Abstract
This paper proposes a cloud-based framework that optimizes the three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of multiple types of sensor data captured from multiple remote robots. A working environment using multiple remote robots requires massive amounts of data processing in real-time, which cannot be achieved using a single computer. In the proposed framework, reconstruction is carried out in cloud-based servers via distributed data processing. Consequently, users do not need to consider computing resources even when utilizing multiple remote robots. The sensors’ bulk data are transferred to a master server that divides the data and allocates the processing to a set of slave servers. Thus, the segmentation and reconstruction tasks are implemented in the slave servers. The reconstructed 3D space is created by fusing all the results in a visualization server, and the results are saved in a database that users can access and visualize in real-time. The results of the experiments conducted verify that the proposed system is capable of providing real-time 3D scenes of the surroundings of remote robots.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, various innovative technological systems, such as multimedia contexts [1,2,3,4,5,6], video codecs [7,8], healthcare systems [9,10], and smart indoor security systems [11,12] are being actively researched. In the area of cloud computing, a failure rules aware node resource provision policy for heterogeneous services consolidated in cloud computing infrastructure has been proposed [10]. Various applications for human pose estimation, tracking, and recognition using red-green-blue (RGB) cameras and depth cameras have also been proposed [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. A depth camera gives an image in each frame that contains information about the distance from the camera to other objects around the camera’s position. In contrast, an RGB camera gives a color image in each frame. The security problems in distributed environment and cloud database as a service (DBaaS) have also been studied [25,26,27].
Cloud computing [28,29] provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand. In this study, we employed the cloud model to create a three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction framework for multiple remote robots. The 3D reconstruction [30,31,32,33,34,35,36] has been widely studied as an approach to enhance the sense of reality and immersion for users. However, accomplishing this technique in real-time and with high quality is challenging, particularly with multiple remote robots. In many tasks, such as rescue or tracking terrain, multiple remote robots are required to expand the working area. Each robot often has a light detection and ranging (Lidar) sensor, several cameras, and an inertial measurement unit-global positioning system (IMU-GPS) sensor attached. A Lidar sensor returns a point cloud that senses the surface of the terrain around the robot. The cameras are either 2D or stereo, and the images obtained from them are used to compute color points or texture coordinates. The IMU-GPS sensor is used to check the position and direction of each robot. An enormous amount of data is obtained from the multiple sensors attached to each robot. Processing these bulk data in real-time is impossible using a single computer with limited power. Thus, we propose a cloud system that optimizes the reconstruction of these large amounts of sensor data from multiple remote robots. In this framework, we create a master-slave server model in which the master server distributes the data to be processed to multiple slave servers to increase the computing ability. The segmentation servers use our previously proposed algorithm [37] to separate each frame of the point cloud data into two groups: ground and non-ground. The first group consists of ground points of terrain that the robots can traverse. The second group consists of non-ground points that the robots cannot traverse, such as buildings, walls, cars, and trees. The reconstruction servers process the ground and non-ground data differently. Furthermore, the non-ground data are modeled using colored particles [35]. On the other hand, the ground data are reconstructed by meshing and texture mapping [36]. The results from all reconstruction servers are then sent to a visualization server to save in a database. We employ a file database where users can access and visualize the 3D scene around all the robots.
2. Related Works
Reconstruction of 3D scenes from point clouds is an important task for many systems such as autonomous vehicles and rescue robots. Several studies have been conducted on reconstruction in both indoor and outdoor environments [30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. In the indoor environment, Izadi et al. [30] and Popescu and Lungu [31] employed a Microsoft Kinect sensor. Khatamian and Arabnia [32] reviewed several 3D surface reconstruction methods from unoriented input point clouds and concluded that none of them are able to run in real-time. In [33,34,35,36], the authors used one 3D laser range scanner combined with cameras and an IMU-GPS sensor for the outdoor environment. Because the features of ground and non-ground data are different, they have to be segmented and reconstructed separately. Over the past few years, many segmentation methods [38,39,40,41,42,43] have been proposed. However, these methods have disadvantages related to accuracy and processing time. We previously introduced a new ground segmentation algorithm [37] that works well with various terrains at high speed.
