Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
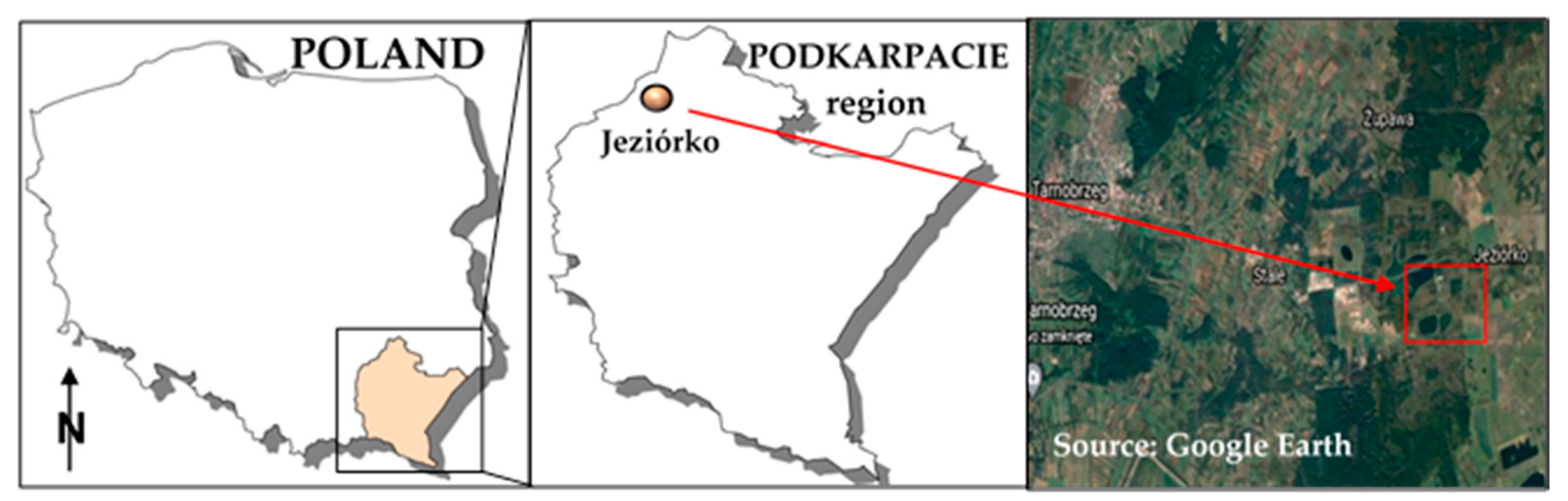
2.1. Description of the Experiment
2.2. Soil Samples
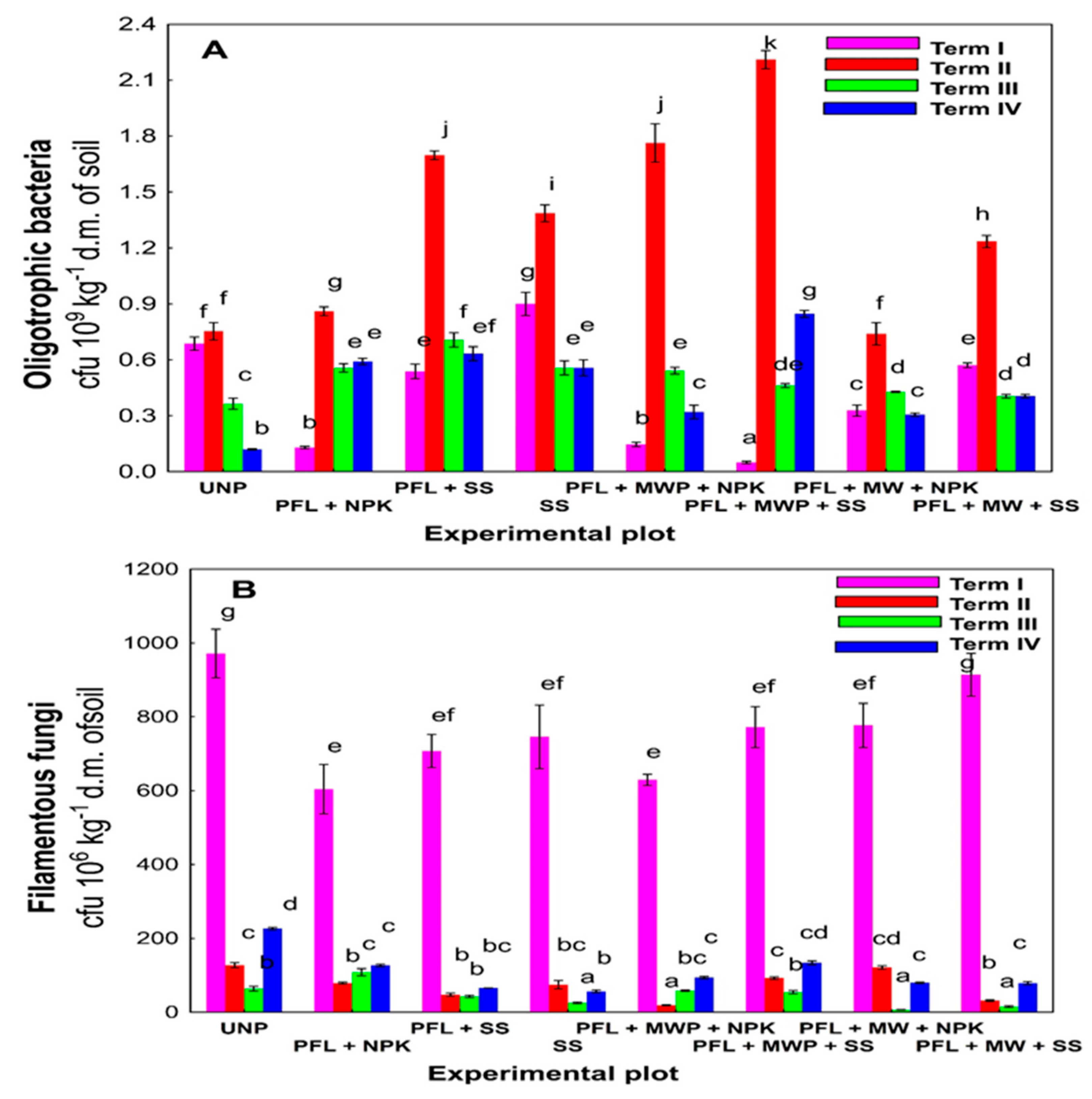
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
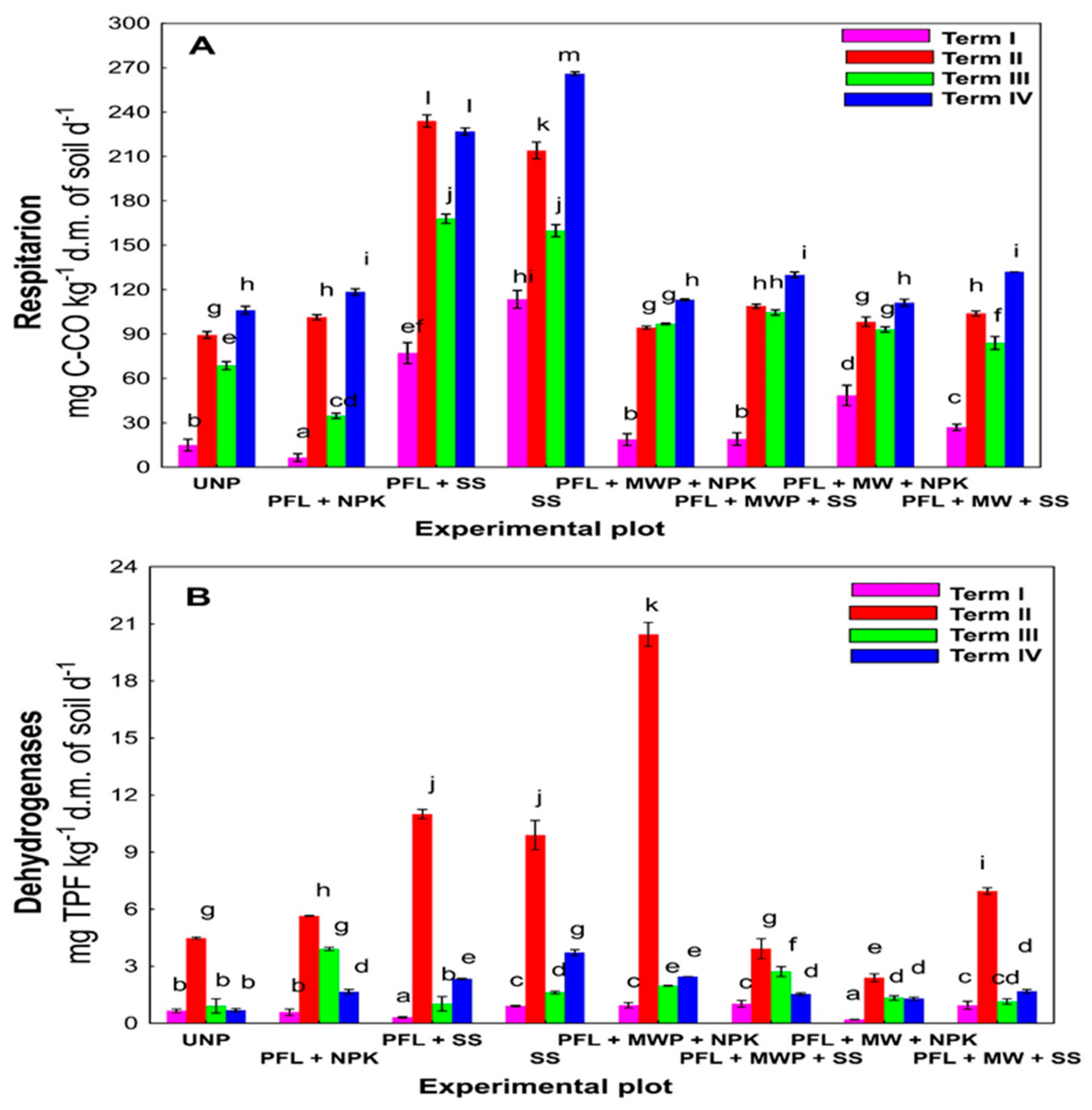
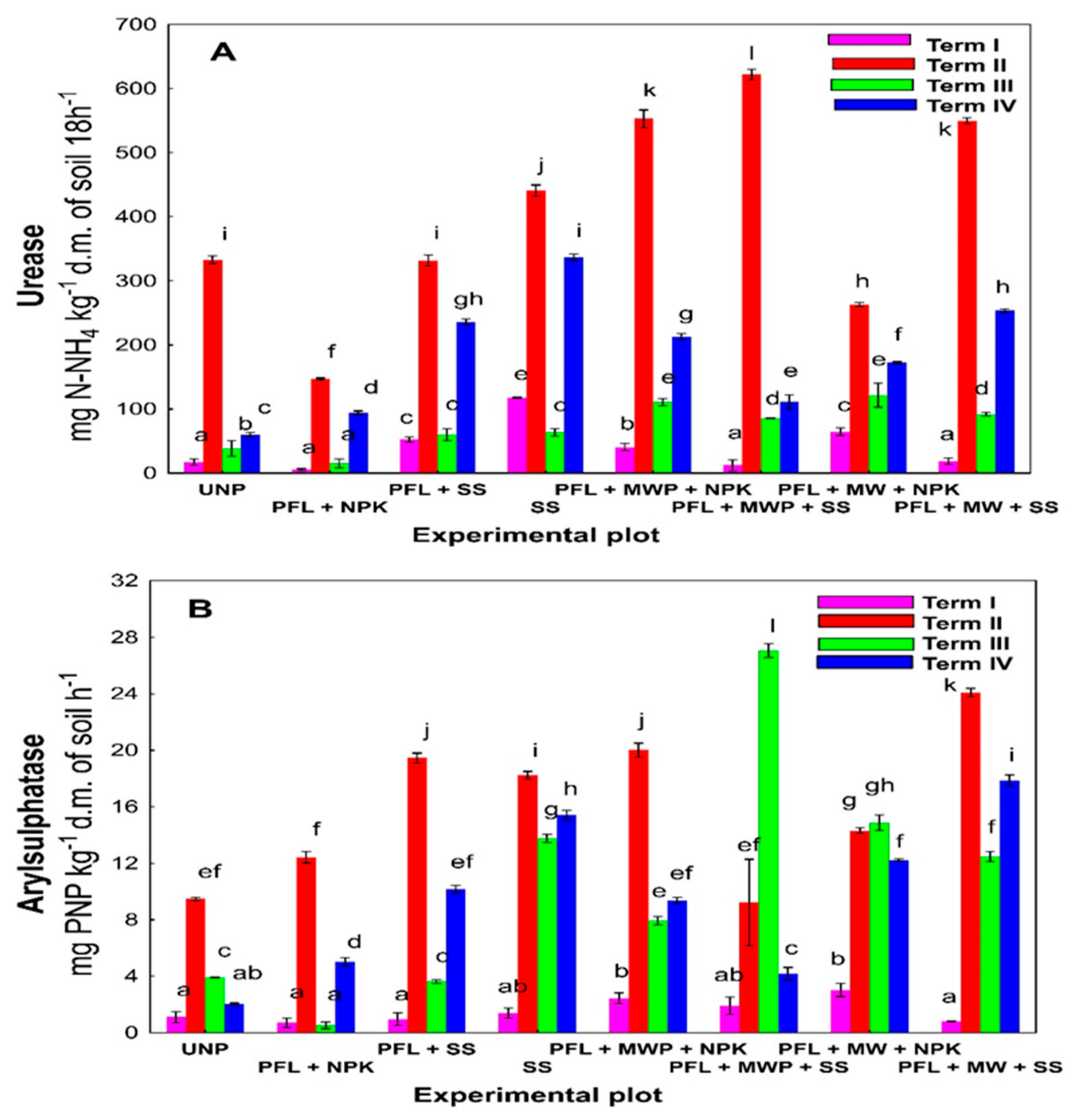
2.4. Biochemical and Enzymatic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
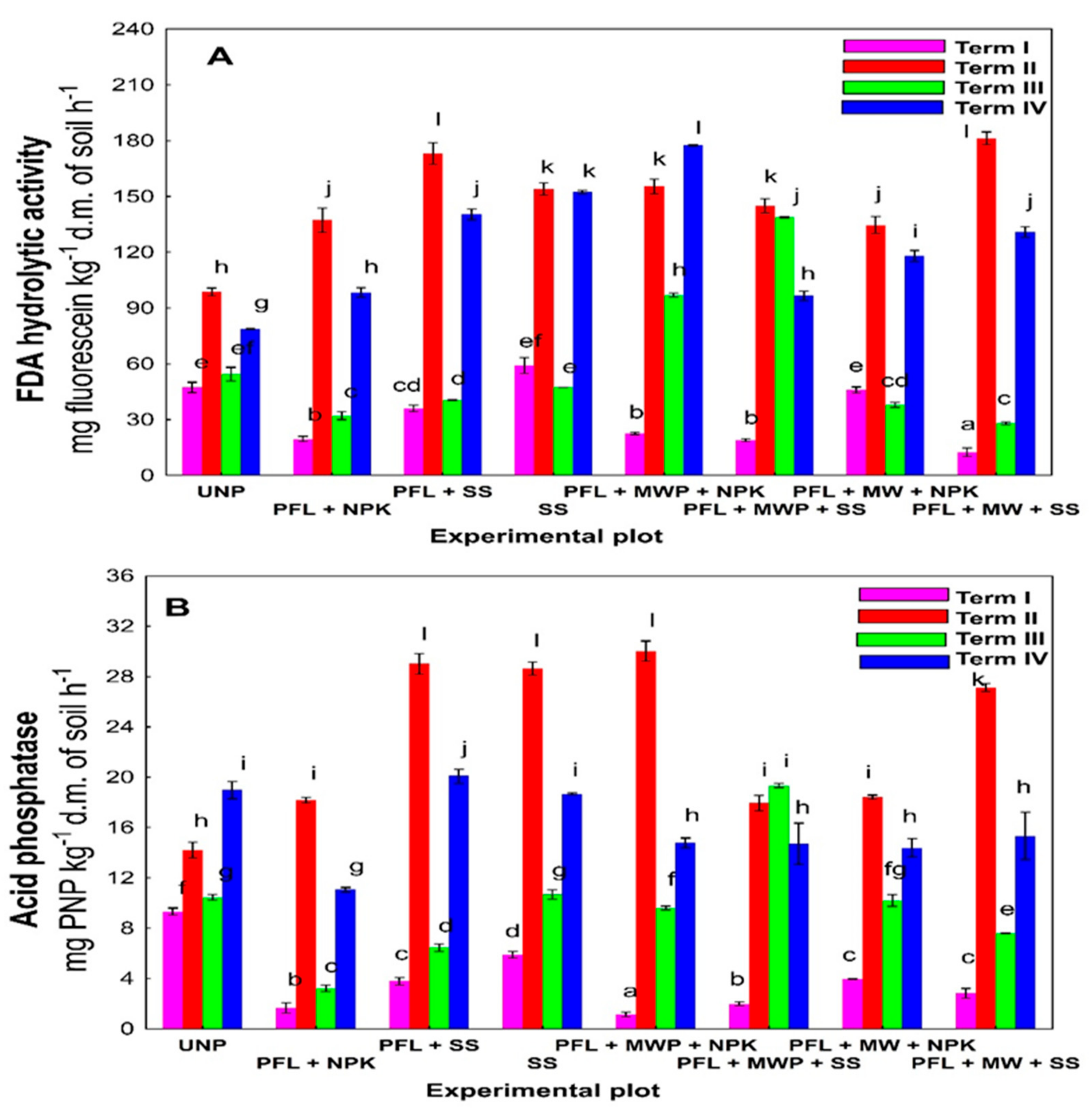
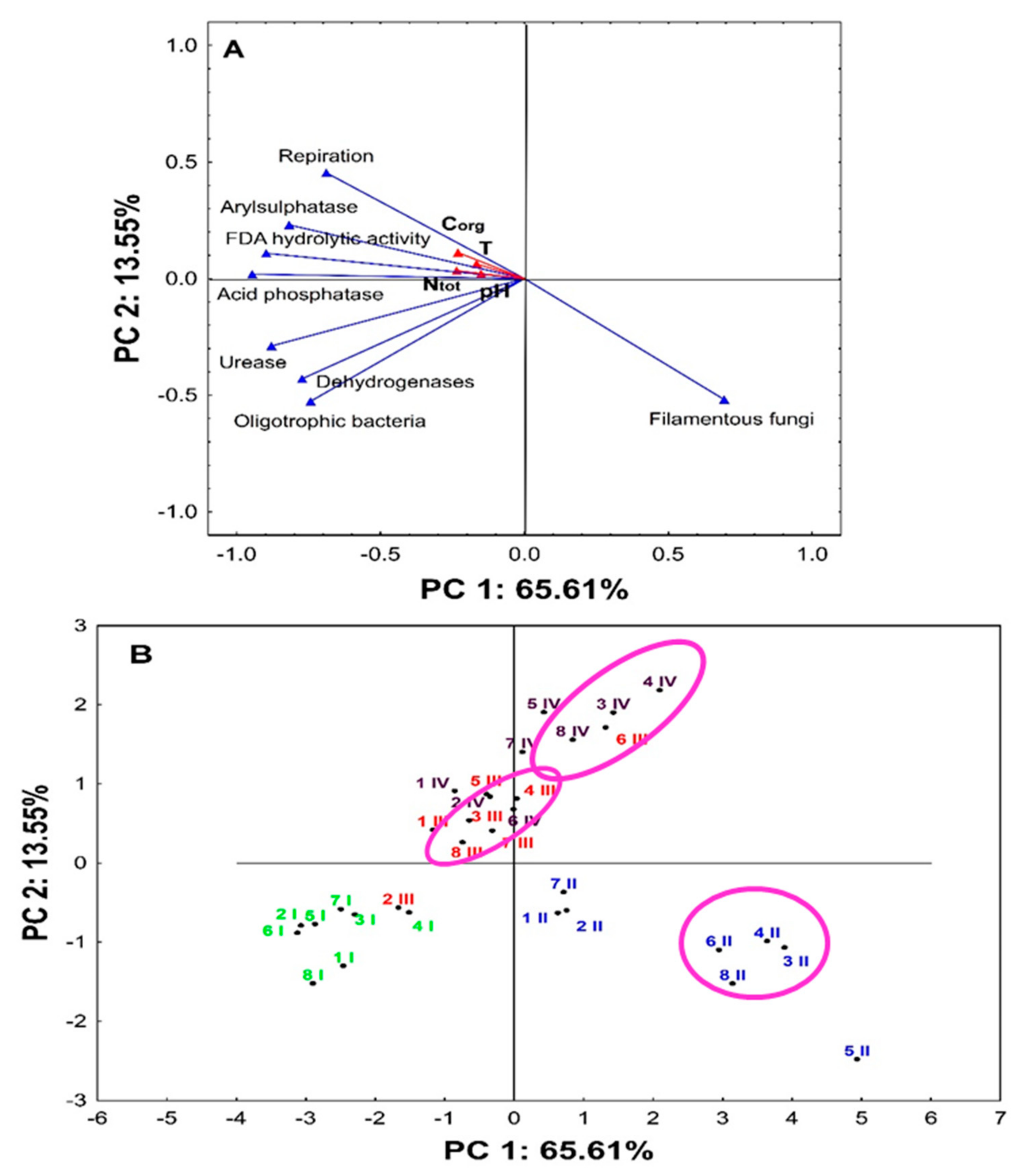
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, J.; Bossio, D.A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rillig, M.C. The concept and future prospects of soil health. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Natural and Artificial Soil Amendments for the Efficient Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soil. In Phyto and Rhizo Remediation; Arora, N.K., Kumar, N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, W.L.; Perez, T.; Mayer, A.; Jones, A.R. The role of soil in the contribution of food and feed. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2021, 376, 20200181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.; Saxena, J.; Basta, N.; Hundal, L.; Busalacchi, D.; Dick, R.P. Application of organic amendments to restore degraded soil: Effects on soil microbial properties. