Rare Earth Elements Enrichment in the Upper Eocene Tošići-Dujići Bauxite Deposit, Croatia, and Relation to REE Mineralogy, Parent Material and Weathering Pattern
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
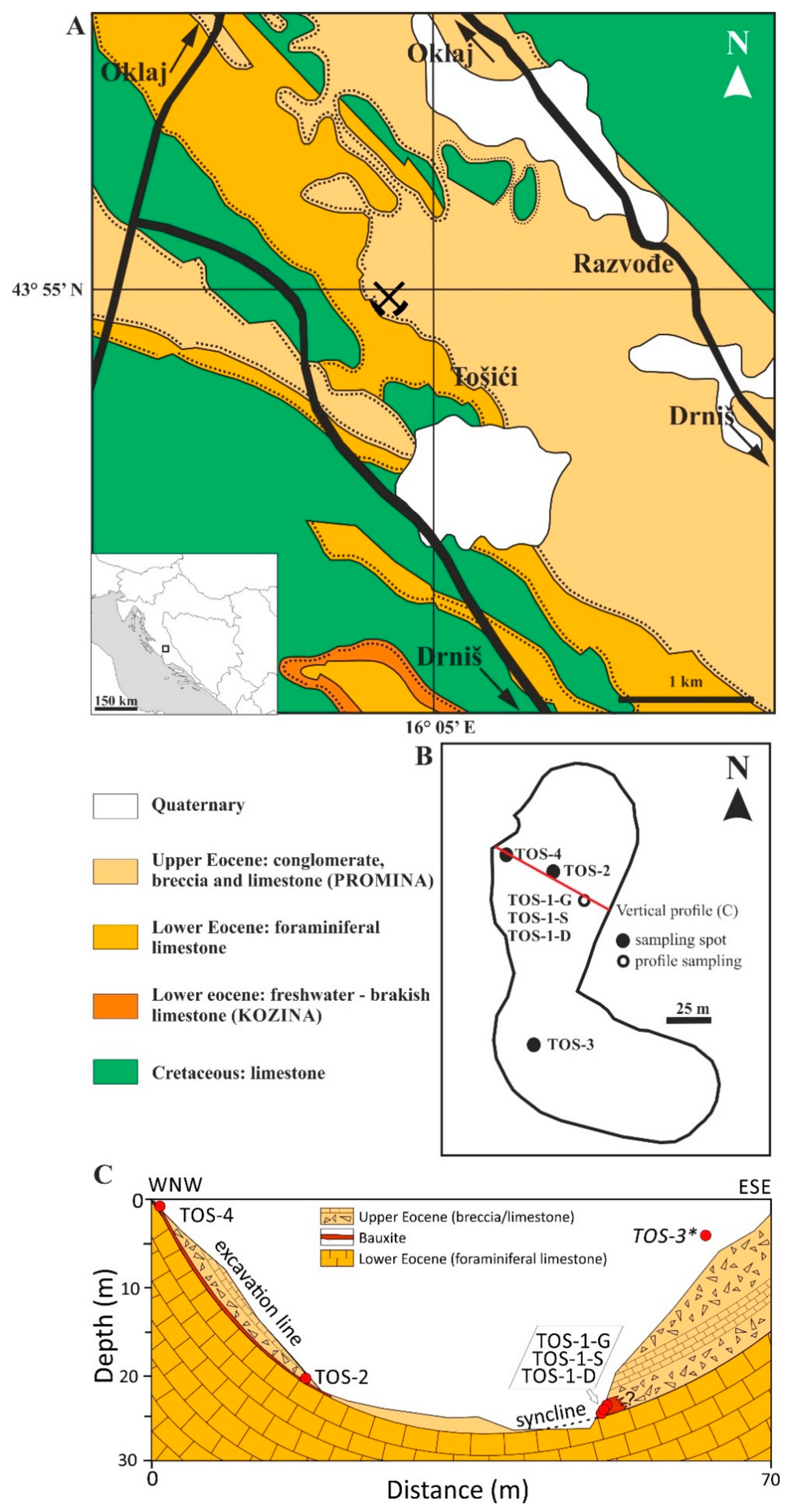
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Textural and Mineralogical Properties
| Sample | Topographic Depth (m) | Texture | Major Phases | Minor Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOS-1-D | 25 | Pseudoporphyritic with anhedral to globular gibbsite, and hematite nodules up to 200 μm in very fine grained matrix | gibbsite, hematite | böhmite, anatase, nordstrandite |
| TOS-1-S | 24 | Microgranular with anhedral to subhedral gibbsite up to 100 μm in diameter | gibbsite, hematite | goethite, böhmite, anatase, rutile |
| TOS-1-G | 23 | Panidiomorphic to granular texture, idiomorphic gibbsite and sphaerical hematite, all up to 100 μm | gibbsite, kaolinite, hematite | anatase, böhmite |
| TOS-2 | 19 | Pisoidic (gibbsitic in core), also including anhedral gibbsite 20–100 μm in diameter, hematitic nodules up to 150 μm | gibbsite, hematite | böhmite, anatase, nordstrandite, illite |
| TOS-3 | 3.5 | Pisoidic (more hematitic) with microgranular (subpanidiomoprhic) to pseudoporphyritic structure also including subhedral gibbsite; secondary filled crevices implying redeposition | gibbsite, kaolinite, goethite, hematite | anatase, böhmite, illite |
| TOS-4 | 0.5 | Microgranular, anhedral to subhedral gibbsite grains up to 50 μm in diameter, also nodules with tiny hematite and anatase | gibbsite, kaolinite, hematite | anatase |
4.2. Geochemical Signature
4.2.1. REE Distribution
| Bauxite Age/REE Subdivision Totals | Vojnik-Maganik Bauxite Region (Montenegro) * | Vojnik-Maganik & Prekornica Bauxite Region (Montenegro) * | Parnassos-Giona (Greece) | Vecchia Miniera Abruzzi (Italy) | Campo Felice, Abruzzi (Italy) | Tošići-Dujići (Croatia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bauxite/ paleorelief Age | Late Triassic | Early Jurassic | Late Jurassic-Middle Cretaceous | Early/Late Cretaceous | Early/Late Cretaceous | Late Eocene |
| Y | 128 | 128 | 44–159 | 72–93 | 83–105 | 127–1346 |
| Total Ln | 840 | 929 | 343–1122 | 631–912 | 592–933 | 832–2150 |
| LREE | 755 | 841 | 317–948 | 567–664 | 526–854 | 724–1589 |
| HREE | 213 | 216 | 71–333 | 134–160 | 152–183 | 217–1907 |
| Total REE | 968 | 1057 | 387–1282 | 718–984 | 689–1038 | 959–3496 |
| LREE/HREE | 3.5 | 3.9 | 2.8–4.5 | 3.7–6.3 | 3.2–4.7 | 0.4–3.4 |
4.2.2. REE Fractionation, Implications to Origin of Parent Material, and Its Fate during Bauxitization
4.3. REE Mineralogy
4.4. Chemical Weathering Intensity
4.5. Mass Change Calculations and Relation to Parent Material
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marković, S. Hrvatske Mineralne Sirovine; Institut za Geološka Istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 2002; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough, K.M.; Schilling, J.; Jonsson, E.; Kalvig, P.; Charles, N.; Tuduri, J.; Deady, E.A.; Sadeghi, M.; Schiellerup, H.; Müller, A.; et al. Europe’s rare earth element resource potential: An overview of REE metallogenetic provinces and their geodynamic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deady, É.A.; Mouchos, E.; Goodenough, K.; Williamson, B.J.; Wall, F. A review of the potential for rare-earth element resources from European red muds: Examples from Seydişehir, Turkey and Parnassus-Giona, Greece. Mineral. Mag. 2016, 80, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deady, E.; Mouchos, E.; Goodenough, K.; Williamson, B.; Wall, F. Rare earth elements in karst-bauxites: A novel untapped European resource? In Proceedings of the ERES2014: 1st European Rare Earth Resources Conference, Milos, Greece, 4–7 September 2014; pp. 