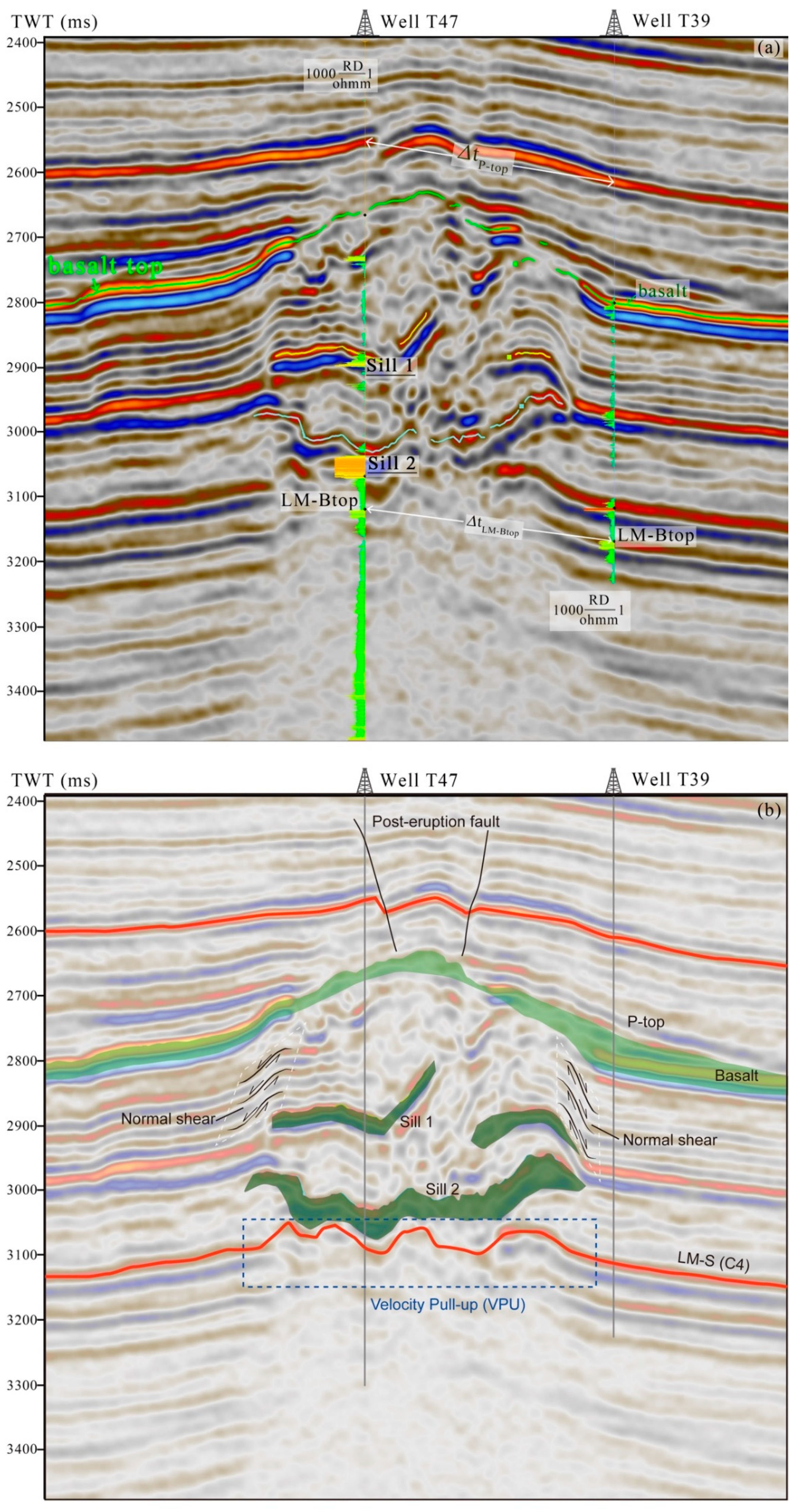
4.3. Roof Uplifting Identified in Seismic Cube
5. Discussion
5.1. Sill and Basalt Thickness Estimated by Seismic Method
- (1)
- Select Permian–Triassic boundary (P-top) as top and bioclast limestone top surface (LM-Btop) as bottom. LM-Btop is beneath all seven magmatic layers at the location of T47, and is not affected by the igneous intrusions, thus this layer is used as a reference horizontal surface.
- (2)
- The time difference between T39 and T47 at P-top (Δtp-top) is 58 ms, and the time difference ΔtLM-Btop at LM-Btop is 56 ms (Figure 6b). Comparing T39 and T47, the time thickness difference Δt = Δtp-top − ΔtLM-Btop = 58 − 56 = 2 ms.