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavigelli, M.A.; Robertson, G.P. The functional significance of denitrifier community composition in a terrestrial ecosystem. Ecology 2000, 81, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Kandeler, E.; Ruggiero, P. Enzyme activities and microbial and biochemical processes in soil. In Enzymes in the Environment: Activity, Ecology and Applications; Burns, R.G., Dick, R.P., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Ma, C.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Soil amendment alters soil physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure of a replanted apple orchard. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 216, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Rodrigues, D.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P.; de Varennes, A.; Cruz, N.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Rodrigues, S. Use of wastes from the pulp and paper industry for the remediation of soils degraded by mining activities: Chemical, biochemical and ecotoxicological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J. Enzymatic activity as an indicator of regeneration processes in degraded soil reclaimed with various types of waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narendrula-Kotha, R.; Nkongolo, K.K. Changes in enzymatic activities in metal contaminated and reclaimed lands in Northern Ontario (Canada). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 140, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Żukowska, G.; Bik, M.; Szewczuk, C.; Zawadzki, K. Role of mineral wool and sewage sludge in increasing the nitrogen content in soilless reclaimed formations. Chem. Ind. 2012, 91, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Muhammad, N.; Wua, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification—a critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gąsior, J.; Właśniewski, S.; Drozd, I.; Kreczkiwska, H.; Nazarkiewicz, M. Effect of organic additives on vegetation of plants grown in landfill soil after ozokerite processing. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J. Indicators of microbial activity in the assessment of soil condition subjected to several years of reclamation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likus-Cieślik, J.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Chodak, M. Chemistry of sulfur-contaminated soil substrate from a former frasch extraction method sulfur mine leachate with various forms of litter in a controlled experiment. Water, Soil, Air Pollut. 2018, 229, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekaran, U.; Sandhu, S.S.; Qiu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Gonzalez Hernandez, J.L. Biochar and manure addition influenced soil microbial community structure and enzymatic activities at eroded and depositional landscape positions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 31, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A.; Faz, A.; Bååth, E. Microbial growth and community structure in acid mine soils after addition of different amendments for soil reclamation. Geoderma 2016, 272, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzykowski, M.; Daniels, W.L. Estimation of carbon sequestration by pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) ecosystems developed on reforested post-mining sites in Poland on differing mine soil substrates. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likus-Cieślik, J.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Szostak, M.; Szulczewski, M. Spatial distribution and concentration of sulfur in relation to vegetation cover and soil properties on a reclaimed sulfur mine site (Southern Poland). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwik-Ziomek, A.; Brzezińska, M.; Lemanowicz, J.; Koper, J.; Szarlip, P. Biological parameters in technogenic soils of a former sulphur mine. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J.; Oleszczuk, P.; Jezierska-Tys, S.; Kwiatkowska, E. Effect of reclamation treatments on microbial activity and phytotoxicity of soil degraded by the sulphur mining industry. Environ. Poll. 2019, 252 (Part B), 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foght, J.; Aislabie, J. Enumeration of Soil Microorganisms. In Manual of Soils Analysis. Part 5. Monitoring and Assessing Soil Bioremediation; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J. Use of acid, rose bengal and streptomycin in the plate method for estimating soil fungi. Soil Sci. 1950, 19, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühling, A.; Tyler, G. Heavy metal pollution and decomposition of spruce needly litter. Oikos 1973, 24, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, A. Zur Methodik der Bestimmung der Dehydrogenaseactivität in Boden mittels Triphenyltetrazolium chlorid (TTC). Landwirtsch. Forsch. 1968, 21, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zantua, M.J.; Bremner, J.M. Comparison of methods of assaying urease activity in soils. Soil Biol, Biochem. 1975, 7, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenol phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Arylsulfatase activity of soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1970, 34, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurer, J.; Rosswall, T. Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial acticity in soil and litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frąc, M.; Jezierska-Tys, S.; Yaguchi, T. Occurrence, detection, and molecular and metabolic characterization of heat-resistant fungi in soils and plants and their risk to human health. Adv. Agron. 