Identifying the Differences in Symmetry of the Anthropometric Parameters of the Upper Limbs in Relation to Manual Laterality between Athletes Who Practice Sports with and without a Ball
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Information about Asymmetries in Sports
1.2. Specific Information on Asymmetries in Sports That Involve the Use and Non-Use of Implements with the Hands
1.3. Statement of the Problem, Where the Problematic Situation Is Clearly Identified and the Importance of this Study Is Justified
1.4. Objectives of this Study and Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
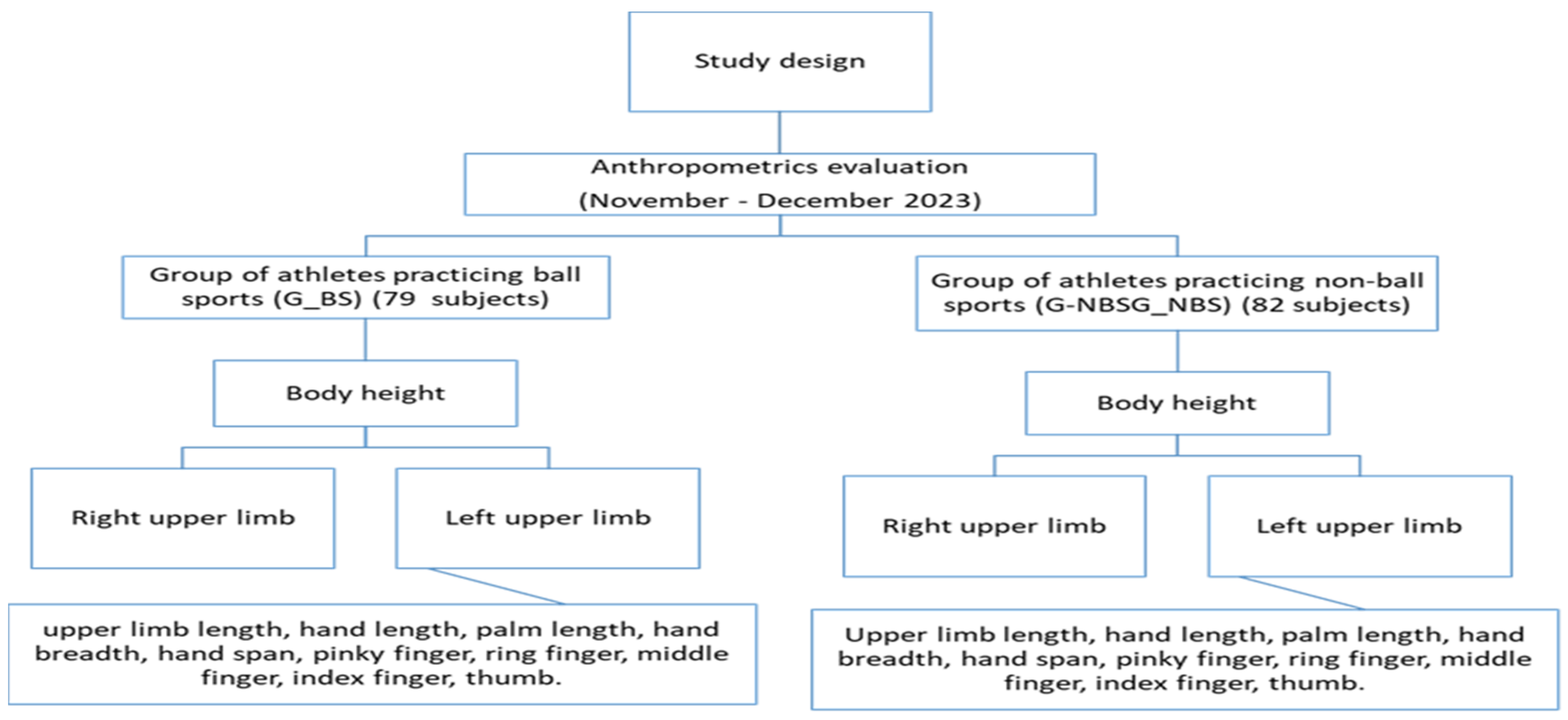
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Measures
- –
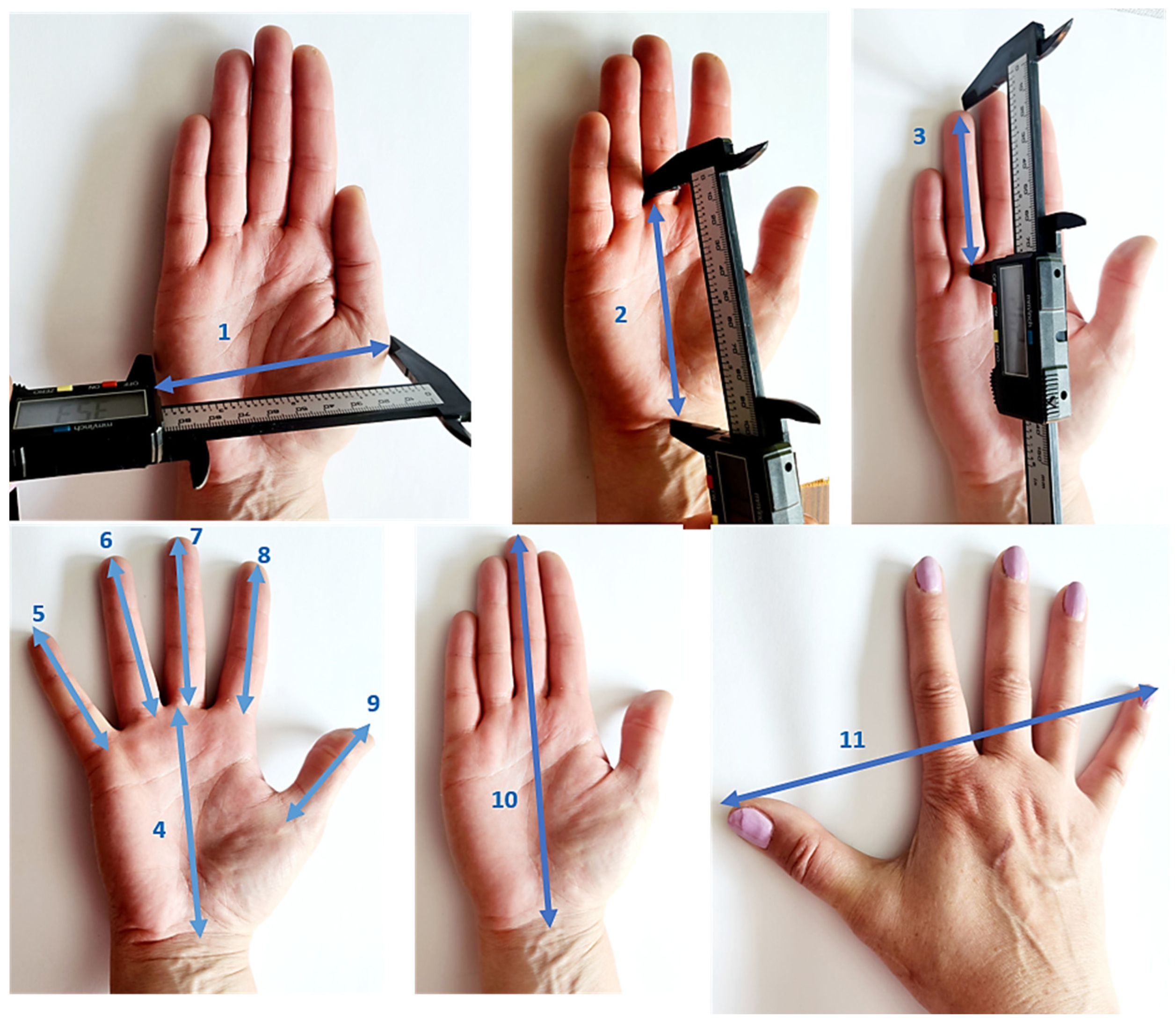
- Height—the distance between the vertex and the level of the sole (support surface) in the orthostatic position.
- –
- Upper limb length—the distance between the acromion and the dactylion in the orthostatic position with the upper limb in maximum extension.
- –
- Hand length—the distance between the styloid line and the dactylion.
- –
- Palm length—the distance between the styloid line and the proximal phalanges between the middle and ring finger.
- –
- Hand breadth—the direct distance from the most lateral point on the head of the second metacarpal to the most medial point on the head of the fifth metacarpal.
- –
- Hand span—the distance between the proximal phalanges of the pinky finger and the distal phalanges of the thumb, with the fingers being brought to the maximum angles.
- –
- Pinky finger—the distance between the proximal phalanges and distal phalanges of the pinky finger.
- –
- Ring finger—the distance between the proximal phalanges and distal phalanges of the ring finger.
- –
- Middle finger—the distance between the proximal phalanges and distal phalanges of the middle finger.
- –
- Index finger—the distance between the proximal phalanges and distal phalanges of the index finger.