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimović, Z.; Pantó, G. Authigenic rare earth minerals in karst-bauxites and karstic nickel deposits. In Rare Earth Minerals, Chemistry, Origin and Ore Deposits; Jones, P.A., Wall, F., Williams, C.T., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996; pp. 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Radusinović, S.; Jelenković, R.; Pačevski, A.; Simić, V.; Božović, D.; Holclajtner-Antunović, I.; Životić, D. Content and mode of occurrences of rare earth elements in the Zagrad karstic bauxite deposit (Nikšić area, Montenegro). Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 406–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, G.; Panto, G.; Varhegyi, G. Rare metals in Hungarian bauxites and conditions of their utilization. Trav. ICSOBA Int. Comm. Study Bauxite Alumina Alum. 1976, 13, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, M.; Rollinson, G.; Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Santoro, L. Quantitative mineralogical characterization of karst bauxite deposits in the southern Apennines, Italy. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mongelli, G. Ce-anomalies in the textural components of Upper Cretaceous karst bauxites from the Apulian carbonate platform (southern Italy). Chem. Geol. 1997, 140, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G.; Boni, M.; Buccione, R.; Sinisi, R. Geochemistry of the Apulian karst bauxites (southern Italy): Chemical fractionation and parental affinities. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanović, A.; Sikirica, V.; Sakač, K. Osnovna Geološka Karta SFRJ 1:100.000. Tumač za List Drniš L33–9; Institut za Geološka Istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 1972; Savezni Geološki Institut: Beograd, Yugoslavia, 1978; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kruk, B.; Dedić, Ž.; Kovačević Galović, E.; Kruk, L. Osnove Gospodarenja Mineralnim Sirovinama na Području Općine Promina u Šibensko-Kninskoj Županiji, Documentation fund 50/14; Hrvatski geološki institut: Zagreb, Croatia, 2014; pp. 40–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sakač, K. O paleoreljefu i pseudopaleoreljefu boksitnih ležišta područja krša. Geološki Vjesn. 1966, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sakač, K. Analiza eocenskog paleoreljefa i tektonskih zbivanja u području Drniša u Dalmaciji s obzirom na postanak ležišta boksita. Geološki Vjesn. 1970, 23, 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanović, A.; Sikirica, V.; Marković, S.; Sakač, K. Osnovna Geološka Karta SFRJ 1:100.000. List Drniš L33–9; Institut za Geološka Istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 1967–1972; Savezni Geološki Institut: Beograd, Yugoslavia, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Bárdossy, G.; Aleva, G.J.J. Lateritic bauxites. Dev. Econ. Geol. 1990, 27, 1–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, G. Karst Bauxites: Bauxite Deposits on Karbonate Rocks (Developments in Economic Geology); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; pp. 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- Valeton, I. Bauxites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972; pp. 1–226. [Google Scholar]