Paquette et al. [44] employed orthorgonal lines to determine the orientation of the mobile robot. In [45,46], the authors proposed a method for navigating a multi-robot system through an environment while obeying spatial constraints. Mohanarajah et al. [47] presented architecture, protocol, and parallel algorithms for collaborative 3D mapping in the cloud with low-cost robots. Jessup et al. [48] proposed a solution for refining transformation estimates between the reference frames of two maps using registration techniques with commonly mapped portions of the environment. Another study [49] investigated a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system based on a distributed framework for optimization and storage of bulk sensing data in the cloud. In [50,51], the authors supplemented the insufficient computing performance of a robot client using a cloud server for collaboration and knowledge sharing between robots. Sim et al. [52] proposed a calibration scheme for fusing 2D images and 3D points. For fast transfer data among the computers in the network, we use the UDP-based data transfer protocol (UDT) [53] which UDP stands for user datagram protocol. This method can transfer data at high speeds (10 Gbit/s). In our research, the data are compressed to decrease the bandwidth for transmission via the network and reduce storage space in the database. The compression is an important task in many studies [54,55,56,57]. There are two types of compression: lossy and lossless. For 2D images, we use a lossy compression method, and a lossless compression method is employed for other data. We employ a fast and high ratio compression method library [58].
The studies cited above involve server-based data processing technology for processing bulk sensor data generated from a number of clients. The insufficient computing performance of the client was obviated by employing a distributed processing environment using a cloud server. However, one common feature of the studies cited above is reliance on batch-processing methods, rather than real-time processing. In contrast, we propose a real-time platform for the reconstruction of 3D scenes from point clouds and 2D images acquired by sensors attached to multiple robots.
3. Framework Design
The cloud-based 3D reconstruction framework acquires data from multiple sensors attached to multiple remote robots. The data are used to reconstruct the 3D scene in real-time. Figure 1 gives an overview of the framework. Suppose that we have n remote robots working simultaneously, each with k sensors comprising several 2D cameras, a 3D range sensor, and an IMU-GPS. The 2D cameras return color images of the environment around each robot. In each frame, the 3D range sensor releases numerous laser rays and returns a point cloud. The IMU-GPS sensor is used to detect the position and navigation of each robot. We therefore construct a framework that creates a working environment for these n robots in real-time. The framework contains one master server, one visualization server, m segmentation servers, and m reconstruction servers (m ≥ n). Each robot has one computer that acquires all the data from multiple sensors. The data are compressed before sending to the master server via wireless communication.
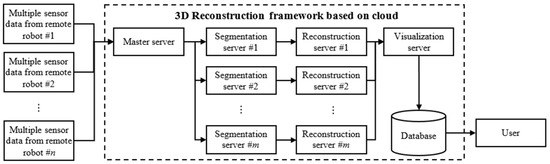
Figure 1.
Overview of our three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction framework based on the cloud for multiple remote robots.
After considering the computing resources of all slaves, the master distributes the data to the m segmentation servers. In each segmentation server, the data are decompressed, then, by using IMU-GPS data, and all points are converted from local to global coordinates. We separate the point cloud into two parts: ground and non-ground. The segmentation result is again compressed before being sent to its corresponding reconstruction server. In each reconstruction server, all of the data are first decompressed and then used to reconstruct the virtual 3D scene. Then, the results from all reconstruction servers are compressed again and transferred to the visualization server to be saved in the database. Users can then access the database and obtain the 3D scene of the working area of all the remote robots.
3.1. Ground Segmentation Algorithm
We employ our ground segmentation algorithm [37]. The main idea of this algorithm is to divide a point cloud into small groups, each called a vertical-line. The pseudo-code representing our idea is shown in Algorithm 1. First, we decompress the point cloud and IMU-GPS data. As the frame data gained from the range sensor are in the local coordinates, we have to convert them into global coordinates. We employ the method presented in [35] to change the coordinates of all 3D points in each frame dataset with small distortions. For example, robot #k starts collecting 3D points at time . At time , the local coordinate system of a 3D point is centered at robot position . To change the coordinate system of all points, we use the following formula:
where is the 3D vector from the 3D sensor location to the GPS sensor location. is the 3D vector from the starting position of robot #k to one fixed point, which is chosen as an origin of the global coordinate. is the rotation matrix of robot #k at time . The error of this method is only a few centimeters. In addition, this method is capable of merging point clouds captured by many robots. After segmentation, we compress ground and non-ground groups separately before sending them to a corresponding reconstruction server.
| Algorithm 1 Ground segmentation |
| Convert all points into global coordinate() |
| FOR EACH vertical-line IN a frame data |
| WHILE NOT (all points in the vertical-line are labeled) |
| Assign a start-ground point() |
| Find a threshold point() |
| Assign points’ label() |
| END |
| END |
3.2. Terrain Reconstruction Algorithm
The method used to reconstruct the 3D terrain is based on the ideas presented in [35,36]. The architecture running in each reconstruction server is illustrated in Figure 2. Following the ground segmentation step, each set of frame data is divided into two groups. We apply a projection method using texture buffers and non-ground points. A set of colored points is obtained using the calibration method [52]. These colored points are split into several nodes based on the x–z coordinates. Then, the non-ground result of each node is compressed and sent to the visualization server. The ground points are used to update the ground mesh, which is a set of nodes. The size of each ground node is equal to the size of the non-ground node outlined above. We then implement texture mapping from the ground mesh and texture buffers. The ground surface result is also compressed and sent to the visualization server. We employ the zip library (ZLIB) [58] for compression and decompression because it is lossless and fast. Each block in Figure 2 is described in detail in [35,36]. However, sending the ground and non-ground reconstruction result data is a challenging task, even after compressing the data. More details of the sending result data are given in the ensuing section.
