Dynamics of a Stochastic Vector-Borne Model with Plant Virus Disease Resistance and Nonlinear Incidence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
- (i)
- (ii)
- (i)
- In the open domain U and some neighborhood thereof, the smallest eigenvalue of the diffusion matrix is bounded away from zero.
- (ii)
- If , the mean time τ at which a path issuing from x reaches the set U is finite, and for every compact .
3. Main Results
3.1. Extinction of Model (3)
3.2. Stationary Distribution and Ergodicity of Model (3)
- (i)
- (ii)
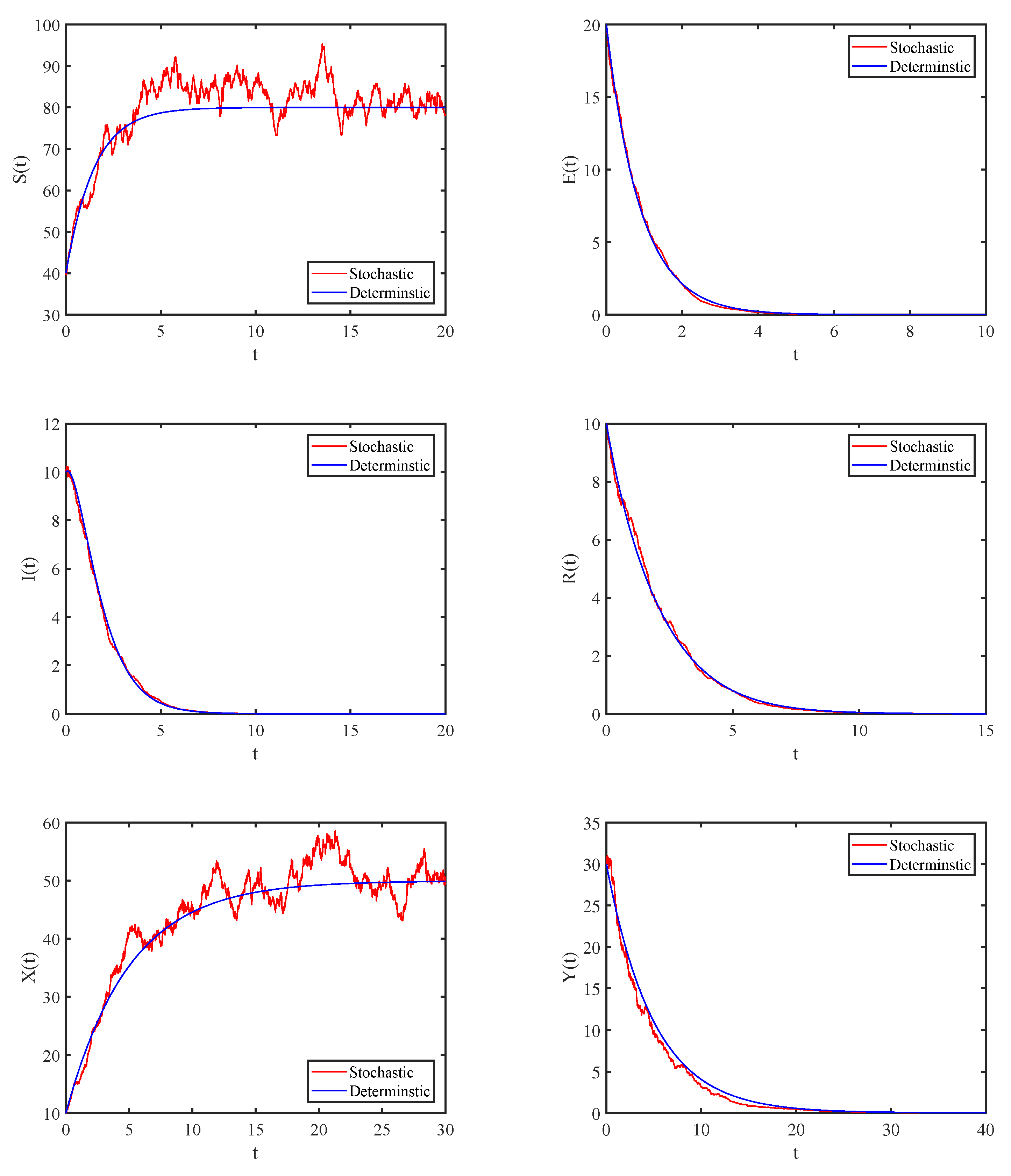
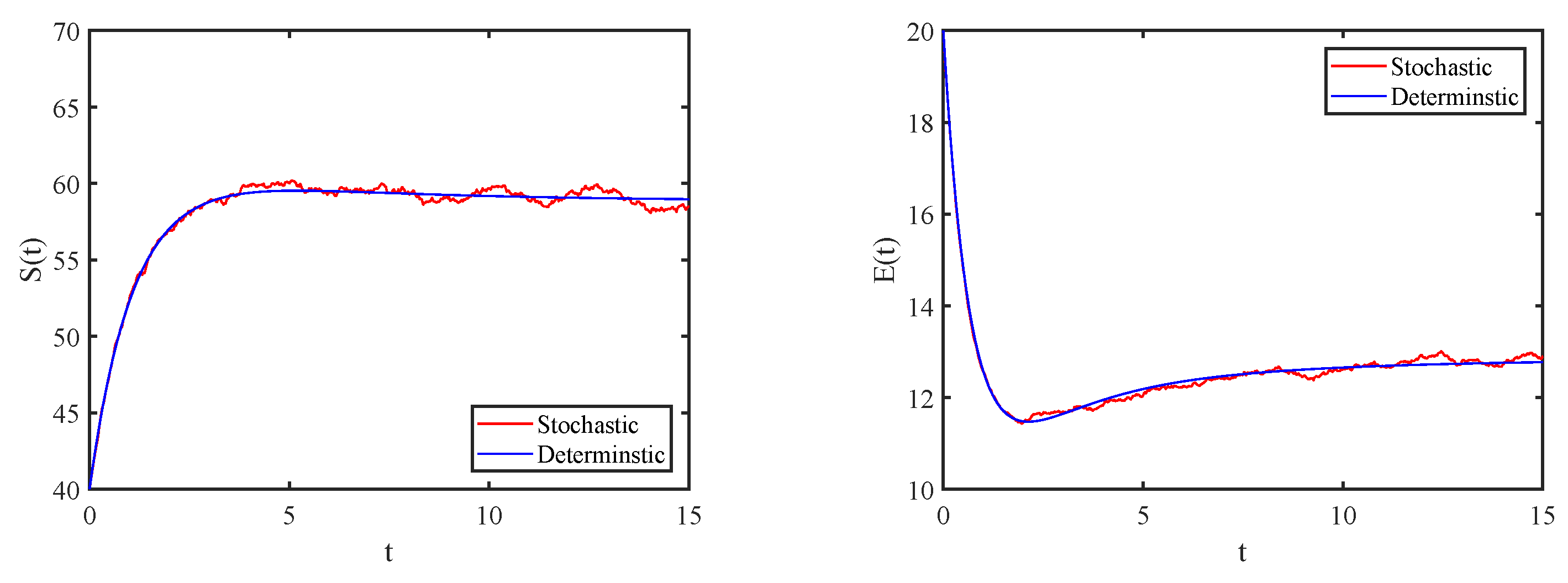
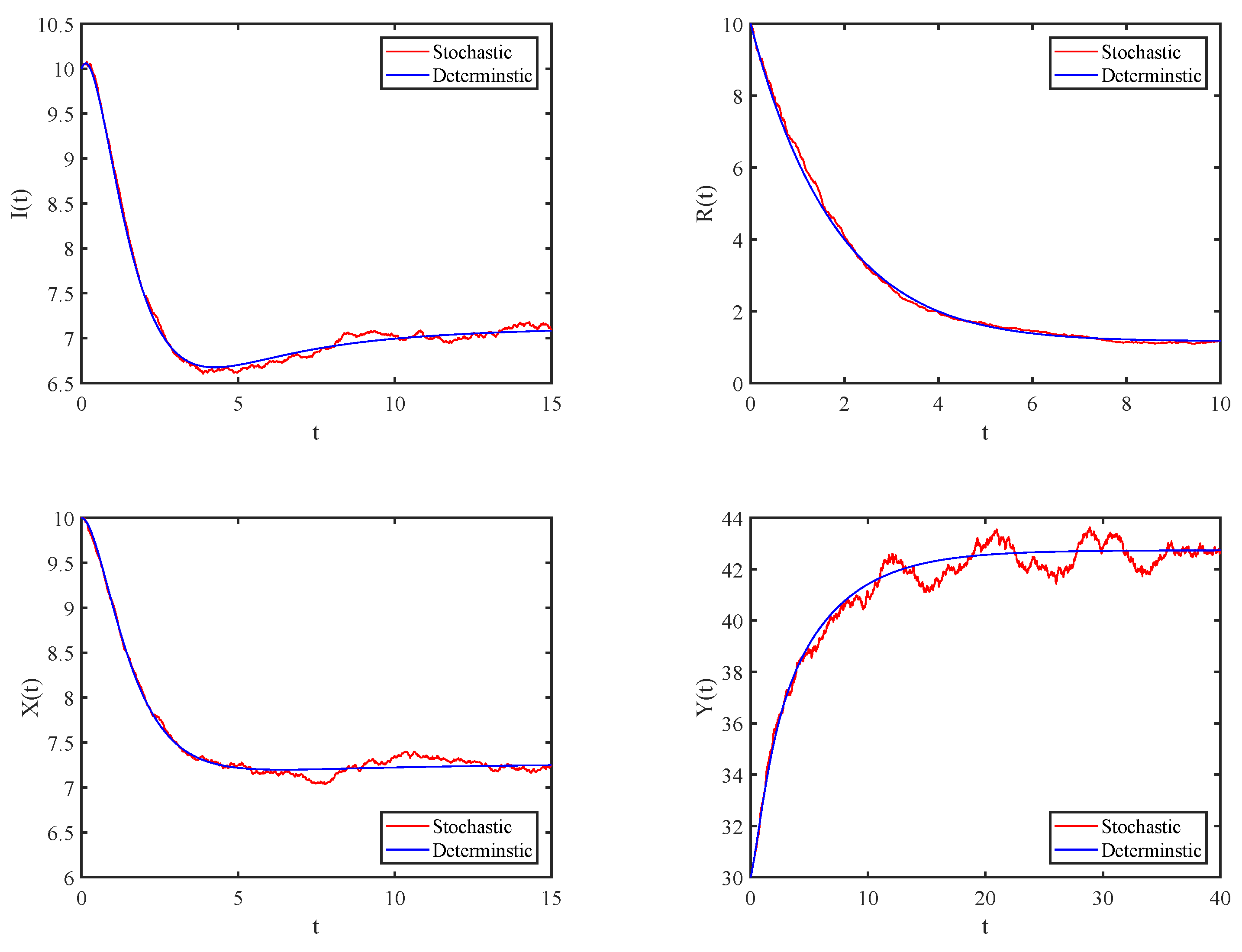
4. Numerical Simulations
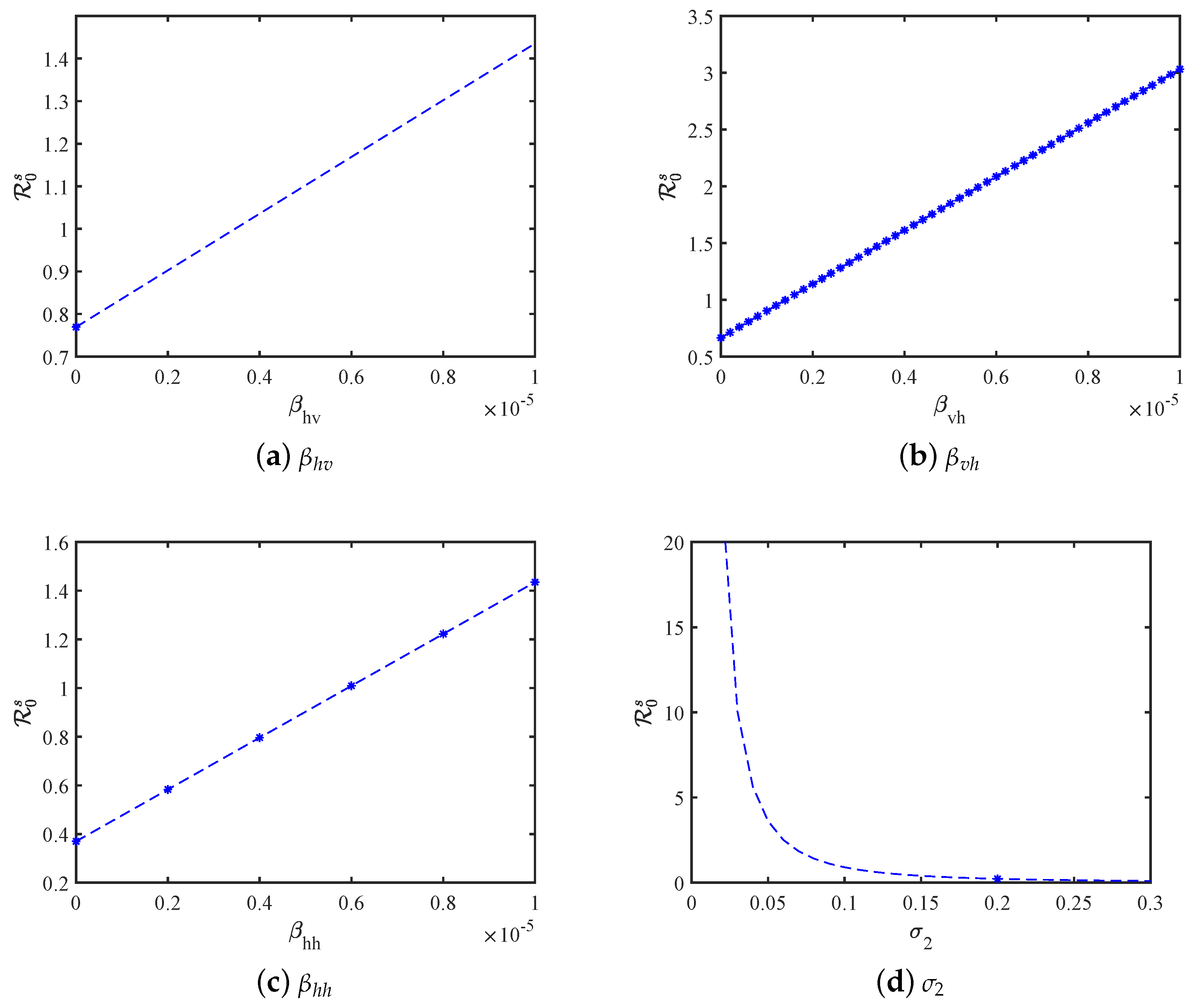
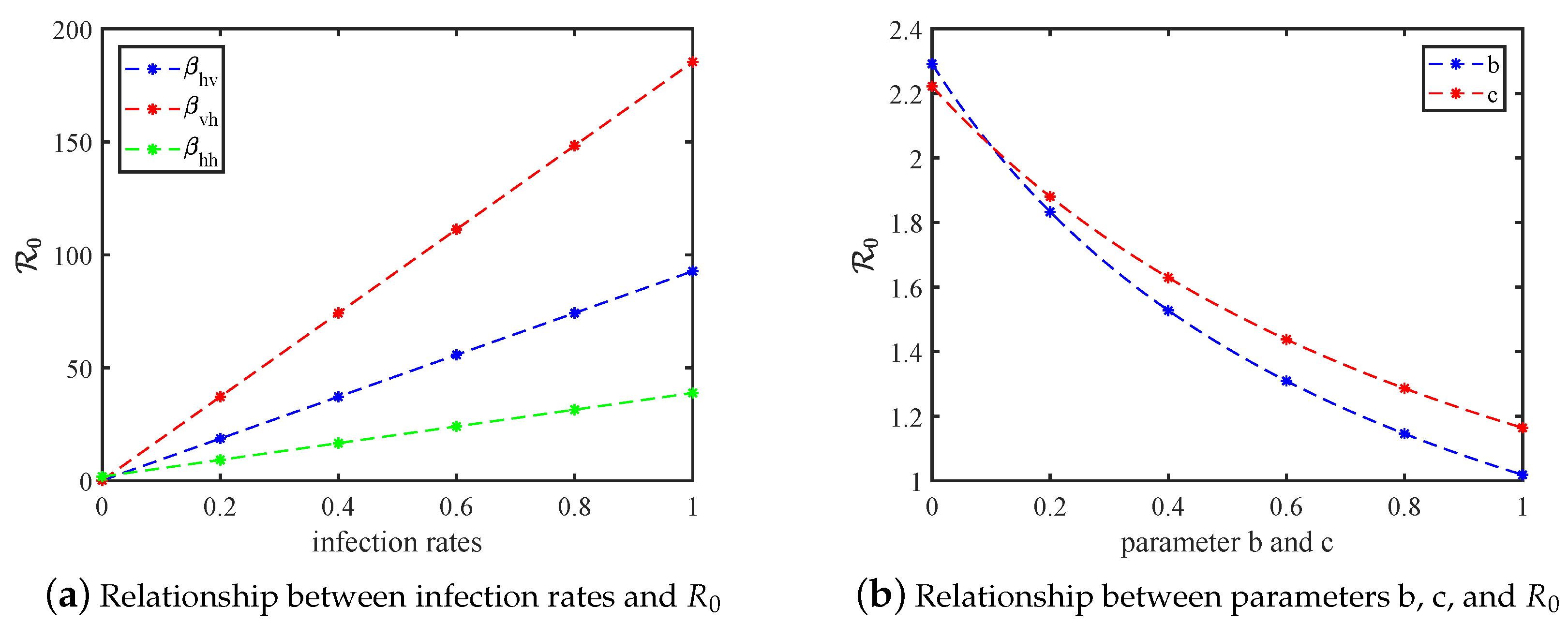
5. Sensitivity Analysis
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fei, L.Z.; Zou, L.; Chen, X.W. Global analysis for an epidemical model of vector-borne plant viruses with disease resistance and nonlinear incidence. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2020, 10, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Gong, Y.; Fang, R. Research progress and perspective of tripartite interaction of virus-vector-plant in vector-borne viral diseases. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 845–855. [Google Scholar]