2015, 132, 161–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halecki, W.; Klatka, S. Aplication of Soil Productivity Index after Eight Years of Soil Reclamation with Sewage Sludge Amendments. Environ. Manage. 2021, 67, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żukowska, G.; Baran, S.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A. The organic carbon content and fractional composition of organic matter in ground reclaimed with sewage sludge. Chem. Ind. 2012, 91, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefis and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manage. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 15 years of manure and mineral fertilizers on enzyme activities in particle-size fractions in a North China Plain soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.M.; Romero, E.; Fernandez-Bayo, J.; Vivas, A.; Nogales, R. Effect of natural vegetation strips and herbicides on enzyme activities and bacterial diversity in olive-orchard systems. In Soil Enzymology in the Recycling of Organic Wastes and Environmental Restoration; Trasar-Cepeda, C., Hernandez, T., Garcia, C., Gonzalez-Carcedo, S., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pajares, S.; Gallardo, J.; Etchevers, D. Enzymatic activity and carbon mineralization in Mexican tepetates cultivated under different management practices. In Soil Enzymology in the Recycling of Organic Wastes and Environmental Restoration; Trasar-Cepeda, C., Hernandez, T., Garcia, C., Gonzalez-Carcedo, S., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, S.; Hermann, J.; Żukowska, G.