- –
- Thumb—the distance between the proximal phalanges and distal phalanges of the thumb.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussions
Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afonso, J.; Peña, J.; Sá, M.; Virgile, A.; García-de-Alcaraz, A.; Bishop, C. Why Sports Should Embrace Bilateral Asymmetry: A Narrative Review. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.; Turner, A.; Read, P. Effects of inter-limb asymmetries on physical and sports performance: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettariga, F.; Turner, A.; Maloney, S.; Maestroni, L.; Jarvis, P.; Bishop, C. The Effects of Training Interventions on Interlimb Asymmetries: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Strength Cond. J. 2022, 44, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, S.J. The Relationship between Asymmetry and Athletic Performance: A Critical Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badau, D.; Badau, A.; Joksimović, M.; Manescu, C.O.; Manescu, D.C.; Dinciu, C.C.; Margarit, I.R.; Tudor, V.; Mujea, A.M.; Neofit, A.; et al. Identifying the Level of Symmetrization of Reaction Time According to Manual Lateralization between Team Sports Athletes, Individual Sports Athletes, and Non-Athletes. Symmetry 2024, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, H.; Rajabi, H.; Farzad, B.; Bayati, M.; Jeffreys, I. Anthropometry of world-class elite handball players according to the playing position: Reports from men’s handball world championship 2013. J. Hum. Kinet. 2013, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vukotic, M.; Corluka, M.; Vasiljevic, I.; Bubanja, M. Differences in the morphological characteristics and body composition of handball players WHC Levalea in Montenegro and WHC Grude in Bosnia and Herzegovina. J. Anthropol. Sport Phys. Educ. 2018, 2, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venneri, M.A.; Franceschini, E.; Sciarra, F.; Rosato, E.; D’Ettorre, G.; Lenzi, A. Human genital tracts microbiota: Dysbiosis crucial for infertility. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The Connection between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hohmann, A.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Pion, J.; Gao, B. Physiological, Anthropometric, and Motor Characteristics of Elite Chinese Youth Athletes from Six Different Sports. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanovic, B. Comparative Study of Morphological Characteristics and Body Composition between Different Team Players from Serbian Junior National League: Soccer, Handball, Basketball and Volleyball. Int. J. Morphol. 2019, 37, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbakk, Ø. The Role of Sport Science in the New Age of Digital Sport. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnamo, V. Sensor Technology for Sports Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicijevic, D.; Pérez-Castilla, A.; Miras-Moreno, S.; Ortega-Becerra, M.; Morenas-Aguilar, M.D.; Smajla, D.; Sarabon, N.; García-Ramos, A. Effect of a High-Intensity Handball-Specific Fatigue Protocol Focused on the Leg Contralateral to the Throwing Arm on Interlimb Asymmetries. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2023, 37, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Lake, J.; Loturco, I.; Papadopoulos, K.; Turner, A.; Read, P. Inter-limb Asymmetries: The Need for an Individual Approach to Data Analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exell, T.A.; Irwin, G.; Gittoes, M.J.; Kerwin, D.G. Implications of intra-limb variability on asymmetry analyses. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Turner, A.; Read, P. Training Methods and Considerations for Practitioners to Reduce Inter-Limb Asymmetries. Strength Cond. J. 2017, 40, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanovic, B.; Vukasevic, V. Differences in anthropometric characteristics between junior handball and volleyball players. J. Anthropol. Sport Phys. Educ. 2020, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzimanouil, D.; Oxizoglou, N. Evaluation of the morphological characteristics and motor skills in the national junior handball teams of Greece and Yugoslavia. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 2004, 46, 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi, H.; Yamanaka, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Futatsubashi, G.; Kadota, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Nakazawa, K. Acquisition of novel ball-related skills associated with sports experience. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, A.A.; Jadidian, A.A. The effect of hand dimensions, hand shape and some anthropometric characteristics on handgrip strength in male grip athletes and non-athletes. J Hum Kinet. 2011, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjevic, B.; Zarkovic, B.; Katanic, B.; Jabucanin, B.; Popovic, S.; Masanovic, B. Morphological Characteristics and Situational Precision of U15 and U16 Elite Male Players from Al-Ahli Handball Club (Bahrein). Sports 2022, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieseler, G.; Hermassi, S.; Hoffmeyer, B.; Schulze, S.; Irlenbusch, L.; Bartels, T.; Delank, K.S.; Laudner, K.G.; Schwesig, R. Differences in anthropometric characteristics in relation to throwing velocity and competitive level in professional male team handball: A tool for talent profiling. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.Ö. Evaluating the Relation between Dominant and Non-Dominant Hand Perimeters and Handgrip Strength of Basketball, Volleyball, Badminton and Handball Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 3297–3309. [Google Scholar]
