Methodologies for the Possible Integral Generation of Geopolymers Based on Copper Tailings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
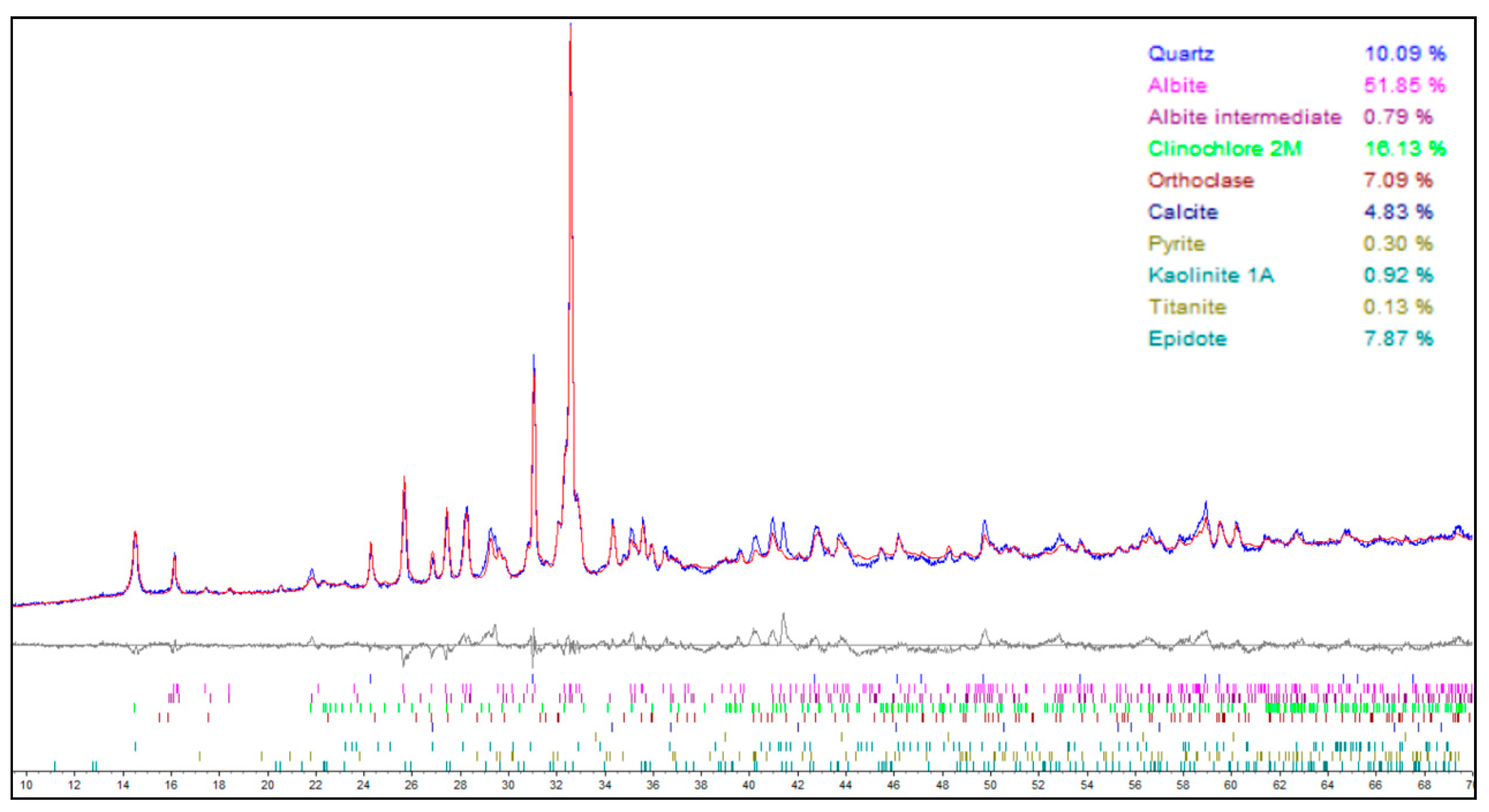
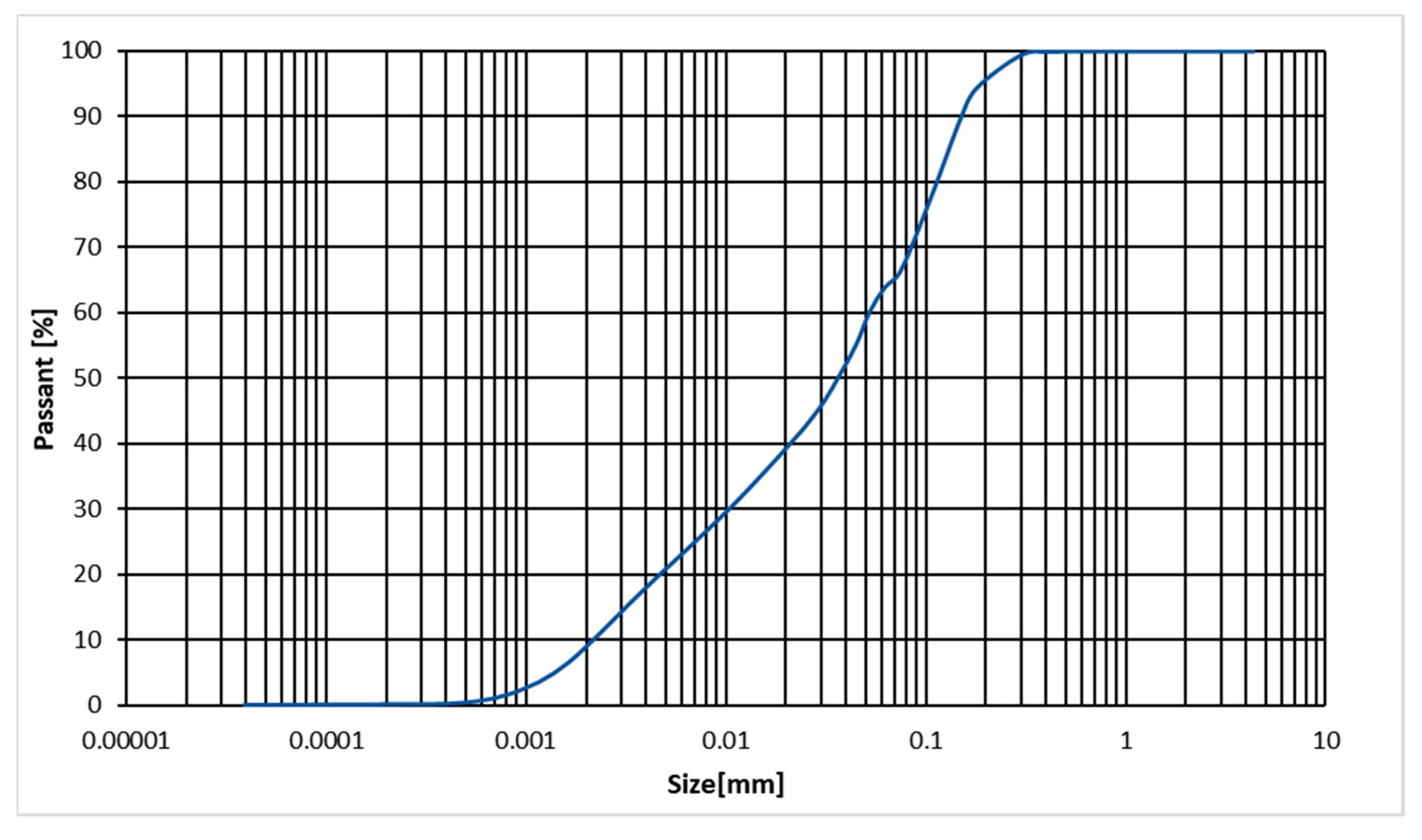
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Variables
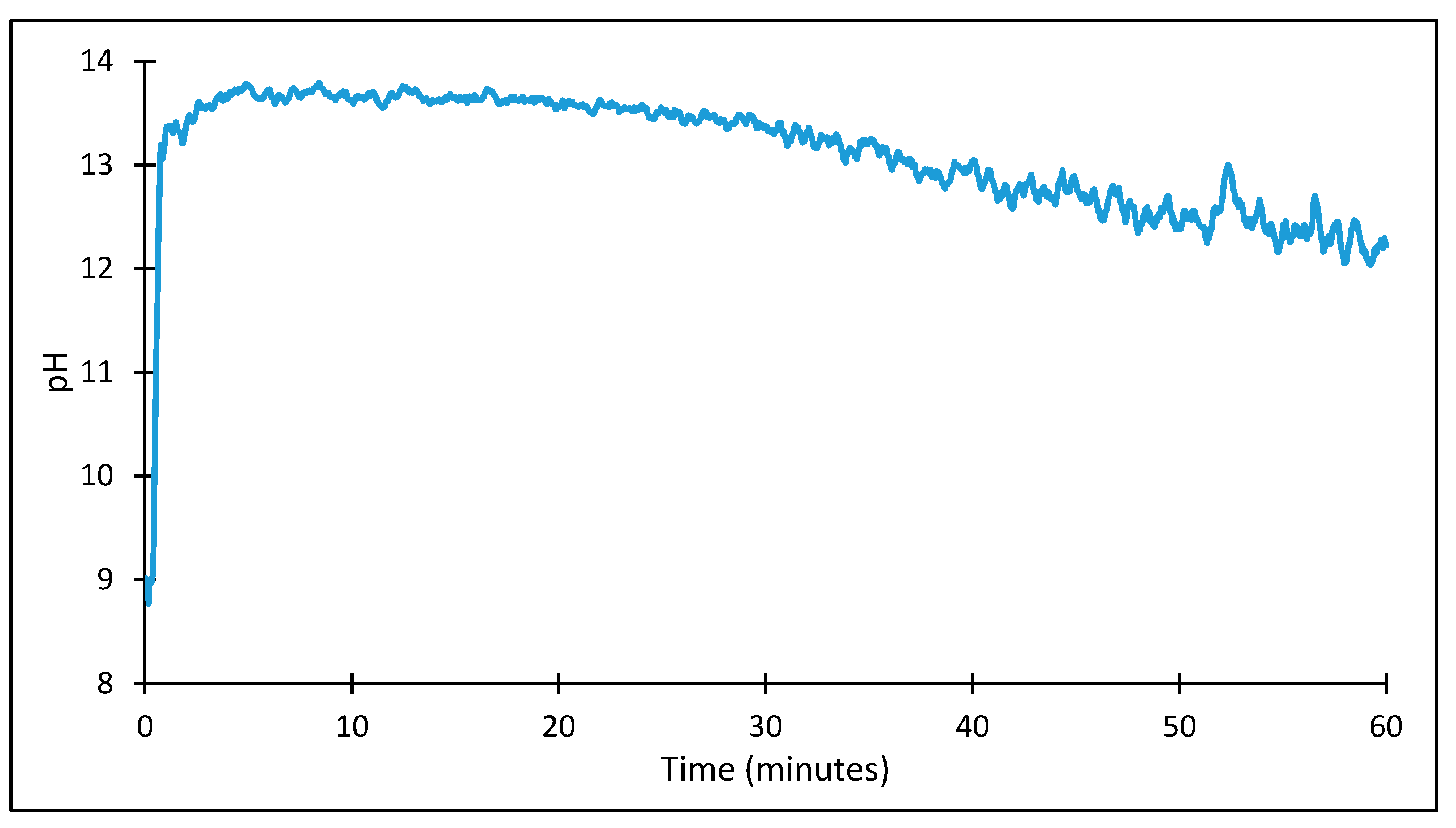
2.2.1. Alkaline Concentration
2.2.2. Water/Solids Ratio
2.3. Methodologies
2.3.1. Method I
2.3.2. Method II
2.3.3. Method III
2.3.4. Method IV
2.3.5. Method V
2.3.6. Method VI
2.3.7. Method VII
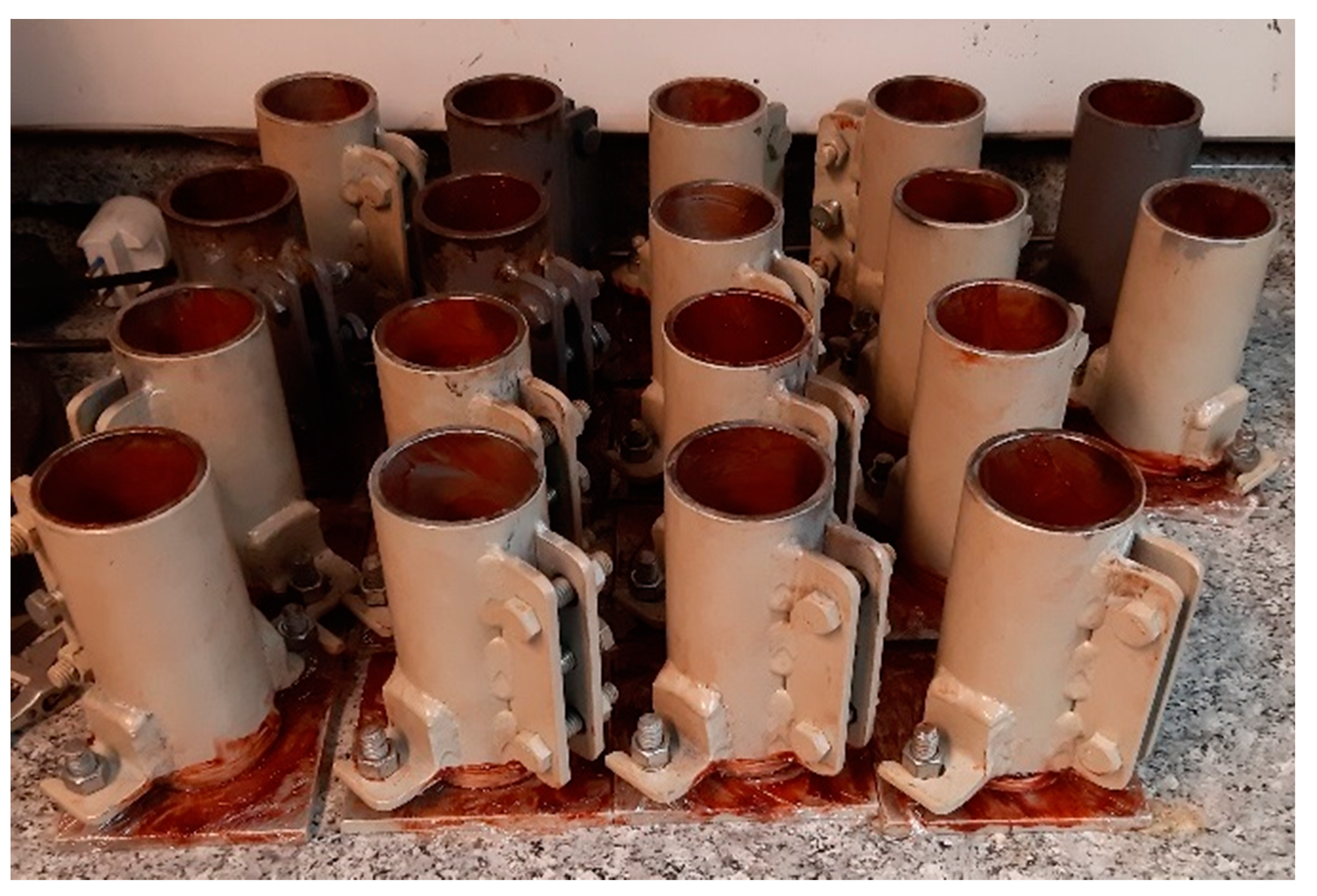
2.4. Testing Procedure
3. Results
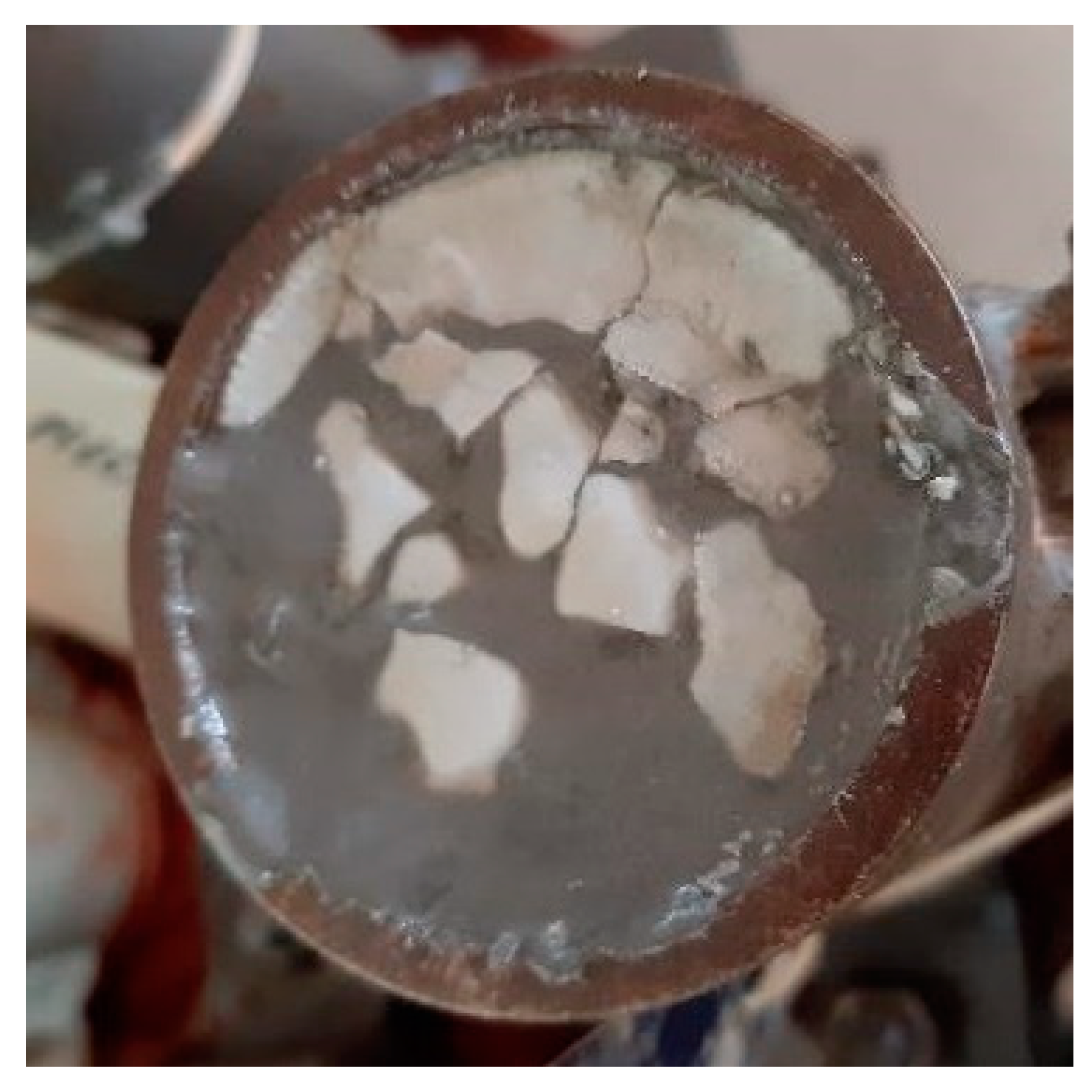
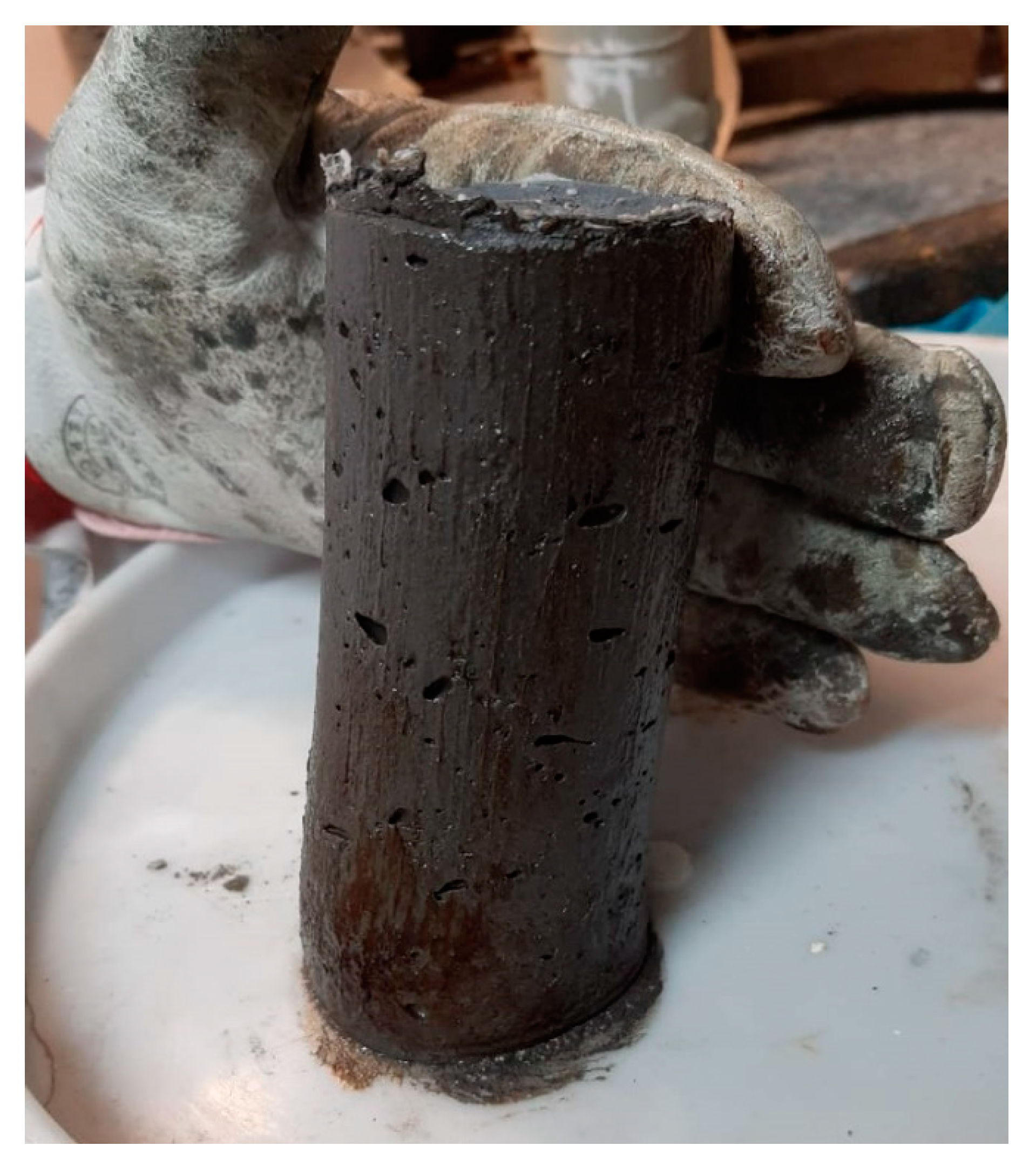
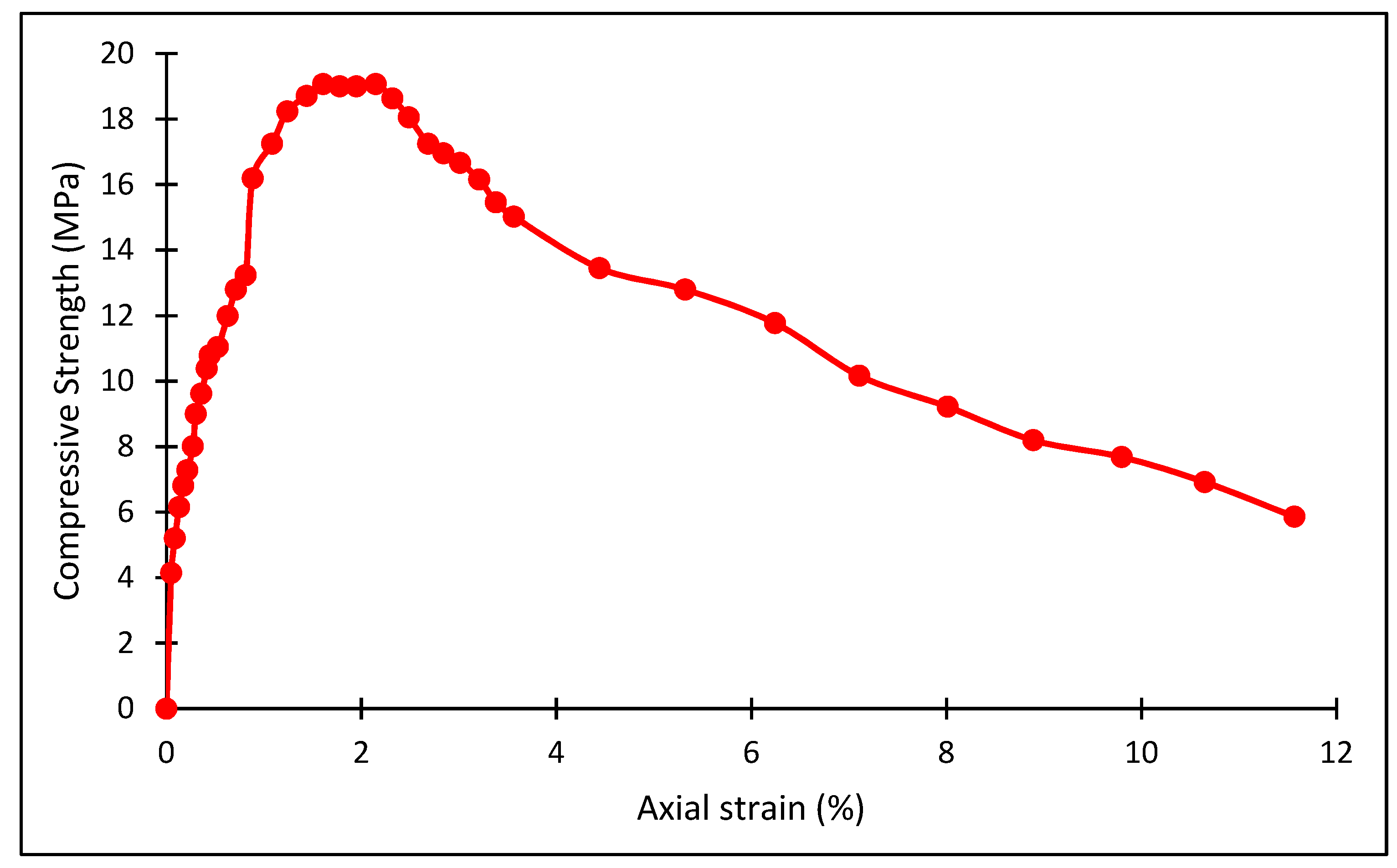
3.1. Method I
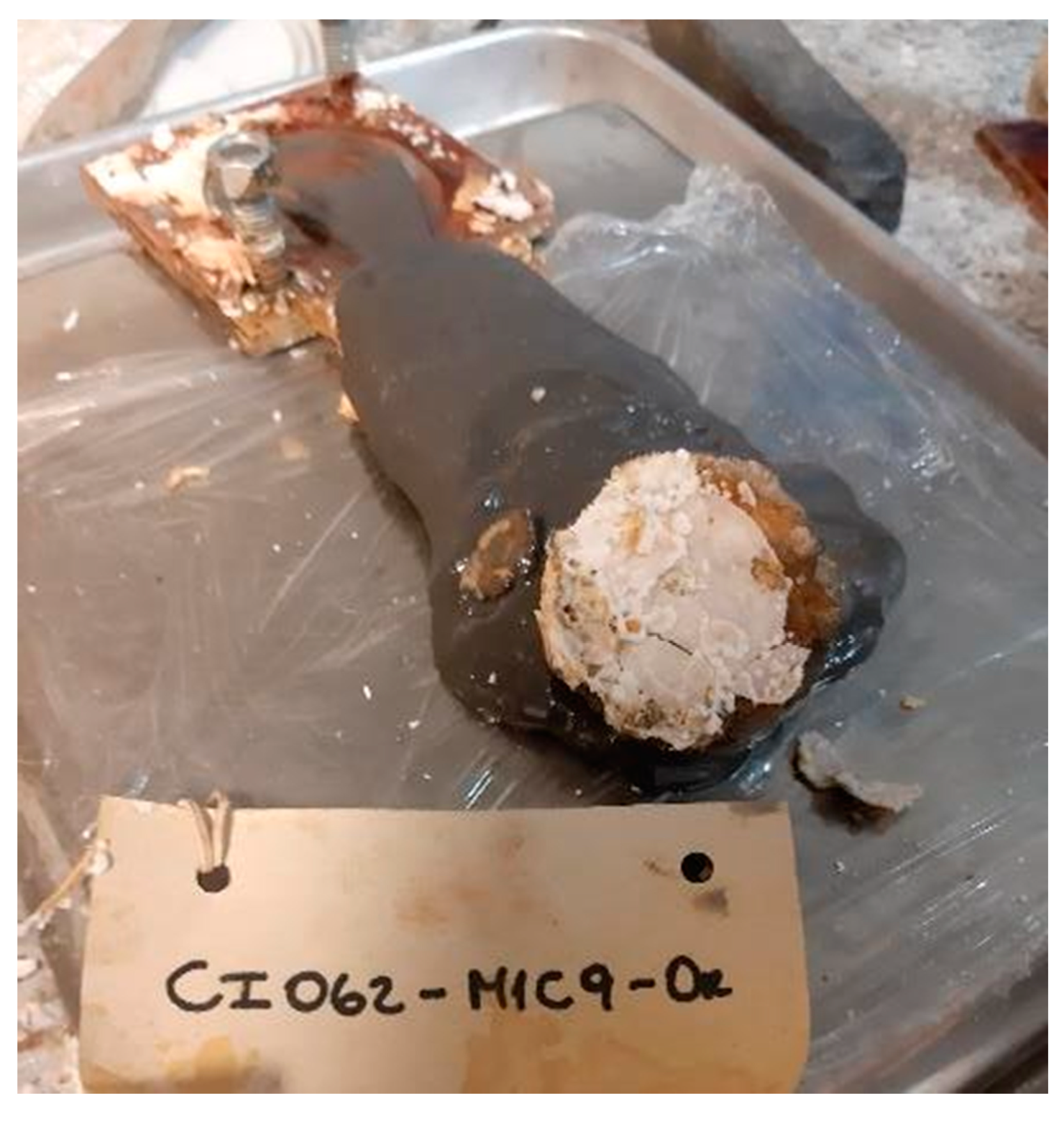
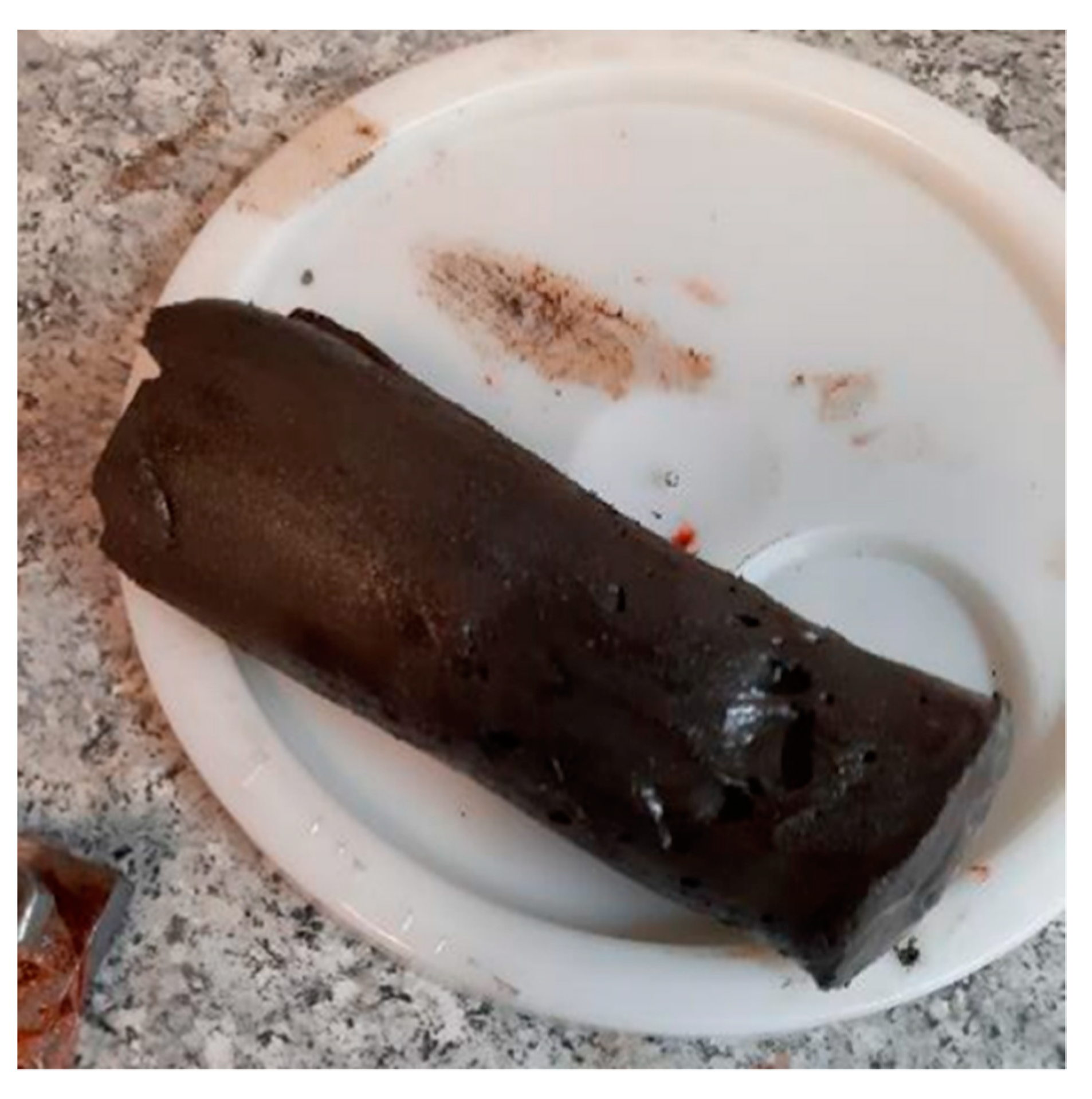
3.2. Method II
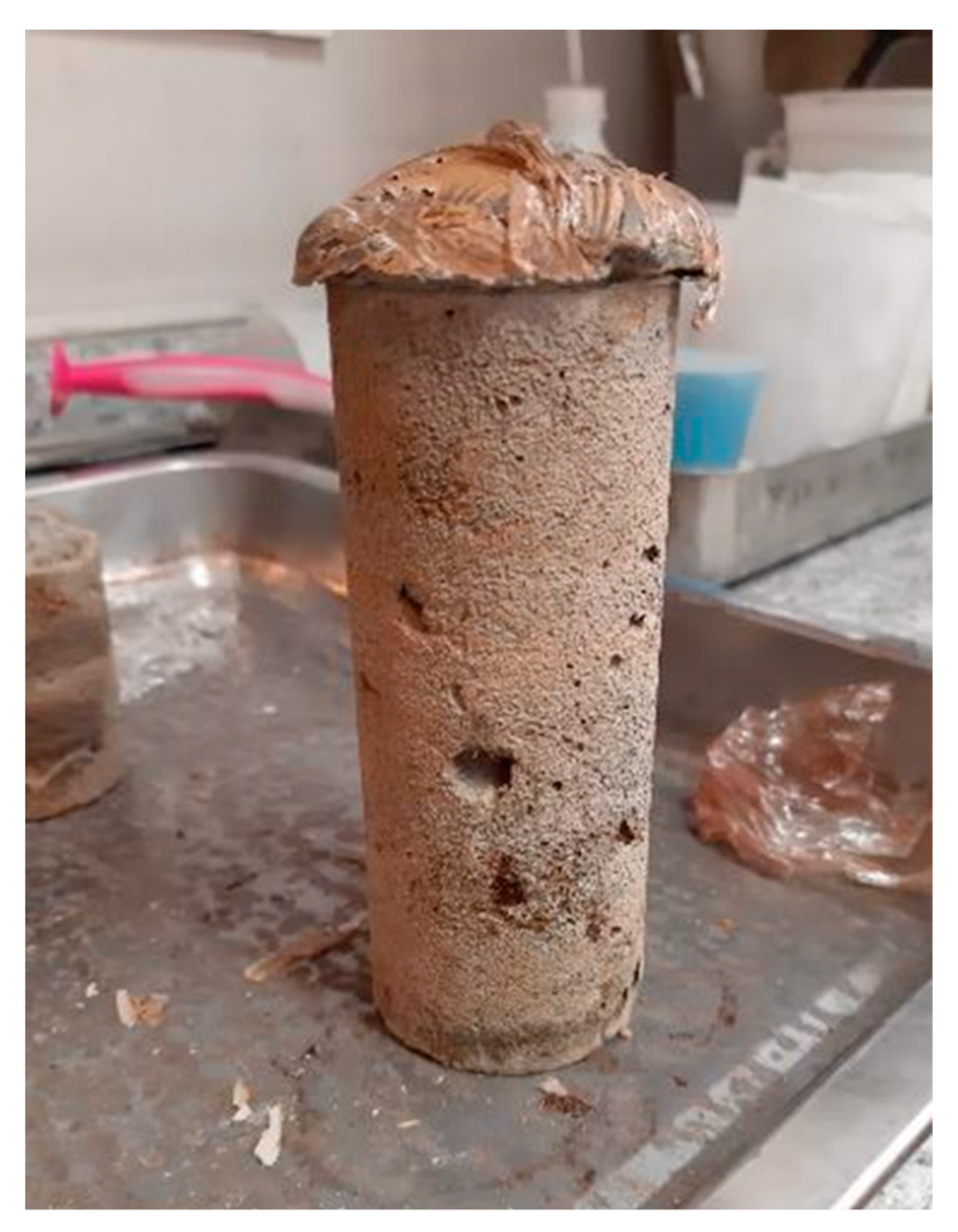
3.3. Method III
3.4. Method IV
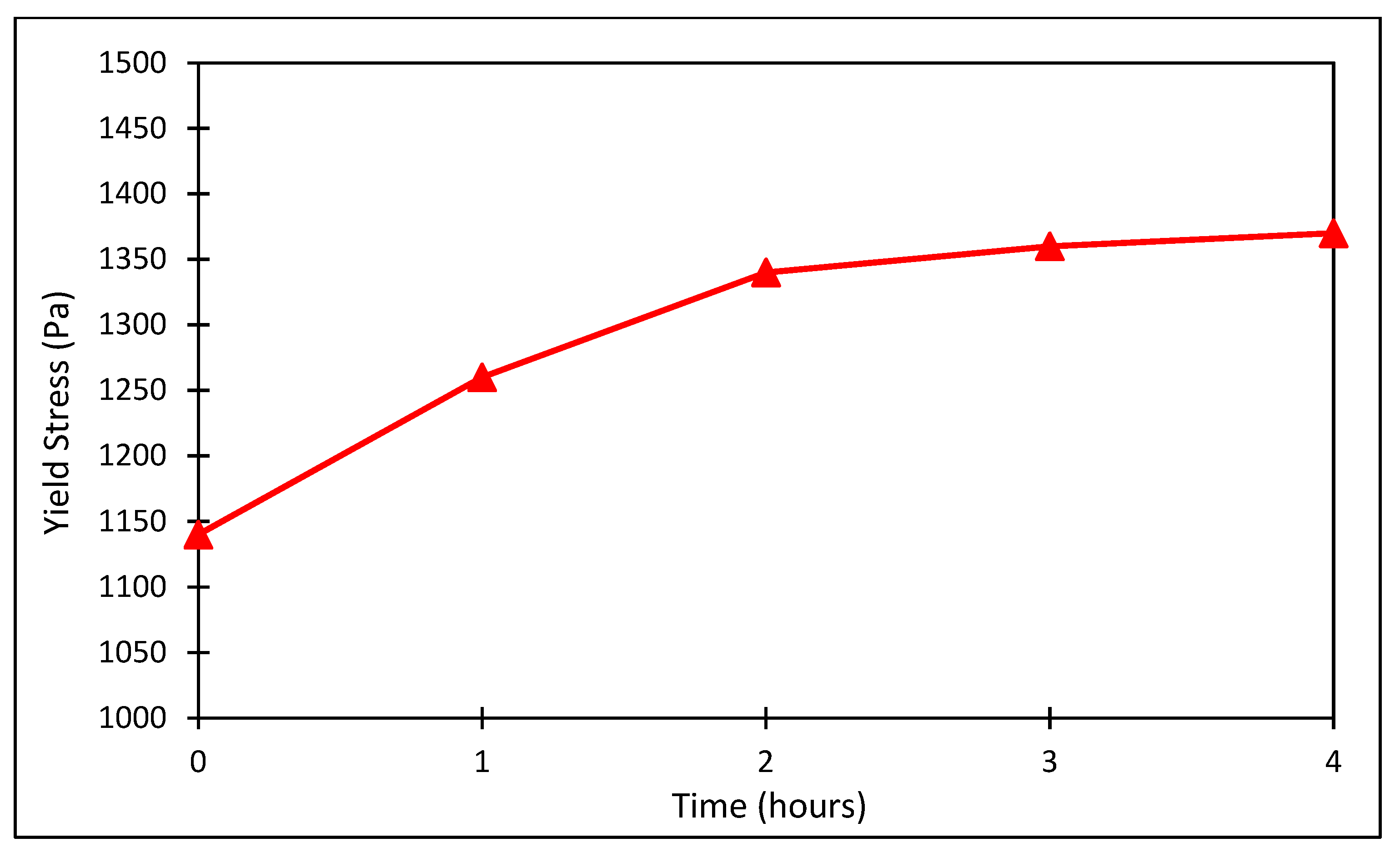
3.5. Method V
3.6. Method VI
3.7. Method VII
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, Q.; Rao, F.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y. Immobilization forms of ZnO in the solidification/stabilization (S/S) of a zinc mine tailing through geopolymerization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5728–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xu, W.; Song, S.; Rao, F.; Xia, L. Effects of curing temperature on the compressive strength and microstructure of copper tailing-based geopolymers. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmari, S.; Zhang, L. Production of eco-friendly bricks from copper mine tailings through geopolymerization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Feng, Q.; An, D.; Zhang, J. Use of Mine Tailings as Precast Construction Materials through Alkali Activation. Min. Metall. Explor. 