High-Performance Carrier Phase Recovery for Local Local Oscillator Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
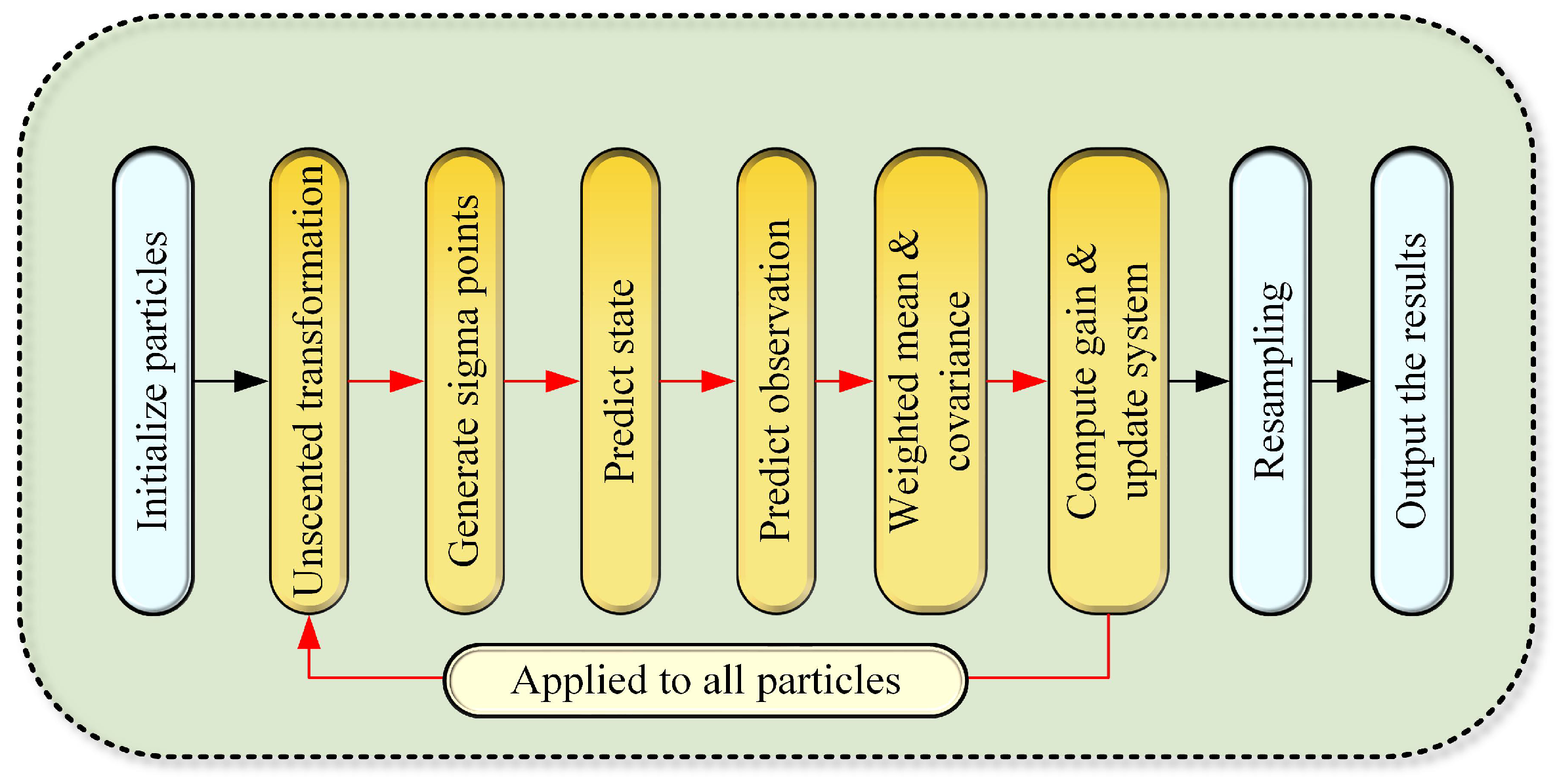
2. A Phase Prediction Model Based on Unscented Particle Filter
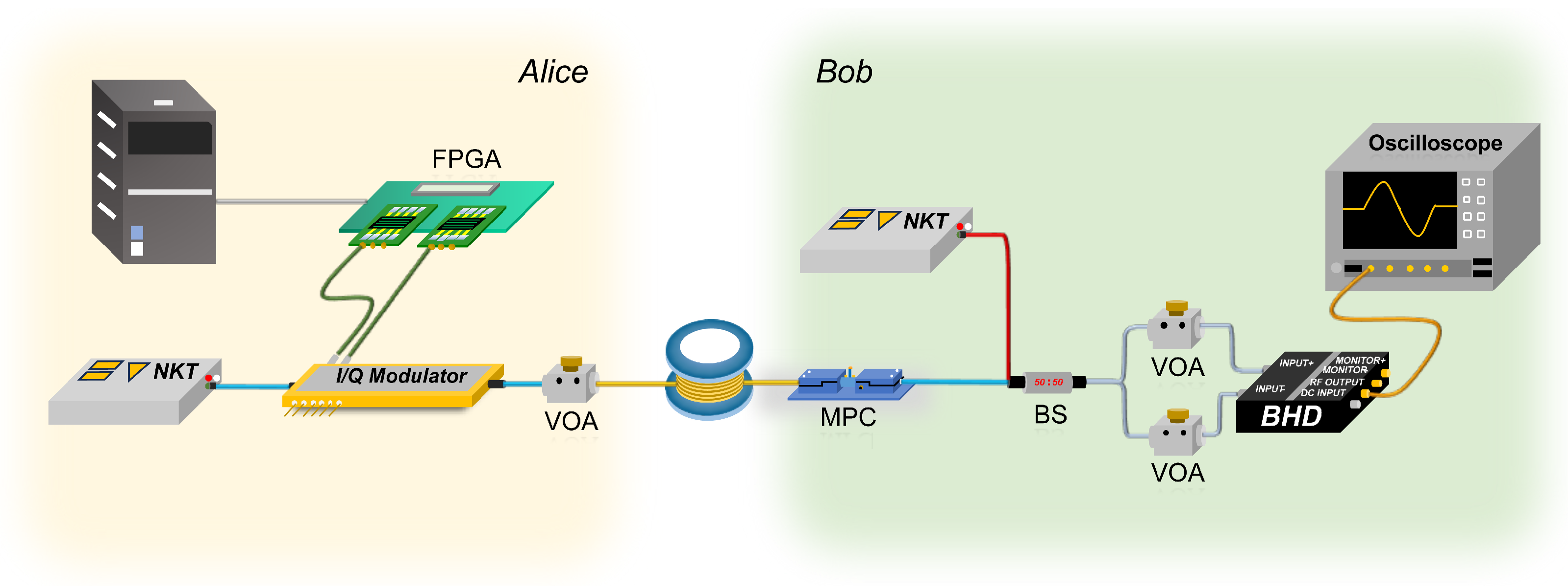
3. Local Local Oscillator CV-QKD Experimental Scheme
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Digital Signal Processing Based on UPF Algorithm
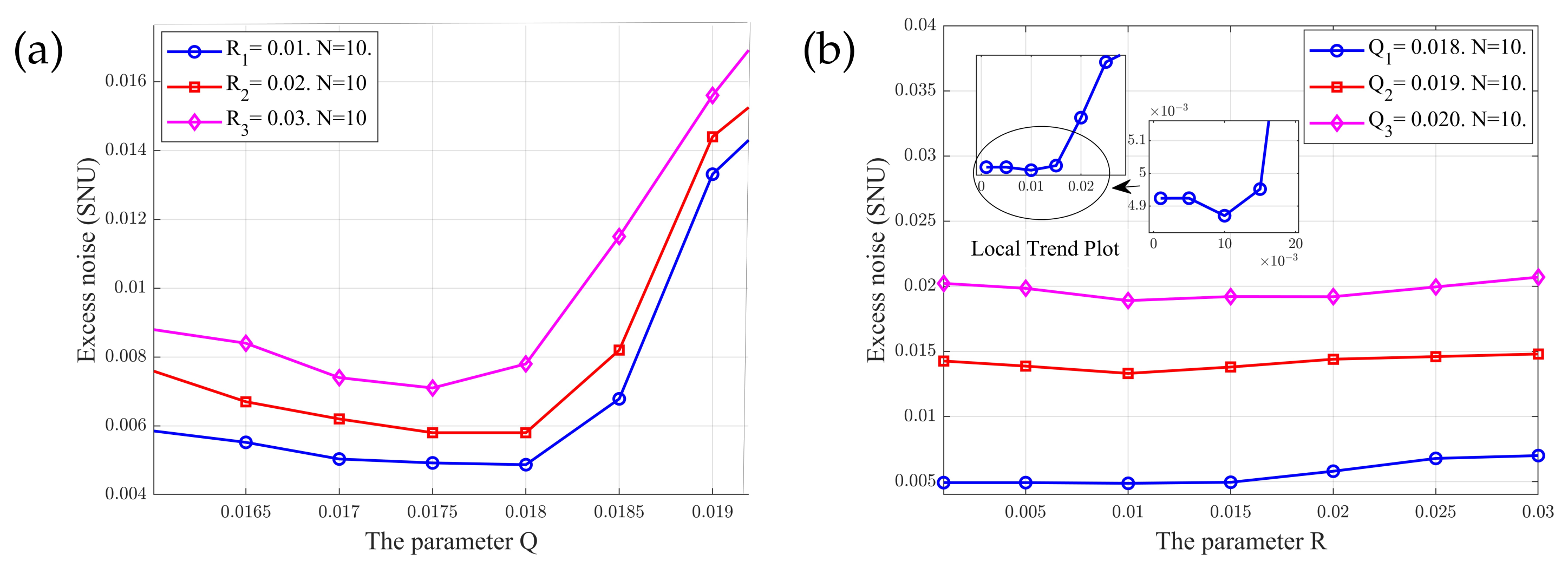
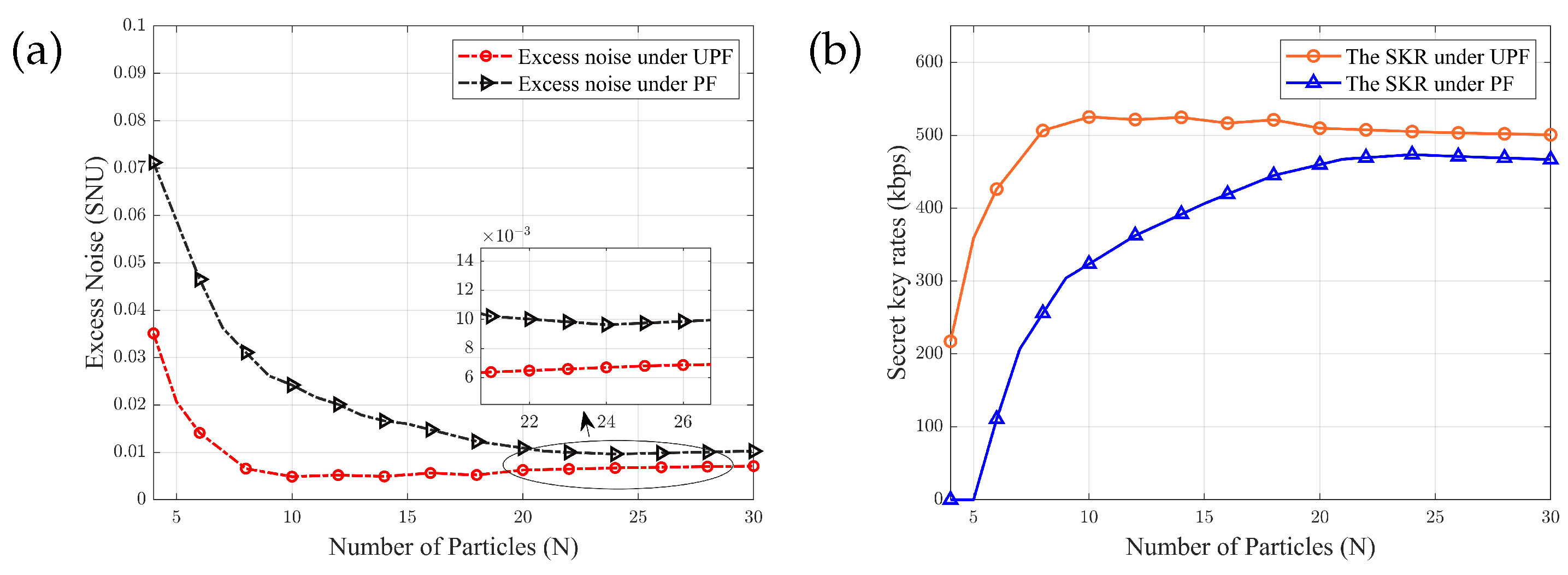
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Initialization
- Prediction and update
- Resample and output the results as follows:
Appendix B
References
- Pirandola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunandar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.K.; Pan, J.W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A. Composable security proof for continuous-variable quantum key distribution with coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorai, S.; Grangier, P.; Diamanti, E.; Leverrier, A. Asymptotic security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 021059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Upadhyaya, T.; Lütkenhaus, N. Asymptotic security analysis of discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 041064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirandola, S. Composable security