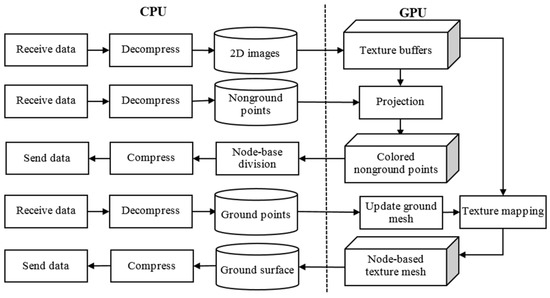
Figure 2.
Terrain reconstruction framework in each reconstruction server.
3.3. Reconstruction Data Processing
In previous studies [47,48,49,50,51], colored points were used to make particles. Thus, the size of the resulting data was relatively small. We also do not need to consider any overlapping problem. In our system, we model ground data via triangular meshes and texture mapping to enable better reconstruction quality. We employ a high speed, accurate, and stable method [53] for transferring big data via the network. However, sending the ground surface result in every frame would result in two problems. First, the size of the data is significant and the network cannot satisfy the transfer. Second, it is difficult to avoid overlapping data in a visualization server. To solve these problems, we send the reconstruction results of the ground and non-ground data in different ways. For colored non-ground points, we count the total number of points. If the number of colored points is larger than a maximum value, we compress all node data and send the data to the visualization server. For the ground surface data, we propose a new transmission algorithm. As mentioned above, the ground data are divided into a set of mesh nodes. Each mesh node is processed independently; hence, we also send the surface data of each node separately using Algorithm 2. The Threshold is one of the values used to consider sending ground surface data. In general, if the Ratio is smaller than the Threshold, the ground surface data are not sent. Never_Send_Data is a global variable with an initial value TRUE. If the function returns FALSE, it means no data should be sent. Otherwise, we compress the data and send them to the visualization server. Figure 3 represents the working area of each robot. The sending data of each robot are independent. Each node is represented by a cell and the blue line demonstrates the orthogonal line mentioned in Algorithm 2. Each robot has one orthogonal line in the x–z surface. The orthogonal line has two characteristics. First, it goes through each robot’s position. Second, it is perpendicular to the robot’s direction.
| Algorithm 2 Sending ground surface data |
| Ratio ← Number_Of_Triangles/Maximum_Triangles |
| Estimated_Ratio ← Number_Of_Triangles/Estimated_Number_Of_Triangles |
| Threshold ← Medium_Value |
| Intersection_Status ← Check intersection between orthogonal line and Node() |
| Dynamic_Increasing_Delta_1 ← (1 − Previous_Ratio)/2 |
| IF Intersection_Status = TRUE THEN |
| IF Never_Send_Data = TRUE THEN |
| Threshold ← Small_Value |
| ELSE IF (Ratio − Previous_Ratio) < Dynamic_Increasing_Delta_1 THEN |
| RETURN FALSE |
| END |
| END |
| IF Never_Send_Data = TRUE THEN |
| IF (Ratio < Threshold) OR (Estimated_Ratio < Threshold) THEN |
| RETURN FALSE |
| ELSE |
| Previous_Ratio ← Ratio |
| Never_Send_Data ← FALSE |
| END |
| ELSE |
| Dynamic_Increasing_Delta_2 ← (1 − Previous_Ratio)/4 |
| IF (Ratio − Previous_Ratio) < Dynamic_Increasing_Delta_2 THEN |
| Dist ← Distance between Node’s center and orthogonal line() |
| IF (Dist < Size_Of_Node) AND (Ratio > Previous_Ratio) THEN |
| Previous_Ratio ← Ratio |
| ELSE |
| Return FALSE |
| END |
| END |
| Previous_Ratio ← Ratio |
| END |
| END |
| Compress Data() |
| Send Data() |
| RETURN TRUE |
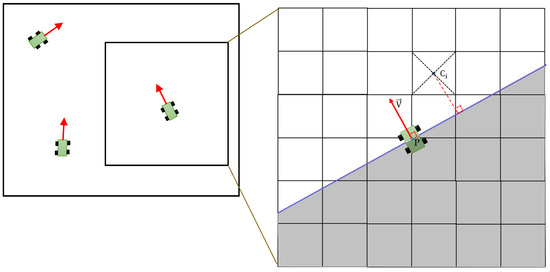
Figure 3.