2020, 37, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranchie, F.A.; Shukla, S.K.; Habibi, D. Utilisation of iron ore mine tailings for the production of geopolymer bricks. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2014, 30, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Patel, A.K.; Kumar, M. Reappraisal review on geopolymer: A new era of aluminosilicate binder for metal immobilization. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Liu, J.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Jiang, Q. Property and microstructure of aluminosilicate inorganic coating for concrete: Role of water to solid ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, K.Z.; Johari, M.A.M.; Demirboğa, R. Assessment of important parameters involved in the synthesis of geopolymer composites: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaai, Y.; Yahia, A.; Mostafa, A.; Aggoun, S.; Kadri, E.-H. Rheology of fly ash-based geopolymer: Effect of NaOH concentration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadoushan, M.J.; Ramezanianpour, A.A. The effect of type and concentration of activators on flowability and compressive strength of natural pozzolan and slag-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görhan, G.; Aslaner, R.; Şinik, O. The effect of curing on the properties of metakaolin and fly ash-based geopolymer paste. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 97, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurruddin, M.F.; Haruna, S.; Mohammed, B.S.; Galal, I. Methods of curing geopolymer concrete: A review. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Kayali, O. Effect of initial water content and curing moisture conditions on the development of fly ash-based geopolymers in heat and ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderji, S.Y.; Chen, B.; Ahmad, M.R.; Shah, S.F.A. Fresh and hardened properties of one-part fly ash-based geopolymer binders cured at room temperature: Effect of slag and alkali activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Shaikh, F.; Mishra, J.; Lazorenko, G.; Kasprzhitskii, A. Mine tailings-based geopolymers: Properties, applications and industrial prospects. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 17826–17843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications, 2nd ed.; Institut Geopolymere: Saint Quentin, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahedan, N.; Abdullah, M.; Mahmed, N.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Tammas-Williams, S.; Li, L.-Y.; Aziz, I.; Vizureanu, P.; Wysłocki, J.; Błoch, K.; et al. Properties of a New Insulation Material Glass Bubble in Geo-Polymer Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, N.A.; Rangan, B.V. Geopolymer concrete: A review of development and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Our World in Concrete & Structures, Singapore, 25–27 August 2010; pp. 25–27. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/ (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Ouffa, N.; Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Trauchessec, R.; Lecomte, A. Alkaline dissolution potential of aluminosilicate minerals for the geosynthesis of mine paste backfill. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Tian, S.; Sun, Q.; Li, B.; Cai, C.; Xia, Y.; Wei, X.; Mu, Q. Preparation and microstructure of fly ash geopolymer paste backfill material. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjarrez, L.; Nikvar-Hassani, A.; Shadnia, R.; Zhang, L. Experimental Study of Geopolymer Binder Synthesized with Copper Mine Tailings and Low-Calcium Copper Slag. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S. Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, M.; Ranjith, P.; Rathnaweera, T.; Perera, S. Recent advances in alkaline cement binders: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmari, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of activator type/concentration and curing temperature on alkali-activated binder based on copper mine tailings. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 5933–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.H.; Xia, M.; Nematollahi, B.; Shi, C. Ambient temperature cured ‘just-add-water’ geopolymer for 3D concrete printing applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, M.M.; Canpolat, O. Effect of various NaOH molarities and various filling materials on the behavior of fly ash based geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, R.M.; Man, Z.; Azizli, K.A. Concentration of NaOH and the Effect on the Properties of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Zhao, K.-F.; Xie, F.-Z.; Li, H.; Wang, D.-M. Effect of water-binding ability of amorphous gel on the rheology of geopolymer fresh pastes with the different NaOH content at the early age. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouhet, R.; Cyr, M.; Bucher, R. Influence of the initial water content in flash calcined metakaolin-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Shafiq, N. Effects of Sand/Fly Ash and the Water/Solid Ratio on the Mechanical Properties of Engineered Geopolymer Composite and Mix Design Optimization. Minerals 2020, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahoti, M.; Yang, E.-H.; Tan, K.H. Influence of Mix Design Parameters on Geopolymer Mechanical Properties and Microstructure. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 2017, 37, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagral, M.R.; Ostwal, T.; Chitawadagi, M.V. Effect Of Curing Temperature And Curing Hours On The Properties Of Geo-Polymer Concrete. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Res. 2014, 4, 2250–3005. [Google Scholar]
- Lahoti, M.; Narang, P.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.-H. Mix design factors and strength prediction of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 11433–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Dinakar, P.; Rao, B.H. Mix design development of fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag based geopolymer concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ahmari, S.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and characterization of fly ash modified mine tailings-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obenaus-Emler, R.; Falah, M.; Illikainen, M. Assessment of mine tailings as precursors for alkali-activated materials for on-site applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouhet, R.; Cyr, M. Carbonation in the pore solution of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Castel, A.; Noushini, A. Carbonation of a