Symmetry-Aware Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network with Optimization Techniques for Accurate Workload and Resource Time Series Prediction in Cloud Computing Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
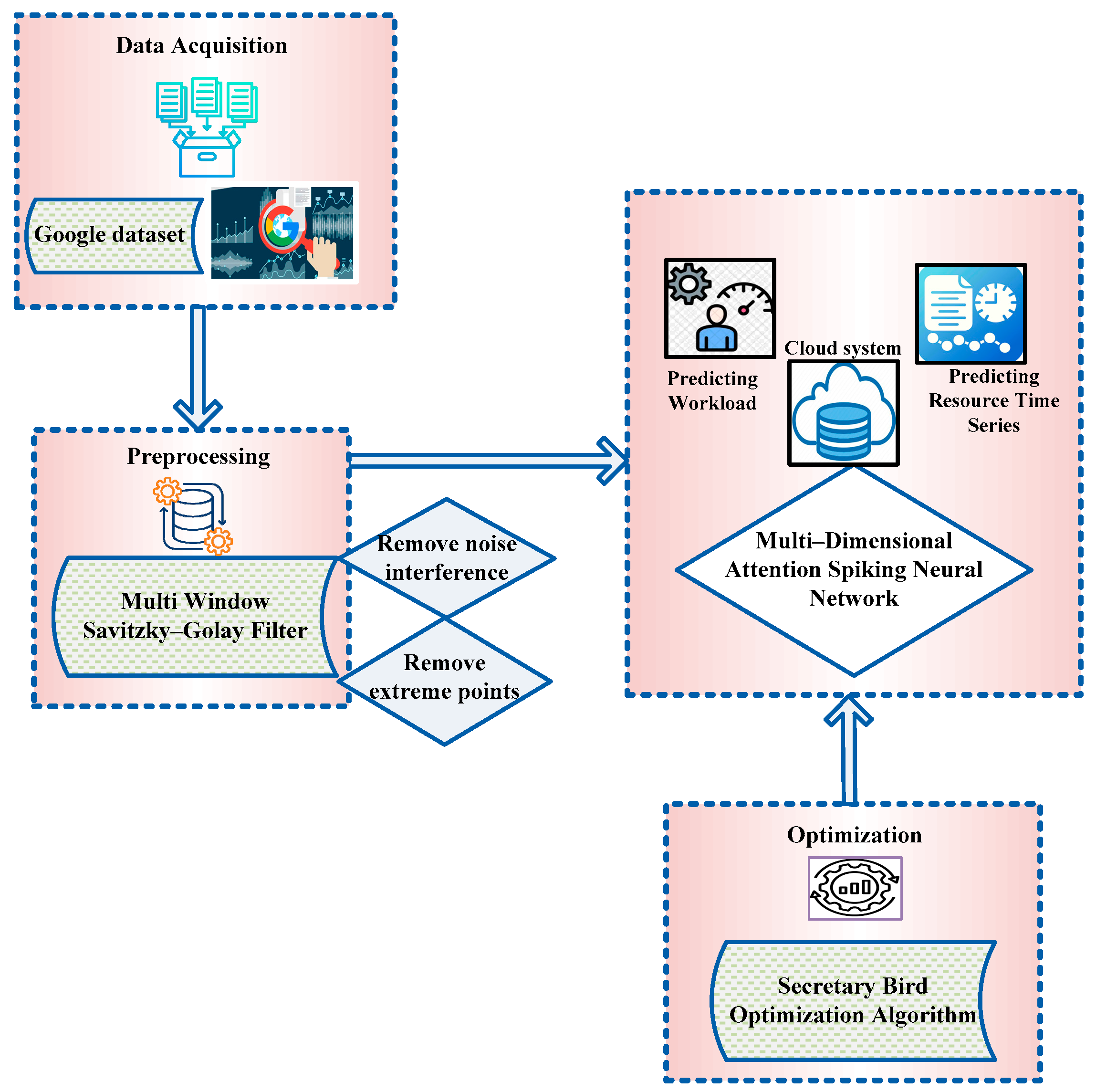
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Data Acquisition
3.2. Preprocessing Under Multi Window Savitzky–Golay Filter
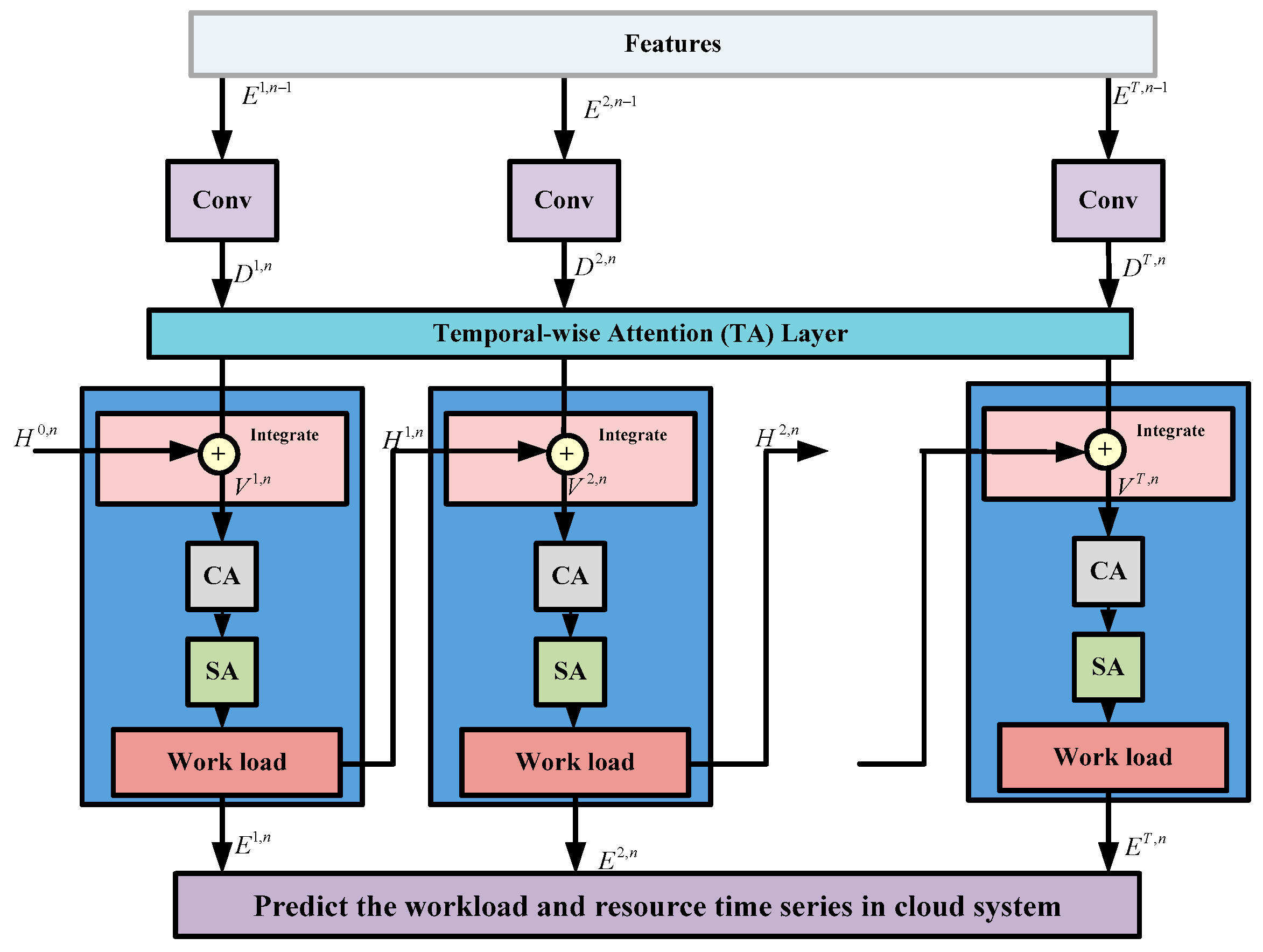
3.3. Predicting the Workload with Resource Time Series Using the Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network
3.4. Optimization Utilizing Secretary Bird Optimization Algorithm
4. Results
4.1. Performance Metrics
4.1.1. RMSLE
4.1.2. MSE
4.1.3. MAE
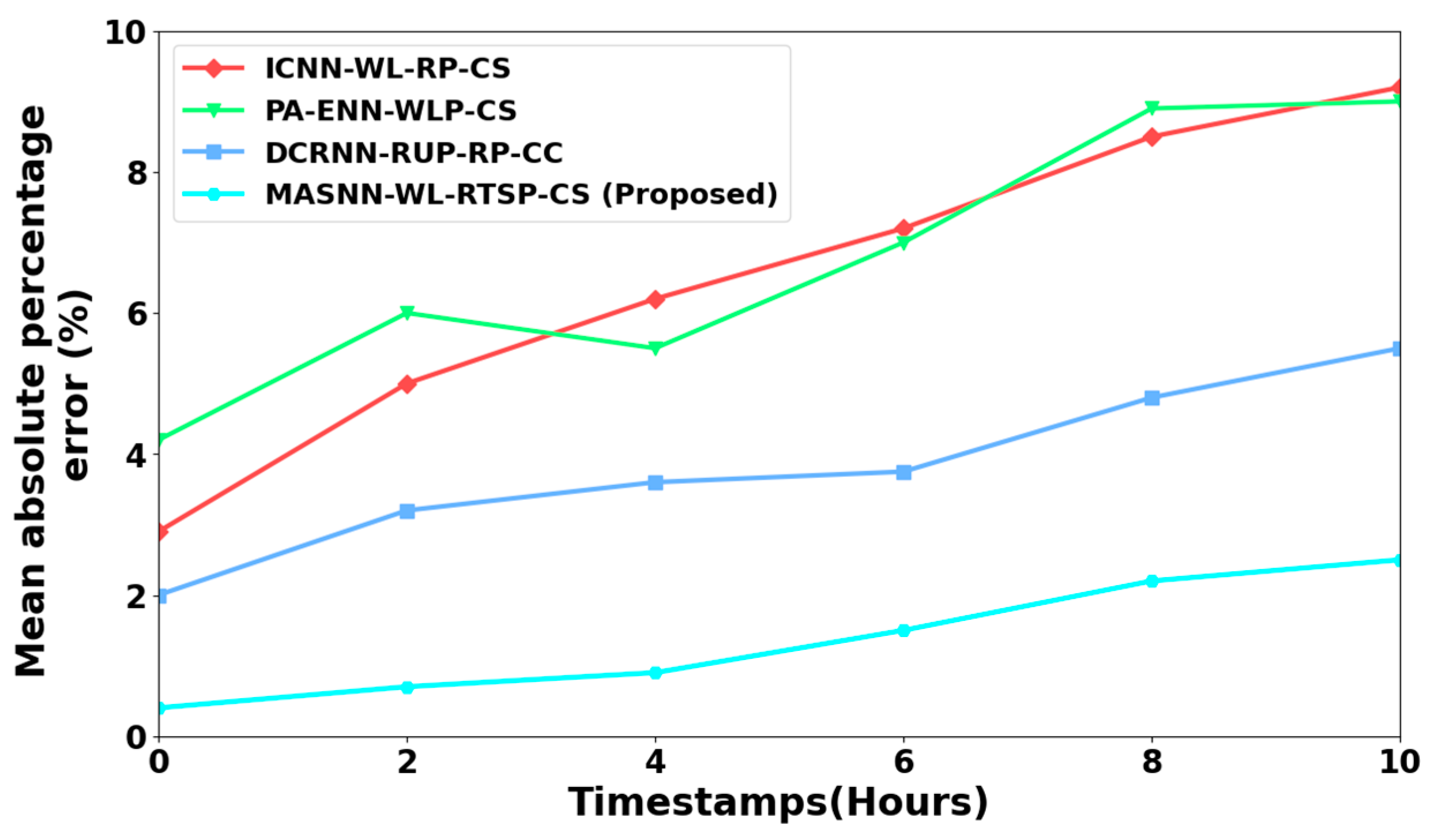
4.1.4. MAPE
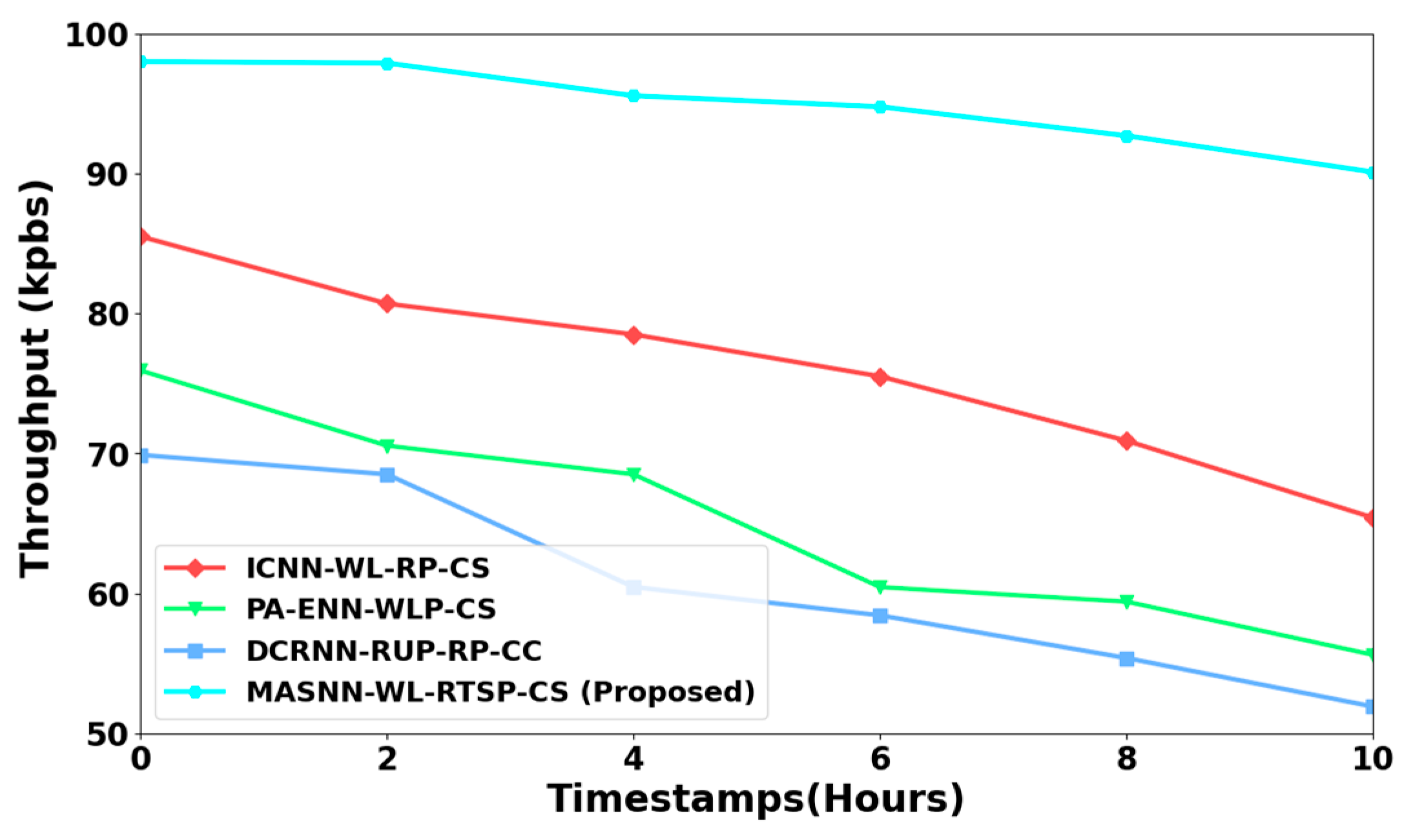
4.1.5. Throughput
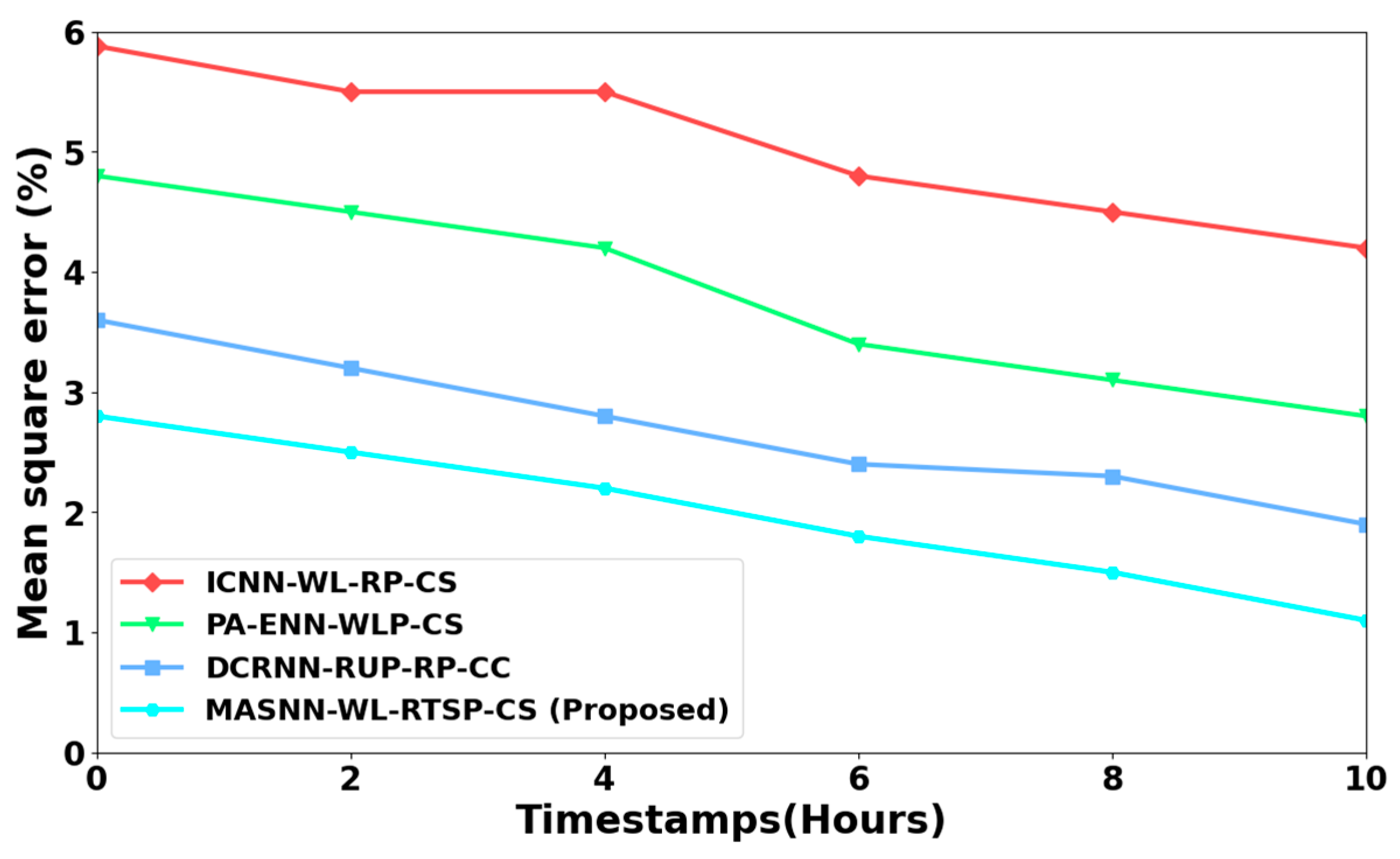
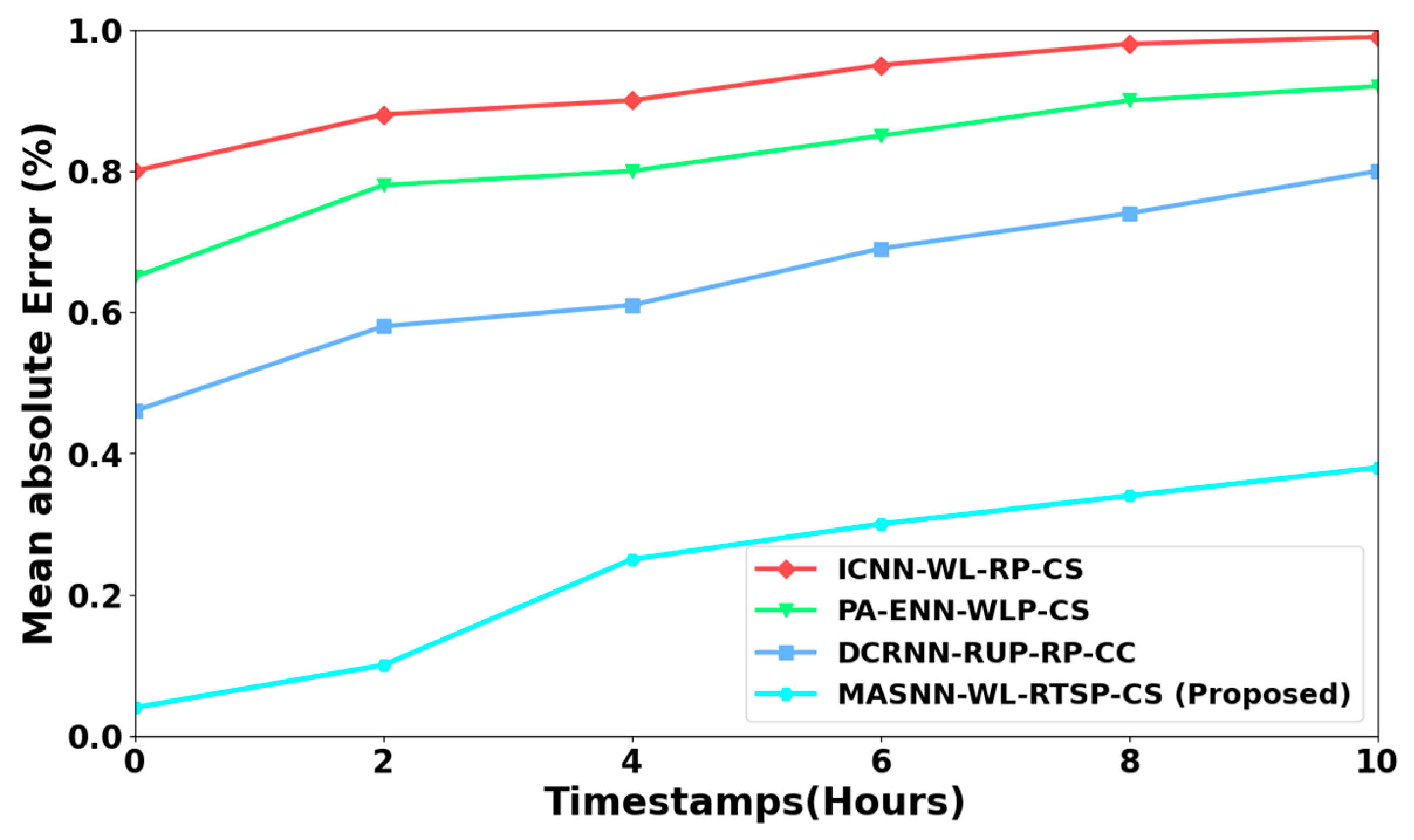
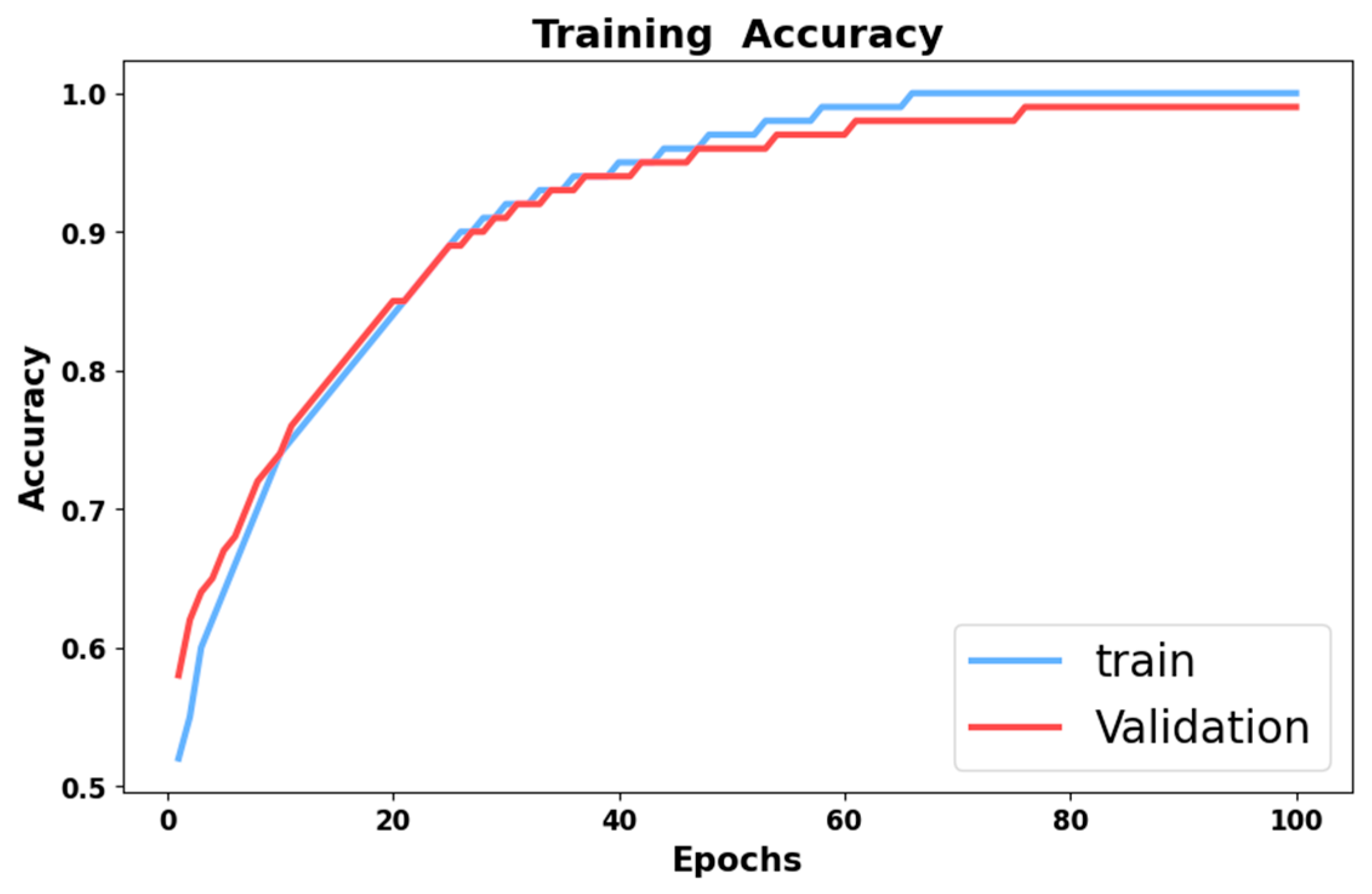
4.2. Performance Analysis
4.3. Ablation Study
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gadhavi, L.J.; Bhavsar, M.D. Adaptive cloud resource management through workload prediction. Energy Syst. 2022, 13, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, D.; Qin, Z.; Buyya, R. Online cloud resource prediction via scalable window waveform sampling on classified workloads. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 117, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Singh, A.K.; Buyya, R. Self directed learning based workload forecasting model for cloud resource management. Inf. Sci. 2021, 543, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, J.; Patel, Y.S. STOWP: A light-weight deep residual network integrated windowing strategy for storage workload prediction in cloud systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Onge, C.; Benmakrelouf, S.; Kara, N.; Tout, H.; Edstrom, C.; Rabipour, R. Generic SDE and GA-based workload modeling for cloud systems. J. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, E.; Kushwaha, D.S. A hybrid CNN-LSTM model for predicting server load in cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjoub, G.; Bentahar, J.; Wahab, O.A.; Bataineh, A.S. Deep and reinforcement learning for automated task scheduling in large-scale cloud computing systems. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2021, 33, e5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Singh, A.K.; Buyya, R. OP-MLB: An online VM prediction-based multi-objective load balancing framework for resource management at cloud data center. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 2804–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amekraz, Z.; Hadi, M.Y. CANFIS: A chaos adaptive neural fuzzy inference system for workload prediction in the cloud. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49808–49828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Tahir, M.; Sardaraz, M.; Alourani, A. A resource utilization prediction model for cloud data centers using evolutionary algorithms and machine learning techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Bilal, M.; Yoon, S.K. Intelligent time-series forecasting framework for non-linear dynamic workload and resource prediction in cloud. Comput. Netw. 2023, 225, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogani, J.; Khunjush, F.; Seydali, M. Host load prediction in cloud computing with discrete wavelet transformation (dwt) and bidirectional gated recurrent unit (bigru) network. Comput. Commun. 2023, 198, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Singh, A.K. Performance assessment of time series forecasting models for cloud datacenter networks’ workload prediction. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 116, 1949–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, P.; Osypanka, P. Cloud resource demand prediction using machine learning in the context of qos parameters. J. Grid Comput. 2021, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, K.; Pavana, C.; Sindhu, K.; Kollengode, C. Unsupervised Modeling of Workloads as an Enabler for Supervised Ensemble-based Prediction of Resource Demands on a Cloud. In Advances in Data Computing, Communication and Security: Proceedings of I3CS2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Saxena, D.; Kumar, J.; Gupta, V. A quantum approach towards the adaptive prediction of cloud workloads. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 32, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, C. On accurate prediction of cloud workloads with adaptive pattern mining. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 160–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalaji, N. Cloud load estimation with deep logarithmic network for workload and time series optimization. J. Soft Comput. Paradig. 2021, 3, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Balamurugan, V.; Cyriac, R.; Sundaravadivazhagan, B. COSCO2: AI-augmented evolutionary algorithm based workload prediction framework for sustainable cloud data centers. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2023, 34, e4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Song, C.; Wu, H.; Gill, S.S.; Ye, K.; Xu, C. esDNN: Deep neural network based multivariate workload prediction in cloud computing environments. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2022, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, M. Integrated deep learning method for workload and resource prediction in cloud systems. Neurocomputing 2021, 424, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Kumar, J.; Singh, A.K.; Schmid, S. Performance analysis of machine learning centered workload prediction models for cloud. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2023, 34, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asaly, M.S.; Bencherif, M.A.; Alsanad, A.; Hassan, M.M. A deep learning-based resource usage prediction model for resource provisioning in an autonomic cloud computing environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10211–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sayed, M.M. Workload time series cumulative prediction mechanism for cloud resources using neural machine translation technique. J. Grid Comput. 2022, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, S.; He, S.; Xiao, L. Workload time series prediction in storage systems: A deep learning based approach. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogani, J.; Khunjush, F.; Mahmoudi, M.R.; Seydali, M. Multivariate workload and resource prediction in cloud computing using CNN and GRU by attention mechanism. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 3437–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.L.; Valli, S. Time series-based workload prediction using the statistical hybrid model for the cloud environment. Computing 2023, 105, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/derrickmwiti/google-2019-cluster-sample (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, R. Smooth Deep Learning Magnetotelluric Inversion based on Physics-informed Swin Transformer and Multi-Window Savitzky-Golay Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4505214. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Deng, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, G. Attention spiking neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; He, L. Secretary bird optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic for solving global optimization problems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanin, N.; Simic, V.; Zivkovic, M.; Alrasheedi, M.; Petrovic, A. Cloud computing load prediction by decomposition reinforced attention long