Example of working area for each robot from the top view.
To calculate the distance from each node’s center to the orthogonal line in Algorithm 2, we employ Equation (2). In this equation, V and P are the current direction and the position of the mobile robot, respectively, and is the center of node i:
We use two diagonal lines to check the intersection between the orthogonal line and each node, as shown in Figure 3. We also calculate it using the four functions illustrated in Equation (3). If , we conclude that the orthogonal line cuts node i. In Equation (3), s is the size of each node.
To save the reconstruction result in the visualization server, we create a database with the data structure shown in Figure 4. This database is organized in a set of nodes, each containing data about a cube area, which is equal to the size of each node in the reconstruction step. We divide each node’s data into four parts. The first part is colored non-ground points. For visualization in the user’s application, we perform particle rendering from these colored points. The other parts are the texture image, vertex buffer, and index buffer containing data about the ground surface. In order to speed up writing and save the storage space, all data are stored in compressed format.
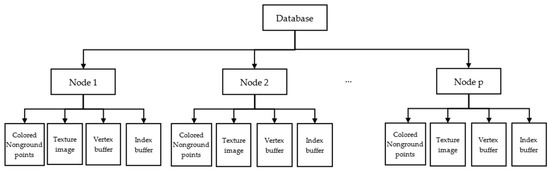
Figure 4.
Database structure in the visualization server.
4. Experiments and Analysis
We conducted two experiments and evaluated the proposed framework. We employed multiple datasets comprising data captured from a Lidar sensor (Velodyne HDL-32E, Velodyne Inc, Morgan Hill, CA, USA), an IMU-GPS sensor (customized by us), and three 2D cameras (Prosilica GC655C, Allied Vision Inc, Exton, PA, USA) to simulate multiple robots. Table 1 gives a listing of the computers used in the system. We used three segmentation servers and three reconstruction servers. In each reconstruction server, we employed an NVIDIA graphics card (NVIDIA Inc, Santa Clara, CA, USA), each of a different type and with different amounts of memory, for graphics processing unit (GPU) computing. The user’s application was executed on the same PC as the visualization server. Our experiments utilized three simulation robots. The robots sent the IMU-GPS data, point clouds, and images to the master server in real-time and each robot returned approximately 60,000 points per second. As the frame rate of the Velodyne sensor is 10 fps, we therefore captured 10 images per second from each 2D camera. Using three cameras, we obtained 30 images per second. The resolution of each 2D image was 640 × 480 pixels. To reduce the size of the image data, we needed a fast and high ratio compression. In our experiments, we employed a lossy compression method with JPEG standard. For storing data in the visualization server, we used a file database. We created four folders to contain the colored non-ground points, texture images, vertex buffers, and index buffers, with the corresponding data saved in four files in corresponding folders. Each file was separated by name, which is the coordinate of the node’s center. For future work, we will consider employing another database management system (DBMS). For high-speed data transfer, we employed the UDT protocol [53] which is a UDP-based method.

Table 1.
Configuration of the computers used in the experiment.
4.1. Experimental Results
After running the experiments, the user was able to see the results in real-time. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the results of the first experiment. Figure 5a,b demonstrate the 2D and 3D scenes of the user viewer after running the system for a few seconds. Figure 5c,d show the results after the three robots worked for approximately one minute. The three robots scanned a mountain road approximately 800 m long. Each blue cell in the 2D map denotes one node from the top view. The x–z size of the node is 12.7 m. We also captured four 3D screenshots, as shown in Figure 6. These screenshots were taken at the positions illustrated in Figure 5c. Using the same method, Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the results of the second experiment. The results show that our framework is able to reconstruct 3D scenes from multiple remote robots at the same time. As shown below, we successfully generated visualization results using the proposed framework in real-time.
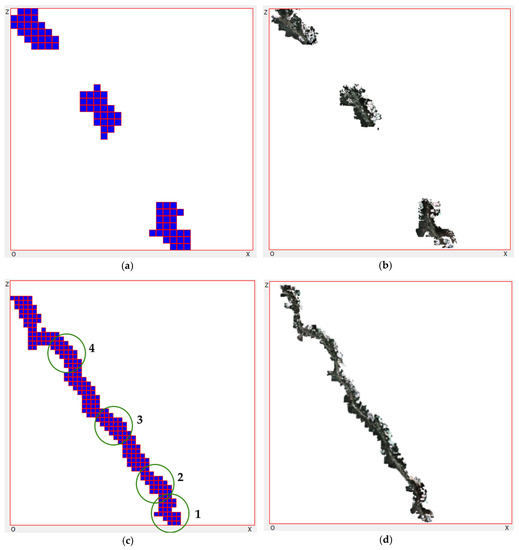
Figure 5.