low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2017, 69, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Vollpracht, A. One year geopolymerisation of sodium silicate activated fly ash and metakaolin geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L. Activating solution chemistry for geopolymers. In Geopolymers Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: New Delhi, India, 2009; pp. 50–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Rees, C.A. Geopolymer Synthesis Kinetics. In Geopolymers Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: New Delhi, India, 2009; pp. 118–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjito, D.; Rangan, B.V. Development and properties of low-calcium fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Res. Rep. GC 2005, 94. Available online: http://www.geopolymer.org/fichiers_pdf/curtin-flyash-GP-concrete-report.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Kong, D.L.Y.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Factors affecting the performance of metakaolin geopolymers exposed to elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmari, S.; Parameswaran, K.; Zhang, L. Alkali Activation of Copper Mine Tailings and Low-Calcium Flash-Furnace Copper Smelter Slag. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, A.; Provis, J.; Qiao, G.; van Deventer, J.S. The interrelationship between surface chemistry and rheology in alkali activated slag paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.; Van Deventer, J. Effect of silicate activator pH on the leaching and material characteristics of waste-based inorganic polymers. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharzouni, A.; Joussein, E.; Samet, B.; Baklouti, S.; Rossignol, S. Effect of the reactivity of alkaline solution and metakaolin on geopolymer formation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 410, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyte, L.M. Fly Ash Glass Chemistry and Inorganic Polymer Cements; Woodhead Publishing Limited: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Composition and microstructure of alkali activated fly ash binder: Effect of the activator. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Nanostructure/microstructure of fly ash geopolymers. Geopolym. Struct. Process. Prop. Ind. Appl. 2009, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Shibata, J. Mechanism of zeolite synthesis from coal fly ash by alkali hydrothermal reaction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2002, 64, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
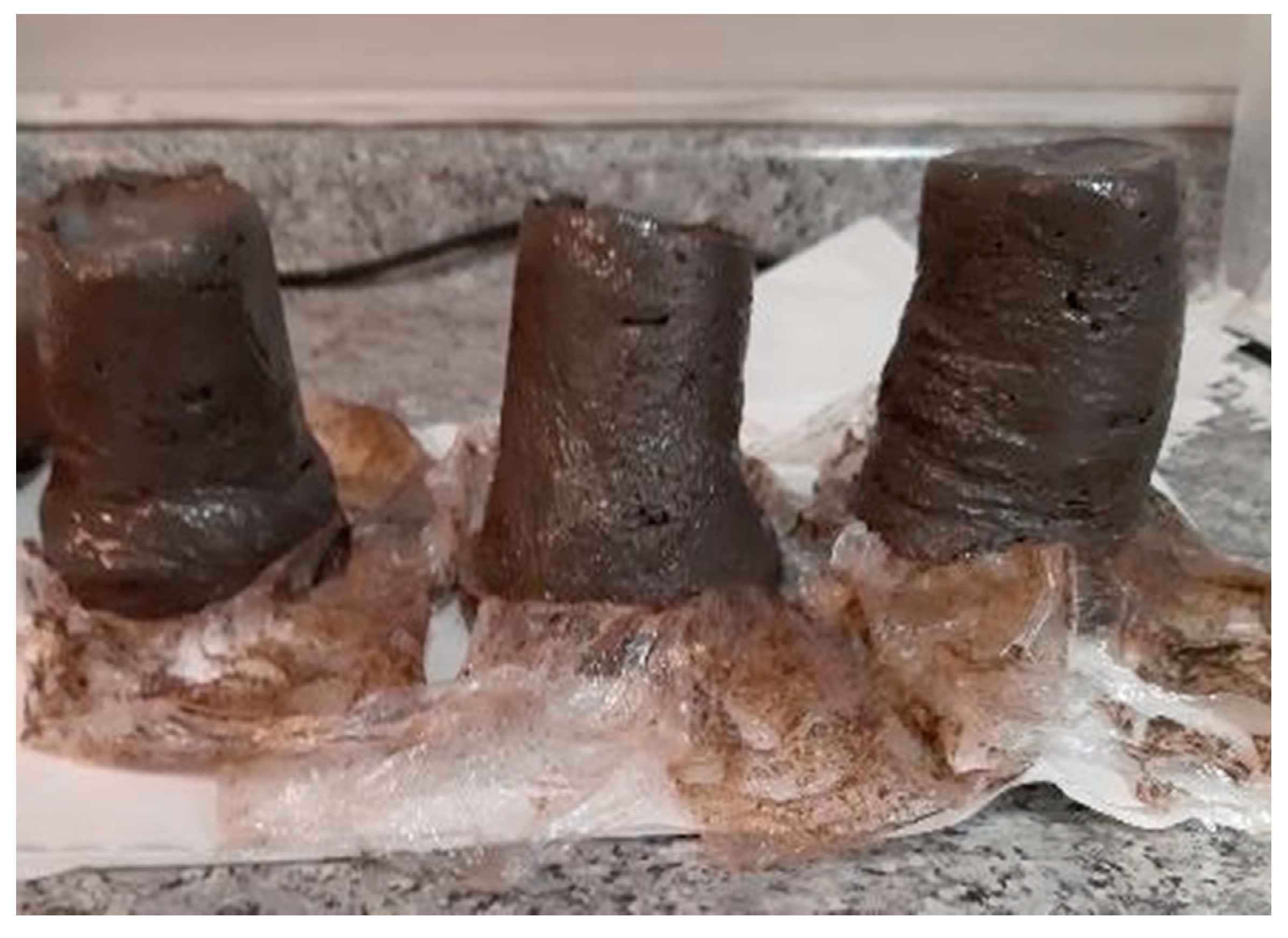
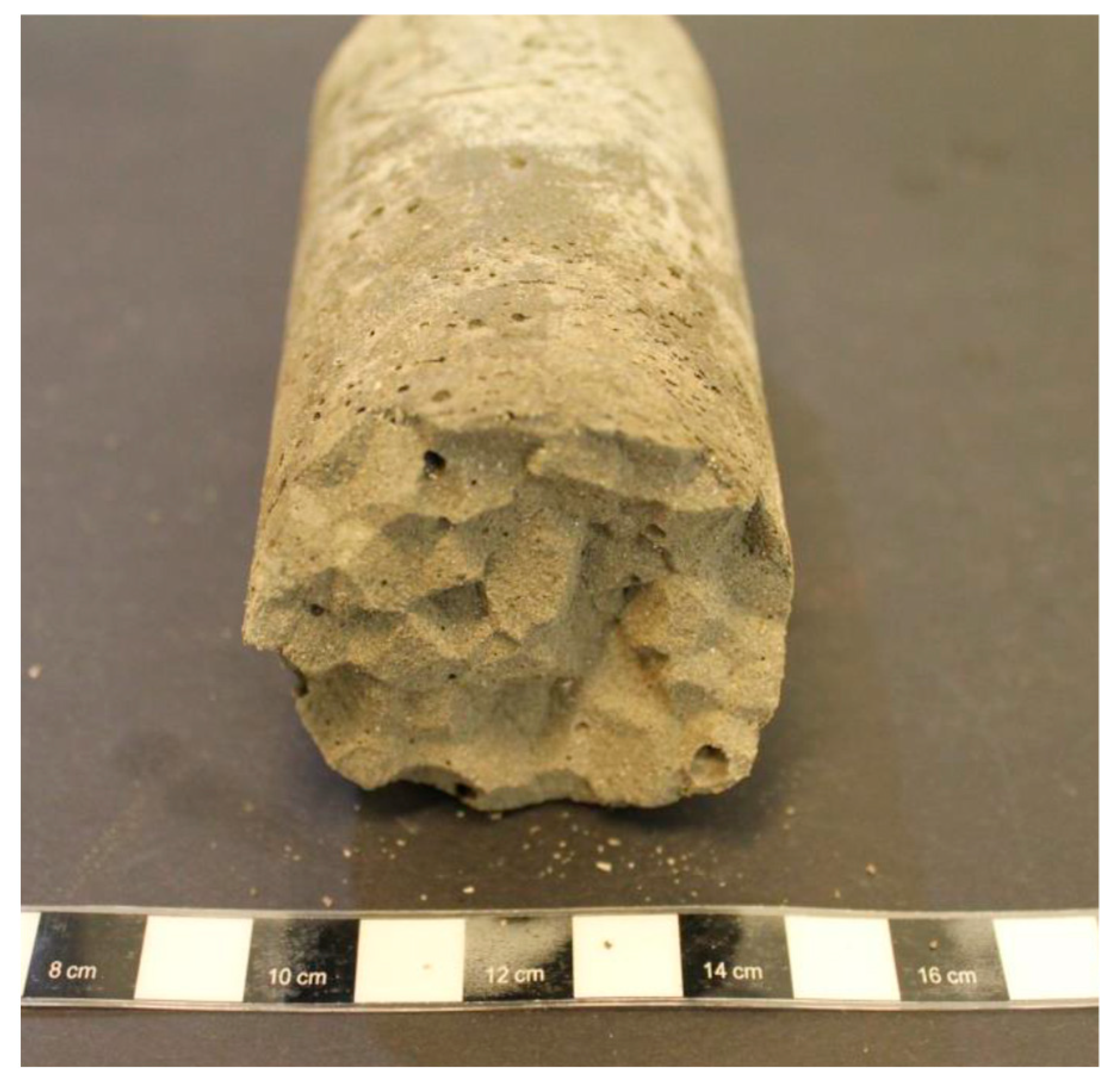



















| Element | Concentration [mg/L] | Element | Concentration [mg/L] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 26.95 | K | 1.19 |
| Al | 9.50 | Ti | 0.60 |
| Fe | 8.05 | Mn | 0.25 |
| Ca | 3.28 | S | 0.12 |
| Na | 2.67 | Cr | <0.01 |
| Mg | 2.10 |
| Element | Concentration [mg/L] | Element | Concentration [mg/L] |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 215 | Ta | <1.00 |
| K | 210 | Th | <1.00 |
| Na | 158 | Tl | <1.00 |
| K | 28 | W | <1.00 |
| Mg | 23 | As | <0.50 |
| Al | <5 | La | <0.50 |
| Fe | <5 | Li | <0.50 |
| Ti | <5 | P | <0.50 |
| Sr | 1.7 | Sb | <0.50 |
| Ga | <1.00 | Sc | <0.50 |
| Nb | <1.00 | Te | <0.50 |
| Sn | <1.00 | Ag | <0.25 |
| - | - | Bi | <0.25 |