- Akoth, O.P.; Pascal, M.D.; Hans-Michael, P.; Pappu, H.R. Predictive models for tomato spotted wilt virus spread dynamics, considering frankliniella occidentalis specific life processes as influenced by the virus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154533. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kim, S.T. An insight into the tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), tomato and thrips interaction. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 12, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiteux, L.S.; Giordano, L.B. Genetic basis of resistance against two tospovirus species in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Euphytica 1993, 71, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Ben-Arieh, D.; Zhao, S.; Wu, C.H. Using spatial games to model and simulate tomato spotted wilt virus-western flowers thrip dynamic system. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2018, 38, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.; Ullman, D.; German, T. Tospovirus-thrips interactions. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, S.N.; Kuang, Y.; Ben-Arieh, D.; Margolis, D. New mathematical models for vector-borne disease: Transmission of tomato spotted wilt virus. In Bridging Research and Good Practices towards Patients Welfare; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo, N.; Eftimie, R.; Forni, G. What is the in-host dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 virus? A challenge within a multiscale vision of living systems. Netw. Heterog. Media 2024, 19, 655–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniffe, N.J.; Gilligan, C.A. Invasion, persistence and control in epidemic models for plant pathogens: The effect of host demography. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeger, M.J.; Van, D.; Mcroberts, N. Modelling transmission characteristics and epidemic development of the tospovirus–thrip interaction. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2015, 9, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsello, S.C.; Beaudoin, A.L.P.; Groves, R.L.; Nault, B.; Kennedy, G.G. The influence of temperature and precipitation on spring dispersal of Frankliniella fusca changes as the season progresses. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 134, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatinwo, R.O.; Paz, J.O.; Brown, S.L.; Kemerait, R.C.; Hoogenboom, G. A predictive model for spotted wilt epidemics in peanut based on local weather conditions and the tomato spotted wilt virus risk index. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.K.; Igoe, M.; Power, A.G.; Bosque-Pérez, N.; Peace, A. Modeling approach influences dynamics of a vector-borne pathogen system. Bull. Math. Biol. 2019, 81, 2011–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zhao, H.; Tang, S. Global dynamic analysis of a vector-borne plant disease model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2014, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, A.S.; Szklarczyk, M.; Gajewski, Z.; Zukowska, E.; Michalik, B.; Kobylko, T.; Strzalka, K. Selection of tomato plants resistant to a local Polish isolate of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). J. Appl. Genet. 