Mineral Chemistry, S-Pb-O Isotopes, and S/Se Ratios of the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) Sulfide Deposit in North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Constraints on the Parental Magma Composition, Evolution, and Sulfur Saturation Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Regional Geology
3. Deposit Geology
3.1. Mining Area Geology
3.2. Mafic-Ultramafic Intrusions
3.3. Ni-(Cu) Ore Body and Mineralization
3.3.1. Characteristics of Ni-(Cu) Ore Body
3.3.2. Sulfides and Ni-(Cu) Mineralization
3.4. Samples and Petrography
4. Analytical Methods
4.1. Electron Microprobe Analysis
4.2. Sulfide S-Pb Isotope Analysis
4.3. Whole-Rock O Isotope Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Mineral Chemistry
5.1.1. Olivine
5.1.2. Pyroxene
5.1.3. Plagioclase
5.1.4. Hornblende
5.2. S-Pb Isotopes of Sulfide
5.2.1. S Isotopes
5.2.2. Pb Isotopes
5.3. Whole-Rock O Isotopes and S/Se Ratios
5.3.1. O Isotopes
5.3.2. S/Se Ratios
6. Discussion
6.1. Parental Magma
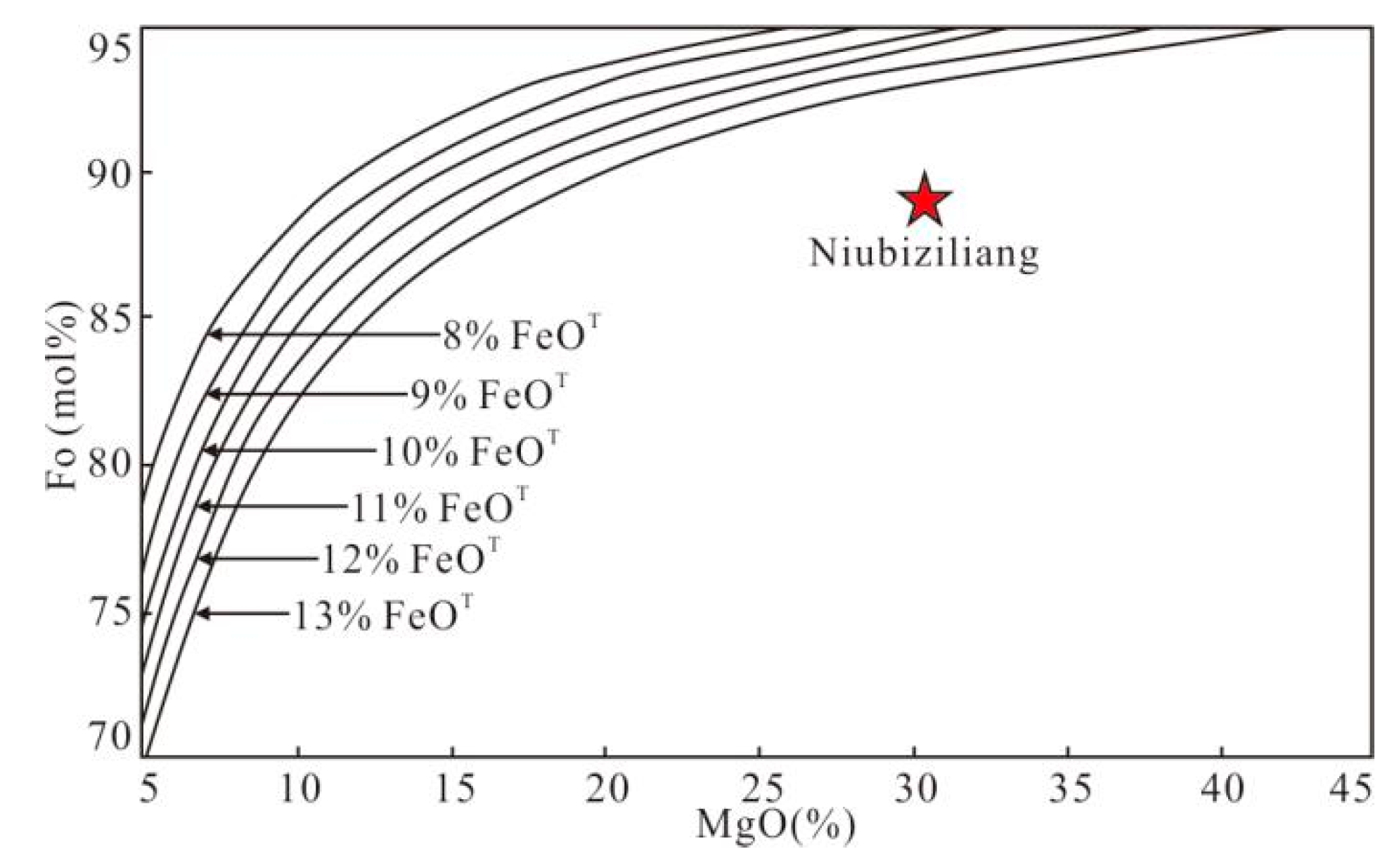
6.2. Estimation of Mineral Crystallization Conditions
6.2.1. Olivine
6.2.2. Pyroxene
6.2.3. Hornblende
6.3. Magmatic Evolution
6.3.1. Fractional Crystallization
6.3.2. Crustal Assimilation and Contamination
6.4. Sulfur Saturation Mechanism
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, L.S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xie, G.Q. Temporal-spatial distribution and geodynamic setting of magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposits in China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2561–2594. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, P.C.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Hergt, J.; Naldrett, A.J.; Gorbechev, N.S.; Fedorenko, V.A.; Doherty, W. Remobilisation of the continental lithosphere by a mantle plume: Major-, trace-element, and Sr-, Nd-, and Pb-isotope evidence from picritic and tholeiitic lavas of the Noril’sk District, Siberian Trap, Russia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 114, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldrett, A.J. World-class Ni-Cu-PGE deposits: Key factors in their genesis. Miner. Depos. 1999, 34, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Naldrett, A.J. Melting reactions of gneissic inclusions with enclosing magma at Voisey’s Bay, Labrador, Canada: Implications with respect to ore genesis. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Arndt, N.; Windley, B.; Zhou, M.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Harris, C. Field relationships and geochemical constraints on the emplacement of the Jinchuan intrusion and its Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposit, Gansu, China. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, G.L.; Sun, D.Y. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the post-orogenic Cu-Ni sulfide-bearing mafic-ultramafic complexes in Jilin Province, NE China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.L.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.L.; Qiu, G.L.; Dai, J.F. The new exploration of magmatic mineralization: Small intrusion mineralization and geological prospecting breakthrough. Northwest. Geol. 2012, 45, 1–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.S.; Ripley, E.M. The giant Jinchuan Ni-Cu-(PGE) deposit: Tectonic setting, magma evolution, ore genesis and exploration implications. Rev. Econ. Geol. 2011, 17, 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono-Marziano, G.; Ferraina, C.; Gaillard, F.; Di Carlo, I.; Arndt, N. Assimilation of sulfur and carbonaceous rocks: Experimental study, thermodynamic and application to the Noril’sk-Talnakh region (Russia). Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 90, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.S.; Naldrett, A.J. Sulfide capacity of magma: A quantitative model and its application to the formation of sulfide ores at Sudbury. Econ. Geol. 1993, 88, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Li, C.L.; Zhuang, Y.; Geng, A.Q.; Wang, X.P. The copper-nickle mine features of Niubiziliang in north-west margin of Chaidamu Basin, and discoverable significance. Northwest. Geol. 2012, 45, 202–210. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Kang, Z.; Ling, J.L.; Zhao, S.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Shen, D.L.; Jiang, C.Y. Geological feature and genesis of Niubiziliang Cu-Ni sulphide deposit in the northern margin of Qaidam Block. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2012, 34, 12–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.L.; Zhao, Y.F.; Kang, Z.; Jiang, C.Y.; Song, Z.B.; Zhao, S.X.; Wang, Y.G. Petrogenesis and mineralization of Niubiziliang mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the northern margin of Qaidam Block, NW China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1628–1646. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.L.; Song, Y.F.; Jiang, C.Y.; Song, Z.B.; Zhao, Y.F. Platinum-group elements and Re-Os isotopic characters of the Niubiziliang Ni-Cu deposit in the northern margin of the Qaidam Block, Northwest China. Geol. Explor. 2014, 50, 138–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, B.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.B.; Shao, J. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of Niubiziliang mafic-ultramafic intrusion on the northwest margin of Qaidam Basin, Qinghai. Geol. China 2015, 42, 482–493. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Li, B.L.; Peng, B.; Xu, C.H.; Li, R.H.; Wang, F.; Shen, D.L. Geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) sulfide deposit, North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Implications for magmatic source, geodynamic setting, and petrogenesis. Lithos 2019, 326–327, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.L.; Wang, J.C.; Lv, B.F.; Lin, Y.X.; Xia, B. Structural features of the Altun Mountain and its fault systems during Mesozoic and Cenozoic. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2008, 28, 295–300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.L.; Tian, X.C. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Niubiziliang granodiorite in northern margin of Qaidam Basin. Glob. Geol. 2017, 36, 93–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.H.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Bai, Y.N.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.F.; Yu, L. U-Pb dating, geochemistry, and Hf isotopic compositions of diorite from the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) deposit in Qinghai Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 2273–2284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Li, B.L.; Chen, G.J.; Li, R.H.; Yu, L.; Qian, Y.; Wang, L.; Huo, L.; Wang, L.L.; et al. Research Report of Ore-Controlling Conditions and Prospecting Breakthrough of the Magmatic Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposits in Niubiziliang Area, Qinghai Province; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.F.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, L.; Li, R.H.; Yu, L.; Wang, F.; Shen, D.L. Geochronology, geochemistry and Hf isotope of monzogranite in Niubiziliang of Qinghai. Glob. Geol. 2016, 19, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.L. Petrogenesis of Mafic-Ultramafic Intrusions and Minerogenesis of Nickel Sulfide Deposit in the Periphery of Qaidam Block, Qinghai China. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Dick, H.J.B.; Bullen, T. Chromian spinel as a petrogenetic indicator in abyssal and alpine-type peridotites and spatially associated lavas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1984, 86, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Metallogenesis of Nickel Deposits in Eastern Kunlun Orogen, Qinghai Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.S.; Mao, J.W.; Zhou, Z.H.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.F. Mineral chemistry of ore-bearing ultramafic rocks from the Hongqiling No. 1 and 7 intrusions in Jilin University: Constraints on the magmatic processes and the metallogenesis of Ni-Cu sulfide deposits. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 319–344. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.M.; Song, X.Y.