- (3)
- Flattening the well logging curves of T39 and T47 along the P-top, which represents a horizontal topography at the eruption time of the Permian flood basalt. The depth difference at LM-Btop between T39 and T47 can be calculated based on the logging data, which is Δh = 88 m.
- (4)
- According to the acoustic logging data (DT), the averaged acoustic velocity of T47 at the lowest 88 m (shown as Δh in Figure 7) is V2 = 4450 m/s; the dual time difference corresponding to the depth of difference is Δtl = ΔhV2 × 2 × 1000 = 88/4450 × 2 × 1000 = 40 ms.
- (5)
- Likewise, by using the acoustic logging curve (DT), we can obtain the average velocity between P-top and LM-Btop from the two different lithologies: the average velocity of clastic rock is Vlow = 3500 m/s, the average velocity of mafic magmatic rock is Vhigh = 5800 m/s.
- (6)
- The difference of pull-up time depth ΔtVPU due to igneous intrusions is equal to the time-thickness difference between the two wells (obtained in step 2) minus the dual time difference corresponding to the depth of difference (obtained in step 4), i.e., ΔtVPU = Δtl − Δt =2 − 40 = −38 ms. The negative number here represents that at the direction of the time difference at the velocity pull-up (VPU) case, ΔtVPU is negative.
5.2. Forced Fold Amplitude Measured by Wireline Data
5.3. Comparison between Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness
5.4. Possible Sources of Error in Seismic Studies of Forced Folds
5.5. The Possible Role of Limestone Layers in Hardening Up of the Roof Layers
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The TZ-47 fold represents overburden deformation above a stack of magmatic sills intruded in the Tarim Basin, NW China;
- (2)
- The amplitude of roof uplift at the area penetrated by well T47 is 155.0 m;
- (3)
- The total sill thickness estimated by the seismic method is 171.4 m and that calculated by the well log method is 181.0 m, which are consistent with the decompacted roof uplift amplitude (~159.9 to 225.8 m), suggesting a dominantly elastic deformation of this forced fold;
- (4)
- When using just the seismic method, we may miss some invisible sills and interbedded sedimentary strata, as well as vertical structural features, which may result in underestimation or overestimation of sill thickness, respectively;
- (5)
- Carbonate layers may have played an important role in the hardening up of the roof layers and in helping to avoid inelastic deformations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Alexander, R.C. On the emplacement of tabular granites. J. Geol. Soc. 1998, 155, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.M.; Cartwright, J. Saucer-shaped sill with lobate morphology revealed by 3D seismic data: Implications for resolving a shallow-level sill emplacement mechanism. J. Geol. Soc. 2006, 163, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Hunt-Stewart, E.; Jackson, C.A.-L. Volcano growth mechanisms and the role of sub-volcanic intrusions: Insights from 2D seismic reflection data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 373, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Hardman, J.P.; Reeve, M.T. Decoding sill emplacement and forced fold growth in the Exmouth Sub-basin, offshore northwest Australia: Implications for hydrocarbon exploration. Interpretation 2017, 5, SK11–SK22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Pollard, D.D. Mechanics of growth of some laccolithic intrusions in the Henry mountains, Utah, I. Tectonophysics 1973, 18, 261–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, D.D.; Johnson, A.M. Mechanics of growth of some laccolithic intrusions in the Henry mountains, Utah, II. Tectonophysics 1973, 18, 311–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, D.W.; Matthews, V., III. Faulting and Forced Folding in the Rocky Mountains Foreland. In Laramide Folding Associated with Basement Block Faulting in the Western United States; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1978; Volume 151, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sturkell, E.; Einarsson, P.; Sigmundsson, F.; Geirsson, H.; Ólafsson, H.; Pedersen, R.; Dalfsen, E.D.Z.-V.; Linde, A.T.; Sacks, S.I.; Stefánsson, R. Volcano geodesy and magma dynamics in Iceland. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2006, 150, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.S.J.; Biggs, J.; Neuberg, J.W. Monitoring Volcanoes. Science 2012, 335, 1310–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebmeier, S.K.; Andrews, B.J.; Araya, M.C.; Arnold, D.W.D.; Biggs, J.; Cooper, C.; Cottrell, E.; Furtney, M.; Hickey, J.; Jay, J.; et al. Synthesis of global satellite observations of magmatic and volcanic deformation: Implications for volcano monitoring & the lateral extent of magmatic domains. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.; Magee, C.; Jackson, C.A.-L. Unravelling intrusion-induced forced fold kinematics and ground deformation using 3D seismic reflection data. Volcanica 2018, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Hoggett, M.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Jones, S.M. Burial-Related Compaction Modifies Intrusion-Induced Forced Folds: Implications for Reconciling Roof Uplift Mechanisms Using Seismic Reflection Data. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Stanik, A.; Horsman, E.; Tikoff, B.; Blanquat, M.D.S.; Habert, G. Emplacement of multiple magma sheets and wall rock deformation: Trachyte Mesa intrusion, Henry Mountains, Utah. J. Struct. Geol. 2008, 30, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedel, T.; Kjoberg, S.; Planke, S.; Magee, C.; Galland, O.; Schofield, N.