short-term memory network optimized by modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.H.; Wu, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, H.C. Migration-based load balance of virtual machine servers in cloud computing by load prediction using genetic-based methods. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 49760–49773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Objectives | Models | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi, J. et al. [21] | To improve workload and resource prediction accuracy in cloud systems. | Logarithmic operation, smoothing, bi-directional, and grid LSTM networks. | It provides low MAPE. | It provides high RMSLE. |
| Saxena, D. et al. [22] | To enhance the performance analysis of ML-based workload prediction. | Evolutionary Neural Networks, Quantum Neural Network, and LSTM-RNN. | It provides high throughput. | It provides high MAE. |
| Al-Asaly, M.S. et al. [23] | To improve CPU usage forecasting and manage workload fluctuations. | Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network. | It provides low MAPE. | It provides high MSE. |
| Al-Sayed, M.M. et al. [24] | To develop workload sequence estimation as a translation task. | Attention Seq2Seq method and Recurrent Neural Network. | It provides high normalized correlation. | It provides high structural similarity index measure. |
| Ruan, L. et al. [25] | To improve storage workload time series prediction. | CrystalLP using LSTM. | It provides low MAE. | It provides high computation time. |
| Dogani, J. et al. [26] | To predict multivariate workload with resource usage in cloud systems. | Hybrid CNN-GRU with attention. | It provides low MSE. | It provides low MAPE. |
| Devi, K.L. et al. [27] | To enhance workload prediction accuracy in cloud data centers. | GRU, LSTM, CNN, and BiLSTM. | It provides low RMSLE. | It provides low throughput. |
| Methods | Performance Metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE (%) | MAE (%) | Convergence Time (s) | |
| PSO [32] | 2.2 | 0.54 | 10.2 |
| GA [33] | 2.5 | 0.62 | 12.5 |
| SBOA (Proposed) | 1.1 | 0.38 | 7.3 |
| Authors | Performance Metrics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSLE (%) | MSE (%) | MAE (%) | MAPE (%) | Computational Time (s) | Throughput (KPBS) | |
| Bi, J. et al. [21] | 3.2 | 4.2 | 0.99 | 9.15 | 250 | 65.4 |
| Saxena, D. et al. [22] | 2.2 | 2.8 | 0.92 | 9.4 | 190 | 55.6 |
| Al-Asaly, M.S. et al. [23] | 1.3 | 1.9 | 0.88 | 6.2 | 260 | 51.9 |
| Al-Sayed, M.M. et al. [24] | 3.8 | 4.5 | 0.98 | 9.2 | 211.27 | 70.9 |
| Ruan, L. et al. [25] | 2.5 | 3.1 | 0.9 | 9 | 192.32 | 59.4 |
| Dogani, J. et al. [26] | 1.7 | 2.3 | 0.74 | 5.5 | 123.27 | 55.3 |
| Devi, K.L. et al. [27] | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0.95 | 8.9 | 219.53 | 70.8 |
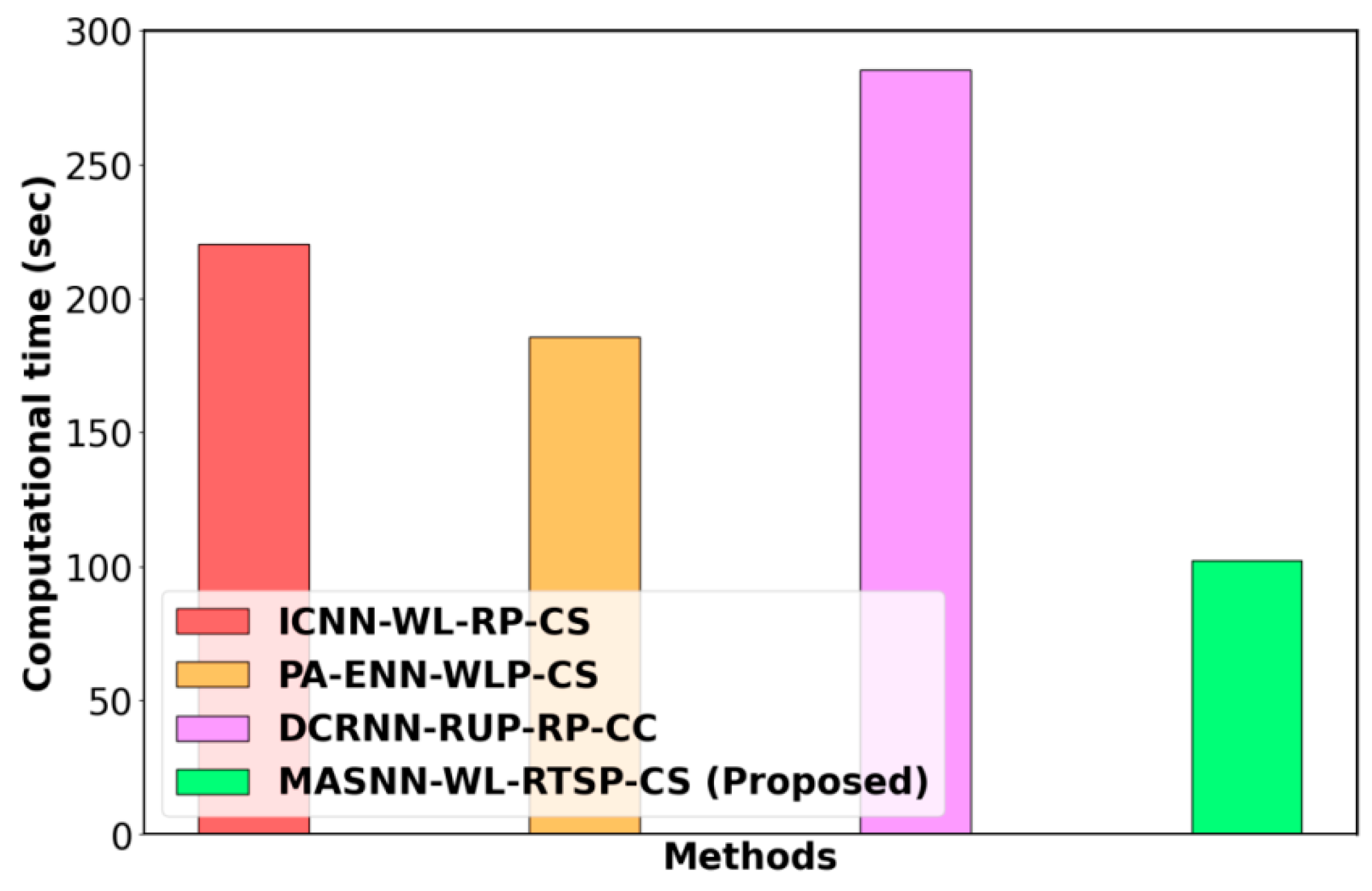
| MASNN-WL- RTSP-CS (Proposed) | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.38 | 3.7 | 99 | 97.89 |
| Ablation Model | Metrics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSLE (%) | MSE (%) | MAE (%) | MAPE (%) | |