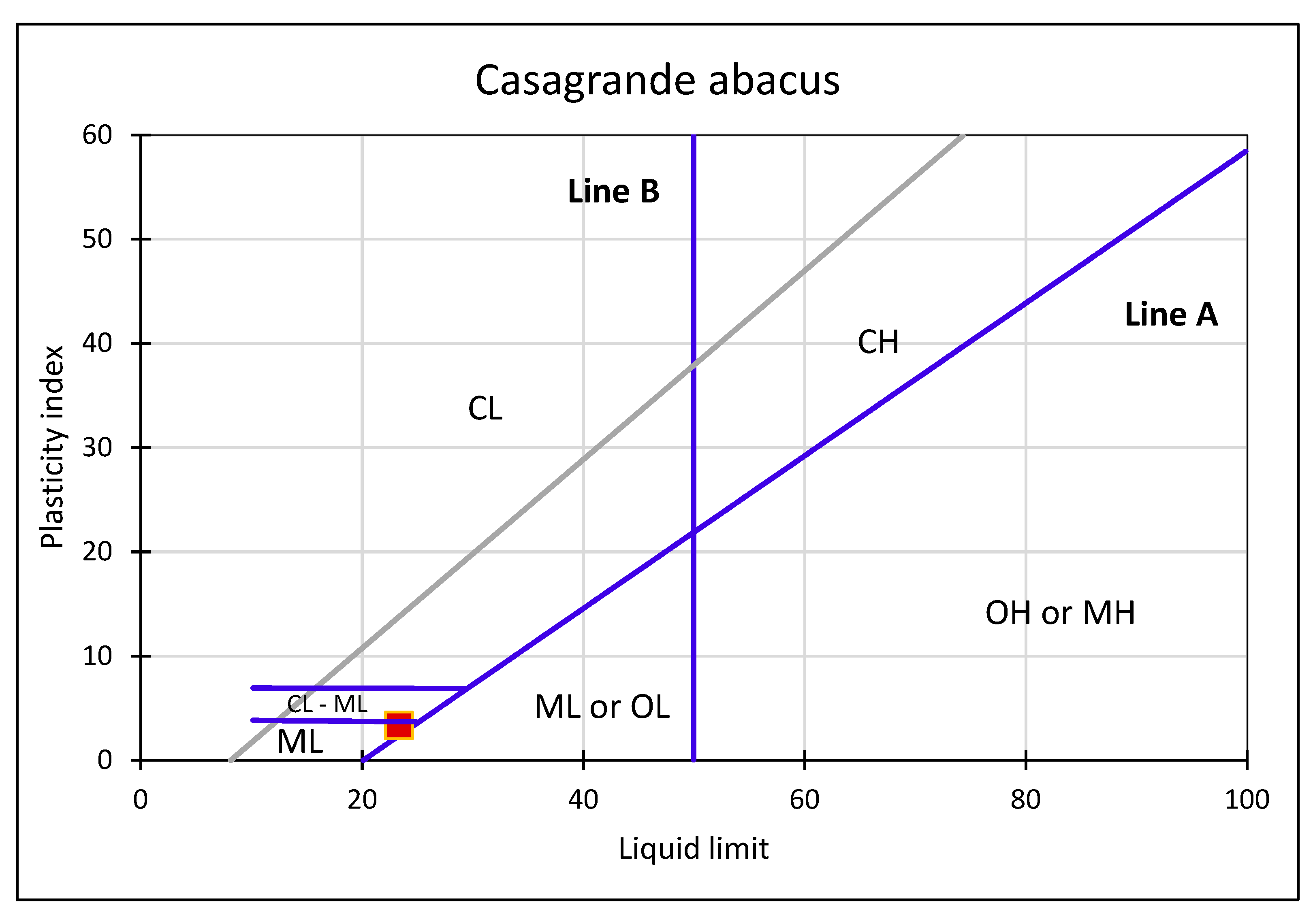
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Liquid limit | 23.3% |
| Plastic limit | 19.7% |
| Shrinkage limit | 20.5% |
| Plasticity index | 3.5% |
| N° | Concentration [M] | Water/Solids [%] | Mixture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | 30 | M1-C1 |
| 2 | 14 | 30 | M1-C2 |
| 3 | 16 | 30 | M1-C3 |
| 4 | 12 | 35 | M1-C4 |
| 5 | 14 | 35 | M1-C5 |
| 6 | 16 | 35 | M1-C6 |
| 7 | 12 | 40 | M1-C7 |
| 8 | 14 | 40 | M1-C8 |
| 9 | 16 | 40 | M1-C9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo, H.; Collado, H.; Droguett, T.; Sánchez, S.; Vesely, M.; Garrido, P.; Palma, S. Methodologies for the Possible Integral Generation of Geopolymers Based on Copper Tailings. Minerals 2021, 11, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121367
Castillo H, Collado H, Droguett T, Sánchez S, Vesely M, Garrido P, Palma S. Methodologies for the Possible Integral Generation of Geopolymers Based on Copper Tailings. Minerals. 2021; 11(12):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121367
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo, Hengels, Humberto Collado, Thomas Droguett, Sebastián Sánchez, Mario Vesely, Pamela Garrido, and Sergio Palma. 2021. "Methodologies for the Possible Integral Generation of Geopolymers Based on Copper Tailings" Minerals 11, no. 12: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121367
APA StyleCastillo, H., Collado, H., Droguett, T., Sánchez, S., Vesely, M., Garrido, P., & Palma, S. (2021). Methodologies for the Possible Integral Generation of Geopolymers Based on Copper Tailings. Minerals, 11(12), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121367