Real-time visualization results viewed by the user in the first experiment: (a) 2D scene after three robots ran for a few seconds; (b) 3D scene after three robots ran for a few seconds; (c) 2D scene after three robots worked approximately 1 min; and (d) 3D scene after three robots worked approximately 1 min.
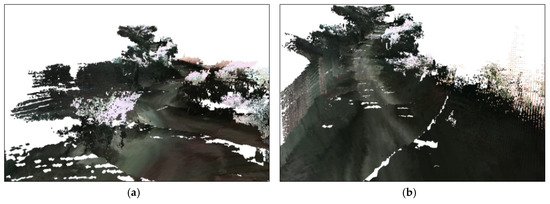
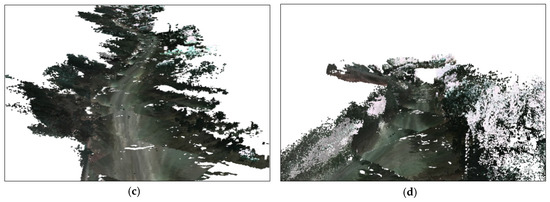
Figure 6.
Screenshots of the 3D scene: (a–d) at positions 1, 2, 3, 4 in Figure 5c, respectively.
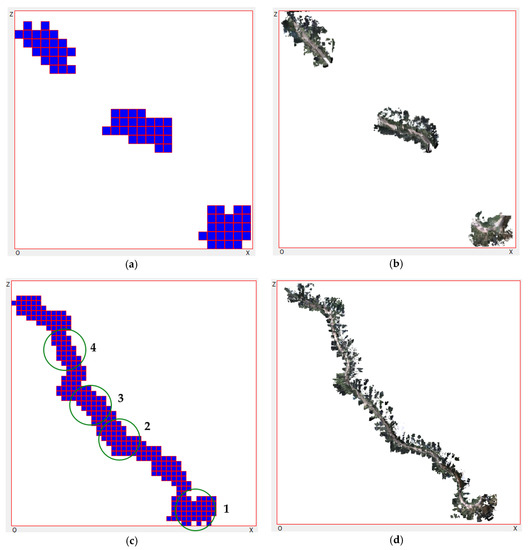
Figure 7.
Real-time visualization result viewed by the user in the second experiment: (a) 2D scene after three robots ran for a few seconds; (b) 3D scene after three robots ran for a few seconds; (c) 2D scene after three robots worked approximately 50 s; and (d) 3D scene after three robots worked approximately 50 s.
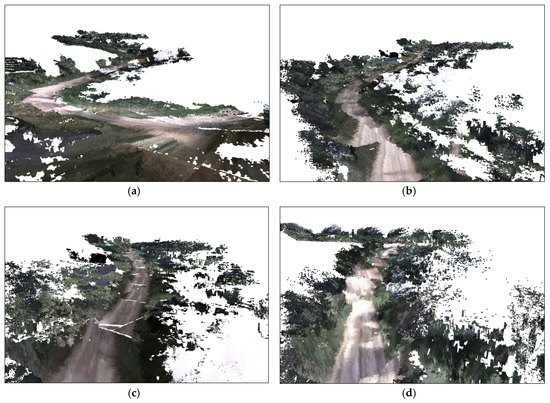

Figure 8.
Screenshots of the 3D scene: (a–d) at positions 1, 2, 3, 4 in Figure 7c, respectively.
4.2. Experimental Analysis
To evaluate the proposed system, we measured the processing time and network usage. The segmentation and reconstruction time per frame in each server are depicted in Figure 9 and Figure 10. Table 2 shows the average segmentation time of each server. The average processing time per frame in each segmentation server of the first and second experiment are 2.69 and 2.84 ms, respectively. Each segmentation server, therefore, can run at a rate of 352 fps. Table 3 shows the average reconstruction time of each reconstruction server. The average reconstruction time per frame is 34.57 ms for the first experiment and 37.41 ms for the second. Hence, each reconstruction server is capable of running at a rate of 27 fps. The frame rate of the Velodyne sensor is 10 fps; hence, our system can process data in real-time. Figure 11 and Figure 12 show the total network usage for each robot per second. Table 4 presents the average network usage of each robot in megabytes per second. In the first experiment, 4.28 MB/s is needed for each robot to transfer data via the network. The average bandwidth for each robot is 3.99 MB/s in the second experiment. In both experiments, the required bandwidth is higher than the bandwidth requirement of [47] (500 KB/s) and [49] (1 MB/s). However, whereas we utilized ground mesh and texture mapping, previous studies used only color points. In addition, we employed different sensors and our method has better visualization quality in outdoor environments than [47,49]. The results show that our system can perform suitably in the environment using wireless communication.