| Without MWSGF | 3.2 | 4.2 | 0.99 | 9.15 |
| WithMASNN | 2.2 | 2.8 | 0.92 | 9.4 |
| Without SBOA | 1.3 | 1.9 | 0.88 | 6.2 |
| MASNN-WL-RTSP-CS (Proposed) | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.38 | 3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karpagam, T.; Kanniappan, J. Symmetry-Aware Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network with Optimization Techniques for Accurate Workload and Resource Time Series Prediction in Cloud Computing Systems. Symmetry 2025, 17, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030383
Karpagam T, Kanniappan J. Symmetry-Aware Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network with Optimization Techniques for Accurate Workload and Resource Time Series Prediction in Cloud Computing Systems. Symmetry. 2025; 17(3):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030383
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarpagam, Thulasi, and Jayashree Kanniappan. 2025. "Symmetry-Aware Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network with Optimization Techniques for Accurate Workload and Resource Time Series Prediction in Cloud Computing Systems" Symmetry 17, no. 3: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030383
APA StyleKarpagam, T., & Kanniappan, J. (2025). Symmetry-Aware Multi-Dimensional Attention Spiking Neural Network with Optimization Techniques for Accurate Workload and Resource Time Series Prediction in Cloud Computing Systems. Symmetry, 17(3), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030383