- Zaccagni, L.; Toselli, S.; Bramanti, B.; Gualdi-Russo, E.; Mongillo, J.; Rinaldo, N. Handgrip Strength in Young Adults: Association with Anthropometric Variables and Laterality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; González-Custodio, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Timón, R.; Olcina, G.; Brazo-Sayavera, J. Anthropometric and Physical Performance of Youth Handball Players: The Role of the Relative Age. Sports 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantsev, A.A.; Bespyatkin, V.E.; Travkov, D.A.; Bakhtiarova, T.V. Determination of anthropometric indicators of the hand of athletes on the basis of computer vision. Theory Pract. Phys. Cult. 2023, 5, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pion, J.; Segers, V.; Fransen, J.; Debuyck, G.; Deprez, D.; Haerens, L.; Vaeyens, R.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. Generic anthropometric and performance characteristics among elite adolescent boys in nine different sports. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, P.; Kiran, S.; Barut, C. Morphological and functional aspects of hand in relation to age, gender and sports playing condition. Acta Medica Int. 2014, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort-Vanmeerhaeghe, A.; Bishop, C.; Buscà, B.; Vicens-Bordas, J.; Arboix-Alió, J. Seasonal variation of inter-limb jumping asymmetries in youth team-sport athletes. J Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadka, M.; Gaweł, M.; Tomczyk-Warunek, A.; Turżańska, K.; Blicharski, T. Relationship between Upper Limb Functional Assessment and Clinical Tests of Shoulder Mobility and Posture in Individuals Participating in Recreational Strength Training. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.G.; Shin, A.Y.; Kaufman, K.R. Upper extremity asymmetry due to nerve injuries or central neurologic conditions: A scoping review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöckel, T.; Weigelt, M. Plasticity of human handedness: Decreased one-hand bias and inter-manual performance asymmetry in expert basketball players. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hondt, J.; Chapelle, L.; Droogenbroeck, L.V.; Aerenhouts, D.; Clarys, P.; D’Hondt, E. Bioelectrical impedance analysis as a means of quantifying upper and lower limb asymmetry in youth elite tennis players: An explorative study. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpinar, S. Decreased inter-limb differences in female basketball players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2016, 56, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar]
- van der Feen, F.E.; Zickert, N.; Groothuis, T.G.G.; Geuze, R.H. Does hand skill asymmetry relate to creativity, developmental and health issues and aggression as markers of fitness? Laterality 2020, 25, 53–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, J.; Schnitzler, A.; Witte, O.W.; Freund, H. Handedness and asymmetry of hand representation in human motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.K.; Cochrane, T. Mobility impairment, muscle imbalance, muscle weakness, scapular asymmetry and shoulder injury in elite volleyball athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2001, 41, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Chu, K.; Miao, Q.; Ping, L.; Zhong, W.; Qi, S.; Zhang, M. Bilateral Asymmetry of Hand Force Production in Dynamic Physically-Coupled Tasks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdukiewicz, A.; Pietraszewska, J.; Andrzejewska, J.; Chromik, K.; Stachoń, A. Asymmetry of Musculature and Hand Grip Strength in Bodybuilders and Martial Artists. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijewski, M.; Burdukiewicz, A.; Pietraszewska, J.; Andrzejewska, J.; Stachoń, A. Asymmetry of Muscle Mass Distribution and Grip Strength in Professional Handball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapelle, L.; Bishop, C.; D’Hondt, J.; Rommers, N.; D’Hondt, E.; Clarys, P. Development of upper and lower extremity functional asymmetries in male and female elite youth tennis players: A longitudinal study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2023, 63, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinimehr, S.H.; Anbarian, M.; Norasteh, A.A.; Fardmal, J.; Khosravi, M.T. The comparison of scapular upward rotation and scapulohumeral rhythm between dominant and non-dominant shoulder in male overhead athletes and non-athletes. Man. Ther. 2015, 20, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijewski, M.; Burdukiewicz, A.; Stachoń, A.; Pietraszewska, J. Differences in anthropometric variables and muscle strength in relation to competitive level in male handball players. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudiere, A.; de Rugy, A.; Danion, F.R. Right-left hand asymmetry in manual tracking: When poorer control is associated with better adaptation and inter-limb transfer. Psychol. Res. 2024, 88, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koźlenia, D.; Struzik, A.; Domaradzki, J. Force, Power, and Morphology Asymmetries as Injury Risk Factors in Physically Active Men and Women. Symmetry 2022, 14, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, B.M.; Ruff, C.B. Limb bone bilateral asymmetry: Variability and commonality among modern humans. J. Hum. Evol. 2006, 50, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, D.M.; Hurley, M.M.; Foundas, A.L. Right and left handedness defined: A multivariate approach using hand preference and hand performance measures. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol. Behav. Neurol. 2001, 14, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Caamaño-Navarrete, F.; Delgado-Floody, P.; Martinez-Salazar, C.; Jerez-Mayorga, D. Speed and throwing the ball are related to jump capacity and skeletal muscle mass in university basketball players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021, 61, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aandstad, A. Reference data on anthropometrics, aerobic fitness and muscle strength in young Norwegian men and women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, L.; D’Hondt, E.; Rommers, N.; Clarys, P. Development of Upper-Extremity Morphological Asymmetries in Male and Female Elite Youth Tennis Players: A Longitudinal Study. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2023, 36, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Fernández, L.; García-Sillero, M.; Jurado-Castro, J.M.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; García-Romero, J.; Benítez-Porres, J. Influence of limb dominance on body and jump asymmetries in elite female handball. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort-Vanmeerhaeghe, A.; Bishop, C.; Buscà, B.; Aguilera-Castells, J.; Vicens-Bordas, J.; Gonzalo-Skok, O. Inter-limb asymmetries are associated with decrements in physical performance in youth elite team sports athletes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde-Sotres, Á.; Bores-Cerezal, A.; Mecías-Calvo, M.; Barcala-Furelos, M.; Aparicio-Obregón, S.; Calleja-González, J. Detection of Upper Limb Asymmetries in Athletes According to the Stage of the Season—A Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolidis, N.; Emmanouil, Z. The influence of the anthropometric characteristics and handgrip strength on the technical skills of young basketball players. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2015, 15, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Visnapuu, M.; Jürimäe, T. Handgrip strength and hand dimensions in young handball and basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyol, P.; Tutkun, E.; Cebi, M. The influence of hand finger length ratio on the motoric and functional dominance of women dancer’s athletes and sedentaries. Int. J. Acad. Res. 2016, 8, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Eler, N. The correlation between right hand finger ratio (2D: 4D) and the parameters of anthropometric and physical fitness in children. J. Hum. Sci. 2018, 15, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, H.; Aksoy, C.; Eskici, G.; Köroğlu, Y. Analysis of the relationship between 2d: 4d finger length ratios and leg strength among athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 17, 977–981. [Google Scholar]
- Barut, C.; Sevinc, O.; Sumbuloglu, V. Evaluation of hand asymmetry in relation to hand preference. Coll. Antropol. 2011, 35, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, T.; Anyanwu, G.E. Anthropometric evaluation of hand dimensions and hand index in a young Nigerian population. Appl. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Memarian, A.; Aghakhani, K.; Nasab, N.P. Evaluation of height based on measurement of width, circumference, thickness of palm and width, circumference of the wrist in Iranian adults by gender. J. Punjab Acad. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarimoghadam, R.; Shabani, M.; Lotfi, Y.; Ghasemi, F.; Mohammadi, Y. A study of hand anthropometry dimensional on middle-aged women and male in Hamadan. Iran J. Ergon. 2018, 6, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memishi, S.; Ameti, V.; Arifi, F. Standing Height and Its Estimation Utilizing Length of Hand Measurements of Both Gender Adolescents from North Region of Kosovo; District of Mitrovica. J. Educ. Health Sport 2019, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematpour, L.; Golbaghi, A.; Mosavi, M.; Deris, J. Comparison of anthropometric dimensions of farmers’ hands in four different Iranian ethnicities. J. Occup. Hyg. Eng. Vol. 2020, 7, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hajaghazadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Mohebbi, I.; Khalkhali, H. Hand anthropometric dimensions and strengths in workers: A comparison of three occupations. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Ind. 2022, 32, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Chandna, P.; Deswal, S. Analysis of hand anthropometric dimensions of male industrial workers of Haryana state. Int. J. Eng. (IJE) 2011, 5, 242–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, M.M.; Scheffler, C. Bilateral asymmetry in left handers increased concerning morphological laterality in a recent sample of young adults. Anthropol. Anz. Ber. Uber Die Biol.