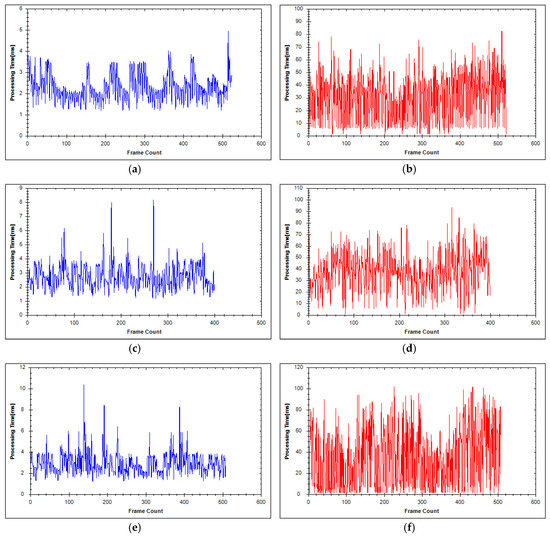
Figure 9.
Segmentation and reconstruction time in milliseconds in each server per frame in the first experiment: (a,c,e) Segmentation time per frame in segmentation servers 1, 2, and 3, respectively; and (b,d,f) reconstruction time per frame in reconstruction servers 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
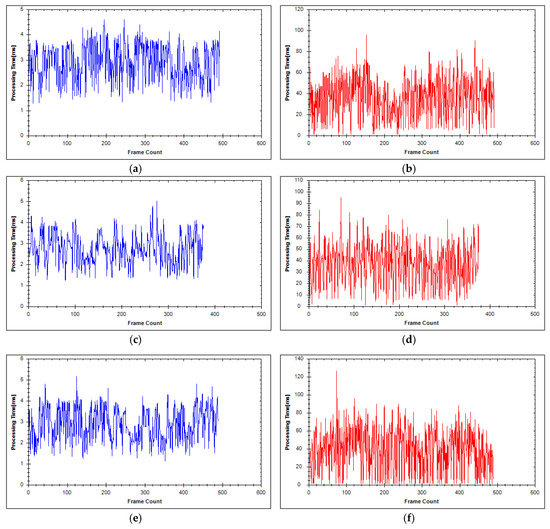
Figure 10.
Segmentation and reconstruction time in milliseconds in each server per frame in the second experiment: (a,c,e) Segmentation time per frame in segmentation servers 1, 2, and 3, respectively; and (b,d,f) reconstruction time per frame in reconstruction servers 1, 2, and 3, respectively.

Table 2.
Average processing time in each Segmentation server.

Table 3.
Average processing time in each Reconstruction server.
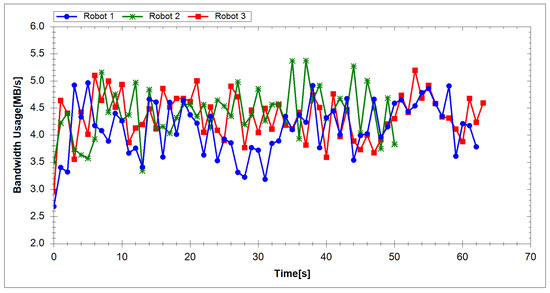
Figure 11.
Network usage (in megabytes per second) for each robot in the first experiment.
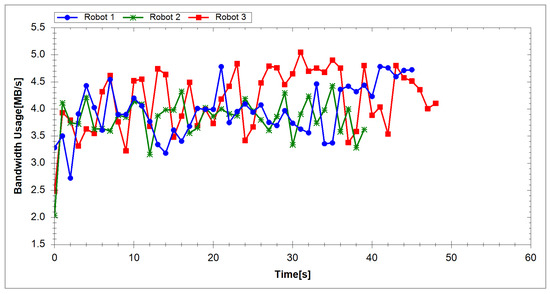
Figure 12.
Network usage (in megabytes per second) for each robot in the second experiment.

Table 4.
Average network usage for each robot.