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A. Mineral wool in environmental shaping and protection. In Environmental Waste Utilisation. Theoretical and Practical Basics; Baran, S., Łabętowicz, J., Krzywy, E., Eds.; WRiL: Warsaw, Poland, 2011; pp. 120–149. [Google Scholar]
- McTee, R.M.; Lekberg, Y.; Bullington, L.; Rummel, A.; Mummey, D.L.; Ramsey, P.W.; Hinman, N.W. Restoring ecological properties of acidic soils contaminated with elemental sulfur. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Property | Unit | Degraded Soil | Mineral Wool | Sewage Sludge | Flotation Lime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | % sand % silt % fine fract. | 91 3 6 | n.o. | n.o. | 35 29 36 |
| pH | 1 mol KCl | 4.3 | 5.3-6.6 | 6.4 | 6.8 |
| T | cmol(+)·kg−1 | 7.0 | 60.9 | 54.5 | 122.9 |
| N total | g· kg−1 | 0.3 | 5.3 | 28.0 | 10.4 |
| Corg. | 2.0 | 28.5 | 193.8 | 2.6 |
| Experimental Treatments | Sorptive Capacity T, cmol(+)kg−1 | Corg., g·kg−1 | N Total, g·kg−1 | PH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 6 | Year7 | Year 6 | Year 7 | Year 6 | Year 7 | Year 6 | Year 7 | |
| UNP (control) | 7.0 | 7.8 | 2.03 | 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 4.2 | 4.7 |
| PFL + NPK | 14.4 | 15.0 | 2.52 | 2.18 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| PFL + SS | 15.5 | 20.5 | 4.20 | 4.43 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 6.9 | 6.9 |
| SS | 8.7 | 8.7 | 4.50 | 4.65 | 0.53 | 0.63 | 6.5 | 5.4 |
| PFL + MWP + NPK | 14.9 | 19.7 | 3.98 | 3.88 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 7.4 | 7.3 |
| PFL + MWP + SS | 15.6 | 17.8 | 4.47 | 3.90 | 1.37 | 1.33 | 7.1 | 7.0 |
| PFL + MW + NPK | 14.6 | 16.3 | 3.40 | 3.45 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 7.4 | 7.3 |
| PFL + MW + SS | 15.7 | 17.4 | 5.50 | 4.85 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 6.9 | 6.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joniec, J.; Żukowska, G.; Bik-Małodzińska, M.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Rojek, K. Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry. Minerals 2021, 11, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111226
Joniec J, Żukowska G, Bik-Małodzińska M, Kwiatkowska E, Rojek K. Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111226
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoniec, Jolanta, Grażyna Żukowska, Marta Bik-Małodzińska, Edyta Kwiatkowska, and Kamila Rojek. 2021. "Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111226
APA StyleJoniec, J., Żukowska, G., Bik-Małodzińska, M., Kwiatkowska, E., & Rojek, K. (2021). Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry. Minerals, 11(11), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111226







