Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
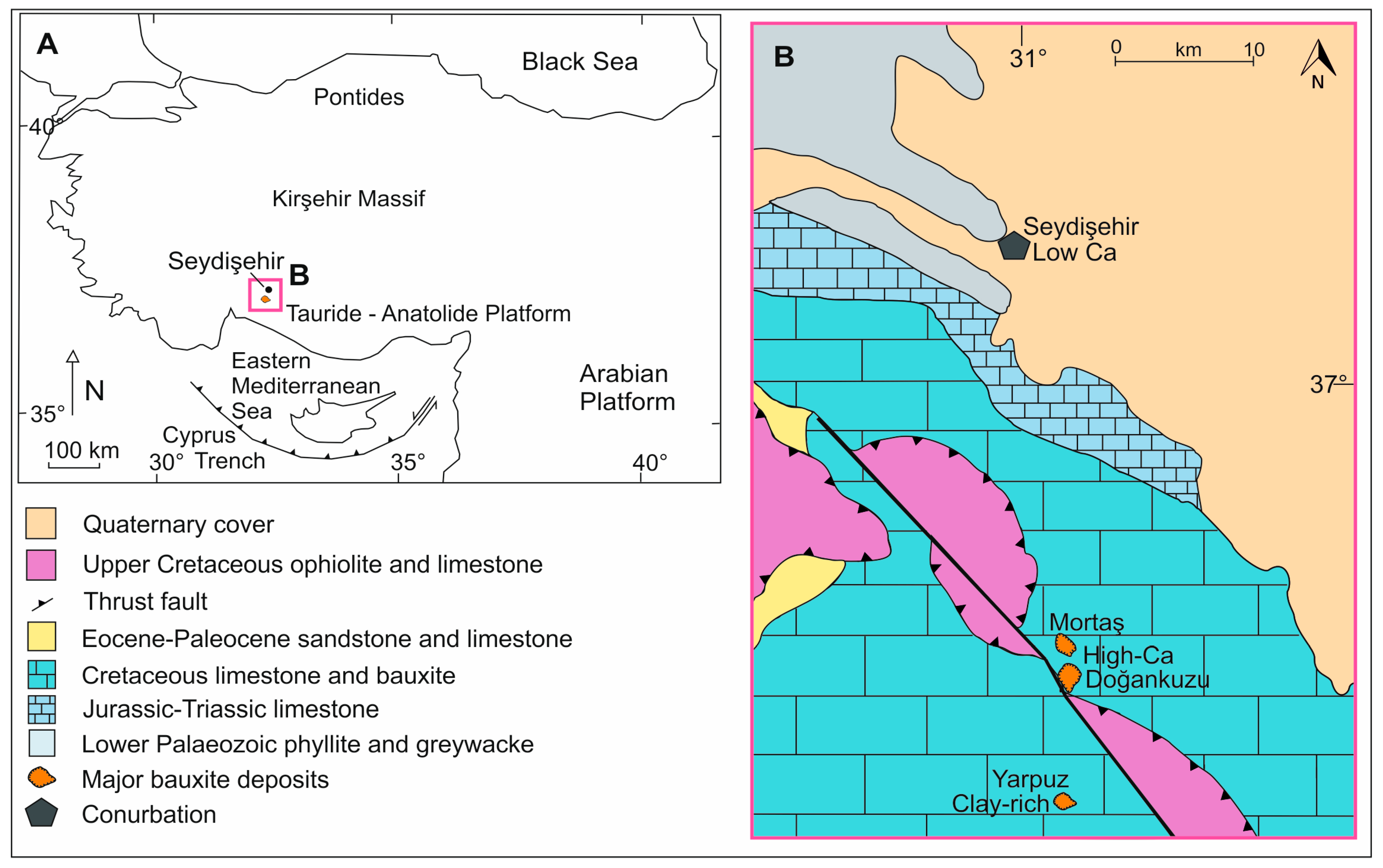
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Characterisation
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.2.2. Sequential Chemical Extraction
2.3. Bioleaching Experiment Setup
3. Results
3.1. Materials
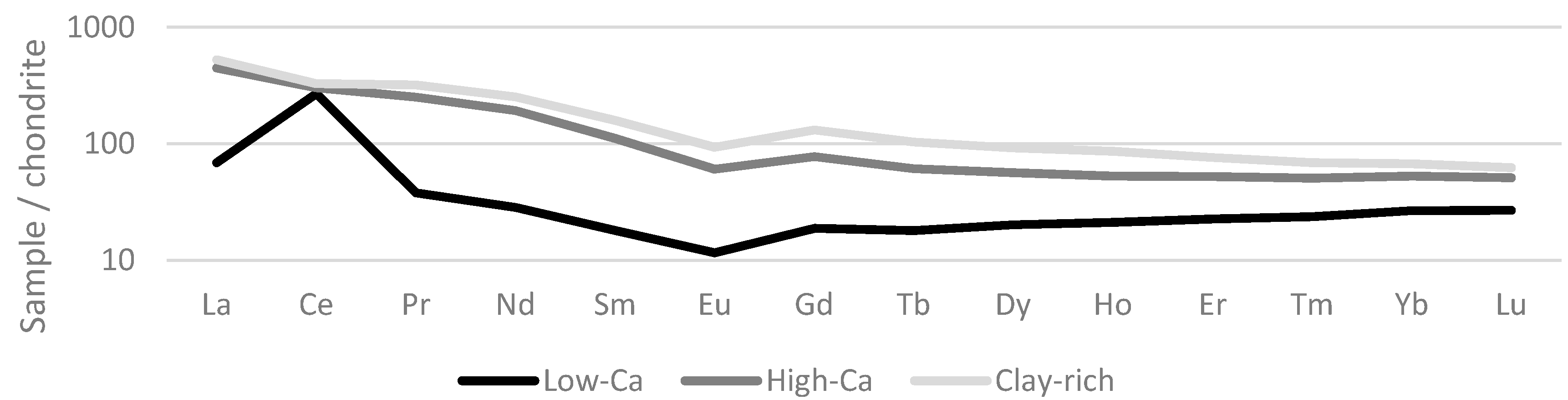
3.1.1. Mineralogy
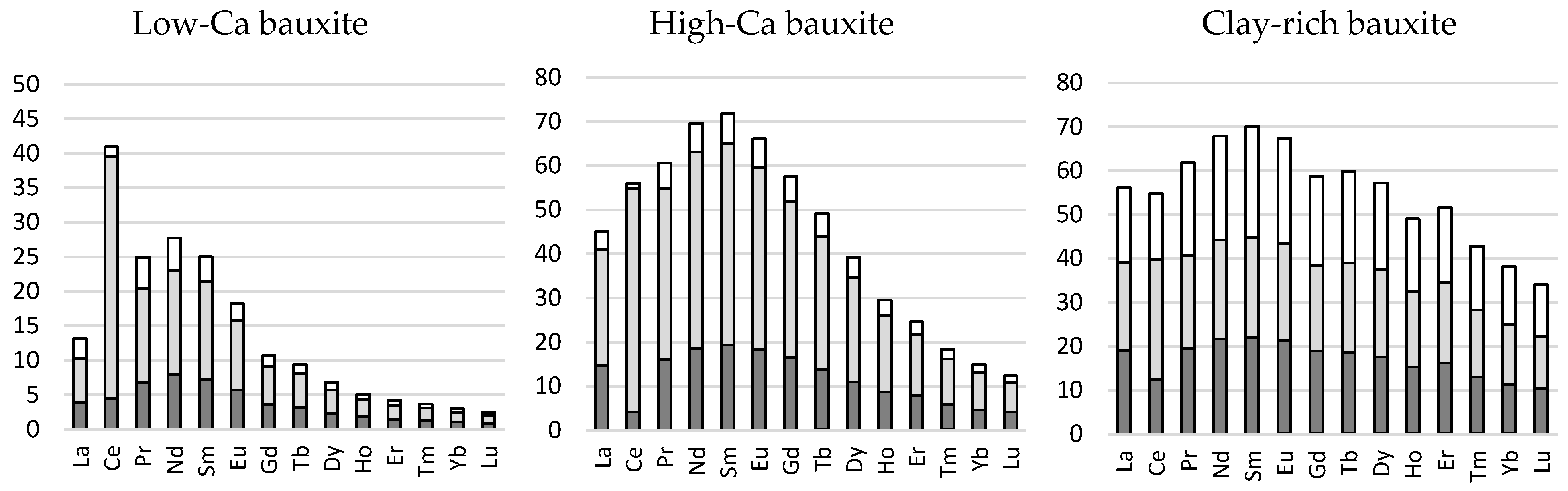
3.1.2. Sequential Extraction
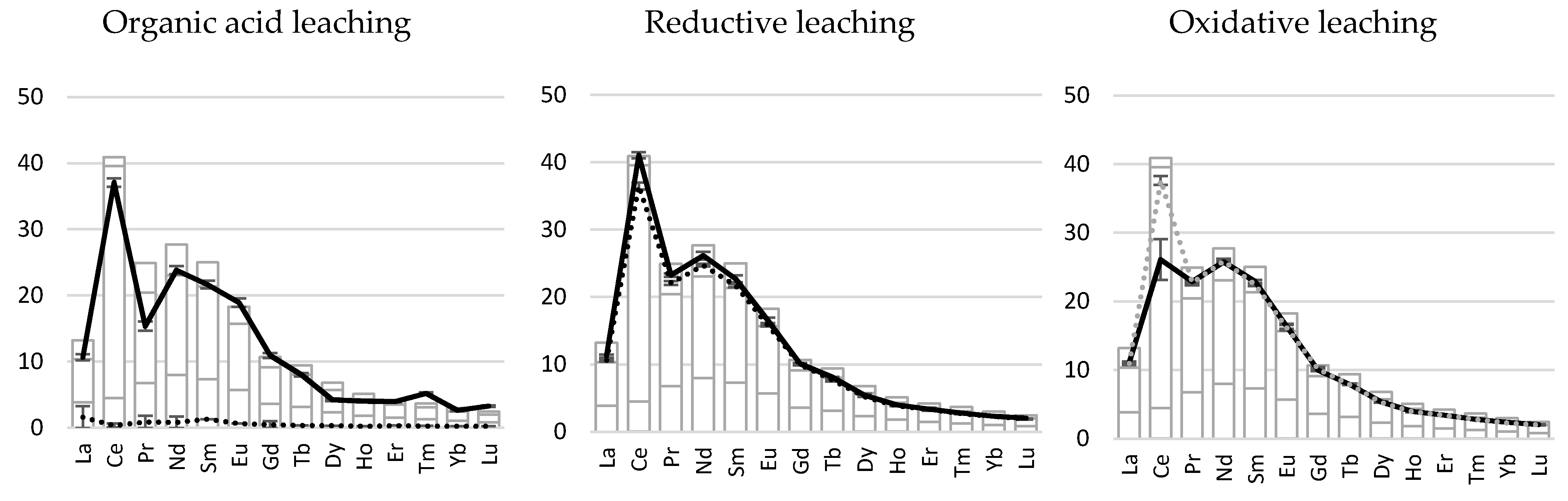
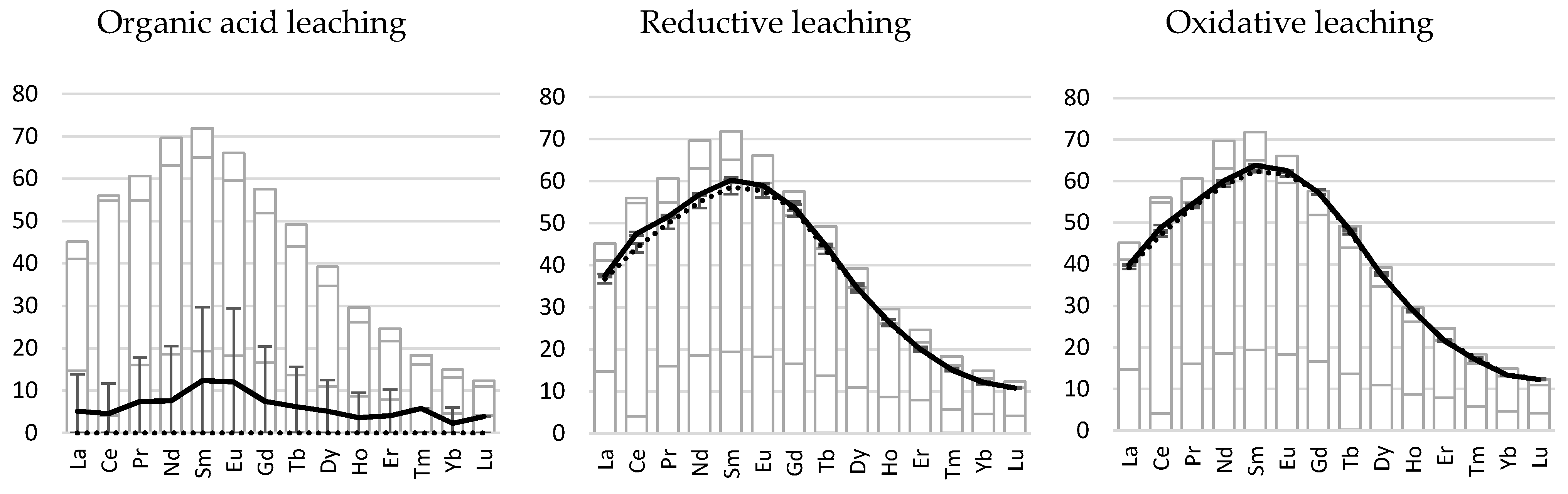
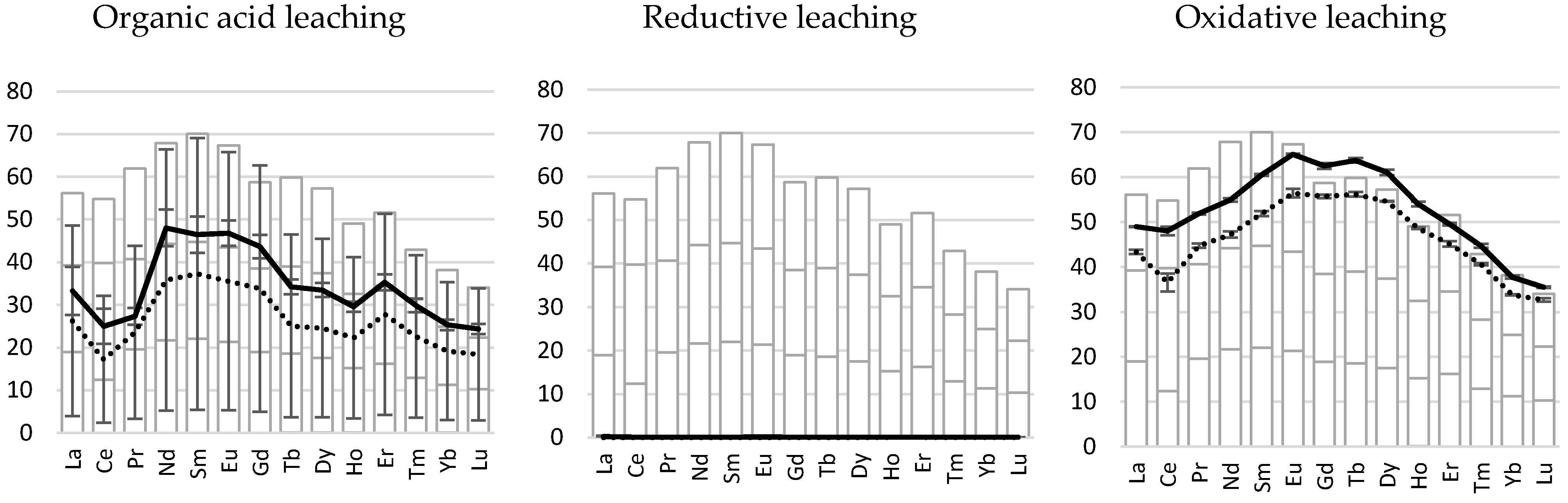
3.2. Bioleaching Experiment
3.2.1. Low-Ca Bauxite
3.2.2. High-Ca Bauxite
3.2.3. Clay-Rich Bauxite
4. Discussion
5. Implications for Industry
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodenough, K.M.; Wall, F.; Merriman, D. The Rare Earth Elements: Demand, Global Resources, and Challenges for Resourcing Future Generations. Nat. Resour. Res. 2017, 27, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Idoine, N.E.; Wrighton, C.E.; Raycraft, E.R.; Hobbs, S.F.; Shaw, R.A.; Everett, P.; Kresse, C.; Deady, E.A.; Bide, T. World Mineral Production 2014-18; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, F. Rare earth elements. In Critical Metals Handbook; Gunn, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Borra, C.R.; Mermans, J.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Selective recovery of rare earths from bauxite residue by combination of sulfation, roasting and leaching. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, G. Karst Bauxites; Bauxite Deposits on Carbonate Rocks; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Group: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimovic, Z.; Pantó, G. Contribution to the geochemistry of the rare earth elements in the karst-bauxite deposits of Yugoslavia and Greece. Geoderma 1991, 51, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.; Rollinson, G.; Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Santoro, L. Quantitative Mineralogical Characterization of Karst Bauxite Deposits in the Southern Apennines, Italy. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, P.; Mongelli, G.; Oggiano, G.; Dinelli, E. Geological, geochemical and mineralogical features of some bauxite deposits from Nurra (Western Sardinia, Italy): Insights on conditions of formation and parental affinity. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deady, É.A.; Mouchos, E.; Goodenough, K.; Williamson, B.J.; Wall, F. A review of the potential for rare-earth element resources from European red muds: Examples from Seydişehir, Turkey and Parnassus-Giona, Greece. Mineral. Mag. 2016, 80, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, G.J.; Brierley, J.A.; Brierley, C.L. Bioleaching review part B: Progress in bioleaching: Applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 63, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; Grail, B.M.; Johnson, D.B. Reductive bioprocessing of cobalt-bearing limonitic laterites. Miner. Eng. 2017, 106, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoda, B.; Potysz, A.; Kmiecik, E. Bacterial leaching of critical metal values from Polish copper metallurgical slags using Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J. Envrion. Manag. 2019, 236, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; du Plessis, C.A. Biomining in reverse gear: Using bacteria to extract metals from oxidised ores. Miner. Eng. 2015, 75, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, K.B.; Grail, B.M.; Plessis, C.A.d.; Johnson, D.B. Reductive dissolution of ferric iron minerals: A new approach for bio-processing nickel laterites. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancucheo, I.; Grail, B.M.; Hilario, F.; du Plessis, C.; Johnson, D.B. Extraction of copper from an oxidized (lateritic) ore using bacterially catalysed reductive dissolution. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6297–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Gregory, S. Comparison of Heterotrophic Bioleaching and Ammonium Sulfate Ion Exchange Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from a Madagascan Ion-Adsorption Clay. Minerals 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Kinetics at the solid-water interface: Adsoprtion, dissolution of minerals, nucleation, and crystal growth. In Aquatic Geochemistry, Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; Stumm, W., Morgan, J.