- Temur, S.; Kansun, G. Geology and petrography of the Masatdagi diasporic bauxites, Alanya, Antalya, Turkey. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 27, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, R.W.N.D.; De Araujo Rocha, G.; Montes, C.R.; Vieira-Coelho, A.C. Synthesis and characterization of boehmites obtained from gibbsite in presence of different environments. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Argenio, B.; Mindszenty, A. Bauxites and related paleokarst: Tectonic and climatic event markers at regional unconformities. Eclogae Geol. Helv. 1995, 88, 459–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, K.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Tang, H.S.; Wang, Z.G.; Yan, H.W.; Han, T.; Chen, W.Y. Mineralogical characteristics of the karstic bauxite deposits in the Xiuwen ore belt, Central Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.E.; Hill, V.G. Occurrence of Nordstrandite and its possible significance in Jamaica bauxites. Trav. ICSOBA Int. Comm. Study Bauxite Alumina Alum. 1974, 11, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Triebold, S.; Luvizotto, G.L.; Tolosana-Delgado, R.; Zack, T.; von Eynatten, H. Discrimination of TiO2 polymorphs in sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 161, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadnejad, F.; Zamanian, H.; Taghipour, B.; Zarasvandi, A.; Buccione, R.; Salamab Ellahi, S. Mineralogical and geochemical evolution of the Bidgol bauxite deposit, Zagros Mountain Belt, Iran: Implications for ore genesis, rare earth elements fractionation and parental affinity. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 86, 755–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimovic, Z.; Pantó, G. Contribution to the geochemistry of the rare earth elements in the karst-bauxite deposits of Yugoslavia and Greece. Geoderma 1991, 51, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahi, S.S.; Taghipour, B.; Zarasvandi, A.; Bird, M.I.; Somarin, A.K. Mineralogy, geochemistry and stable isotope studies of the Dopolan bauxite deposit, Zagros mountain, Iran. Minerals 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meshi, A.; Hoxha, I.; Milushi, I. Chromitites in the Mirdita ophiolite (Albania): Structure and genetic implications. J. Alp. Geol. 2005, 47, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cudennec, Y.; Lecerf, A. The transformation of ferrihydrite into goethite or hematite, revisited. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleva, G.J.J. Laterites: Concepts, Geology, Morphology and Chemistry; InternatiSoil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC): Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Schellmann, W. A new definition of laterite. Mem. Geol. Surv. India 1986, 120, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Putzolu, F.; Papa, A.P.; Mondillo, N.; Boni, M.; Balassone, G.; Mormone, A. Geochemical characterization of bauxite deposits from the Abruzzi Mining district (Italy). Minerals 2018, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mameli, P.; Mongelli, G.; Oggiano, G.; Dinelli, E. Geological, geochemical and mineralogical features of some bauxite deposits from Nurra (Western Sardinia, Italy): Insights on conditions of formation and parental affinity. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radusinović, S.; Papadopoulos, A. The potential for REE and associated critical metals in karstic bauxites and bauxite residue of Montenegro. Minerals 2021, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wakita, H.; Ray, P.; Schmit, R.A. Abundances of 14 rare-earth elements and 12 other trace elements in Apollo 12 samples: Five igneous and one breccia rocks and four soils. In Proceedings of the Second Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 11–14 January 1971; The M.I.T. Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; Volume 2, pp. 1319–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Laufer, F.; Yariv, S.; Steinberg, M. The adsorption of quadrivalent cerium by kaolinite. Clay Miner. 1984, 19, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaor, D.A.H.; Sorrell, C.C. Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Boni, M.; Chelle-Michou, C.; Cretella, S.; Mormone, A.; Putzolu, F.; Santoro, L.; Scognamiglio, G.; Tarallo, M. Rare earth elements (REE) in Al- and Fe-(oxy)-hydroxides in bauxites of provence and languedoc (Southern France): Implications for the potential recovery of rees as by-products of bauxite mining. Minerals 2019, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.; Yang, X.; Werner, J.M.; Honaker, R.Q. Application of Eh-pH Diagrams on Acid Leaching Systems for the Recovery of REEs from Bastnaesite, Monazite and Xenotime. Metals 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskin, L.A.; Haskin, M.A.; Frey, F.A.; Wildeman, T.R. Relative and Absolute Terrestrial Abundances of the Rare Earths. In Origin and Distribution of the Elements; Ahrens, L.H., Ed.; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 889–912. [Google Scholar]
- Mongelli, G. REE and other trace elements in a granitic weathering profile from “Serre”, southern Italy. Chem. Geol. 1993, 103, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, H.; Ahmadnejad, F.; Zarasvandi, A. Mineralogical and geochemical investigations of the Mombi bauxite deposit, Zagros Mountains, Iran. Chemie Erde 2016, 76, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, W.H.; Bonavia, F.F.; Sanna, G. Argillite debris converted to bauxite during karst weathering: Evidence from immobile element geochemistry at the Olmedo Deposit, Sardinia. Miner. Depos. 1997, 32, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, E.; Sauer, D. Beitrag zur Geochemie von titan, chrom, nikel, cobalt, vanadium und molibdan in bauxitischen gestermenund problem der stofflichen herkunft des aluminiums. Trav. ICSOBA Int. Comm. Study Bauxite Alumina Alum. 1968, 5, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Condie, K.C. Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: Contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chem. Geol. 1993, 104, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A.A. A system of nomenclature for rare-earth minerals. Am. Mineral. 1966, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss, P.; Levinson, A.A. A system of nomenclature for rare-earth mineral species: Revision and extension. Am. Mineral. 