New Candidate Ultralow-Velocity Zone Locations from Highly Anomalous SPdKS Waveforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
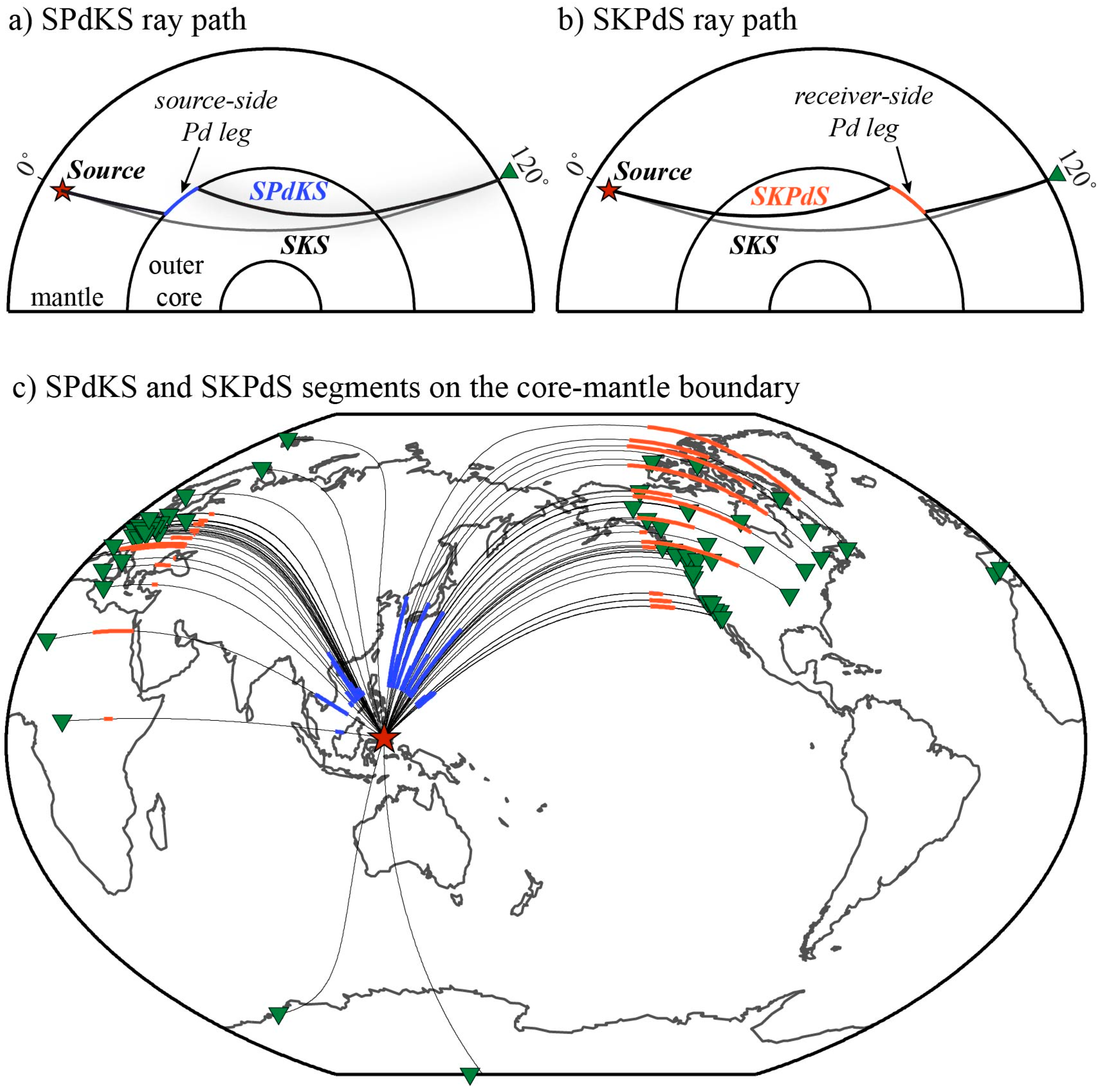
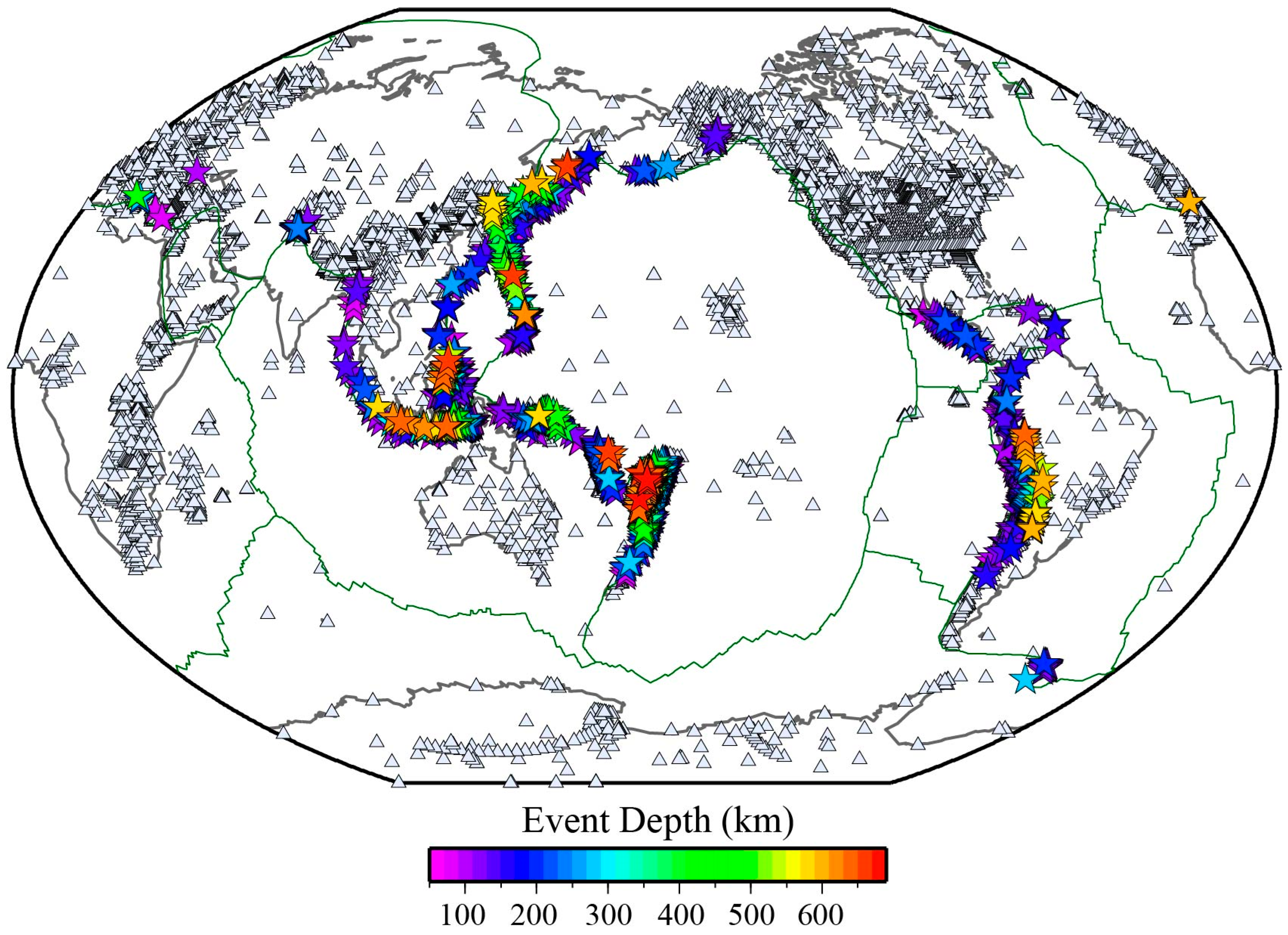
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seismic Data
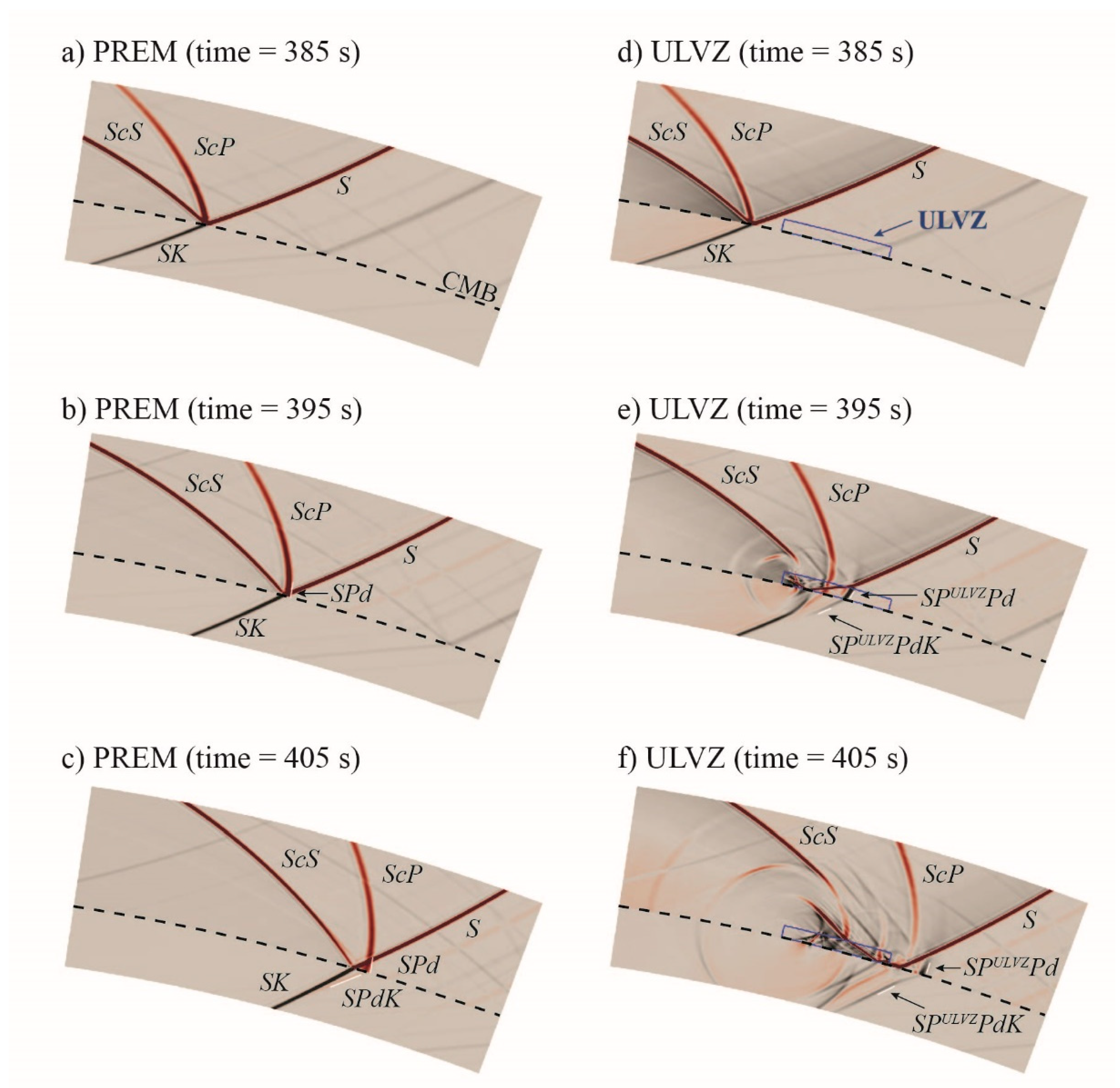
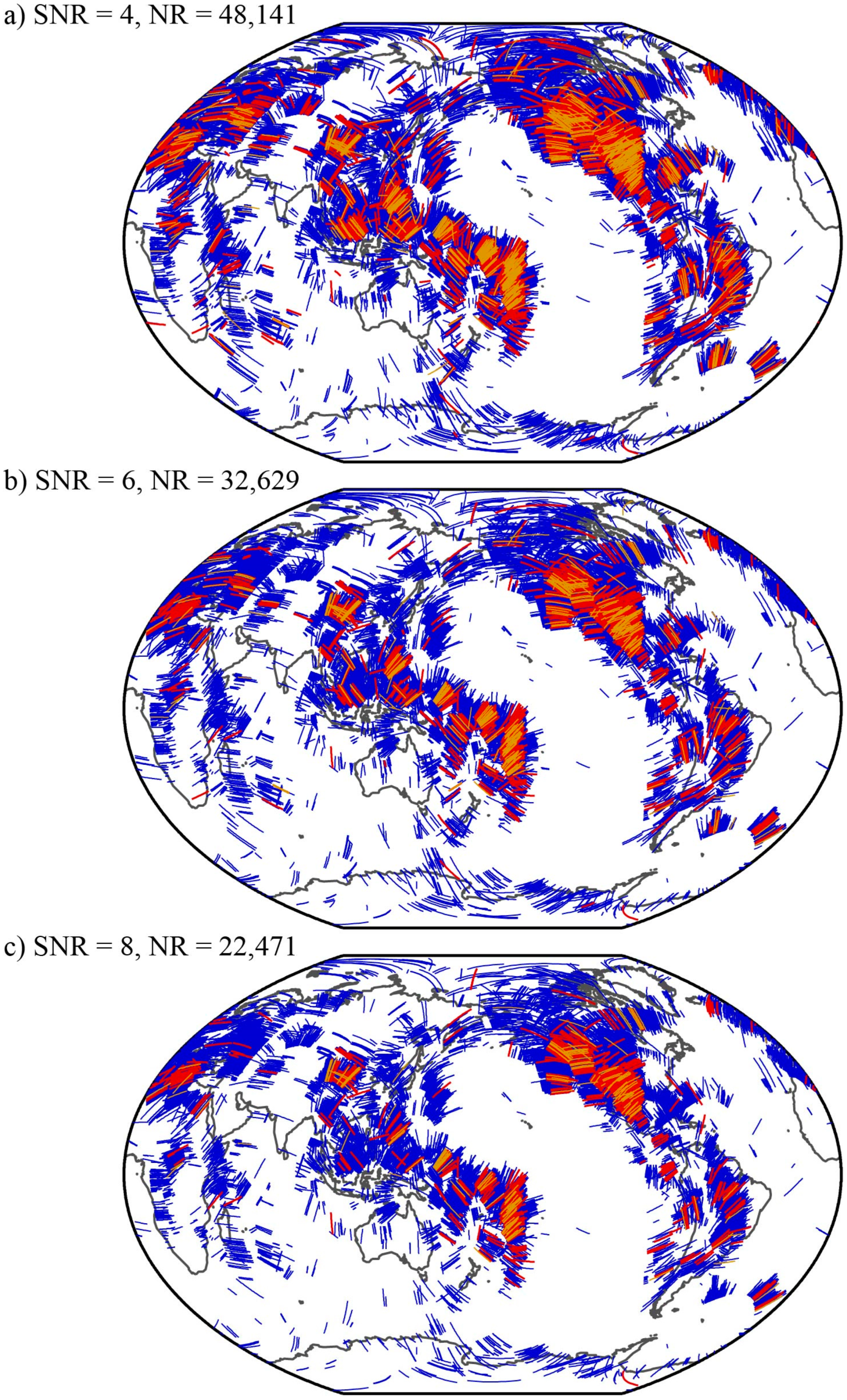
2.2. Anomaly Detection Method
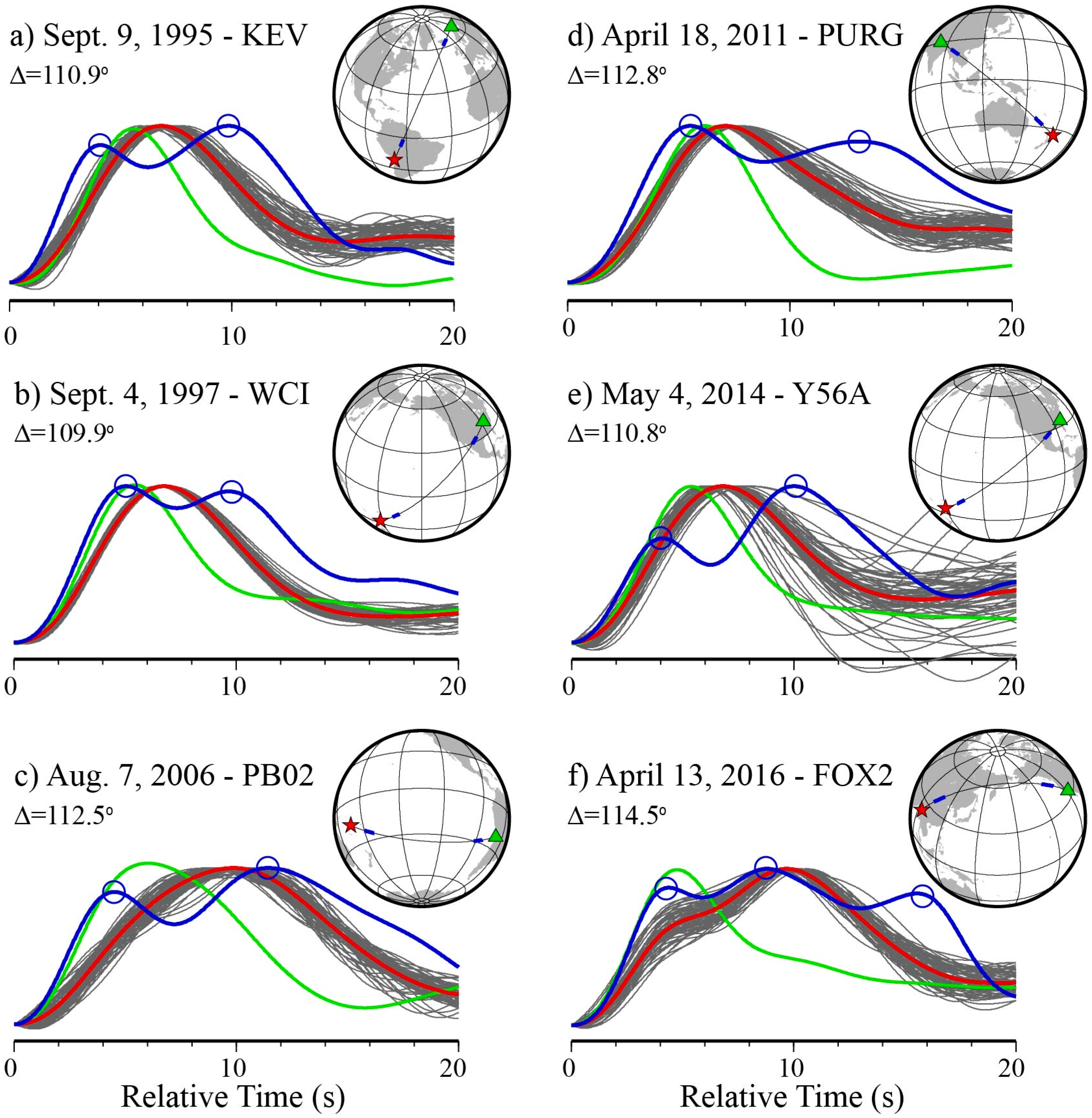
3. Results
3.1. Anomaly Detection Results
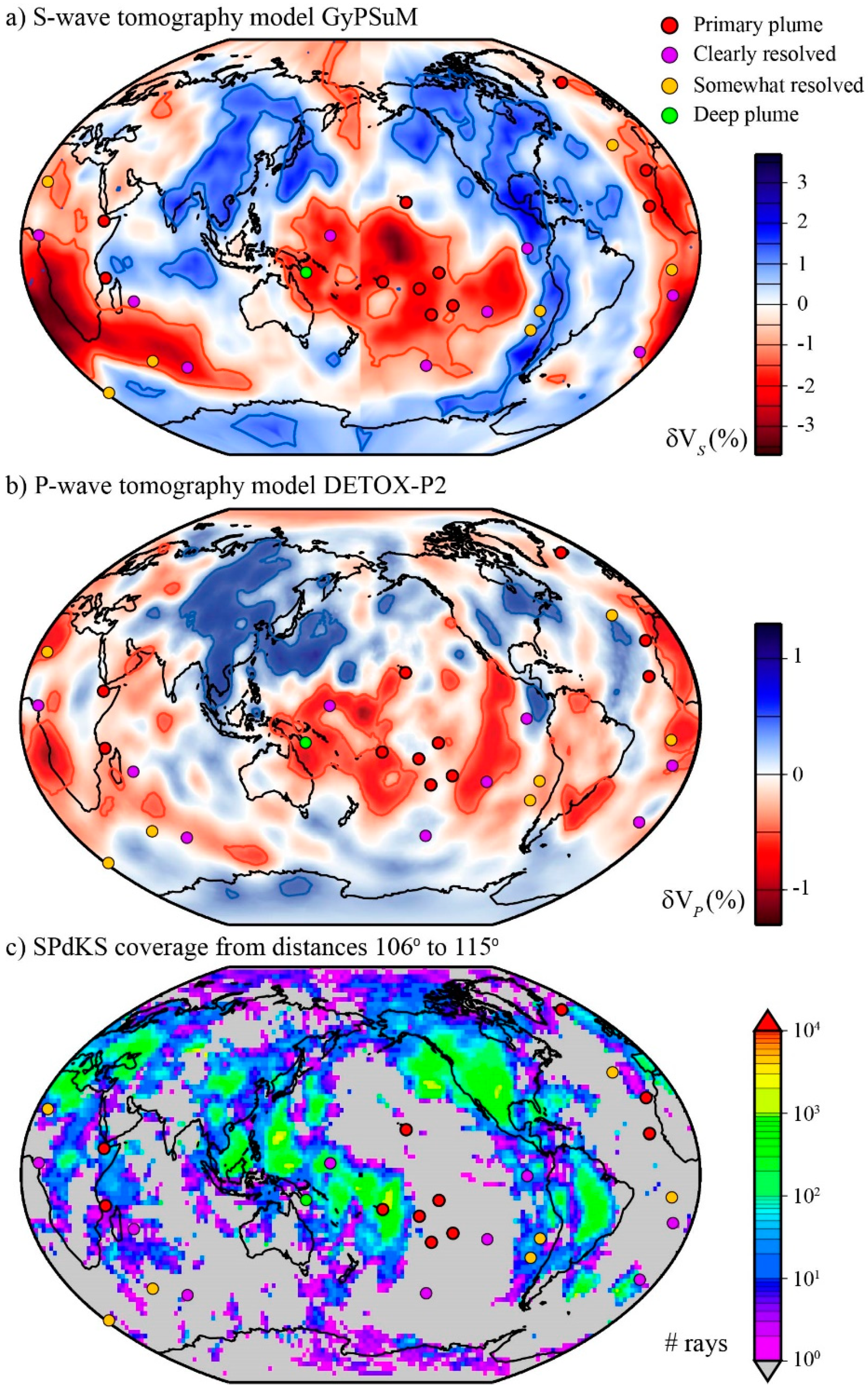
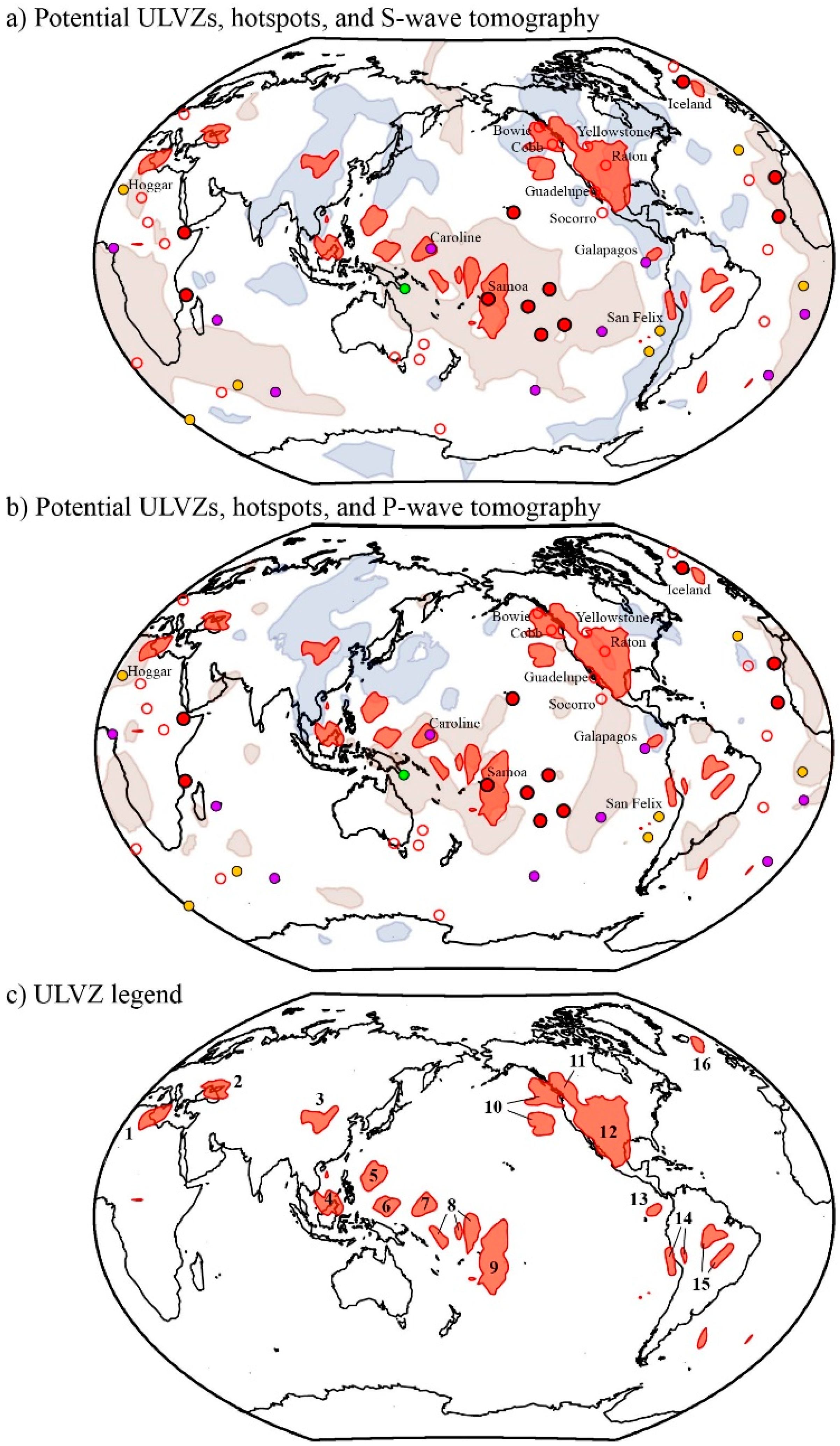
3.2. Inversion Results
4. Discussion
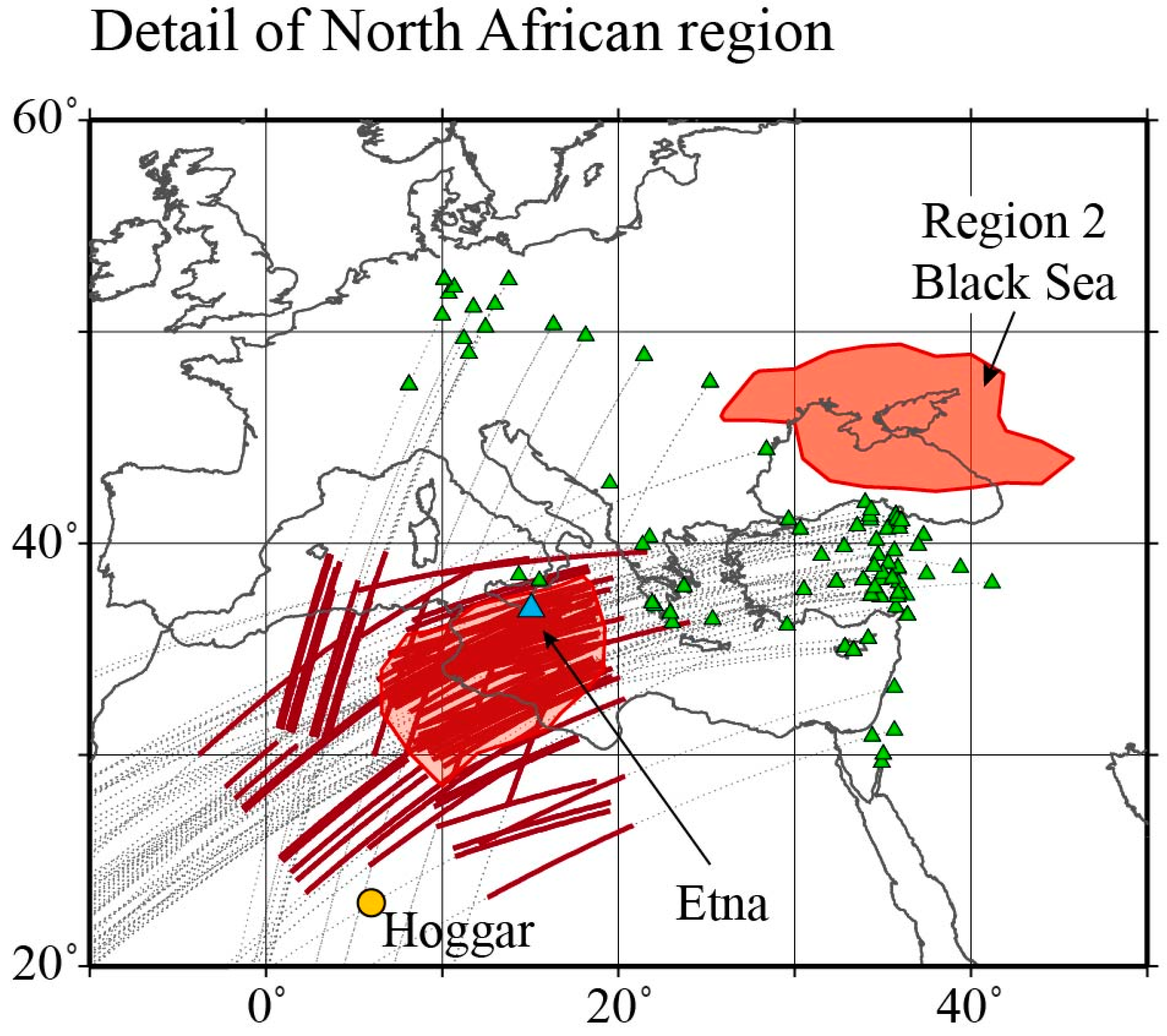
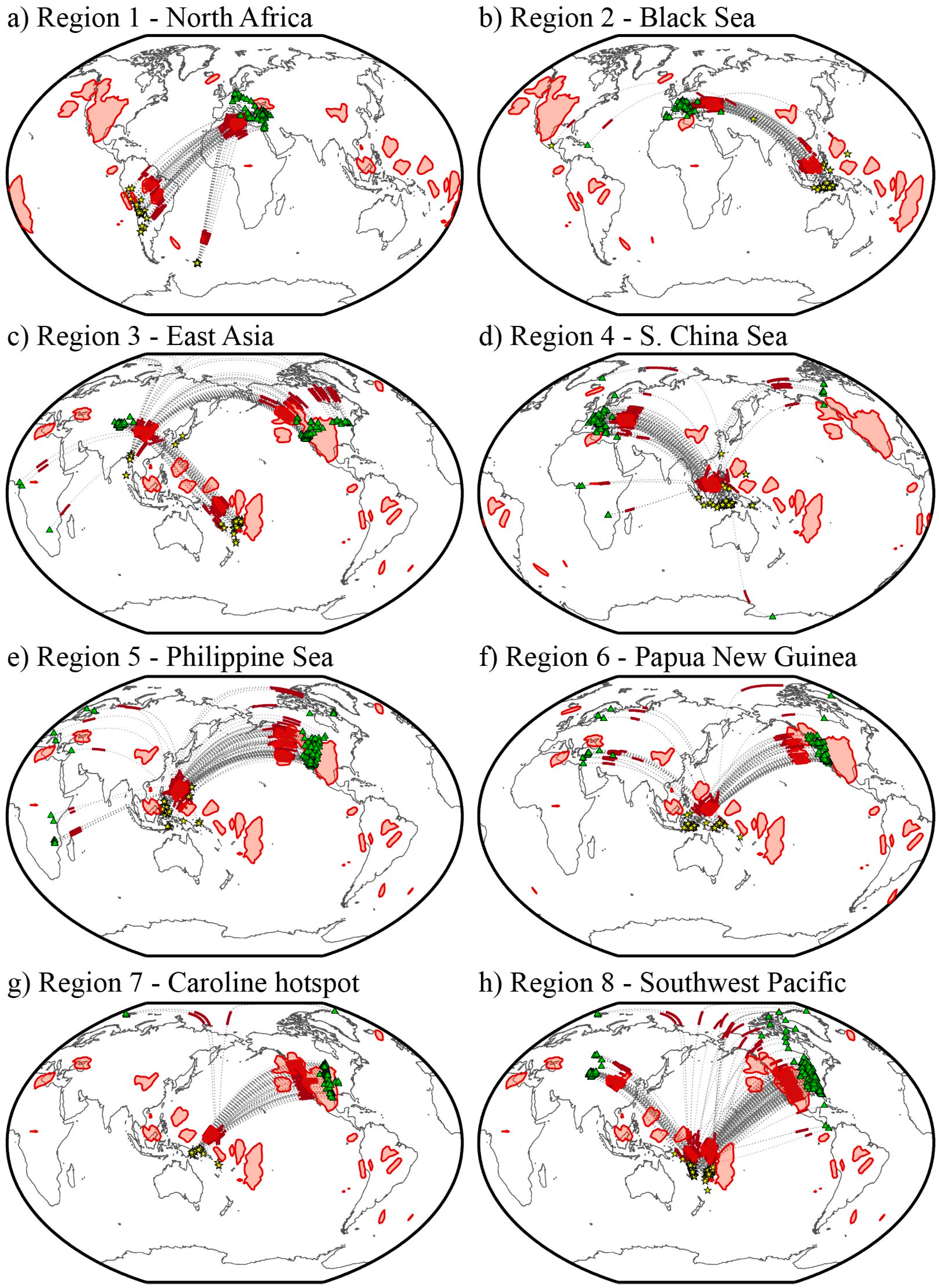
4.1. Region 1—North Africa
4.2. Region 2—Black Sea
4.3. Region 3—East Asia
4.4. Region 4—South China Sea
4.5. Region 5—Philippine Sea
4.6. Region 6—North of Papua New Guinea
4.7. Region 7—Caroline Hotspot
4.8. Region 8—Southwest Pacific
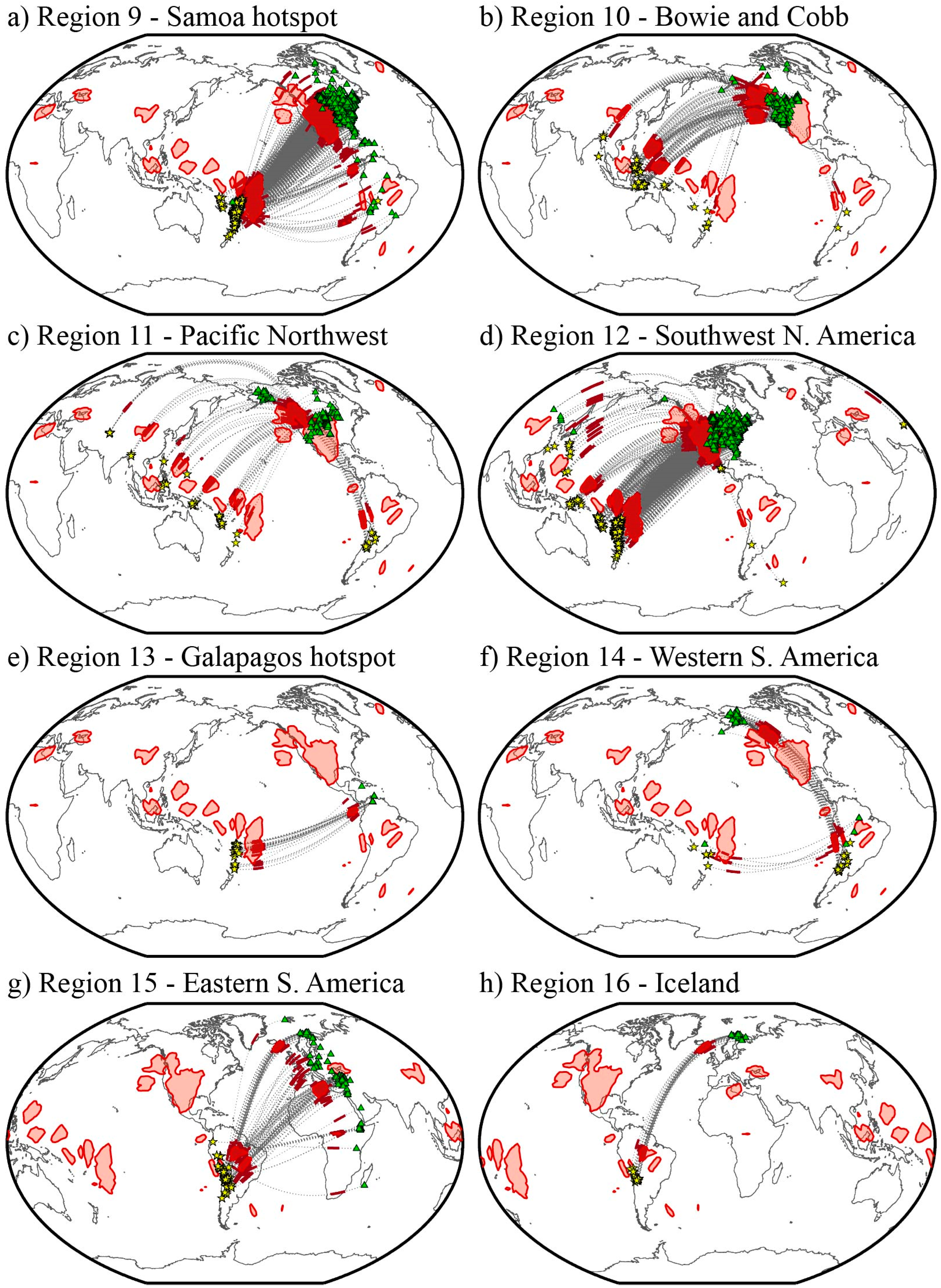
4.9. Region 9—Samoa Hotspot
4.10. Region 10—Bowie and Cobb Hotspots
4.11. Region 11—Pacific Northwest
4.12. Region 12—Southwestern North America
4.13. Region 13—Galapagos Hotspot
4.14. Region 14—Western South America
4.15. Region 15—Eastern South America
4.16. Region 16—Iceland
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garnero, E.J.; Grand, S.P.; Helmberger, D.V. Low P-wave velocity at the base of the mantle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, E.J.; Helmberger, D.V. A very slow basal layer underlying large-scale low-velocity anomalies in the lower mantle beneath the Pacific: Evidence from core phases. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1995, 91, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Garnero, E.J. Ultralow velocity zone locations: A global assessment. Gcubed 2018, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revenaugh, J.; Meyer, R. Seismic Evidence of Partial Melt Within a