-Anthropol. Lit. 2016, 73, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulaksiz, G.; Gözil, R. The effect of hand preference on hand anthropometric measurements in healthy individuals. Ann. Anat. 2002, 184, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Preciado, L.L.; Vallarta-Robledo, J.R.; Chávez-Palencia, C.; Lizárraga-Corona, E.; Larrosa-Haro, A. Bilateral asymmetry in arm anthropometric measurements according to laterality and nutritional status in children and adolescents from 6 to 12 years old. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2022, 34, e23585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, J.; Mirzaei Majarshin, V.; Sheikhmozafari, M.J.; Ahmadi, O. Anthropometric Dimensions of Hands and Feet in Different Ages of People Living in, Iran. Int. J. Musculoskelet. Pain Prev. 2021, 6, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hălmaciu, I.; Suciu, B.A.; Trambitas, C.; Vunvulea, V.; Ivanescu, A.; Clipa, A.; Adascalitei, P.; Brinzaniuc, K.; Fodor, D. It is Useful to Use Plastic Anatomical Models in Teaching Human Anatomy? Mater. Plast. 2018, 15, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundorf, A.; Getzmann, S.; Gajewski, P.D.; Larra, M.F.; Wascher, E.; Ocklenburg, S. Stress exposure, hand preference, and hand skill: A deep phenotyping approach. Laterality 2023, 28, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandler, W.M.; Morris, A.P.; Evans, D.M.; Scerri, T.S.; Kemp, J.P.; Timpson, N.J.; St Pourcain, B.; Smith, G.D.; Ring, S.M.; Stein, J.; et al. Common variants in left/right asymmetry genes and pathways are associated with relative hand skill. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egoyan, A.; Parulava, G.; Baker, S.; Gilhen-Baker, M.; Roviello, G.N. Movement Asymmetries: From Their Molecular Origin to the Analysis of Movement Asymmetries in Athletes. Life 2023, 13, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yarossi, M.; Jacobs-Skolik, S.L.; Furmanek, M.P.; Brooks, D.; Erdogmus, D.; Tunik, E. Synergistic Activation Patterns of Hand Muscles in Left-and Right-Hand Dominant Individuals. J. Hum. Kinet. 2021, 76, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lee, Y.J.; Aruin, A.S. Anticipatory and compensatory postural adjustments in conditions of body asymmetry induced by holding an object. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, S.; Galis, F.; Ten Broek, C.; Heikinheimo, K.; Wijnaendts, L.C.; Delen, S.; Bots, J. When right differs from left: Human limb directional asymmetry emerges during very early development. Laterality 2014, 19, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mala, L.; Maly, T.; Camirelli, R.; Dornowski, M.; Zahalka, F.; Petr, M.; Hrasky, P.; Bujnovský, D. Gender differences in strength lateral asymmetries, limbs morphology and body composition in adolescent judo athletes. Arch. Budo 2017, 13, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Karcher, C.; Buchheit, M. Anthropometric and physical performance requirements to be selected in elite handball academies: Is being left-handed an advantage? SPSR 2017, 9, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Madruga-Parera, M.; Bishop, C.; Fort-Vanmeerhaeghe, A.; Beato, M.; Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Romero-Rodríguez, D. Effects of 8 Weeks of Isoinertial vs. Cable-Resistance Training on Motor Skills Performance and Inter-limb Asymmetries. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorshorst, T.; Weir, G.; Hamill, J.; Holt, B. (Archery’s signature: An electromyographic analysis of the upper limb. Evol. Hum. Sci. 2022, 4, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bampouras, T.M.; Wilson, A.J.; Papadopoulos, K. Upper limb muscle strength and knee frontal plane projection angle asymmetries in female water-polo players. Sports Biomech. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Moysi, J.; Dorado, C.; Olmedillas, H.; Serrano-Sanchez, J.A.; Calbet, J.A. Bone and lean mass inter-arm asymmetries in young male tennis players depend on training frequency. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, N.; Shitara, H.; Tajika, T.; Ichinose, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kuboi, T.; Shimoyama, D.; Kamiyama, M.; Miyamoto, R.; Endo, F.; et al. Relationship between upper limb injuries and hip range of motion and strength in high school baseball pitchers. J. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 29, 23094990211003347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, H.A.; Cai, Z.; Dove, H.; Hostetter, G.; Brice, T.; Chien, A.; Sum, J.C.; Hawkins, A.; Li, B.; Michener, L.A. Hip Abductor Strength Asymmetry: Relationship to Upper Extremity Injury in Professional Baseball Players. Sports Health 2023, 15, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokha, M.; Sprague, P.A.; Gatens, D.R. Predicting Musculoskeletal Injury in National Collegiate Athletic Association Division II Athletes from Asymmetries and Individual-Test Versus Composite Functional Movement Screen Scores. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzysztofik, M.; Trybulski, R.; Trąbka, B.; Perenc, D.; Łuszcz, K.; Zajac, A.; Alexe, I.A.; Dobrescu, T.; Moraru, C.E. The impact of resistance exercise range of motion on the magnitude of upper-body post-activation performance enhancement. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechita, F. Effects corrective gymnastics physical education and sport lesson. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Braşov. Ser. IX Sci. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Group | Side | Minimum | Maximum | X | SD | Variance | Kurtosis | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper limb length | G_NBS | Right | 69.00 | 79.00 | 74.004 | 3.141 | 9.867 | −1.110 | 4.24 |