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Xiao, J.F.; Li, S.B.; Guan, J.X. Correlation between Ni and MgO contents of olivine in Segment I of the Jinchuan intrusion, NW China, and its geological implication. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 3369–3378. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, N. Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Mineral. Mag. 1988, 52, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.X.; Liao, Q.A. Petrogenesis and Cpx mineral chemistry of Cenozoic basalts from Zhejiang and Fujian of Eastern China. Volcanol. Miner. Resour. 1996, 17, 16–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, I. Feldspars defined and described: A pair of posters published by the Mineralogical Society. Sources and Supporting Information. Mineral. Mag. 2010, 74, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leake, B.E.; Woolley, A.R.; Arps, C.E.S.; Birch, W.D.; Gilbert, M.C.; Grice, J.D.; Hawthorne, F.C.; Kato, A.; Kisch, H.J.; Krivovichev, V.G.; et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles: Report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the international mineralogical association commission on new minerals and mineral names. Int. Conf. Form. Concept Anal. 1997, 4390, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.Y.; An, S.Y. On chemical characteristics of calcic amphiboles from igneous rocks and their petrogenesis significance. Miner. Petrol. 1984, 3, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, E.M.; Li, C.S. Applications of stable and radiogenic isotopes to magmatic Cu-Ni-PGE deposits: Examples and cautions. Earth Sci. Front. 2007, 14, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbo tectonics-the model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Holwell, D.A.; McDonald, I.; Boyce, A. The application of S isotopes and S/Se ratios in determining ore-forming processes of magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulfide deposits: A cautionary case study from the northern Bushveld Complex. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 148–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeder, P.L.; Emslie, R.F. Olivine-liquid equilibrium. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1970, 29, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.R.; Travis, G.A. The nickel sulfide deposits of Western Australia in global perspective. Econ. Geol. 1981, 76, 1291–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, F.S. A method for identifying primary magma—Examples from picrite and alkali basalts. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2003, 33, 130–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.M.; Song, X.Y.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Xiao, J.F.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, G.F.; Guan, J.X.; Liu, S.R.; Zheng, W.Q. Parental magma composition of the Jinchuan intrusion, Gansu Province and MELTS thermodynamic modelling of fractional crystallization. Acta Geol. Sin. 2009, 83, 1302–1315. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.S.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, W.Y.; Ripley, E.M. Geochronology, petrology and Hf-S isotopes of the newly-discovered, world-class Xiarihamu magmatic Ni-Cu deposit in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, western China. Lithos 2015, 216–217, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Gao, Z.M.; Luo, T.Y.; Qi, J.D.; He, Y.J.; Yang, T.X. Inversion of primary magma composition for Jinbaoshan ultramafic intrusion, Yunnan. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2002, 18, 70–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H. Nickel content of basaltic magmas: Identification of primary magmas and a measure of the degree of olivine fractionation. Lithos 1977, 10, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.X. Magmatic Petrology; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 140–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Simkin, T.; Smith, J.V. Minor element distribution in olivine. J. Geol. 1970, 78, 304–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D. Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, J.C.; Benoit, V.; Girardeau, J. Equilibrium state of diopside-bearing harzburgites from ophiolites: Geobarometric and geodynamic implications. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1984, 85, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papike, J.J.; Cameron, K.L.; Baldwin, K. Amphiboles and pyroxenes: Characterization of other than quadrilateral components and estimates of ferric iron from microprobe data. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. Programs 1974, 6, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Bagiński, B.; Dzierzanowski, P.; Macdonald, R.; Upton, B.G.J. Complex relationships among coexisting pyroxenes: The Palaeogene Eskdalemuir dyke, Scotland. Mineral. Mag. 2009, 73, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfi, F.; Renzulli, A.; Puerini, M. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: An overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 160, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, F.A.; Green, D.H.; Roy, S.D. Integrated models of basalt petrogenesis: A study of quartz tholeiites to olivine melilities from south eastern Australia utilizing geochemical and experimental petrological data. J. Petrol. 1978, 19, 463–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.H. Genesis of archean Peridotitic magmas and constraints on archean geothermal gradients and teetonies. Geology 1975, 3, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Späth, A.; Le Roex, A.P.; Opiyo-Akech, N. Plume-lithosphere interaction and the origin of continental rift-related alkaline volcanism-the Chyulu Hills Volcanic Province, Southern Kenya. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 765–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.Y. Several recently proposed geothermometers. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 1991, 10, 7–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Depaolo, D.J. Trace element and isotopic effects of combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 53, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, B.L.; Wang, G.; Li, S.J.; Zhao, T.F.; Li, L.; Zhi, Y.B. Thegeochemistry and geochronology of the Xiarihamu II mafic-ultramafic complex, Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China: Implications for the genesis of magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.R.; Alvi, S.H.; Balaram, V. Geochemistry of the mafic dykes in parts of the Singhbhum granitoid complex: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, D.C.; Keays, R.R. Insights into the behaviour of precious metals in primitive, S-undersaturated magmas: Evidence from the Heazlewood River Complex, Tasmania. Can. Mineral. 1990, 28, 553–577. [Google Scholar]
- Queffurus, M.; Barnes, S.J. A review of sulfur to selenium ratios in magmatic nickel-copper and platinum-group element deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 69, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstrand, O.R.; Cogolu, E. Se/S Evidence Relating to Genesis of Sulphides in the Crystal Lake Gabbro, Thunder Bay, Ontario; Geological Association of Canada-Abstract Programs; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 1986; Volume 11, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, M. Relationship between Se/S and sulfur isotope ratios of hydrothermal sulfide minerals. Miner. Depos. 1976, 11, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.G.; Lambert, D.D.; Frick, L.R. Re-Os isotopic evidence for genesis of Archaean nickel ores from uncontaminated komatiites. Nature 1996, 382, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Du, A.D.; Lu, J.R.; Qu, W.J.; Chen, J.F. Re-Os (ICP-MS) dating of the mass ores in Jinchuan Cu-Ni-Pt deposit. Sci. China (Ser. D) 2005, 35, 241–245. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Yang, J.M.; Qu, W.J.; Du, A.D.; Wang, Z.L.; Han, C.M. Re-Os dating of Cu-Ni sulfide ores from Huangshandong deposit in Xinjiang and Its geodynamic significance. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, R.H.; Karleen, E.D. Nickel partitioning between olivine and silicate melt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1978, 40, 203–219. [Google Scholar]