Possibly Ubiquitous Low-Velocity Layer at the Base of the Mantle. Science 1997, 277, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmberger, D.V.; Wen, L.; Ding, X. Seismic evidence that the source of the Iceland hotspot lies at the core-mantle boundary. Nature 1998, 396, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidale, J.E.; Hedlin, M.A.H. Evidence for partial melt at the core-mantle boundary north of Tonga from the strong scattering of seismic waves. Nature 1998, 391, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, Q.; Garnero, E.J. Seismic Evidence for Partial Melt at the Base of Earth’s Mantle. Science 1996, 273, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reasoner, C.; Revenaugh, J. ScP constraints on ultralow-velocity zone density and gradient thickness beneath the Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 28173–28182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, E.; Revenaugh, J. A broadband seismic study of the lowermost mantle beneath Mexico: Constraints on ultralow velocity zone elasticity and density. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 30809–30820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, N.A.; Grand, S.P. Partial melting in the deepest mantle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S.; Garnero, E.J.; Williams, Q.; Manga, M. Seismological constraints on a possible plume root at the core-mantle boundary. Nature 2005, 435, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Leyton, F.; Koper, K.D. Partial melt in the lowermost mantle near the base of a plume. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 168, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, M.; Jeanloz, R. Implications of a metal-bearing chemical boundary layer in D” for mantle dynamics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3091–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, J.; Jackson, J.M.; Sturhahn, W.; Zhang, D. Sound