for continuous variable quantum key distribution: Trust levels and practical key rates in wired and wireless networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 043014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, A.; Brown, P.; Leverrier, A. Explicit asymptotic secret key rate of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with an arbitrary modulation. Quantum 2021, 5, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Guo, H. Rate compatible reconciliation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution using Raptor-like LDPC codes. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2021, 64, 260311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, H. Continuous-mode quantum key distribution with digital signal processing. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2023, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. High-efficiency rate-adaptive reconciliation in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 109, 012604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, F.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z. Multiple-quadrature-amplitude-modulation continuous-variable quantum key distribution realization with a downstream-access network. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 109, 052429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Non-Gaussian reconciliation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 054084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Huang, P.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudenbach, F.; Schrenk, B.; Pacher, C.; Hentschel, M.; Fung, C.H.F.; Karinou, F.; Poppe, A.; Peev, M.; Hübel, H. Pilot-assisted intradyne reception for high-speed continuous-variable quantum key distribution with true local oscillator. Quantum 2019, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Liu, H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Y. Practical continuous-variable quantum secret sharing using plug-and-play dual-phase modulation. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 3876–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Huang, P.; Zeng, G. Multi-rate and multi-protocol continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Qi, D.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Experimental upstream transmission of continuous variable quantum key distribution access network. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 3327–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, Y.; Pi, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Xu, B. Experimental demonstration of high-rate discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 3307–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Tian, H.