2003, 44, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrand, L.; Almeida, M.M.S.; Orilio, A.F.; Dal Bo, E.; Resende, R.O.; Garcia, M.L. Biological and molecular characterization of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) resistance-breaking isolates from Argentina. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, M.; Kassa, S.; Lungu, E. Stochastic plant–herbivore interaction model with Allee effect. J. Math. Biol. 2019, 79, 2183–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddington, J.R.; May, R.M. Harvesting natural populations in a randomly fluctuating environment. Science 1977, 197, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Charpentier, B. Stochastic modeling of plant virus propagation with biological control. Mathematics 2021, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gard, T.C. Introduction to Stochastic Differential Equations; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 84, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.Y.; Jiang, D.Q.; Li, X.Y. Qualitative analysis of a stochastic ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Shi, N.; Li, X. Global stability and stochastic permanence of a non-autonomous logistic equation with random perturbation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2008, 340, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Shi, N.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic sirs epidemic model with standard incidence. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 469, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Xing, Y. Dynamics of a stochastic heroin epidemic model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2019, 351, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, F. Dynamical analysis of a stochastic predator-prey model with an allee effect. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 340980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.B. Dynamics of a stochastic sveir epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. Symmetry 2024, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic virus dynamics model with intracellular delay and humoral immunity. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2019, 9, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huo, H.; Xiang, H.; Shi, Q.; Li, D. The threshold of a stochastic siqs epidemic model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 482, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, X.H. The threshold of a deterministic and a stochastic siqs epidemic model with varying total population size. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 91, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.B.; Zheng, L. Complex dynamics of a stochastic SIR epidemic model with vertical transmission and varying total population size. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 33, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Marion, G.; Renshaw, E. Environmental brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 2002, 97, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasminiskii, R.Z. Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations; Sijthoff & Noordhoff: Alphen Aan Den Rijn, The Netherland, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Strang, G. Linear algebra and its applications. Math. Comput. 1988, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Yin, G. Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems. Siam J. Control Optim. 2007, 46, 1155–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Dynamics of a Stochastic Vector-Borne Model with Plant Virus Disease Resistance and Nonlinear Incidence. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16091122
Zhang L, Wang X, Zhang X. Dynamics of a Stochastic Vector-Borne Model with Plant Virus Disease Resistance and Nonlinear Incidence. Symmetry. 2024; 16(9):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16091122
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liang, Xinghao Wang, and Xiaobing Zhang. 2024. "Dynamics of a Stochastic Vector-Borne Model with Plant Virus Disease Resistance and Nonlinear Incidence" Symmetry 16, no. 9: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16091122
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, X., & Zhang, X. (2024). Dynamics of a Stochastic Vector-Borne Model with Plant Virus Disease Resistance and Nonlinear Incidence. Symmetry, 16(9), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16091122