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Jerram, D.A. Mechanisms of overburden deformation associated with the emplacement of the Tulipan sill, mid-Norwegian margin. Interpretation 2017, 5, SK23–SK38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedel, T.; Galland, O.; Haug, Ø.T.; Dumazer, G.; Breitkreuz, C. Coulomb failure of Earth’s brittle crust controls growth, emplacement and shapes of igneous sills, saucer-shaped sills and laccoliths. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 510, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, N.J.; Brown, D.J.; Magee, C.; Stevenson, C.T. Sill morphology and comparison of brittle and non-brittle emplacement mechanisms. J. Geol. Soc. 2012, 169, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, O.; Spacapan, J.B.; Rabbel, O.; Mair, K.; Soto, F.G.; Eiken, T.; Schiuma, M.; Leanza, H.A. Structure, emplacement mechanism and magma-flow significance of igneous fingers—Implications for sill emplacement in sedimentary basins. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 124, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacapan, J.B.; Galland, O.; Leanza, H.A.; Planke, S. Igneous sill and finger emplacement mechanism in shale-dominated formations: A field study at Cuesta del Chihuido, Neuquén Basin, Argentina. J. Geol. Soc. 2016, 174, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, C.H.; Schofield, N.; Jerram, D.A.; Howell, J.A. Basin-scale architecture of deeply emplaced sill complexes: Jameson Land, East Greenland. J. Geol. Soc. 2016, 174, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, N.; Schofield, N.; Pugliese, S.; Watson, D.; Holford, S.; Muirhead, D.; Brown, R.; Healy, D. Igneous intrusions in the Faroe Shetland basin and their implications for hydrocarbon exploration; new insights from well and seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 92, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.M.; Cartwright, J. The three-dimensional geometry and growth of forced folds above saucer-shaped igneous sills. J. Struct. Geol. 2006, 28, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.A.-L.; Schofield, N.; Golenkov, B. Geometry and controls on the development of igneous sill-related forced folds: A 2-D seismic reflection case study from offshore southern Australia. GSA Bull. 2013, 125, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Bastow, I.D.; Vries, B.V.W.D.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Hetherington, R.; Hagos, M.; Hoggett, M. Structure and dynamics of surface uplift induced by incremental sill emplacement. Geology 2017, 45, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, N.; Holford, S.P.; Millett, J.; Brown, D.J.; Jolley, D.W.; Passey, S.R.; Muirhead, D.; Grove, C.; Magee, C.; Murray, J.; et al. Regional magma plumbing and emplacement mechanisms of the Faroe-Shetland Sill Complex: Implications for magma transport and petroleum systems within sedimentary basins. Basin Res. 2017, 29, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, N.; Schofield, N.; Gardiner, D.; Holt, L.; Grove, C.; Watson, D.; Alexander, A.; Poore, H. Overthickening of sedimentary sequences by igneous intrusions. J. Geol. Soc. 2019, 176, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Ni, Y.N.; Gong, F.H.; Lu, H.N.; Huang, Z.B.; Lin, H.L. A Guide to the Stratigraphic Investigation on the Periphery of the Tarim Basin; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Niu, G. Geological and geochronological evidence for the Precambrian evolution of the Tarim Craton and surrounding continental fragments. Precambrian Res. 2008, 160, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents: Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia. Precambrian Res. 2003, 122, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, D.; Meng, L. Early Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province in northwest China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Campbell, I.H.; Allen, C.M.; Guan, P.; Pan, W.; Chen, M.; Yu, H.; Zhu, W. The Tarim picrite–basalt–rhyolite suite, a Permian flood basalt from northwest China with contrasting rhyolites produced by fractional crystallization and anatexis. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2010, 160, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, W.; Guan, D.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, X.; Su, J.; He, J.; Wu, X. 3D seismic interpretation of subsurface eruptive centers in a Permian large igneous province, Tazhong Uplift, central Tarim Basin, NW China. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 105, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-G.; Wei, X.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Liu, H.-Q.; Cao, J. The Early Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province: Main characteristics and a plume incubation model. Lithos 2014, 204, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Gong, M.Y. A giant felsic pyroclastic flow eruption in the Tarim Flood Basalt Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tian, W.; Shi, Y.; Guan, P. Volcanic structure of the Tarim flood basalt revealed through 3-D seismological imaging. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jackson, C.A.-L. Seismic reflection imaging and controls on the preservation of ancient sill-fed magmatic vents. J. Geol. Soc. 2012, 169, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, J.R.; Maresh, J. The properties, morphology and distribution of igneous sills: Modelling, borehole data and 3D seismic from the Faroe-Shetland area. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2002, 197, 271–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posamentier, H.W.; Doré, A.G.; Vining, B.A. Application of 3D seismic visualization techniques for seismic stratigraphy, seismic geomorphology and depositional systems analysis: Examples from fluvial to deep-marine depositional environments. Geol. Soc. Lond. Pet. Geol. Conf. Ser. 2005, 6, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, N.; Heaton, L.; Holford, S.P.; Archer, S.G.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Jolley, D.W. Seismic imaging of ‘broken bridges’: Linking seismic to outcrop-scale investigations of intrusive magma lobes. J. Geol. Soc. 2012, 169, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.; Hutton, D. Geometry and growth of sill complexes: Insights using 3D seismic from the North Rockall trough. Bull. Volcanol. 2004, 66, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, W.; Shi, Y. Data Processing Methods for 3D Seismic Imaging of Subsurface Volcanoes: Applications to the Tarim Flood Basalt. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 126, e55930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widess, M.B. HOW thin is a thin bed? Geophysics 1973, 38, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; John, A.; Katherine, G. How Thin Is a Thin Bed? An Alternative Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2008 SEG Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–14 November 2008; pp. 834–838. [Google Scholar]
- Rider, M.; Kennedy, M. The Geological Interpretation of Well Logs, 3rd ed.; Rider-French Consulting Ltd.: Glasgow, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, K.; Jin, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zou, S. Late Carboniferous crustal uplift of the Tarim plate and its constraints on the evolution of the Early Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province. Lithos 2014, 204, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, L.; Woodford, A. Morpho-tectonics and mechanism of emplacement of the dolerite rings and sills of the western Karoo, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 1999, 102, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Symonds, P.; Planke, S.; Frey, O.; Skogseid, J. Volcanic evolution of the Western Australian continental margin and its implications for basin development. Sediment. Basins West. Aust. 1998, 2, 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tian, W.; Wei, Z.H.; Gong, M.Y.; Li, X.M. Volcanic conduits of the Tarim Flood Basalt Province: 3D structure and thermogenic gas release. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Planke, S.; Rasmussen, T.; Rey, S.S.; Myklebust, R. Seismic Characteristics and Distribution of Volcanic Intrusions and Hydrothermal Vent Complexes in the Vøring and Møre Basins. In Geological Society, London, Petroleum Geology Conference Series; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 833–844. [Google Scholar]
- Polteau, S.; Ferre, E.C.; Planke, S.; Neumann, E.-R.; Chevallier, L. How are saucer-shaped sills emplaced? Constraints from the Golden Valley Sill, South Africa. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Jackson, C.A.-L.; Schofield, N. The influence of normal fault geometry on igneous sill emplacement and morphology. Geology 2013, 41, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.L.; Jackson, C.A.L.; Schofield, N. Diachronous sub-volcanic intrusion along deep-water margins: Insights from the Irish Rockall Basin. Basin Res. 2014, 26, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoni, M.; Bonafede, M.; Boschi, E. Downslope flow models of a Bingham liquid: Implications for lava flows. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1986, 30, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, S.; Galland, O.; De Winter, N.; Goderis, S.; Claeys, P.; Debaille, V.; Boulvais, P.; Kervyn, M. Structural and Geochemical Interactions Between Magma and Sedimentary Host Rock: The Hovedøya Case, Oslo Rift, Norway. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2020, 21, 8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Maharaj, S.M.; Wrona, T.; Jackson, C.A.-L. Controls on the expression of igneous intrusions in seismic reflection data. Geosphere 2015, 11, 1024–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jing, B.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Li, T. Prediction of S-wave velocity in the wellblock ZG5-7, middle Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2012, 32, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, G.M. Early Diagenesis and Lithification in Carbonate Sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 1964, 34, 777–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Forced Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness Constrained by Wireline and 3-D Seismic Data Suggest an Elastic Magma-Induced Deformation in Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals 2021, 11, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030293
Tian W, Li X, Wang L. Forced Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness Constrained by Wireline and 3-D Seismic Data Suggest an Elastic Magma-Induced Deformation in Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030293
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Wei, Xiaomin Li, and Lei Wang. 2021. "Forced Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness Constrained by Wireline and 3-D Seismic Data Suggest an Elastic Magma-Induced Deformation in Tarim Basin, NW China" Minerals 11, no. 3: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030293
APA StyleTian, W., Li, X., & Wang, L. (2021). Forced Fold Amplitude and Sill Thickness Constrained by Wireline and 3-D Seismic Data Suggest an Elastic Magma-Induced Deformation in Tarim Basin, NW China. Minerals, 11(3), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030293