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Experimental demonstration of LLO continuous-variable quantum key distribution with polarization loss compensation. IEEE Photonics J. 2023, 15, 7600109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S. Experimental demonstration of a quantum downstream access network in continuous variable quantum key distribution with a local local oscillator. Photonics Res. 2024, 12, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajomer, A.A.; Derkach, I.; Jain, N.; Chin, H.M.; Andersen, U.L.; Gehring, T. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution over 100-km fiber with local local oscillator. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Qi, D.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S. Experimental Implementation of Four-User Downstream Access Network Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 6662–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Du, S.; Liu, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Experimental demonstration of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over optical fiber. Optica 2022, 9, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for Eve in practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A—At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 88, 022339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E. Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A—At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 87, 062313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Lougovski, P.; Pooser, R.; Grice, W.; Bobrek, M. Generating the local oscillator “locally” in continuous-variable quantum key distribution based on coherent detection. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, D.B.; Brif, C.; Coles, P.J.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Camacho, R.M.; Urayama, J.; Sarovar, M. Self-referenced continuous-variable quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 041010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.S.; Savory, S.J. Digital signal processing for coherent transceivers employing multilevel formats. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, P.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G. Polarization-state tracking based on Kalman filter in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 26689–26700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, T.A.; Hirano, T.; Puttnam, B.J.; Rademacher, G.; Luís, R.S.; Fujiwara, M.; Namiki, R.; Awaji, Y.; Takeoka, M.; Wada, N.; et al. Wavelength division multiplexing of continuous variable quantum key distribution and 18.3 Tbit/s data channels. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Maeda, K.; Sasaki, T.; Koashi, M. Finite-size security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with digital signal processing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Huang, P.; Lin, D.; Wang, C.; Zeng, G. High-speed continuous-variable quantum key distribution without sending a local oscillator. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3695–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, A.; Alléaume, R. Self-coherent phase reference sharing for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 012316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G. High key rate continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2794–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleis, S.; Rueckmann, M.; Schaeffer, C.G. Continuous variable quantum key distribution with a real local oscillator using simultaneous pilot signals. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, H.M.; Jain, N.; Zibar, D.; Andersen, U.L.; Gehring, T. Machine learning aided carrier recovery in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.J. The scaled unscented transformation. In Proceedings of the 2002 American Control Conference (IEEE Cat. No. CH37301), Anchorage, AK, USA, 8–10 May 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 6, pp. 4555–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.; Clifford, P.; Fearnhead, P. Improved particle filter for nonlinear problems. IEE Proc.-Radar Sonar Navig. 1999, 146, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, E.A.; Van Der Merwe, R. The unscented Kalman filter for nonlinear estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2000 Adaptive Systems for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control Symposium (Cat. No. 00EX373), Lake Louise, AB, Canada, 4 October 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Pirandola, S.; Laurenza, R.; Ottaviani, C.; Banchi, L. Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Merwe, R.; Doucet, A.; De Freitas, N.; Wan, E. The unscented particle filter. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2000, 13, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Leverrier, A.; Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A—At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 81, 062343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossier, S.; Diamanti, E.; Debuisschert, T.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Grangier, P. Improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems by using optical preamplifiers. J. Phys. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 42, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
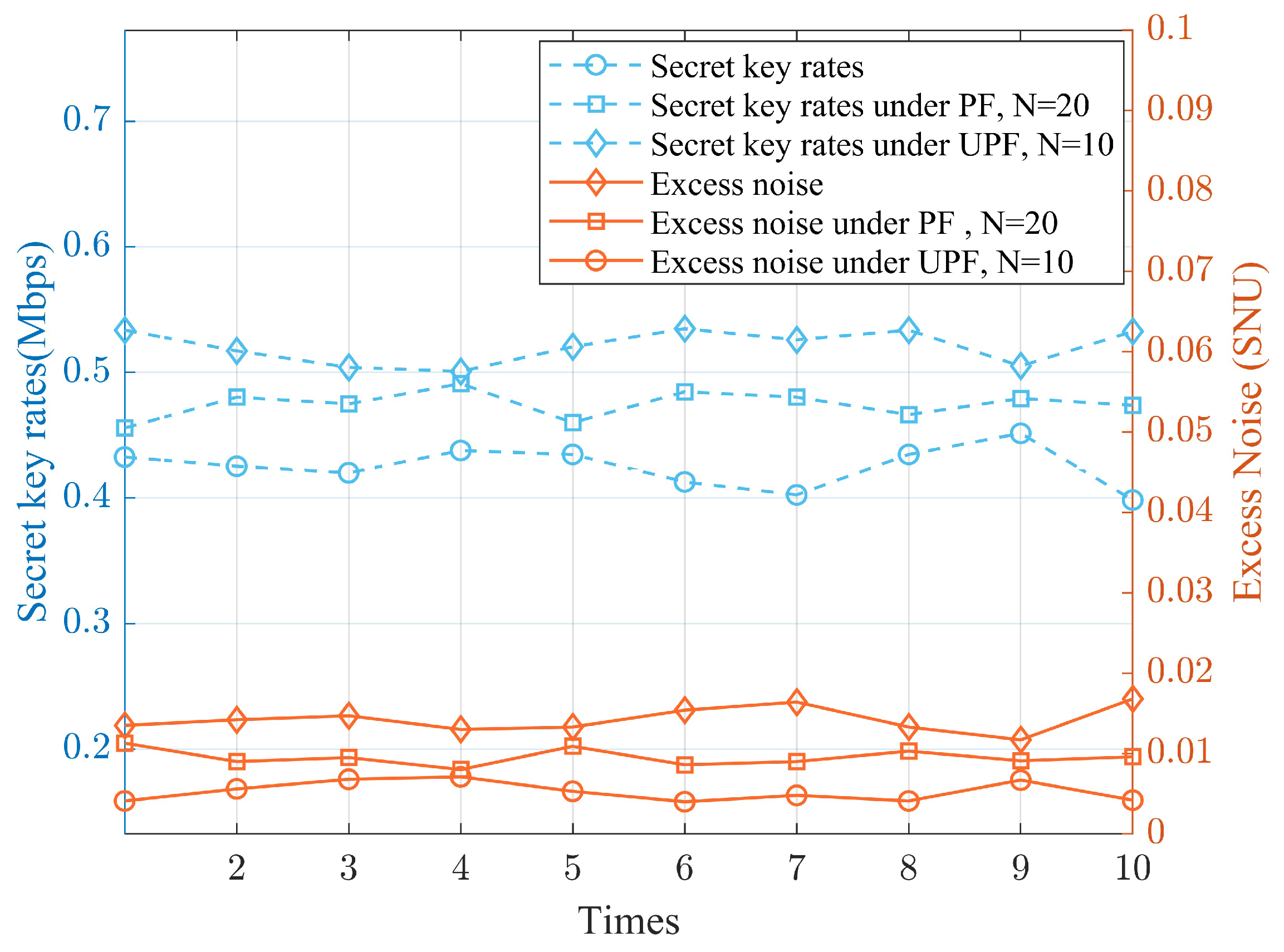
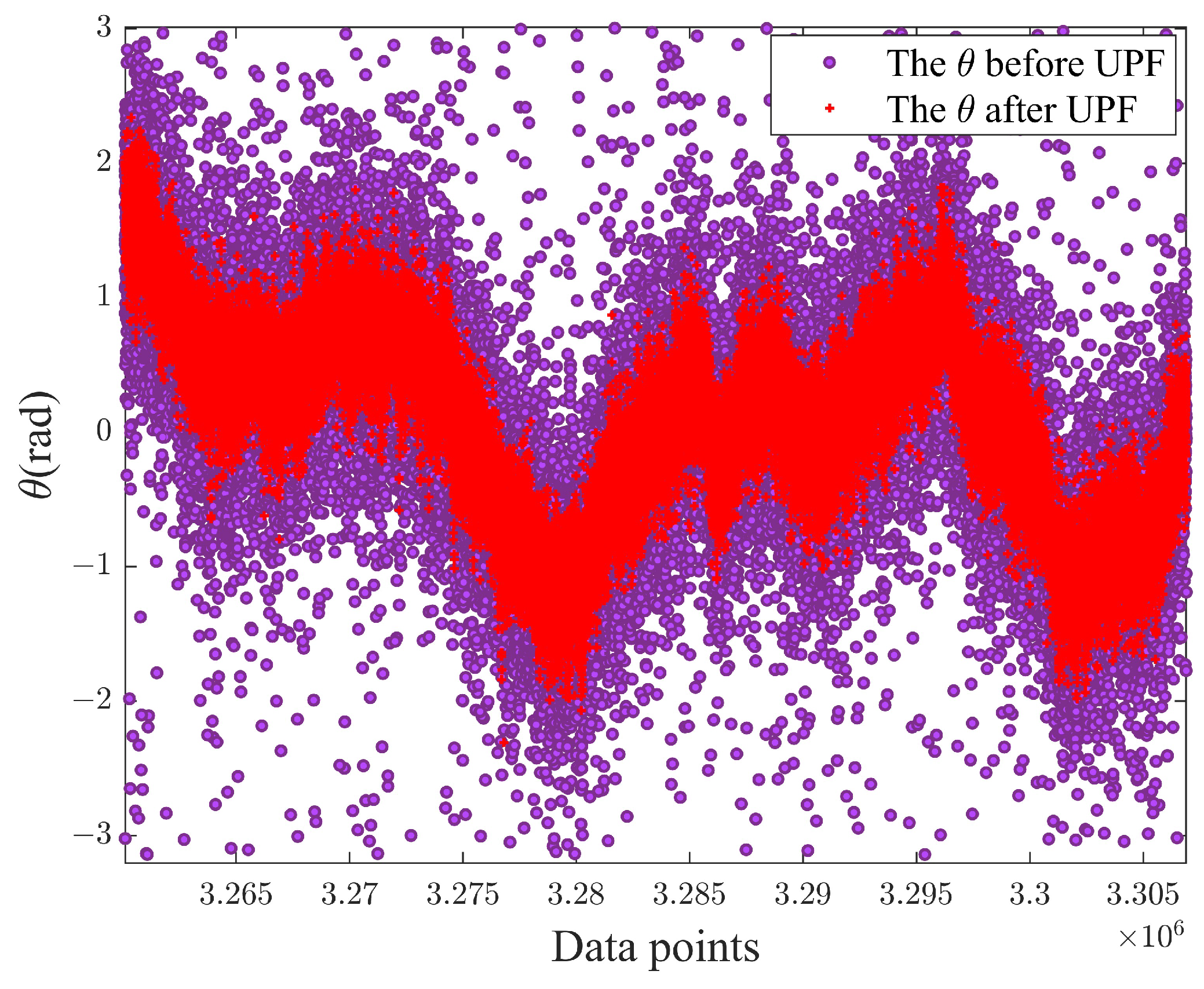
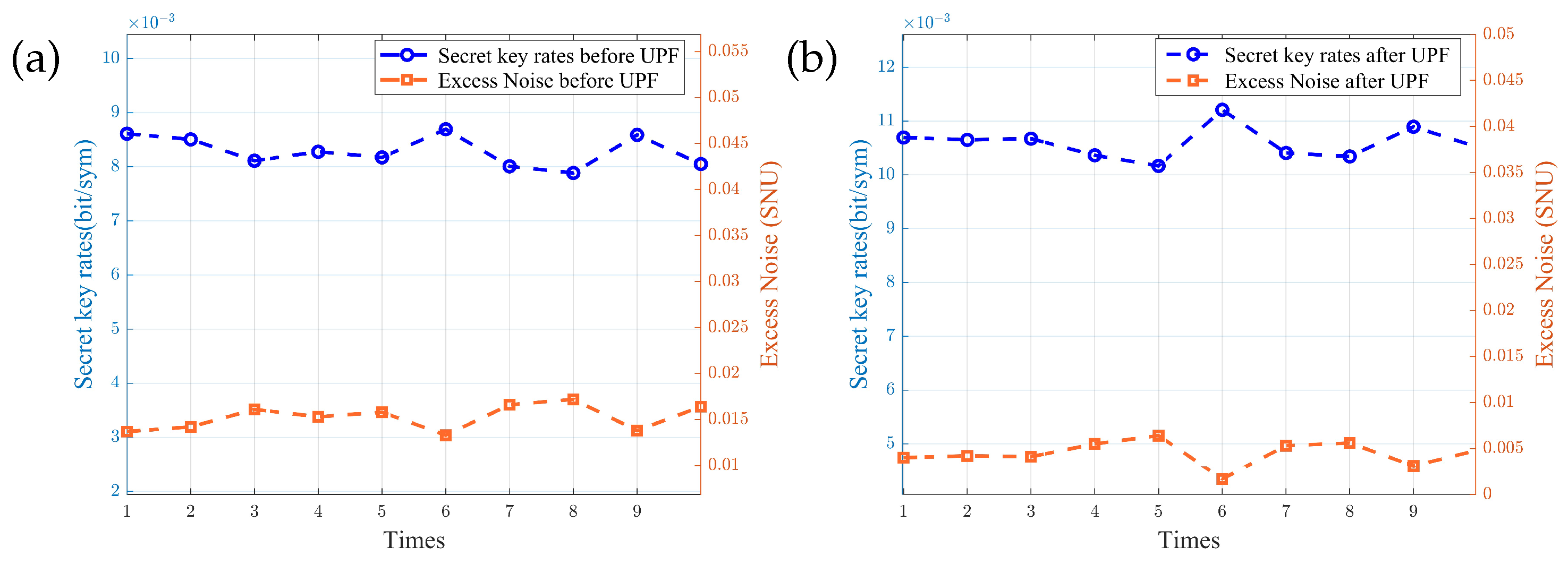
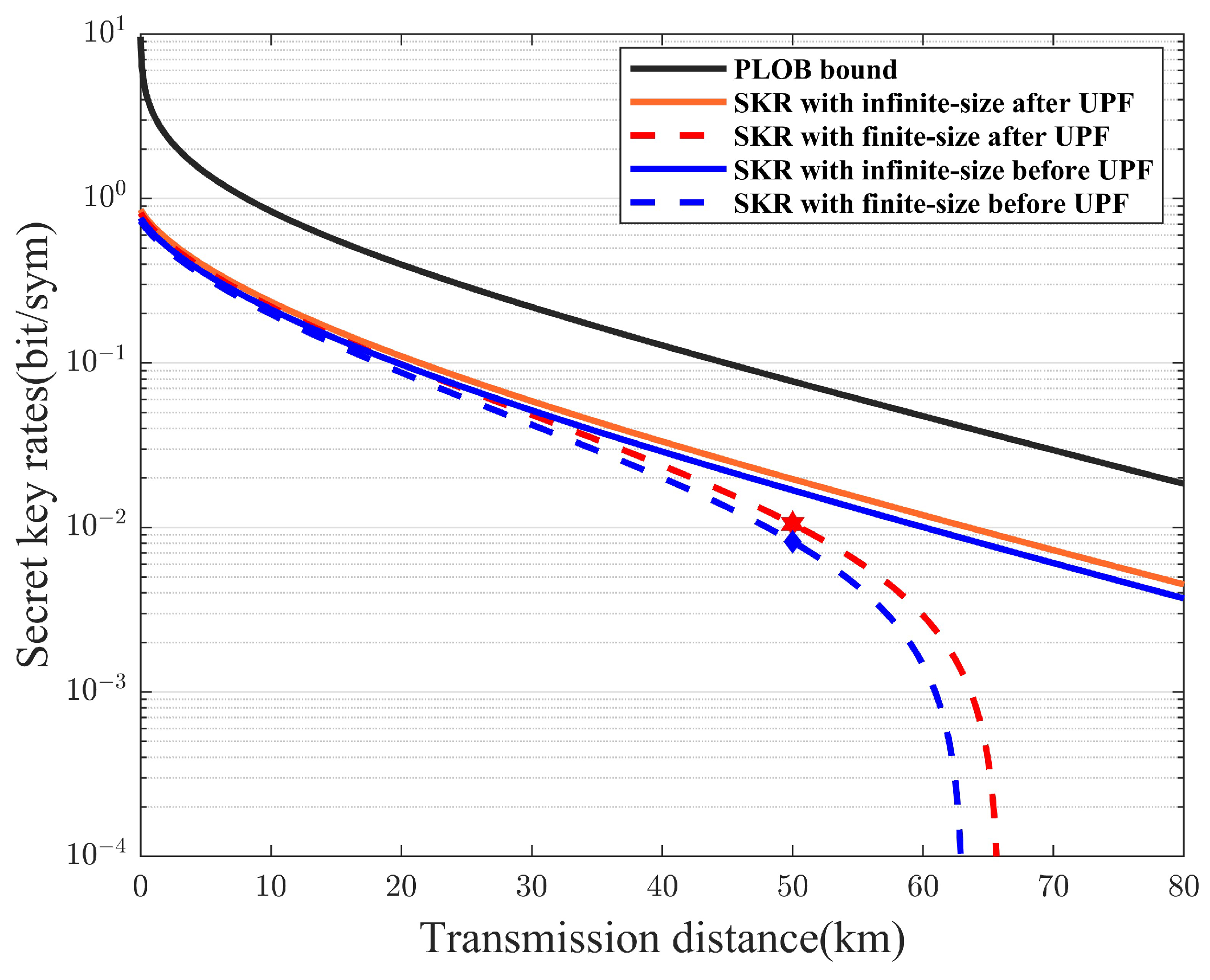
| Transmission Distance (km) | Modulation Variance (SNU) | Detection Efficiency | Electric Noise (SNU) | Reconciliation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 4.01 | 0.481 | 0.0271 | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Qi, D.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, X. High-Performance Carrier Phase Recovery for Local Local Oscillator Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Symmetry 2025, 17, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17010139
Ma J, Zhou C, Qi D, Chen Z, Sun Y, Yu S, Wang X. High-Performance Carrier Phase Recovery for Local Local Oscillator Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Symmetry. 2025; 17(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17010139
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jiayu, Chao Zhou, Dengke Qi, Ziyang Chen, Yongmei Sun, Song Yu, and Xiangyu Wang. 2025. "High-Performance Carrier Phase Recovery for Local Local Oscillator Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution" Symmetry 17, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17010139
APA StyleMa, J., Zhou, C., Qi, D., Chen, Z., Sun, Y., Yu, S., & Wang, X. (2025). High-Performance Carrier Phase Recovery for Local Local Oscillator Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Symmetry, 17(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17010139