5. Conclusions
In many systems, such as rescue or tracking terrains, multiple remote robots working simultaneously result in more efficiency than a single robot. However, reconstruction for multiple remote robots is challenging. This paper proposed a 3D reconstruction framework for multiple remote robots on the cloud. The proposed framework utilizes a master-slave server model, thereby enabling distributed processing of bulk data generated by multiple sensors. To evaluate our proposed framework, we conducted experiments in which three remote robots were simulated. The input data were processed on segmentation servers and reconstruction servers. Then, the resulting data were fused in a visualization server. The experimental results obtained confirm that our system is capable of providing real-time 3D scenes of the surroundings of all remote robots. In addition, users need not consider the computing resource. Further study is needed to expand the proposed framework to reduce the network usage and apply it to real robots. We plan to increase the quality of the 3D reconstruction by meshing and texture mapping non-ground data. We also plan to research special cases such as limited bandwidth and varying ability of the master server.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and future Planning (NRF-2015R1A2A2A01003779).
Author Contributions
Phuong Minh Chu and Seoungjae Cho have written the source codes. The main contribution of Simon Fong is the development direction of the framework. Kyungeun Cho and Yong Woon Park contributed to the discussion and analysis of the results. Phuong Minh Chu have written the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kamal, S.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Lee, K. Suppressing the effect of ICI power using dual sinc pulses in OFDM-based systems. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Falchetti, A.; Arrano, H.F.; Kamal, S.; Lee, K. Evaluation of the improved parametric linear combination pulse in digital baseband communication systems. In Proceedings of the Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) Conference, Jeju, Korea, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Lee, K. Family of Nyquist-I Pulses to Enhance Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing System Performance. IETE Tech. Rev. 2016, 33, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Kamal, S.; Lee, K. BER enhancement of OFDM-based systems using the improved parametric linear combination pulse. In Proceedings of the Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) Conference, Jeju, Korea, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 743–745. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Lee, K. Subsiding OOB Emission and ICI power using iPOWER pulse in OFDM systems. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 16, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Lee, K. Nyquist-I pulses designed to suppress the effect of ICI power in OFDM systems. In Proceedings of the Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC) International Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 24–28 August 2015; pp. 1412–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Sarif, N.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, T.S. Human activity recognition via recognized body parts of human depth silhouettes for residents monitoring services at smart homes. Indoor Built Environ. 2013, 22, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Robust human activity recognition from depth video using spatiotemporal multi-fused features. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. A depth video sensor-based life-logging human activity recognition system for elderly care in smart indoor environments. Sensors 2014, 14, 11735–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. A depth video-based human detection and activity recognition using multi-features and embedded hidden Markov models for health care monitoring systems. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell. 2017, 4, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Meng, D. Failure rules based mode resource provision policy for cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications (ISPA), Taipei, Taiwan, 6–9 September 2010; pp. 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, D. Global security using human face understanding under vision ubiquitous architecture system. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2006, 13, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Puwein, J.; Ballan, L.; Ziegler, R.; Pollefeys, M. Joint camera pose estimation and 3D human pose estimation in a multi-camera setup. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Singapore, 1–5 November 2014; pp. 473–487. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D. Ridge body parts features for human pose estimation and recognition from RGB-D video data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies, Hefei, China, 11–13 July 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Human depth sensors-based activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and hidden markov model for smart environments. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, R.; Morlok, R.; Papanikolopoulos, N. Dual-camera system for multi-level activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2004), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Jalal, A.; Kim, D. Depth images-based human detection, tracking and activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and modified HMM. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 11, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Individual detection-tracking-recognition using depth activity images. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence, Goyang, Korea, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, A.; Jalal, A.; Kamal, S. Dense RGB-D Map-Based Human Tracking and Activity Recognition using Skin Joints Features and Self-Organizing Map. KSII Trans. Int. Inf. Syst. 2015, 9, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Depth Map-based Human Activity Tracking and Recognition Using Body Joints Features and Self-Organized Map. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies, Hefei, China, 11–13 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S. Real-Time Life Logging via a Depth Silhouette-based Human Activity Recognition System for Smart Home Services. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance, Seoul, Korea, 26–29 August 2014; pp. 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Jalal, A. A hybrid feature extraction approach for human detection, tracking and activity recognition using depth sensors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Farooq, A.; Kim, D. A spatiotemporal motion variation features extraction approach for human tracking and pose-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision, Fukuoka, Japan, 15–17 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, S. The Mechanism of Edge Detection using the Block Matching Criteria for the Motion Estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Computer Interaction, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–27 July 2005; pp. 