- Shima, H.; Naldrett, A.J. Solubility of sulfur in an ultramafic melt and the relevance of the system Fe-S-O. Econ. Geol. 1975, 70, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlandt, R.F. Sulfide saturation of basalt and andesite melts at high pressures and temperatures. Am. Mineral. 1982, 67, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogenes, J.A.; O’Neill, H.S.C. The relative effects of pressure, temperature and oxygen fugacity on the solubility of sulfide in mafic magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, W.D.; Barnes, S.J.; Waal, S.A.D. Exploration for magmatic Ni-Cu-PGE sulphide deposits: A review of recent advances in the use of geochemical tools, and their application to some South African ores. S. Afr. J. Geol. 1998, 101, 237–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lambertt, D.D.; Walker, R.J.; Morgan, J.W. Re-Os and Sm-Nd isotope geochemistry of the Stillwater Complex, montana: Implications for the prteogenesis of the J-M Reef. J. Petrol. 1998, 35, 1717–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Ore Block | Ore Body | Type of Ore Body | Length (m) | Thickness (m) | Occurrence | Mineralization Characteristics | Ore Grade | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(%) | Cu(%) | Co(%) | ||||||||
| Ore block II | M1 | G-M1 | High-grade industrial ore body | 200 | 1.22~22.6 | 174°∠72° | It contains massive ores, which mainly includes pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, and pentlandite with many hydrothermal pyrites as well, and the hosted rocks are mainly harzburgite and lherzaolite. | Max 1.57, average 0.50 | Max 0.79, average 0.29 | Max 0.079, average 0.030 |
| D-M1 | Low-grade ore body | 100 | 1.18 | The ore-hosted rocks are mainly harzburgite, lherzolite and olivine pyroxenite with the major disseminated sulfides and locally crumb, sideronitic sulfides. They contain variable amounts pyrrhotites, chalcopyrites, pentlandites and pyrites, and the higher contents of sulfide, the higher ore grade. | 0.21~0.36, average 0.24 | 0.19~0.26 | 0.015~0.029 | |||
| M2 | Low-grade ore body | 80 | 1.50 | 194°∠67° | 0.20~0.30, average 0.23 | 0.11~0.12 | 0.023~0.025 | |||
| M3 | Mineralization body | 0.92 | Average 0.21 | Average 0.12 | Average 0.016 | |||||
| M4 | Concealed mineralization body | 0.93 | Max 0.33, average 0.29 | 0.07~0.22 | 0.014~0.0.019 | |||||
| Ore block III | M5 | Concealed mineralization body | 0.89 | Average 0.32 | Average 0.30 | Average 0.017 | ||||
| M6 | Concealed ore body | 240 | 0.68~2.15 | Max 0.39, average 0.29 | 0.06~0.20 | 0.012~0.018 | ||||
| M7 | Concealed industrial ore body | 320 | 0.39~2.58 | Max 0.48, average 0.32 | 0.10~0.36 | 0.015~0.023 | ||||
| M8 | Concealed ore body | 80 | 0.75~1.16 | Max 0.31, average 0.26 | 0.07~0.14 | 0.016~0.019 | ||||
| M9 | Concealed ore body | 80 | 6.90 | Max 0.28, average 0.23 | Max 0.32, average 0.22 | Max 0.018, average 0.016 | ||||
| M10 | G-M10 | Concealed industrial ore body | 80 | 2.33 | Max 1.06, average 0.69 | 0.03~0.36 | 0.011~0.057 | |||
| D-M10 | Concealed ore body | 80 | 6.89 | Max 0.65, average 0.25 | 0.04~0.37 | 0.01~0.032 | ||||
| Sample | Rock Type | Mineralization | Testting Sulfide | δ34S(‰) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBZL-II-ZK0801-B1 | Harzburgite | Massive ore | Pentlandite | −1.5 | This paper |
| NBZL-II-ZK0801-B11 | Lherzolite | Massive ore | Pentlandite | −0.8 | |
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B20 | Olivine pyroxenite | Disseminated ore | Pyrrhotite | 3.9 | |
| Pyrite | 1.4 | ||||
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B21 | Websterite | Disseminated ore | Pentlandite | 3.7 | |
| Pyrrhotite | 0.7 | ||||
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B22 | Olivine pyroxenite | Disseminated ore | Pyrrhotite | 7.4 | |
| NS-1 | Pyrite | −1.4 | Ling, 2014 [22] | ||
| NS-2 | Pyrite | −1.8 | |||
| NS-3 | Pyrite | −0.1 | |||
| NS-4 | Pyrite | −2.8 | |||
| NS-5 | Pyrite | −8.4 | |||
| In-situ 1 | Cu-Ni sulfide | 9.47 | |||
| In-situ 2 | Cu-Ni sulfide | 6.79 | |||
| In-situ 3 | Cu-Ni sulfide | 0.32 |