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 1022. [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell, K.J.; Byrne, R.H. Rare earth element complexation by carbonate and oxalate ions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, K.; Kutschke, S.; Matys, S.; Raff, J.; Hlawacek, G.; Lederer, F.L. Bio-recycling of metals: Recycling of technical products using biological applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L.J. Role of microorganisms in bioleaching of rare earth elements from primary and secondary resources. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; Castro, F.D.; Prasad, S.; Rtimi, S. Emerging technologies for the recovery of rare earth elements (REEs) from the end-of-life electronic wastes: A review on progress, challenges, and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulnia, P.; Barthen, R.; Lakaniemi, A.-M. A critical review of bioleaching of rare earth elements: The mechanisms and effect of process parameters. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lian, B. Bioleaching of rare earth and radioactive elements from red mud using Penicillium tricolor RM-10. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.M.; El-Aassy, I.E.; El-Feky, M.G.; Sallam, A.M.; El-Sayed, E.M.; Nada, A.A.; Harpy, N.M. Fungal leaching of rare earth element from Lower Carboniferous carbonaceous shales, Southwestern Egypt. Rom. J. Biophys. 2014, 24, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.-S.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-C. Use of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria to Leach Rare Earth Elements from Monazite-Bearing Ore. Minerals 2015, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, V.L.; Zhuang, W.Q.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from monazite sand. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Becker, T.; Eksteen, J.J.