1988, 73, 422–423. [Google Scholar]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Stetzenbach, K.J.; Byrne, R.H. The solubility control of rare earth elements in natural terrestrial waters and the significance of PO43- and CO32- in limiting dissolved rare earth concentrations: A review of recent information. Aquat. Geochem. 1995, 1, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom-Fendley, S.; Brady, A.E.; Wall, F.; Gunn, G.; Dawes, W. REE minerals at the Songwe Hill carbonatite, Malawi: HREE-enrichment in late-stage apatite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmandt, D.S.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Ehrig, K.; Wade, B.P.; Gilbert, S.; Kamenetsky, V.S. Rare earth element phosphate minerals from the olympic dam Cu-U-Au-Ag deposit, South Australia: Recognizing temporal-spatial controls on ree mineralogy in an evolved iocg system. Can. Mineral. 2019, 57, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, R.T.; Barnes, H.L. Formation processes of framboidal pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L.; Liang, X. Geochemical record of chemical weathering and monsoon climate change since the early Miocene in the South China Sea. Paleoceanography 2006, 21, PA4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Major/Trace Component | TOS-1-D | TOS-1-S | TOS-1-G | TOS-2 | TOS-3 | TOS-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major components (wt%) | ||||||
| SiO2 | 2.21 | 4.14 | 8.98 | 2.49 | 6.78 | 14.2 |
| Al2O3 | 47.12 | 46.43 | 47.34 | 46.82 | 33.79 | 41.05 |
| Fe2O3 | 19.05 | 19.65 | 12.57 | 19.97 | 35.08 | 17.83 |
| MgO | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.32 |
| CaO | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 0.37 |
| Na2O | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| K2O | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.16 |
| TiO2 | 2.3 | 2.22 | 2.38 | 2.1 | 1.54 | 2.05 |
| P2O5 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.15 |
| MnO | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.112 | 0.125 | 0.153 | 0.133 | 0.092 | 0.165 |
| Ni | 397 | 393 | 704 | 479 | 564 | 554 |
| Sc | 67 | 69 | 55 | 75 | 67 | 61 |
| LOI | 27 | 25.8 | 26.1 | 25.9 | 20.6 | 22.9 |
| Total | 99.44 | 99.42 | 99.32 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.45 |
| Rare earth elements (mg/kg) | ||||||
| Y | 127.3 | 179.1 | 353.9 | 1346.1 | 1328 | 408.1 |
| La | 197.4 | 214 | 228.7 | 465.2 | 158.5 | 191.7 |
| Ce | 364.4 | 361.4 | 368.5 | 347.8 | 253.4 | 283.4 |
| Pr | 32.98 | 38.94 | 45.57 | 113.06 | 37.81 | 36.84 |
| Nd | 118 | 144.3 | 203.3 | 523.6 | 199.3 | 148.9 |
| Sm | 24.13 | 27.75 | 49.54 | 109.69 | 59.83 | 37.25 |
| Eu | 5.51 | 6.67 | 11.85 | 29.42 | 15.69 | 9.61 |
| Gd | 22.73 | 28.7 | 55.66 | 182.12 | 82.03 | 48.79 |
| Tb | 3.88 | 4.67 | 7.99 | 24.92 | 11.6 | 7.86 |
| Dy | 23.61 | 29.5 | 46.27 | 149.25 | 70.48 | 49.31 |
| Ho | 4.95 | 6.07 | 9.87 | 35.82 | 17.08 | 10.98 |
| Er | 15.12 | 18.33 | 28.2 | 95.43 | 52.9 | 32.17 |
| Tm | 2.27 | 2.67 | 3.73 | 10.7 | 6.8 | 4.41 |
| Yb | 14.64 | 17.51 | 22.74 | 54.64 | 38.69 | 26.43 |
| Lu | 2.25 | 2.62 | 3.38 | 8.1 | 6.15 | 4 |
| LREE | 742.42 | 793.06 | 907.46 | 1588.77 | 724.53 | 707.7 |
| HREE | 216.75 | 289.17 | 531.74 | 1907.08 | 1613.73 | 592.05 |
| Total REE | 959.17 | 1082.23 | 1439.2 | 3495.85 | 2338.26 | 1299.75 |
