Explicit K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods for Charged Particle System in General Magnetic Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Charged Particle System
3. K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods Based on Splitting Methods
3.1. K-Symplectic Methods for the Charged Particle System
3.2. Symplectic-like Methods for the Charged Particle System
4. Numerical Methods
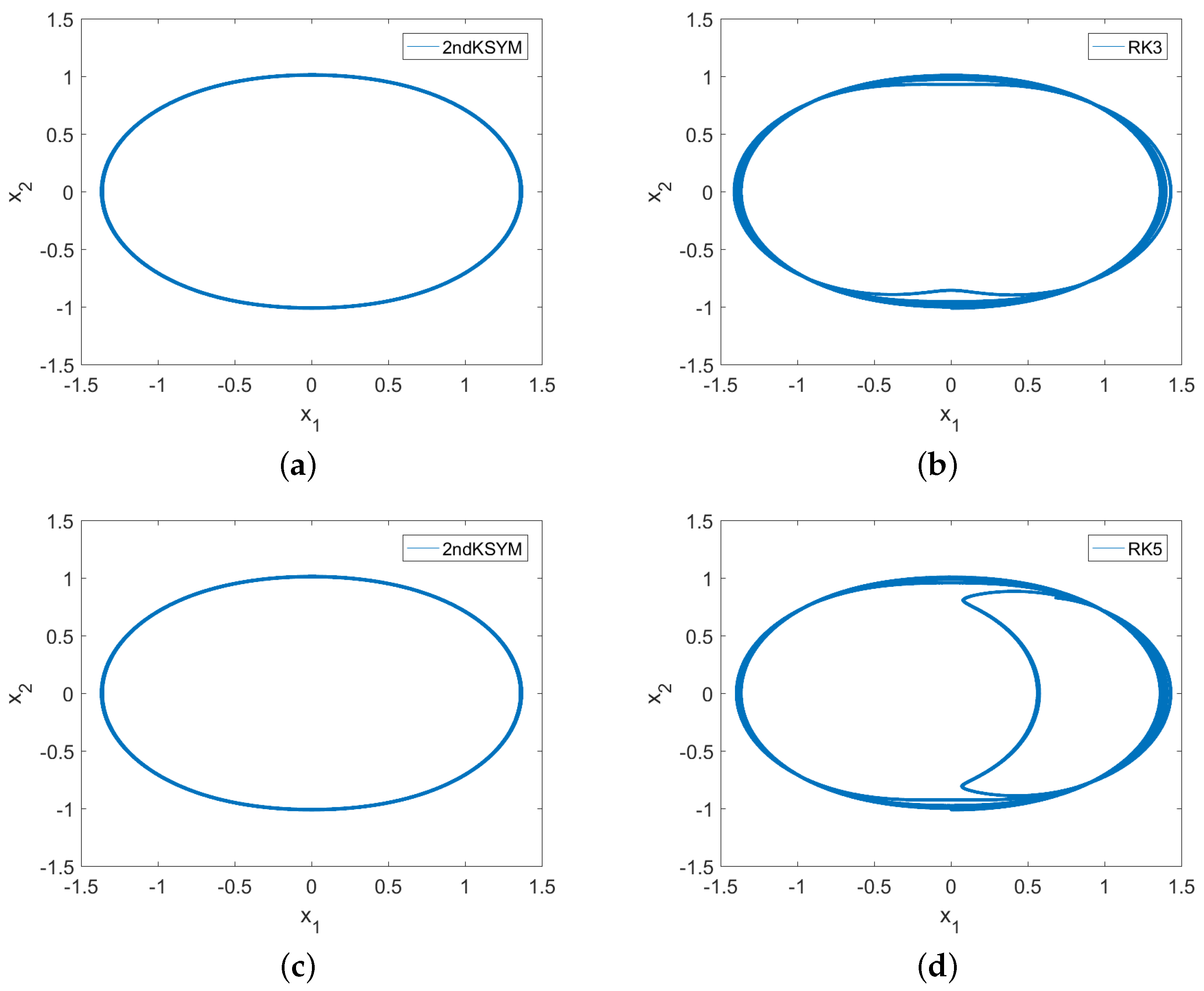
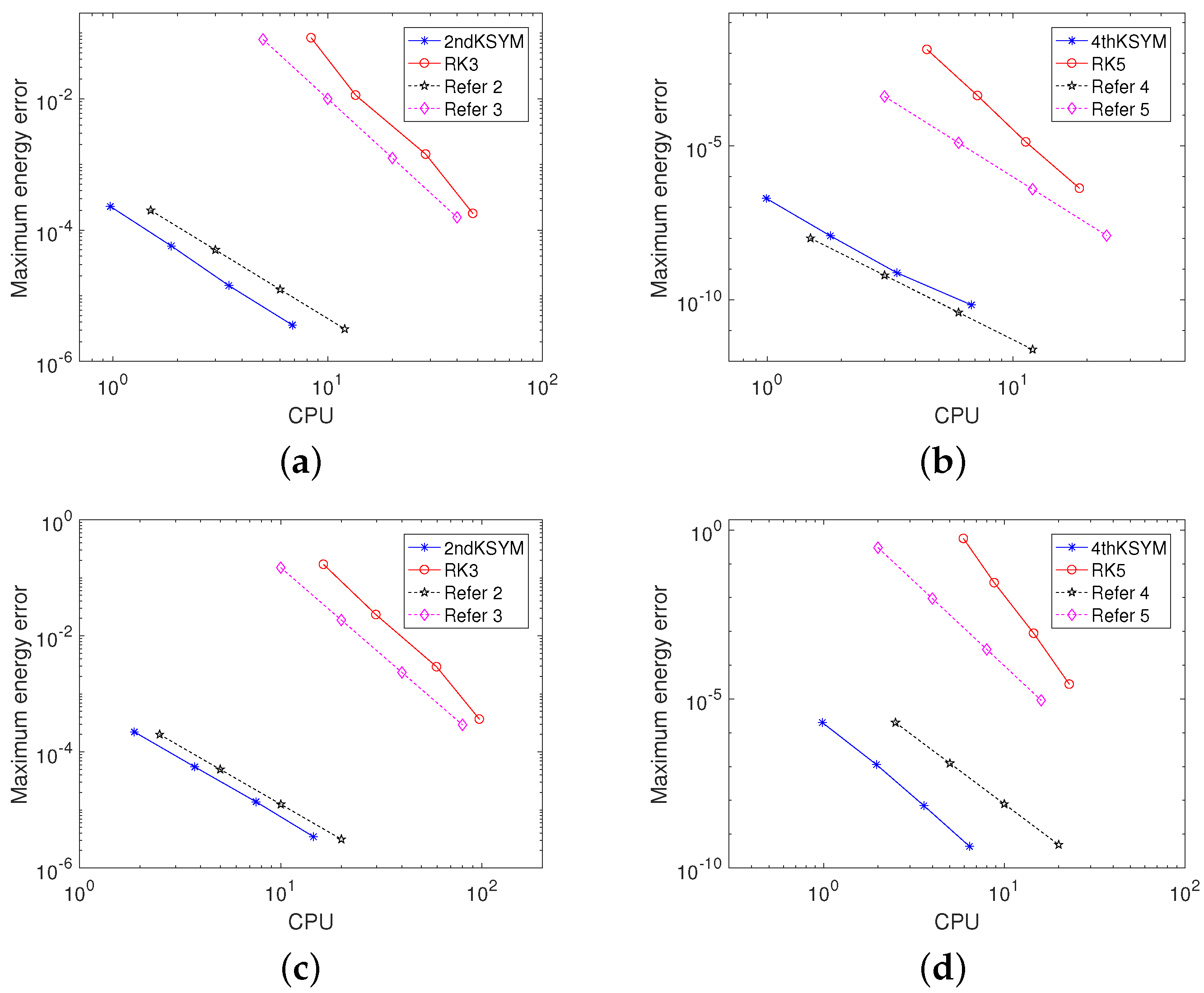
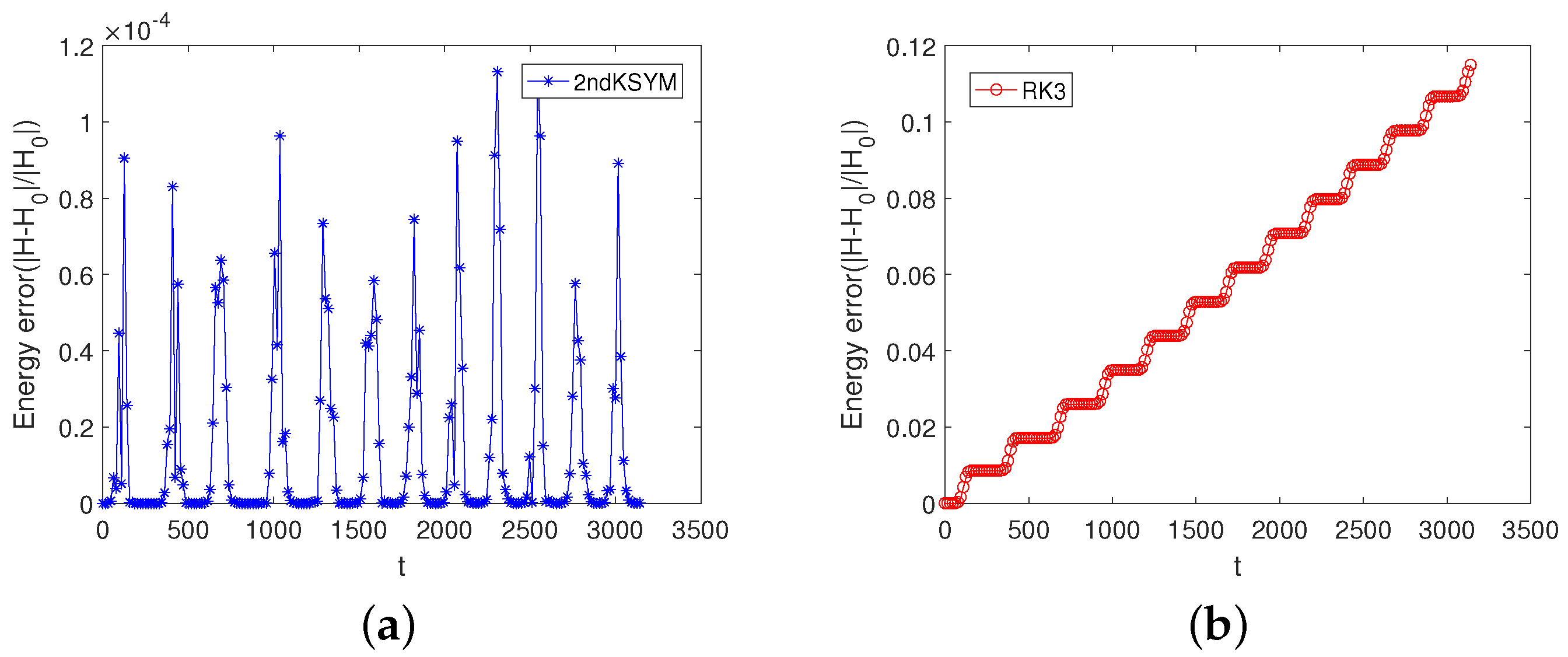
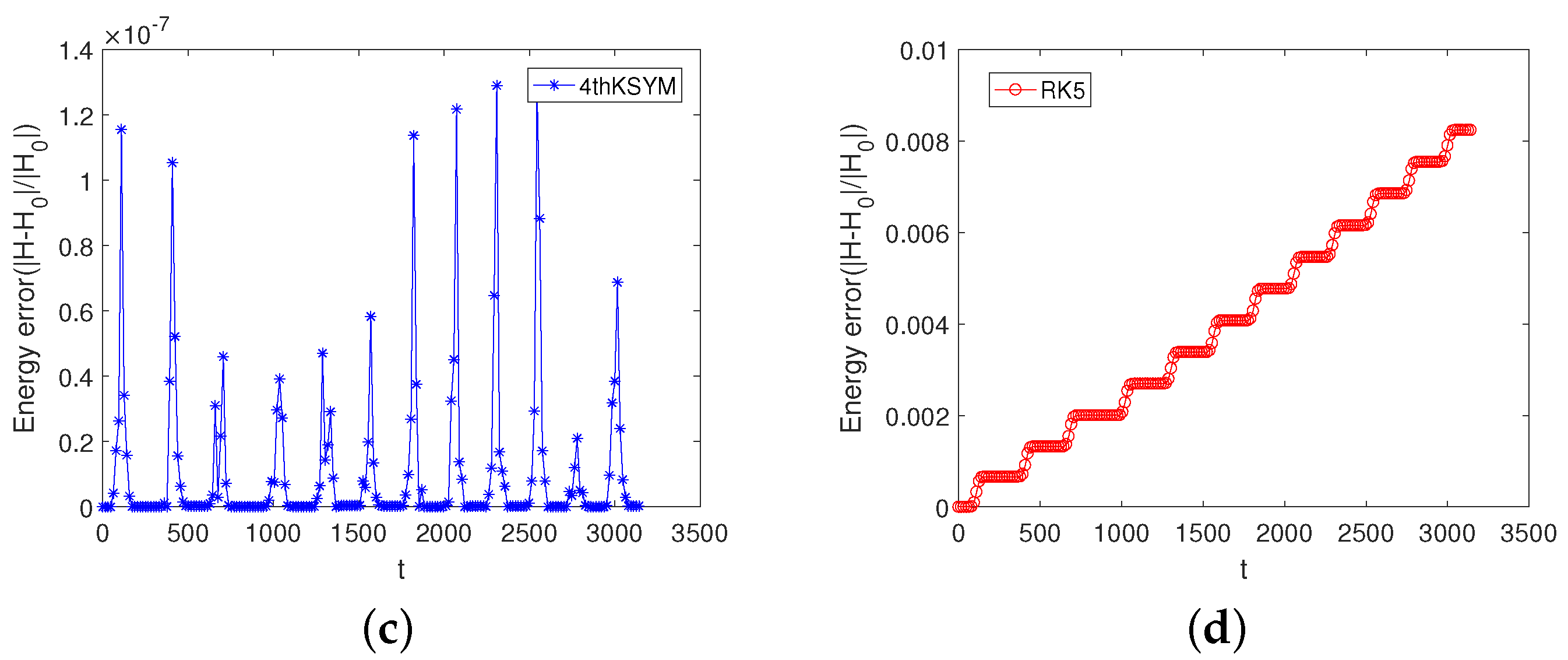
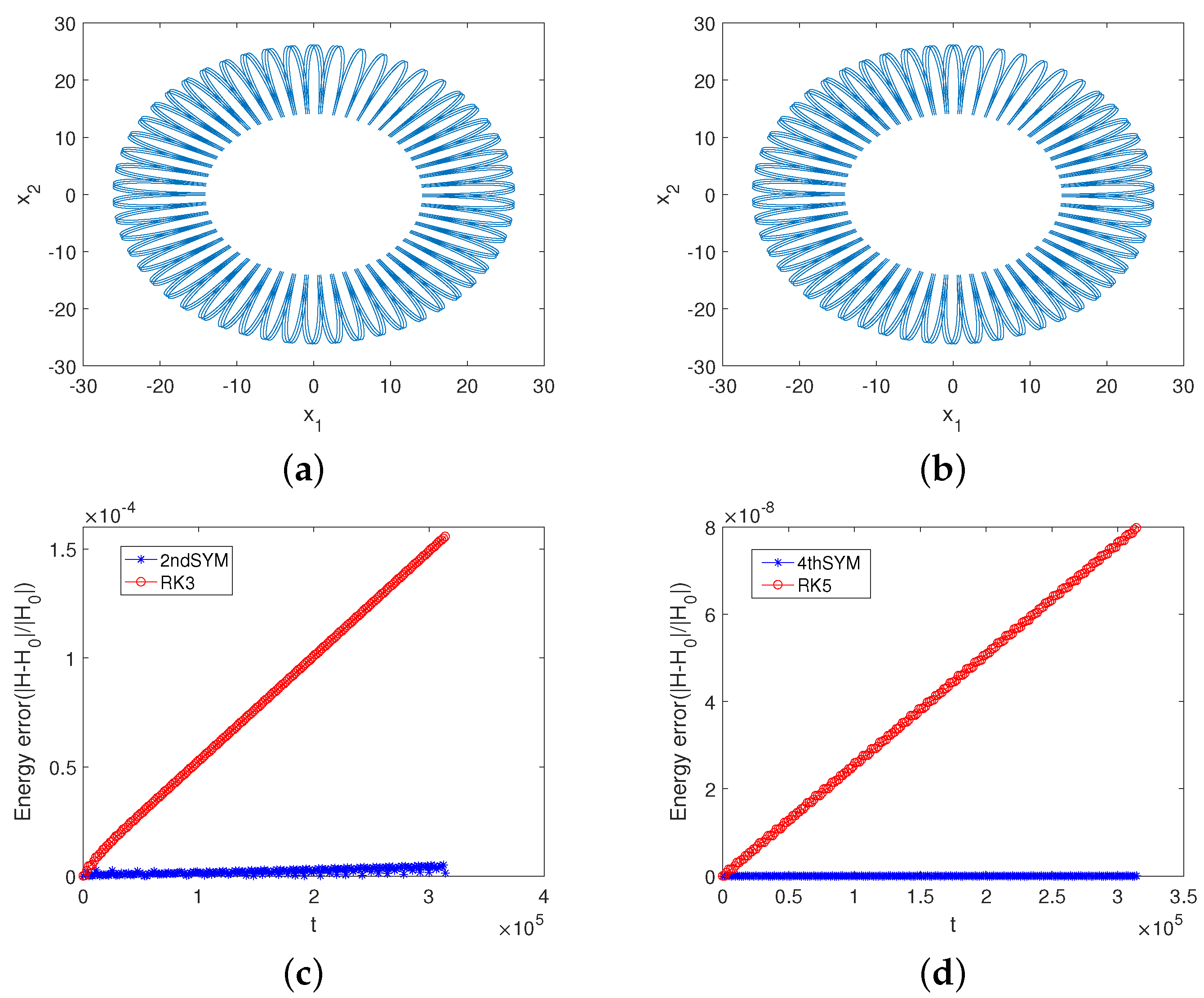
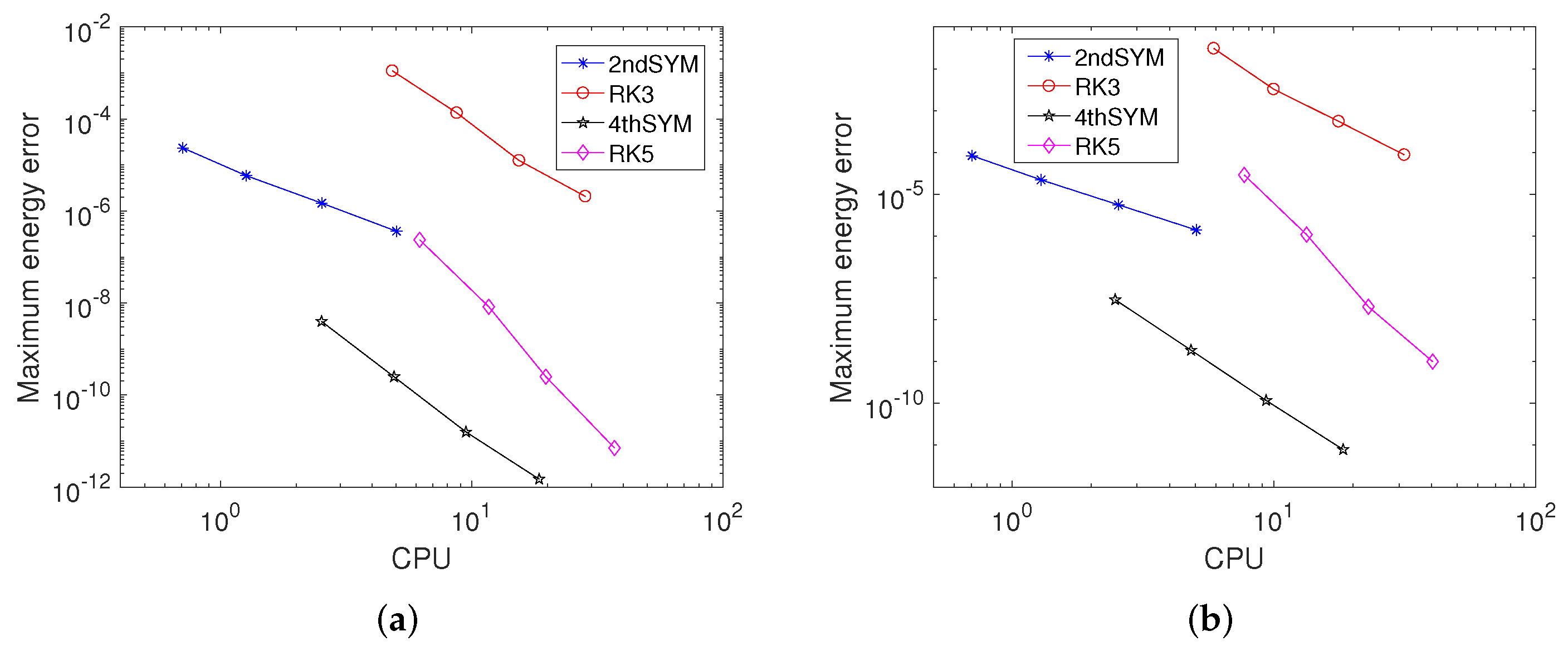
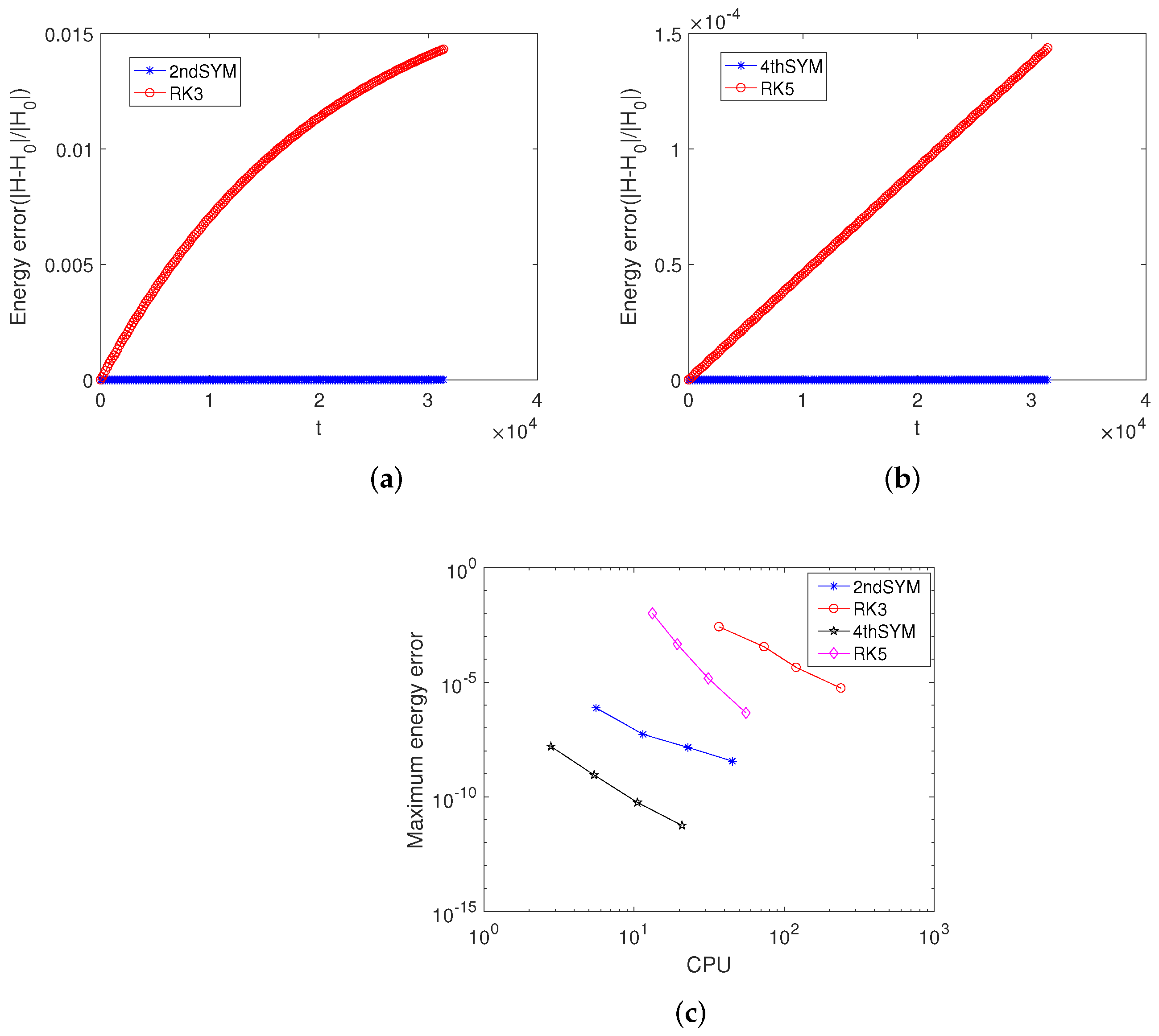
5. Numerical Experiments
5.1. Example 1
5.2. Example 2
5.3. Example 3
5.4. Example 4
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhang, R.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, J.; Qin, H. High order volume-preserving algorithms for relativistic charged particles in general electromagnetic fields. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 092109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.L.; Qin, H.; Tang, Y.F.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Xiao, J.Y. Explicit symplectic algorithms based on generating functions for charged particle dynamics. Phys. Rev. E. 2016, 94, 013205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.L.; Wang, Y.L.; He, Y.; Xiao, J.Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, H.; Tang, Y.F. Explicit symplectic algorithms based on generating functions for relativistic charged particle dynamics in time-dependent electromagnetic field. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 022117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, D. On Symmetric Methods for Charged Particle Dynamics. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K. Collected Works of Feng Kang (II); National Defence Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K. On Difference Schemes and Symplectic Geometry. In Proceedings of 1984 Beijing Symposium on Differential Geometry and Differential Equations; Feng, K., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985; pp. 42–58. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Qin, M.Z. Symplectic Geometric Algorithms for Hamiltonian System; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Serna, J.M.; Calvo, M.P. Numerical Hamiltonian Problems; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.F.; Pérez-García, V.M.; Vázquez, L. Symplectic Methods for the Ablowitz-Ladik Model. Appl. Math. Comput. 1997, 82, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnano, L.; Iavernaro, F. Line Integral Methods for Conservative Problems; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brugnano, L.; Zhang, C.J.; Li, D.F. A class of energy-conserving Hamiltonian boundary value methods for nonlinear Schrödinger equation with wave operator. Commun. Nonlin. Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2018, 60, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.J. Construction of volume-preserving difference schemes for source-free systems via generating functions. J. Comput. Math. 1994, 12, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Z.J. Generating functions for volume-preserving mappings and Hamilton-Jacobi equations for source-free dynamical systems. Sci. China Ser. A 1994, 37, 1172–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Channell, P.J.; Scovel, J.C. Symplectic Integration of Hamiltonian Systems. Nonlinearity 1990, 3, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairer, E.; Lubich, C.; Wanner, G. Geometric Numerical Integration: Structure-Preserving Algorithms for Ordinary Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski, P.; Maslanka, P. Relativistic symmetries and Hamiltonian formalism. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, M.; Sardon, C.; Ragnisco, O. Time-dependent Hamiltonian mechanics on a locally conformal symplectic manifold. Symmetry 2023, 15, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, V.I. Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Albosaily, S.; Mohammed, W.W.; Aiyashi, M.A.; Abdelrahman, M.A.E. Exact solutions of the (2 + 1)-dimensional stochastic chiral nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.A.; Agarwal, P.; Chung, J.D.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Hamed, Y.S. Analysis of optical solitons for nonlinear Schrödinger equation with detuning term by iterative transform method. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanes, S.; Moan, P.C. Splitting Methods for Non-autonomous Hamiltonian Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2001, 170, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Sun, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Qin, H. Explicit K-symplectic algorithms for charged particle dynamics. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.B.; Zhao, Y.L. Symplectic all-at-once method for Hamiltonian systems. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.B.; Tang, Y.F.; Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, Y.H. Symplectic simulation of dark solitons motion for nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Numer. Algorithms 2019, 81, 1485–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihajoki, P. Explicit methods in extended phase space for inseparable Hamiltonian problems. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 2015, 121, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.L. Explicit symplectic approximation of nonseparable Hamiltonians: Algorithm and long time performance. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 043303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Wu, X. An optimized Forest-Ruth-like algorithm in extended phase space. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2018, 29, 1850006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardana, B.; Ohsawa, T. Semiexplicit symplectic integrators for non-separable Hamiltonian systems. Math. Comput. 2023, 92, 251–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, T. Preservation of Quadratic Invariants by Semiexplicit Symplectic Integrators for Non-separable Hamiltonian Systems. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.10546. [Google Scholar]
- Strang, G. On the construction and comparison of difference schemes. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1968, 5, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanes, S.; Moan, P.C. Practical symplectic partitioned Runge-Kutta and Runge-Kutta-Nystrom methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2002, 142, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.C. Implicit Runge-Kutta Processes. Math. Comput. 1964, 18, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairer, E.; Nørsett, S.P.; Wanner, G. Solving Ordinary Differential Equation I: Nonstiff Problems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Tian, H.; Qin, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H. Explicit K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods for Charged Particle System in General Magnetic Field. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061146
Lu Y, Yuan J, Tian H, Qin Z, Chen S, Zhou H. Explicit K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods for Charged Particle System in General Magnetic Field. Symmetry. 2023; 15(6):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061146
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yulan, Junbin Yuan, Haoyang Tian, Zhengwei Qin, Siyuan Chen, and Hongji Zhou. 2023. "Explicit K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods for Charged Particle System in General Magnetic Field" Symmetry 15, no. 6: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061146
APA StyleLu, Y., Yuan, J., Tian, H., Qin, Z., Chen, S., & Zhou, H. (2023). Explicit K-Symplectic and Symplectic-like Methods for Charged Particle System in General Magnetic Field. Symmetry, 15(6), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061146