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Watkin, E.L.J. Microbial contact enhances bioleaching of rare earth elements. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 3, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, W.A.G.; Desouky, O.A.N.; Hussien, S.S.E. Bioleaching of some Rare Earth Elements from Egyptian Monazite using Aspergillus ficuum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 809–823. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Bian, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from bastnaesite-bearing rock by actinobacteria. Chem. Geol. 2018, 483, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancucheo, I.; Oliveira, G.; Lopes, M.; Johnson, D. Bioreductive Dissolution as a Pretreatment for Recalcitrant Rare-Earth Phosphate Minerals Associated with Lateritic Ores. Minerals 2019, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, X.; Shi, B.; Song, G.; Tang, Y. Leaching of valuable metals from red mud via batch and continuous processes by using fungi. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Shi, B.; Yao, M.; Zhang, Y. Bioleaching of Major, Rare Earth, and Radioactive Elements from Red Mud by using Indigenous Chemoheterotrophic Bacterium Acetobacter sp. Minerals 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizkova, M.; Mezricky, D.; Rucki, M.; Toth, T.M.; Nahlik, V.; Lanta, V.; Bisova, K.; Zachleder, V.; Vitova, M. Bio-mining of Lanthanides from Red Mud by Green Microalgae. Molecules 2019, 24, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K.; Kappler, A. Ehrlich’s Geomicrobiology, 6th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 654. [Google Scholar]
- Karavaiko, G.I.; Avakyan, Z.A.; Ogurtsova, L.V.; Safonova, O.F. Microbiological processing of bauxite. In Biohydrometallurgy. Proceedings of the International Symposium; Salley, J., McGready, R.G.L., Wichlacz, L., Eds.; CANMRT: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1989; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Papassiopi, N.; Vaxevanidou, K.; Paspaliaris, I. Effectiveness of iron reducing bacteria for the removal of iron from bauxite ores. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sheng, X.-F.; He, L.-Y.; Shan, Y. Improving bio-desilication of a high silica bauxite by two highly effective silica-solubilizing bacteria. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Modak, J.M.; Natarajan, K.A. Biobeneficiation of bauxite using Bacillus polymyxa: Calcium and iron removal. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 48, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, N.; Banik, A.K. Optimisation of physical factors for bioleaching of silica and iron from bauxite ore by a mutant strain of Aspergillus niger. Res. Ind. 1995, 40, 441. [Google Scholar]
- Ogurtsova, L.V.; Karavaiko, G.I.; Avakyan, Z.A.; Korenevsii, A.A. Activity of various microorganisms in extracting elements from bauxite. Microbiology 1989, 58, 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Karadağ, M.M.; Küpeli, Ş.; Arýk, F.; Ayhan, A.; Zedef, V.; Döyen, A. Rare earth element (REE) geochemistry and genetic implications of the Mortaş bauxite deposit (Seydişehir/Konya–Southern Turkey). Geochemistry 2009, 69, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Handbook of Microbiological Media, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.; Hein, J.R.; Hanilci, N. Genesis of the Dogankuzu and Mortas Bauxite Deposits, Taurides, Turkey: Separation of Al, Fe, and Mn and Implications for Passive Margin Metallogeny. Econ. Geol. 2002, 97, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Hughes, J.; Mariano, A. Crystal chemistry of the monazite and xenotime structures. Am. Mineral. 1995, 80, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.-J.; Pagel, M.; Muller, J.-P.; Bilong, P.; Michard, A.; Guillet, B. Cerium anomalies in lateritic profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.H.; Kim, K.-H. Rare earth precipitation and coprecipitation behavior: The limiting role of PO43− on dissolved rare earth concentrations in seawater Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 57, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, D.M.; Sobral, L.G.S.; Olson, G.J.; Olson, S.B. Acid leaching of a copper ore by sulphur-oxidizing microorganisms. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 147, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnel, R. The role of cationic and anionic scavengers in laterites. Chem. Geol. 1987, 60, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchos, E.; Wall, F.; Williamson, B.J.; Palumbo-Roe, B. Easily leachable rare earth element phases in the Parnassus-Giona bauxite deposits, Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2016, 50, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Step | Reagent | Fraction Label | Nominal Target Phase(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | 1 M MgCl2 (pH 7.0) | Water soluble | Soluble and exchangeable cations |
| Step 2 | 0.11 M acetic acid | Acid soluble | Carbonates |
| Step 3 | 0.5 M hydroxylammonium chloride (pH 1.5) | Reducible | Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides |
| Step 4 | 9.8 M hydrogen peroxide then 1 M ammonium acetate (pH 2.0) | Oxidisable | Organic matter and sulphides |
| Mechanism | Organism | Medium | Stage 1: Growth | Stage 2: Leaching |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic acid bioleaching | Aspergillus sp. | Sucrose-rich medium | Aerobic | Aerobic |
| Reductive bioleaching | A. ferrooxidans | Basal salts medium plus sulphur | Aerobic | Anaerobic |
| Oxidative bioleaching | A. ferrooxidans | Basal salts medium plus sulphur | Aerobic | Aerobic |
| Leaching Fluid | Microorganism | pH | Total Fe (mg∙L−1) | Reduced Fe as % of Total Fe | Al (mg∙L−1) | TREE * (µg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic acid leaching | Aspergillus sp. | 2.04 | 0.352 | n.d. | < d.l | 6.44 |
| Uninoculated | 7.37 | 0.37 | n.d. | < d.l | 0.00 | |
| Reductive and oxidative leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.82 | 113 | 0.0 | < d.l | 0.275 |
| Uninoculated | 1.89 | 50.6 | 89.9 | 0.490 | 0.401 |
| Bauxite | Al g∙kg−1 | Fe g∙kg−1 | Si g∙kg−1 | Ti g∙kg−1 | Ca g∙kg−1 | TREE mg∙kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Ca | 296 | 109 | 32.1 | 13.4 | 0.537 | 221 |