| Left | 68.00 | 80.00 | 74.071 | 3.296 | 10.867 | −0.766 | 4.45 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 74.00 | 86.00 | 80.063 | 3.569 | 12.740 | −1.014 | 4.46 | |
| Left | 74.00 | 87.00 | 80.317 | 3.941 | 15.533 | −0.999 | 4.91 | ||
| Hand length | G_NBS | Right | 17.10 | 21.60 | 18.509 | 1.298 | 1.686 | 0.538 | 7.01 |
| Left | 17.00 | 21.50 | 18.449 | 1.167 | 1.362 | 1.258 | 6.33 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 18.00 | 21.50 | 19.579 | 1.178 | 1.387 | −1.436 | 6.02 | |
| Left | 18.00 | 21.60 | 19.525 | 1.138 | 1.296 | −1.402 | 5.83 | ||
| Palm length | G_NBS | Right | 9.60 | 12.00 | 10.976 | 0.741 | 0.549 | −0.872 | 6.75 |
| Left | 9.50 | 12.100 | 11.000 | 0.766 | 0.586 | −0.945 | 6.96 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 11.00 | 13.00 | 11.880 | 0.653 | 0.427 | −0.920 | 5.50 | |
| Left | 11.10 | 13.10 | 11.854 | 0.638 | 0.407 | −0.706 | 5.38 | ||
| Hand breadth | G_NBS | Right | 6.80 | 9.00 | 7.759 | 0.724 | 0.525 | −1.293 | 9.33 |
| Left | 6.70 | 9.10 | 7.754 | 0.730 | 0.533 | −1.274 | 9.41 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 7.10 | 9.50 | 8.372 | 0.666 | 0.444 | −0.731 | 7.96 | |
| Left | 7.20 | 9.50 | 8.371 | 0.656 | 0.430 | −0.623 | 7.84 | ||
| Hand span | G_NBS | Right | 18.00 | 22.00 | 19.842 | 1.205 | 1.452 | −0.815 | 6.07 |
| Left | 18.00 | 22.50 | 19.878 | 1.276 | 1.629 | −0.502 | 6.42 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 20.00 | 25.50 | 22.171 | 1.738 | 3.022 | −1.050 | 7.84 | |
| Left | 20.10 | 25.00 | 22.172 | 1.688 | 2.850 | −0.989 | 7.61 | ||
| Pinky finger | G_NBS | Right | 5.10 | 6.40 | 5.589 | 0.360 | 0.129 | 0.116 | 6.44 |
| Left | 5.20 | 6.50 | 5.592 | 0.378 | 0.143 | 0.209 | 6.76 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 5.50 | 7.00 | 6.263 | 0.439 | 0.193 | −1.091 | 7.01 | |
| Left | 5.60 | 7.20 | 6.223 | 0.462 | 0.213 | −0.644 | 7.42 | ||
| Ring finger | G_NBS | Right | 6.10 | 7.80 | 7.111 | 0.491 | 0.241 | −0.783 | 6.90 |
| Left | 6.20 | 7.90 | 7.124 | 0.491 | 0.241 | −0.995 | 6.89 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 6.50 | 8.10 | 7.523 | 0.452 | 0.205 | −0.198 | 6.01 | |
| Left | 6.60 | 8.20 | 7.504 | 0.447 | 0.200 | −0.218 | 5.96 | ||
| Middle finger | G_NBS | Right | 6.60 | 8.30 | 7.348 | 0.471 | 0.222 | −0.884 | 6.41 |
| Left | 6.80 | 8.20 | 7.356 | 0.436 | 0.190 | −0.689 | 5.93 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 7.20 | 8.80 | 8.056 | 0.505 | 0.255 | −1.090 | 6.27 | |
| Left | 7.10 | 8.80 | 8.029 | 0.496 | 0.246 | −0.735 | 6.18 | ||
| Index finger | G_NBS | Right | 6.20 | 7.50 | 6.738 | 0.388 | 0.150 | −0.804 | 5.76 |
| Left | 6.20 | 7.60 | 6.740 | 0.365 | 0.134 | 0.097 | 5.42 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 6.60 | 8.10 | 7.322 | 0.473 | 0.224 | −1.043 | 6.46 | |
| Left | 6.50 | 8.00 | 7.300 | 0.457 | 0.209 | −1.065 | 6.26 | ||
| Thumb | G_NBS | Right | 4.80 | 6.50 | 5.422 | 0.369 | 0.136 | 1.779 | 6.81 |
| Left | 4.70 | 6.60 | 5.401 | 0.353 | 0.125 | 2.842 | 6.54 | ||
| G_BS | Right | 5.40 | 6.70 | 5.948 | 0.403 | 0.163 | −1.127 | 6.78 | |
| Left | 5.30 | 6.60 | 5..919 | 0.414 | 0.171 | −1.398 | 6.99 |
| Parameters | Group | Side | Mean | SD | ΔX | SD | 95% CI | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||||
| Upper limb length | G_NBS | Right | 74.004 | 3.141 | −0.067 | 0.406 | −0.156 | 0.022 | −1.498 | 0.138 |
| Left | 74.071 | 3.296 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 80.063 | 3.569 | −0.253 | 0.524 | −0.371 | −0.136 | −4.292 | <0.001 | |
| Left | 80.317 | 3.941 | ||||||||
| Hand length | G_NBS | Right | 18.509 | 1.298 | 0.060 | 0.321 | −0.011 | 0.130 | 1.685 | 0.096 |
| Left | 18.449 | 1.167 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 19.579 | 1.138 | 0.053 | 0.212 | 0.006 | 0.101 | 2.232 | 0.028 | |
| Left | 19.525 | 0.653 | ||||||||
| Palm length | G_NBS | Right | 10.976 | 0.741 | −0.024 | 0.108 | −0.048 | −0.001 | −2.038 | 0.045 |
| Left | 11.000 | 0.766 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 11.880 | 0.653 | 0.025 | 0.110 | 0.001 | 0.050 | 2.040 | 0.045 | |
| Left | 11.854 | 0.638 | ||||||||
| Hand breadth | G_NBS | Right | 7.759 | 0.724 | 0.005 | 0.038 | −0.004 | 0.013 | 1.157 | 0.251 |
| Left | 7.754 | 0.730 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 8.372 | 0.666 | 0.001 | 0.038 | −0.007 | 0.010 | 0.300 | 0.765 | |
| Left | 8.371 | 0.656 | ||||||||
| Hand span | G_NBS | Right | 19.842 | 1.205 | −0.037 | 0.131 | −0.065 | −0.008 | −2.529 | 0.113 |
| Left | 19.878 | 1.276 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 22.171 | 1.738 | −0.001 | 0.164 | −0.038 | 0.036 | −0.068 | 0.946 | |
| Left | 22.172 | 1.688 | ||||||||
| Pinky finger | G_NBS | Right | 5.589 | 0.360 | −0.002 | 0.035 | −0.010 | 0.005 | −0.630 | 0.530 |
| Left | 5.592 | 0.378 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 6.263 | 0.439 | 0.041 | 0.094 | 0.019 | 0.062 | 3.827 | <0.001 | |
| Left | 6.223 | 0.462 | ||||||||
| Ring finger | G_NBS | Right | 7.111 | 0.491 | −0.013 | 0.056 | −0.026 | −0.001 | −2.164 | 0.033 |
| Left | 7.124 | 0.491 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 7.523 | 0.452 | 0.019 | 0.072 | 0.003 | 0.035 | 2.352 | 0.021 | |
| Left | 7.504 | 0.447 | ||||||||
| Middle finger | G_NBS | Right | 7.348 | 0.471 | −0.009 | 0.093 | −0.029 | 0.012 | −0.829 | 0.409 |