velocity and density of magnesiowüstites: Implications for ultralow-velocity zone topography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, J.K.; Jackson, J.M.; Sturhahn, W. Very low sound velocities in iron-rich (Mg,Fe)O: Implications for the core-mantle boundary region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.P.; Thorne, M.S.; Miyagi, L.; Rost, S. A compositional origin to ultralow-velocity zones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffett, B.A.; Garnero, E.J.; Jeanloz, R. Sediments at the Top of Earth’s Core. Science 2000, 290, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, Q.; Revenaugh, J.; Garnero, E.J. A Correlation Between Ultra-Low Basal Velocities in the Mantle and Hot Spots. Science 1998, 281, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Romanowicz, B. Seismic evidence for partial melting at the root of major hot spot plumes. Science 2017, 357, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, M.S.; Garnero, E.J.; Jahnke, G.; Igel, H.; McNamara, A.K. Mega Ultra Low Velocity Zone and Mantle Flow. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 364, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottaar, S.; Romanowicz, B. An unusually large ULVZ at the base of the mantle near Hawaii. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 355–356, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmberger, D.V.; Ni, S.; Wen, L.; Ritsema, J. Seismic evidence for ultralow-velocity zones beneath Africa and eastern Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 23865–23878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.J.; Thorne, M.S.; Rost, S. SPdKS analysis of ultralow-velocity zones beneath the western Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Helmberger, D.V. Horizontal transition from fast to slow structures at the core-mantle boundary; South Atlantic. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 187, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanacore, E.A.; Rost, S.; Thorne, M.S. Ultralow-velocity zone geometries resolved by multidimensional waveform modeling. Geophys. J. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Helmberger, D.V.; Lai, V.H.; Gurnis, M.; Jackson, J.M.; Yang, H.-Y. Slab control on the northeastern edge of the mid-Pacific LLSVP near Hawaii. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 3142–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, M.S.; Takeuchi, N.; Shiomi, K. Melting at the edge of a slab in the deepest mantle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8000–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, D.J.; Wicks, J.K.; Gurnis, M.; Jackson, J.M. A geodynamic and mineral physics model of a solid-state ultralow-velocity zone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 303, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, E.J.; Helmberger, D.V. Further structural constraints and uncertainties of a thin laterally varying ultralow-velocity layer at the base of the mantle. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 12495–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Helmberger, D.V. Probing an Ultra-low velocity zone at the Core Mantle Boundary with P and S Waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Helmberger, D.V. A two-dimensional P-SV hybrid method and its application to modeling localized structures near the core-mantle boundary. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 17901–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewonski, A.M.; Anderson, D.L. Preliminary reference Earth model. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1981, 25, 297–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.; Nissen-Meyer, T.; van Driel, M.; Al-Attar, D. AxiSEM3D: A new fast method for global wave propagation in 3-D Earth models with undulating discontinuities. In Abstract DI23A-2596 Presented at 2016 Fall Meeting; AGU: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, K.; Nissen-Meyer, T.; van Driel, M.; Hosseini, K.; Al-Attar, D. AxiSEM3D: Broad-band seismic wavefields in 3-D global earth models with undulating discontinuities. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 217, 2125–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, E.J.; Jeanloz, R. Fuzzy Patches on the Earth’s Core-Mantle Boundary? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2777–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S.; Revenaugh, J. Seismic Detection of Rigid Zones at the Top of the Core. Science 2001, 294, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, M.S.; Garnero, E.J. Inferences on ultralow-velocity zone structure from a global analysis of SPdKS waves. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earthquakes Canada, N.R.C. Continuous Waveform Archive, AutoDRM@seismo.NRCan.gc.ca. Available online: https://earthquakescanada.nrcan.gc.ca/stndon/CNSN-RNSC/index-en.php (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Valentine, A.P.; Woodhouse, J.H. Approaches to automated data selection for global seismic tomography. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 182, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDecar, J.C.; Crosson, R.S. Determination of teleseismic relative phase arrival times using multi-channel cross-correlation and least squares. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1990, 80, 150–169. [Google Scholar]
- French, S.W.; Romanowicz, B. Broad plumes rooted at the base of the Earth’s mantle beneath major hotspots. Nature 2015, 525, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, N.A.; Forte, A.M.; Boschi, L.; Grand, S.P. GyPSuM: A joint tomographic model of mantle density and seismic wave speeds. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, K.; Sigloch, K.; Tsekhmistrenko, M.; Zaheri, A.; Nissen-Meyer, T.; Igel, H. Global mantle structure from multifrequency tomography using P, PP and P-diffracted waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 220, 96–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, G. Methods for Seismic Wave Propagation on Local and Global Scales with Finite Differences; Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität: München, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, G.L. Theoretical seismograms of core phases calculated by frequency-dependent full wave theory, and their interpretation. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 51, 275–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachhai, S.; Tkalčić, H.; Dettmer, J. Bayesian inference for ultralow velocity zones in the Earth’s lowermost mantle: Complex ULVZ beneath the east of the Philippines. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 8346–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachhai, S.; Dettmer, J.; Tkalčić, H. Ultra-low velocity zones beneath the Philippine and Tasman Seas revealed by a trans-dimensional Bayesian waveform inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 1302–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, B. Plumes in a convecting mantle: Models and observations for individual hotspots. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 11,127–111,152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelli, R.; Nolet, G.; Dahlen, F.A.; Masters, G. A catalogue of deep mantle plumes: New results from finite frequency tomography. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekic, V.; Cottaar, S.; Dziewonski, A.M.; Romanowicz, B. Cluster analysis of global lower mantle tomography: A new class of structure and implications for chemical heterogeneity. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 357–358, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, S.P. Mantle shear-wave tomography and the fate of subducted slabs. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2002, 360, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, K.; Yamada, A.; Zhao, D. Seismological constraints on the ultralow velocity zones in the lowermost mantle from core-reflected waves. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2007, 165, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wen, L. Seismic structure and ultra-low velocity zones at the base of the Earth’s mantle beneath Southeast Asia. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2014, 233, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S.; Garnero, E.J.; Stefan, W. Thin and intermittent ultralow-velocity zones. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, E.J.; Vidale, J.E. ScP; a probe of ultralow velocity zones at the base of the mantle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Helmberger, D.V. Ultra-Low Velocity Zones Near the Core-Mantle Boundary from Broadband PKP Precursors. Science 1998, 279, 1701–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persh, S.E.; Vidale, J.E.; Earle, P.S. Absence of short-period ULVZ precursors to PcP and ScP from two regions of the CMB. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, J.C.; van der Hilst, R.D. The core-mantle boundary under the Gulf of Alaska: No ULVZ for shear waves. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 176, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondenay, S.; Fischer, K.M. Constraints on localized core-mantle boundary structure from multichannel, broadband SKS coda analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.L.; Grand, S.P. Lower-mantle plume beneath the Yellowstone hotspot revealed by core waves. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanacore, E.; Niu, F. Characterization of the D” beneath the Galapagos Islands using SKKS and SKS waveforms. Earthq. Sci. 2011, 24, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottaar, S.; Li, Z. An ultra-low velocity zone beneath the Galapagos hotspot. In American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting 2019; abstract DI53A-0043; AGU: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, T.J.; Crotwell, H.P.; Groves, C.; Oliver-Paul, P. SOD: Standing Order for Data. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2004, 75, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F. New, Improved Version of Generic Mapping Tools Released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1998, 79, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, M.S. SACTOOLS v1.0.0. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1314738#.XlXgtEoRXIU (accessed on 18 July 2018). [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thorne, M.S.; Pachhai, S.; Leng, K.; Wicks, J.K.; Nissen-Meyer, T. New Candidate Ultralow-Velocity Zone Locations from Highly Anomalous SPdKS Waveforms. Minerals 2020, 10, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030211
Thorne MS, Pachhai S, Leng K, Wicks JK, Nissen-Meyer T. New Candidate Ultralow-Velocity Zone Locations from Highly Anomalous SPdKS Waveforms. Minerals. 2020; 10(3):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleThorne, Michael S., Surya Pachhai, Kuangdai Leng, June K. Wicks, and Tarje Nissen-Meyer. 2020. "New Candidate Ultralow-Velocity Zone Locations from Highly Anomalous SPdKS Waveforms" Minerals 10, no. 3: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030211
APA StyleThorne, M. S., Pachhai, S., Leng, K., Wicks, J. K., & Nissen-Meyer, T. (2020). New Candidate Ultralow-Velocity Zone Locations from Highly Anomalous SPdKS Waveforms. Minerals, 10(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030211