| High-Ca | 241 | 99.1 | 23.9 | 11.9 | 64.1 | 477 |
| Clay-rich | 176 | 119 | 12.7 | 8.9 | 132 | 583 |
| Sample | Alteration | CaCO3 | Cerianite | Fluorcarbonate | Xenotime | Fe Oxide Phases * | Other REE Phases—Unidentified |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Ca | Fresh | Limited CaCO3 phases | X | X | X | X | |
| High-Ca | Fresh | Visible clasts of limestone | X | X | X | ||
| Clay-rich | Altered | Veinlets of secondary CaCO3 | X | X | X |
| Bioleaching Technique | Microorganism | pH | Change in Total Fe (mg∙L−1) | Reduced Fe as % of Total Fe | Change in Al (mg∙L−1) | Change in TREE * (µg∙L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||||||
| Organic acid leaching | Aspergillus sp. | 2.32 ± 0.02 | 1.73 ± 0.05 | 16.0 ± 5.8 | n.d. | 139 ± 11 | 170 ± 8 |
| Uninoculated | 7.41 ± 0.02 | 5.29 ± 1.41 | 0.287 ± 0.365 | n.d. | 1.21 ± 1.75 | 6.93 ± 12.0 | |
| Reductive leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.88 ± 0.02 | 2.01 ± 0.02 | 16.2 ± 3.7 | 90.3 ± 0.3 | 125 ± 1 | 199 ± 1 |
| Uninoculated | 1.94 ± 0.02 | 2.19 ± 0.01 | 4.54 ± 0.57 | 85.7 ± 1.1 | 124 ± 4 | 189 ± 0 | |
| Oxidative leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.80 ± 0.03 | 1.85 ± 0.01 | 8.50 ± 0.87 | 2.24 ± 1.23 | 125 ± 4 | 203 ± 2 |
| Uninoculated | 1.86 ± 0.06 | 2.24 ± 0.01 | 2.24 ± 1.23 | 84.3 ± 1.5 | 130 ± 4 | 202 ± 1 | |
| Bioleaching Technique | Microorganism | pH | Change in Total Fe (mg∙L−1) | Reduced Fe as % Total Fe | Change in Al (mg∙L−1) | Change in Total REE (µg∙L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||||||
| Organic acid leaching | Aspergillus sp. | 7.16 ± 0.08 | 2.18 ± 0.44 | 20.1 ± 10.7 | n.d. | 53.7 ± 5.2 | 626 ± 1042 |
| Uninoculated * | 7.96 ± 0.01 | 7.66 ± 0.11 | <d.l. | n.d. | 0.015 ± 0.001 | <d.l. | |
| Reductive leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.72 ± 0.01 | 1.81 ± 0.01 | 8.05 ± 2.23 | 68.6 ± 12.1 | 55.9 ± 0.9 | 5556 ± 77 |
| Uninoculated | 1.75 ± 0.02 | 1.93 ± 0.03 | 12.1 ± 2.0 | 72.4 ± 0.6 | 59.3 ± 1.8 | 5394 ± 90 | |