| Sample | NBZL-II-ZK0801-B11 | NBZL-III-ZK0801-B20 | NBZL-III-ZK0801-B21 | NBZL-III-ZK0801-B22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rock Type | Harzburgite | Olivine pyroxenite | Websterite | Olivine pyroxenite | |
| Testing Sulfide | Pentlandite | Pyrrhotite | Pyrite | Pyrrhotite | Pentlandite |
| 206Pb/204Pb | 21.359 | 18.153 | 18.334 | 17.958 | 19.574 |
| 207Pb/204Pb | 16.161 | 15.604 | 15.655 | 15.549 | 15.819 |
| 208Pb/204Pb | 42.379 | 38.265 | 38.610 | 38.363 | 40.108 |
| 206Pb/207Pb | 1.3216 | 1.1634 | 1.1711 | 1.1549 | 1.2374 |
| t(Ma) | −1000 | 357.8 | 289.5 | 432.3 | −402.6 |
| μ | 10.65 | 9.50 | 9.58 | 9.42 | 9.79 |
| ω | 42.73 | 37.27 | 38.17 | 38.29 | 38.88 |
| Th/U | 3.88 | 3.80 | 3.86 | 3.93 | 3.84 |
| V1 | 250.93 | 67.09 | 80.21 | 64.39 | 149.05 |
| V2 | 180.90 | 54.51 | 60.83 | 42.44 | 109.59 |
| △α | 265.24 | 75.32 | 86.05 | 63.77 | 159.5 |
| △β | 55.72 | 19.34 | 22.67 | 15.74 | 33.38 |
| △γ | 149.34 | 37.76 | 47.12 | 40.42 | 87.75 |
| Sample | Rock Type | Mineralization | δ18OV-SMOW (‰) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBZL-II-DB-B8 | Harzburgite | Disseminated sulfides | 7.4 | This paper |
| NBZL-II-DB-B9 | Harzburgite | Disseminated sulfides | 8.1 | |
| NBZL-III-DB-B8 | Gabbro | Starspot pyrite locally | 6.7 | |
| NBZL-III-DB-B9 | Gabbro | Starspot pyrite locally | 7.1 | |
| 401-I-G4-2 | Harzburgite | Disseminated sulfides | 6.6 | Ling, 2014 [22] |
| 401-I-G5 | Harzburgite | Disseminated sulfides | 5.1 | |
| II 5-14 | Gabbro | Starspot pyrite locally | 6.8 | |
| II 5-15 | Gabbro | Starspot pyrite locally | 7.8 | |
| II 6-5 | Olivine-pyroxene hornblendite | Disseminated sulfides | 6.5 |
| Sample | Rock Type | S(ppm) | Se(ppm) | Te(ppm) | S/Se |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBZL-II-ZK0302-B15 | Harzburgite | 1845 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 5185 |
| NBZL-II-DB-B14 | Gabbro | 615 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 1864 |
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B20 | Olivine pyroxenite | 1640 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 5230 |
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B21 | Websterite | 4100 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 3927 |
| NBZL-III-ZK0801-B22 | Olivine pyroxenite | 2665 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 5890 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Tan, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, F.; Shen, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Mineral Chemistry, S-Pb-O Isotopes, and S/Se Ratios of the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) Sulfide Deposit in North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Constraints on the Parental Magma Composition, Evolution, and Sulfur Saturation Mechanism. Minerals 2020, 10, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100837
Li L, Sun F, Liu H, Tan S, Yu L, Wang F, Shen D, Wang X, Wang Y. Mineral Chemistry, S-Pb-O Isotopes, and S/Se Ratios of the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) Sulfide Deposit in North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Constraints on the Parental Magma Composition, Evolution, and Sulfur Saturation Mechanism. Minerals. 2020; 10(10):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100837
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Liang, Fengyue Sun, Huiwen Liu, Shucheng Tan, Lu Yu, Fei Wang, Dali Shen, Xueping Wang, and Yonggang Wang. 2020. "Mineral Chemistry, S-Pb-O Isotopes, and S/Se Ratios of the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) Sulfide Deposit in North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Constraints on the Parental Magma Composition, Evolution, and Sulfur Saturation Mechanism" Minerals 10, no. 10: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100837
APA StyleLi, L., Sun, F., Liu, H., Tan, S., Yu, L., Wang, F., Shen, D., Wang, X., & Wang, Y. (2020). Mineral Chemistry, S-Pb-O Isotopes, and S/Se Ratios of the Niubiziliang Ni-(Cu) Sulfide Deposit in North Qaidam Orogenic Belt, NW China: Constraints on the Parental Magma Composition, Evolution, and Sulfur Saturation Mechanism. Minerals, 10(10), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100837