| Left | 7.356 | 0.436 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 8.056 | 0.505 | 0.027 | 0.090 | 0.006 | 0.047 | 2.620 | 0.011 | |
| Left | 8.029 | 0.496 | ||||||||
| Index finger | G_NBS | Right | 6.738 | 0.388 | −0.002 | 0.082 | −0.020 | 0.015 | −0.271 | 0.787 |
| Left | 6.740 | 0.365 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 7.322 | 0.473 | 0.022 | 0.055 | 0.009 | 0.034 | 3.496 | 0.001 | |
| Left | 7.300 | 0.457 | ||||||||
| Thumb | G_NBS | Right | 5.422 | 0.369 | 0.021 | 0.073 | 0.005 | 0.037 | 2.562 | 0.012 |
| Left | 5.401 | 0.353 | ||||||||
| G_BS | Right | 5.948 | 0.403 | 0.029 | 0.072 | 0.013 | 0.045 | 3.600 | 0.001 | |
| Left | 5,919 | 0,414 | ||||||||
| Parameters | Groups | Side | F | p(F) | t | p(t) | ΔX | SED | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||||
| Upper limb length | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 1.944 | 0.165 | 11.447 | <0.001 | 6.060 | 0.529 | 5.014 | 7.105 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 3.981 | 0.048 | 10.923 | <0.001 | 6.246 | 0.572 | 5.116 | 7.375 | |
| Hand length | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 0.320 | 0.573 | 5.471 | <0.001 | 1.070 | 0.196 | 0.684 | 1.456 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 2.122 | 0.147 | 5.922 | <0.001 | 1.077 | 0.182 | 0.718 | 1.436 | |
| Palm length | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 1.268 | 0.262 | 8.201 | <0.001 | 0.904 | 0.110 | 0.686 | 1.122 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 2.751 | 0.099 | 7.676 | <0.001 | 0.854 | 0.111 | 0.635 | 1.074 | |
| Hand breadth | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 3.275 | 0.072 | 5.590 | <0.001 | 0.614 | 0.110 | 0.397 | 0.830 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 4.564 | 0.034 | 5.638 | <0.001 | 0.617 | 0.109 | 0.401 | 0.833 | |
| Hand span | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 11.748 | 0.001 | 9.911 | <0.001 | 2.329 | 0.235 | 1.865 | 2.794 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 6.545 | 0.011 | 9.748 | <0.001 | 2.294 | 0.235 | 1.829 | 2.759 | |
| Pinky finger | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 7.075 | 0.009 | 10.675 | <0.001 | 0.674 | 0.063 | 0.550 | 0.799 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 7.664 | 0.006 | 9.508 | <0.001 | 0.631 | 0.066 | 0.500 | 0.762 | |
| Ring finger | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 1.700 | 0.194 | 5.531 | <0.001 | 0.412 | 0.074 | 0.265 | 0.559 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 1.869 | 0.174 | 5.124 | <0.001 | 0.379 | 0.074 | 0.233 | 0.526 | |
| Middle finger | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 0.693 | 0.406 | 9.208 | <0.001 | 0.708 | 0.077 | 0.556 | 0.860 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 0.748 | 0.388 | 9.154 | <0.001 | 0.673 | 0.074 | 0.528 | 0.818 | |
| Index finger | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 4.896 | 0.028 | 8.575 | <0.001 | 0.584 | 0.068 | 0.449 | 0.718 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 6.727 | 0.010 | 8.598 | <0.001 | 0.560 | 0.065 | 0.431 | 0.688 | |
| Thumb | G_BS-G_NBS | Right | 8.770 | 0.004 | 8.641 | <0.001 | 0.526 | 0.061 | 0.406 | 0.646 |
| G_BS-G_NBS | Left | 16.926 | <0.001 | 8.548 | <0.001 | 0.518 | 0.061 | 0.398 | 0.637 | |
| Parameters | G_NBS | G_BS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | DA | Direction of Asymmetry | SI | DA | Direction of Asymmetry | |
| Upper limb length | −0.090 | −0.045 | Left | −0.317 | −0.158 | Left |
| Hand length | 0.325 | 0.162 | Right | 0.276 | 0.138 | Right |
| Palm length | −0.218 | −0.109 | Left | 0.219 | 0.110 | Right |
| Hand breadth | 0.064 | 0.032 | Right | 0.012 | 0.006 | Right |
| Hand span | −0.181 | −0.091 | Left | −0.005 | −0.002 | Left |
| Pinky finger | −0.054 | −0.027 | Left | 0.641 | 0.320 | Right |
| Ring finger | −0.183 | −0.091 | Left | 0.253 | 0.126 | Right |
| Middle finger | −0.109 | −0.054 | Left | 0.336 | 0.168 | Right |
| Index finger | −0.030 | −0.015 | Left | 0.301 | 0.150 | Right |
| Thumb | 0.388 | 0.194 | Right | 0.489 | 0.244 | Right |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badau, A.; Badau, D. Identifying the Differences in Symmetry of the Anthropometric Parameters of the Upper Limbs in Relation to Manual Laterality between Athletes Who Practice Sports with and without a Ball. Symmetry 2024, 16, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16050558
Badau A, Badau D. Identifying the Differences in Symmetry of the Anthropometric Parameters of the Upper Limbs in Relation to Manual Laterality between Athletes Who Practice Sports with and without a Ball. Symmetry. 2024; 16(5):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16050558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadau, Adela, and Dana Badau. 2024. "Identifying the Differences in Symmetry of the Anthropometric Parameters of the Upper Limbs in Relation to Manual Laterality between Athletes Who Practice Sports with and without a Ball" Symmetry 16, no. 5: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16050558
APA StyleBadau, A., & Badau, D. (2024). Identifying the Differences in Symmetry of the Anthropometric Parameters of the Upper Limbs in Relation to Manual Laterality between Athletes Who Practice Sports with and without a Ball. Symmetry, 16(5), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16050558