| Oxidative leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.61 ± 0.02 | 1.68 ± 0.01 | 24.5 ± 8.5 | 2.58 ± 1.20 | 64.4 ± 2.9 | 6062 ± 50 |
| Uninoculated | 1.57 ± 0.09 | 1.75 ± 0.03 | 31.0 ± 0.6 | 58.4 ± 3.1 | 60.5 ± 1.8 | 5787 ± 169 | |
| Bioleaching Technique | Microorganism | pH | Change in Total Fe (mg∙L−1) | Reduced Fe as % of Total Fe | Change in Al (mg∙L−1) | Change in Total REE (µg∙L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||||||
| Organic acid leaching | Aspergillus sp. | 7.26 ± 0.10 | 3.00 ± 0.08 | 24.5 ± 1.1 | n.d. | 32.4 ± 11.7 | 4939 ± 621 |
| Uninoculated | 8.01 ± 0.01 | 5.69 ± 0.73 | 12.5 ± 9.7 | n.d. | 9.26 ± 7.87 | 3731 ± 3187 | |
| Reductive leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.98 ± 0.06 | 6.92 ± 0.45 | −77.0 ± 16.3 | 94.0 ± 0.5 | <d.l. | 12.5 ± 15.5 |
| Uninoculated | 2.08 ± 0.20 | 7.38 ± 0.18 | −47.5 ± 16.2 | 71.1 ± 16.2 | <d.l. | 0.503 ± 0.338 | |
| Oxidative leaching | A. ferrooxidans | 1.75 ± 0.05 | 2.07 ± 0.02 | 26.3 ± 2.1 | 4.57 ± 0.72 | 44.8 ± 0.9 | 7850 ± 101 |
| Uninoculated | 1.80 ± 0.03 | 2.91 ± 0.30 | 12.6 ± 5.6 | 93.9 ± 5.0 | 39.6 ± 3.3 | 6499 ± 119 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barnett, M.J.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Deady, E.A.; Gregory, S.P. Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite. Minerals 2020, 10, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080649
Barnett MJ, Palumbo-Roe B, Deady EA, Gregory SP. Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite. Minerals. 2020; 10(8):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080649
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarnett, Megan J., Barbara Palumbo-Roe, Eimear A. Deady, and Simon P. Gregory. 2020. "Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite" Minerals 10, no. 8: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080649
APA StyleBarnett, M. J., Palumbo-Roe, B., Deady, E. A., & Gregory, S. P. (2020). Comparison of Three Approaches for Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite. Minerals, 10(8), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10080649