| Ce/Ce* | 1.01 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.34 | 0.73 | 0.75 |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.70 |
| La/Yb | 8.72 | 7.91 | 6.51 | 5.51 | 2.65 | 4.69 |
| Reconstructed Composition [%] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOS-1-D | TOS-1-S | TOS-1-G | TOS-2 | TOS-3 | TOS-4 | TOS-P (Argillaceous Component) | |
| SiO2 | 1.38 | 2.69 | 5.43 | 1.71 | 6.34 | 9.97 | 27.36 |
| Al2O3 | 29.50 | 30.11 | 28.64 | 32.10 | 31.59 | 28.83 | 12.96 |
| Fe2O3 | 11.93 | 12.74 | 7.60 | 13.69 | 32.80 | 12.52 | 5.76 |
| MgO | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 41.76 |
| CaO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Na2O | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.44 |
| K2O | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 1.44 |
| TiO2 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 | 1.44 |
| P2O5 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 1.44 |
| MnO | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 2.88 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.43 |
| Total | 45.10 | 47.52 | 43.98 | 49.51 | 73.21 | 53.44 | 96.90 |
| EF | 0.4550 | 0.4791 | 0.4443 | 0.5015 | 0.7398 | 0.5389 | 1 |
| Mass Changes [%] | |||||||
| SiO2 | −25.97 | −24.67 | −21.92 | −25.65 | −21.02 | −17.38 | 0 |
| Al2O3 | 16.54 | 17.16 | 15.68 | 19.14 | 18.63 | 15.87 | 0 |
| Fe2O3 | 6.17 | 6.99 | 1.85 | 7.93 | 27.04 | 6.76 | 0 |
| MgO | −41.68 | −41.67 | −41.64 | −41.67 | −41.62 | −41.53 | 0 |
| CaO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Na2O | −1.43 | −1.43 | −1.43 | −1.43 | −1.40 | −1.41 | 0 |
| K2O | −1.43 | −1.42 | −1.39 | −1.41 | −1.14 | −1.33 | 0 |
| TiO2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 |
| P2O5 | −1.31 | −1.30 | −1.29 | −1.17 | −1.05 | −1.33 | 0 |
| MnO | −2.32 | −2.69 | −2.44 | −2.80 | −2.80 | −2.80 | 0 |
| Cr2O3 | −0.36 | −0.35 | −0.34 | −0.34 | −0.35 | −0.32 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomašić, N.; Čobić, A.; Bedeković, M.; Miko, S.; Ilijanić, N.; Gizdavec, N.; Matošević, M. Rare Earth Elements Enrichment in the Upper Eocene Tošići-Dujići Bauxite Deposit, Croatia, and Relation to REE Mineralogy, Parent Material and Weathering Pattern. Minerals 2021, 11, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111260
Tomašić N, Čobić A, Bedeković M, Miko S, Ilijanić N, Gizdavec N, Matošević M. Rare Earth Elements Enrichment in the Upper Eocene Tošići-Dujići Bauxite Deposit, Croatia, and Relation to REE Mineralogy, Parent Material and Weathering Pattern. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111260
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomašić, Nenad, Andrea Čobić, Matija Bedeković, Slobodan Miko, Nikolina Ilijanić, Nikola Gizdavec, and Mario Matošević. 2021. "Rare Earth Elements Enrichment in the Upper Eocene Tošići-Dujići Bauxite Deposit, Croatia, and Relation to REE Mineralogy, Parent Material and Weathering Pattern" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111260
APA StyleTomašić, N., Čobić, A., Bedeković, M., Miko, S., Ilijanić, N., Gizdavec, N., & Matošević, M. (2021). Rare Earth Elements Enrichment in the Upper Eocene Tošići-Dujići Bauxite Deposit, Croatia, and Relation to REE Mineralogy, Parent Material and Weathering Pattern. Minerals, 11(11), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111260