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Zeb, M.A. Security and QoS Optimization for distributed real time environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 27–29 December 2007; pp. 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, K. Security model for cloud database as a service (DBaaS). In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Cloud Technologies and Applications, Marrakech, Morocco, 2–4 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; IjazUddin. Security architecture for third generation (3G) using GMHS cellular network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies, Islamabad, Pakistan, 12–13 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, J.; Mishra, M.R. Mitigating Threats and Security Metrics in Cloud Computing. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 12, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Lee, C. A Security Protection Framework for Cloud Computing. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, S.; Kim, D.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Newcombe, R.; Kohli, P.; Shotton, J.; Hodges, S.; Freeman, D.; Davison, A.; et al. KinectFusion: Real-time 3D Reconstruction and Interaction Using a Moving Depth Camera. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2011; pp. 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C.R.; Lungu, A. Real-Time 3D Reconstruction Using a Kinect Sensor. In Computer Science and Information Technology; Horizon Research Publishing: San Jose, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Khatamian, A.; Arabnia, H.R. Survey on 3D Surface Reconstruction. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 12, 338–357. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, D.; Herman, H.; Kelly, A.; Rander, P.; Ziglar, J. Real-time Photo-realistic Visualization of 3D Environments for Enhanced Tele-operation of Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 1518–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.; Capstick, E.; Huber, D.; Herman, H.; Rander, P.; Warner, R. Real-Time Photorealistic Virtualized Reality Interface For Remote Mobile Robot Control. In Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 70, pp. 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Cho, K. Real-time terrain reconstruction using 3D flag map for point clouds. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2013, 74, 3459–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cho, S.; Cho, K.; Um, K.; Won, C.S.; Sim, S. Traversable Ground Surface Segmentation and Modeling for Real-Time Mobile Mapping. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Cho, S.; Cho, K. Fast ground segmentation for LIDAR Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing Application and Wireless Sensor Network (UCAWSN-16), Jeju, Korea, 6–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, J.; Marcotegui, B. Point Cloud Segmentation towards Urban Ground Modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Moosmann, F.; Pink, O.; Stiller, C. Segmentation of 3D Lidar Data in non-flat Urban Environments using a Local Convexity Criterion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Xi’an, China, 3–5 June 2009; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Douillard, B.; Underwood, J.; Kuntz, N.; Vlaskine, V.; Quadros, A.; Morton, P.; Frenkel, A. On the Segmentation of 3D LIDAR Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 2798–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, J. Segmentation-based ground points detection from mobile laser scanning point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Workshop on Image and Data Fusion, Kona, HI, USA, 21–23 July 2015; pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Kim, J.; Ikram, W.; Cho, K.; Jeong, Y.; Um, K.; Sim, S. Sloped Terrain Segmentation for Autonomous Drive Using Sparse 3D Point Cloud. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomori, Z.; Gargalik, R.; Hrmo, I. Active segmentation in 3d using kinect sensor. In Proceedings of the International Conference Computer Graphics Visualization and Computer Vision, Plzen, Czech, 25–28 June 2012; pp. 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Paquette, L.; Stampfler, R.; Dube, Y.; Roussel, M. A new approach to robot orientation by orthogonal lines. In Proceedings of the CVPR’88, Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 5–9 June 1988; pp. 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann, B.; Schulz, D. Coordinated Navigation of Multi-Robot Systems with Binary Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann, B.; Brunner, M.; Schulz, D. Spatially constrained coordinated navigation for a multi-robot system. Ad Hoc Netw. 2012, 11, 1919–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanarajah, G.; Usenko, V.; Singh, M.; Andrea, R.D.; Waibel, M. Cloud-based collaborative 3D mapping in real-time with low-cost robots. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessup, J.; Givigi, S.N.; Beaulieu, A. Robust and Efficient Multi-Robot 3D Mapping with Octree Based Occupancy Grids. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 3996–4001. [Google Scholar]
- Riazuelo, L.; Civera, J.; Montiel, J.M.M. C2TAM: A Cloud framework for cooperative tracking and mapping. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Park, H.S. A Cloud-based Integrated Development Environment for Robot Software Development. J. Inst. Control Robot. Syst. 2015, 21, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, B.G.; Bae, J.H. Cloudboard: A Cloud-Based Knowledge Sharing and Control System. KIPS Trans. Softw. Data Eng. 2015, 4, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Sock, J.; Kwak, K. Indirect Correspondence-Based Robust Extrinsic Calibration of LiDAR and Camera. Sensors 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Grossman, R.L. UDT: UDP-based data transfer for high-speed wide area networks. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 1777–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, D.; Xu, Y. Frame buffer compression without color information loss. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 27–29 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, S. Advanced performance achievement using multi-algorithmic approach of video transcoder for low bit rate wireless communication. ICGST Int. J. Graph. Vis. Image Process. 2005, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Rasheed, Y.A. Collaboration achievement along with performance maintenance in video streaming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Interactive Computer Aided Learning, Villach, Austria, 26–28 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, C.A.; Jayavant, R. Digital images, compression, decompression and your system. In Proceedings of the Conference Record WESCON/94, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27–29 September 1994; pp. 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- ZLIB. Available online: http://www.zlib.net (accessed on 10 September 2016).
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).